Evolution of Reproductive Traits and Implications for Adaptation and Diversification in the Yam Genus Dioscorea L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
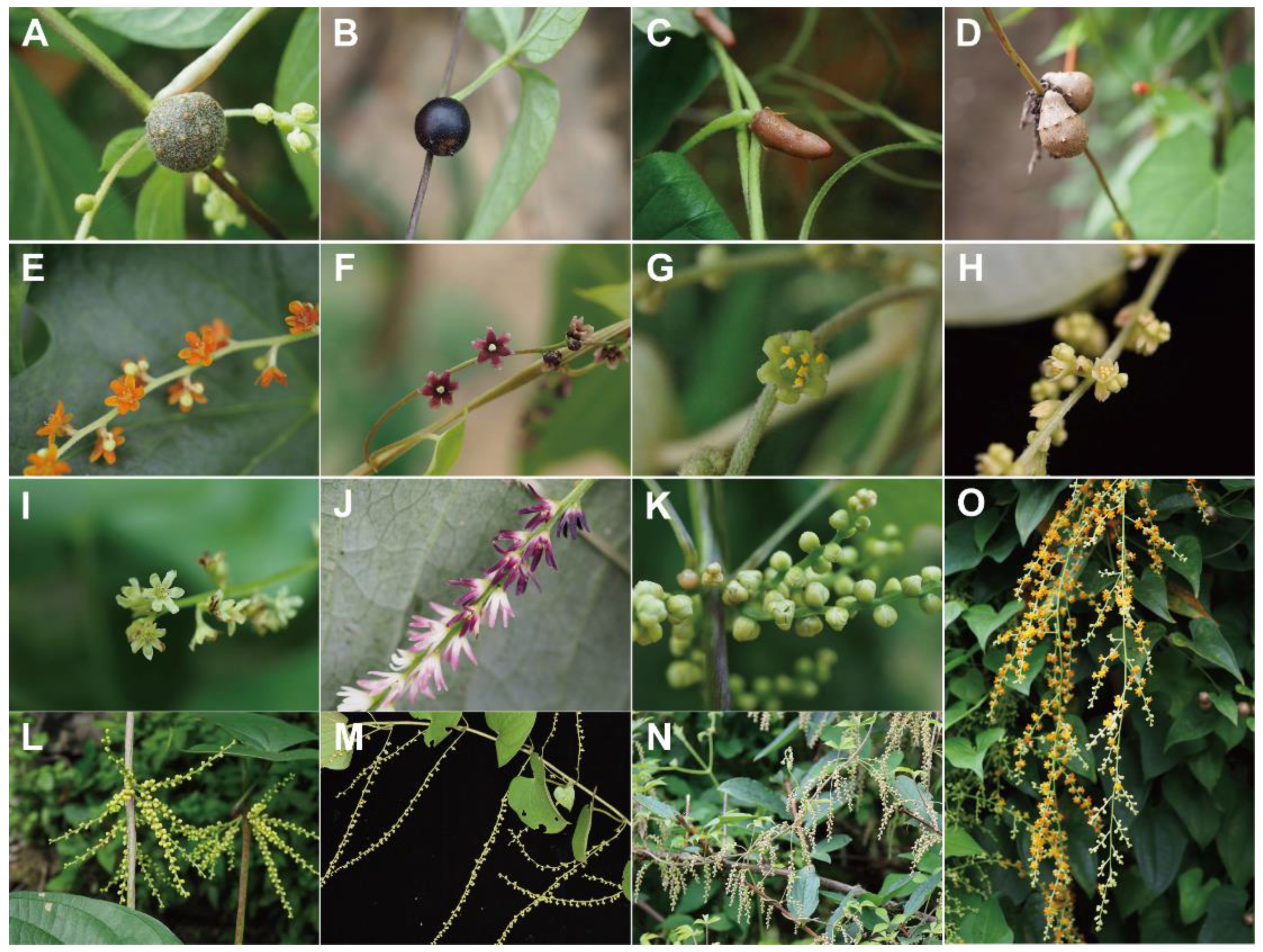
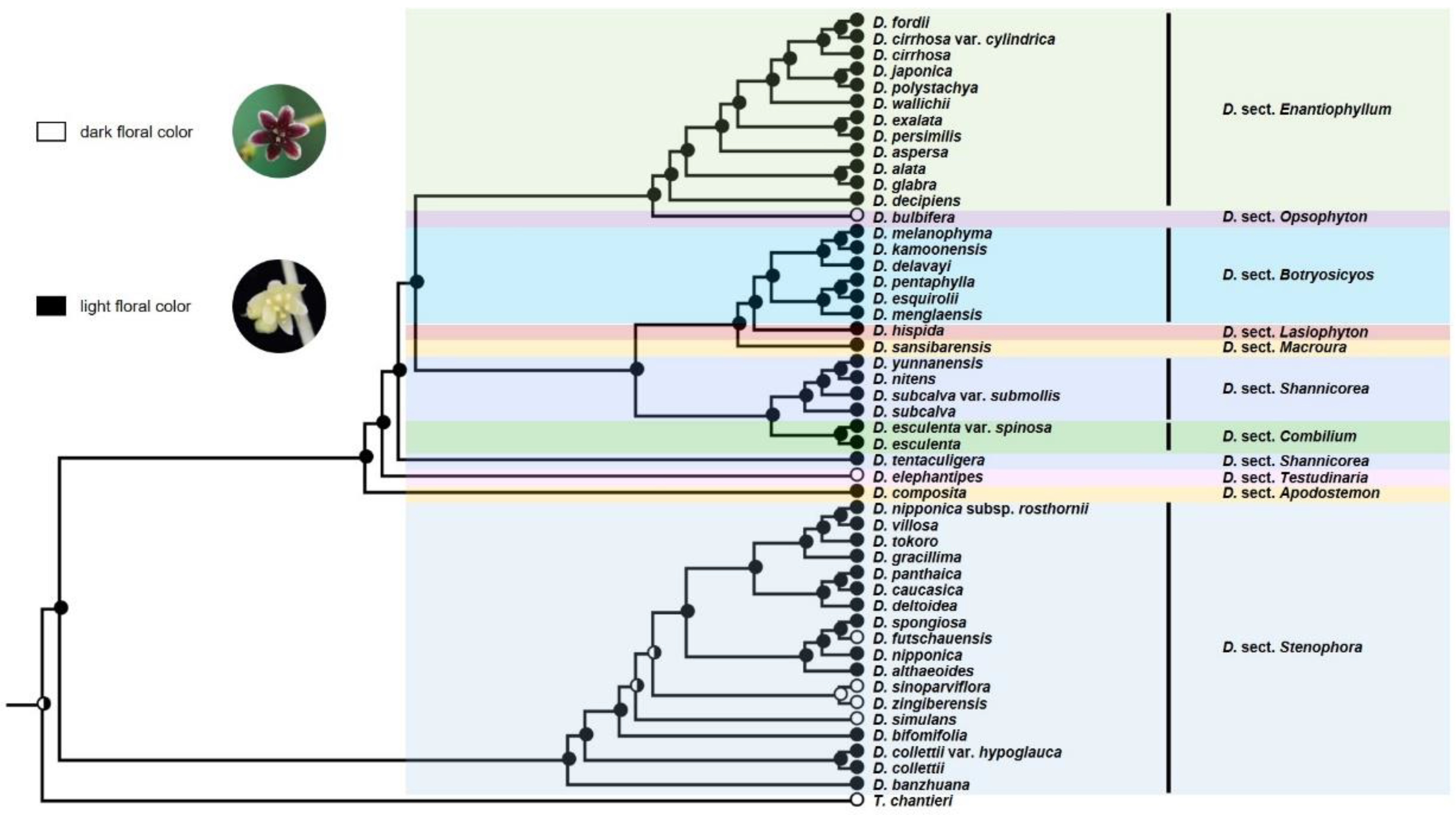
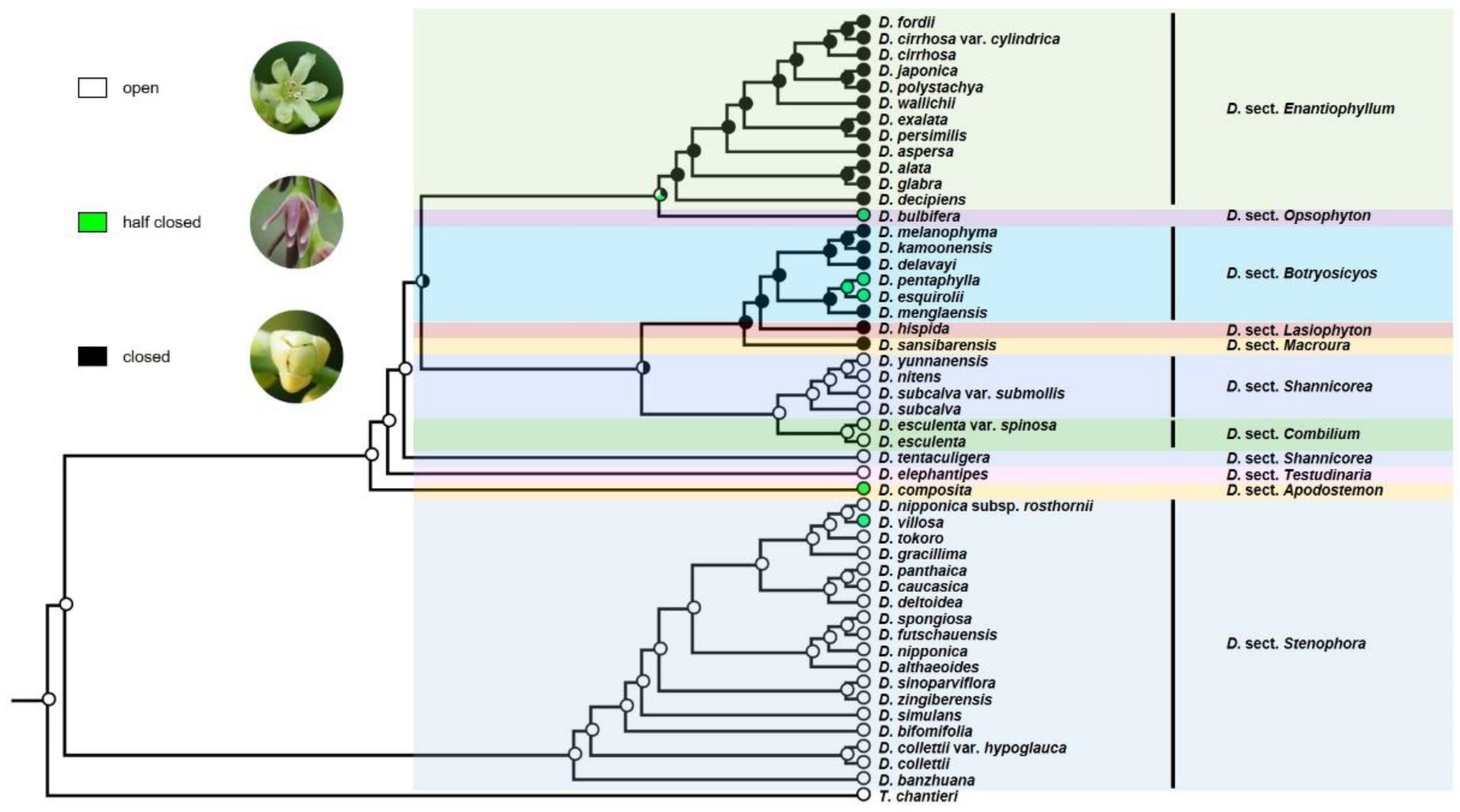
2.4. Character Coding and Ancestral State Reconstruction
3. Results
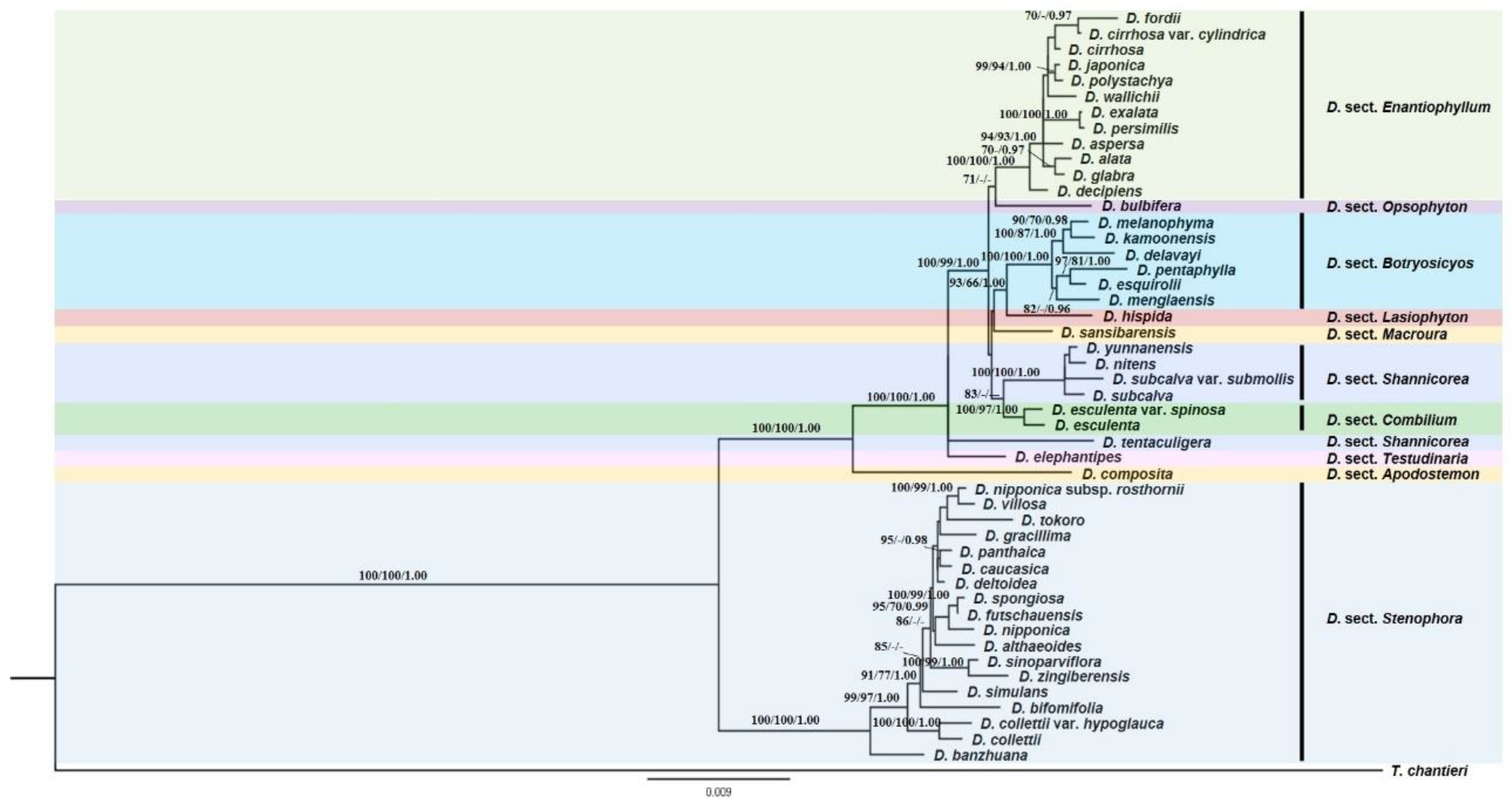
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
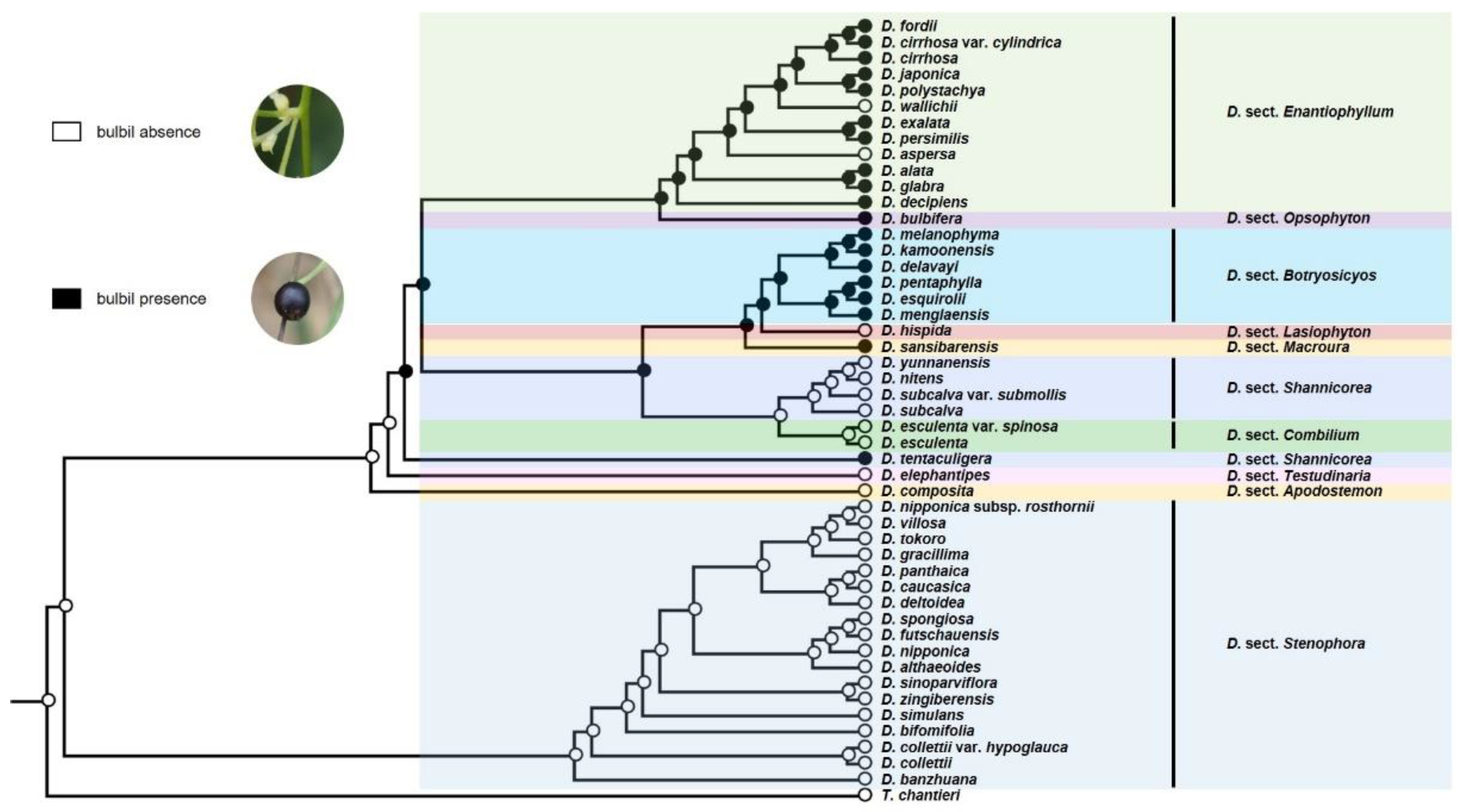
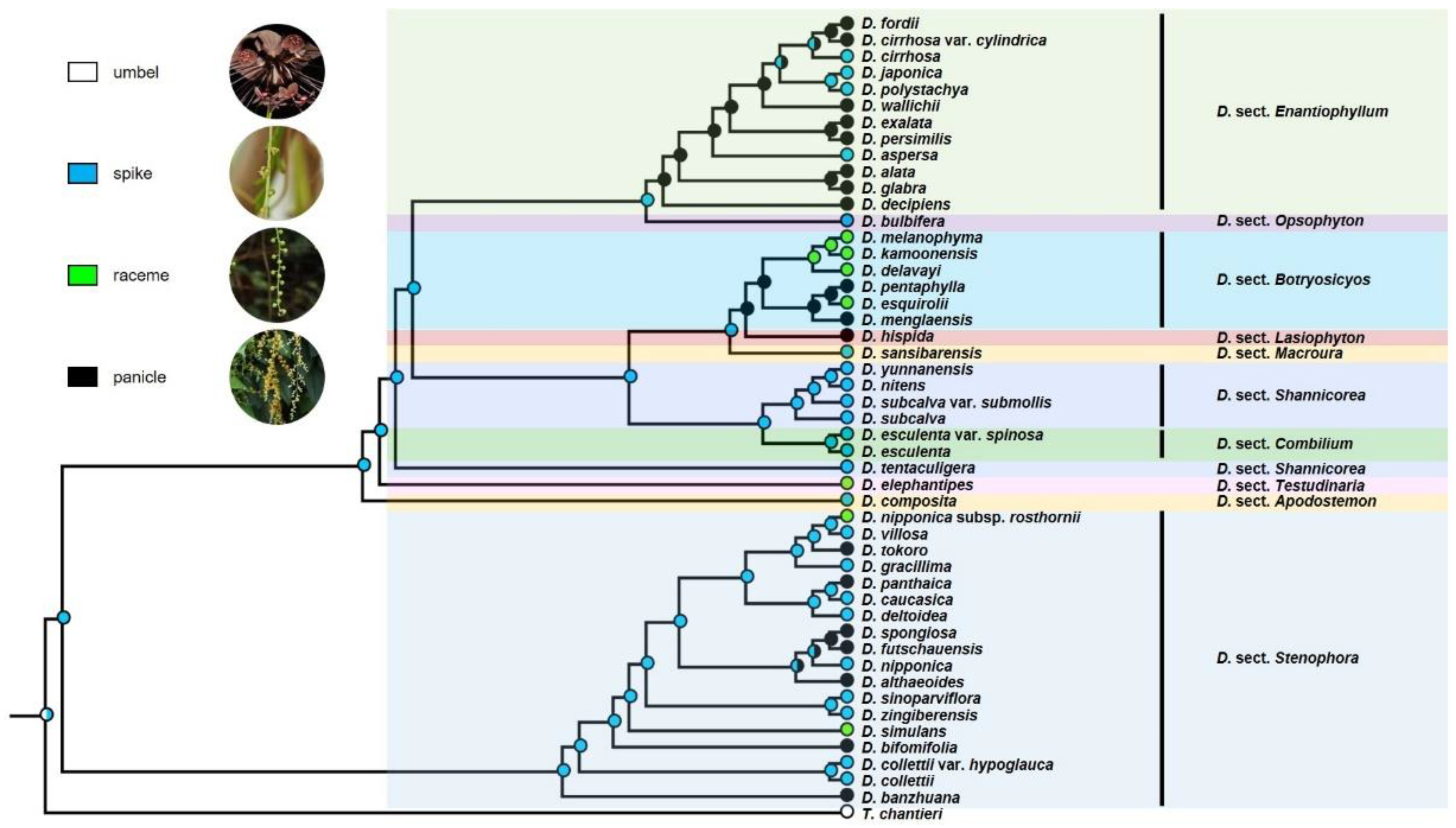
3.2. Ancestral Character State Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of Organs for Vegetative Propagation and Diversity in the Reproductive Strategy
4.2. Evolution of Floral Characters and Their Relation to Sexual Propagation
4.3. Infrageneric Relationships and Taxonomic States of Several Species
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Govaerts, R.; Wilkin, P.; Raz, L.; Téllez-Valdés, O. World checklist of Dioscoreaceae. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2018. Available online: https://wcsp.science.kew.org/ (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Wilkin, P.; Schols, P.; Chase, M.W.; Chayamarit, K.; Furness, C.A.; Huysmans, S.; Rakotonasolo, F.; Smets, E.; Thapyai, C. A plastid gene phylogeny of the yam genus, Dioscorea: Roots, fruits and Madagascar. Syst. Bot. 2005, 30, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, H. Dioscoreaceae. Flowering plants. Monocotyledons. Lilianae (except Orchidaceae). In The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants; Kubitzk, K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 3, pp. 216–235. [Google Scholar]
- Asiedu, R.; Sartie, A. Crops that feed the world. Yams. Food Secur. 2010, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, E.J.; Wilkin, P.; Sarasan, V.; Fraser, P.D. Metabolite profiling of Dioscorea (yam) species reveals underutilized biodiversity and renewable sources for high-value compounds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlgren, G. An undated angiosperm classification. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1989, 100, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignouna, H.; Abang, M.; Asiedu, R.; Geeta, R. True yams (Dioscorea): A biological and evolutionary link between eudicots and grasses. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2009, 11, pdb.emo136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.; Kumar, Y. Foliar epidermal, stem and petiole anatomy of Meghalayan Dioscorea L. (Dioscoreaceae) and its systematic implication. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Uline, E.B. Eine monographie de Dioscoreaceen. Bot. Jahrb. 1898, 25, 126–165. [Google Scholar]
- Knuth, R. Dioscoreaceae. In Das Pflanzenreich, 87 (IV 43); Engler, H.G.A., Ed.; Verlag von Wilhelm Engelmann (Druck von Breitkopf & Härtel in Leipzig): Leipzig, Germany, 1924; pp. 1–387. [Google Scholar]
- Burkill, I.H. The organography and the evolution of Dioscoreaceae, the family of the yams. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1960, 56, 319–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruel, J.; Segarra-Moragues, J.G.; Raz, L.; Forest, F.; Wilkin, P.; Sanmartín, I.; Catalán, P. Late cretaceous-early eocene origin of yams (Dioscorea, Dioscoreaceae) in the Laurasian Palaearctic and their subsequent oligocenemiocene diversification. