Another Chapter in the History of the European Invasion by the Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis: The Iberian Peninsula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extractions
2.2. mtDNA Sequencing and Analyses
2.3. Microsatellite Genotyping and Analyses
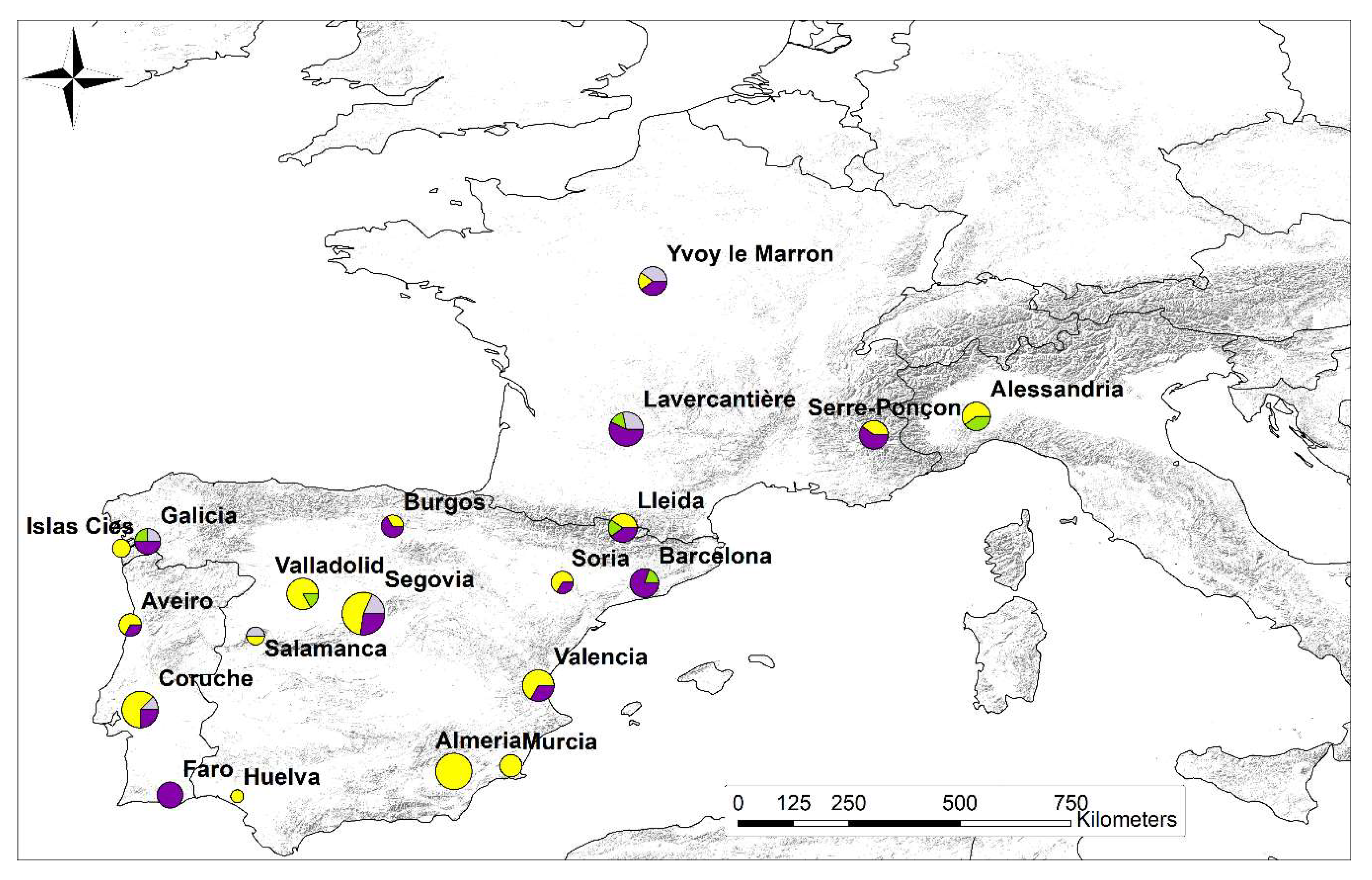
3. Results
3.1. mtDNA
3.2. Microsatellite Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity and Structure of the Iberian Populations
4.2. Routes of Invasion in the Iberian Peninsula
4.3. Cone Trade Market and the Invasion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kenis, M.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Roques, A.; Timms, L.; Péré, C.; Cock, M.J.W.; Settele, J.; Augustin, S.; Lopez-Vaamonde, C. Ecological Effects of Invasive Alien Insects. In Ecological Impacts of Non-Native Invertebrates and Fungi on Terrestrial Ecosystems; Langor, D.W., Sweeney, J., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 21–45. ISBN 978-1-4020-9679-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, A. Predicting the Impacts of an Introduced Species from Its Invasion History: An Empirical Approach Applied to Zebra Mussel Invasions: Predicting Impacts of Introduced Species: An Empirical Approach. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, M.; García-Berthou, E. Homogenization Dynamics and Introduction Routes of Invasive Freshwater Fish in the Iberian Peninsula. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Opp, S.B.; Berlocher, S.H.; Roderick, G.K. Are Bottlenecks Associated with Colonization? Genetic Diversity and Diapause Variation of Native and Introduced Rhagoletis Completa Populations. Oecologia 2006, 149, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didham, R.; Tylianakis, J.; Gemmell, N.; Rand, T.; Ewers, R. Interactive Effects of Habitat Modification and Species Invasion on Native Species Decline. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubrock, P.J.; Turbelin, A.J.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Novoa, A.; Taylor, N.G.; Angulo, E.; Ballesteros-Mejia, L.; Bodey, T.W.; Capinha, C.; Diagne, C.; et al. Economic Costs of Invasive Alien Species across Europe. NeoBiota 2021, 67, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Capinha, C.; Dawson, W.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Kleunen, M.; Kühn, I.; et al. Projecting the Continental Accumulation of Alien Species through to 2050. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Blackburn, T.M.; Garnas, J.; Pyšek, P.; Rabitsch, W.; Richardson, D.M.; Wingfield, M.J.; Liebhold, A.M.; Duncan, R.P. Temporal and Interspecific Variation in Rates of Spread for Insect Species Invading Europe during the Last 200 Years. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraimout, A.; Debat, V.; Fellous, S.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Foucaud, J.; Pudlo, P.; Marin, J.-M.; Price, D.K.; Cattel, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Deciphering the Routes of Invasion of Drosophila Suzukii by Means of ABC Random Forest. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bras, A.; Lombaert, E.; Kenis, M.; Li, H.; Bernard, A.; Rousselet, J.; Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A. The Fast Invasion of Europe by the Box Tree Moth: An Additional Example Coupling Multiple Introduction Events, Bridgehead Effects and Admixture Events. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 3865–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardinelli, I.; Zandigiacomo, P. Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann (Heteroptera, Coreidae): A Conifer Seed Bug Recently Found in Northern Italy. J. For. Sci. 2001, 47, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.J.; Tescari, G.; Villa, M. A Nearctic Pest of Pinaceae Accidentally Introduced into Europe: Leptoglossus Occidentalis (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Northern Italy. Entomol. News 2001, 112, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur, V.; Lombaert, E.; Guillemaud, T.; Courtial, B.; Strong, W.; Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A. The Rapid Spread of Leptoglossus Occidentalis in Europe: A Bridgehead Invasion. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, S.E.; Borden, J.H. Distribution and Impact of Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann (Hemiptera: Coreidae) in Seed Orchards in British Columbia. Can. Entomol. 1996, 128, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, V.; Yart, A.; Guilbon, S.; Lorme, P.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Roques, A. The Invasive Leptoglossus Seed Bug, a Threat for Commercial Seed Crops, but for Conifer Diversity? Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 1833–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracalini, M.; Cerboneschi, M.; Croci, F.; Panzavolta, T.; Tiberi, R.; Biancalani, C.; Macconi, S.; Tegli, S. Alien Pest Molecular Diagnostics: Can DNA Traces Be Exploited to Assess the Damage Caused by the Western Conifer Seed Bug on Stone Pine Fructification? Bull. Insectology 2015, 68, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Farinha, A.C.O.; Silva, J.E.P.; Correia, A.C.; Sousa, E.M.R.; Roques, A.; Branco, M. Is Leptoglossus Occidentalis Entirely Responsible for the High Damage Observed on Cones and Seeds of Pinus Pinea? Results from a Fertirrigation Trial in Portugal. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 429, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizal, E. Two Invasive Alien Insect Species, Leptoglossus Occidentals (Heteroptera: Coreidae) and Cydalima Perspectalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), and Their Distribution and Host Plants in Istanbul Province, Turkey. Fla. Entomol. 2012, 95, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemer, N. Report on Insect Pests Associated with Cone Net Losses and Their Management in Pinus Pinea Forests in Lebanon; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Calama, R.; Gordo, J.; Raposo, R.; Elvira, M.; Mutke, S.; Pascual, S.; Pardos, M. Evolución de Daños en Piña Inmadura de Pinus Pinea L; Jornada final del proyecto PROPINEA; Diputación de Valladolid, Pedrajas de S. Esteban: Valladolid, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Calama, R.; Gordo, J.; Mutke, S.; Madrigal, G.; Conde, M.; Raposo, R.; Elvira, M.; Pardos, M. Variabilidad espacio-temporal en el daño asociado a Leptoglossus occidentalis en pinares de Pinus pinea de la provincia de Valladolid. In Proceedings of the Poster presented at the 7 Spanish Forest Congress, Plasencia, Spain, 26–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jamâa, M.L.B.; Mejri, M.; Naves, P.; Sousa, E. Detection of Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Heteroptera: Coreidae) in Tunisia. Afr. Entomol. 2013, 21, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, S.; Martínez, J.; Gordo, J.; Nicolas, J.; Herrero Sierra, N.; Pastor, A. Calama Severe Seed Yield Loss in Mediterranean Stone Pine Cones. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mediterranean Pines, Solsona, Spain, 22–26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasquinho, I.; Correia, A.C.; Mutke, S. Mediterranean Pine Nuts from Forests and Plantations. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Meeting on Mediterranean Stone Pine for Agroforestry; INIAV: Zaragoza, Spain; CIHEAM: Oeiras, Portugal, 2017; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- EUFORGEN. Technical Report for 2009 and Financial Report for Phase III (2005–2009); EUFORGEN: Barcelona, Spain, 2009; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Farinha, A.O.; Branco, M.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Maurício, A.; Yart, A.; Guerreiro, V.; Sousa, E.M.R.; Roques, A. Micro X-Ray Computed Tomography Suggests Cooperative Feeding among Adult Invasive Bugs Leptoglossus Occidentalis on Mature Seeds of Stone Pine Pinus Pinea: Consumption of P. Pinea Seeds by L. Occidentalis. Agr For. Entomol 2018, 20, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinha, A.O.; Carvalho, C.; Correia, A.C.; Branco, M. Impact Assessment of Leptoglossus Occidentalis in Pinus Pinea: Integrating Population Density and Seed Loss. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 496, 119422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, S.; Calama, R. Producción de Piña y Rendimientos en Piñón en los Países Mediterráneos; Diputación de Valladolid, Pedrajas de S. Esteban: Valladolid, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson Handley, L.-J.; Estoup, A.; Evans, D.M.; Thomas, C.E.; Lombaert, E.; Facon, B.; Aebi, A.; Roy, H.E. Ecological Genetics of Invasive Alien Species. BioControl 2011, 56, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoup, A.; Guillemaud, T. Reconstructing Routes of Invasion Using Genetic Data: Why, How and so What? Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 4113–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombaert, E.; Guillemaud, T.; Cornuet, J.-M.; Malausa, T.; Facon, B.; Estoup, A. Bridgehead Effect in the Worldwide Invasion of the Biocontrol Harlequin Ladybird. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagu, A.; Robinson, K.; Noack, A.; Nahrung, H.; Lawson, S.; Lo, N. Global Incursion Pathways of Thaumastocoris Peregrinus, an Invasive Australian Pest of Eucalypts. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3501–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urvois, T.; Perrier, C.; Roques, A.; Sauné, L.; Courtin, C.; Li, Y.; Johnson, A.J.; Hulcr, J.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Kerdelhué, C. A First Inference of the Phylogeography of the Worldwide Invader Xylosandrus Compactus. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 95, 1217–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallez, S.; Castagnone, C.; Lombaert, E.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Guillemaud, T. Inference of the Worldwide Invasion Routes of the Pinewood Nematode Bursaphelenchus Xylophilus Using Approximate Bayesian Computation Analysis. Peer Community J. 2021, 1, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, V. Invasion de La Punaise Américaine Leptoglossus Occidentalis En Europe: Une Contribution à La Compréhension Des Invasions Fulgurantes. Ph.D. Thesis, Université d’Orléans, Orléans, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boubou, A.; Migeon, A.; Roderick, G.K.; Auger, P.; Cornuet, J.-M.; Magalhães, S.; Navajas, M. Test of Colonisation Scenarios Reveals Complex Invasion History of the Red Tomato Spider Mite Tetranychus Evansi. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allendorf, F.W.; Lundquist, L.L. Introduction: Population Biology, Evolution, and Control of Invasive Species. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, D.G.; Caseys, C.; Cousens, R.D.; Hahn, M.A.; Heredia, S.M.; Hübner, S.; Turner, K.G.; Whitney, K.D.; Rieseberg, L.H. What We Still Don’t Know about Invasion Genetics. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2277–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harry, M.; Solignac, M.; Lachaise, D. Molecular Evidence for Parallel Evolution of Adaptive Syndromes in Fig-Breeding Lissocephala (Drosophilidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 1998, 9, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermiin, L.S.; Crozier, R.H. The Cytochrome b Region in the Mitochondrial DNA of the Ant Tetraponera Rufoniger: Sequence Divergence in Hymenoptera May Be Associated with Nucleotide Content. J. Mol. Evol. 1994, 38, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the Sensitivity of Progressive Multiple Sequence Alignment through Sequence Weighting, Position-Specific Gap Penalties and Weight Matrix Choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Dudley, J.; Tamura, K. MEGA: A Biologist-Centric Software for Evolutionary Analysis of DNA and Protein Sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A Software for Comprehensive Analysis of DNA Polymorphism Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, M.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. TCS: A Computer Program to Estimate Gene Genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of Molecular Variance Inferred from Metric Distances among DNA Haplotypes: Application to Human Mitochondrial DNA Restriction Data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin Suite Ver 3.5: A New Series of Programs to Perform Population Genetics Analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, V.; Courtial, B.; Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.A. Isolation and Characterization of 11 Polymorphic Microsatellite Markers in the Highly Invasive Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus Occidentalis (Heteroptera, Coreidae). Conserv. Genet Resour. 2014, 6, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. Arlequin (Version 3.0): An Integrated Software Package for Population Genetics Data Analysis. Evol. Bioinform. 2005, 1, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. Genalex 6: Genetic Analysis in Excel. Population Genetic Software for Teaching and Research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing Tables of Statistical Tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, S.T. Hp-Rare 1.0: A Computer Program for Performing Rarefaction on Measures of Allelic Richness. Mol Ecol Notes 2005, 5, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, M.-P.; Estoup, A. Microsatellite Null Alleles and Estimation of Population Differentiation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation of Statistical Computing. 2020. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Jombart, T.; Devillard, S.; Balloux, F. Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components: A New Method for the Analysis of Genetically Structured Populations. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: A R Package for the Multivariate Analysis of Genetic Markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. Ape 5.0: An Environment for Modern Phylogenetics and Evolutionary Analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meeûs, T.; Goudet, J. A Step-by-Step Tutorial to Use HierFstat to Analyse Populations Hierarchically Structured at Multiple Levels. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2007, 7, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of Population Structure Using Multilocus Genotype Data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the Number of Clusters of Individuals Using the Software Structure: A Simulation Study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; vonHoldt, B.M. Structure Harvester: A Website and Program for Visualizing Structure Output and Implementing the Evanno Method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2011, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A. CLUMPP: A Cluster Matching and Permutation Program for Dealing with Label Switching and Multimodality in Analysis of Population Structure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopelman, N.M.; Mayzel, J.; Jakobsson, M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Mayrose, I. Clumpak: A Program for Identifying Clustering Modes and Packaging Population Structure Inferences across K. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N.A. Distruct: A Program for the Graphical Display of Population Structure. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugosch, K.M.; Parker, I.M. Founding Events in Species Invasions: Genetic Variation, Adaptive Evolution, and the Role of Multiple Introductions. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facon, B.; Pointier, J.-P.; Jarne, P.; Sarda, V.; David, P. High Genetic Variance in Life-History Strategies within Invasive Populations by Way of Multiple Introductions. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosi, M.; Miller, N.J.; Kim, K.S.; Giordano, R.; Estoup, A.; Guillemaud, T. Invasion of Europe by the Western Corn Rootworm, Diabrotica Virgifera Virgifera: Multiple Transatlantic Introductions with Various Reductions of Genetic Diversity. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 3614–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, J.J.; Lavin, B.R.; Burke, R.L.; Rugiero, L.; Capula, M.; Luiselli, L. The Desire for Variety: Italian Wall Lizard (Podarcis Siculus) Populations Introduced to the United States via the Pet Trade Are Derived from Multiple Native-Range Sources. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javal, M.; Roques, A.; Haran, J.; Hérard, F.; Keena, M.; Roux, G. Complex Invasion History of the Asian Long-Horned Beetle: Fifteen Years after First Detection in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzurenko, M.; Ranger, C.M.; Hulcr, J.; Galko, J.; Kaňuch, P. Origin of Non-Native Xylosandrus Germanus, an Invasive Pest Ambrosia Beetle in Europe and North America. J. Pest. Sci. 2021, 94, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.-P.; Rédei, D.; Kment, P.; Bu, W.-J. Effect of Geographic Background and Equilibrium State on Niche Model Transferability: Predicting Areas of Invasion of Leptoglossus Occidentalis. Biol. Invasions 2014, 16, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, J.; Escolà, O. Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann,1910, a Nearctic Bug (Hemiptera, Heteroptera, Coreidae) Found in Catalonia, Spain. Sessió Conjunta d’Entomologia Institució Catalana d’História Natural 2005, 13, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso-Silva, J. The North American Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera, Coreidae), New to Portugal. Arq. Entomolóxicos 2010, 4, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Valcárcel, J.; Prieto Piloña, F. La Contribución de Registros Fotográficos En Internet Para Estudios Faunísticos: El Caso de La Expansión Iberobalear de La Especie Invasora Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera, Coreidae). Arq. Entomoloxicos 2010, 4, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ribes, J.; Goula, M.G.; Pagola-Carte, S.; Solé, F.G.; Español, E.R. Addicions i Correccions al Catàleg Dels Heteròpters de Catalunya (Insecta, Hemiptera, Heteroptera). Sess. Conjunta D’entomologia 2008, 13–14, 107–165. [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel, J.P.; Portillo, P. Primer Registro de Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Hemiptera, Coreidae) Para Murcia (S.E. de La Península Ibérica). Arquivos Entomolóxicos 2009, 2, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez, M.; Costas, M.; Outerelo, R.; Melero-Alcíbar, R. Una Chinche Invasora En La Comunidad de Madrid, Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heidemann, 1910 (Heteroptera: Coreidae). Heteropterus Rev. Entomol. 2009, 9, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bossdorf, O.; Auge, H.; Lafuma, L.; Rogers, W.E.; Siemann, E.; Prati, D. Phenotypic and Genetic Differentiation between Native and Introduced Plant Populations. Oecologia 2005, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosi, M.; Miller, N.J.; Toepfer, S.; Estoup, A.; Guillemaud, T. Stratified Dispersal and Increasing Genetic Variation during the Invasion of Central Europe by the Western Corn Rootworm, Diabrotica Virgifera Virgifera: D. v. Virgifera Expansion in Central Europe. Evol. Appl. 2011, 4, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, B.; Pointier, J.-P.; Glaubrecht, M.; Poux, C.; Jarne, P.; David, P. A Molecular Phylogeography Approach to Biological Invasions of the New World by Parthenogenetic Thiarid Snails. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 3027–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, D.M.; Lapointe, D.A.; Fleischer, R.C. Bottlenecks and Multiple Introductions: Population Genetics of the Vector of Avian Malaria in Hawaii. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Buckley, Y.M.; Lowe, A.J. Testing the Role of Genetic Factors across Multiple Independent Invasions of the Shrub Scotch Broom (Cytisus Scoparius). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 4662–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolbe, J.J.; Glor, R.E.; Rodríguez Schettino, L.; Lara, A.C.; Larson, A.; Losos, J.B. Genetic Variation Increases during Biological Invasion by a Cuban Lizard. Nature 2004, 431, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, J.; Darling, J. Paradox Lost: Genetic Diversity and the Success of Aquatic Invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koerber, T.W. Leptoglossus Occidentalis (Hemiptera, Coreidae), a Newly Discovered Pest of Coniferous Seed. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1963, 56, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, H.; Pettenella, D. Pine Nuts: A Review of Recent Sanitary Conditions and Market Development. Forests 2017, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, S.; Calama, R.; Neaymeh, E.N.; Roques, A. Impact of the Dry Cone Syndrome on Commercial Kernel Yield of Stone Pine Cones. In Mediterranean Pine Nuts from Forests and Plantations; Carrasquinho, I., Correia, A.C., Mutke, S., Eds.; CIHEAM: Zaragoza, Spain, 2017; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Mutke, S.; Calama, R.; González-Martínez, S.C.; Montero, G.; Gordo, F.J.; Bono, D.; Gil, L. Mediterranean Stone Pine: Botany and Horticulture. Hortic. Rev. 2012, 39, 153–201. [Google Scholar]
