Looking at the Expansion of Three Demersal Lessepsian Fish Immigrants in the Greek Seas: What Can We Get from Spatial Distribution Modeling?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
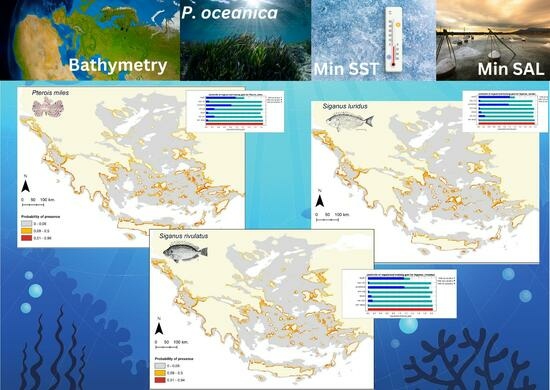
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Golani, D. Impact of Red Sea fish migrants through the Suez Canal on the aquatic environment of the Eastern Mediterranean. Bull. Ser. Yale Sch. For. Environ. Stud. 1998, 103, 375–387. [Google Scholar]
- Edelist, D.; Rilov, G.; Golani, D.; Carlton, J.T.; Spanier, E. Restructuring the Sea: Profound shifts in the world’s most invaded marine ecosystem. Divers. Distrib. 2013, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachle, P.K.; Oikonomou, A.; Pantazi, M.; Stergiou, K.I.; Zenetos, A. Can Biological Traits Serve as Predictors for Fishes’ Introductions, Establishment, and Interactions? The Mediterranean Sea as a Case Study. Biology 2022, 11, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Por, F.D. Lessepsian Migration: The Influx of Red Sea Biota into the Mediterranean by Way of the Suez Canal; Ecological Studies 23; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Galanidi, M.; Zenetos, A. Data-Driven Recommendations for Establishing Threshold Values for the NIS Trend Indicator in the Mediterranean Sea. Diversity 2022, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S.; Danovaro, R.; Rothman, S.B.S.; Gevili, R.; Goren, M. Invasive biota in the deep-sea Mediterranean: An emerging issue in marine conservation and management. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Sioulas, A.; Wennhage, H.; Pihl, L. Diversity, structure and function of fish assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica beds in an area of the eastern Mediterranean Sea and the role of non-indigenous species. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 2338–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öndes, F.; Ünal, V. The dominance of non-indigenous species in the catch composition of small-scale fisheries: A case study from the Kaş–Kekova Special Environmental Protection Area, Türkiye, Eastern Mediterranean. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2023, 53, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Albano, P.G.; Garcia, E.L.; Stern, N.; Tsiamis, K.; Galanidi, M. Established non-indigenous species increased by 40% in 11 years in the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Wallentinus, I.; Zenetos, A.; Leppäkoski, E.; Çinar, M.E.; Oztürk, B.; Grabowski, M.; Golani, D.; Cardoso, A.C. Impacts of invasive alien marine species on ecosystem services and biodiversity: A pan-European review. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.A. An overview of thirty years of research on ballast water as a vector for aquatic invasive species to freshwater and marine environments. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2015, 18, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. East is east and West is west? Management of marine bioinvasions in the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 201, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givan, O.; Parravicini, V.; Kulbicki, M.; Belmaker, J. Trait structure reveals the processes underlying fish establishment in the Mediterranean. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2017, 26, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, I.; Chartosia, N.; Antoniou, C.; Kleitou, P.; Georgiou, A.; Stern, N.; Hadjioannou, L.; Jimenez, C.; Andreou, V.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; et al. They are here to stay: The biology and ecology of lionfish (Pterois miles) in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2020, 97, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulman, A.; Harris, H.E.; Doumpas, N.; Deniz Akbora, H.; Mabruk, A.; Azzurro, E.; Bariche, M.; Çiçek, B.A.; Deidun, A.; Demirel; et al. Low pufferfish and lionfish predation in their native and invaded ranges suggests human control mechanisms may be necessary to control their Mediterranean abundances. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 670413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, A.G.; Campbell, A.H.; Coleman, R.A.; Edgar, G.J.; Jormalainen, V.; Reynolds, P.L.; Sotka, E.E.; Stachowicz, J.J.; Taylor, R.B.; Vanderklift, M.A.; et al. Global patterns in the impact of marine herbivores on benthic primary producers. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Yildirim, D.; Ballesteros, E. Alien marine fishes deplete algal biomass in the eastern Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumi, S. Distribution patterns of the invasive herbivore Siganus luridus (Rüppell, 1829) and its relation to native benthic communities in the central Aegean Sea, Northeastern Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. 2014, 35, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Galanidi, M.; Zenetos, A.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Giovos, I.; Karachle, P.K.; Fournari–Konstantinidou, I.; Kytinou, E.; Issaris, Y.; Azzurro, E.; et al. Updating the occurrences of Pterois miles in the Mediterranean Sea, with considerations on thermal boundaries and future range expansion. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 21, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursanidis, D.; Kougioumoutzis, K.; Minasidis, V.; Chartosia, N.; Kletou, D.; Kalogirou, S. Uncertainty in Marine Species Distribution Modelling: Trying to Locate Invasion Hotspots for Pterois miles in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragičević, B.; Ugarković, P.; Krželj, M.; Zurub, D.; Dulčić, J. New record of Pterois cf. miles (Actinopterygii: Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae) from the eastern middle Adriatic Sea (Croatian waters): Northward expansion. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2021, 51, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P.J. Update on geographic spread of invasive lionfishes (Pterois volitans [Linnaeus, 1758] and P. miles [Bennett, 1828]) in the Western North Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico. Aquat. Invasions 2010, 5 (Suppl. 1), S117–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Stancanelli, B.; Di Martino, V.; Bariche, M. Range expansion of the common lionfish Pterois miles (Bennett, 1828) in the Mediterranean Sea: An unwanted new guest for Italian waters. BioInvasions Rec. 2017, 6, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, I.M.; Smith, N.S. The lionfish Pterois sp. invasion: Has the worst-case scenario come to pass? J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 660–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.C.; Currin, C.A.; Whitfield, P.E. Diet of invasive lionfish on hard bottom reefs of the Southeast USA: Insights from stomach contents and stable isotopes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 432, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini-Foka, M.; Mastis, S.; Kondylatos, G.; Batjakas, I.E. Alien and native fish in gill nets at Rhodes, eastern Mediterranean (2014–2015). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2017, 97, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleitou, P.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Giovos, I.; Kletou, D.; Savva, I.; Cai, L.L.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Charitou, A.; Elia, M.; Katselis, G.; et al. Conflicting interests and growing importance of non-indigenous species in commercial and recreational fisheries of the Mediterranean Sea. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2022, 29, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, B.; Sims, C. Can We Love Invasive Species to Death? Creating Efficient Markets for Invasive Species Harvests. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2023, 85, 443–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parravicini, V.; Azzurro, E.; Kulbicki, M.; Belmaker, J. Niche shift can impair the ability to predict invasion risk in the marine realm: An illustration using Mediterranean fish invaders. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Petitpierre, B.; Broennimann, O.; Daehler, C.; Kueffer, C. Unifying niche shift studies: Insights from biological invasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol. Model. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amen, M.; Azzurro, E. Lessepsian fish invasion in Mediterranean marine protected areas: A risk assessment under climate change scenarios. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 77, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, C. Species distribution modelling of invasive alien species; Pterois miles for current distribution and future suitable habitats. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2020, 6, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amen, M.; Azzurro, E. Integrating univariate niche dynamics in species distribution models: A step forward for marine research on biological invasions. J. Biogeogr. 2020, 47, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Soto, S.; Garofalo, G.; Maynou, F. Fistularia commersonii in the Mediterranean Sea: Invasion history and distribution modeling based on presence-only records. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coro, G.; Vilas, L.G.; Magliozzi, C.; Ellenbroek, A.; Scarponi, P.; Pagano, P. Forecasting the ongoing invasion of Lagocephalus sceleratus in the Mediterranean Sea. Ecol. Model. 2018, 371, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, L.J.; Gallagher, R.V.; Thuiller, W.; Downey, P.O.; Leishman, M.R.; Hughes, L. Different climatic envelopes among invasive populations may lead to underestimations of current and future biological invasions. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursanidis, D.; Kalogirou, S.; Azzurro, E.; Parravicini, V.; Bariche, M.; Zu Dohna, H. Habitat suitability, niche unfilling and the potential spread of Pterois miles in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, C.G.; Tarroso, P.; Brito, J.C. Predicting species distribution at range margins: Testing the effects of study area extent, resolution and threshold selection in the Sahara–Sahel transition zone. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenetos, A.; Arianoutsou, M.; Bazos, I.; Balopoulou, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Dimiza, M.; Drakopoulou, P.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kondylatos, G.; Koutsikos, N.; et al. ELNAIS: A collaborative network on aquatic alien species in Hellas (Greece). Manag. Biol. Invasions 2015, 6, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetta, F.; Agius, D.; Balistreri, P.; Bariche, M.; Bayhan, Y.; Çakir, M.; Ciriaco, S.