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruel, J.; Forest, F.; Paun, O.; Chase, M.W.; Devey, D.; Couto, R.S.; Gabriel, J.; Segarra-Moragues Catalán, P.; Wilkin, P. A nuclear Xdh phylogenetic analysis of yams (Dioscorea: Dioscoreaceae) congruent with plastid trees reveals a new Neotropical lineage. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 187, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.S.; Martins, A.C.; Bolson, M.; Lopez, R.C.; Smidt, E.C.; Braga, J.M.A. Time calibrated tree of Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae) indicates four origins of yams in the Neotropics since the Eocene. Bot. J. Lin. Soc. 2018, 188, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, H.; Yamashita, J.; Fuse, S.; Pooma, R.; Poopath, M.; Tobe, H.; Tamura, M.N. A large-scale phylogenetic analysis of Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae), with reference to character evolution and subgeneric recognition. Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 2020, 71, 103–128. [Google Scholar]
- Endress, P.K. Diversity and Evolution Biology of Tropical Flowers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 511. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, K.M.; Tsai, J.L.; Chen, M.Y.; Ku, H.M.; Liu, S.C. Molecular phylogeny of Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae) in East and Southeast Asia. Blumea J. Plant Taxon. Plant Geogr. 2013, 58, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffin, E.; Brodribb, T.J.; Hill, R.S.; Thomas, P.; Lowe, A.J. Leaf evolution in Southern Hemisphere conifers tracks the angiosperm ecological radiation. Proc. Biol Sci. 2012, 279, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Xue, J.Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, M.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhou, G.C.; Hang, Y.Y. Taxonomic and phylogenetic significance of leaf venation characteristics in Dioscorea plants. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2018, 70, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, O.; Muasya, A.M.; Catalán, P.; Shongwe, E.Z.; Viruel, J.; Wilkin, P.; Van der Bank, M. Diversification into novel habitats in the Africa clade of Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae): Erect habit and elephant’s foot tubers. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.R.; Ding, Z.Z.; Qin, H.Z. A phytogeographical study on the family Dioscoreaceae. Acta Bot. Boreale-Occident. Sin. 1994, 14, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.Z.; Gilbert, M.G. Dioscoreaceae. In Flora of China; Wu, Z.Y., Raven, P.H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2000; Volume 24, p. 284. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small amounts of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, Y.P.; Wu, B.C.; Zhao, Y.M.; Chen, J.Q.; Hang, Y.Y. Phylogeny of Dioscorea sect. Stenophora based on chloroplast matK, rbcL and trnL-F sequences. J. Syst. Evol. 2008, 46, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Taberlet, P.T.; Gielly, L.; Patou, G.; Bouvet, J. Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol. Biol. 1991, 17, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, J.; Bousquet, J. Evolution of the mitochondrial rps3 intron in perennial and annual angiosperms and homology to nad5 intron 1. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7, improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H. Maximum-likelihood estimation of phylogeny from DNA sequences when substitution rates differ over sites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Mirarab, S.; Bayzid, M.S.; Boussau, B.; Warnow, T. Statistical binning enables an accurate coalescent-based estimation of the avian tree. Science 2014, 346, 1250463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M. Van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, M.