Morphological Modifications and Injuries of Corals Caused by Symbiotic Feather Duster Worms (Sabellidae) in the Caribbean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
| Host Species | Curaçao | Bonaire | St. Eustatius |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia | |||
| Agariciidae | |||
| Agaricia agaricites (Linnaeus, 1758) | a | e | - |
| Agaricia fragilis Dana, 1846 | a | - | f |
| Agaricia humilis (Verrill, 1901) | a | - | - |
| Agaricia lamarcki Milne Edwards & Haime, 1851 | a,b,d | - | f |
| Helioseris cucullata (Ellis and Solander, 1786) | a | - | f |
| Astrocoeniidae | |||
| Stephanocoenia intersepta (Esper, 1795) | a,b | - | f |
| Faviidae: Faviinae | |||
| Colpophyllia natans (Houttuyn, 1772) | a,b | - | - |
| Diploria labyrinthiformis (Linnaeus, 1758) | a | - | f |
| Pseudodiploria strigosa (Dana, 1846) | a,d | - | - |
| Faviidae: Mussiinae | |||
| Mycetophyllia aliciae Wells, 1973 | - | - | f |
| Meandrinidae | |||
| Eusmilia fastigiata (Pallas, 1766) | b | - | - |
| Meandrina jacksoni Weil & Pinzón, 2011 | - | - | f |
| Meandrina meandrites (Linnaeus, 1758) | a,c | e | f |
| Merulinidae | |||
| Dendrogyra cylindrus (Ehrenberg, 1834) | a | - | - |
| Orbicella annularis (Ellis & Solander, 1786) | a | - | f |
| Orbicella faveolata (Ellis & Solander, 1786) | a | e | - |
| Orbicella franksi (Gregory, 1895) | a,b,d | e | f |
| Montastraeidae | |||
| Montastraea cavernosa (Linnaeus, 1767) | a,b | - | - |
| Pocilloporidae | |||
| Madracis auretenra Locke, Weil & Coates, 2007 | a,b | - | - |
| Madracis decactis (Lyman, 1859) | a | - | - |
| Madracis pharensis (Heller, 1868) | a,b | e | f |
| Madracis senaria Wells, 1973 | a,b | e | - |
| Poritidae | |||
| Porites astreoides Lamarck, 1816 | a,d | e | f |
| Porites porites (Pallas, 1766) | - | - | f |
| Rhizangiidae | |||
| Siderastrea siderea (Ellis & Solander, 1768) | a,b | - | f |
| Cnidaria: Hydrozoa | |||
| Milleporidae | |||
| Millepora alcicornis Linnaeus, 1758 | a | e | - |
| Millepora complanata Lamarck, 1816 | a | - | - |
| Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Alcyonacea | |||
| Anthothelidae | |||
| Erythropodium caribaeorum (Duchassaing & Michelotti, 1860) | a | - | - |
| Chordata: Tunicata: Ascidiacea | |||
| Didemnidae | |||
| Trididemnum solidum (Van Name, 1902) | a,b | - | - |
| Porifera spp. | a | - | - |
| Unidentified dead coral with/without algae | a | - | - |
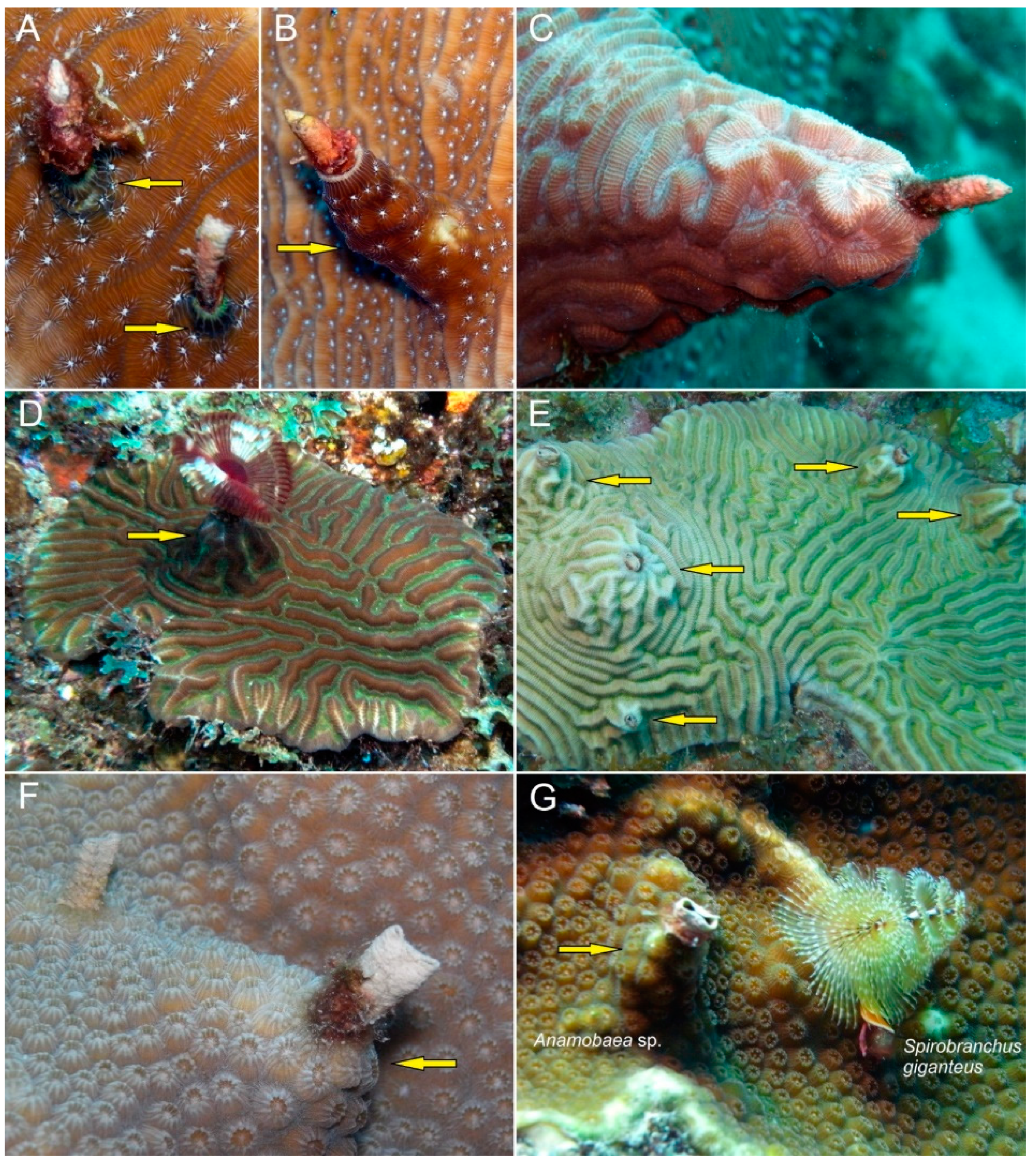
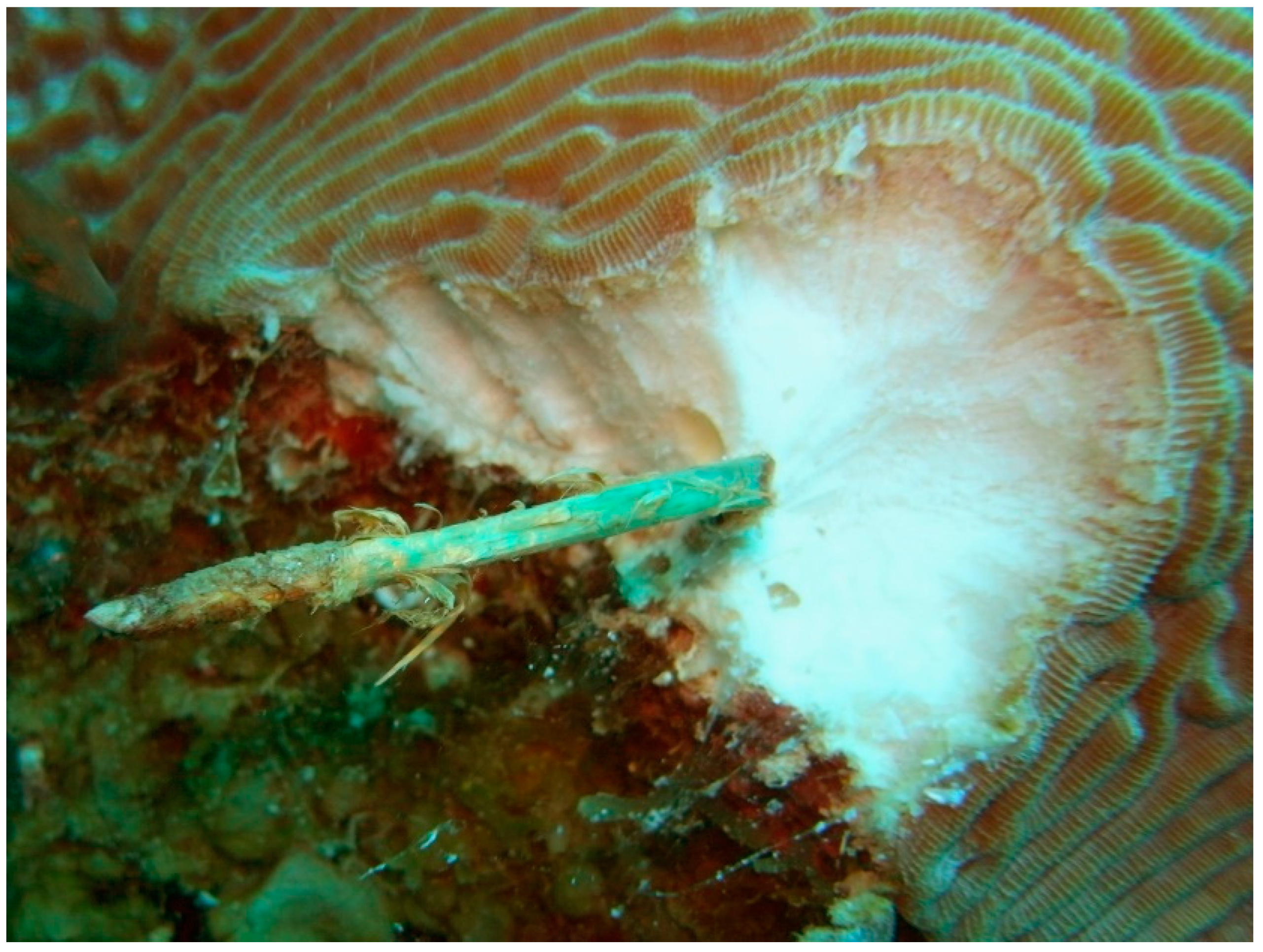
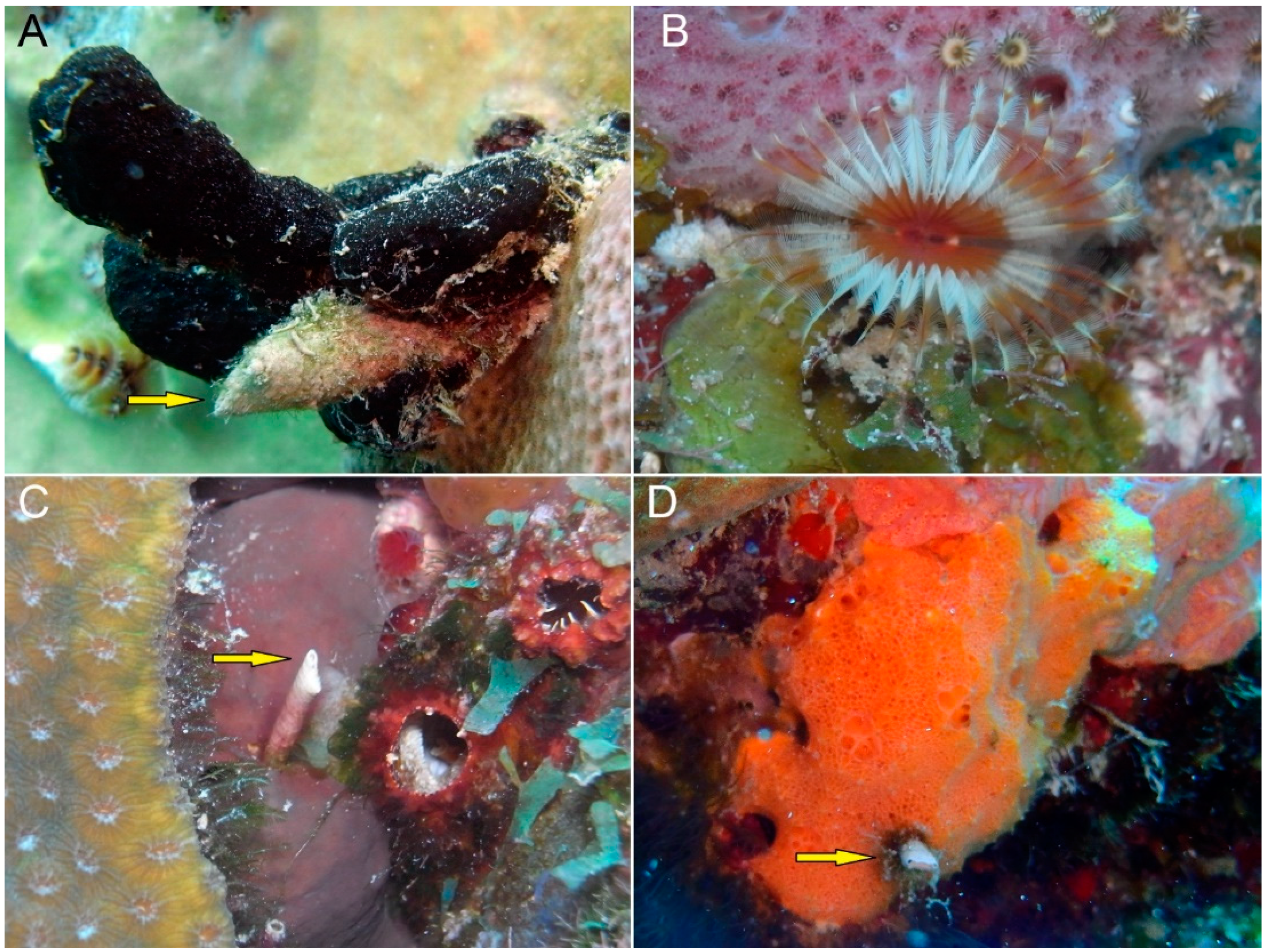
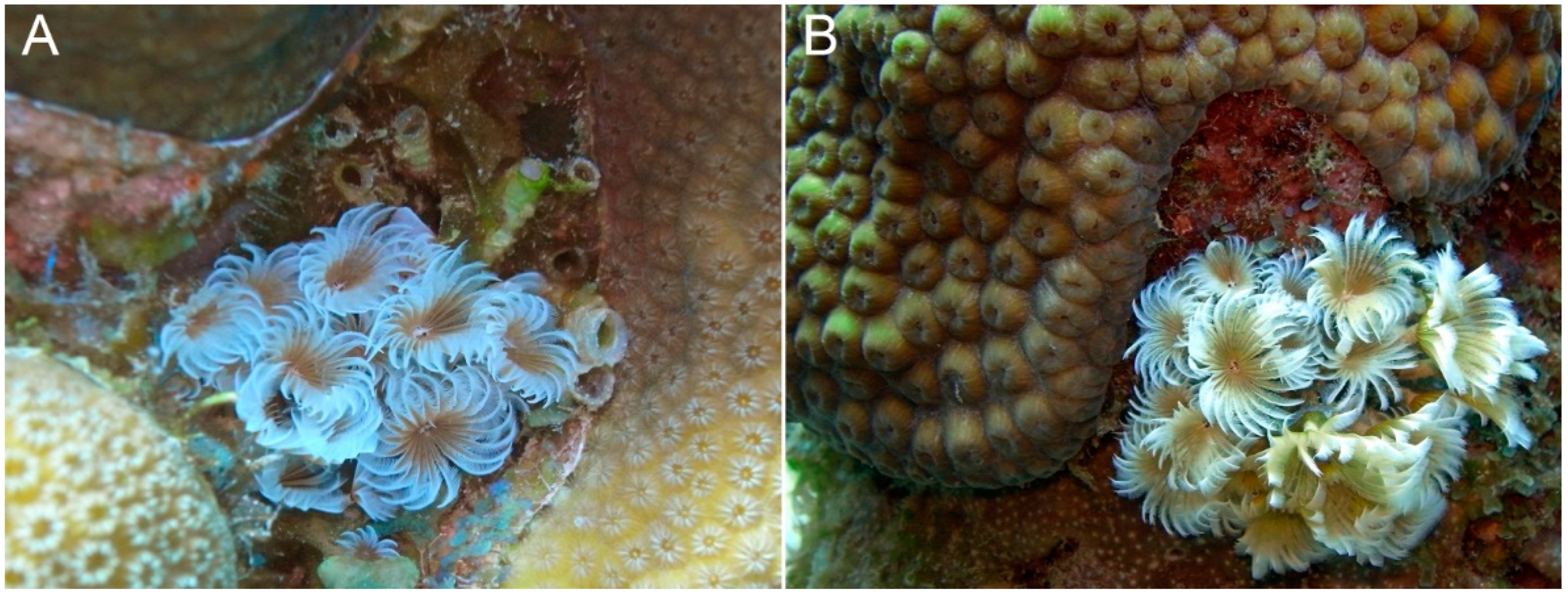
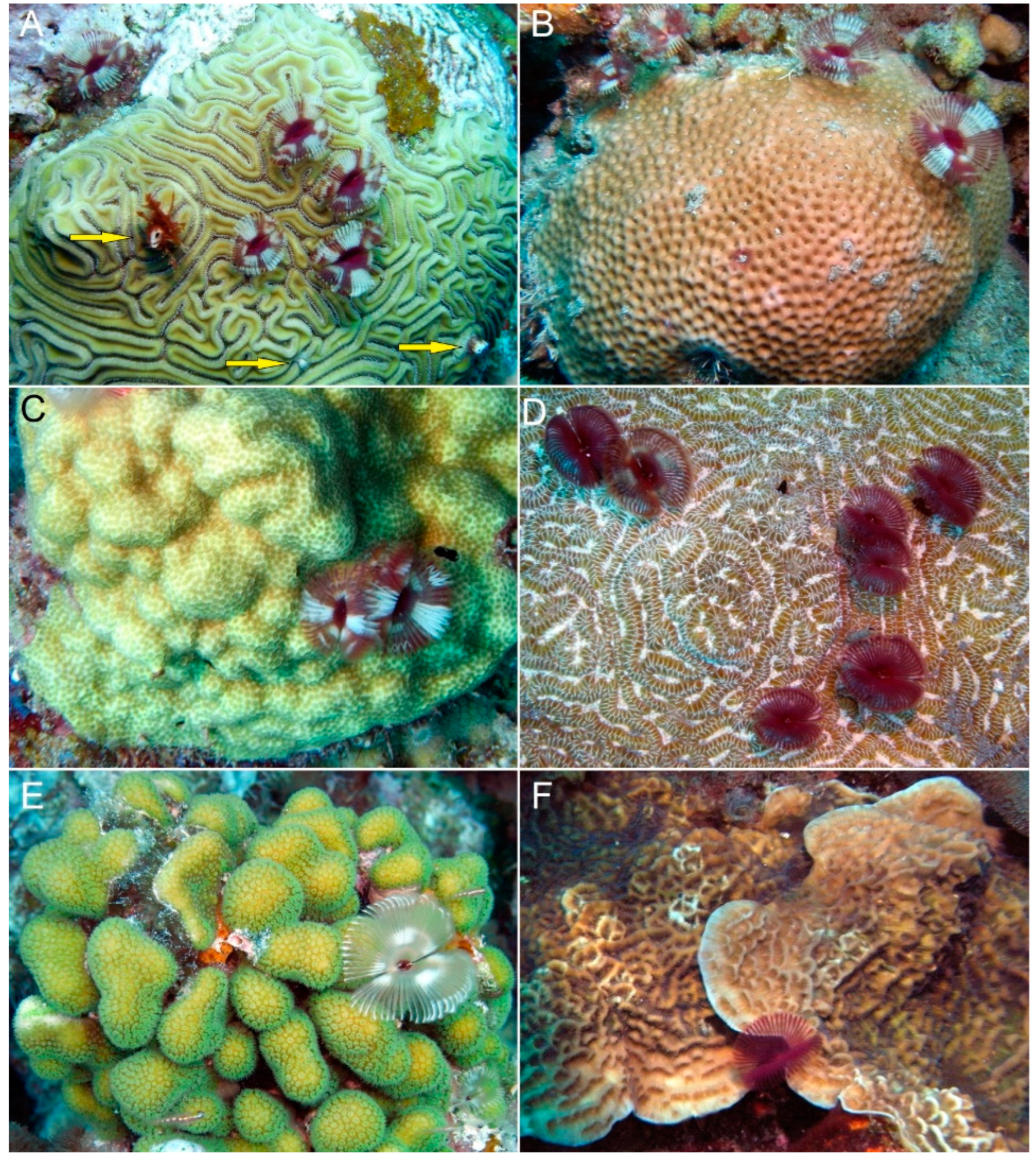
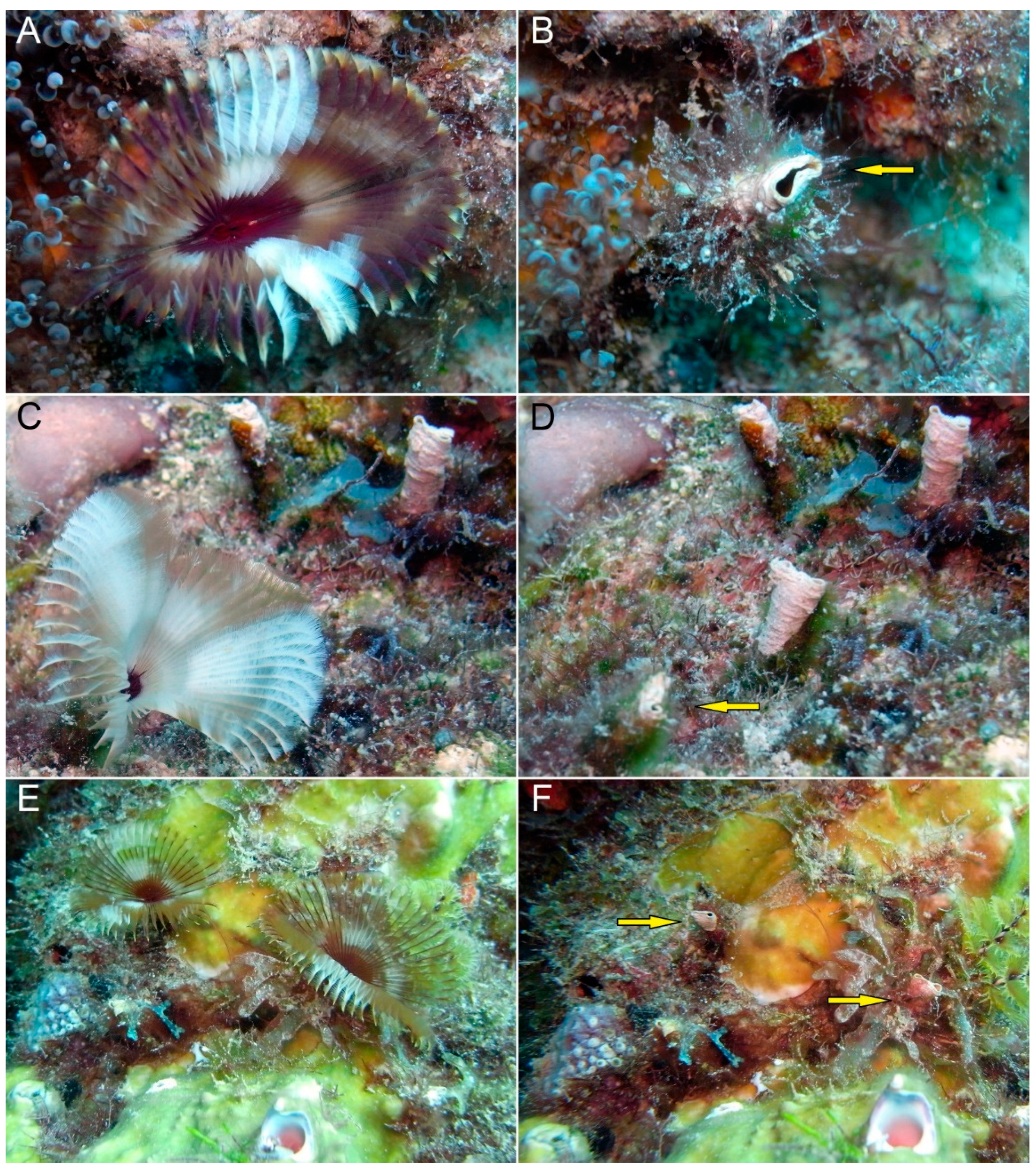


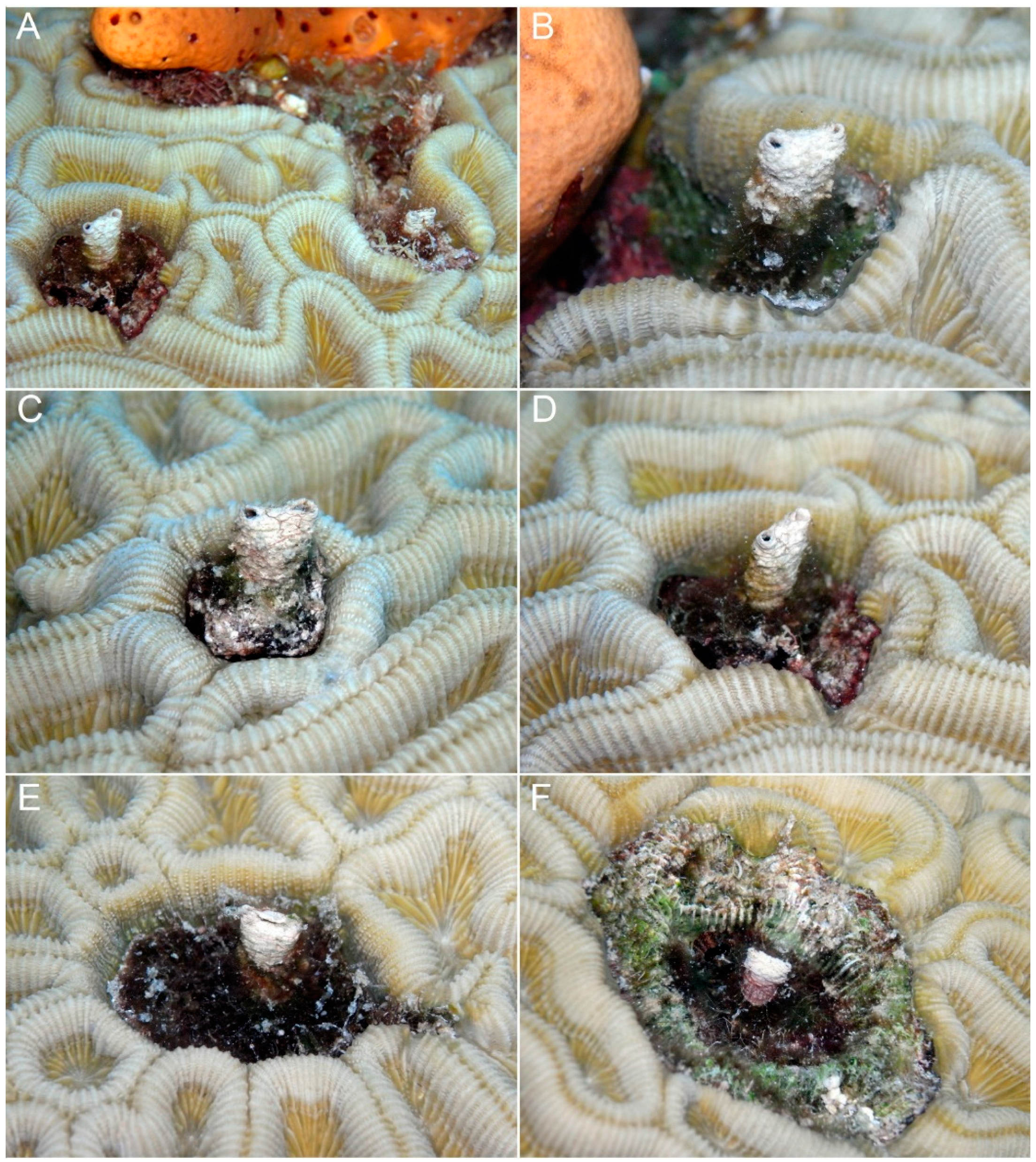
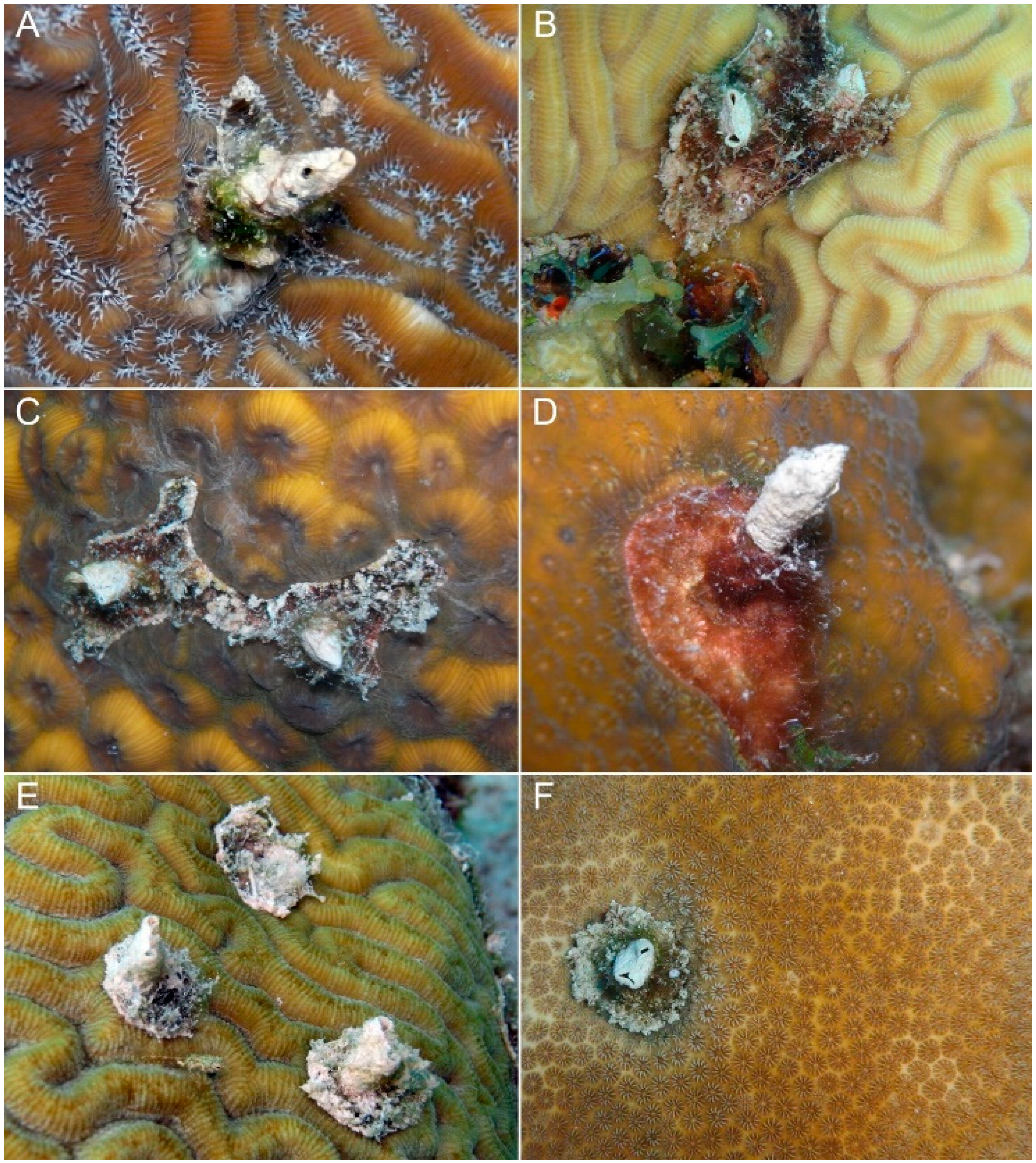




4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reaka-Kudla, M.L. The global biodiversity of coral reefs: A comparison with rain forests. In Biodiversity II: Understanding and Protecting Our Natural Resources; Reaka-Kudla, M.L., Wilson, D.E., Wilson, E.O., Eds.; Joseph Henry/National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton, N.; Brainard, R.E.; Fisher, R.; Moews, M.; Plaisance, L.; Caley, M.J. Coral reef biodiversity. In Life in the World’s Oceans: Diversity, Distribution and Abundance; McIntyre, A.D., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, P.W.; Enochs, I.C. Invertebrates and their roles in coral reef ecosystems. In Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition; Dubinsky, Z., Stambler, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 273–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.R.; Kuempel, C.D.; Altieri, A.H. The resilience of reef invertebrate biodiversity to coral mortality. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P. Animal symbioses in coral reef communities: A review. Symbiosis 1988, 5, 161–184. [Google Scholar]