- Gapon, D.A. First Records of the Western Conifer Seed Bug Leptoglossus Occidentalis Heid. (Heteroptera, Coreidae) from Russia and Ukraine, Regularities in Its Distribution and Possibilities of Its Range Expansion in the Palaearctic Region. Entmol. Rev. 2013, 93, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, B.; Crespin, L.; Loiseau, A.; Lombaert, E.; Magro, A.; Estoup, A. Can Things Get Worse When an Invasive Species Hybridizes? The Harlequin Ladybird Harmonia Axyridis in France as a Case Study: Postinvasion Hybridization in Harmonia Axyridis. Evol. Appl. 2011, 4, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Origin | Region | Latitude | Longitude | Year of Collection | Host | mtDNA | Microsatellites | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Haplotype | Hd | π | N | He | Ho | AR | PAR | ||||||
| Eastern America | Montreal, Canada | 45.562 | −73.563 | 2011 | 5 | H20 (1); H51 (3); H27 (1) | 0.700 | 0.004 | 14 | 0.540 | 0.519 | 2.88 | 0.636 | |
| Pittston, USA | 44.222 | −69.756 | 2011 | 7 | H20 (5); H51 (2) | 0.536 | 0.002 | 25 | 0.568 | 0.524 | 2.88 | 0.909 | ||
| Europe | Yvoy-le-Marron, France | 47.632 | 1.854 | 2012 | 5 | H5(2); H20 (1); H51 (2) | 0.800 | 0.003 | 31 | 0.623 | 0.508 | 2.96 | 0.091 | |
| Lavercantière, France | 44.637 | 1.318 | 2011 | 7 | H5(2); H23 (1); H51 (4) | 0.667 | 0.003 | 30 | 0.606 | 0.547 | 2.91 | 0.182 | ||
| Serre-Ponçon, France | 44.523 | 6.332 | 2011 | 5 | H20 (2); H51 (3) | 0.600 | 0.003 | 29 | 0.571 | 0.468 | 2.89 | 0.000 | ||
| Alessandria, Italy | 44.897 | 8.406 | 2011 | 5 | H20 (3); H23 (2) | 0.600 | 0.003 | 26 | 0.603 | 0.531 | 2.91 | 0.182 | ||
| Iberian Peninsula | Barcelona, Spain * | 41.520 | 1.687 | 2012 | 5 | H23 (1); H51 (4) | 0.400 | 0.002 | 20 | 0.491 | 0.486 | 2.48 | 0.091 | |
| Valencia, Spain * | 39.447 | −0.463 | 2012 | 6 | H20 (4); H51 (2) | 0.533 | 0.002 | 20 | 0.487 | 0.385 | 2.51 | 0.000 | ||
| Almeria, Spain | 37.712 | −2.172 | 2012 | 8 | H20 (8) | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0.386 | 0.392 | 2.08 | 0.000 | ||
| Burgos, Spain | 42.672 | −3.417 | 2015 | P. pinaster | 3 | H20 (1); H51 (2) | 0.667 | 0.003 | 25 | 0.576 | 0.475 | 2.88 | 0000 | |
| Galicia, Spain | 42.364 | −8.622 | 2015 | P. pinaster | 4 | H5 (1); H23 (1); H51 (2) | 0.833 | 0.004 | 30 | 0.607 | 0.528 | 2.96 | 0.000 | |
| Lleida, Spain | 42.637 | 1.247 | 2013 | 5 | H20 (2); H23 (1); H51 (2) | 0.800 | 0.003 | 20 | 0.603 | 0.468 | 2.97 | 0.000 | ||
| Salamanca, Spain | 40.451 | −6.19 | 2015 | P. pinea | 2 | H5 (1); H20 (1) | 1.000 | 0.003 | ||||||
| Segovia, Spain | 40.902 | −4.007 | 2012 | 11 | H5 (2); H20 (6); H51 (3) | 0.733 | 0.003 | 14 | 0.564 | 0.410 | 2.84 | 0.000 | ||
| Soria, Spain | 41.536 | 0.023 | 2013 | 3 | H20 (2); H51 (1) | 0.667 | 0.003 | 12 | 0.564 | 0.410 | 2.55 | 0.182 | ||
| Valladolid, Spain | 41.304 | −5.233 | 2015 | P. pinea | 6 | H20 (5); H23 (1) | 0.333 | 0.001 | 14 | 0.555 | 0.413 | 2.77 | 0.000 | |
| Murcia, Spain | 37.826 | −1.016 | 2013 | 3 | H20 (3) | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| Islas Cies, Spain | 42.227 | −8.905 | 2012 | 2 | H20 (2) | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| Huelva, Spain | 37.211 | −6.563 | 2012 | P. pinea | 1 | H20 (1) | - | - | ||||||
| Aveiro, Portugal | 40.674 | −8.727 | 2015 | P. pinaster | 3 | H20 (2); H51 (1) | 0.667 | 0.003 | 23 | 0.596 | 0.437 | 2.96 | 0.000 | |
| Coruche, Portugal | 38.961 | −8.527 | 2015 | P. pinea | 5 + 3 | H5 (1); H20 (3 + 2); H51 (1 + 1) | 0.700 | 0.003 | 27 | 0.615 | 0.506 | 3.02 | 0.182 | |