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. Version 3.5.1. 2018. Available online: http://www.mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Cook, R.E. Growth and development in clonal plant populations. In Population Biology and Evolution of Clonal Organisms; Jackson, J.B.C., Buss, L.W., Cook, R.E., Eds.; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA; London, UK, 1985; pp. 259–296. [Google Scholar]
- Rønsted, N.; Law, S.; Thornton, H.; Fay, M.F.; Chase, M.W. Molecular phylogenetic evidence for the monophyly of Fritillaria and Lilium (Liliaceae; Liliales) and the infrageneric classification of Fritillaria. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 35, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.C.; Chang, M.C.; Ling, P.P.; Ting, C.T.; Dou, F.P. A cytotaxonomic study on Chinese Dioscorea L.—The chromosome numbers and their relation to the origin and evolution of the genus. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 1985, 23, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, L.D.; Wilson, L.A.; Passam, H.C. The origin, development and germination of bulbils in two Dioscorea species. Ann. Bot. 1982, 50, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayensu, E.S. Anatomy of the Monocotyledons, VI. Dioscoreales; Clarendon Press: Oxforod, UK, 1972; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Ronsheim, M.L.; Bever, J.D. Genetic variation and evolutionary trade-offs for sexual and asexual reproductive modes in Allium vineale (Liliaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2000, 87, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, C.G.; Lui, K.; Bronson, K.; Corradini, P.; Bruineau, A. Population genetic consequences of extreme variation in sexual and clonal reproduction in an aquatic plant. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, B.L.; Armbruster, G.F.J.; Scheepens, J.F.; Stöcklin, J. Distribution of bulbil- and seed-producing plants of Poa alpina (Poaceae) and their growth and reproduction in common gardens suggest adaptation to different elevations. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmer, P. Pollination and Floral Ecology; Priceton University Press: Priceson, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–792. [Google Scholar]
- Patiny, S. Evolution of Plant-Pollinator Relationships; Cambrige University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 1–477. [Google Scholar]
- Mondo, J.M.; Agre, P.A.; Edemodu, A.; Adebola, P.; Asiedu, R.; Akoroda, M.O.; Asfaw, A. Floral biology and pollination efficiency in yam (Dioscorea spp.). Agriculture 2020, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, S.G.; Sakai, A.K.; Culley, T.M.; Campbell, D.R.; Dunbar-Wallis, A.K. Predicting the pathway to wind pollination: Heritabilities and genetic correlations of inflorescence traits associated with wind pollination in Schiedea salicaria (Caryophyllaceae). J. Evol. Biol. 2006, 19, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Nagasaki, O.; Ishii, H.S.; Ushimaru, A. Inflorescence architecture affects pollinator behaviour and mating success in Spiranthes sinensis (Orchidaceae). New Phytol. 