Genetic Introgression and Morphological Variation in Naked-Back Bats (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae: Pteronotus Species) along Their Contact Zone in Central America
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological Analyses
2.2. Correlation between Forearm Length and Latitude
2.3. Molecular Data
2.3.1. Sampling
2.3.2. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, Editing and Alignment
2.3.3. Species Tree
2.3.4. Evolutionary Relationships
2.3.5. mtDNA Diversity and Structure
2.3.6. Microsatellinte Data Analyses
2.3.7. nDNA Genetic Population Structure
3. Results
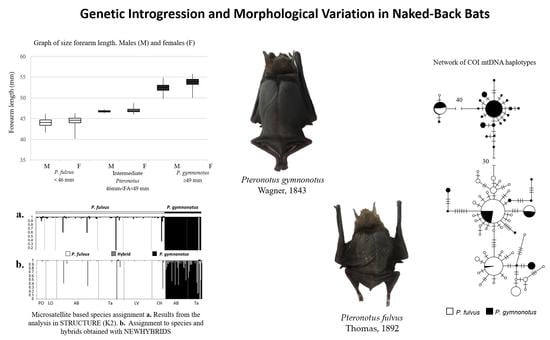
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.2. Correlation between Forearm Length and Latitude
3.3. Molecular Analysis
3.3.1. Species Tree
3.3.2. Evolutionary Relationships
3.3.3. mtDNA Diversity and Structure
3.3.4. Microsatellinte Markers Checking
3.3.5. nDNA Genetic Population Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avise, J.C.; Arnold, J.; Ball, R.M.; Bermingham, E.; Lamb, T.; Neigel, J.E.; Reeb, C.A.; Saunders, N.C. Intraspecific phylogeography the mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 489–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.L.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Ingram, K.K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evolut. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Thong, V.D.; Bates, P.J.J.; Jones, G.; Zhang, S.; Rossiter, S.J. Multiple cases of asymmetric introgression among horseshoe bats detected by phylogenetic conflicts across loci. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 110, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-García, T.A.; Vázquez-Domínguez, E. Comparative phylogeography: Designing studies while surviving the process. BioScience 2011, 61, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, S.; Martínez-Arias, V. Cambios recientes en la sistemática y taxonomía de murciélagos Neotropicales (Mammalia: Chiroptera). Therya 2014, 5, 167–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, E.; Nerva, L.; Lovari, S. Reclassification of the serows and gorals: The end of a neverending story? Mammal. Rev. 2019, 49, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbound, C.N.; Hisheh, S.; Suyanto, A.; How, R.A.; Schmitt, L.H. Markedly discordant mitochondrial DNA and allozyme phylogenies of tube-nosed fruit bats, Nyctimene, at the Australian–Oriental biogeographical interface. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 93, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nesi, N.; Nakouné, E.; Cruaud, C.; Hassanin, A. DNA barcoding of African fruit bats (Mammalia, Pteropodidae). The mitochondrial genome does not provide a reliable discrimination between Epomophorus gambianus and Micropteropus pusillus. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2011, 334, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, T.R.; Cordeiro, M.; Marshall, D.C.; Simon, C. Differentiating between Hypotheses of Lineage Sorting and Introgression in New Zealand Alpine Cicadas (Maoricicada dugdale). Syst. Biol. 2006, 5, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallet, J. Hybridization as an invasion of the genome. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pease, J.B.; Hahn, M.W. Detection and polarization of introgression in a five-taxon phylogeny. Syst. Biol. 2015, 64, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.L. Natural hybridization as an evolutionary forcé. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1992, 23, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Rossiter, S.J. Historical male-mediated introgression in horseshoe bats revealed by multilocus DNA sequence data. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1352–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuillan, M.A.; Rice, A.M. Differential effects of climate and species interactions on range limits at a hybrid zone: Potential direct and indirect impacts of climate change. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 5120–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, J.A. Geographic Variation, Speciation, and Clines; Monographs in Population Biology 10; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1977; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, W.S. An evaluation of narrow hybrid zones in vertebrates. Q. Rev. Biol. 1997, 52, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratelli, R.; Peracchi, A.L.; Dias, D.; De Oliveira, J.A. Geographic variation in South American populations of Myotis nigricans (Schinz, 1821) (Chiroptera, Vespertilionidae), with the description of two new species. Mamm. Biol. 2011, 76, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín, R.A.; Arita, H.T.; Sánchez, O. Identificación de los Murciélagos de México, Clave de Campo, 2nd ed.; Instituto de Ecología: Mexico City, Mexico, 2008; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Castañeda, S.T.; Álvarez, T.; González-Ruiz, N. Keys for Identifying Mammals of Mexico in the Field and in the Laboratory; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2017; p. 522. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, S.W.; Campbell, P.; Kingston, T.; Zubaid, A.; Francis, C.M.; Kunz, T.H. Molecular phylogeny of hipposiderid bats from Southeast Asia and evidence of cryptic diversity. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 62, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puechmaille, S.J.; Allegrini, B.; Benda, P.; Gürün, K.; Šrámek, J.; Ibañez, C.; Juste, J.; Bilgin, R. A new species of the Miniopterus schreibersii species complex (Chiroptera: Miniopteridae) from the Maghreb Region, North Africa. Zootaxa 2014, 3794, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juste, J.; Ruedi, M.; Puechmaille, S.J.; Salicini, I.; Ibáñez, C. Two new cryptic bat species within the Myotis nattereri species complex (Vespertilionidae, Chiroptera) from the Western Palaearctic. Acta Chiropt. 2018, 20, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, A.; Spada, M.; Russo, D.; Mucedda, M.; Agnelli, P.; Crottini, A.; Ferri, E.; Martinoli, A.; Casiraghi, M. Integrated Operational Taxonomic Units (IOTUs) in echolocating bats: A bridge between molecular and traditional taxonomy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40122. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.D. Systematics of the chiropteran family Mormoopidae. Misc. Publ. Univ. Kans. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1972, 56, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, N.B.; Conway, T.M. Phylogenetic relationships of mormoopids bats (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae) based on morphological data. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2001, 258, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, A.C. Family Mormoopidae. Ghost-faced Bats, Naked-backed Bats and Mustached Bats. In Handbook of the Mammals of the World; Wilson, D.E., Mittermeier, R.A., Eds.; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, España, 2019; Volume 9, pp. 424–443. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, W.E. The characters of seven genera of bats with foliaceous appendages to the nose. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond. 1821, 13, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E. A revision of the genera of bats (Vespertilionidae), and the description of some new genera and species. Mag. Zool. Bot. 1838, 2, 483–505. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, N.B. Order Chiroptera. In Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic, 3rd ed.; Wilson, D.E., Reeder, D.M., Eds.; John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 312–529. [Google Scholar]
- Clare, E.L.; Lim, B.K.; Fenton, M.B.; Hebert, P.D.N. Neotropical Bats: Estimating Species Diversity with DNA Barcodes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22648. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, A.C.; Marroig, G. Integrating multiple evidences in taxonomy: Species diversity and phylogeny of mustached bats (Mormoopidae: Pteronotus). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 103, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Wilchis, R.; Flores-Romero, M.; Guevara-Chumacero, L.M.; Serrato-Díaz, A.; Díaz-Larrea, J.; Salgado-Mejia, F.; Ibañez, C.; Salles, L.O.; Juste, J. Evolutionary scenarios associated with the Pteronotus parnellii cryptic species-complex (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae). Acta Chiropt. 2016, 18, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zárate-Martínez, D.G.; López-Wilchis, R.; Ruiz-Ortíz, J.D.; Barriga-Sosa, I.L.A.; Serrato, D.A.; Ibáñez, C.; Juste, J.; Guevara-Chumacero, L.M. Intraspecific evolutionary relationships and diversification patterns of the Wagner’s mustached bat, Pteronotus personatus (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae). Acta Chiropt. 2018, 20, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis-Oritt, N.; Porter, C.A.; Baker, R.J. Molecular Systematics of the Family Mormoopidae (Chiroptera) based on cytochrome b and recombination activating gene 2 sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 20, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávalos, L.M. The geography of diversification in the mormoopids (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 88, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G.G.; Macdougall, T.B.; Marcus, J.R. Two new mammals from Mexico. Am. Mus. Novit. 1958, 1871, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, T.; Álvarez-Castañeda, S.T. Notas sobre el estado taxonómico de Pteronotus davyi en Chiapas y de Hylonycteris en México (Mammalia: Chiroptera). An. Esc. Nac. Cien. Biol. 1991, 34, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, R.J.; Arita, H.T. Pteronous gymnonotus. In Los mamíferos Silvestres de México; Ceballos, G., Oliva, G., Eds.; Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad: Distrito Federal, Mexico, 2005; p. 747. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.K. Pteronotus davyi. Mamm. Species 1989, 346, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, R.S. Animal Care and Use Committee of the American Society of Mammalogists. Guidelines of the American Society of Mammalogists for the use of wild mammals in research and education. J. Mamm. 2016, 97, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Lineamientos para la Conducción Ética de la Investigación, la Docencia y la Difusión de la División de Ciencias Biológicas y de la Salud; Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana: Iztapalapa, Mexico, 2010; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Hintze, J. 2011 PASS 11; NCSS; LLC: Kaysville, UT, USA, 2011; Available online: www.ncss.com (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Ochoa, J.G.; Castellanos, H.; Ibañez, C. Records of bats and rodents from Venezuela. Mammalian 1988, 52, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.; Gregorin, R. Quirópteros da Estação Ecológica da Serra das Araras, Mato Grosso, Brasil, com o primeiro registro de Artibeus gnomus e A. anderseni para o cerrado. Lundiana 2004, 5, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Da Rocha, P.A.; Feijó, J.A.; Mikalauskas, J.S.; Ferrari, S.F. First records of mormoopid bats (Chiroptera, Mormoopidae) from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Mammalia 2011, 75, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.S.G. 2016a USAC Mammals Collection. Version 8.1. Museo de Historia Natural de la USAC MUSHNAT. Occurrence Dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/16fwgc accessed via GBIF.org. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/859263445 (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Pérez, C.S.G. 2016b USAC Mammals Collection. Version 8.1. Museo de Historia Natural de la USAC MUSHNAT. Occurrence Dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/16fwgc accessed via GBIF.org. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/859263507 (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Feijó, A.; Da Rocha, P.A. Morcegos da Estação Ecológica Aiuaba, Ceará, nordeste do Brasil: Uma unidade de proteção integral na Caatinga. Mastozool. Neotrop. 2017, 24, 333–351. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J. 2020a MSB Mammal Collection (Arctos). Version 35.37. Museum of Southwestern Biology. Occurrence Dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/oirgxw accessed via GBIF.org. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/2303054715 (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Cook, J. 2020b MSB Mammal Collection (Arctos). Version 35.37. Museum of Southwestern Biology. Occurrence Dataset https://doi.org/10.15468/oirgxw accessed via GBIF.org. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/1828901377 (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- López-Wilchis, R.; (Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana, Mexico City, Mexico). Personal Communication, 2020.
- Borisenko, A.V.; Lim, B.K.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcoding in surveys of small mammal communities: A field study in Suriname. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.A.; Phillips, C.D.; Baker, R.J. Timeframes of speciation, reticulation, and hybridization in the bulldog bat explained through phylogenetic analyses of all genetic transmission elements. Syst. Biol. 2013, 63, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, M.D.; Lim, B.K.; Eger, J.L.; Borisenko, A.V. ROM Mammals—Southern Central America (Unpublished).
- López-Wilchis, R.; Méndez-Rodríguez, A.; Juste, J.; García-Mudarra, J.L.; Salgado-Mejia, F.; Guevara-Chumacero, L.M. The Big Naked-backed Bat, Pteronotus gymnonotus (J. A. Wagner, 1843), Chiroptera, Mormoopidae, in its northernmost geographic distribution range. Therya 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lopera-Barrero, N.M.; Povh, J.A.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Gomes, P.C.; Jacometo, C.B.; Silva Lopes, T.D. Comparación de protocolos de extracción de ADN con muestras de aleta y larva de peces: Extracción modificada con cloruro de sodio. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2008, 35, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baker, R.C.; Porter, J.P.; Van Den, R.B. Systematics of Bats of the Family Phillostomidae Based on RAG2 DNA Sequences. Occas. Pap. Mus. Tex. Tech. Univ. 2000, 202, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Dewaard, J.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. An inexpensive, automation- friendly protocol for recovering high-quality DNA. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, G.N.; Jacobs, D.S.; Matthee, C.A. A nuclear DNA phylogenetic perspective on the evolution of echolocation and historical biogeography of extant bats (Chiroptera). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1869–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ashton, B.; Buxton, S.; Cheung, M.; Cooper, A.; Duran, C.; Field, M.; Heled, J.; Kearse, M.; Markowitz, S.; et al. Geneious v 5.6.4 Created by Biomatters. 2012. Available online: http://www.geneious.com (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Rodríguez, A.; López-Wilchis, R.; Díaz, A.S.; Del Río-Portilla, M.A.; Guevara-Chumacero, L.M. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite marker loci in the Wagner’s mustached bat Pteronotus psilotis (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae) and cross-amplification in other related species. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Maldonado, J.E.; Arita, H.T.; Wilkinson, G.S.; Fleischer, R.C. Characterization of microsatellite loci in the Jamaican fruit-eating bat Artibeus jamaicensis and cross-species amplification. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2002, 2, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. A Software Platform for Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis. BEAST 2. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for Inference of Large Phylogenetic Trees in Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments; Workshop (GCE): New Orleans, LA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A. Figtree v 1.1.2; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, A.C.; Marroig, G. Timing and patterns of diversification in the Neotropical bat genus Pteronotus (Mormoopidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 108, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Sucard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swofford, D.L. Paup*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates, Inc., Publishers: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic Model Averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, M.E.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Comparative performance of Bayesian and AIC-based measures of phylogenetic model uncertainty. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by Sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandelt, H.-J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfenninger, M.; Posada, D. Phylogeographic history of the land snail Candidula unifasciata (Helicellinae, Stylommatophora): Fragmentation, corridor migration, and secondary contact. Evolution 2002, 56, 1776–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. Arlequín ver 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2005, 1, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Wills, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. Microchecker: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, M.-P.; Estoup, A. Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. 2001 FSTAT, a Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices (Version 2.9.3). Available online: http://www.unil.ch/izea/softwares/fstat.html (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetic 2000, 155, 945–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software Structure: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A.; Vonholdt, B.M. Structure Harvester: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.C.; Thompson, E.A. A model-based method for identifying species hybrids using multilocus genetic data. Genetics 2002, 160, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgarella, C.; Lorenzo, Z.; Jabbour-Zahab, R.; Lumaret, R.; Guichoux, E.; Petit, R.J.; Soto, Á.; Gil, L. Detection of hybrids in nature: Application to oaks (Quercus suber and Q. ilex). Heredity 2009, 102, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, A.C. Sistemática e História Evolutiva do Gênero de Morcegos Notropical Pteronotus (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae); Doctorate-Instituto de Biociêncies da Universidade de São Paulo, Departamento de Genética e Biologia Evolutiva: São Paulo, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Avise, J.C. Molecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution; Sinauer: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004; p. 684. [Google Scholar]
- Currat, M.; Ruedi, M.; Petit, R.J.; Excoffier, L. The hidden side of invasions: Massive introgression by local genes. Evolution 2008, 62, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bi, K.; Fu, J.K. Frequent mitochondrial gene introgression among high elevation Tibetan megophryid frogs revealed by conflicting gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 2856–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; He, G.; Hua, P.; Jones, G.; Zhang, S.; Rossiter, S.J. Historical introgression and the persistence of ghost alleles in the intermediate horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus affinis). Mol. Ecol. 2012, 22, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Chen, S.F.; Fang, Y.P.; Cotton, J.A.; Parker, J.D.; Csorba, G.; Lim, B.K.; Eger, J.L.; Chen, C.H.; Chuo, C.H.; et al. Speciation processes in putative island endemic sister bat species: False impressions from mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 5910–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gompert, Z.; Forister, M.L.; Fordyce, J.A.; Nice, C.C. Widespread mito-nuclear discordance with evidence for introgressive hybridization and selective sweeps in Lycaeides. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 5231–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.M.A.; Levin, S.A. Leaky prezygotic isolation and porous genomes: Rapid introgression of maternally inherited DNA. Evolution 2005, 59, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo-Ferreira, J.; Boursot, P.; Randi, E.; Kryukov, A.; Suchentrunk, F.; Ferrand, N.; Alves, P.C. The rise and fall of the mountain hare (Lepus timidus) during Pleistocene glaciations: Expansion and retreat with hybridization in the Iberian Peninsula. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, P.; Excoffier, L.; Ruedi, M. Recurrent replacement of mtDNA and cryptic hybridization between two sibling bat species Myotis myotis and Myotis blythii. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 3101–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artyushin, I.V.; Bannikova, A.A.; Lebedev, V.S.; Kruskop, S.V. Mitochondrial DNA relationships among North Palaearctic Eptesicus (Vespertilionidae, Chiroptera) and past hybridization between common Serotine and Northern bat. Zootaxa 2009, 2262, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Juste, J.; Benda, P.; Garcia-Mudarra, J.L.; Ibanez, C. Phylogeny and systematics of Old W orld serotine bats (genus Eptesicus, Vespertilionidae, Chiroptera): An integrative approach. Zool. Scr. 2013, 42, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.J.; Excoffier, L. Gene flow and species delimitation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Mao, X.; Sun, H.; Irwin, D.M.; Zhang, S.; Hua, P. Introgression of mitochondrial DNA promoted by natural selection in the Japanese pipistrelle bat (Pipistrellus abramus). Genetica 2014, 142, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachtrog, D.; Thornton, K.; Clark, A.; Andolfatto, P. Extensive introgression of mitochondrial DNA relative to nuclear genes in the Drosophila yakuba species group. Evolution 2006, 60, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Rossiter, S.J.; Zhang, S. Lineage divergence and historical gene flow in the Chinese horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus sinicus). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.B.; Freyer, C.; Elson, J.L.; Wredenberg, A.; Cansu, Z.; Trifunovic, A.; Larsson, N.G. Strong purifying selection in transmission of mammalian mitochondrial DNA. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Rossiter, S.J. Differential introgression among loci across a hybrid zone of the intermediate horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus affinis). BMC Evol. Biol. 2014, 14, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, J.C.; Johnson, J.B. Phylogeography and biogeography of the lower Central American Neotropics: Diversification between two continents and between two seas. Biol Rev. 2014, 89, 767–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.J.; Crawford, A.J.; Bermingham, E. Phylogeography of the Pygmy Rain Frog (Pristimantis ridens) across the lowland wet forests of isthmian Central America. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 47, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanowicz, W.; Piksa, K.; Tereba, A. Hybridization hotspots at bat swarming sites. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno-Cuadros, A.; Razgour, O.; Garcia-Mudarra, J.L.; Mingo-Casas, P.; Sandonís, V.; Redondo, A.; Ibáñez, C.; de Paz, O.; Martinez-Alós, S.; Pérez, S.G.; et al. Comparative phylogeography and asymmetric hybridization between cryptic bat species. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2019, 57, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi-Codaccioni, O.; Beugin, M.P.; De Vienne, D.M.; Portanier, E.; Fouchet, D.; Kaerle, C.; Muselet, L.; Queney, G.; Petit, E.J.; Regis, C.; et al. Coexistence of two sympatric cryptic bat species in French Guiana: Insights from genetic, acoustic and ecological data. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.M. Walker’s Bats of the World, 5th ed; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 1991; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.E. Reproduction in Neotropical bats. Period Biol. 1973, 75, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hayssen, V.; Van Tienhoven, A.; Van Tienhoven, A. Asdell’s Patterns of Mammalian Reproduction: A Compendium of Species-Specific Data, 2nd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1993; p. 1023. [Google Scholar]
- Aljanabi, S.M.; Martinez, I. Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4692–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, S.; Barry, A.; Abreu, J.; Minie, B.; Nolan, J.; Delorey, T.M.; Young, G.; Fennell, T.J.; Allen, A.; Ambrogio, L. A scalable, fully automated process for construction of sequence-ready human exome targeted capture libraries. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faircloth, B.C.; Glenn, T.C. Not all sequence tags are created equal: Designing and validating sequence identification tags robust to indels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoe, T.A.; Poole, A.W.; De Koning, A.P.J.; Jones, K.L.; Tomback, D.F.; Oyler-McCance, S.J.; Fike, J.A.; Lance, S.L.; Streicher, J.W.; Smith, E.N.; et al. Rapid microsatellite identification from Illumina paired-end genomic sequencing in two birds and a snake. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Acronym | Sympatric/Allopatric | Study Localities | Country | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE | Allopatric | Laguna Encantada, Veracruz | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| CH | Sympatric | Cerro Huatulco, Oaxaca | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| LV | Sympatric | La Venta, Oaxaca | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| MT | Sympatric | Martínez de la Torre, Oaxaca | Mexico | P. gymnonotus |
