The Foraging Window for Greater White-Fronted Geese (Anser albifrons) Is Consistent with the Growth Stage of Carex
Abstract
1. Introduction
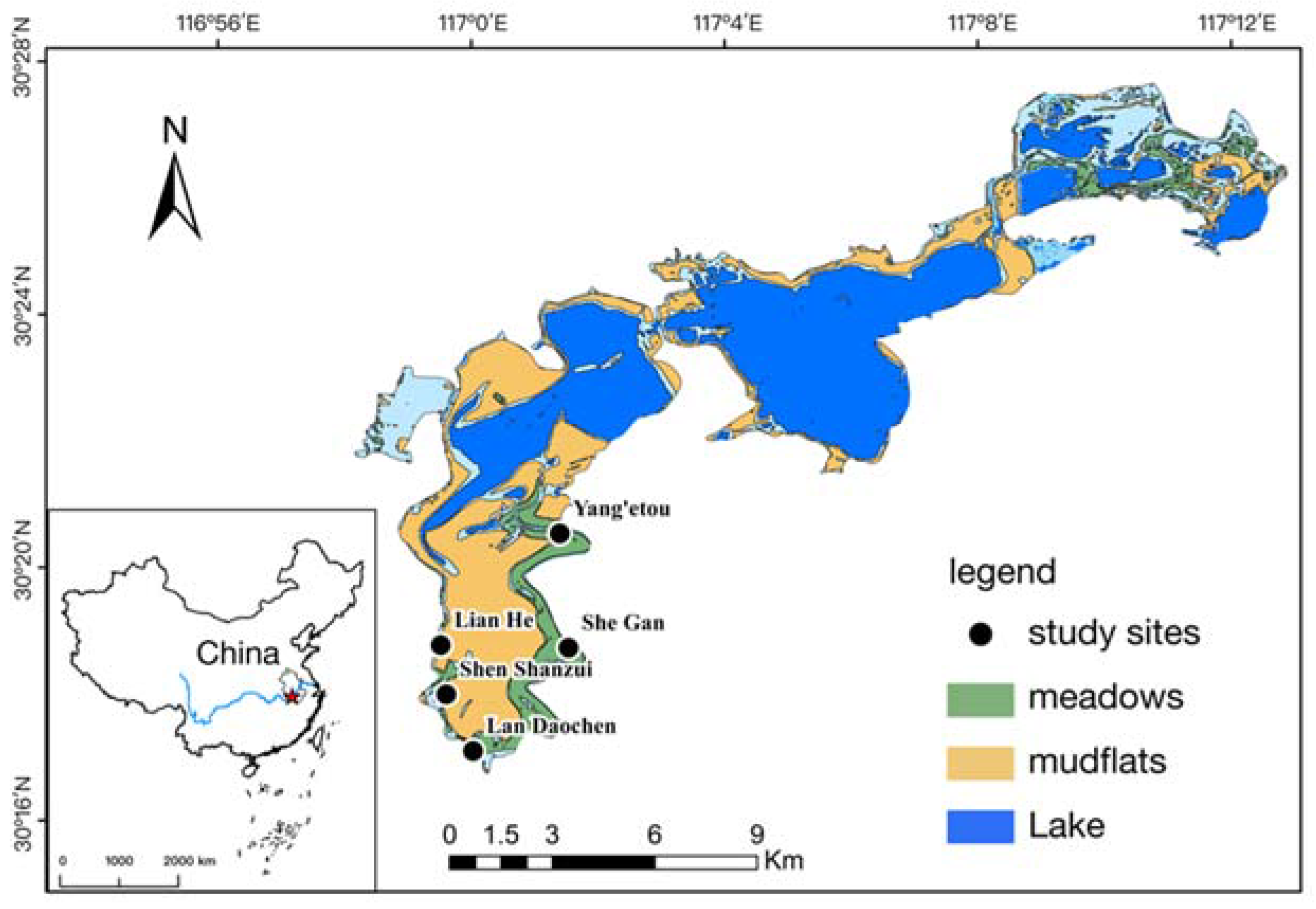
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charnov, E.L. Optimal foraging, the marginal value theorem. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1976, 9, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, L.; Song, Y.; Xu, W. Foraging behavior of the greater white-fronted goose (Anser albifrons) wintering at Shengjin Lake: Diet shifts and habitat use. Avian Res. 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerens, J.M.; Gawlik, D.E.; Herring, G.; Cook, M.I. Dynamic habitat selection by two wading bird species with divergent foraging strategies in a seasonally fluctuating wetland. The Auk 2011, 128, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Říha, M.; Prchalová, M. Models of animal distributions in inland waters. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 292–301. ISBN 978-0-12-822041-2. [Google Scholar]
- Durant, D.; Fritz, H.; Blais, S.; Duncan, P. The functional response in three species of herbivorous Anatidae: Effects of sward height, body mass and bill size. J. Anim. Ecology 2003, 72, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, G.S.; Paxton, M.; King, J.; Beuster, H. Foraging guild membership explains variation in waterbird responses to the hydrological regime of an arid-region flood-pulse river in Namibia: Community dynamics of waterbirds in Namibia. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, K.; Benvenuti, S.; Dall’Antonia, L.; Kampp, K.; Ribolini, A. Time allocation and foraging behavior of chick-rearing Brünnich’s Guillemots Uria Lomvia in high-arctic greenland. Ibis 2008, 142, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, D.; Fritz, H. Variation of pecking rate with sward height in wild wigeon Anas Penelope. J. Ornithol. 2006, 147, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, L.; Song, Y. Water level management plan based on the ecological demands of wintering waterbirds at Shengjin Lake. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, P.; Sinha, A.; Mondal, P.; Khan, T.N. Calendar-effects and temperature-impacts in migratory waterbirds at three tropical Indian wetlands. Acta Oecologica 2012, 43, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saino, N.; Szep, T.; Romano, M.; Rubolini, D.; Spina, F.; Moller, A.P. Ecological conditions during winter predict arrival date at the breeding quarters in a trans-saharan migratory bird. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Xia, S.; Yu, X.; Rao, D.; JIN, B. A study on the suitable time window of feeding vegetation fit for overwintering geese in Poyang Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 7539–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, P.D.; Bryant, J.P.; Chapin, F.S. Resource availability and plant antiherbivore defense. Science 1985, 230, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmshurst, J.F.; Fryxell, J.M.; Hudsonb, R.J. Forage quality and patch choice by Wapiti (Cervus elaphus). Behav. Ecol. 1995, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, W.; Ye, X. Effects of waterbird herbivory on dominant perennial herb Carex thunbergii in Shengjin Lake. Diversity 2022, 14, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Wen, L.; Feng, D.; Zhang, H.; Lei, G. Delayed flood recession in central Yangtze floodplains can cause significant food shortages for wintering geese: Results of inundation experiment. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, L. The relationship between seasonal water level fluctuation and habitat availability for wintering waterbirds at Shengjin Lake, China. Bird Conserv. Int. 2019, 29, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhou, L.; Mahtab, N.; Fan, S.; Song, Y. The influence of food density, flock size, and disturbance on the functional response of Bewick’s Swans (Cygnus columbianus bewickii) in wintering habitats. Animals 2019, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, L.Z.; Xu, W. Diversity of wintering waterbirds enhanced by restoring aquatic vegetation at Shengjin Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, N.; Xu, W. Effects of variation in food resources on foraging habitat use by wintering hooded cranes (Grus monacha). Avian Res. 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Lu, J.-J. Feeding ecology of two wintering geese species at Poyang Lake, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1999, 14, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cong, P.; Barter, M.; Fox, A.D.; Cao, L. The changing abundance and distribution of greater white-fronted geese Anser albifrons in the Yangtze River Floodplain: Impacts of recent hydrological changes. Bird Conserv. Int. 2012, 22, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Q.; Solovyeva, D.; Lameris, T.; Batbayar, N.; Bysykatova-Harmey, I.; Lee, H.; Emelyanov, V.; Rozenfeld, S.B.; Park, J.; et al. Population trends and migration routes of the east Asian bean goose Anser fabalis middendorffii and A. f. serrirostris. Wildfowl 2020, 6, 124–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, P.N. Sampling methods in behavior research. Poult. Sci. 1992, 71, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Guan, L.; Lu, C.; Lei, G.; Wen, L.; Liu, G. Optimising hydrological conditions to sustain wintering waterbird populations in Poyang Lake National Natural Reserve: Implications for dam operations. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2366–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosholn, M.; Anciães, M. Focal animal sampling. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–3. ISBN 978-3-319-47829-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, L.; Zhao, N.; Beauchamp, G. Vigilance and activity time-budget adjustments of wintering hooded cranes, Grus monacha, in human-dominated foraging habitats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Zhou, L.; Song, Y. Shifts in foraging behavior of wintering hooded cranes (Grus monacha) in three different habitats at Shengjin Lake, China. Avian Res. 2016, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Meng, Q.