| Faro, Portugal | 37.236 | −7.922 | 2015 | P. pinaster | 4 | H51 (4) | 0 | 0 | 4+ | - | - | - | - | |
| E. America | Italy | France | Spain | Portugal | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Populations | Montreal | Pittston | Alessandria | Yvoy-le-Marron | Laverc. | Serre-Ponçon | Barcelona | Lleida | Soria | Valencia | Almeria | Burgos | Valladolid | Segovia | Galicia | Aveiro |
| Montreal | - | |||||||||||||||
| Pittston | 0.039 | - | ||||||||||||||
| Alessandria | 0.072 | 0.034 | - | |||||||||||||
| Yvoy-le-Marron | 0.076 | 0.035 | 0.040 | - | ||||||||||||
| Lavercantière | 0.079 | 0.030 | 0.034 | 0.004 | - | |||||||||||
| Serre-Ponçon | 0.073 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.014 | 0.018 | - | ||||||||||
| Barcelona | 0.089 | 0.061 | 0.100 | 0.104 | 0.086 | 0.070 | - | |||||||||
| Lleida | 0.130 | 0.050 | 0.072 | 0.029 | 0.044 | 0.039 | 0.081 | - | ||||||||
| Soria | 0.155 | 0.076 | 0.109 | 0.076 | 0.104 | 0.063 | 0.151 | 0.066 | - | |||||||
| Valencia | 0.128 | 0.035 | 0.075 | 0.090 | 0.094 | 0.091 | 0.141 | 0.096 | 0.090 | - | ||||||
| Almeria | 0.273 | 0.164 | 0.203 | 0.178 | 0.205 | 0.180 | 0.254 | 0.147 | 0.070 | 0.149 | - | |||||
| Burgos | 0.111 | 0.038 | 0.057 | 0.020 | 0.035 | 0.032 | 0.112 | 0.022 | 0.059 | 0.046 | 0.130 | - | ||||
| Valladolid | 0.167 | 0.100 | 0.112 | 0.066 | 0.094 | 0.079 | 0.171 | 0.048 | 0.028 | 0.112 | 0.091 | 0.043 | - | |||
| Segovia | 0.124 | 0.042 | 0.085 | 0.033 | 0.050 | 0.037 | 0.123 | 0.016 | 0.048 | 0.063 | 0.121 | 0.001 | 0.025 | - | ||
| Galicia | 0.120 | 0.041 | 0.061 | 0.019 | 0.030 | 0.024 | 0.113 | 0.020 | 0.052 | 0.068 | 0.135 | 0.005 | 0.044 | 0.011 | - | |
| Aveiro | 0.106 | 0.039 | 0.044 | 0.020 | 0.032 | 0.025 | 0.117 | 0.025 | 0.054 | 0.062 | 0.140 | 0.009 | 0.056 | 0.013 | 0.003 | - |
| Coruche | 0.125 | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.027 | 0.040 | 0.036 | 0.128 | 0.023 | 0.060 | 0.084 | 0.136 | 0.026 | 0.047 | 0.030 | 0.023 | 0.010 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farinha, A.O.; Branco, M.; Courtin, C.; Lesieur, V.; Gallego, D.; Sanchez-Garcia, F.J.; Sousa, E.; Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A.; Bras, A. Another Chapter in the History of the European Invasion by the Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis: The Iberian Peninsula. Diversity 2023, 15, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010064
Farinha AO, Branco M, Courtin C, Lesieur V, Gallego D, Sanchez-Garcia FJ, Sousa E, Roques A, Auger-Rozenberg M-A, Bras A. Another Chapter in the History of the European Invasion by the Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis: The Iberian Peninsula. Diversity. 2023; 15(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarinha, Ana Oliveira, Manuela Branco, Claudine Courtin, Vincent Lesieur, Diego Gallego, Francisco Javier Sanchez-Garcia, Edmundo Sousa, Alain Roques, Marie-Anne Auger-Rozenberg, and Audrey Bras. 2023. "Another Chapter in the History of the European Invasion by the Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis: The Iberian Peninsula" Diversity 15, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010064
APA StyleFarinha, A. O., Branco, M., Courtin, C., Lesieur, V., Gallego, D., Sanchez-Garcia, F. J., Sousa, E., Roques, A., Auger-Rozenberg, M.-A., & Bras, A. (2023). Another Chapter in the History of the European Invasion by the Western Conifer Seed Bug, Leptoglossus occidentalis: The Iberian Peninsula. Diversity, 15(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15010064







