The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and General Analysis of Approaches
2.2. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
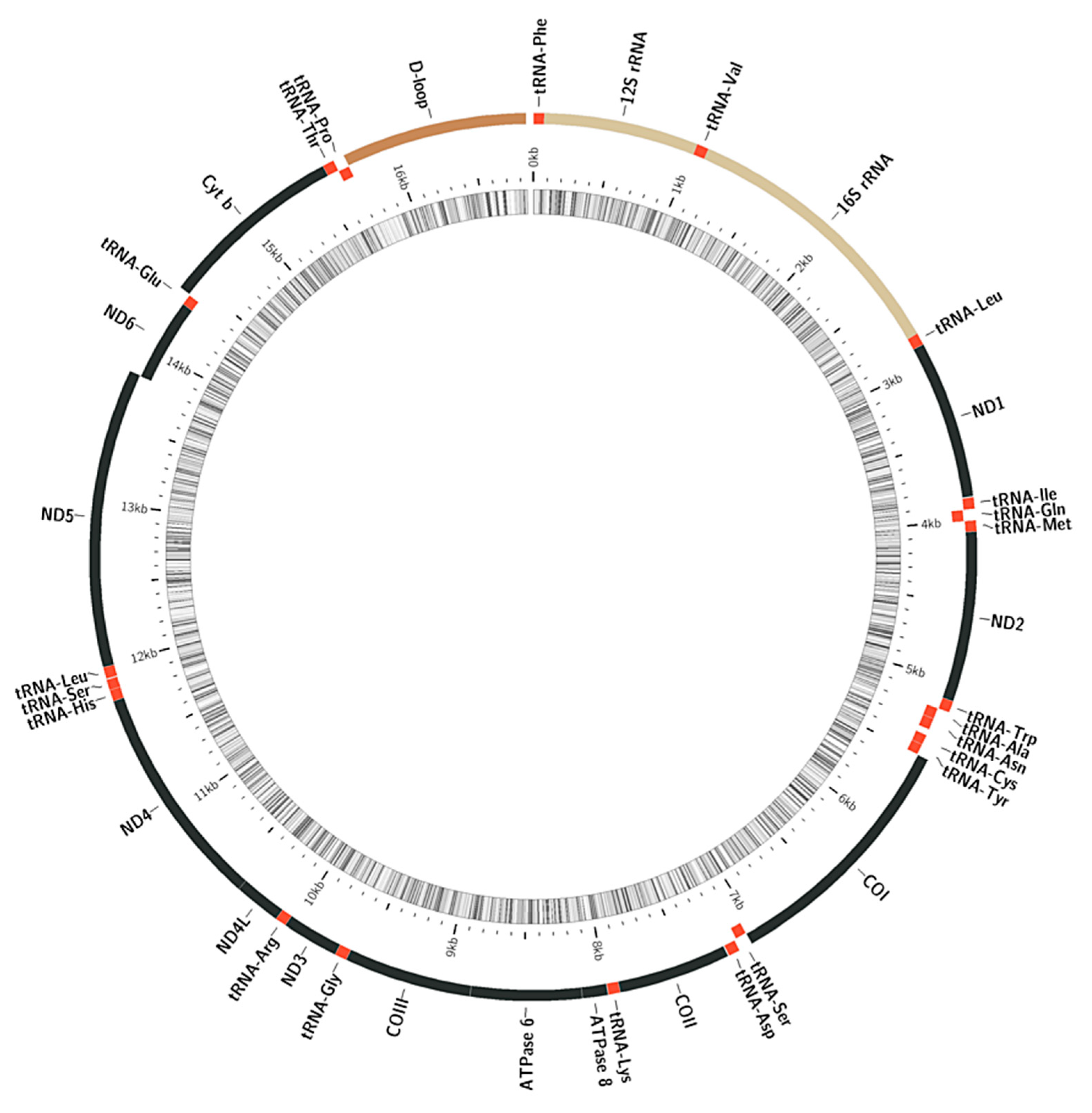
3.1. Structure and Variability of the Mitochondrial Genome of the Yellow-Stripe Flounder Pseudopleuronectes Herzensteini and Other Members of the Family Pleuronectidae
3.2. Analysis of Properties of Sequences
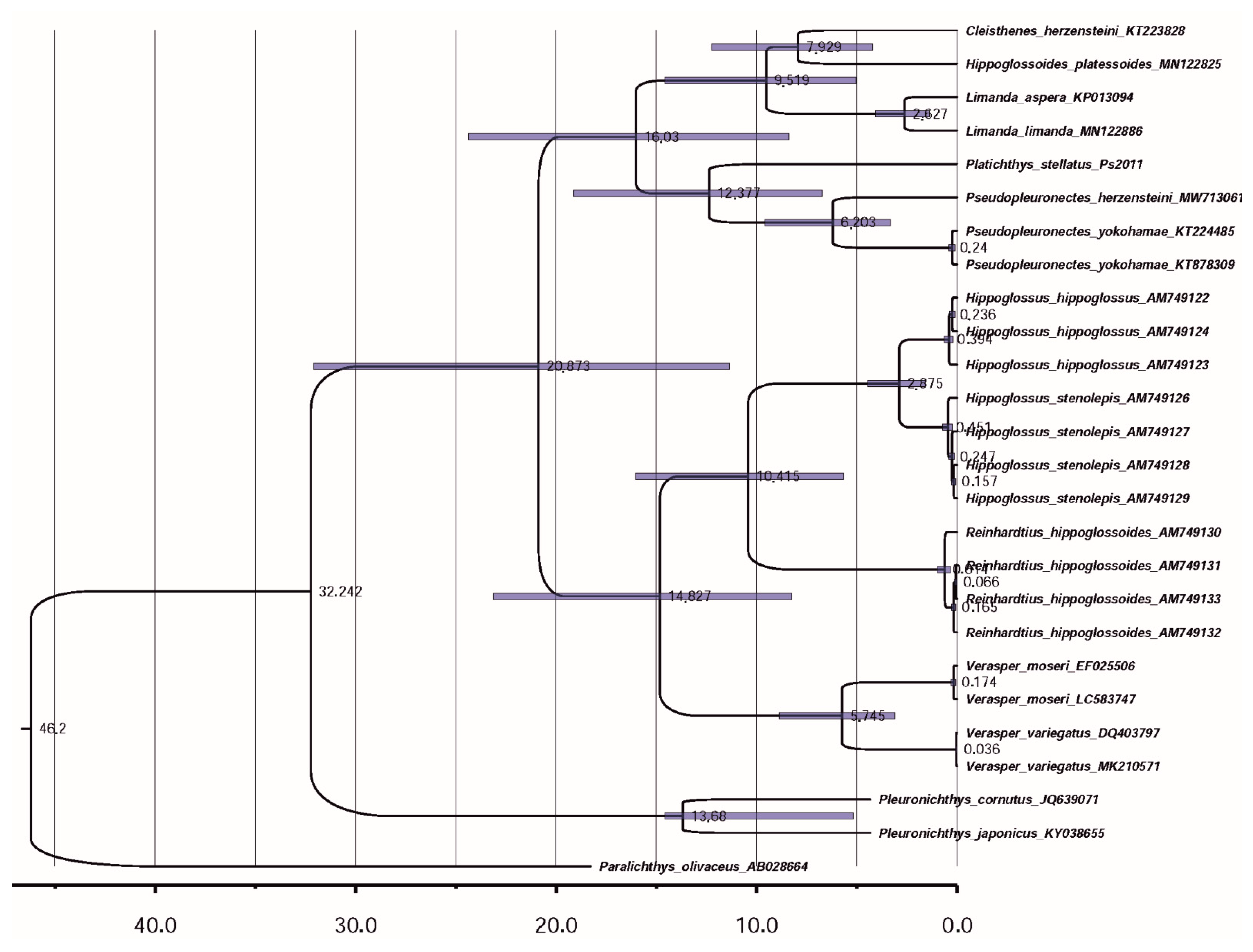
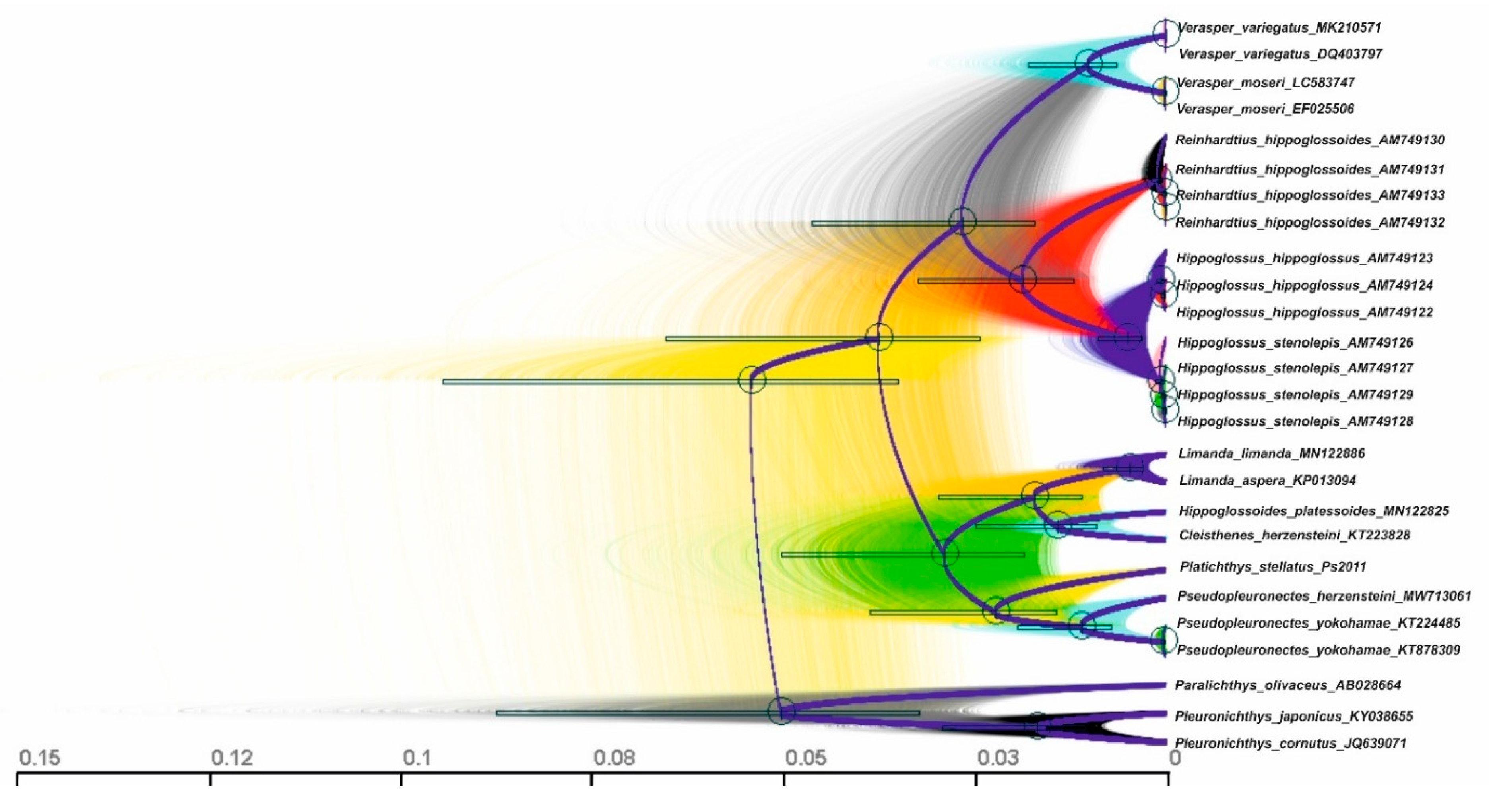
3.3. Reconstruction of Gene Trees and Analysis of Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships
3.3.1. Molecular Phylogenetics and Dating of Divergence of Flounders of the Family Pleuronectidae
3.3.2. Phylogenetic Relationships and Molecular Systematics of the Studied Representatives of the Suborder Pleuronectoidei
4. Discussion
4.1. The Structure and Variability of Mitogenome Yellow-Stripe Flounder Pseudopleuronectes Herzensteini and Other Studied Representatives of the Family Pleuronectidae
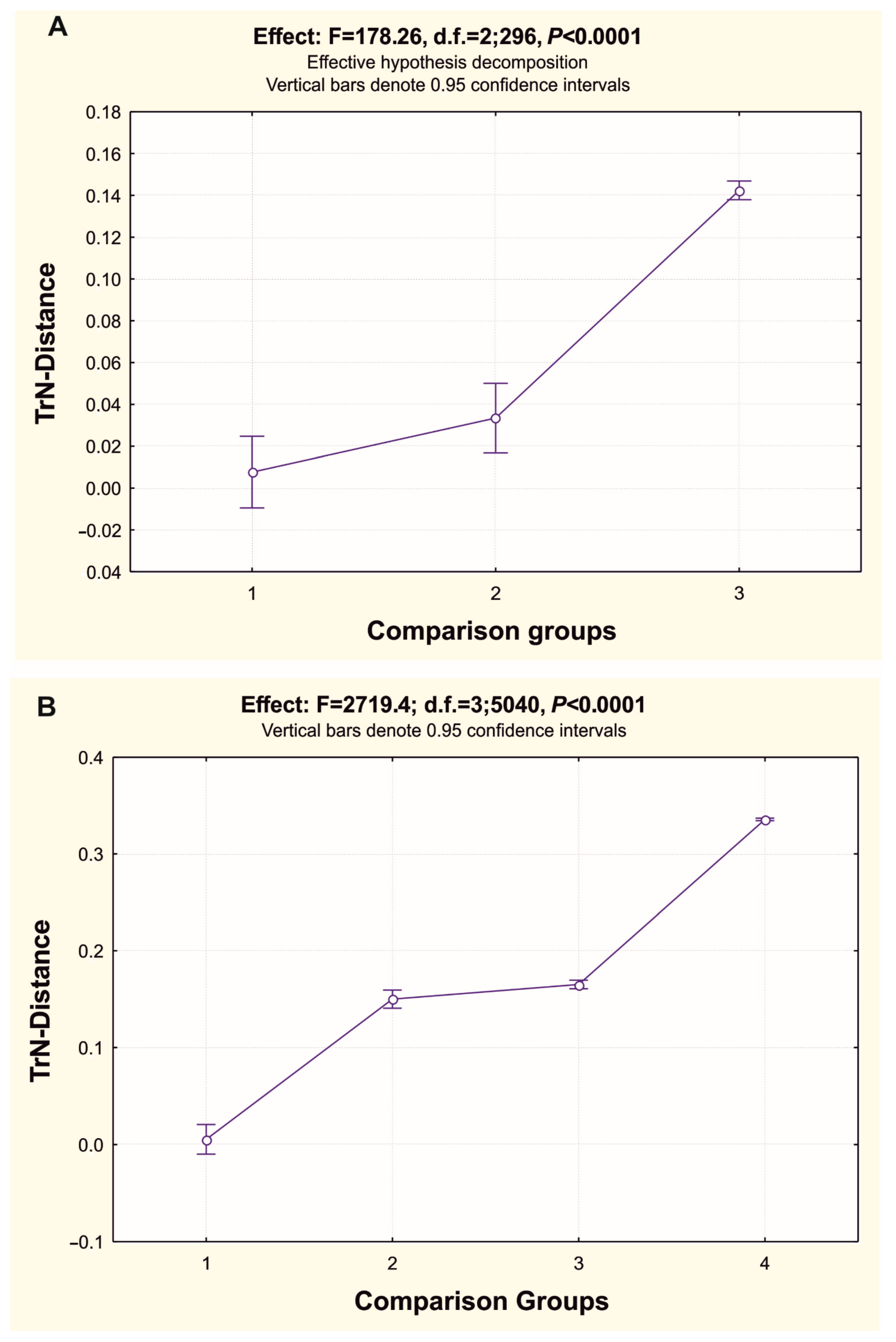
4.2. Gene tree Topology Analysis of the Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships in the Family Pleuronectidae and in the Suborder Pleuronectoidei, and Levels of Genetic Divergence in the Hierarchy of Evolutionary Units (Populations of Species and Ranked Taxa)
Family Pleuronectidae
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keast, A.; Chapleau, F. A phylogenetic reassessment of the monophyletic status of the family Soleidae, with comments on the suborder Soleoidei (Pisces; Pleuronectiformes). Can. J. Zool. 1988, 66, 2797–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.A.; Chapleau, F. Monophyly and intrarelationships of the family Pleuronectidae (Pleuronectiformes), with a revised classification. Fish. Bull. 1998, 96, 686–726. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, I.R. A Systematic Monograph of the Flatfishes (Heterosomata). Volume I. Psettodidae, Bothidae, Pleuronectidae; British Museum: London, UK, 1934; 459p. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, K. Interrelationships of the family Pleuronectidae (Pisces: Pleuronectiformes). In Memoirs of the Faculty of Fisheries, Hokkaido University; Hokkaido University: Sapporo, Japan, 1984; Volume 31, pp. 95–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, G.U.; Fedorov, V.V. Fishes of Japan Sea and Nearby Parts of Okhotsk and Yellow Seas. Part 6. Teleostomi. Osteichthyes. Actinopterigii. XXXI. Pleuronectiformes; Sankt-Petersburg University Press: Sankt-Petersburg, Russia, 1993; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Chapleau, F. Pleuronectiform relationships: A cladistic reassessment. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1993, 52, 516–540. [Google Scholar]
