Genome-Based Classification of Pedobacter albus sp. nov. and Pedobacter flavus sp. nov. Isolated from Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Cultivation
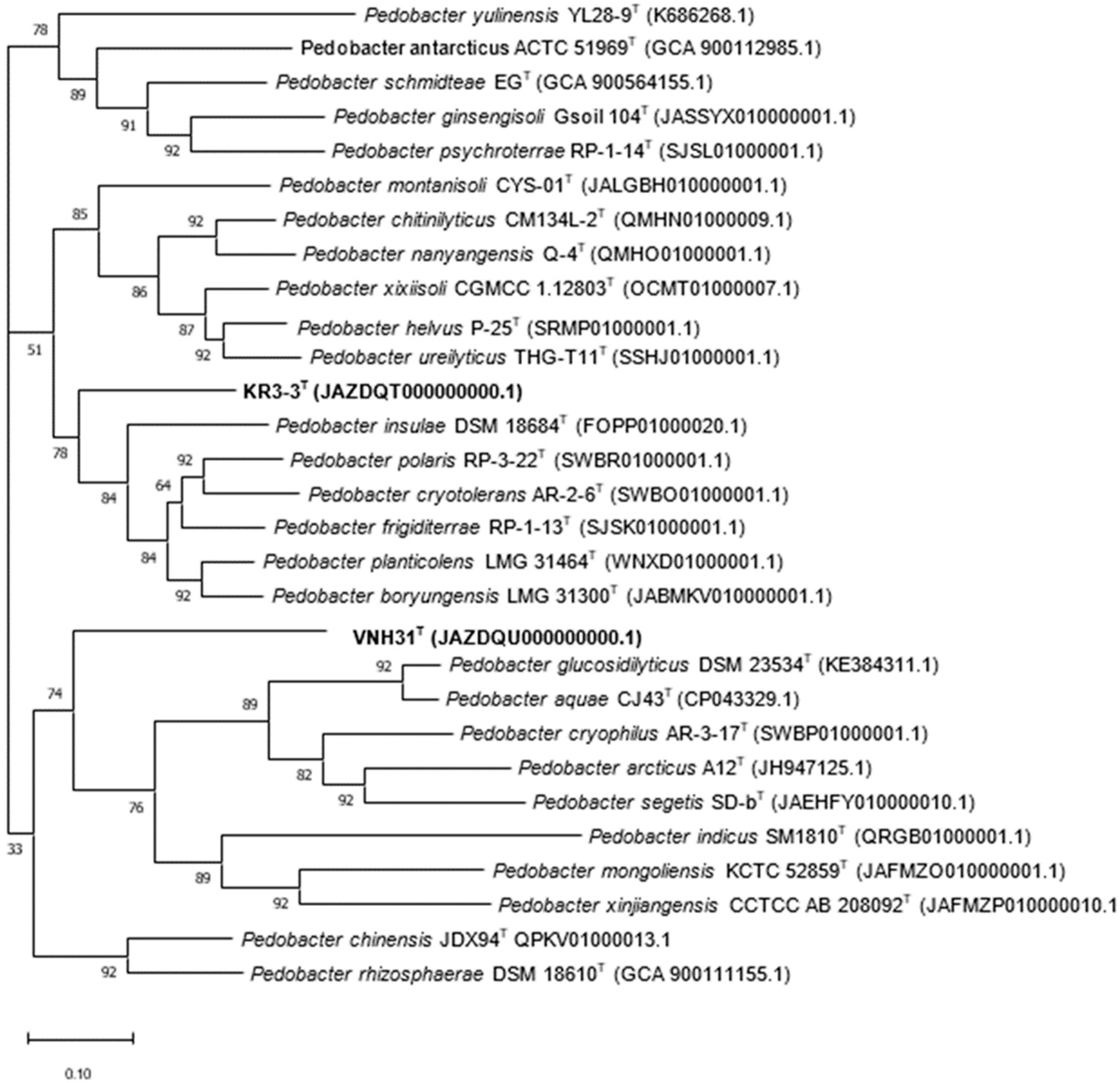
2.2. Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S rRNA
2.3. Genome Sequence Analysis
2.4. Physiology and Chemoaxonomy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Sequencing and Genome Characteristics
