Environmental Factors Affecting Amphibian Communities in River Basins of the Southern Apennines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
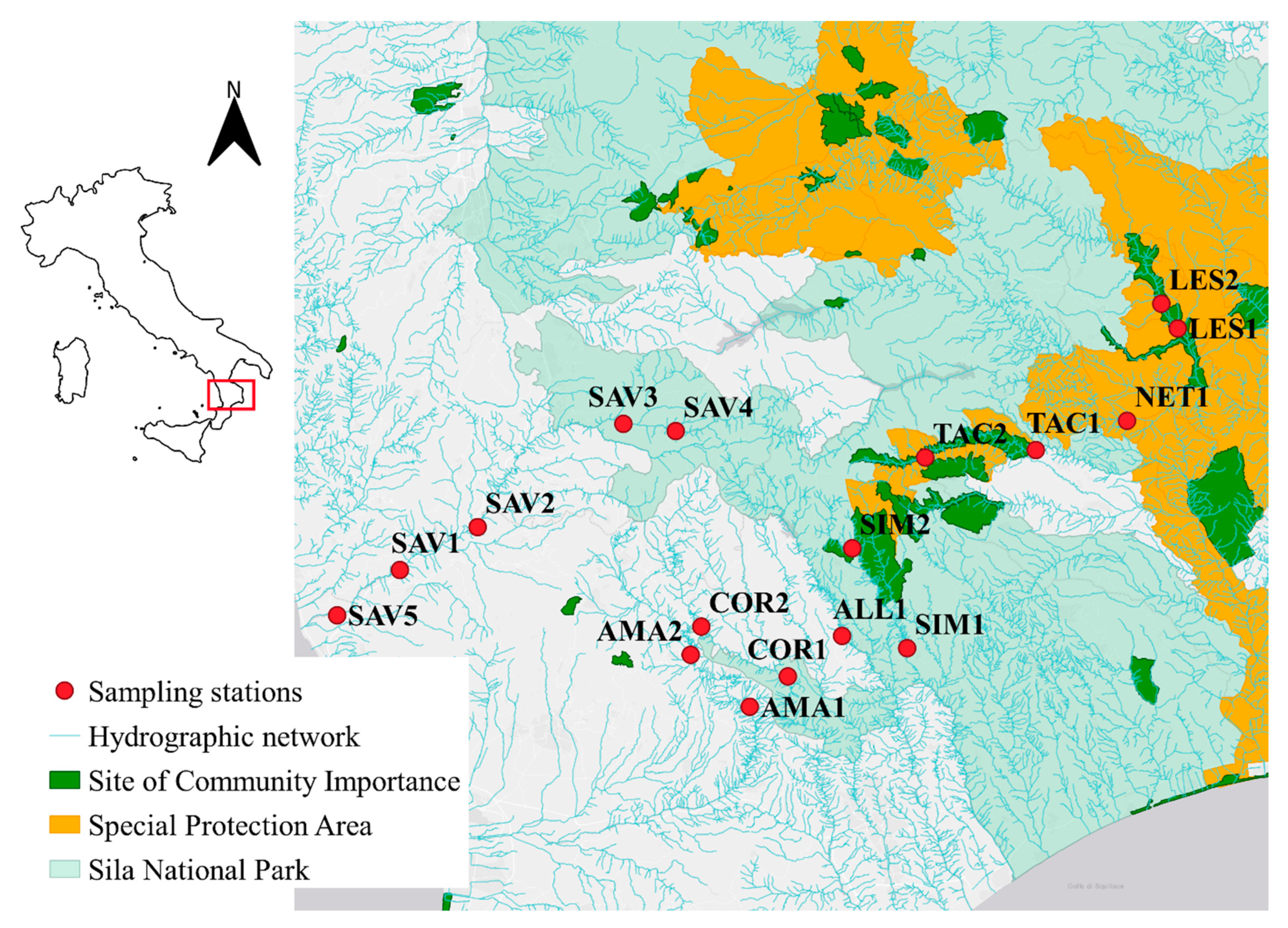
2.1. Field Sampling
2.2. Amphibian Monitoring
2.3. Environmental Features of the Breeding Sites
2.4. Otter and Fish Monitoring
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shiklomanov, L.A. World freshwater resources. In Water in Crisis: A Guide to World’s Freshwater Resources; Gleick, P.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.V.; Tockner, K. Biodiversity: Towards a unifying theme for river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, B.; Rundle, S. Threats to the running water ecosystems of the world. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Powell, G.V.N.; Wikramanayake, E.D. Conservation biology for the biodiversity in crisis. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, R.; Thieme, M.L.; Revenga, C.; Bryer, M.; Kottelat, M.; Bogutskaya, N.; Coad, B.; Mandrak, N.; Balderas, S.C.; Bussing, W.; et al. Freshwater ecoregions of the world: A new map of biogeographic units for freshwater biodiversity conservation. BioScience 2008, 58, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, B. Anfibi e Rettili (Amphibia-Reptilia); CNR: Roma, Italy, 1987; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Manenti, R.; Barzaghi, B.; Nessi, A.; Cioccarelli, S.; Villa, M.; Ficetola, G.F. Not Only Environmental Conditions but Also Human Awareness Matters: A Successful Post-Crayfish Plague Reintroduction of the White-Clawed Crayfish (Austropotamobius pallipes) in Northern Italy. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.J.; Angulo, A.; Lewis, J.P.; Moore, R.D.; Rabb, G.B.; Moreno, J.G. The amphibian extinction crisis—What will it take to put the action into the amphibian conservation action plan? SAPIENS 2012, 5, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Rondinini, C.; Bonardi, A.; Baisero, D.; Padoa-Schioppa, E. Habitat availability for amphibians and extinction threat: A global analysis. Divers. Distrib. 2015, 21, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, D.B.; Vredenburg, V.T. Are we in the midst of the sixth mass extinction? A view from the world of amphibians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11466–11473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reading, C.J. Linking global warming to amphibian declines through its effects on female body condition and survivorship. Oecologia 2007, 151, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, D.B. Climate change implicated in amphibian and lizard declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8201–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, K.R.; Diffendorfer, J.; Mendelson, J.R.; Sears, M.W. Riding the wave: Reconciling the roles of disease and climate change in amphibian declines. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, J.R.; Raffel, T.R.; Romansic, J.M.; McCallum, H.; Hudson, P.J. Evaluating the links between climate, disease spread, and amphibian declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17436–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.C.; Metzger, J.P.; Martensen, A.C.; Ponzoni, F.J.; Hirota, M.M. The Brazilian Atlantic forest: How much is left, and how is the remaining forest distributed? Implications for conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amen, M.; Bombi, P. Global warming and biodiversity: Evidence for climate-linked amphibian declines in Italy. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 3060–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amen, M.; Pietrangeli, B.; Bologna, M.A. Human provoked amphibian decline in central Italy and the efficacy of protected areas. Wildl. Res. 2010, 37, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartel, T.; Schweiger, O.; Ollerer, K.; Cogalniceanu, D.; Arntzen, J.W. Amphibian distribution in a traditionally managed rural landscape of eastern Europe: Probing the effect of landscape composition. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Marziali, L.; Rossaro, B.; De Bernardi, F.; Padoa-Schioppa, E. Landscape–stream interactions and habitat conservation for amphibians. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; De Bernardi, F.; Ficetola, G.F. Pastures vs forests: Do traditional pastoral activities negatively affect biodiversity? The case of amphibian communities. NW J. Zool. 2013, 9, 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- Manenti, R.; Pennati, R. Environmental factors associated with amphibian breeding in streams and springs: Effects of habitat and fish occurrence. Amphibia-Reptilia 2016, 37, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberti, R.; von Hardenberg, A. Impact of introduced fish on common frog (Rana temporaria) close to its altitudinal limit in alpine lakes. Amphibia-Reptilia 2012, 33, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kats, L.B.; Petranka, J.W.; Sih, A. Antipredator defenses and the persistence of amphibian larvae with fishes. Ecology 1988, 69, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holomuzki, J.R. Oviposition sites and fish-deterrent mechanisms of two stream anurans. Copeia 1995, 1995, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecnar, S.J.; M’Closkey, R.T. The effects of predatory fish on amphibian species richness and distribution. Biol. Conserv. 1997, 79, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.L.; Fill, J.M.; Davies, S.J.; Louw, M.; Rebelo, A.D.; Thorp, C.J.; Vimercati, G.; Measey, J. A global meta-analysis of the ecological impacts of alien species on native amphibians. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20182528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayzulin, A.I. Impact Assessment of the Amur Sleeper Perccottus glenii Dybowski, 1877 on Amphibians in Samara Oblast. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 818. [Google Scholar]
- Prigioni, C. La lontra. Una Vita Silenziosa Negli Ambienti Acquatici; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Roper, T.J. Badger; Harper Collins Publishers: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Birks, J. Polecats; Whittet Books Ltd.: Stansted, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jedrzejewska, B.; Sidorovich, V.E.; Pikulik, M.M.; Jedrzejewsky, W. Feeding habits of the otter and the American mink in Bialowieza Primeval Forest (Poland) compared to other Eurasian populations. Ecography 2001, 24, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remonti, L.; Prigioni, C.; Balestrieri, A.; Sgrosso, S.; Priore, G. Trophic flexibility of the otter (Lutra lutra) in southern Italy. Mamm. Biol. 2008, 73, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.; Copp, G.H.; Masson, L.; Miranda, R.; Murai, M.; Sayer, C.D. Changes in the diet of a recovering Eurasian otter population between the 1970s and 2010. Aquat. Conserv. 2012, 22, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri, A.; Remonti, L.; Vezza, P.; Prigioni, C.; Copp, G.H. Do non-native fish as prey favour the conservation of the threatened indigenous Eurasian otter? Freshwater Biol. 2013, 58, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiroldo, G.; Villa, A.; Tremolada, P.; Gariano, P.; Balestrieri, A.; Delfino, M. Amphibians in Eurasian otter Lutra lutra diet: Osteological identification unveils hidden prey richness and male-biased predation on anurans. Mammal. Rev. 2019, 49, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiroldo, G.; Gariano, P.; Balestrieri, A.; Manenti, R.; Pini, E.; Tremolada, P. Predation on amphibians may enhance Eurasian otter recovery in southern Italy. Zool. Sci. 2019, 36, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri, A.; Remonti, L.; Prigioni, C. Toward Extinction and Back: Decline and Recovery of Otter Populations