Phylogenomic Insights into the Phylogeography of Halophila baillonii Asch.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
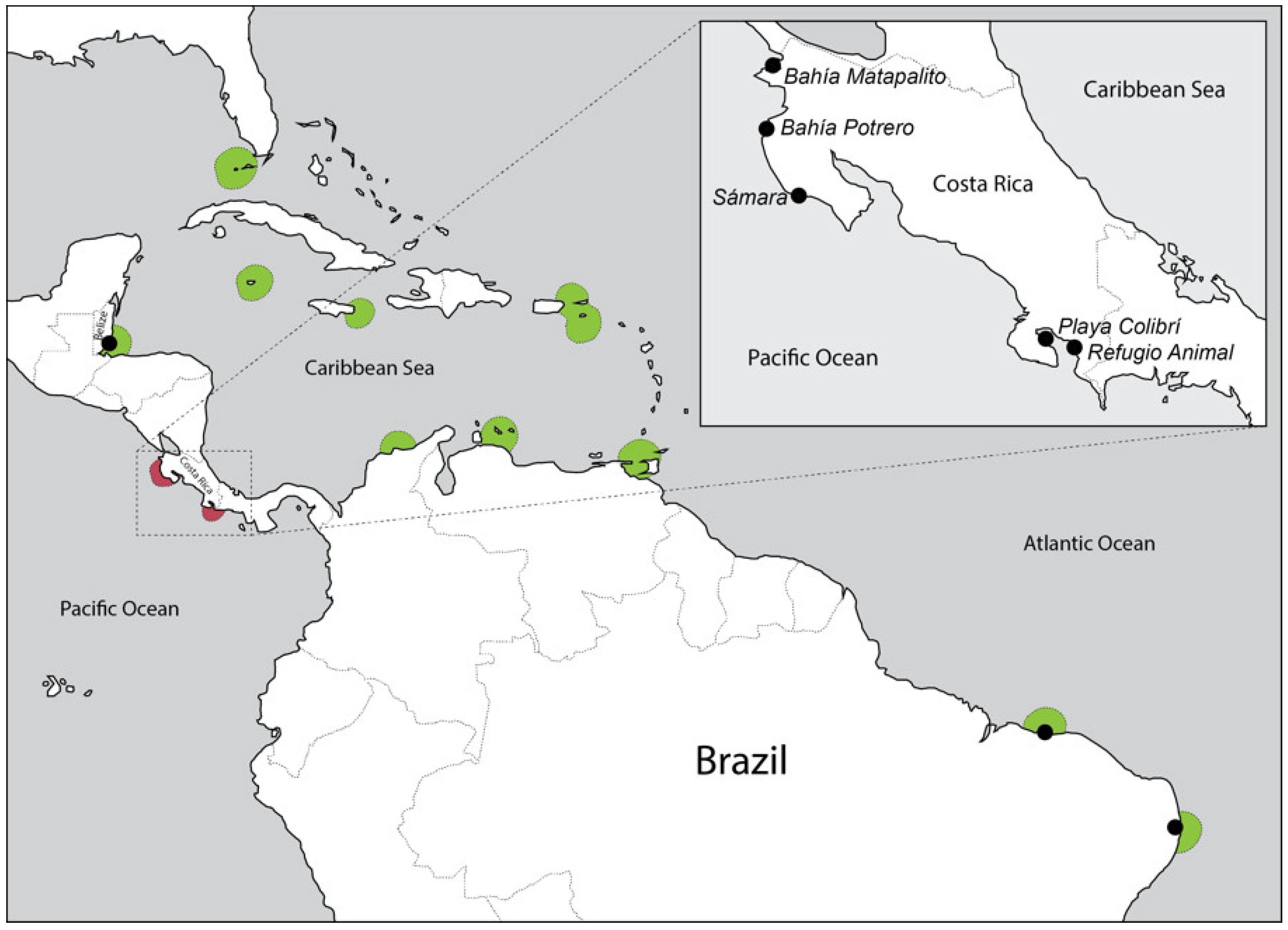
| # | Sample Name | Species | Country of Origin | Coastline * | Sampling Site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H. baillonii Belize 1 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 2 | H. baillonii Belize 2 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 3 | H. baillonii Belize 3 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 4 | H. baillonii Belize 4 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 5 | H. baillonii Belize 5 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 6 | H. baillonii Belize 6 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 7 | H. baillonii Belize 7 | H. baillonii | Belize | Caribbean | Placencia |
| 8 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 1.1 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Golfo Dulce, Refugio Animal |
| 9 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 2.1 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Golfo Dulce, Playa Colibrí |
| 10 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 2.2 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Golfo Dulce, Playa Colibrí |
| 11 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 2.3 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Golfo Dulce, Playa Colibrí |
| 12 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 2.4 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Golfo Dulce, Playa Colibrí |
| 13 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 3.1 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Bahía Matapalito |
| 14 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 3.2 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Bahía Matapalito |
| 15 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 3.3 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Bahía Matapalito |
| 16 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 4.1 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Bahía Potrero |
| 17 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 4.2 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Bahía Potrero |
| 18 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 5.1 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Sámara |
| 19 | H. baillonii Costa Rica 5.2 | H. baillonii | Costa Rica | Pacific | Sámara |
| 20 | H. australis Australia 1 | H. australis | Australia | - | Port Noarlunga |
| 21 | H. australis Australia 2 | H. australis | Australia | - | SA Pearsons Sanctuary Zone |
| 22 | H. australis Australia 3 | H. australis | Australia | - | VIC Flinders Island |
| 23 | H. beccari Singapore | H. beccari | Singapore | - | Mandi |
| 24 | H. decipiens Australia | H. decipiens | Australia | - | QLD Lowe Isles |
| 25 | H. decipiens Spain | H. decipiens | Spain | - | Canary Islands El Hierro |
| 26 | H. engelmanii Mexico | H. engelmanii | Mexico | - | Puerto Progreso |
| 27 | H. engelmanii USA | H. engelmanii | USA | - | Florida Black Water Sound |
| 28 | H. ovalis Australia 1 | H. ovalis | Australia | - | WA Rottnest Island Parker Bay |
| 29 | H. ovalis Japan | H. ovalis | Japan | - | Okinawa |
| 30 | H. ovalis Antigua | H. ovalis | Antigua and Barbuda | - | Antigua |
| 31 | H. ovalis Australia 2 | H. ovalis | Australia | - | WA Two People Bay |
| 32 | H. ovalis Madagascar | H. ovalis | Madagascar | - | Andrevo Tulear |
| 33 | H. ovalis Mauritius | H. ovalis | Mauritius | - | Flic en Flac |
| 34 | H. spinulosa Singapore | H. spinulosa | Singapore | - | Check Java |
| 35 | H. stipulacea Zanzibar | H. stipulacea | Tanzania, Zanzibar | - | Chwaka Bay |
| 36 | H. stipulacea Virgin Islands | H. stipulacea | USA, Virgin Islands | - | St Thomas |
