Black Mantle Tissue of Endolithic Mussels (Leiosolenus spp.) Is Cloaking Borehole Orifices in Caribbean Reef Corals
Abstract
:Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, B.; Pemberton, S.G. Lithophaga borings and their influence on the diagenesis of corals in the Pleistocene Ironshore Formation of Grand Cayman Island, British West Indies. Palaios 1988, 3, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owada, M. Functional morphology and phylogeny of the rock-boring bivalves Leiosolenus and Lithophaga (Bivalvia: Mytilidae): A third functional clade. Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaps, P.; Denis, V. Can organisms associated with live scleractinian corals be used as indicators of coral reef status? Atoll Res. Bull. 2008, 566, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorauf, J.E.; Harries, P.J. Rotatory colonies of the corals Siderastrea radians and Solenastraea ssp. (Cnidaria, Scleractinia), from the Pleistocene Bermont formation, south Florida, USA. Palaeontology 2009, 52, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kázmér, M.; Taborosi, D. Bioerosion on the small scale–examples from the tropical and subtropical littoral. Hantkeniana 2012, 7, 37–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bagur, M.; Richardson, C.A.; Gutiérrez, J.L.; Arribas, L.P.; Doldan, M.S.; Palomo, M.G. Age, growth and mortality in four populations of the boring bivalve Lithophaga patagonica from Argentina. J. Sea Res. 2013, 81, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, P.W.; Manzello, D.P. Bioerosion and coral reef growth: A dynamic balance. In Coral Reefs in the Anthropocene; Birkeland, C., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Perasso, C.S.; Antonelli, F.; Petriaggi, B.D. Marine bivalves colonizing Roman artefacts recovered in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and in the Blue Grotto in Capri (Naples, Italy): Boring and nestling species. Int. Biodeter. Biodegrad. 2015, 98, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wizemann, A.; Nandini, S.D.; Stuhldreier, I.; Sánchez-Noguera, C.; Wisshak, M.; Westphal, H.; Rixen, T.; Christian, W.; Reymond, C.E. Rapid bioerosion in a tropical upwelling coral reef. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MolluscaBase eds. MolluscaBase. Lithophaginae H. Adams & A. Adams, 1857. World Register of Marine Species. 2022. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=510723 (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Zann, L.P. Living Together in the Sea; T.F.H. Publications: Neptune, NY, USA, 1980; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith, R.C. Coral bioerosion: Damage relative to skeletal density. Am. Nat. 1981, 117, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, P.A. Biological destruction of coral reefs. Coral Reefs 1986, 4, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B.; Risk, M.J. The effect of Lithophaga (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) boreholes on the strength of the coral Porites lobata. Coral Reefs 1988, 7, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, M.M.; Maher, R.L.; Correa, A.M.S.; Moeller, H.V.; Lemoine, N.P.; Shantz, A.A.; Burkepile, D.E.; Silbiger, N.J. Macroborer presence on corals increases with nutrient input and promotes parrotfish bioerosion. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.T.; Tsang, R.H.L.; Ang, P. Did borers make corals more susceptible to a catastrophic disease outbreak in Hong Kong? Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonge, C.M. Adaptation to rock boring in Botula and Lithophaga (Lamellibranchia, Mytilidae) with a discussion on the evolution of this habit. J. Cell Sci. 1955, 3, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audino, J.A.; Serb, J.M.; Marian, J.E.A.R. Phylogeny and anatomy of marine mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) reveal convergent evolution of siphon traits. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 190, 592–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, G.N. Ecological aspects of some coral-boring gastropods and bivalves of the northwestern Red Sea. Am. Zool. 1969, 9, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, L.R.L.; Gonçalves, E.P. Anatomical study on Myoforceps aristatus, an invasive boring bivalve in S.E. Brazilian coast (Mytilidae). Pap. Avulsos Zool. 2006, 46, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleemann, K.H. Lithophaga (Bivalvia) from dead coral from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. J. Molluscan Stud. 1984, 50, 192–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, K. Boring and growth in chemically boring bivalves from the Caribbean, Eastern Pacific and Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. Senckenberg. Marit. 1990, 22, 101–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gohar, H.A.F.; Soliman, G.N. On three mytilid species boring in living corals. Publ. Mar. Biol. Sta. Al-Ghardaqa 1963, 12, 65–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zottoli, R.A.; Carriker, M.R. Burrow morphology, tube formation, and microarchitecture of shell dissolution by the spionid polychaete Polydora websteri. Mar. Biol. 1974, 27, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W. Excavation patterns and spiculae dimensions of the boring sponge Cliona celata from the SW Netherlands. Senckenb. Marit. 1983, 15, 55–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.J.; Hsieh, H.L. Burrow architecture of the spionid polychaete Polydora villosa in the corals Montipora and Porites. Zool. Stud. 2000, 39, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Buschbaum, C.; Buschbaum, G.; Schrey, I.; Thieltges, D.W. Shell-boring polychaetes affect gastropod shell strength and crab predation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido Mantas, T.; Pola, L.; Cerrano, C.; Gambi, M.C.; Calcinai, B. Bioerosion features of boring polydorid polychaetes in the North Adriatic Sea. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 1969–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bakker, D.M.; Webb, A.E.; van den Bogaart, L.A.; van Heuven, S.M.A.C.; Meesters, E.H.; van Duyl, F.C. Quantification of chemical and mechanical bioerosion rates of six Caribbean excavating sponge species found on the coral reefs of Curaçao. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearley, R.F.; Ekdale, A.A. Modern marine bioerosion by macroinvertebrates, northern Gulf of California. Palaios 1989, 4, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highsmith, R.C. Burrowing by the bivalve mollusc Lithophaga curta in the living reef coral Montipora berryi and a hypothesis of reciprocal larval recruitment. Mar. Biol. 1980, 56, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, K.H. Boring bivalves and their host corals from the Great Barrier Reef. J. Molluscan Stud. 1980, 46, 13–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C. Notes on boring bivalves from Phuket, Thailand. Ophelia 1976, 15, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantera, J.R.; Contreras, R. Bivalvos perforadores de esqueletos de corales escleractiniarios en la Isla de Gorgona, Pacífico Colombiano. Rev. Biol. Trop. 1988, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, M.M.; Menezes, N.M.; Johnsson, R.; Neves, E. The adverse effects of cryptochirid crabs (Decapoda: Brachyura) on Siderastrea stellata Verril, 1868 (Anthozoa: Scleractinia): Causes and consequences of cavity establishment. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van der Meij, S.E.T. Gall crab city: An aggregation of endosymbiotic crabs inhabiting a colossal colony of Pavona clavus. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Hernández, J.E.; de Gier, W.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M.; Hoeksema, B.W. The scleractinian Agaricia undata as a new host for the coral-gall crab Opecarcinus hypostegus at Bonaire, southern Caribbean. Symbiosis 2020, 81, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperaki, M.M.; Hill, C.E.; Hoeksema, B.W. The effects of wave exposure and host cover on coral-associated fauna of a centuries-old artificial reef in the Caribbean. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 176, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Harper, C.E.; Langdon-Down, S.J.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; Spaargaren, R.; Timmerman, R.F. Host range of the coral-associated worm snail Petaloconchus sp. (Gastropoda: Vermetidae), a newly discovered cryptogenic pest species in the southern Caribbean. Diversity 2022, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Timmerman, R.F.; Spaargaren, R.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Langdon-Down, S.J.; Harper, C. Morphological modifications and injuries of corals caused by feather duster worms (Sabellidae: Anamobaea sp.) in the Caribbean. Diversity 2022, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-S.; Shen, P. A living mechanical file: The burrowing mechanism of the coral-boring bivalve Lithophaga nigra. Mar. Biol. 1988, 97, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahel, G.; Marie, D.; Beninger, P.G.; Eckstein, S.; Genin, A. In situ evidence for pre-capture qualitative selection in the tropical bivalve Lithophaga simplex. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 6, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, B.K.K.; Tan, J.C.H.; Ganmanee, M. Living in a growing host: Growth pattern and dwelling formation of the scallop Pedum spondyloideum in massive Porites spp. corals. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaps, P. Association between the scallop Pedum spondyloideum (Bivalvia: Pteriomorphia: Pectinidae) and scleractinian coralsfrom Nosy Be, Madagascar. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2020, 61, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B. Aspects of living coral associates in Jamaica. In Proceedings of the 5th International Coral Reef Congress, Tahiti, France, 27 May–1 June 1985; Volume 5, pp. 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, P.J.B. A new species of Lithophaga (Bivalvia: Lithophaginae) boring corals in the Caribbean. J. Molluscan Stud. 1986, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B. Associations between corals and macro-infaunal invertebrates in Jamaica, with a list of Caribbean and Atlantic coral associates. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1987, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, P.J.B. Distribution, habitat and morphology of the Caribbean coral and rock-boring bivalve, Lithophaga bisulcata (d’Orbigny) (Mytilidae: Lithophaginae). J. Molluscan Stud. 1988, 5, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.B. Initial settlement behaviour and survivorship of Lithophaga bisulcata (d’Orbigny) (Mytilidae: Lithophaginae). J. Molluscan Stud. 1988, 54, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinagre, C.; Silva, R.; Mendonça, V.; Flores, A.A.V.; Baeta, A.; Marques, J.C. Food web organization following the invasion of habitat-modifying Tubastraea spp. corals appears to favour the invasive borer bivalve Leiosolenus aristatus. Ecol. Ind. 2018, 85, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentich-Scott, P.; Dinesen, G.E. Rock and coral boring Bivalvia (Mollusca) of the middle Florida Keys, USA. Malacologia 2004, 46, 339–354. [Google Scholar]
- Bromley, R.G. Biocrosion of Bermuda reefs. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 1978, 23, 169–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, L.R. The dynamics of the community associated with a marine scleractinian coral. Int. Rev. Gesamt. Hydrobiol. 1970, 55, 13–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oigman-Pszczol, S.S.; Creed, J.C. Distribution and abundance of fauna on living tissues of two Brazilian hermatypic corals (Mussismilia hispida (Verril, 1902) and Siderastrea stellata Verril, 1868). Hydrobiologia 2006, 563, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchon, P.; Perry, C.T. Taphonomic differentiation of Acropora palmata facies in cores from Campeche Bank reefs, Gulf of México. Sedimentology 2004, 51, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, S.K.; Hensley, C. Gastrochaenolites Leymerie in the Cenozoic of the Antillean region (review). Ichnos 2006, 13, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, K.H. Gastrochaenolites hospitium sp. nov., trace fossil by a coral-associated boring bivalve from the Eocene and Miocene of Austria. Geol. Carpath. 2009, 60, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisshak, M.; Knaust, D.; Bertling, M. Bioerosion ichnotaxa: Review and annotated list. Facies 2019, 65, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.; Braga, J.C.; Owada, M.; Aguirre, J.; Lipps, J.H.; Takayanagi, H.; Iryu, Y. Boring bivalve traces in modern reef and deeper-water macroid and rhodolith beds. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokady, O.; Bonar, D.B.; Arazi, G.; Loya, Y. Coral host specificity in settlement and metamorphosis of the date mussel Lithophaga lessepsiana (Vaillant, 1865). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 146, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokady, O.; Arazi, G.; Bonar, D.B.; Loya, Y. Settlement and metamorphosis specificity of Lithophaga simplex Iredale (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) on Red Sea corals. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 162, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.W.; Hoeg, J.T.; Chan, B.K.K. How do coral barnacles start their life in their hosts? Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreyer, N.; Tsai, P.-C.; Olesen, J.; Kolbasov, G.A.; Høeg, J.T.; Chan, B.K.K. Independent and adaptive evolution of phenotypic novelties driven by coral symbiosis in barnacle larvae. Evolution 2022, 76, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, J.R. Coral preference behaviour by planktotrophic larvae of Spirobranchus giganteus corniculatus (Serpulidae: Polychaeta). Coral Reefs 1987, 6, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, J.R.; Conlin, B.E.; Hunte, W. Habitat selection in the tropical polychaete Spirobranchus giganteus. Mar. Biol. 1990, 104, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretzsohn, F.; Tsuchyia, M. Preliminary survey of the coral boring Bivalvia fauna of Okinawa, southern Japan. In Proceedings of the 7th International Coral Reef Symposium, Guam, 22–26 June 1992; Volume 1, pp. 404–412. [Google Scholar]