- Vernau, O.; Moreau, C.; Catzeflis, F.M.; Renaud, F. Phylogeny of flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes): Comparisons and contradictions of molecular and morpho-anatomical data. J. Fish Biol. 1994, 45, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Park, T.-J.; Vinnikov, K.A.; Ivankov, V.N.; Sharina, S.N.; Lee, J.-S. Cytochrome b (Cyt-b) gene sequence analysis in six flatfish species (Teleostei, Pleuronectidae), with phylogenetic and taxonomic insights. Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur-R, R.; Broughton, R.E.; Wiley, E.O.; Carpenter, K.; López, J.A.; Li, C.; Holcroft, N.I.; Arcila, D.; Sanciangco, M.; Cureton, J.C., II; et al. The tree of life and a new classification of bony fishes. PLoS Curr. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur-R, R.; Li, C.; Munroe, T.A.; Ballesteros, J.A.; Ortí, G. Addressing gene tree discordance and non-stationarity to resolve a multi-locus phylogeny of the flatfishes (Teleostei: Pleuronectiformes). Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 763–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, K.A.; Thomson, R.C.; Munroe, T.A. Revised classification of the righteye flounders (Teleostei: Pleuronectidae) based on multilocus phylogeny with complete taxon sampling. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 125, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.A.; López, J.A.; Satoh, T.P.; Chen, W.J.; Miya, M. Mitochondrial genomic investigation of flatfish monophyly. Gene 2014, 551, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.A.; Chanet, B.; Chen, J.-N.; Lee, M.-Y. Origins and relationships of the Pleuronectoidei: Molecular and morphological analysis of living and fossil taxa. Zool. Scr. 2019, 48, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaoka, K. Studies on the sinistral flounder found in the waters around Japan. Taxonomy, anatomy, and phylogeny. Shimonoseki Univ. Fish. 1969, 18, 65–340. [Google Scholar]
- Chabanaud, P. Le problème de la phylogénèse des Heterosomata. Bull. De L’institut Océanographique De Monaco 1949, 950, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Sharina, S.N.; Saitoh, K.; Imoto, J.M.; Hanzawa, N.; Redin, A.D. Phylogenetic relationships of Russian Far Eastern Flatfish (Pleuronectiformes, Pleuronectidae) based on two mitochondrial gene sequences, Co-1 and Cyt-b, with inferences in order phylogeny using complete mitogenome data. Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 27, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-J.; Bonillo, C.; Lecointre, G. Repeatability of clades as a criterion of reliability: A case study for molecular phylogeny of Acanthomorpha (Teleostei) with larger number of taxa. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 262–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettai, A.; Lecointre, G. Further support for the clades obtained by multiple molecular phylogenies in the acanthomorph bush. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2005, 328, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.L.; Wheeler, W.C. Venom evolution widespread in fishes: A phylogenetic road map for the bioprospecting of piscine venoms. J. Hered. 