- Montano, S. The extraordinary importance of coral-associated fauna. Diversity 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaps, P.; Denis, V. Can organisms associated with live scleractinian corals be used as indicators of coral reef status? Atoll Res. Bull. 2008, 566, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stella, J.S.; Pratchett, M.S.; Hutchings, P.A.; Jones, G.P. Coral-associated invertebrates: Diversity, ecology importance and vulnerability to disturbance. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 2011, 49, 43–104. [Google Scholar]
- DeVantier, L.M.; Reichelt, R.E.; Bradbury, R.H. Does Spirobranchus giganteus protect host Porites from predation by Acanthaster planci: Predator pressure as a mechanism of coevolution? Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 32, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.S. Influence of coral symbionts on feeding preferences of crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci in the western Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tzvi, O.; Einbinder, S.; Brokovich, E. A beneficial association between a polychaete worm and a scleractinian coral? Coral Reefs 2006, 25, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzé, H.; Lecellier, G.; Mills, S.C.; Planes, S.; Berteaux-Lecellier, V.; Stewart, H. Juvenile Trapezia spp. crabs can increase juvenile host coral survival by protection from predation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 515, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, S.; Fattorini, S.; Parravicini, V.; Berumen, M.L.; Galli, P.; Maggioni, D.; Arrigoni, R.; Seveso, D.; Strona, G. Corals hosting symbiotic hydrozoans are less susceptible to predation and disease. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20172405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, H.L.; Holbrook, S.J.; Schmitt, R.J.; Brooks, A.J. Symbiotic crabs maintain coral health by clearing sediments. Coral Reefs 2006, 25, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, J.S.; Osenberg, C.W.; Stier, A. The vermetid gastropod Dendropoma maximum reduces coral growth and survival. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carballo, J.L.; Bautista, E.; Nava, H.; Cruz-Barraza, J.A.; Chávez, J.A. Boring sponges, an increasing threat for coral reefs affected by bleaching events. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 872–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bakker, D.M.; Webb, A.E.; van den Bogaart, L.A.; van Heuven, S.M.A.C.; Meesters, E.H.; van Duyl, F.C. Quantification of chemical and mechanical bioerosion rates of six Caribbean excavating sponge species found on the coral reefs of Curaçao. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Wels, D.; Scott, C.M.; ten Hove, H.A. Filamentous turf algae on tube worms intensify damage in massive Porites corals. Ecology 2019, 100, e02668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Wels, D.; van der Schoot, R.J.; ten Hove, H.A. Coral injuries caused by Spirobranchus opercula with and without epibiotic turf algae at Curaçao. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Harper, C.E.; Langdon-Down, S.J.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; Spaargaren, R.; Timmerman, R.F. Host range of the coral-associated worm snail Petaloconchus sp. (Gastropoda: Vermetidae), a newly discovered cryptogenic pest species in the southern Caribbean. Diversity 2022, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinn, O.; Zatoń, M.; Tovar-Hernández, M.A. Tube microstructure and formation in some feather duster worms (Polychaeta, Sabellidae). Mar. Biol. 2018, 165, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humann, P.; Deloach, N.; Wilk, L. Reef Creature Identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas, 3rd ed.; New World Publications: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2013; 366p. [Google Scholar]