in Italy. In Problematic Wildlife—A Cross-Disciplinary Approach; Angelici, F.M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovacchini, S.; Antonucci, A.; Bartolomei, R.; Bandini, M.; Caldarella, M.; De Castro, G.; De Riso, L.; Di Marzio, M.; Fabrizio, M.; Fulco, E.; et al. Conservation status of Eurasian otter Lutra lutra in Italy. In Proceedings of the Eurasian Otter Workshop, Online, 26–28 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gariano, P.; Balestrieri, A. “Otter, come out!”: Taking away the stone on the southernmost Italian Lutra lutra population. Ecoscience 2018, 25, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.L.; Scott, N.J., Jr. Visual Encounter Surveys. In Measuring and Monitoring Biological Diversity; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, R.K.; Zippel, K. Reproduction and Larval Rearing of Amphibians. ILAR J. 2007, 48, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezza, P.; Zanin, A.; Parasiewicz, P. Manuale Tecnico- Operativo Per la Modellazione e la Valutazione Dell’integrità Dell’habitat Fluviale; ISPRA–Manuali e Linee Guida 154/2017; Maggio: Roma, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reuther, C.; Dolch, D.; Green, R.; Jahrl, J.; Jefferies, D.; Krekemeyer, A.; Kucerova, M.; Madsen, A.B.; Romanowski, J.; Roche, K.; et al. Surveying and Monitoring Distribution and Population Trends of the Eurasian Otter (Lutra lutra). Habitat 2000, 12, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, S.M.; Mason, C.F. The otter Lutra lutra in Southern Italy. Biol. Conserv. 1983, 25, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fièvet, E.; Bonnet-Arnaud, P.; Mallet, J.P. Efficiency and sampling bias of electrofishing for freshwater shrimp and fish in two Caribbean streams, Guadeloupe Island. Fish. Res. 1999, 44, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.M.; Lellis, W.A.; Bennett, R.M.; Johnson, C.S. Landscape determinants of nonindigenous fish invasions. Biol. Invasions 2001, 3, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verneaux, J. Les poisons et la qualité des cour d’eau. Ann. Sci. l’Université Fr.-Comté 1981, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.T.; Thurow, R.F.; Guzevic, J.W. An evaluation of multipass electrofishing for estimating the abundance of stream-dwelling salmonids. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1994, 133, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, D.I. Modeling the probability of resource use: The effect of, and dealing with, detecting a species imperfectly. J. Wildl. Manag. 2006, 70, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rodriguez, C.; Bustamante, J.; Diaz-Paniagua, C.; Guisan, A. Integrating detection probabilities in species distribution models of amphibians breeding in Mediterranean temporary ponds. Diver. Distrib. 2012, 18, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.84). 2017. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, P.; Bates, D. Mixed-Effect Models in S and S-PLUS; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, M.; Maechler, H.J.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility Among Packages for Zero-inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, K. Mu-MIn: Multi-Model Inference. R Package Version 0.12.2/r18. 2009. Available online: http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/mumin/ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: http://www.r-project.org/index.html (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Seyedhashemi, H.; Moatar, F.; Vidal, J.P.; Diamond, J.S.; Beaufort, A.; Chandesris, A.; Valette, L. Thermal signatures identify the influence of dams and ponds on stream temperature at the regional scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenazzi, A.; Kupferberg, S.J. Variation in thermal niche of a declining river-breeding frog: From counter-gradient responses to population distribution