2006, 97, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dettaï, A.; Cruaud, C.; Couloux, A.; Desoutter-Meniger, M.; Lecointre, G. RNF213, a new nuclear marker for acanthomorph phylogeny. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 50, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J.; Eytan, R.I.; Dornburg, A.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Davis, M.P.; Wainwright, P.C.; Friedman, M.; Smith, W.L. Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13698–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J.; Dornburg, A.; Eytan, R.I.; Keck, B.P.; Smith, W.L.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Price, S.A.; Burbrink, F.T.; Friedman, M.; et al. Phylogeny and tempo of diversification in the superradiation of spiny-rayed fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12738–12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.A.; Chen, W.-J.; López, J.A. Are flatfishes (Pleuronectiformes) monophyletic? Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancur-R, R.; Ortí, G. Molecular evidence for the monophyly of flatfishes (Carangimorpharia: Pleuronectiformes). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 73, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; 512p. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Inferring Phylogenies; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth, B. Effective population size and patterns of molecular evolution and variation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GenBank NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, W.; Fukunaga, T.; Isagozawa, R.; Yamada, K.; Maeda, Y.; Satoh, T.P.; Sado, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Takeshima, H.; Miya, M.; et al. MitoFish and MitoAnnotator: A Mitochondrial Genome Database of Fish with an Accurate and Automatic Annotation Pipeline. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozas, J.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Messegyer, X.; Rozas, R. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2496–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Bouckaert, R.R. Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis with BEAST; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, R.; Kwong, S.; Vaidya, G.; Peter, K.; Ng, L. DNA Barcoding and Taxonomy in Diptera: A Tale of High Intraspecific Variability and Low Identification Success. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed Phylogenetics and Dating with Confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.4. 2016. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MitoFish WEB Bench. Available online: http://mitofish.aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp/annotation/input.html (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Search and Contextual Analysis of Transfer RNA Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A Program for Improved Detection of Transfer RNA Genes in Genomic Sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, K.; Hayashizaki, K.; Yokoyama, Y.; Asahida, T.; Toyohara, H.; Yamashita, Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) mitochondrial genome: Structural properties and cue for resolving teleostean relationships. J. Hered. 