- Bok, M.J.; Capa, M.; Nilsson, D.E. Here, there and everywhere: The radiolar eyes of fan worms (Annelida, Sabellidae). Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capa, M.; Kupriyanova, E.; Nogueira, J.M.D.M.; Bick, A.; Tovar-Hernández, M.A. Fanworms: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. Diversity 2021, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capa, M.; López, E. Sabellidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) living in blocks of dead coral in the Coiba National Park, Panamá. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2004, 84, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Knight-Jones, P. Species of Branchiomma (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) from the Caribbean Sea and Pacific coast of Panama. Zootaxa 2006, 1189, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Salazar-Vallejo, S.I. Sabellids (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) from the Grand Caribbean. Zool. Stud. 2006, 45, 24–66. [Google Scholar]
- Giangrande, A.; Licciano, M.; Gambi, M.C. A collection of Sabellidae (Polychaeta) from Carrie Bow Cay (Belize, western Caribbean Sea) with the description of two new species. Zootaxa 2007, 1650, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Salazar-Silva, P. Catalogue of Sabellidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Grand Caribbean Region. Zootaxa 2008, 1894, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastida-Zavala, J.R.; Buelna, A.S.R.; De Leon-Gonzalez, J.A.; Camacho-Cruz, K.A.; Carmona, I. New records of sabellids and serpulids (Polychaeta: Sabellidae, Serpulidae) from the Tropical Eastern Pacific. Zootaxa 2016, 4184, 401–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila-Jiménez, Y.; Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Simōes, N. The social feather duster worm Bispira brunnea (Polychaeta: Sabellidae): Aggregations, morphology and reproduction. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; García-Garza, M.E.; de León-González, J.A. Sclerozoan and fouling sabellid worms (Annelida: Sabellidae) from Mexico with the establishment of two new species. Biodivers. Data J. 2020, 8, e57471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, W.K. Animal associates of living reef corals. In Biology and Geology of Coral Reefs III. Biology 2; Jones, O.A., Endean, R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zann, L.P. Living Together in the Sea; T.F.H. Publications: Neptune, NY, USA, 1980; 416p. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, P.J.B. Aspects of living coral associates in Jamaica. In Proceedings of the 5th International Coral Reef Congress, Tahiti, French Polynesia, 27 May–1 June 1985; Volume 5, pp. 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, P.J.B. Associations between corals and macro-infaunal invertebrates in Jamaica, with a list of Caribbean and Atlantic coral associates. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1987, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, C.T. Macroborers within coral framework at Discovery Bay, north Jamaica: Species distribution and abundance, and effects on coral preservation. Coral Reefs 1998, 17, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.B. Biology and ecology of the hydrocoral Millepora on coral reefs. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2000, 50, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.M.M. Fauna living in colonies of Mussismilia hispida (Verrill) (Cnidaria: Scleractinia) in four South-eastern Brazil Islands. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2003, 46, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Monroy, M.; Solano, O.D. Estructura de la comunidad epifaunal asociada a colonias de vida libre del hydrocoral Millepora alcicornis Linnaeus, 1758 en Bahía Portete, Caribe Colombiano. Bol. Investig. Mar. Cost. 2006, 35, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Oigman-Pszczol, S.S.; Creed, J.C. Distribution and abundance of fauna on living tissues of two Brazilian hermatypic corals (Mussismilia hispida (Verril 1902) and Siderastrea stellata Verril, 1868). Hydrobiologia 2006, 563, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.S.; Jones, G.P.; Pratchett, M.S. Variation in the structure of epifaunal invertebrate assemblages among coral hosts. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 957–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van der Meij, S.E.T.; Fransen, C.H.J.M. The mushroom coral as a habitat. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2012, 92, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van Beusekom, M.; ten Hove, H.A.; Ivanenko, V.N.; van der Meij, S.E.T.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M. Helioseris cucullata as a host coral at St. Eustatius. Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lymperaki, M.M.; Hill, C.E.; Hoeksema, B.W. The effects of wave exposure and host cover on coral-associated fauna of a centuries-old artificial reef in the Caribbean. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 176, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Symbiotic polychaetes: Review of known species. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1998, 36, 217–340. [Google Scholar]
- Molodtsova, T.N.; Britayev, T.A.; Martin, D. Cnidarians and their polychaete symbionts. In The Cnidaria, Past, Present and Future; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 387–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Symbiotic polychaetes revisited: An update of the known species and relationships (1998–2017). Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 2018, 56, 371–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.M.M.; Knight-Jones, P. A new species of Pseudobranchiomma Jones (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) found amongst Brazilian coral, with a redescription of P. punctata (Treadwell, 1906) from Hawaii. J. Nat. Hist. 2002, 36, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.M.M.; Amaral, A.C.Z. Amphicorina schlenzae, a small sabellid (Polychaeta, Sabellidae) associated with a stony coral on the coast of Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2000, 67, 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; ten Hove, H.A.; Vinn, O.; Zatoń, M.; de León-González, J.A.; García-Garza, M.E. Fan worms (Annelida: Sabellidae) from Indonesia collected by the Snellius II Expedition (1984) with descriptions of three new species and tube microstructure. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzoni, F.; Arrigoni, R.; Stefani, F.; Reijnen, B.T.; Montano, S.; Hoeksema, B.W. Phylogenetic position and taxonomy of Cycloseris explanulata and C. wellsi (Scleractinia: Fungiidae): Lost mushroom corals find their way home. Contrib. Zool. 2012, 81, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, E.; Gil, J.; Tanaka, K.; Kupriyanova, E.K. Notaulax yamasui sp. n. (Annelida, Sabellidae) from Okinawa and Ogasawara, Japan, with notes on its ecology. ZooKeys 2017, 660, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tovar-Hernández, M.A.; Pineda-Vera, A. Taxonomía y estrategias reproductivas del poliqueto sabélido Bispira brunnea (Treadwell, 1917) del Caribe Mexicano. Cienc. Mar. 2008, 21, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, E.; Nishihira, M. Use of annual density banding to estimate longevity of infauna of massive corals. Fish. Sci. 1999, 65, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Meij, S.E.T.; Fransen, C.H.J.M.; Pasman, L.R.; Hoeksema, B.W. Phylogenetic ecology of gall crabs (Cryptochiridae) as associates of mushroom corals (Fungiidae). Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 5770–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompmaker, A.A.; Portell, R.W.; van der Meij, S.E.T. Trace fossil evidence of coral-inhabiting crabs (Cryptochiridae) and its implications for growth and paleobiogeography. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrana, L.; Caulier, G.; Todinanahary, G.; Lepoint, G.; Eeckhout, I. Characteristics of the infestation of Seriatopora corals by the coral gall crab Hapalocarcinus marsupialis Stimpson, 1859 on the great reef of Toliara, Madagascar. Symbiosis 2016, 69, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Butôt, R.; García-Hernández, J.E. A new host and range record for the gall crab Fungicola fagei as a symbiont of the mushroom coral Lobactis scutaria in Hawai’i. Pac. Sci. 2018, 72, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.K.; Wong, K.J.H.; Cheng, Y.R. Biogeography and host usage of coral-associated crustaceans: Barnacles, copepods, and gall crabs as model organisms. In The Natural History of the Crustacea: Evolution and Biogeography of the Crustacea; Thiel, M., Poore, G.C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; Volume 8, pp. 183–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; García-Hernández, J.E. Host-related morphological variation of dwellings inhabited by the crab Domecia acanthophora in the corals Acropora palmata and Millepora complanata (Southern Caribbean). Diversity 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruce, A.J. Notes on some Indo-Pacific Pontoniinae. XIV. Observations on Paratypton siebenrocki Balss. Crustaceana 1969, 17, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B.; Reiswigh, M.; Marcottbe, M. Ecology, functional morphology, behaviour, and feeding in coral- and sponge-boring species of Upogebia (Crustacea: Decapoda: Thalassinidea). Can. J. Zool. 1988, 66, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B. Distribution, habitat and morphology of the Caribbean coral-and rock-boring bivalve, Lithophaga bisulcata (d’Orbigny) (Mytilidae: Lithophaginae). J. Molluscan Stud. 1988, 54, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, K. Boring and growth in chemically boring bivalves from the Caribbean, Eastern Pacific and Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Senckenb. Marit. 1990, 22, 101–154. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, B.K.K.; Tan, J.C.H.; Ganmanee, M. Living in a growing host: Growth pattern and dwelling formation of the scallop Pedum spondyloideum in massive Porites spp. corals. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaps, P. Association between the scallop Pedum spondyloideum (Bivalvia: Pteriomorphia: Pectinidae) and scleractinian corals from Nosy Be, Madagascar. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2020, 61, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittenberger, A.; Gittenberger, E. Cryptic, adaptive radiation of endoparasitic snails: Sibling species of Leptoconchus (Gastropoda: Coralliophilidae) in corals. Org. Divers. Evol. 2011, 11, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dojiri, M. Isomolgus desmotes, new genus, new species (Lichomolgidae), a gallicolous poecilostome copepod from the scleractinian coral Seriatopora hystrix Dana in Indonesia, with a review of gall-inhabiting crustaceans of anthozoans. J. Crust. Biol. 1988, 8, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-H.; Yamashiro, H. Two species of poecilostomatoid copepods inhabiting galls on scleractinian corals in Okinawa, Japan. J. Crust. Biol. 2007, 27, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Moudrova, S.V.; Bouwmeester, J.; Berumen, M.L. First report of tubular corallites on Stylophora caused by a symbiotic copepod crustacean. Coral Reefs 2014, 33, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shelyakin, P.V.; Garushyants, S.K.; Nikitin, M.A.; Mudrova, S.V.; Berumen, M.; Speksnijder, A.G.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Fontaneto, D.; Gelfand, M.S.; Ivanenko, V.N. Microbiomes of gall-inducing copepod crustaceans from the corals Stylophora pistillata (Scleractinia) and Gorgonia ventalina (Alcyonacea). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygier, M.J.; Cairns, S.D. Suspected neoplasms in deep-sea corals (Scleractinia: Oculinidae: Madrepora spp.) reinterpreted as galls caused by Petrarca madreporae n. sp. (Crustacea: Ascothoracida: Petrarcidae). Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 24, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachikawa, H.; Grygier, M.J.; Cairns, S.D. Live specimens of the parasite Petrarca madreporae (Crustacea: Ascothoracida) from the deep-water coral Madrepora oculata in Japan, with remarks on the development of its spectacular galls. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.K.; Dreyer, N.; Gale, A.S.; Glenner, H.; Ewers-Saucedo, C.; Pérez-Losada, M.; Kolbasov, G.A.; Crandall, K.A.; Høeg, J.T. The evolutionary diversity of barnacles, with an updated classification of fossil and living forms. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, 193, 789–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, G.S. Tube-dwelling coral symbionts induce significant morphological change in Montipora. Symbiosis 2009, 49, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, G.S.; Martinez, C.M. Mutualist-induced morphological changes enhance growth and survival of corals. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, F.; Puce, S.; Caragnano, A.; Maggioni, D.; Pica, D.; Seveso, D.; Galli, P.; Montano, S. Symbiont footprints highlight the diversity of scleractinian-associated Zanclea hydrozoans (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa). Zool. Scr. 2019, 48, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, D.; Arrigoni, R.; Seveso, D.; Galli, G.; Berumen, M.L.; Denis, V.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Huang, D.; Manca, F.; Pica, D.; et al. Evolution and biogeography of the Zanclea-Scleractinia symbiosis. Coral Reefs 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, D.; Saponari, L.; Seveso, D.; Galli, P.; Schiavo, A.; Ostrovsky, A.N.; Montano, S. Green fluorescence patterns in closely related symbiotic species of Zanclea (Hydrozoa, Capitata). Diversity 2020, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colgan, M.W. Growth rate reduction and modification of a coral colony by a vermetid mollusc Dendropoma maxima. In Proceedings of the 5th International Coral Reef Congress, Tahiti, French Polynesia, 27 May–1 June 1985; Volume 6, pp. 