2012, 193, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.R. Floral color changes as cues for pollinators. Nature 1991, 354, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streisfeld, M.A.; Kohn, J.R. Environment and pollinator-mediated selection on parapatric floral races of Mimulus aurantiacus. J. Evol. Biol. 2007, 20, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Conchou, L.; Bessière, J.M.; Cazals, G.; Schatz, B.; Imbert, E. Flower color polymorphism in Iris lutescens (Iridaceae): Biochemical analyses in light of plant-insect interactions. Phytochemistry 2013, 94, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchhala, N.; Johnsen, S.; Smith, S.D. Competition for hummingbird pollination shapes flower color variation in Andean Solanaceae. Evolution 2014, 68, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, A.S.; Artuso, S.; Pamperl, S.; Michelangeli, F.A.; Penneys, D.S.; Fernández-Fernández, D.M.; Alvear, M.; Almeda, F.; Armbruster, W.S.; Staedler, Y.; et al. Modularity increases rate of floral evolution and adaptive success for functionally specialized pollination systems. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, D.; Berger, A.; von Balthazar, M.; Chartier, M.; Sherafati, M.; Schönenberger, J.; Manafzadeh, S.; Staedler, Y.M. Modularity and evolution of flower shape: The role of function, development, and spandrels in Erica. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, E.A.; Dexter, K.G.; Stone, H.B. Reproductive character displacement and potential underlying drivers in a species-rich and florally diverse lineage of tropical angiosperms (Ruellia; Acanthaceae). Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 4719–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Hang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.F. The pollination of Dioscorea nipponica ssp. rosthornii. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2008, 17, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sadik, S.; Okereke, O.U. Flowering Pollen Grain Germination, Fruiting, Seed Germination and Seedling Development of White Yam, Dioscorea rotundata Poir. Anm. Bot. 1975, 39, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuki, I.; Ishida, K.; Kikuzawa, K. Sexual and vegetative reproduction in the aboveground part of a dioecious clonal plant, Dioscorea japonica (Dioscoreaceae). Ecol. Res. 2005, 20, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Yan, Q.Q.; Sun, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zhou, Y.F.; Hang, Y.Y. A preliminary study on pollination biology of three species in Dioscorea (Dioscoreaceae). Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 436–444. [Google Scholar]
- Soto Gomez, M.; Pokorny, M.B.; Kantar, F.; Forest, I.J.; Leitch, B.; Gravendeel, P.; Wilkin, S.; Graham, W.; Viruel, J. A customized nuclear target enrichment approach for developing a phylogenomic baseline for Dioscorea yams (Dioscoreaceae). Appl. Plant Sci. 2019, 7, e11254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Ting, C.T.; Chin, H.C.; Su, P.; Tang, S.Y.; Chang, H.C. A preliminary systematic study of Dioscorea L. sect. Stenophora Uline. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 1979, 17, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
| Species | Locality | Voucher | GenBank Accession No. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| matK | trnL-F | rbcL | psbA-trnH | rpl36-rps8 | nad1 | rps3 | |||
| Dioscorea nipponica Makino | Lin’an, Zhejiang, China | NAS 0648570 | AY957600 * | DQ841308 | AF307455 * | GQ265171 | GQ265222 | GQ265123 | GQ265268 |
| D. nipponica subsp. rosthornii (Prain & Burkill) C. T. Ting | Tianshui, Gansu, China | NAS 0648571 | DQ974184 | DQ841309 | DQ408178 | GQ265172 | GQ265223 | GQ265122 | GQ265269 |