2000, 91, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H. Molecular Evolution; Sinauer Ass.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Van der Laan, R. (Eds.) Eshmayer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References. California Academy of Sciences. 2022. Available online: https://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Clayton, D.A. Replication and transcription of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1991, 7, 453–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Kong, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Jiang, J.X. Utility of tRNA genes from the complete mitochondrial genome of Psetta maxima for implying a possible sister-group relationship to the Pleuronectiformes. Zool Stud. 2011, 50, 665–681. [Google Scholar]
- Redin, A.D.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. Phylogenetic relationships of flounders from the family Pleuronectidae (Ostichties: Pleuronectiformes) based on S16 rRNA gene. Russ. J. Genet. 2021, 57, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chen, S.; Kong, X.; Si, L.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Flatfish monophyly refereed by the relationship of Psettodes in Carangimorphariae. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Redin, A.D. Estimates of genetic introgression, gene tree reticulation, taxon divergence, and sustainability of DNA barcoding based on genetic molecular markers. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2019, 9, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckle, M.Y.; Thaler, D.S. Why should mitochondria define species? Hum. Evol. 2018, 33, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Chapter 1: Analysis of sequence diversity at mitochondrial genes on different taxonomic levels. Applicability of DNA Based Distance Data in Genetics of Speciation and Phylogenetics. In Genetic Diversity; Mahoney, C.L., Springer, D.A., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Sequence divergence at mitochondrial genes in animals: Applicability of DNA data in genetics of speciation and molecular phylogenetics. Mar. Genom. 2011, 49, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Sequence divergence at Co-1 and Cyt-b mtDNA on different taxonomic levels and genetics of speciation in animals. Mitochondrial DNA 2011, 2, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Sequence Diversity at Cyt-b and Co-1 mtDNA Genes in Animal Taxa Proved Neo-Darwinism. Phylogenet. Evol. Biol. 2013, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotova, A.O.