3.2. Phenotypic Characteristics
4. Conclusions
4.1. Description of Pedobacter albus sp. nov.
4.2. Description of Pedobacter flavus sp. nov.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parte, A.C. LPSN—List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (bacterio.net), 20 years on. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Shivaji, S. Pedobacter. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, J., Chun, P., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, K.; Cao, M.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Pedobacter mongoliensis sp. nov., isolated from grassland soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.J.; Hong, J. Pedobacter solisilvae sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 4814–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Oh, H.W.; Oh, T.K. Pedobacter insulae sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, L.T.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Cha, C.J. Pedobacter aquae sp. nov., a multi-drug resistant bacterium isolated from fresh water. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2022, 115, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, Y.; Jang, H.J.; Park, M.; Song, J.; Cho, J.C. Pedobacter aquicola sp. nov., isolated from freshwater. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Sheng, M.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; He, J. Pedobacter puniceum sp. nov. isolated from sludge. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 4186–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanparys, B.; Heylen, K.; Lebbe, L.; De Vos, P. Pedobacter caeni sp. nov., a novel species isolated from a nitrifying inoculum. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Švec, P.; Králová, S.; Busse, H.-J.; Kleinhagauer, T.; Kýrová, K.; Pantůček, R.; Mašlaňová, I.; Staňková, E.; Němec, M.; Holochová, P.; et al. Pedobacter psychrophilus sp. nov., isolated from fragmentary rock. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Y.; Li, N.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Song, X.Y. Pedobacter indicus sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Sun, P.; Mao, X.J.; Du, Y.L.; Liu, B.Y.; Sun, J.G. Pedobacter zeae sp. nov., an endophytic bacterium isolated from maize root. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahal, R.H.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Kim, D.U.; Kim, J. Nine novel psychrotolerant species of the genus Pedobacter isolated from Arctic soil with potential antioxidant activities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2537–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Mu, H.; Ren, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, J. Genome-based classification of Pedobacter polysacchareus sp. nov., isolated from Antarctic soil producing exopolysaccharide. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2023, 370, fnad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J.; Garrity, G.M. Proposals to clarify how type strains are deposited and made available to the scientific community for the purpose of systematic research. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically United database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Pevzner, P.A. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Zagnitko, O. The RAST server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 7.0: New and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures, and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W46–W50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.I.; Kim, Y.O.; Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Baek, I.; Chun, J. UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lányi, B. Classical and rapid identification method for medically important bacteria. In Method in Microbiology 19; Cowell, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1987; pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, A.B.; Fulton, M. A simplified method of staining endospores. Science 1933, 77, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautz, H.; Reichenbach, H. A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Micobiol. Lett. 1980, 8, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnikin, D.E.; O’donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasser, M. Identification of Bacteria by Gas Chromatography of Cellular Fatty Acids Technical Note # 101; MIDI Inc.: Newwark, DE, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Christensen, H.; Arahal, D.R.; da Costa, M.S.; Trujillo, M.E. Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colony color on R2A | Yellow | White | White | Light yellow | Yellow | Rose red | Light pink |
| Temperature range for growth (°C) | 15–37 | 10–35 | 15–35 | 10–30 | 4–28 | 4–28 | 4–37 |
| Optimal growth temperature (°C) | 25–30 | 25–30 | 25–30 | 25–28 | 15–20 | 15–20 | 28 |
| pH range for growth | 6.5–9.0 | 6.0–8.5 | 5.5–9.5 | 6.0–10 | 6.0–10.0 | 6.0–10.5 | 6.0–9.0 |
| pH optimum for growth | 8.0–8.5 | 6.5–8.0 | 7.0–7.5 | 6.5–7.5 | 7.0–9.0 | 7.0–9.0 | 7.0 |
