Factors Regulating Population Stand Structure in Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae), a Masting North American Desert Shrub
Abstract
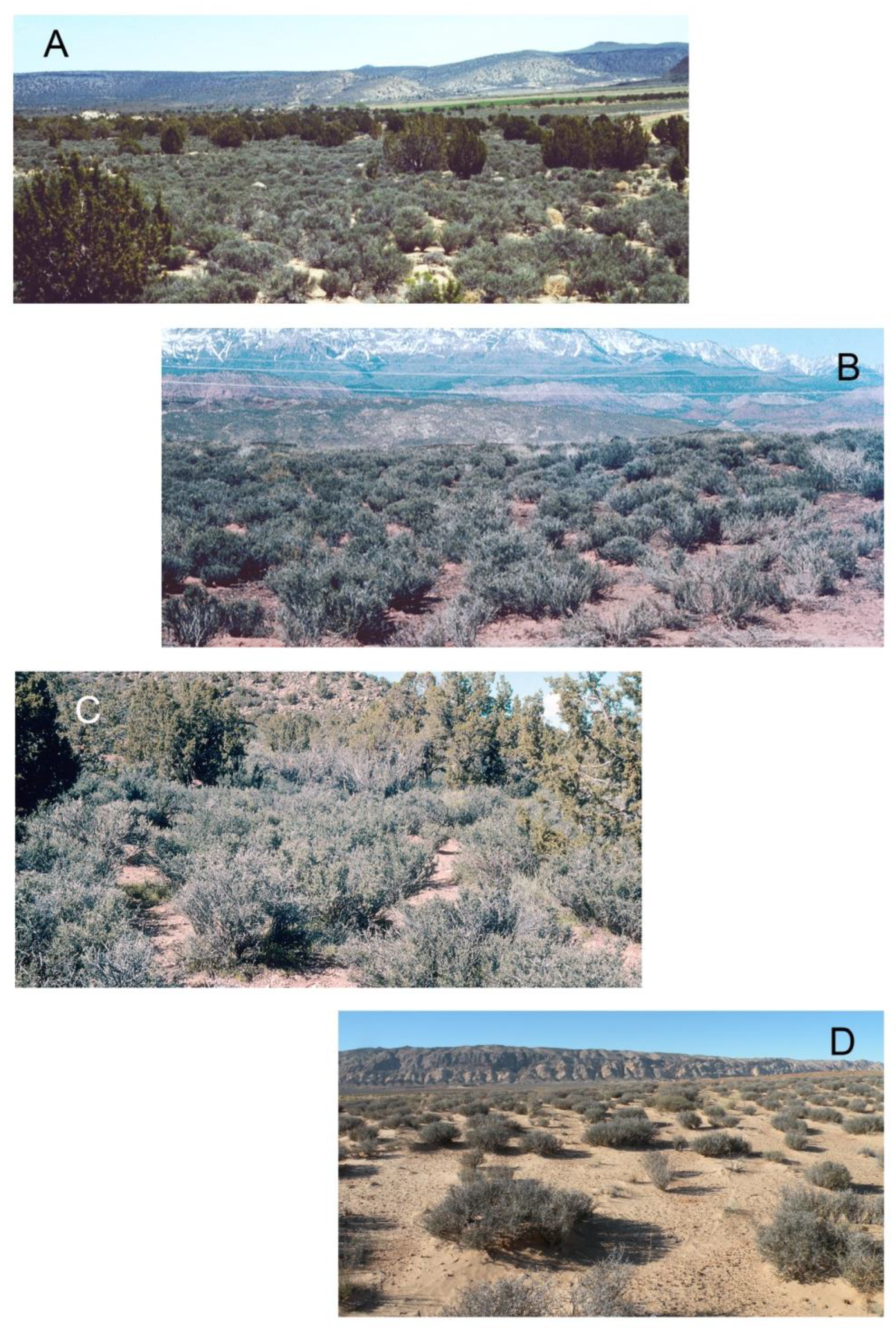
:1. Introduction
| Site Code | Site Name | Latitude | Longitude | Elev (m) | Mean Soil Depth (cm) | Substrate | Mean Annual Precip. (mm) | Mean Jan Min Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring Mtns. NV | ||||||||
| BDI | Blue Diamond Turnoff | 36°01′51.08″ N | 115°23′08.23″ W | 1041 | 26.1 | limestone | 178 | 0.79 |
| RRO | Red Rocks Overlook | 36°06′58.86″ N | 115°26′40.49″ W | 1174 | 16.8 | limestone | 224 | 0.15 |
| LPT | Lower Potosi | 35°59′48.92″ N | 115°28′19.11″ W | 1451 | -- | limestone | 314 | −1.38 |
| PPS | Potosi Pass | 36°00′52.77″ N | 115°29′58.20″ W | 1667 | -- | limestone | 353 | −2.11 |
| Beaver Dam Mtns. UT | ||||||||
| CCL | Castle Cliff ** | 37°04′23.10″ N | 113°52′21.26″ W | 1213 | 39.0 | limestone | 305 | 2.21 |
| WHL | * Winchester Hills ** | 37°13′25.30″ N | 113°37′53.89″ W | 1227 | 48.8 | sandstone/basalt | 312 | −0.21 |
| VYR | * Veyo Road ** | 37°16′24.30″ N | 113°38′37.98″ W | 1423 | 71.0 | shale | 352 | −1.01 |
| BDS | * Beaver Dam Summit ** | 37°06′01.14″ N | 113°49′19.89″ W | 1484 | 23.6 | igneous intrusive | 331 | 1.13 |
| St. George Basin UT | ||||||||
| LGR | * LeGrande | 37°10′33.30″ N | 113°20′18.50″ W | 985 | 74.4 | sand/ basalt | 280 | −1.14 |
| TOQ | * Toquerville Turnoff | 37°16′47.82″ N | 113°18′41.20″ W | 1164 | 44.2 | basalt | 322 | −1.70 |
| BRW | Browse Turnoff ** | 37°21′43.47″ N | 113°15′51.67″ W | 1295 | 21.0 | igneous intrusive | 359 | −3.17 |
| Colorado Plateau UT | ||||||||
| HIT | Hite ** | 37°53′21.59″ N | 110°24′50.96″ W | 1232 | 12.5 | shale | 227 | −4.67 |
| DDT | * Dirty Devil Turnoff ** | 38°09′34.64″ N | 110°37′14.66″ W | 1500 | 30.6 | sandstone | 177 | −8.49 |
| NHK | * North Hanksville ** | 38°47′35.90″ N | 110°26′12.28″ W | 1343 | 74.4 | sandstone | 168 | −9.40 |
| LRK | * Little Rockies | 37°45′35.54″ N | 110°39′06.30″ W | 1700 | 24.0 | igneous intrusive | 230 | −5.96 |
| SLV | Salt Valley (Arches NP) | 38°45′40.65″ N | 109°36′02.04″ W | 1497 | 77.4 | sandstone | 242 | −8.00 |
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Blackbrush Community Composition
3.2. Blackbrush Stand Structure
3.3. Blackbrush Size Structure
3.4. Blackbrush Drought Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. Inferring Stand History from Demographic Information
4.1.1. Veyo Road Study Site
4.1.2. LeGrande Study Site
4.1.3. Toquerville Study Site
4.1.4. North Hanksville Study Site
4.1.5. Little Rockies Study Site
4.2. The Role of Seed Dispersal
4.3. Blackbrush Conservation Issues
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stebbins, G.L.; Major, J. Endemism and speciation in the California flora. Ecol. Monogr. 1965, 35, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.; Meyer, S.E. Paleoclimate effects and geographic barriers shape regional population genetic structure of blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae). Botany 2012, 90, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B.; Kitchen, S.G.; Pendleton, R.L.; Pendleton, B.K.; Germino, M.J.; Rehfeldt, G.E.; Meyer, S.E. Adaptive responses reveal contemporary and future ecotypes in a desert shrub. Ecol. App. 2014, 24, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowns, J.E.; West, N.E. Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima Torr.) on Southwestern Utah Rangelands; Research Report 27; Utah Agricultural Experiment Station, Utah State University: Logan, Utah, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- West, N.E. Colorado Plateau-Mohavian blackbrush semi-desert. In Temperate Deserts and Semi-Deserts; West, N.E., Ed.; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 399–411. [Google Scholar]