| D. althaeoides R. Knuth | Dêqên, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648572 | EU407548 | EU301741 | EU407550 | GQ265182 | GQ265233 | GQ265135 | GQ265281 |
| D. tokoro Makino | Anhua, Hunan, China | NAS 0648573 | DQ974186 | DQ841312 | DQ408180 | GQ265174 | GQ265225 | GQ265125 | GQ265271 |
| D. zingiberensis C. H. Wright | Mt. Hengshan, Hunan, China | NAS 0646476 | AY973831 * | DQ841318 | AY939889 * | GQ265154 | GQ265206 | GQ265105 | GQ265251 |
| D. sinoparviflora C. T. Ting, M. G. Gilbert & N. J. Turland | Lijiang, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648574 | DQ974179 | DQ841326 | DQ408171 | GQ265163 | GQ265212 | GQ265112 | GQ265258 |
| D. deltoidea Wall. ex Griseb. | Kunming, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648575 | EF614207 | DQ841305 | EF614218 | GQ265169 | GQ265220 | GQ265120 | GQ265266 |
| D. panthaica Prain & Burkill | Lijiang, Yunnan, China | Y. F. Zhou & B. C. Wu 200308015 | GQ265088 | GQ265291 | GQ265187 | GQ265184 | GQ265235 | GQ265136 | GQ265283 |
| D. biformifolia C. Pei & C. T. Ting | Mt. Eshan, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648576 | EU407549 | EU301742 | EU301740 | GQ265147 | GQ265196 | GQ265097 | GQ265243 |
| D. gracillima Miq. | Mt. Lushan, Jiangxi, China | NAS 0648577 | DQ974190 | DQ841315 | DQ408164 | GQ265150 | GQ265201 | GQ265101 | GQ265247 |
| D. collettii Hook. f. var. collettii | Jinghong, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648578 | DQ974178 | DQ841300 | DQ408173 | GQ265141 | GQ265192 | GQ265093 | GQ265239 |
| D. collettii var. hypoglauca (Palibin) C. Pei & C. T. Ting | Mt. Hengshan, Hunan, China | NAS 0648579 | DQ974176 | DQ841319 | EF614220 | GQ265155 | GQ265205 | GQ265106 | GQ265252 |
| D. futschauensis Uline ex R. Knuth | Yongtai, Fujian, China | NAS 0648580 | DQ974175 | DQ841316 | DQ408166 | GQ265151 | GQ265202 | GQ265102 | GQ265248 |
| D. spongiosa J. Q. Xi, M. Mizuno & W. L. Zhao | Mt. Hengshan, Hunan, China | NAS 0648581 | DQ974191 | DQ841317 | DQ974194 | GQ265153 | GQ265204 | GQ265104 | GQ265250 |
| D. banzhuana C. Pei & C. T. Ting | Mengzi, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648582 | DQ974182 | DQ841301 | DQ408174 | GQ265167 | GQ265218 | GQ265118 | GQ265264 |
| D. simulans Prain & Burkill | Guilin, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648583 | EF614206 | DQ841320 | EF614217 | GQ265138 | GQ265189 | GQ265090 | GQ265236 |
| D. esculenta (Lour.) Burkill | Lingshui, Hainan, China | NAS 0648585 | AY956497 * | DQ841298 | AY904794 * | GQ265180 | GQ265231 | GQ265131 | GQ265277 |
| D. esculenta var. spinosa (Roxburgh ex Prain & Burkill) R. Knuth | Lingshui, Hainan, China | B. C. Wu200804023 | GQ265087 | GQ265290 | GQ265186 | GQ265181 | GQ265232 | GQ265134 | GQ265280 |
| D. tentaculigera Prain & Burkill | Lincang, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648465 | GQ265089 | GQ265292 | GQ265188 | GQ265183 | GQ265234 | GQ265137 | GQ265282 |
| D. yunnanensis Prain & Burkill | Lijiang, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648459 | EF614209 | GQ265288 | EF614221 | GQ265161 | GQ265213 | GQ265113 | GQ265259 |
| D. subcalva Prain & Burkill | Tianlin, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648544 | EF614208 | EF614222 | EF614214 | GQ265160 | GQ265211 | GQ265111 | GQ265257 |
| D. subcalva var. submollis (R. Knuth) C. T. Ting & P. P. Ling | Mt. Jinfo, Chongqing, China | NAS 0648545 | EF614204 | GQ265287 | EF614216 | GQ265152 | GQ265203 | GQ265103 | GQ265249 |
