Complete Chloroplast Genome of Cnidium monnieri (Apiaceae) and Comparisons with Other Tribe Selineae Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taxon Sampling and DNA Sequencing
2.2. Chloroplast Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Codon Usage, RNA Editing, Repeat Sequence, and SSR of C. monnieri Cp Genome
2.4. Comparative Chloroplast Genomic Analysis
2.5. Evolutionary and Phylogenomic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the C. monnieri Cp Genome
3.2. Repeat Sequence and SSRs
3.3. Codon Usage, RNA Editing, and Ka/Ks in Protein-Coding Genes
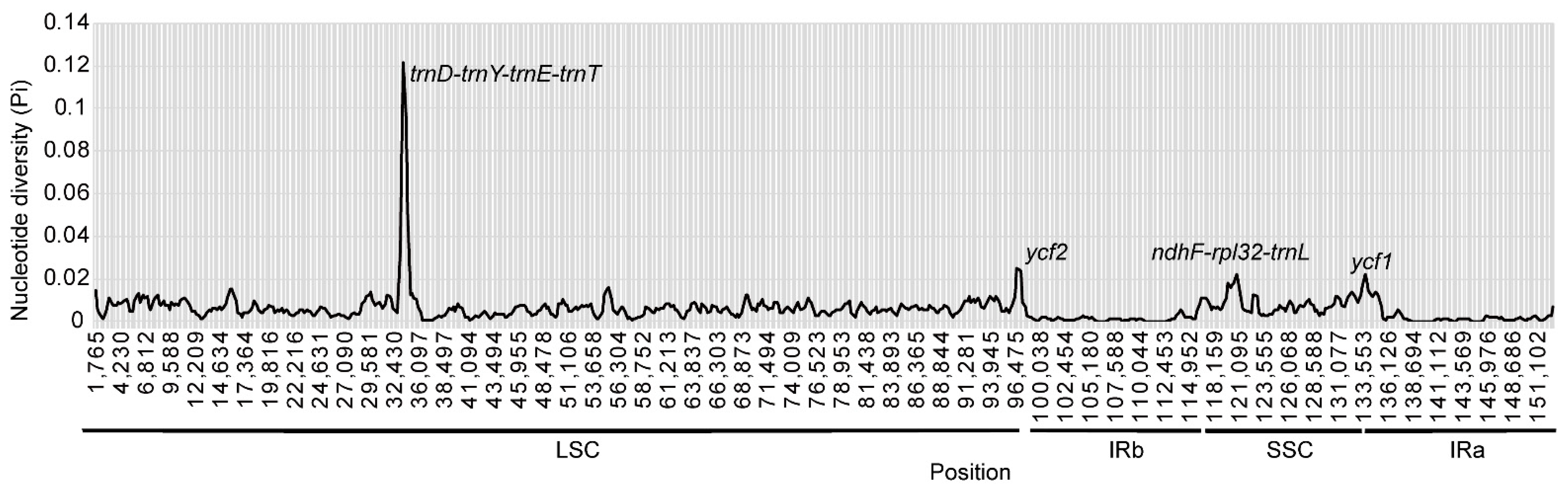
3.4. Comparative Analyses
3.5. Phylogeny Inference
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pu, F.D.; Watson, M.F. Cnidium Cusson. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005; Volume 14, pp. 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- China Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China Part I; Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhang, Q.; Qin, L.; He, W.; Van Puyvelde, L.; Maes, D.; Adams, A.; Zheng, H.; De Kimpe, N. Coumarins from Cnidium monnieri and their antiosteoporotic activity. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, A.W.H.; Lenon, G.B. Phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology of Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.M.; Jia, M.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, N.D.; Wen, X.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Qin, L.P. Cnidium monnieri: A review of traditional uses, phytochemical and ethnopharmacological properties. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 835–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.L.; LI, Q.; Zhang, C.Y. Physical and chemical identification of Fructus cnidii and its false Apium graveolens fruits. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2001, 18, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Downie, S.R.; Spalik, K.; Katz-Downie, D.S.; Reduron, J. Major clades within Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae as inferred by phylogenetic analysis of nrDNA ITS sequences. Plant Div. Evol. 2010, 128, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.Z.; Wei, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Downie, S.R. Molecular phylogenetics of Ligusticum (Apiaceae) based on nrDNA ITS sequences: Rampant polyphyly, placement of the Chinese endemic species, and a much-reduced circumscription of the genus. Int. J. Plant. Sci. 2020, 181, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, H.E.; Emes, M.J. Nonphotosynthetic metabolism in plastids. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 51, 111–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Khurana, J.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, P. An update on chloroplast genomes. Plant Syst. Evol. 2008, 271, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Jin, J.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Chase, M.W.; Soltis, D.E.; Li, H.T.; Yang, J.B.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. Diversification of Rosaceae since the Late Cretaceous based on plastid phylogenomics. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Alonso, R.; Ibañez, V.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Dopazo, J. A phylogenetic analysis of 34 chloroplast genomes elucidates the relationships between wild and domestic species within the genus Citrus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2015–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, K.; Nobis, M.; Myszczyński, K.; Klichowska, E.; Sawicki, J. Plastid super-barcodes as a tool for species discrimination in feather grasses (Poaceae: Stipa). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, Y.P.; Salmaki, Y.; Drew, B.T.; Wilson, T.C.; Scheen, A.C.; Celep, F.; Bräuchler, C.; Bendiksby, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. An updated tribal classification of Lamiaceae based on plastome phylogenomics. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Dong, W.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, L. Phylogenomic and evolutionary dynamics of inverted repeats across Angelica plastomes. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xie, D.F.; Guo, X.L.; Zheng, Z.Y.; He, X.J.; Zhou, S.D. Comparative analysis of the complete plastid genome of five Bupleurum species and new insights into DNA barcoding and phylogenetic relationship. Plants 2020, 9, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Xie, X.; Chen, A.; Li, F.; Tian, E.; Chao, Z. The chloroplast genomes of four Bupleurum (Apiaceae) species endemic to Southwestern China, a diversity center of the genus, as well as their evolutionary implications and phylogenetic inferences. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yue, M.; Niu, C.; Ma, X.F.; Li, Z.H. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of four endangered herbals of Notopterygium. Genes 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Li, Z.X.; Xie, D.F.; Gui, L.J.; Peng, C.; Wen, J.; He, X.J. Plastomes of eight Ligusticum species: Characterization, genome evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, M.; Lindgreen, S.; Orlando, L. AdapterRemoval v2: Rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.K.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.B. The complete chloroplast genome of Melanosciadium pimpinelloideum (Apiaceae), an endemic species of China. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020, 5, 2371–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Li, M. The complete plastome of Peucedanum praeruptorum (Apiaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019, 4, 3612–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Geng, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, M. Characterization of the complete plastome of Saposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz.) Schischk. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020, 5, 786–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samigullin, T.H.; Logacheva, M.D.; Terenteva, E.I.; Degtjareva, G.V.; Vallejo-Roman, C.M. Plastid genome of Seseli montanum: Complete sequence and comparison with plastomes of other members of the Apiaceae family. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2010, 8, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analysis with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Downie, S.R.; Yu, Y.; He, X. Historical biogeography of the Angelica group (Apiaceae tribe Selineae) inferred from analyses of nrDNA and cpDNA sequences. J. Syst. Evol. 2012, 50, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Xie, D.F.; Price, M.; Ren, T.; Deng, Y.Q.; Gui, L.J.; Guo, X.L.; He, X.J. Backbone phylogeny and evolution of Apioideae (Apiaceae): New insights from phylogenomic analyses of plastome data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 161, 107183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, H.; Downie, S.R.; Liu, Z.W.; Gong, X. A molecular phylogeny of Chinese Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae inferred from nuclear ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. Taxon 2008, 57, 402–416. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Downie, S.R.; Peng, H. Towards a more robust molecular phylogeny of Chinese Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae: Additional evidence from nrDNA ITS and cpDNA intron (rpl16 and rps16) sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 53, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.N.; Ruhlman, T.A.; Sabir, J.S.; Hajrah, N.H.; Alharbi, N.S.; Al-Malki, A.L.; Bailey, C.D.; Jansen, R.K. Plastid genome sequences of legumes reveal parallel inversions and multiple losses of rps16 in papilionoids. J. Syst. Evol. 2015, 53, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Yang, Y.C.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Z.L. Comparative plastid genomes of Primula species: Sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Jin, J.J.; Li, H.T.; Yang, J.B.; Mandala, V.S.; Croley, M.; Mostow, R.; Douglas, N.A.; Chase, M.W.; Christenhusz, M.J.M.; et al. Plastid phylogenomic insights into the evolution of Caryophyllales. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 134, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Al- Harrasi, A. Gene loss and evolution of the plastome. Genes 2020, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Song, J.Y.; Gao, H.H.; Zhu, Y.J.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.H.; Yao, H.; Sun, C.; Li, X.E.; Li, C.Y.; et al. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akashi, H. Codon bias evolution in Drosophila. Population genetics of mutation-selection drift. Gene 1997, 205, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Lee, W.; Hottes, A.K.; Shapiro, L.; McAdams, H.H. Codon usage between genomes is constrained by genome-wide mutational processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Ying, Z.; Yu, S.; Wang, Q.; Liao, G.; Ge, Y.; Cheng, R. Complete chloroplast genome of Stephania tetrandra (Menispermaceae) from Zhejiang Province: Insights into molecular structures, comparative genome analysis, mutational hotspots and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, T.; Bai, G.; Zhao, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Fagopyrum dibotrys: Genome features, comparative analysis and phylogenetic relationships. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.Q.; Zhang, H.; Shen, H. Chloroplast genome sequence of Chongming lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) and comparative analyses with other legume chloroplast genomes. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Huang, S.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. Abundant RNA editing sites of chloroplast protein-coding genes in Ginkgo biloba and an evolutionary pattern analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Zehrmann, A.; Verbitskiy, D.; Härtel, B.; Brennicke, A. RNA editing in plants and its evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, T.G.; da Silva, G.M.; de Santana, L.A.; de Oliveira, J.D.; Rogalski, J.M.; Balsanelli, E.; de Souza, E.M.; de Oliveira Pedrosa, F.; Rogalski, M. Phylogenetic and evolutionary features of the plastome of Tropaeolum pentaphyllum Lam. (Tropaeolaceae). Planta 2020, 252, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santana Lopes, A.; Pacheco, T.G.; Nimz, T.; do Nascimento Vieira, L.; Guerra, M.P.; Nodari, R.O.; de Souza, E.M.; de Oliveira Pedrosa, F.; Rogalski, M. The complete plastome of macaw palm [Acrocomia aculeata (Jacq.) Lodd. ex Mart.] and extensive molecular analyses of the evolution of plastid genes in Arecaceae. Planta 2018, 247, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.X. The complete chloroplast genomes of three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) species: Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaf, S.; Waqas, M.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, M.A.; Kang, S.M.; Imran, Q.M.; Shahzad, R.; Bilal, S.; Yun, B.W.; Lee, I.J. The complete chloroplast genome of wild rice (Oryza minuta) and its comparison to related species. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Lee, H.L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaila, T.; Chaduvla, P.K.; Saxena, S.; Bahadur, K.; Gahukar, S.J.; Chaudhury, A.; Sharma, T.R.; Singh, N.K.; Gaikwad, K. Chloroplast genome sequence of Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millspaugh) and Cajanus scarabaeoides (L.) Thouars: Genome organization and comparison with other Legumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, S. Complete chloroplast genome of medicinal plant Lonicera japonica: Genome rearrangement, intron gain and loss, and implications for phylogenetic studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisinger, M.M.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Extreme reconfiguration of plastid genomes in the angiosperm family Geraniaceae: Rearrangements, repeats, and codon usage. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, J.; Schwarz, E.; Ellison, N.; Zhang, J.; Baeshen, N.A.; Mutwakil, M.; Jansen, R.; Ruhlman, T. Evolutionary and biotechnology implications of plastid genome variation in the inverted-repeat-lacking clade of legumes. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, W.B.; Tan, Y.H.; Liu, B.; Yao, X.; Jin, J.; Michael, P.; Yang, J.B.; Corlett, R.T. Evolutionary comparisons of the chloroplast genome in Lauraceae and insights into loss events in the Magnoliids. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2354–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauz-Santos, L.A.; Da Costa, Z.P.; Callot, C.; Cauet, S.; Zucchi, M.I.; Bergès, H.; Van den Berg, C.; Vieira, M.L.C. A repertory of rearrangements and the loss of an inverted repeat region in Passiflora chloroplast genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makalowski, W.; Boguski, M.S. Evolutionary parameters of the transcribed mammalian genome: An analysis of 2820 orthologous rodent and human sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9407–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.C.; Chen, S.L.; Xiao, P.G. Molecular evolution and positive Darwinian selection of the chloroplast maturase matK. J. Plant Res. 2010, 123, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allahverdiyeva, Y.; Mamedov, F.; Mäenpää, P.; Vass, I.; Aro, E.M. Modulation of photosynthetic electron transport in the absence of terminal electron acceptors: Characterization of the rbcL deletion mutant of tobacco. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1709, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Bédard, J.; Hirano, M.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Oishi, M.; Imai, M.; Takase, M.; Ide, T.; Nakai, M. Uncovering the protein translocon at the chloroplast inner envelope membrane. Science 2013, 339, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.B.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Shahzad, K.; Li, Z.H. Comparative chloroplast genomics of Dipsacales species: Insights into sequence variation, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilu, K.W.; Black, C.M.; Oza, D. Impact of gene molecular evolution on phylogenetic reconstruction: A case study in the rosids (Superorder Rosanae, Angiosperms). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.P.; Xu, C.; Li, C.H.; Sun, J.H.; Zuo, Y.J.; Shi, S.; Cheng, T.; Guo, J.J.; Zhou, S.L. ycf1, the most promising plastid DNA barcode of land plants. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J.; Wurdack, K.J.; Zimmer, E.A.; Weigt, L.A.; Janzen, D.H. Use of DNA barcodes to identify flowering plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8369–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, C.J.; Waters, D.L.; Edwards, M.A.; Bowen, S.G.; Rice, N.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Henry, R.J. Chloroplast genome sequences from total DNA for plant identification. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yu, Y.; Xie, D.F.; Peng, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. A transcriptome-based study on the phylogeny and evolution of the taxonomically controversial subfamily Apioideae (Apiaceae). Ann. Bot. 2020, 125, 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Li, W.H.; Sharp, P.M. Rates of nucleotide substitution vary greatly among plant mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9054–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sequence Lengths (bp) | Number of Genes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | LSC | SSC | IR | Total | Protein-Coding | tRNA | rRNA | GC(%) | |
| C. monnieri | 147,371 | 94,361 | 17,552 | 17,729 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.4 |
| A. dahurica | 146,918 | 93,604 | 17,676 | 17,819 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.5 |
| A. gigas | 146,918 | 93,120 | 17,582 | 18,108 | 128 | 83 | 36 | 8 | 37.6 |
| A. laxifoliata | 147,026 | 93,191 | 17,493 | 18,171 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.5 |
| G. littoralis | 147,477 | 93,496 | 17,555 | 18,213 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.5 |
| L. buchtormensis | 147,036 | 91,969 | 17,469 | 18,799 | 127 | 83 | 36 | 8 | 37.6 |
| Lig. likiangense | 148,196 | 92,305 | 17,575 | 19,158 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.5 |
| Lig. thomsonii | 147,462 | 93,363 | 17,591 | 18,254 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.6 |
| M. pimpinelloideum | 164,431 | 76,445 | 17,565 | 35,211 | 144 | 99 | 37 | 8 | 37.5 |
| P. japonicum | 164,653 | 75,584 | 17,551 | 35,759 | 144 | 99 | 37 | 8 | 37.5 |
| P. praeruptorum | 147,197 | 92,161 | 17,610 | 18,713 | 128 | 84 | 35 | 8 | 37.6 |
| S. divaricata | 147,834 | 93,202 | 17,324 | 18,654 | 129 | 85 | 36 | 8 | 37.5 |
| Ses. montanum | 147,823 | 92,620 | 17,479 | 18,862 | 127 | 82 | 36 | 8 | 37.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, T.; Aou, X.; Tian, R.; Li, Z.; Peng, C.; He, X. Complete Chloroplast Genome of Cnidium monnieri (Apiaceae) and Comparisons with Other Tribe Selineae Species. Diversity 2022, 14, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050323
Ren T, Aou X, Tian R, Li Z, Peng C, He X. Complete Chloroplast Genome of Cnidium monnieri (Apiaceae) and Comparisons with Other Tribe Selineae Species. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050323
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Ting, Xueyimu Aou, Rongming Tian, Zhenbing Li, Chang Peng, and Xingjin He. 2022. "Complete Chloroplast Genome of Cnidium monnieri (Apiaceae) and Comparisons with Other Tribe Selineae Species" Diversity 14, no. 5: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050323
APA StyleRen, T., Aou, X., Tian, R., Li, Z., Peng, C., & He, X. (2022). Complete Chloroplast Genome of Cnidium monnieri (Apiaceae) and Comparisons with Other Tribe Selineae Species. Diversity, 14(5), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050323