| 37 | H. stipulacea UAE | H. stipulacea | United Arab Emirates | - | Mubarraz Island |
| 38 | H. tricostata Australia | H. tricostata | Australia | - | QLD Lowe Isles |
| 39 | H. baillonii Brazil 1.1 | H. baillonii | Brazil | Atlantic | Ponta do Socó, Praia das Pedras |
| 40 | H. baillonii Brazil 1.2 | H. baillonii | Brazil | Atlantic | Ponta do Socó, Praia das Pedras |
| 41 | H. baillonii Brazil 1.3 | H. baillonii | Brazil | Atlantic | Ponta do Socó, Praia das Pedras |
| 43 | H. baillonii Brazil 2.1 | H. baillonii | Brazil | Atlantic | Barra do Mamanguape, Banco d’areia |
| 44 | H. baillonii Brazil 2.2 | H. baillonii | Brazil | Atlantic | Barra do Mamanguape, Banco d’areia |
| 45 | H. baillonii Brazil 2.3 | H. baillonii | Brazil | Atlantic | Barra do Mamanguape, Banco d’areia |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, DNA Extractions and Library Preparation
2.2. Post Sequencing Data Processing Targeted Genes
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nordlund, L.M.; Koch, E.W.; Barbier, E.B.; Creed, J.C. Seagrass ecosystem services and their variability across genera and geographical regions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O´Brien, K.R.; Waycott, M.; Maxwell, P.; Kendrick, G.A.; Udy, J.W.; Ferguson, A.J.; Kilminster, K.; Scanes, P.; McKenzie, L.J.; McMohon, K.; et al. Seagrass ecosystem trajectory depends on the relative timescales of resistance, recovery and disturbance. Mar. Pollut Bull 2018, 134, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilminster, K.; McMahon, K.; Waycott, M.; Kendrick, G.A.; Scanes, P.; McKenzie, L.; O’Brien, K.R.; Lyons, M.; Ferguson, A.; Maxwell, P. Unravelling complexity in seagrass systems for management: Australia as a microcosm. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 534, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.; Carruthers, T.; Dennison, W.; Waycott, M. Global seagrass distribution and diversity: A bioregional model. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; McMahon, K.; Lavery, P. A Guide to Southern Temperate Seagrasses; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Waycott, M.; van Dijk, K.-j.; Calladine, A.; Bricker, E.; Biffin, E. Genomics-Based Phylogenetic and Population Genetic Analysis of Global Samples Confirms Halophila johnsonii Eiseman as Halophila ovalis (R.Br.) Hook.f. Front Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 740958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creed, J.C.; Samper-Villarreal, J. Clarification of the nomenclature of the seagrass Halophila baillonii Ascherson. Aquat. Bot. 2019, 154, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tussenbroek, B.; Barba Santos, M.G.; Wong, J.G.R.; Van Dijk, J.K.; Waycott, M. A Guide to the Tropical Seagrasses of the Western Atlantic; Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Short, F.; Carruthers, T.; van Tussenbroek, B.; Zieman, J. Halophila baillonii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010. Version 3.1. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/173382/7004500 (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Bourg, A.; Sibaja-Cordero, J.A.; Cortés, J. Presence of a Halophila baillonii Asch. (Hydrocharitaceae) Seagrass Meadow and Associated Macrofauna on the Pacific Coast of Costa Rica. Pac. Sci. 2014, 68, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, J. Requiem for an eastern Pacific seagrass bed. Rev Biol Trop 2001, 49 (Suppl. 2), 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Bolaños, R.C.; Heidemeyer, M.; Vargas, M.M.; Vargas, R.M. Characterization of seagrasses at two new locations in the Eastern tropical pacific (El Jobo and Matapalito, Costa Rica). Aquat. Bot. 2020, 165, 103237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Van Tussenbroek, B.I.; Cortés, J. Seagrasses of Costa Rica: From the mighty Caribbean to the dynamic meadows of the Eastern Tropical Pacific. Rev Biol Trop 2018, 66 (Suppl. 