patterns. Freshw. Biol. 2017, 62, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, A.R.; Wildy, E.L.; Belden, L.K.; Hatch, A. The influence of abiotic and biotic factors on amphibians in ephemeral ponds with special reference to long-toed salamanders (Ambystoma macrodactylum). Isr. J. Zool. 2001, 47, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, R.C.; Cohen, N.W. A Natural History of Amphibians; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrogio, A.; Mezzadri, S. Girini d’Italia-Tadpoles of Italy; Gravia Edizioni: Piacenza, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, I.; Atatür, M.K. Turkish Herpetofauna; The Republic of Turkey, Ministry of Environment Publications: Ankara, Turkey, 1997.
- Vignoli, L.; D’Amen, M.; Della Rocca, F.; Bologna, M.A.; Luiselli, L. Contrasted influences of moon phases on the reproduction and movement patterns of four amphibian species inhabiting different habitats in central Italy. Amphibia–Reptilia 2014, 35, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, G.J.; Eterovick, P.C.; De Andrade, D.V. Tribute to R.G. Boutilier: Skin colour and body temperature changes in basking Bokermannohyla alvarengai (Bokermann 1956). J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, C.J.; Preziosi, R. Basking behaviour and ultraviolet B radiation exposure in a wild population of Pelophylax lessonae in Northern Italy. Herpetol. Bull. 2013, 124, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, K.M.; Whitaker, B.R. Amphibian Medicine and Captive Husbandry; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Seymour, R.S. Behavioral thermoregulation by juvenile Green Toads, Bufo debilis. Copeia 1972, 1972, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillywhite, H.B.; Licht, P.; Chelgren, P. The role of behavioral thermoregulation in the growth energetics of the toad, Bufo boreas. Ecology 1973, 54, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, K. The Ecology & Behavior of Amphibians; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, B.D. Predator–prey interactions and breeding-pond use of temporary-pond species in a desert anuran community. Ecology 1983, 64, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binckley, C.A.; Resetarits, W.J. Reproductive decisions under threat of predation: Squirrel treefrog (Hyla squirella) responses to banded sunfish (Enneacanthus obesus). Oecologia 2002, 130, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, J.D.; Dorn, N.J. Fish reduce anuran abundance and decrease herpetofaunal species richness in wetlands. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, V.L.; Sperry, J.H. Reproductive Decisions in Anurans: A Review of How Predation and Competition Affects the Deposition of Eggs and Tadpoles. BioScience 2017, 67, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloskowski, J.; Nieoczym, M.; Stryjecki, R. Between-habitat distributions of pond tadpoles and their insect predators in response to fish presence. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasith, A.; Resh, V.H. Streams in Mediterranean climate regions: Abiotic influences and biotic responses to predictable seasonal events. Ann. Rev. Ecol. System. 1999, 30, 51–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.; Kelly, D.; Overton, J.C.; Gillies, C. Predation and other factors currently limiting New Zealand forest birds. N. Z. J. Ecol. 2010, 34, 86–114. [Google Scholar]