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. Analysis of sequence divergence in redfin (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae, Tribolodon) based on mtDNA and nDNA markers with inferences in systematics and genetics of speciation. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Sequence divergence provide a fit between molecular evolution, Neo-Darwinism and DNA barcoding. In HydromediT2018, Proceedings of the 3rd International Congress on Applied Ichthyology & Aquatic Environment, Volos, Greece, 8–11 November 2018; Berillis, P., Karapanagiotidis, I., Eds.; Department of Ichthyology and Aquatic Environment, School of Agricultural Sciences, University of Thessaly: Volos, Greece, 2018; pp. 463–479. ISBN 978-618-80242-5-0. Available online: www.hydromedit.gr (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Some examples of the use of molecular markers for needs of basic biology and modern society. Animals 2021, 11, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; 333p. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Lee, J.-S. Analysis of nucleotide diversity at genes Cyt-b and Co-1 on population, species, and genera levels. Russ. J. Genet. 2006, 42, 341–362, (In Russian, Translated in English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, S.B.; Marin, J.; Suleski, M.; Madeline, P.; Kumar, S. Tree of life reveals clock-like speciation and diversification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaum, A.M.; Hanner, R. Community engagement in seafood identification using DNA barcoding reveals market substitution in Canadian seafood. DNA Barcodes 2015, 3, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedunoori, A.; Turanov, S.V.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. Fish product mislabeling identified in the Russian far east using DNA barcoding. Gene Rep. 2017, 8, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneyer, V.S.; Rodionov, A. Plant DNA Barcodes. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2019, 9, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Sharina, S.N.; Goto, T.; Chichvarkhin, A.Y.; Balanov, A.A.; Vinnikov, K.A.; Ivankov, V.N.; Hanzawa, N. Cytochrome oxidase 1 gene sequence analysis in six flatfish species (Teleostei, Pleuronectidae) of Far East Russia with inferences in phylogeny and taxonomy. Mitochondrial DNA 2008, 19, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, C.J.; Yuan, H.; Li, C.; Arcila, D.; Betancur-R, R.; Hughes, L.C.; Ortí, G.; Tornabene, L. Exon-capture data and locus screening provide new insights into the phylogeny of flatfishes (Pleuronectoidei). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2022, 166, 107315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillis, D.M.; Mable, B.K.; Moritz, C. Application of molecular systematics: The state of the field and a look to the future. In Molecular Systematics; Hillis, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B., Eds.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 515–543. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z.; Salemi, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lemey, P. Assessing substitution saturation with DAMBE. In The Phylogenetic Handbook; Lemey, P., Salemi, M., Vandamme, A.-M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 615–630. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, C.S.; Beck, J.N.; Wilson, K.A.; Pilcher, E.R.; Kapahi, P.; Brem, R.B. Cross-phenotype association tests uncover genes mediating nutrient response in Drosophila. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Kong, X.; Chen, S.; Shi, W. Mechanisms of gene rearrangement in 13 bothids based on comparison with a newly completed mitogenome of the threespot flounder, Grammatobothus polyophthalmus (Pleuronectiformes: Bothidae. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Z.; Gong, L.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Luo, H.; et al. Large-scale sequencing of flatfish genomes provides insights into the polyphyletic origin of their specialized body plan. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | GenBank Number |
|---|---|
| Acrossocheilus monticola | KT367805 |
| Achirus lineatus | JQ639067 |
| Trinectes maculatus | JQ639070 |
| Neoachiropsetta milfordi | AP014593 |
| Arnoglossus polyspilus | AP014586 |
| Arnoglossus tenuis | KP134337 |
| Asterorhombus intermedius | MK256952 |
| Bothus myriaster | KJ433563 |
| Bothus pantherinus | AP014587 |
| Chascanopsetta lugubris | AP017455 |
| Chascanopsetta lugubris | KJ433561 |
| Crossorhombus azureus | JQ639068 |
| Crossorhombus kobensis | AP014589 |
| Crossorhombus valderostratus | KJ433566 |
| Grammatobothus polyophthalmus | MK770643 |
| Laeops lanceolata | AP014591 |
| Lophonectes gallus | KJ433567 |
| Psettina iijimae | KP134336 |
| Citharoides macrolepidotus | AP014588 |
| Lepidoblepharon ophthalmolepis | AP014592 |
| Cynoglossus abbreviatus | GQ380410 |
| Cynoglossus abbreviatus | JQ349004 |
| Cynoglossus bilineatus | JQ349000 |
| Cynoglossus gracilis | KT809367 |
| Cynoglossus interruptus | LC482306 |
| Cynoglossus itinus | JQ639062 |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | KU497492 |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | KU754054 |
| Cynoglossus joyneri | KY008569 |
| Cynoglossus nanhaiensis | MT117229 |
| Cynoglossus puncticeps | JQ349003 |
| Cynoglossus robustus | LC482305 |
| Cynoglossus roulei | MK574671 |
| Cynoglossus roulei | MN966658 |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | EU366230 |
| Cynoglossus semilaevis | GQ380409 |
| Cynoglossus senegalensis | MH709122 |
| Cynoglossus trulla | JQ348998 |
| Cynoglossus trigrammus | KP057581 |
| Cynoglossus zanzibarensis | KJ433559 |
| Paraplagusia bilineata | JQ349001 |
| Paraplagusia bleekeri | JQ349002 |
| Paraplagusia japonica | JQ639066 |
| Symphurus orientalis | KP992899 |
| Symphurus plagiusa | JQ639061 |
| Cyclopsetta fimbriata | AP014590 |
| Paralichthys adspersus | MW288827 |