1), S53–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Rojas-Ortega, G.; Luis, V.-A.J.; Cortés, J. New sighting of seagrasses in the Eastern Tropical Pacific (Bahía Potrero, Costa Rica). Aquat. Bot. 2018, 151, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Cortés, J. Seagrass characterization on the southern Pacific coast of Costa Rica: History, vegetation, and environment. Bot. Mar. 2020, 63, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Moya-Ramírez, J.; Cortés, J. First characterization of seagrasses at Sámara Bay, Pacific coast of Costa Rica. Aquat. Bot. 2022, 178, 103486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Núñez, J.; Breedy-Shadid, O.; Sánchez-Noguera, C.; Pacheco-Solano, C. Los Ecosistemas Marinos del Refugio de Vida Silvestre La Flor y del Corredor Biológico Paso del Istmo, Rivas, Nicaragua; Proyecto Investigación Marino-Costero: Asegurando las Bases Científicas y Educativas para la Protección y Manejo de Tortugas Marinas en los RVS La Flor y Río Escalante-Chococente; CIMAR, Paso Pacífico, DANIDA: Managua, Nicaragua, 2012; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- O’Dea, A.; Lessios, H.A.; Coates, A.G.; Eytan, R.I.; Restrepo-Moreno, S.A.; Cione, A.L.; Collins, L.S.; de Queiroz, A.; Farris, D.W.; Norris, R.D.; et al. Formation of the Isthmus of Panama. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Short, F.T.; Polidoro, B.; Livingstone, S.R.; Carpenter, K.E.; Bandeira, S.; Bujang, J.S.; Calumpong, H.P.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Coles, R.G.; Dennison, W.C.; et al. Extinction risk assessment of the world’s seagrass species. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; van Dijk, K.-j.; Biffin, E. A hybrid capture RNA bait set for resolving genetic and evolutionary relationships in angiosperms from deep phylogeny to intraspecific lineage hybridization. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.-J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, X.-V.; Nguyen-Nhat, N.-T.; Nguyen, X.-T.; Dao, V.-H.; Liao, L.M.; Papenbrock, J. Analysis of rDNA reveals a high genetic diversity of Halophila major in the Wallacea region. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giachini Tosetto, E.; Bertrand, A.; Neumann-Leitão, S.; Nogueira Júnior, M. The Amazon River plume, a barrier to animal dispersal in the Western Tropical Atlantic. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, G.S.; Rocha, L.A.; Lastrucci, N.S.; Luiz, O.J.; Di Dario, F.; Floeter, S.R. The Amazon-Orinoco Barrier as a driver of reef-fish speciation in the Western Atlantic through time. J. Biogeogr. 2022, 49, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waycott, M.; Freshwater, D.W.; York, R.A.; Calladine, A.; Kenworthy, W.J. Evolutionary trends in the seagrass genus Halophila (Thouars): Insights from molecular phylogeny. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2002, 71, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Marechal, J.P.; Meesters, H.W.G.; Vedie, F.; Hellig, C. Occurrence of the alien seagrass Halophila stipulacea in Martinique (French West Indies). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2013, 6, e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, H.; Ballantine, D.L. Occurrence of the seagrass Halophila stipulacea in the tropical West Atlantic. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2004, 75, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin, Y. Halophila stipulacea, a review of a successful immigration. Aquat. Bot. 1975, 1, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Harwell, M.C.; Inglis, G.J. Ecology of seagrasses seeds and dispersal strategies. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick, G.A.; Orth, R.J.; Statton, J.; Hovey, R.; Ruiz Montoya, L.; Lowe, R.J.; Krauss, S.L.; Sinclair, E.A. Demographic and genetic connectivity: The role and consequences of reproduction, dispersal and recruitment in seagrasses. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, F.T.; Fernandez, E.; Vernon, A.; Gaeckle, J.L. Occurrence of Halophila baillonii meadows in Belize, Central America. Aquat. Bot. 2006, 85, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.D.N. A Heterogeneidade Ambiental em Angiospermas Marinhas e os Efeitos Sobre a Variação Espacial da Macrofauna Associada; Universidade Federal do Ceará: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, K.; Costa, F.; Rocha-Barreira, C. A Halophila baillonis Ascherson bed on the semiarid coast of Brazil. Feddes Repert. 2014, 125, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, N.P.; Costa, F.d.N.; Silva, M.F.S.; Mayo, S.J.; de Andrade, I.M. Seagrasses of Piauí, Brazil: A floristic treatment. Feddes Repert. 2018, 129, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, G.; Beer, S.; Willette, D.A.; Viana, I.G.; Chiquillo, K.L.; Beca-Carretero, P.; Villamayor, B.; Azcárate-García, T.; Shem-Tov, R.; Mwabvu, B.; et al. The tropical seagrass Halophila stipulacea: Reviewing what we know from its native and invasive habitats, alongside identifying knowledge gaps. Front Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, F.O.H.; Vonk, J.A.; Engel, M.S.; Christianen, M.J.A. Expansion and fragment settlement of the non-native seagrass Halophila stipulacea in a Caribbean bay. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMahon, K.; van Dijk, K.-j.; Ruiz-Montoya, L.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krauss, S.L.; Waycott, M.; Verduin, J.; Lowe, R.J.; Statton, J.; Brown, E.; et al. The movement ecology of seagrasses. Proc. R Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2014, 282, 20140878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, I.G.; Siriwardane-de Zoysa, R.; Willette, D.A.; Gillis, L.G. Exploring how non-native seagrass species could provide essential ecosystems services: A perspective on the highly invasive seagrass Halophila stipulacea in the Caribbean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselmann, M.; Geraldi, N.R.; Duarte, C.M.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Díaz-Rúa, R.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Hendriks, I.E.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Marbà, N. Seagrass (Halophila stipulacea) invasion enhances carbon sequestration in the Mediterranean Sea. Global Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2592–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Dijk, K.-j.; Waycott, M.; Biffin, E.; Creed, J.C.; Albertazzi, F.J.; Samper-Villarreal, J. Phylogenomic Insights into the Phylogeography of Halophila baillonii Asch. Diversity 2023, 15, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010111
van Dijk K-j, Waycott M, Biffin E, Creed JC, Albertazzi FJ, Samper-Villarreal J. Phylogenomic Insights into the Phylogeography of Halophila baillonii Asch. Diversity. 2023; 15(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010111
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Dijk, Kor-jent, Michelle Waycott, Ed Biffin, Joel C. Creed, Federico J. Albertazzi, and Jimena Samper-Villarreal. 2023. "Phylogenomic Insights into the Phylogeography of Halophila baillonii Asch." Diversity 15, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010111
APA Stylevan Dijk, K.-j., Waycott, M., Biffin, E., Creed, J. C., Albertazzi, F. J., & Samper-Villarreal, J. (2023). Phylogenomic Insights into the Phylogeography of Halophila baillonii Asch. Diversity, 15(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010111