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zvuloni, A.; Armoza-Zvuloni, R.; Loya, Y. Structural deformation of branching corals associated with the vermetid gastropod Dendropoma maxima. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 363, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, J.S.; McNaughtan, D.; Strong, A.T. Vermetid gastropods mediate within-colony variation in coral growth to reduce rugosity. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Patterson, M.; Vitry, E.; Summers, N.; Miternique, C. Morphological plasticity allows coral to actively overgrow the aggressive sponge Terpios hoshinota (Mauritius, Southwestern Indian Ocean). Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, J.E.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M.; Hoeksema, B.W. Lettuce corals overgrowing tube sponges at St. Eustatius, Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; ten Hove, H.A.; Berumen, M.L. A three-way association causing coral injuries in the Red Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2018, 94, 1525–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samimi Namin, K.; Risk, M.J.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Zohari, Z.; Rezai, H. Coral mortality and serpulid infestations associated with red tide, in the Persian Gulf. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benzoni, F.; Galli, P.; Pichon, M. Pink spots on Porites: Not always a coral disease. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benzoni, F.; Basso, D.; Caragnano, A.; Rodondi, G. Hydrolithon spp. (Rhodophyta, Corallinales) overgrow live corals (Cnidaria, Scleractinia) in Yemen. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubomura, T.; Wee, H.B.; Reimer, J.D. Investigating incidence and possible causes of pink and purple pigmentation response in hard coral genus Porites around Okinawajima Island, Japan. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 41, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, M.C.; Shantz, A.A.; Burkepile, D.E. Newly dominant benthic invertebrates reshape competitive networks on contemporary Caribbean reefs. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Lau, Y.W.; ten Hove, H.A. Octocorals as secondary hosts for Christmas tree worms off Curaçao. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2015, 91, 489–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, R.P.M.; Sybesma, J.; van Duyl, F.C. The ecology of the tropical compound ascidian Trididemnum solidum. II. Abundance, growth and survival. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1981, 6, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, B.; Harrison, P.L.; Scheffers, S.R. Aggressive colonial ascidian impacting deep coral reefs at Bonaire, Netherlands Antilles. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; García-Hernández, J.E.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M.; Olthof, G.; ten Hove, H.A. Extension of the recorded host range of Caribbean Christmas tree worms (Spirobranchus spp.) with two scleractinians, a zoantharian, and an ascidian. Diversity 2020, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; ten Hove, H.A.; Berumen, M.L. Christmas tree worms evade smothering by a coral-killing sponge in the Red Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 48, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hernández, J.E.; Hoeksema, B.W. Sponges as secondary hosts for Christmas tree worms at Curaçao. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugues, M.M.; Bak, R.P.M. Differential competitive abilities between Caribbean coral species and a brown alga: A year of experiments and a long-term perspective. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 315, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nugues, M.M.; Bak, R.P.M. Long-term dynamics of the brown macroalga Lobophora variegata on deep reefs in Curaçao. Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicklighter, C.E.; Hay, M.E. To avoid or deter: Interactions among defensive and escape strategies in sabellid worms. Oecologia 2007, 151, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stabili, L.; Schirosi, R.; Di Benedetto, A.; Merendino, A.; Villanova, L.; Giangrande, A. First insights into the biochemistry of Sabella spallanzanii (Annelida: Polychaeta) mucus: A potentially unexplored resource for applicative purposes. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2011, 91, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, A.; Licciano, M.; Schirosi, R.; Musco, L.; Stabili, L. Chemical and structural defensive external strategies in six sabellid worms (Annelida). Mar. Ecol. 2014, 35, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Schirosi, R.; Licciano, M.; Giangrande, A. Role of Myxicola infundibulum (Polychaeta, Annelida) mucus: From bacterial control to nutritional home site. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 461, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, M.C.L.; Teixeira, V.L.; Santos, C.S.G. A review of “Polychaeta” chemicals and their possible ecological role. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 72–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.A.; Bourne, D.G.; Humphrey, C.M.; Hutson, K.S. Parasites and coral-associated invertebrates that impact coral health. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhavan, D.; Prakash, S.; Kumar, A. Tube dwelling gastropod an indicator of coral reef status at the tropical reef of Palk Bay region, southeast coast of India. Ind. J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2021, 50, 585–587. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.C.W.; Hoeg, J.T.; Chan, B.K.K. How do coral barnacles start their life in their hosts? Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.-C.; Dreyer, N.; Kolbasov, G.A.; Høeg, J.T.; Chan, B.K.K. Sponge symbiosis is facilitated by adaptive evolution of larval sensory and attachment structures in barnacles. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoeksema, B.W.; Timmerman, R.F.; Spaargaren, R.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Langdon-Down, S.J.; Harper, C.E. Morphological Modifications and Injuries of Corals Caused by Symbiotic Feather Duster Worms (Sabellidae) in the Caribbean. Diversity 2022, 14, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050332
Hoeksema BW, Timmerman RF, Spaargaren R, Smith-Moorhouse A, van der Schoot RJ, Langdon-Down SJ, Harper CE. Morphological Modifications and Injuries of Corals Caused by Symbiotic Feather Duster Worms (Sabellidae) in the Caribbean. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050332
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoeksema, Bert W., Rosalie F. Timmerman, Roselle Spaargaren, Annabel Smith-Moorhouse, Roel J. van der Schoot, Sean J. Langdon-Down, and Charlotte E. Harper. 2022. "Morphological Modifications and Injuries of Corals Caused by Symbiotic Feather Duster Worms (Sabellidae) in the Caribbean" Diversity 14, no. 5: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050332
APA StyleHoeksema, B. W., Timmerman, R. F., Spaargaren, R., Smith-Moorhouse, A., van der Schoot, R. J., Langdon-Down, S. J., & Harper, C. E. (2022). Morphological Modifications and Injuries of Corals Caused by Symbiotic Feather Duster Worms (Sabellidae) in the Caribbean. Diversity, 14(5), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050332










