What Insight Does the Alien Plant Species Richness in Greece Offer for the Different Invasion Biology Hypotheses?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Greek Plant Biodiversity Data
2.2. Environmental Factors as Drivers of Biodiversity
2.3. Statistical Analysis
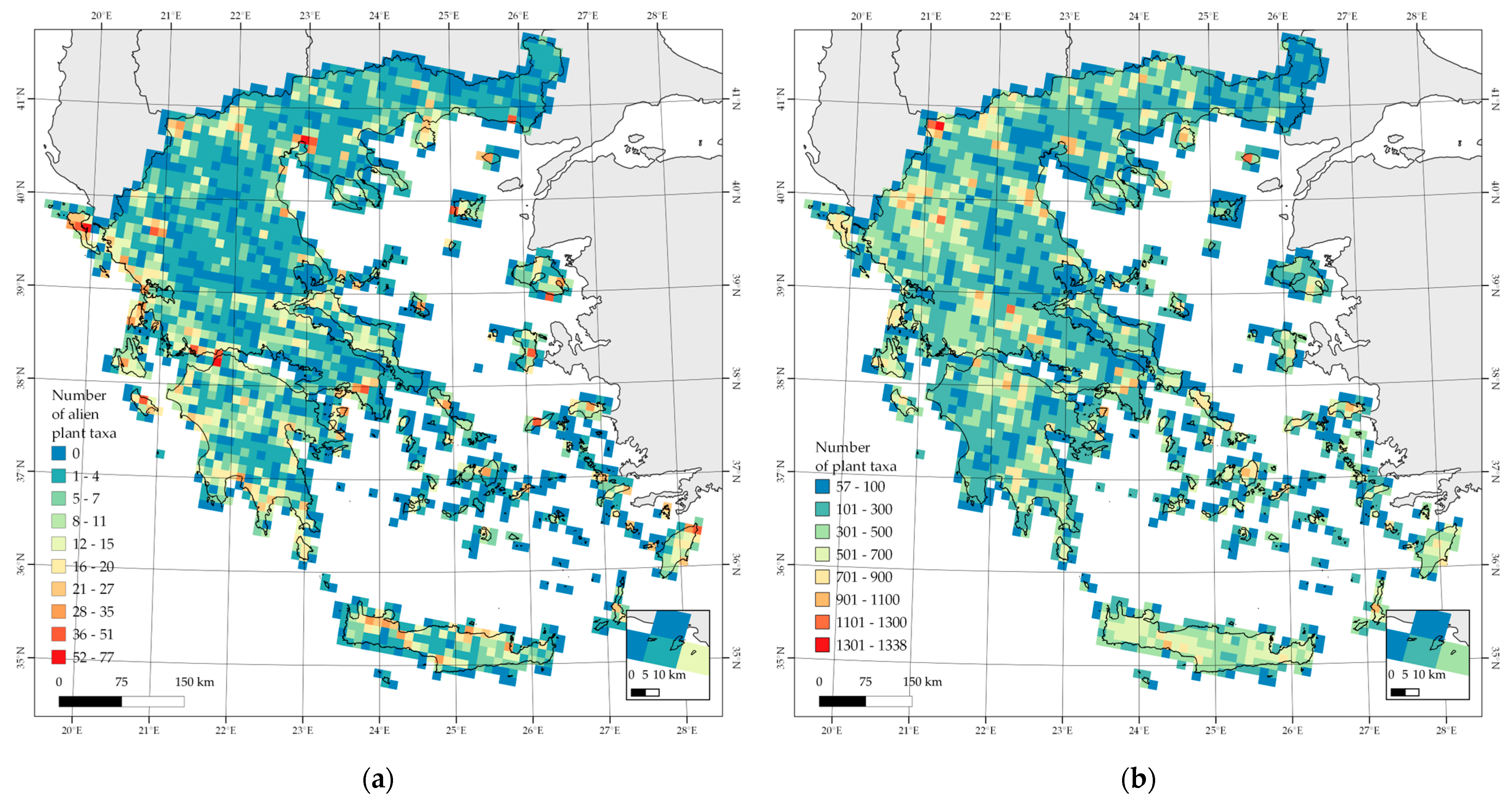
3. Results
3.1. Alien Species Hotspots
3.2. Species Richness Predictors’ Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Inference about the Mechanisms Underlying Alien Species Richness Patterns
4.2. Conservation Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kettunen, M.; Genovesi, P.; Gollasch, S.; Pagad, S.; Starfinger, U.; ten Brink, P.; Shine, C. Technical Support to EU Strategy on Invasive Species (IAS)—Assessment of the Impacts of IAS in Europe and the EU (Final Module Report for the European Commission); Institute for European Environmental Policy (IEEP): London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Catford, J.A.; Jansson, R.; Nilsson, C. Reducing Redundancy in Invasion Ecology by Integrating Hypotheses into a Single Theoretical Framework. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, M.; Havemann, F.; Ruland, F.; Bernard-Verdier, M.; Catford, J.A.; Gómez-Aparicio, L.; Haider, S.; Heger, T.; Kueffer, C.; Kühn, I.; et al. A Conceptual Map of Invasion Biology: Integrating Hypotheses into a Consensus Network. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjarnason, A.; Katsanevakis, S.; Galanidis, A.; Vogiatzakis, I.N.; Moustakas, A. Evaluating hypotheses of plant species invasions on Mediterranean islands: Inverse patterns between alien and endemic species. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, C.M.; García-Berthou, E.; Ganassin, M.J.M.; Agostinho, A.A.; Gomes, L.C. Alien Fish in Neotropical Reservoirs: Assessing Multiple Hypotheses in Invasion Biology. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, E.H.; Banin, L.F.; Fleiss, S.; Hill, J.K.; Hughes, M.; Jelling, A.; Yeong, K.L.; Ola, B.B.; Sailim, A.B.; Tangah, J.; et al. Land-Use Change and Propagule Pressure Promote Plant Invasions in Tropical Rainforest Remnants. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarska, I.; Ehrman, J.M. High Colonization and Propagule Pressure by Ship Ballast as a Vector for the Diatom Genus Pseudo-Nitzschia. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2015, 6, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malavasi, M.; Carboni, M.; Cutini, M.; Carranza, M.L.; Acosta, A.T.R. Landscape Fragmentation, Land-Use Legacy and Propagule Pressure Promote Plant Invasion on Coastal Dunes: A Patch-Based Approach. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarina, M.; Tsianou, M.A.; Boutsis, G.; Andrikou-Charitidou, A.; Karadimou, E.; Kallimanis, A.S. Urbanization and Human Population Favor Species Richness of Alien Birds. Diversity 2020, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Tingley, R.; Kraus, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y. Congener Diversity, Topographic Heterogeneity and Human-Assisted Dispersal Predict Spread Rates of Alien Herpetofauna at a Global Scale. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Padalia, H.; Nandy, S.; Singh, H.; Khaiter, P.; Kalra, N. Does Spatial Heterogeneity of Landscape Explain the Process of Plant Invasion? A Case Study of Hyptis suaveolens from Indian Western Himalaya. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohlgren, T.J.; Binkley, D.; Chong, G.W.; Kalkhan, M.A.; Schell, L.D.; Bull, K.A.; Otsuki, Y.; Newman, G.; Bashkin, M.; Yowhan, S. Exotic Plant Species Invade Hot Spots of Native Plant Diversity. Ecol. Monogr. 1999, 69, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridley, J.D.; Stachowicz, J.J.; Naeem, S.; Sax, D.F.; Seabloom, E.W.; Smith, M.D.; Stohlgren, T.J.; Tilman, D.; von Holle, B. The Invasion Paradox: Reconciling Pattern and Process in Species Invasions. Ecology 2007, 88, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, S.C.; Crandall, R.M.; Pokoski, T.; Stein, C.; Knight, T.M. Phylogenetic and Functional Distinctiveness Explain Alien Plant Population Responses to Competition: Phylogeny and Traits Explain Dominance. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Ledezma, J.N.; Villalobos, F.; Reich, P.B.; Catford, J.A.; Larkin, D.J.; Cavender-Bares, J. Testing Darwin’s Naturalization Conundrum Based on Taxonomic, Phylogenetic, and Functional Dimensions of Vascular Plants. Ecol. Monogr. 2020, 90, e01420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikou-Charitidou, A.; Boutsis, G.; Karadimou, E.; Kallimanis, A.S. Untangling the Positive Association of Phylogenetic, Functional, and Taxonomic Diversity with Alien Bird Species Richness. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikou-Charitidou, A.; Kallimanis, A. The Different Facets of Native Bird Diversity (Taxonomic, Functional and Phylogenetic) as Predictors of Alien Birds Increasing Richness and Expanding Range in Great Britain. Acta Oecol. 2021, 112, 103750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeler, R.A.; Mittermeler, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity Hotspots for Conservation Priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D. Plant Evolution in the Mediterranean; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, R.H.; di Castri, F. Biogeography of Mediterranean Invasions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Basnou, C.; Pyšek, P.; Josefsson, M.; Genovesi, P.; Gollasch, S.; Nentwig, W.; Olenin, S.; Roques, A.; Roy, D.; et al. How Well Do We Understand the Impacts of Alien Species on Ecosystem Services? A Pan-European, Cross-Taxa Assessment. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Wallentinus, I.; Zenetos, A.; Leppäkoski, E.; Çinar, M.E.; Oztürk, B.; Grabowski, M.; Golani, D.; Cardoso, A.C. Impacts of Invasive Alien Marine Species on Ecosystem Services and Biodiversity: A Pan-European Review. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essl, F.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Booy, O.; Brundu, G.; Brunel, S.; Cardoso, A.C.; Eschen, R.; Gallardo, B.; Galil, B.; et al. Crossing Frontiers in Tackling Pathways of Biological Invasions. Bioscience 2015, 65, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, A.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.A.; Blackburn, T.M.; Garnas, J.; Pyšek, P.; Rabitsch, W.; Richardson, D.M.; Wingfield, M.J.; Liebhold, A.M.; Duncan, R.P. Temporal and Interspecific Variation in Rates of Spread for Insect Species Invading Europe during the Last 200 Years. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, Transport and Trouble: Managing Invasive Species Pathways in an Era of Globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kougioumoutzis, K.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Panitsa, M.; Kallimanis, A.; Strid, A.; Dimopoulos, P. Plant Endemism Centres and Biodiversity Hotspots in Greece. Biology 2021, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, P.; Raus, T.; Bergmeier, E.; Constantinidis, T.; Iatrou, G.; Kokkini, S.; Strid, A.; Tzanoudakis, D. Vascular Plants of Greece—An Annotated Checklist. Englera 2013, 31, 1–371. [Google Scholar]