| Highest salt tolerance (%, w/v) | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Hydrolysis of | |||||||
| Casein | − | − | + | − | − | − | − |
| Starch | − | − | + | + | − | − | − |
| Aesculin | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Tween 80 | − | + | − | + | − | − | − |
| Enzymatic reaction | |||||||
| Esterase (C4) | + | + | + | − | − | +/− | + |
| Crystine arylamidase | + | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| Trypsin | − | − | + | − | + | − | − |
| Alpha chymotrypsin | + | − | + | + | + | − | − |
| Alpha galactosidase | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| Beta galactosidase | − | + | + | − | − | + | + |
| Beta glucosidase | − | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Alpha fucosidase | − | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| Electron donor or carbon source | |||||||
| L-arabinose | − | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| D-Mannose | − | + | + | + | + | +/− | + |
| D-maltose | − | + | + | + | + | nd | − |
| Potassium gluconate | − | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| L-rhamnose | − | − | − | − | + | + | − |
| N-acetyl-glucosamine | − | + | + | + | + | nd | + |
| Inositol | − | − | − | + | − | nd | − |
| D-saccharose (sucrose) | − | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| D-maltose | − | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Sodium acetate | + | + | + | − | − | − | − |
| L-alanine | − | − | − | + | − | − | |
| Glycogen | − | − | − | + | + | − | − |
| L-serine | + | + | − | + | − | − | − |
| D-glucose | − | + | + | + | + | +/− | + |
| Salicin | − | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| D-melibiose | − | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| L-arabinose | +/− | − | − | + | + | +/− | + |
| 3-hydroxybutyric acid | − | − | +/− | + | − | − | − |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | − | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| L-proline | + | + | + | + | − | + | − |
| DNA G+C content (mol%) | 32.96 | 44.12 | 46.1 | 39.4 | 34.8 | 33.9 | 43.4 |
| Fatty Acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated | |||||
| C10:0 | 0.19 | 0.62 | |||
| C14:0 | 0.88 | 1.21 | 1.3 | 1.02 | 0.94 |
| C16:0 | 2.48 | 3.49 | 2.73 | 3.24 | 1.62 |
| C18:0 | 3.21 | 0.31 | 0.13 | ||
| Unsaturated | |||||
| C14:1 ω5c | 0.14 | ||||
| C15:1 ω6c | 1.11 | 0.55 | 0.83 | ||
| C16:1 ω5c | 0.69 | 1.05 | 0.73 | 2.67 | 2.64 |
| C17:1 ω6c | 0.16 | 0.29 | |||
| C17:1 ω8c | 0.23 | 0.28 | |||
| C18:1 ω5c | 0.90 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.62 | |
| Branched chain | |||||
| iso C11:0 | 1.70 | 0.37 | |||
| iso C13:0 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.4 | |
| iso C14:0 | 0.35 | 0.20 | |||
| iso C15:0 | 28.68 | 27.36 | 27.73 | 26.83 | 22.32 |
| iso C16:0 | 0.92 | 0.43 | 0.19 | 2.22 | 1.68 |
| iso C17:0 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.31 | ||
| iso F C15:1 | 0.46 | ||||
| iso H C16:1 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 1.90 | ||
| anteiso C11:0 | 0.45 | 0.41 | |||
| anteiso C15:0 | 4.08 | 2.29 | 1.13 | 8.59 | 2.65 |
| anteiso C17:0 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.33 | 0.59 | |
| alcohol-C16:1 ω7c | |||||
| anteiso-C17:1 ω9c | 0.72 | 0.78 | 3.89 | ||
| Hydroxy | |||||
| C8:0 3OH | 0.39 | 0.65 | 0.14 | ||
| C14:0 2OH | 0.55 | 0.83 | 0.4 | 0.41 | |
| C15:0 2OH | 0.49 | 0.14 | 1.46 | ||
| C15:0 3OH | 1.11 | ||||
| C16:0 3OH | 0.77 | 3.36 | 3.37 | 1.41 | 0.3 |
| C17:0 2OH | 0.66 | 0.98 | 0.43 | 0.89 | 7.43 |
| C17:0 3OH | 0.15 | ||||
| iso C14:0 3OH | 0.15 | 0.15 | |||
| iso C15:0 3OH | 3.31 | 2.51 | 2.87 | 1.42 | 2.18 |
| iso C16:0 3OH | 1.50 | 1.17 | 0.45 | 2.79 | |
| iso C17:0 3OH | 10.69 | 11.53 | 10.64 | 8.08 | 8.39 |
| Summed features * | |||||
| Summed Feature 1 | 0.85 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.5 | |
| Summed Feature 3 | 18.57 | 27.02 | 36.94 | 28.60 | 27.57 |
| Summed Feature 4 | 1.85 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.72 | |
| Summed Feature 9 | 14.54 | 5.93 | 4.84 | 2.81 | 6.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuyet, N.L.T.; Kim, J. Genome-Based Classification of Pedobacter albus sp. nov. and Pedobacter flavus sp. nov. Isolated from Soil. Diversity 2024, 16, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050292
Tuyet NLT, Kim J. Genome-Based Classification of Pedobacter albus sp. nov. and Pedobacter flavus sp. nov. Isolated from Soil. Diversity. 2024; 16(5):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050292
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuyet, Nhan Le Thi, and Jaisoo Kim. 2024. "Genome-Based Classification of Pedobacter albus sp. nov. and Pedobacter flavus sp. nov. Isolated from Soil" Diversity 16, no. 5: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050292
APA StyleTuyet, N. L. T., & Kim, J. (2024). Genome-Based Classification of Pedobacter albus sp. nov. and Pedobacter flavus sp. nov. Isolated from Soil. Diversity, 16(5), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050292