- Mokady, O.; Rozenblatt, S.; Graur, D.; Loya, Y. Coral-host specificity of Red Sea Lithophaga bivalves: Interspecific and intraspecific variation in 12S mitochondrial. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleemann, K.H. Association of coral and boring bivalves: Lizard Island (Great Barrier Reef, Australia) versus Safaga (N Red Sea). Beitr. Paläontol. 1995, 20, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kleemann, K.; Hoeksema, B.W. Lithophaga (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), including a new species, boring in mushroom corals (Scleractinia: Fungiidae) at South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Basteria 2002, 66, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Kleemann, K. New records of Fungiacava eilatensis Goreau et al., 1968 (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) boring in Indonesian mushroom corals (Scleractinia: Fungiidae). Basteria 2002, 66, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, T.A.; Yassien, M.H. Bivalve assemblages on living coral species in the Northern Red Sea, Egypt. J. Shellfish Res. 2008, 27, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owada, M. The first record of Leiosolenus simplex (Iredale, 1939) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) Boring into Plesiastrea versipora from Minamata Bay in Japan. Venus 2008, 67, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Owada, M.; Hoeksema, B.W. Molecular phylogeny and shell microstructure of Fungiacava eilatensis Goreau et al. 1968, boring into mushroom corals (Scleractinia: Fungiidae), in relation to other mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Contrib. Zool. 2011, 80, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleemann, K.; Maestrati, P. Pacific Lithophaga (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) from recent French expeditions with the description of two new species. Boll. Malacol. 2012, 48, 73–102. [Google Scholar]
- Printrakoon, C.; Yeemin, T.; Valentich-Scott, P. Ecology of endolithic bivalve mollusks from Ko Chang, Thailand. Zool. Stud. 2016, 55, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H. Phylogeny and evolutionary radiation of the marine mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) based on mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 126, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, J.S.; Pratchett, M.S.; Hutchings, P.A.; Jones, G.P. Coral-associated invertebrates: Diversity, ecology importance and vulnerability to disturbance. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 2011, 49, 43–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van der Meij, S.E.T.; Fransen, C.H.J.M. The mushroom coral as a habitat. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2012, 92, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeksema, B.W. The hidden biodiversity of tropical coral reefs. Biodiversity 2017, 18, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; van Beusekom, M.; ten Hove, H.A.; Ivanenko, V.N.; van der Meij, S.E.T.; van Moorsel, G.W.N.M. Helioseris cucullata as a host coral at St. Eustatius. Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montano, S. The extraordinary importance of coral-associated fauna. Diversity 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.K.L.; Meyer, C. A new species of pea crab of the genus Serenotheres Ahyong & Ng, 2005 (Crustacea, Brachyura, Pinnotheridae) from the date mussel Leiosolenus Carpenter, 1857 (Mollusca, Bivalvia, Mytilidae, Lithophaginae) from the Solomon Islands. ZooKeys 2016, 623, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Gier, W.; Becker, C. A Review of the ecomorphology of pinnotherine pea crabs (Brachyura: Pinnotheridae), with an updated list of symbiont-host associations. Diversity 2020, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
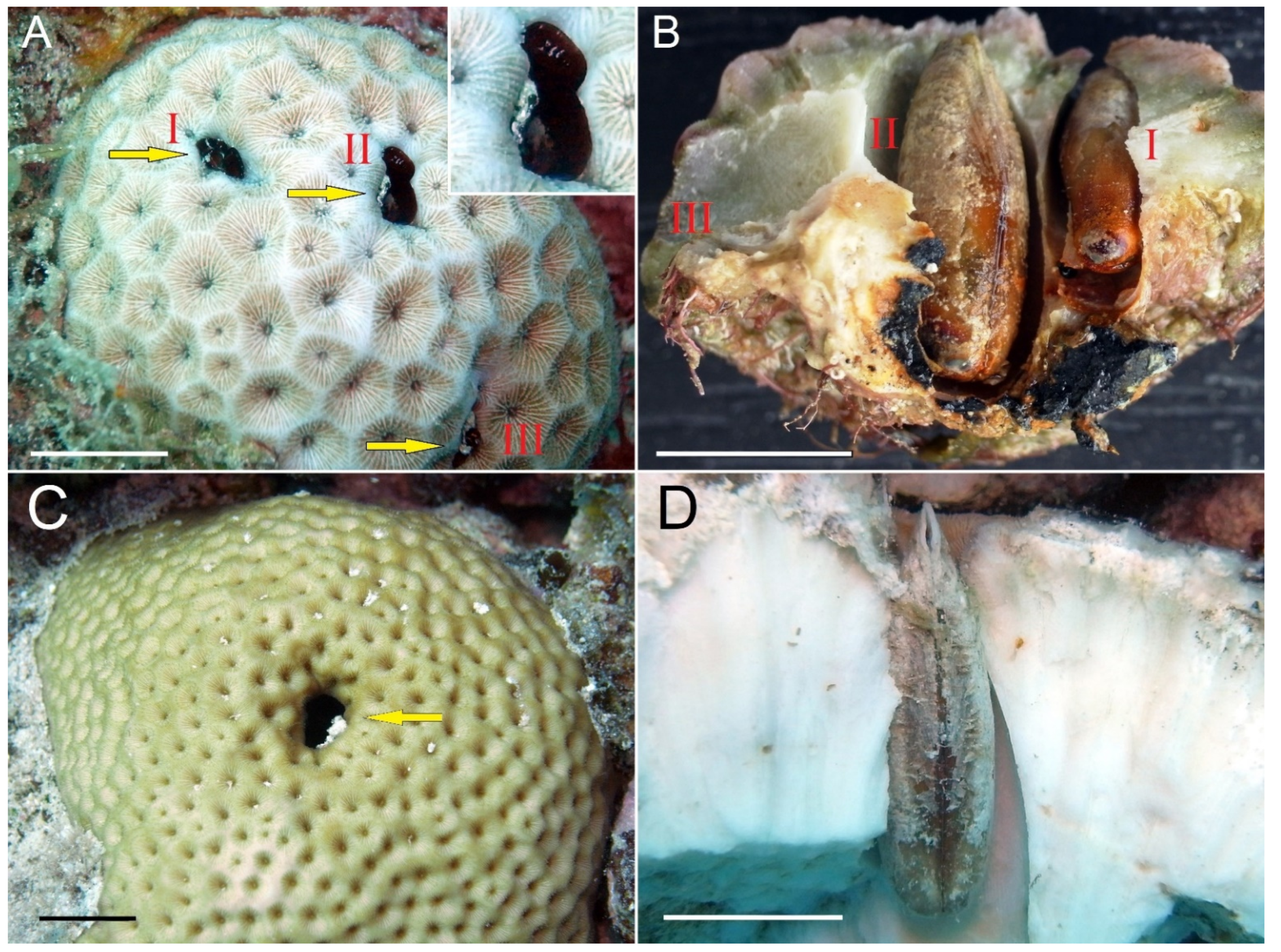

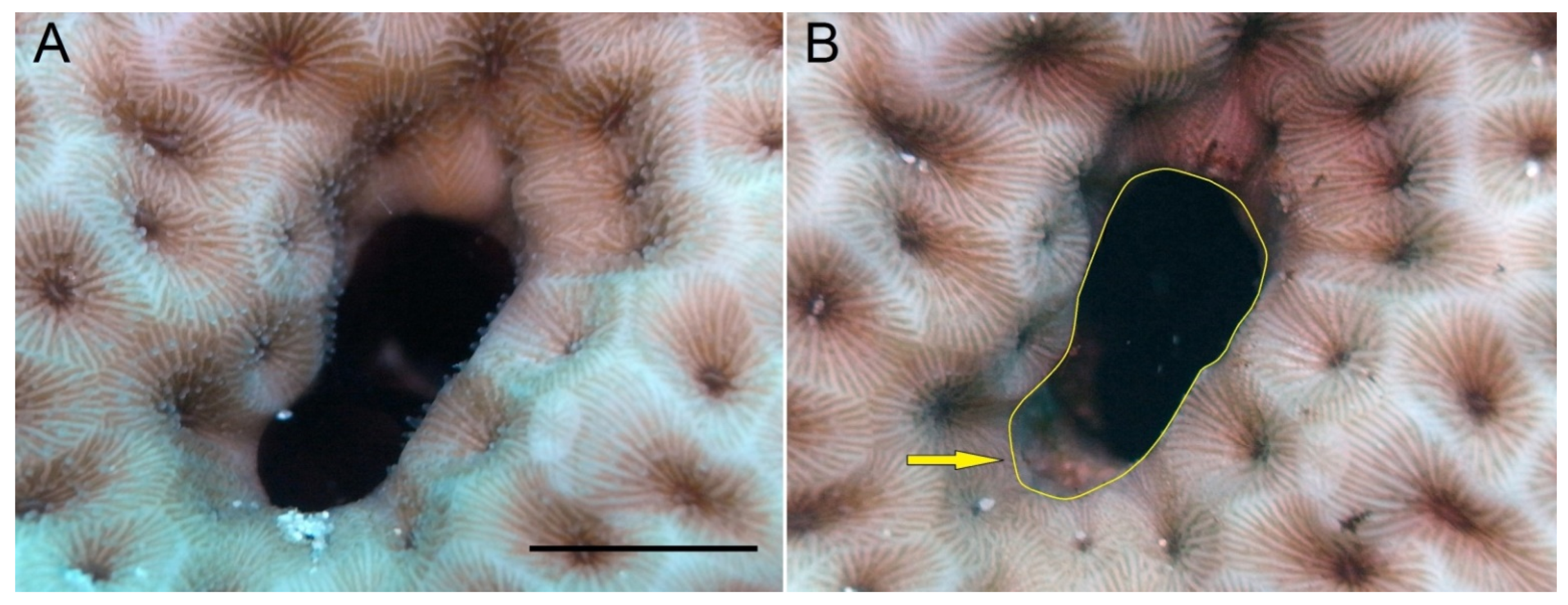
| Host Taxon | Orifice Shape |
|---|---|
| Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia | |
| Agariciidae | |
| Agaricia agaricites (Linnaeus, 1758) | O |
| Agaricia humilis (Verrill, 1901) * | T O |
| Agaricia lamarcki Milne Edwards & Haime, 1851 * | O |
| Astrocoeniidae | |
| Stephanocoenia intersepta (Esper, 1795) | O |
| Faviidae: Faviinae | |
| Colpophyllia natans (Houttuyn, 1772) * | T O |
| Diploria labyrinthiformis (Linnaeus, 1758) * | |
| Favia fragum (Esper, 1793) | O |
| Pseudodiploria strigosa (Dana, 1846) | T O |
| Meandrinidae | |
| Eusmilia fastigiata (Pallas, 1766) * | O |
| Meandrina meandrites (Linnaeus, 1758) * | O |
| Merulinidae | |
| Orbicella annularis (Ellis & Solander, 1786) | O |
| Orbicella faveolata (Ellis & Solander, 1786) * | T O |
| Orbicella franksi (Gregory, 1895) * | T O |
| Montastraeidae | |
| Montastraea cavernosa (Linnaeus, 1767) | O |
| Pocilloporidae | |
| Madracis auretenra Locke, Weil & Coates, 2007 | O |
| Madracis decactis (Lyman, 1859) | T O |
| Madracis pharensis (Heller, 1868) * | T |
| Madracis senaria Wells, 1973 * | T O |
| Poritidae | |
| Porites astreoides Lamarck, 1816 | O |
| Siderastreidae | |
| Siderastrea siderea (Ellis & Solander, 1768) | O |
| Cnidaria: Hydrozoa: Anthoathecata | |
| Milleporidae | |
| Millepora alcicornis Linnaeus, 1758 * | O |
| Millepora complanata Lamarck, 1816 * | T O |
| Dead coral | T |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoeksema, B.W.; Smith-Moorhouse, A.; Harper, C.E.; van der Schoot, R.J.; Timmerman, R.F.; Spaargaren, R.; Langdon-Down, S.J. Black Mantle Tissue of Endolithic Mussels (Leiosolenus spp.) Is Cloaking Borehole Orifices in Caribbean Reef Corals. Diversity 2022, 14, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050401
Hoeksema BW, Smith-Moorhouse A, Harper CE, van der Schoot RJ, Timmerman RF, Spaargaren R, Langdon-Down SJ. Black Mantle Tissue of Endolithic Mussels (Leiosolenus spp.) Is Cloaking Borehole Orifices in Caribbean Reef Corals. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050401
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoeksema, Bert W., Annabel Smith-Moorhouse, Charlotte E. Harper, Roel. J. van der Schoot, Rosalie F. Timmerman, Roselle Spaargaren, and Sean J. Langdon-Down. 2022. "Black Mantle Tissue of Endolithic Mussels (Leiosolenus spp.) Is Cloaking Borehole Orifices in Caribbean Reef Corals" Diversity 14, no. 5: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050401
APA StyleHoeksema, B. W., Smith-Moorhouse, A., Harper, C. E., van der Schoot, R. J., Timmerman, R. F., Spaargaren, R., & Langdon-Down, S. J. (2022). Black Mantle Tissue of Endolithic Mussels (Leiosolenus spp.) Is Cloaking Borehole Orifices in Caribbean Reef Corals. Diversity, 14(5), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050401