- Callison, J.; Brotherson, J.D. Habitat relationships of the blackbrush community (Coleogyne ramosissima) of southwestern Utah. Great Basin Nat. 1985, 45, 321–326. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/41712137 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Webb, R.H.; Steiger, J.W.; Turner, R.M. Dynamics of Mojave Desert shrub assemblages in the Panamint Mountains, California. Ecology 1987, 68, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callison, J.; Brotherson, J.D.; Bowns, J.E. The effects of fire on the blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima) community of southwestern Utah. J. Range Manage. 1985, 38, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.L.; Matchett, J.R. Plant community patterns in unburned and burned blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima) shrublands in the Mojave Desert. W North Am. Nat. 2003, 63, 283–298. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/41717297 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Bowers, J.E.; Webb, R.H.; Pierson, E.A. Succession of desert plants on debris flow terraces, Grand Canyon, Arizona, USA. J. Arid Envirn. 1997, 36, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuliffe, J.R. Markovian dynamics of simple and complex desert plant communities. Am. Nat. 1988, 31, 459–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, M.L. Slow-motion population dynamics in Mojave Desert perennial plants. J. Veg. Sci. 2000, 11, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, T.L. Germination and survival of perennial plant species in the Mojave Desert. Southwest Nat. 1979, 24, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R. Competition between adult and seedling shrubs of Ambrosia dumosa in the Mojave Desert, Nevada. Great Basin Nat. 1989, 49, 79–84. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/41712482 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- McAuliffe, J.R.; Hamerlynck, E.P.; Eppes, M.C. Landscape dynamics fostering the development and persistence of long-lived creosotebush (Larrea tridentata) clones in the Mojave Desert. J. Arid. Environ. 2007, 69, 96–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.E.; Pendleton, B.K. Factors affecting seed germination and seedling establishment of a long-lived desert shrub (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae). Plant Ecol. 2005, 178, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.E.; Pendleton, B.K. Evolutionary drivers of mast seeding in a long-lived desert shrub. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.E.; Pendleton, B.K. Seedling establishment in a masting desert shrub parallels the pattern for forest trees. Acta Oecologica 2015, 65–66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, S.G.; Meyer, S.E.; Carlson, S.L. Mechanisms for maintenance of dominance in a nonclonal desert shrub. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, J.; Meyer, S.E.; Jenkins, S.H. A mast-seeding desert shrub regulates population dynamics and behavior of its heteromyid dispersers. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2275–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, P.L.; Gardner, R.C. Type I error rate comparisons of post hoc procedures for I j Chi-Square tables. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2000, 60, 735–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderWall, S.B. How plants manipulate the scatter-hoarding behavior of seed-dispersing animals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilcore, D. Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae) natural regeneration following fire in the Great Basin-Mojave Transition Zone. Res. Sq. 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, B.K. Coleogyne ramosissima Torr. In The Woody Plant Seed Manual. Agriculture Handbook 727; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 422–425. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.L.; Esque, T.C.; Duck, T. Creosotebush, blackbrush, and interior chaparral shrublands. In Fire Ecology and Management of the Major Ecosystems of Southern Utah, General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-202; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.L.; Matchett, J.R. Spatial and temporal patterns of wildfires in the Mojave Desert, 1980–2004. J. Arid. Environ. 2006, 67, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, S.R.; Gentilcore, D.M.; Chiquoine, L.P. Resilience and alternative stable states after desert wildfires. Ecol. Monogr. 2021, 91, e01432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.C.; Schwinning, S.; Esque, T.C. Seedling ecology and restoration of blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima) in the Mojave Desert, United States. Restor. Ecol. 2014, 22, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoles-Sciulla, S.J.; DeFalco, L.A.; Esque, T.C. Contrasting long-term survival of two outplanted Mojave Desert perennials for post-fire revegetation. Arid. Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, R.L.; Pendleton, B.K.; Meyer, S.E.; Carlson, S.; Morrison, E. Viability of blackbrush seed (Coleogyne ramosissima Torr. [Rosaceae]) following long-term storage. Nativ. Plants J. 2012, 13, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, R.L.; Pendeton, B.K.; Warren, S.D. Response of blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima) seedlings to inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. In Proceedings of the Shrubland Ecotones, Proceedings RMRS-P-11, Ephraim, UT, 12–14 August 1998; McArthur, E.D., Ostler, K.W., Wambolt, C.L., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 245–251. [Google Scholar]







| Dependent Variable | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Adult Clump Height | 92.47 | <0.0001 |
| Adult Clump Crown Diameter | 17.83 | <0.0001 |
| Adult Clump Crown Volume | 22.25 | <0.0001 |
| Adult Clump Density | 14.69 | <0.0001 |
| Total Clump Crown Cover | 14.39 | <0.0001 |
| Total Clump Density | 47.07 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meyer, S.E. Factors Regulating Population Stand Structure in Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae), a Masting North American Desert Shrub. Diversity 2023, 15, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050619
Meyer SE. Factors Regulating Population Stand Structure in Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae), a Masting North American Desert Shrub. Diversity. 2023; 15(5):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050619
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeyer, Susan E. 2023. "Factors Regulating Population Stand Structure in Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae), a Masting North American Desert Shrub" Diversity 15, no. 5: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050619
APA StyleMeyer, S. E. (2023). Factors Regulating Population Stand Structure in Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima: Rosaceae), a Masting North American Desert Shrub. Diversity, 15(5), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050619