| D. nitens Prain & Burkill | Lijiang, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648586 | EF614205 | EF614223 | EF614215 | GQ265162 | GQ265214 | GQ265114 | GQ265260 |
| D. bulbifera L. | Jinghong, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648587 | AY956488 * | EF619352 | AY904791 * | GQ265178 | GQ265229 | GQ265132 | GQ265278 |
| D. melanophyma Prain & Burkill | Mengzi, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648548 | EF614210 | DQ841303 | DQ408176 | GQ265143 | GQ265194 | GQ265095 | GQ265241 |
| D. kamoonensis Kunth | Mengzi, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648549 | EF028332 | DQ841302 | DQ408175 | GQ265142 | GQ265193 | GQ265094 | GQ265240 |
| D. delavayi Franchet | Kunming, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648550 | GQ265085 | GQ265284 | DQ974196 | GQ265148 | GQ265199 | GQ265100 | GQ265246 |
| D. menglaensis H. Li | Jinghong, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648461 | GQ265086 | GQ265285 | GQ265185 | GQ265146 | GQ265198 | GQ265099 | GQ265245 |
| D. pentaphylla Linnaeus | Guilin, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648551 | AY972483 * | DQ841327 | AF307470 * | GQ265140 | GQ265191 | GQ265092 | GQ265237 |
| D. esquirolii Prain & Burkill | Longzhou, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648552 | DQ974177 | DQ841322 | DQ408168 | GQ265139 | GQ265190 | GQ265091 | GQ265238 |
| D. hispida Dennstedt. | Longzhou, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648553 | AY957589 * | DQ841323 | AF307463 * | GQ265145 | GQ265197 | GQ265098 | GQ265244 |
| D. aspersa Prain & Burkill | Mengzi, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648588 | EF614211 | DQ841304 | EF614213 | GQ265168 | GQ265219 | GQ265119 | GQ265265 |
| D. polystachya Turczaninow | Jurong, Jiangsu, China | NAS 0648589 | EF028331 | DQ841313 | DQ408181 | GQ265144 | GQ265195 | GQ265096 | GQ265242 |
| D. japonica Thunberg | Lin’an, Zhejiang, China | NAS 0648590 | DQ974183 | DQ841307 | AF307457 * | GQ265170 | GQ265221 | GQ265121 | GQ265267 |
| D. cirrhosa Loureiro | Longzhou, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648591 | EF028329 | DQ841324 | AY904792 * | GQ265158 | GQ265209 | GQ265109 | GQ265255 |
| D. cirrhosa var. cylindrica C. T. Ting & M. C. Chang | Mt. Diaoluo, Hainan, China | NAS 0648592 | DQ974189 | DQ841314 | DQ408184 | GQ265179 | GQ265230 | GQ265133 | GQ265279 |
| D. wallichii J. D. Hooker | - | - | AY973830 * | - | AY939888 * | - | - | - | - |
| D. glabra Roxburgh | Longzhou, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648593 | AY956501 * | DQ841321 | AF307456* | GQ265157 | GQ265208 | GQ265108 | GQ265254 |
| D. fordii Prain & Burkill | Guilin, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648594 | EF028333 | DQ841299 | DQ974195 | GQ265156 | GQ265207 | GQ265107 | GQ265253 |
| D. persimilis Prain & Burkill | Mingxi, Fujian, China | NAS 0648595 | DQ974193 | DQ841328 | DQ408165 | GQ265175 | GQ265226 | GQ265127 | GQ265273 |
| D. exalata C. T. Ting & M. C. Chang | Tianlin, Guangxi, China | NAS 0648596 | EF028330 | DQ841325 | DQ408170 | GQ265159 | GQ265210 | GQ265110 | GQ265256 |
| D. alata Linnaeus | Jinghong, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648597 | AB040208 * | DQ841331 | AY667098 * | GQ265165 | GQ265216 | GQ265116 | GQ265262 |
| D. decipiens J. D. Hooker | Jinghong, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648598 | DQ974181 | DQ841329 | AF307454 * | GQ265166 | GQ265217 | GQ265117 | GQ265263 |