| Paralichthys dentatus | KU053334 |
| Paralichthys lethostigma | KT896534 |
| Paralichthys olivaceus | AB028664 |
| Pseudorhombus cinnamoneus | JQ639069 |
| Pseudorhombus dupliciocellatus | KJ433562 |
| Cleisthenes pinetorum | KT223828 |
| Clidoderma asperrimum | MK210570 |
| Colistium nudipinnis | JQ639063 |
| Hippoglossoides platessoides | MN122825 |
| Hippoglossus hippoglossus | AM749122 |
| Hippoglossus hippoglossus | AM749123 |
| Hippoglossus hippoglossus | AM749124 |
| Hippoglossus stenolepis | AM749126 |
| Hippoglossus stenolepis | AM749127 |
| Hippoglossus stenolepis | AM749128 |
| Hippoglossus stenolepis | AM749129 |
| Limanda aspera | KP013094 |
| Limanda limanda | MN122886 |
| Pelotretis flavilatus | KC554065 |
| Peltorhamphus novaezeelandiae | JQ639065 |
| Platichthys stellatus | EF424428 |
| Platichthys stellatus | MZ365029 |
| Pleuronichthys cornutus | JQ639071 |
| Pleuronichthys cornutus | KY038655 |
| Pseudopleuronectes herzensteini | MW713061 |
| Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae | KT224485 |
| Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae | KT878309 |
| Reinhardtius hippoglossoides | AM749130 |
| Reinhardtius hippoglossoides | AM749131 |
| Reinhardtius hippoglossoides | AM749132 |
| Reinhardtius hippoglossoides | AM749133 |
| Verasper moseri | EF025506 |
| Verasper moseri | LC583747 |
| Verasper variegatus | DQ403797 |
| Verasper variegatus | MK210571 |
| Psettodes erumei | FJ606835 |
| Samaris cristatus | JQ700101 |
| Samariscus latus | KF494223 |
| Scophthalmus maximus | EU419747 |
| Zeugopterus punctatus | MT410862 |
| Aesopia cornuta | KF000065 |
| Aseraggodes kobensis | KJ601760 |
| Brachirus orientalis | KJ433558 |
| Brachirus orientalis | KJ513134 |
| Heteromycteris japonicus | JQ639060 |
| Liachirus melanospilos | KF573188 |
| Pardachirus pavoninus | AP006044 |
| Pardachirus pavoninus | KJ433565 |
| Pardachirus pavoninus | KJ461620 |
| Zebrias japonicus | KJ433482 |
| Zebrias japonicus | KJ433568 |
| Solea ovata | KF142459 |
| Solea ovata | KJ496338 |
| Solea senegalensis | AB270760 |
| Zebrias crossolepis | KJ433564 |
| Zebrias crossolepis | KT367804 |
| Zebrias quagga | JQ348999 |
| Zebrias zebra | JQ700100 |
| Zebrias zebrinus | KC491209 |
| Zebrias zebrinus | KC519737 |
| Tetraodon mbu | AP011923 |
| Genome Content/Sequences | Pseudopleuronectes herzensteini MW713061 | Platichthys stellatus MZ365029 | Pseudopleuronectes yokohamae KT224485 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size (bp) | 16,845 | 16,992 | 17,383 |
| Gene number, PCGs | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| Gene number, rRNA | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Gene number tRNA | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| tRNA-Phe | 1.68 (+) | 1.68 (+) | 1.68 (+) |
| 12S rRNA | 69.1017 (+) | 69.1017 (+) | 69.1017 (+) |
| tRNA-Val | 1018.1090 (+) | 1018.1090 (+) | 1018.1090 (+) |
| 16S rRNA | 1091.2806 (+) | 1091.2805 (+) | 1091.2806 (+) |