| Ta | Sympatric | Tapijulapa, Tabasco | Mexico | P. fulvus P. gymnonotus |
| AB | Sympatric | Agua Blanca, Tabasco | Mexico | P. fulvus P. gymnonotus |
| LO | Allopatric | Los Ortices, Colima | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| PO | Allopatric | Playa de Oro, Colima | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| Ja | Allopatric | Jalisco | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| Ca | Sympatric | Campeche | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| Ch | Sympatric | Chiapas | Mexico | P. fulvus |
| Gu1 | Sympatric | Tikal, El Petén | Guatemala | P. fulvus |
| Gu2 | Sympatric | Lanquin Caves, Alta Verapaz | Guatemala | P. fulvus P. gymnonotus |
| ES | Sympatric | El Refugio, Ahuachapan | El Salvador | P. fulvus |
| Ho | Sympatric | Colón | Honduras | P. fulvus |
| Be | Sympatric | Gallon Jug, Distrito de Orange Walk | Belize | P. fulvus |
| Ni | Sympatric | Nidiri, Masaya Volcano Park | Nicaragua | P. fulvus P. gymnonotus |
| CR | Sympatric | Barra Honda National Park | Costa Rica | P. fulvus P. gymnonotus |
| Pa | Allopatric | Altos de Campana National Park | Panama | P. gymnonotus |
| Ve | Allopatric | Hato la Florida, Bolivar | Venezuela | P. gymnonotus |
| Do | - | St. Joseph | Dominica | P. davyi |
| TT | - | Arena Reserve, Nariva | Trinidad and Tobago | P. davyi |
| SL | - | Castries | Santa Lucia | P. davyi |
| Gy | Allopatric | Iwokrama Reserve, Potaro-Siparuni | Guyana | P. gymnonotus |
| Su1 | Allopatric | Brokopodo | Surinam | P. gymnonotus |
| Su2 | Allopatric | Bakhuis, Sipaliwini | Surinam | P. gymnonotus |
| Pe | Allopatric | Huánuco | Peru | P. gymnonotus |
| Go | Allopatric | Caverna do Bigode, Goiás | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br1 | Allopatric | Barro Alto, Goiás | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br2 | Allopatric | Tapirapé-Aquiri, Marabá, Pará | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br3 | Allopatric | Carajás, Parauapebas, Pará | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br4 | Allopatric | Canaã dos Carajás, Pará | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br5 | Allopatric | Chapada Diamantina, Bahía | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br6 | Allopatric | Usina Serra Grande, Alagoas | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br7 | Allopatric | Itabaina, Sergipe | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br8 | Allopatric | Aiuba, Ceará, Brazil | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
| Br9 | Allopatric | Jangada, Mato Grosso | Brazil | P. gymnonotus |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Méndez-Rodríguez, A.; Juste, J.; Centeno-Cuadros, A.; Rodríguez-Gómez, F.; Serrato-Díaz, A.; García-Mudarra, J.L.; Guevara-Chumacero, L.M.; López-Wilchis, R. Genetic Introgression and Morphological Variation in Naked-Back Bats (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae: Pteronotus Species) along Their Contact Zone in Central America. Diversity 2021, 13, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13050194
Méndez-Rodríguez A, Juste J, Centeno-Cuadros A, Rodríguez-Gómez F, Serrato-Díaz A, García-Mudarra JL, Guevara-Chumacero LM, López-Wilchis R. Genetic Introgression and Morphological Variation in Naked-Back Bats (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae: Pteronotus Species) along Their Contact Zone in Central America. Diversity. 2021; 13(5):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13050194
Chicago/Turabian StyleMéndez-Rodríguez, Aline, Javier Juste, Alejandro Centeno-Cuadros, Flor Rodríguez-Gómez, Alejandra Serrato-Díaz, Juan Luis García-Mudarra, Luis Manuel Guevara-Chumacero, and Ricardo López-Wilchis. 2021. "Genetic Introgression and Morphological Variation in Naked-Back Bats (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae: Pteronotus Species) along Their Contact Zone in Central America" Diversity 13, no. 5: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13050194
APA StyleMéndez-Rodríguez, A., Juste, J., Centeno-Cuadros, A., Rodríguez-Gómez, F., Serrato-Díaz, A., García-Mudarra, J. L., Guevara-Chumacero, L. M., & López-Wilchis, R. (2021). Genetic Introgression and Morphological Variation in Naked-Back Bats (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae: Pteronotus Species) along Their Contact Zone in Central America. Diversity, 13(5), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13050194