| D. composita Hemsl. | Jinghong, Yunnan, China | NAS 0648405 | DQ974180 | DQ841330 | DQ408172 | GQ265164 | GQ265215 | GQ265115 | GQ265261 |
| D. sansibarensis Pax | Botanical Garden Regen Germany | Y. F. Zhou200403004 | DQ974187 | DQ841296 | AY939883 * | GQ265177 | GQ265228 | GQ265129 | GQ265275 |
| D. caucasica Lipsky | Lyon, France | NAS 0648584 | DQ974188 | DQ841297 | DQ408182 | - | - | GQ265130 | GQ265276 |
| D. elephantipes Engl. | South Africa | N. Sheng200511014 | AY956496 * | DQ841306 | AF307461 * | GQ265176 | GQ265227 | GQ265128 | GQ265274 |
| D. villosa L. | America | NAS 0648463 | - | GQ265286 | DQ006092 * | GQ265149 | GQ265200 | GQ265126 | GQ265272 |
| Tacca chantieri André | - | - | AY973837 * | FJ194472 * | AJ235810 * | EF590744 * | - | DQ786152 * | - |
| Marker | Primer Name | Direction | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| matK | matK MF | forward | ATT TGC GAT CTA TTC ATT CAA T |
| matK MR | reverse | TGA GAT TCC GCA GGT CAT T | |
| rbcL | rbcL m3 | forward | TAT CTT AGC GCC ATT CCG AGT A |
| rbcL m4 | reverse | CGC GGA TAA TTT CAT TAC CTT C | |
| trnL-F | trnL-F c | forward | CGA AAT CGG TAG ACG CTA CG |
| trnL-F f | reverse | ATT TGA ACT GGT GAC ACG AG | |
| psbA- trnH | psbA F1 | forward | AAT GCT CAC AAC TTY CCT CTA |
| trnH R1 | reverse | CCA CTG CCT TGA TCC ACT TG | |
| rpl36- rps8 | rpl36 F1 | forward | TTA CCC YTG TCT YTG TTT ATG |
| rps8 R1 | reverse | CTA CGA GAR GGT TTT ATT GAA | |
| nad1 | nad1 F1 | forward | CCT TGT GAG CAC GTT TGG AT |
| nad1 R1 | reverse | GAC AAT CTC ACT CGA ATT ACA G | |
| rps3 | rps3 F1 | forward | GTT CGA TAC GTC CAC CTA C |
| rps3 R1 | reverse | GTA CGT TTC GGA TAT RGC AC |
| Species | Character | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | ||
| Dioscorea sect. Stenophora | D. nipponica | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| D. nipponica subsp. rosthornii | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. althaeoides | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. tokoro | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. zingiberensis | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| D. sinoparviflora | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| D. deltoidea | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. panthaica | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. biformifolia | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. gracillima | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. collettii | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. collettii var. hypoglauca | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. futschauensis | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| D. spongiosa | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. banzhuana | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. simulans | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| D. caucasica | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. villosa | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| D. sect. Combilium | D. esculenta | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| D. esculenta var. spinosa | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. sect. Shannicorea | D. tentaculigera | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| D. yunnanensis | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. subcalva | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. subcalva var. submollis | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. nitens | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| D. sect. Opsophyton | D. bulbifera | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| D. sect. Botryosicyos | D. melanophyma | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| D. kamoonensis | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. delavayi | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. menglaensis | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. pentaphylla | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |
| D. esquirolii | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| D. sect. Lasiophyton | D. hispida | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| D. sect. Enantiophyllum | D. aspersa | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| D. polystachya | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. japonica | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. cirrhosa | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. cirrhosa var. cylindrica | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. wallichii | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. glabra | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. fordii | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. persimilis | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. exalata | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. alata | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. decipiens | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| D. sect. Apodostemon | D. composita | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| D. sect. Macroura | D. sansibarensis | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| D. sect. Testudinaria | D. elephantipes | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| outgroup | Tacca chantieri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DNA Region | Aligned Length (bp) | Variable Site (bp/%) | Informative Site (bp/%) | Tree Length | CI | RI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| matK | 1032 | 237/23.0 | 163/15.8 | 317 | 0.852 | 0.959 |
| rbcL | 1142 | 134/11.7 | 84/7.4 | 220 | 0.664 | 0.867 |
| trnL-F | 939 | 280/29.8 | 80/8.5 | 385 | 0.816 | 0.905 |
| psbA-trnH | 344 | 113/32.8 | 82/23.8 | 160 | 0.850 | 0.955 |
| rpl36-rps8 | 857 | 111/13.0 | 64/7.5 | 142 | 0.817 | 0.949 |
| nad1 | 1478 | 207/14.0 | 125/8.5 | 246 | 0.902 | 0.949 |
| rps3 | 1426 | 75/5.3 | 19/1.3 | 89 | 0.876 | 0.929 |
| 7 DNA | 7218 | 1157/16.0 | 617/8.5 | 1640 | 0.782 | 0.913 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Sun, X.; Xue, J.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hang, Y. Evolution of Reproductive Traits and Implications for Adaptation and Diversification in the Yam Genus Dioscorea L. Diversity 2022, 14, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050349
Chen M, Sun X, Xue J-Y, Zhou Y, Hang Y. Evolution of Reproductive Traits and Implications for Adaptation and Diversification in the Yam Genus Dioscorea L. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050349
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Min, Xiaoqin Sun, Jia-Yu Xue, Yifeng Zhou, and Yueyu Hang. 2022. "Evolution of Reproductive Traits and Implications for Adaptation and Diversification in the Yam Genus Dioscorea L." Diversity 14, no. 5: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050349
APA StyleChen, M., Sun, X., Xue, J.-Y., Zhou, Y., & Hang, Y. (2022). Evolution of Reproductive Traits and Implications for Adaptation and Diversification in the Yam Genus Dioscorea L. Diversity, 14(5), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050349