| tRNA-Leu | 2807.2880 (+) | 2806.2879 (+) | 2807.2880 (+) |
| ND1 | 2881.3855 (+) | 2880.3854 (+) | 2881.3855 (+) |
| tRNA-Ile | 3861.3931 (+) | 3860.3930 (+) | 3861.3931 (+) |
| tRNA-Gln | 3931.4001 (−) | 3930.4000 (−) | 3931.4001 (−) |
| tRNA-Met | 4001.4069 (+) | 4000.4068 (+) | 4001.4069 (+) |
| ND2 | 4070.5114 (+) | 4069.5113 (+) | 4070.5114 (+) |
| tRNA-Trp | 5115.5186 (+) | 5114.5185 (+) | 5115.5186 (+) |
| tRNA-Ala | 5188.5256 (−) | 5187.5255 (−) | 5188.5256 (−) |
| tRNA-Asn | 5258.5330 (−) | 5257.5329 (−) | 5258.5330 (−) |
| tRNA-Cys | 5368.5432 (−) | 5368.5432 (−) | 5369.5433 (−) |
| tRNA-Tyr | 5433.5500 (−) | 5433.5500 (−) | 5434.5501 (−) |
| COI | 5502.7061 (+) | 5502.7061 (+) | 5503.7062 (+) |
| tRNA-Ser | 7062.7132 (−) | 7062.7132 (−) | 7063.7133 (−) |
| tRNA-Asp | 7147.7217 (+) | 7147.7217 (+) | 7148.7218 (+) |
| COII | 7224.7914 (+) | 7224.7914 (+) | 7225.7915 (+) |
| tRNA-Lys | 7915.7987 (+) | 7915.7987 (+) | 7916.7988 (+) |
| ATPase 8 | 7989.8156 (+) | 7989.8156 (+) | 7990.8157 (+) |
| ATPase 6 | 8147.8829 (+) | 8147.8829 (+) | 8148.8830 (+) |
| COIII | 8830.9614 (+) | 8830.9614 (+) | 8831.9615 (+) |
| tRNA-Gly | 9615.9686 (+) | 9615.9686 (+) | 9616.9687 (+) |
| ND3 | 9687.10035 (+) | 9687.10035 (+) | 9688.10036 (+) |
| tRNA-Arg | 10,036.10104 (+) | 10,036.10104 (+) | 10,037.10105 (+) |
| ND4L | 10105.10401 (+) | 10,105.10401 (+) | 10,106.10402 (+) |
| ND4 | 10,395.11775 (+) | 10,395.11775 (+) | 10,396.11776 (+) |
| tRNA-His | 11,776.11845 (+) | 11,776.11845 (+) | 11,777.11846 (+) |
| tRNA-Ser | 11,846.11912 (+) | 11,846.11912 (+) | 11,847.11913 (+) |
| tRNA-Leu | 11,917.11989 (+) | 11,917.11989 (+) | 11,918.11990 (+) |
| ND5 | 11,990.13828 (+) | 11,990.13828 (+) | 11,991.13829 (+) |
| ND6 | 13,825.14346 (−) | 13,825.14346 (−) | 13,826.14347 (−) |
| tRNA-Glu | 14,347.14415 (−) | 14,347.14415 (−) | 14,348.14416 (−) |
| Cyt b | 14,420.15560 (+) | 14,420.15560 (+) | 14,421.15561 (+) |
| tRNA-Thr | 15,561.15633 (+) | 15,561.15633 (+) | 15,562.15634 (+) |
| tRNA-Pro | 15,633.15703 (−) | 15,634.15704 (−) | 15,634.15704 (−) |
| control region | 15,704.16845 (+) | 15,705.16992 (+) | 15,705.17383 (+) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Redin, A.D.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia. Diversity 2022, 14, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100805
Redin AD, Kartavtsev YP. The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia. Diversity. 2022; 14(10):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100805
Chicago/Turabian StyleRedin, Alexander D., and Yuri Ph. Kartavtsev. 2022. "The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia" Diversity 14, no. 10: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100805
APA StyleRedin, A. D., & Kartavtsev, Y. P. (2022). The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia. Diversity, 14(10), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14100805