- Dimopoulos, P.; Raus, T.; Bergmeier, E.; Constantinidis, T.; Iatrou, G.; Kokkini, S.; Strid, A.; Tzanoudakis, D. Vascular Plants of Greece: An Annotated Checklist. Supplement. Willdenowia 2016, 46, 301–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, P.; Drakou, E.; Kokkoris, I.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kallimanis, A.; Tsiafouli, M.; Bormpoudakis, D.; Kormas, K.; Arends, J. The need for the implementation of an Ecosystem Services assessment in Greece: Drafting the national agenda. One Ecosyst. 2017, 2, e13714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, P.; Bazos, I.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Zografidis, A.; Karadimou, E.; Kallimanis, A.; Raus, T.; Strid, A. A Guide to the Alien Plants of Greece with Reference to the Natura 2000 Protected Areas Network; NECCA: Athens, Greece, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-Km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, N.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Georgiadis, C.; Kaimaris, D.; Dimopoulos, P.; Mitsopoulos, I.; Mallinis, G. National Scale Land Cover Classification for Ecosystem Services Mapping and Assessment, Using Multitemporal Copernicus EO Data and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohlgren, T.J.; Jarnevich, C.; Chong, G.W.; Evangelista, P.H. Scale and Plant Invasions: A Theory of Biotic Acceptance. Preslia 2006, 78, 405–426. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasetto, F.; Duncan, R.P.; Hulme, P.E. Resolving the Invasion Paradox: Pervasive Scale and Study Dependence in the Native-Alien Species Richness Relationship. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, S.; Tordoni, E.; Amici, V.; Bacaro, G.; Carboni, M.; Filibeck, G.; Scoppola, A.; Bagella, S. Contrasting Patterns of Native and Non-Native Plants in a Network of Protected Areas across Spatial Scales. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2035–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, P.G.; Koukoulas, S.; Galanidis, A.; Delipetrou, P.; Gounaridis, D.; Touloumi, K.; Arianoutsou, M. Factors Shaping Alien Plant Species Richness Spatial Patterns across Natura 2000 Special Areas of Conservation of Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, A.J.; Barasona, J.A.; Guerrero-Casado, J.; Oteros, J.; Tortosa, F.S.; Acevedo, P. An Assessment of Conflict Areas between Alien and Native Species Richness of Terrestrial Vertebrates on a Macro-Ecological Scale in a Mediterranean Hotspot. Anim. Conserv. 