- Goldson, S.L.; Bourdôt, G.W.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Byrom, A.E.; Clout, M.N.; McGlone, M.S.; Nelson, W.A.; Popay, A.J.; Suckling, D.M.; Templeton, M.D. New Zealand pest management: Current and future challenges. J. R. Soc. N. Z. 2015, 45, 31–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodé, T.; Holveck, M.J.; Lesbarrères, D.; Pagano, A. Sex-biased predation by polecats influences the mating system of frogs. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, S399–S401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahola, M.; Nordstrom, M.; Banks, P.B.; Laanetu, N.; Korpimaki, E. Alien mink predation induces prolonged declines in archipelago amphibians. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, S.L.; Dill, L.M. Behavioral decisions made under the risk of predation: A review and prospectus. Can. J. Zool. 1990, 68, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, P.; Korpimaki, E.; Banks, P.B.; Nordstrom, M.; Dickman, C.R. Alien predators are more dangerous than native predators to prey populations. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Olmo, J.; López-Martín, J.M.; Palazón, S. The influence of fish abundance on the otter (Lutra lutra) populations in Iberian Mediterranean habitats. J. Zool. 2001, 254, 325e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remonti, L.; Balestrieri, A.; Prigioni, C. Altitudinal gradient of Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) food niche in Mediterranean habitats. Can. J. Zool. 2009, 87, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiroldo, G.; Balestrieri, A.; Remonti, L.; Prigioni, C. Seasonal and habitat-related variaton of otter Lutra lutra diet in a Mediterranean river catchment (Italy). Folia Zool. 2009, 58, 87–97. [Google Scholar]

| Species | Positive Transects (%) | Breeding (%) | Distribution per Habitat (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Courses | Lateral Branches | Pools and Ponds | |||
| Rana italica | 41.4 | 26.4 | 38.8 | 30.6 | 30.6 |
| Rana dalmatina | 8.0 | 8.0 | 14.2 | 42.9 | 42.9 |
| P. kl. esculentus | 12.6 | 1.2 | 9.1 | 27.3 | 63.6 |
| Hyla intermedia | 3.5 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| Bufo bufo | 32.2 | 29.9 | 39.3 | 21.4 | 39.3 |
| Salamandra salamandra | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| Salamandrina terdigitata | 2.3 | 2.3 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Rana italica | Estimate ± (S.E.) | LRT | Pr (>Chi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −19.14 ± (5.66) | ||
| Illuminance | 4.38 ± (1.38) | 18.78 | <0.001 |
| Shrub cover | −4.75 ± (2.62) | 3.12 | 0.077 |
| Slope heterogeneity | 4.05 ± (2.17) | 3.96 | 0.047 |
| Rana dalmatina | Estimate ± (S.E.) | LRT | Pr (>Chi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.60 ± (2.06) | ||
| Water depth | 2.33 ± (1.17) | 5.40 | 0.020 |
| Forest cover | 4.23 ± (3.14) | 3.72 | 0.054 |
| Slope heterogeneity | −4.04 ± (2.49) | 2.66 | 0.103 |
| Watercourse type | 1.19 ± (0.62) | 4.25 | 0.039 |
| Bufo bufo | Estimate ± (S.E.) | LRT | Pr (>Chi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.14 ± (0.60) | ||
| Slope heterogeneity | −2.19 ± (1.40) | 2.50 | 0.114 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nessi, A.; Cioccarelli, S.; Tremolada, P.; Gariano, P.; Grandinetti, M.; Balestrieri, A.; Manenti, R. Environmental Factors Affecting Amphibian Communities in River Basins of the Southern Apennines. Diversity 2023, 15, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050625
Nessi A, Cioccarelli S, Tremolada P, Gariano P, Grandinetti M, Balestrieri A, Manenti R. Environmental Factors Affecting Amphibian Communities in River Basins of the Southern Apennines. Diversity. 2023; 15(5):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050625
Chicago/Turabian StyleNessi, Alessandro, Sara Cioccarelli, Paolo Tremolada, Pasquale Gariano, Maria Grandinetti, Alessandro Balestrieri, and Raoul Manenti. 2023. "Environmental Factors Affecting Amphibian Communities in River Basins of the Southern Apennines" Diversity 15, no. 5: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050625
APA StyleNessi, A., Cioccarelli, S., Tremolada, P., Gariano, P., Grandinetti, M., Balestrieri, A., & Manenti, R. (2023). Environmental Factors Affecting Amphibian Communities in River Basins of the Southern Apennines. Diversity, 15(5), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15050625