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, M. The influence of hydrological variables, climatic variables and food availability on Anatidae in interconnected river-lake systems, the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Floodplain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Shao, R.; Yan, C.; Jin, J.; Shan, J.; Li, F.; Ji, W.; Bin, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Modified hydrological regime from the three gorges dam increases the risk of food shortages for wintering waterbirds in Poyang Lake. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xia, S.; Liu, G.; Wang, M.; Ding, Z.; Yu, P.; Tang, X. Effect of hydrological variation on vegetation dynamics for wintering waterfowl in China’s Poyang Lake wetland. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, D.; Fritz, H.; Duncan, P. Feeding patch selection by herbivorous Anatidae: The influence of body size, and of plant quantity and quality. J. Avian Biol. 2004, 35, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alerstam, T.; Hedenström, A.; Åkesson, S. Long-distance migration: Evolution and determinants. Oikos 2003, 103, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayly, N.J.; Rosenberg, K.V.; Easton, W.E.; Gomez, C.; Carlisle, J.; Ewert, D.N.; Drake, A.; Goodrich, L. Major stopover regions and migratory bottlenecks for Nearctic-Neotropical land birds within the Neotropics: A review. Bird Conserv. Int. 2018, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Sorte, F.A.; Fink, D. Migration distance, ecological barriers and en-route variation in the migratory behavior of terrestrial bird populations: Migratory behavior of terrestrial bird populations. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Foraging Behavior | Pearson Correlation between Plant Characteristics (r) | |
|---|---|---|
| Water Content | Plant Height | |
| Pecking rate | 0.492 | 0.626 |
| Foraging behavior time budget | 0.622 | 0.670 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Song, Y. The Foraging Window for Greater White-Fronted Geese (Anser albifrons) Is Consistent with the Growth Stage of Carex. Diversity 2022, 14, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110943
Zhong Y, Cheng L, Fan Y, Zhou L, Song Y. The Foraging Window for Greater White-Fronted Geese (Anser albifrons) Is Consistent with the Growth Stage of Carex. Diversity. 2022; 14(11):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110943
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yundong, Lei Cheng, Yanguang Fan, Lizhi Zhou, and Yunwei Song. 2022. "The Foraging Window for Greater White-Fronted Geese (Anser albifrons) Is Consistent with the Growth Stage of Carex" Diversity 14, no. 11: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110943
APA StyleZhong, Y., Cheng, L., Fan, Y., Zhou, L., & Song, Y. (2022). The Foraging Window for Greater White-Fronted Geese (Anser albifrons) Is Consistent with the Growth Stage of Carex. Diversity, 14(11), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14110943