2017, 20, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartomeus, I.; Sol, D.; Pino, J.; Vicente, P.; Font, X. Deconstructing the Native-Exotic Richness Relationship in Plants. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.; Bunn, W.A.; Simberloff, D.; Lawton, R.M.; Sanders, N.J. Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Native and Exotic Richness Relationship across Spatial Scales: Favourable Environments for Native Species Are Highly Invasible. Funct. Ecol. 2011, 25, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalusová, V.; Čeplová, N.; Chytrý, M.; Danihelka, J.; Dřevojan, P.; Fajmon, K.; Hájek, O.; Kalníková, V.; Novák, P.; Řehořek, V.; et al. Similar Responses of Native and Alien Floras in European Cities to Climate. J. Biogeogr. 2019, 46, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, L.; Battisti, A.; Bona, E.; Federici, G.; Martini, F.; Pautasso, M.; Hulme, P.E. Alien and Native Plant Life-Forms Respond Differently to Human and Climate Pressures. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essl, F.; Dawson, W.; Kreft, H.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P.; van Kleunen, M.; Weigelt, P.; Mang, T.; Dullinger, S.; Lenzner, B.; et al. Drivers of the Relative Richness of Naturalized and Invasive Plant Species on Earth. AoB Plants 2019, 11, plz051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, E.; Buccheri, M.; Martini, F.; Boscutti, F. Agricultural Land Use Curbs Exotic Invasion but Sustains Native Plant Diversity at Intermediate Levels. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, P.E. Climate change and biological invasions: Evidence, expectations, and response options. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vall-llosera, M.; Llimona, F.; de Cáceres, M.; Sales, S.; Sol, D. Competition, Niche Opportunities and the Successful Invasion of Natural Habitats. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 3535–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, A.; Kowarik, I.; von der Lippe, M. How Traffic Facilitates Population Expansion of Invasive Species along Roads: The Case of Common Ragweed in Germany. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, J.M.; Strayer, D.L. Determinants of Vertebrate Invasion Success in Europe and North America. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panitsa, M.; Iliadou, E.; Kokkoris, I.; Kallimanis, A.; Patelodimou, C.; Strid, A.; Raus, T.; Bergmeier, E.; Dimopoulos, P. Distribution Patterns of Ruderal Plant Diversity in Greece. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 869–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejmánek, M.; Richardson, D.M. What Attributes Make Some Plant Species More Invasive? Ecology 1996, 77, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarina, M.; Sgardelis, S.P.; Michailidou, D.-E.; Tsianou, M.; Andrikou-Charitidou, A.; Touloumis, K.; Kallimanis, A.S. Replacement drives native β-diversity of British avifauna, while richness differences shape alien β-diversity. Divers. Distrib. 2023, 29, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlos, I.S. Responses of Invasive Silverleaf Nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium) Populations to Varying Soil Water Availability. Phytoparasitica 2013, 41, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmira, N.; Douira, A.; Bouhache, M. Ecological Grouping of Solanum elaeagnifolium: A Principal Weed in the Irrigated Tadla Plain (Central Morocco). Weed Res. 1998, 38, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigas, N.; Tsiafouli, M.A.; Katsoulis, G.; Votsi, N.E.; van Kleunen, M. Investigating the invasion pattern of the alien plant Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav. (silverleaf nightshade): Environmental and human-induced drivers. Plants 2021, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkoris, I.P.; Mallinis, G.; Bekri, E.S.; Vlami, V.; Zogaris, S.; Chrysafis, I.; Mitsopoulos, I.; Dimopoulos, P. National set of MAES indicators in Greece: Ecosystem services and management implications. Forests 2020, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallecillo, S.; Maes, J.; Teller, A.; Almenar, J.B.; Barredo, J.I.; Trombetti, M.; Malak, A. EU-wide methodology to map and assess ecosystem condition. In Towards a Common Approach Consistent with a Global Statistical Standard; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
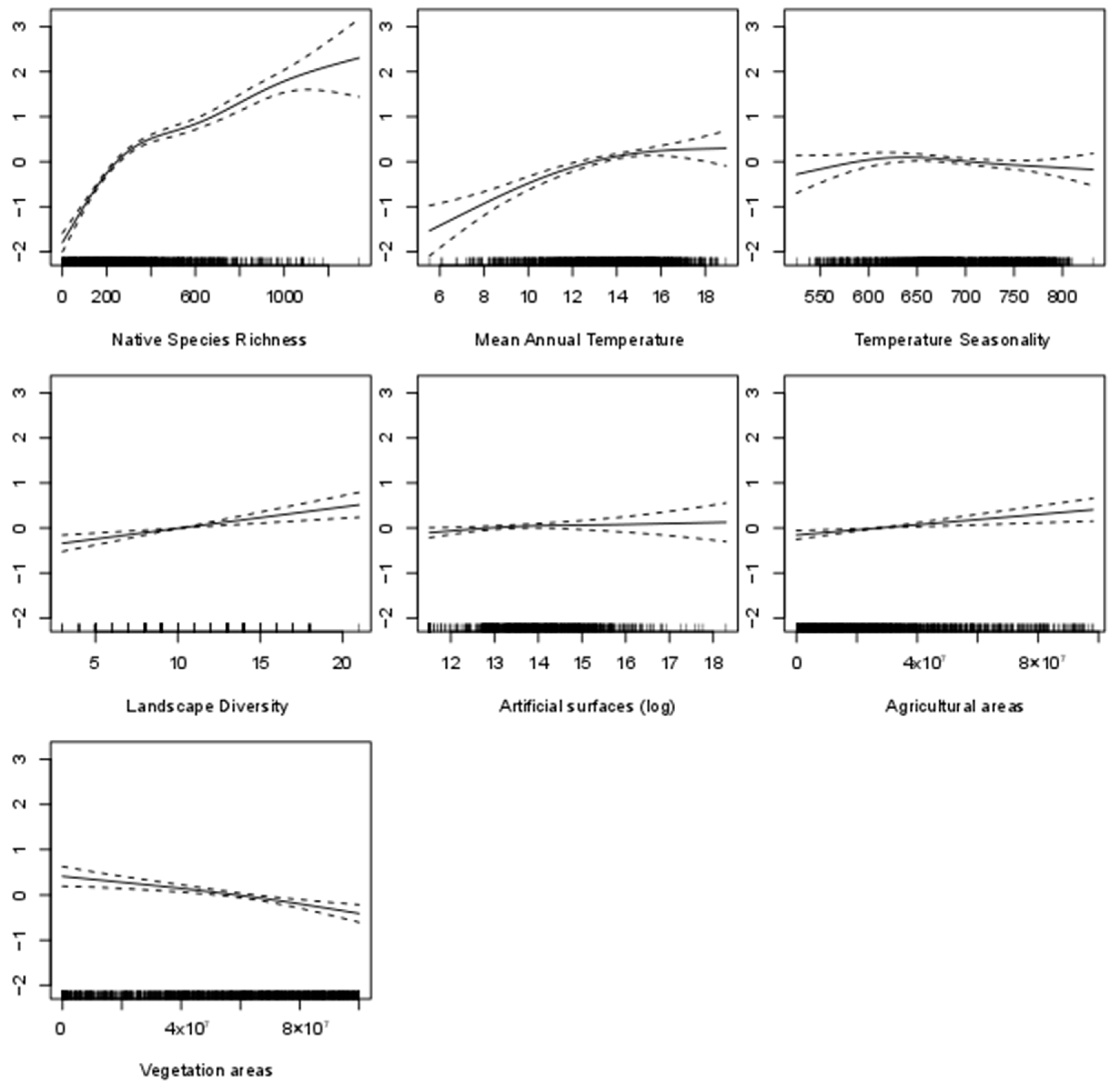
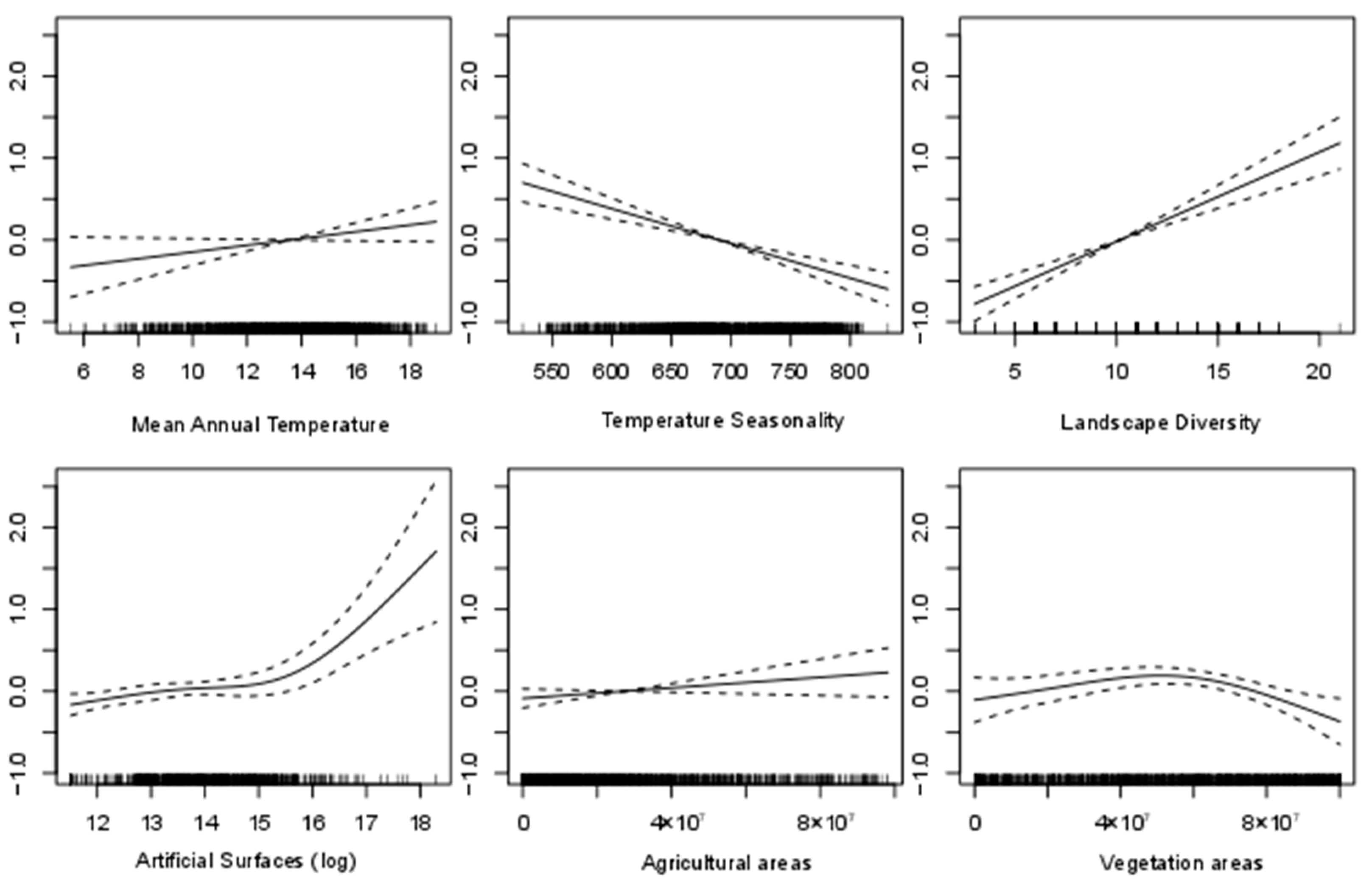