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Deidun, A.; El Zrelli, R.; et al. New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records (October 2015). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2015, 16, 682–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragicevic, B.; Anadoli, O.; Angel, D.; Benabdi, M.; Bitar, G.; Castriota, L.; Crocetta, F.; Deidun, A.; Dulčić, J.; Edelist, D.; et al. New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records (December 2019). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 636–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thessalou-Legaki, M.; Aydogan, O.; BEKAS, P.; Bilge, G.; Boyaci, Y.O.; Brunelli, E.; Circosta, V.; Crocetta, F.; Durucan, F.; Erdem, M.; et al. New Mediterranean Biodiversity Records (December 2012). Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2012, 13, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritis, M.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Dogrammatzi, A.; Nalmpanti, M.; Bourtzis, T.; Maniati, M.; Karachle, P.K. Data collected from questionnaires to fishers in relation to four non-indigenous species. In Deliverable 2.4 in 4ALIEN: Biology and the Potential Economic Exploitation of Four Alien Species in the Hellenic Seas; MIS 5049511: Athens, Greece, 2021. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, A.; Thuiller, W.; Zimmermann, N.E. Habitat Suitability and Distribution Models: With Applications in R; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello-Lammens, M.E.; Boria, R.A.; Radosavljevic, A.; Vilela, B.; Anderson, R.P. spThin: An R package for spatial thinning of species occurrence records for use in ecological niche models. Ecography 2015, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbicki, M.; Beets, J.; Chabanet, P.; Cure, K.; Darling, E.; Floeter, S.R.; Galzin, R.; Green, A.; Harmelin-Vivien, M.; Hixon, M.; et al. Distributions of Indo-Pacific lionfishes Pterois spp. in their native ranges: Implications for the Atlantic invasion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergés, A.; Tomas, F.; Cebrian, E.; Ballesteros, E.; Kizilkaya, Z.; Dendrinos, P.; Karamanlidis, A.A.; Spiegel, D.; Sala, E. Tropical rabbitfish and the deforestation of a warming temperate sea. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scardi, M.; Martin, C.S.; Valavanis, V.; Fraschetti, S.; Belluscio, A.; Gristina, M.; Salomidi, M.; Punzo, E.; Panayotidis, P.; Giannoulaki, M. Modeling of protected habitats using predictor variables. In Task 1.3 in Mediterranean Sensitive Habitats (MEDISEH); Final Report, DG MARE Specific Contract SI2.600741; Hellenic Centre for Marine Research: Heraklion, Greece, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Dudík, M.; Schapire, R.E.; Blair, M.E. Opening the black box: An open-source release of Maxent. Ecography 2017, 40, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M. Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography 2008, 31, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, S.; Barras, A.G.; Arlettaz, R.; Braunisch, V. SDMtune: An R package to tune and evaluate species distribution models. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 11488–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Kearney, M.; Phillips, S. The art of modelling range-shifting species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Zenetos, A.; Belchior, C.; Cardoso, A.C. Invading European Seas: Assessing pathways of introduction of marine aliens. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 76, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.W.; Purkis, S.J. Are lionfish set for a Mediterranean invasion? Modelling explains why this is unlikely to occur. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, M.E.; Miller, J.M.; Whitfield, P.E.; Hare, J.A. Thermal tolerance and potential distribution of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans/miles complex) on the east coast of the United States. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 283, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, S.; Cucco, A.; Antognarelli, F.; Azzurro, E.; Milazzo, M.; Bariche, M.; Butenschön, M.; Kay, S.; Di Bitetto, M.; Quattrocchi, G.; et al. Predicting future thermal habitat suitability of competing native and invasive fish species: From metabolic scope to oceanographic modelling. Conserv. Physiol. 2015, 3, cou059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiddink, J.G.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Cantrill, J.; Davies, A.J. Keeping pace with climate change: What can we learn from the spread of Lessepsian migrants? Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2161–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriel, T.; Pickholtz, R.; Belmaker, J. Large individual-level variability in diel activity and depth use for the common Lionfish (Pterois miles). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 790930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, K.I. Feeding habits of the Lessepsian migrant Siganus luridus in the eastern Mediterranean, its new environment. J. Fish Biol. 1988, 33, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozvarol, Y.; Ertan, O.O.; Turna, I.I. The grazing effect of Siganus luridus Rüppell, 1828 on Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile, 1813 meadows in Turkish Mediterranean coast (Gazipașa/Antalya). J. Food Agric. Environ. 