| Predictor | Alien Species Richness R2 as Single Predictor | Native Species Richness R2 as Single Predictor |
|---|---|---|
| Native species richness | 27.9% (p < 0.0001) | |
| Mean annual temperature | 10.9% (p < 0.0001) | 10.3% (p < 0.0001) |
| Temperature seasonality | 8.1% (p < 0.0001) | 13.4% (p < 0.0001) |
| Precipitation seasonality | 9.7% (p < 0.0001) | 7.1% (p < 0.0001) |
| Artificial surfaces area | 11.1% (p < 0.0001) | 3.2% (p < 0.0001) |
| Agricultural area | 8.2% (p < 0.0001) | 3.3% (p < 0.0001) |
| Vegetation area | 8.1% (p < 0.0001) | 9.0% (p < 0.0001) |
| Wetland area | 0.8% (p = 0.0328) | 0.0% (p = 0.3090) |
| Landscape diversity | 15.1% (p < 0.0001) | 4.1% (p < 0.0001) |
| Landscape fragmentation | 6.6% (p < 0.0001) | 3.2% (p < 0.0001) |
| Transport network | 7.3% (p < 0.0001) | 0.2% (p = 0.1601) |
| Predictors | R2 for Alien Species Richness GAMM Model | R2 for Native Species Richness GAMM Model |
|---|---|---|
| Climatic factors | 15.9% (p < 0.0001) | 25.0% (p < 0.0001) |
| Landscape factors | 29.9% (p < 0.0001) | 18.0% (p < 0.0001) |
| Combined climatic and landscape factors | 32.2% (p < 0.0001) | 29.3% (p < 0.0001) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kallimanis, A.; Kokkoris, I.P.; Bazos, I.; Raus, T.; Strid, A.; Dimopoulos, P. What Insight Does the Alien Plant Species Richness in Greece Offer for the Different Invasion Biology Hypotheses? Diversity 2023, 15, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101067
Kallimanis A, Kokkoris IP, Bazos I, Raus T, Strid A, Dimopoulos P. What Insight Does the Alien Plant Species Richness in Greece Offer for the Different Invasion Biology Hypotheses? Diversity. 2023; 15(10):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101067
Chicago/Turabian StyleKallimanis, Athanasios, Ioannis P. Kokkoris, Ioannis Bazos, Thomas Raus, Arne Strid, and Panayotis Dimopoulos. 2023. "What Insight Does the Alien Plant Species Richness in Greece Offer for the Different Invasion Biology Hypotheses?" Diversity 15, no. 10: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101067
APA StyleKallimanis, A., Kokkoris, I. P., Bazos, I., Raus, T., Strid, A., & Dimopoulos, P. (2023). What Insight Does the Alien Plant Species Richness in Greece Offer for the Different Invasion Biology Hypotheses? Diversity, 15(10), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15101067