2011, 9, 531–533. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, D.C.; Monteagudo, P.C.; Schmitter-Soto, J.J.; Wong, R.I.C.; Torres, H.S.; Sansón, E.C.; Rodríguez, A.G.; Osorio, A.F.; Pantoja, L.E.; Guerra, D.C.; et al. Density, size, biomass, and diet of lionfish in Guanahacabibes National Park, western Cuba. Aquat. Biol. 2016, 24, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannaki, K.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Kampouris, T.E.; Batjakas, I.E. First results on the diet of the invasive Pterois miles (Actinopterygii: Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae) in the Hellenic waters. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2019, 49, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabruzzi, T.F.; Bennett, W.A.; Fangue, N.A. Thermal ecology of red lionfish Pterois volitans from southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia, with comparisons to other Scorpaenidae. Aquat. Biol. 2017, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golani, D. Colonization of the Mediterranean by Red Sea fishes via the Suez Canal-Lessepsian migration. Fish Invasions Mediterr. Sea Change Renew. 2010, 145, 188. [Google Scholar]
- George, C.J.; Athanassiou, V. A two year study of the fishes appearing in the seine fishery of St George Bay, Lebanon. Ann. Del Mus. Civ. Di Stor. Nat. Di Genova 1967, 76, 237–294. [Google Scholar]
- Golani, D. Trophic adaptation of Red Sea fishes to the eastern Mediterranean environment—Review and new data. Isr. J. Zool. 1993, 39, 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- Galil, B.S. Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea—Which, when, where, why? Hydrobiologia 2008, 606, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsidi, M.; Moukas, C.; Tzanatos, E. Trait-based life strategies, ecological niches, and niche overlap in the nekton of the data-poor Mediterranean Sea. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 7129–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Fanelli, E.; Mostarda, E.; Catra, M.; Andaloro, F. Resource partitioning among early colonizing Siganus luridus and native herbivorous fish in the Mediterranean: An integrated study based on gut-content analysis and stable isotope signatures. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2007, 87, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariche, M.; Letourneur, Y.; Harmelin-Vivien, M. Temporal fluctuations and settlement patterns of native and Lessepsian herbivorous fishes on the Lebanese coast (eastern Mediterranean). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2004, 70, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magneville, C.; Leréec Le Bricquir, M.L.; Dailianis, T.; Skouradakis, G.; Claverie, T.; Villéger, S. Long-duration remote underwater videos reveal that grazing by fishes is highly variable through time and dominated by non-indigenous species. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouy, C.; Guilhaumon, F.; Leprieur, F.; Lasram, F.B.R.; Somot, S.; Aznar, R.; Velez, L.; Le Loc’h, F.; Mouillot, D. Projected climate change and the changing biogeography of coastal Mediterranean fishes. J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakopoulos, P.; Maravelias, C.D.; Tserpes, G. The alarming decline of Mediterranean fish stocks. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, I.M.; Akins, L.; Underwood, E.; Curtis-Quick, J.; Green, S.J. Setting the record straight on invasive lionfish control: Culling works. PeerJ PrePrints 2014, 2, e398v1. [Google Scholar]
- Ragkousis, M.; Zenetos, A.; Souissi, J.B.; Hoffman, R.; Ghanem, R.; Taşkın, E.; Muresan, M.; Kaprova, E.; Slynko, E.; Dağlı, E.; et al. Unpublished Mediterranean and Black Sea records of marine alien, cryptogenic, and neonative species. BioInvasions Rec. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solanou, M.; Valavanis, V.D.; Karachle, P.K.; Giannoulaki, M. Looking at the Expansion of Three Demersal Lessepsian Fish Immigrants in the Greek Seas: What Can We Get from Spatial Distribution Modeling? Diversity 2023, 15, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060776
Solanou M, Valavanis VD, Karachle PK, Giannoulaki M. Looking at the Expansion of Three Demersal Lessepsian Fish Immigrants in the Greek Seas: What Can We Get from Spatial Distribution Modeling? Diversity. 2023; 15(6):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060776
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolanou, Maria, Vasilis D. Valavanis, Paraskevi K. Karachle, and Marianna Giannoulaki. 2023. "Looking at the Expansion of Three Demersal Lessepsian Fish Immigrants in the Greek Seas: What Can We Get from Spatial Distribution Modeling?" Diversity 15, no. 6: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060776
APA StyleSolanou, M., Valavanis, V. D., Karachle, P. K., & Giannoulaki, M. (2023). Looking at the Expansion of Three Demersal Lessepsian Fish Immigrants in the Greek Seas: What Can We Get from Spatial Distribution Modeling? Diversity, 15(6), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15060776