Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Diversity: A Case Study for a Macroalgae–Oyster Reef Ecosystem
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
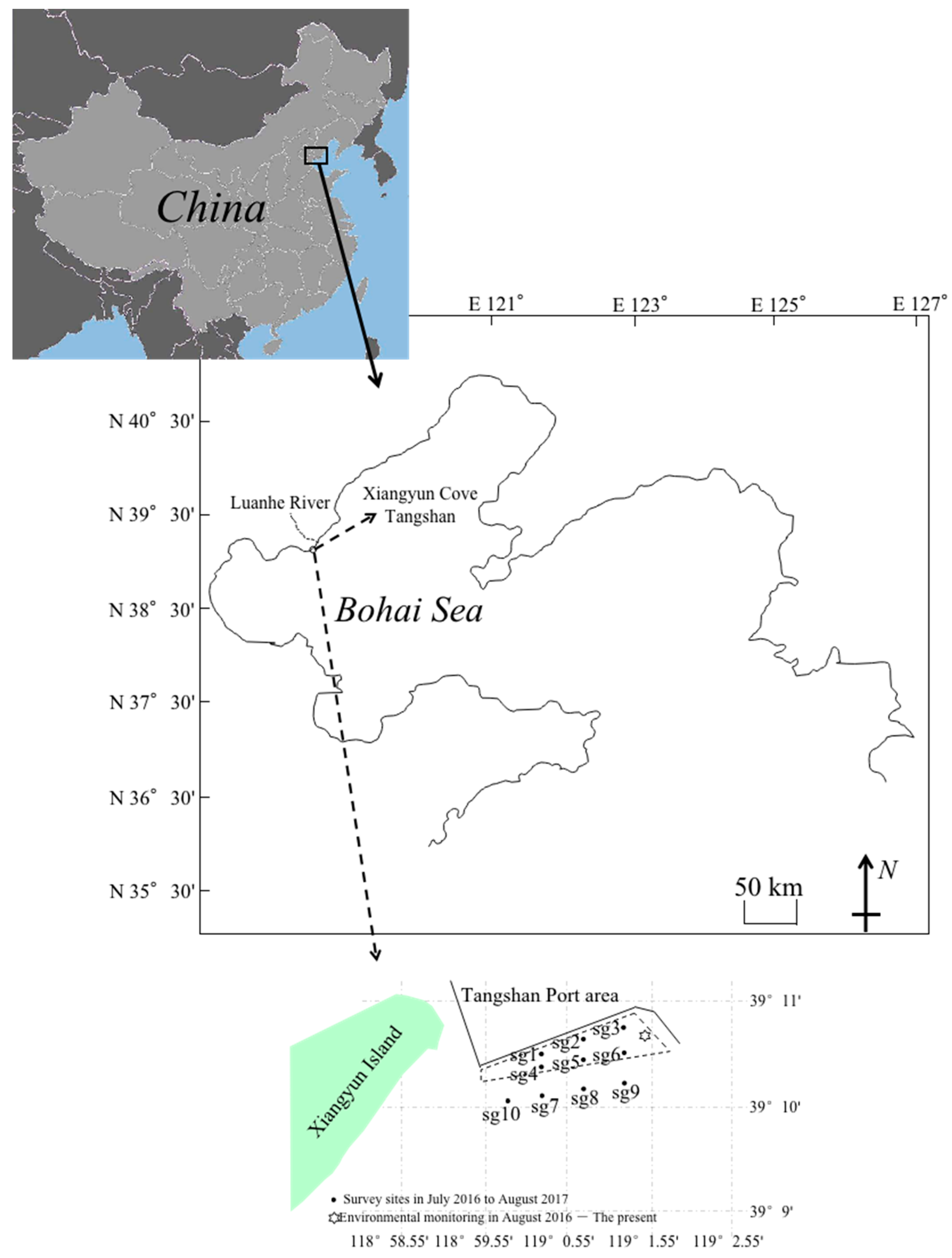
2.2. Study Area and Sampling
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition, Dominant Species, and Abundance
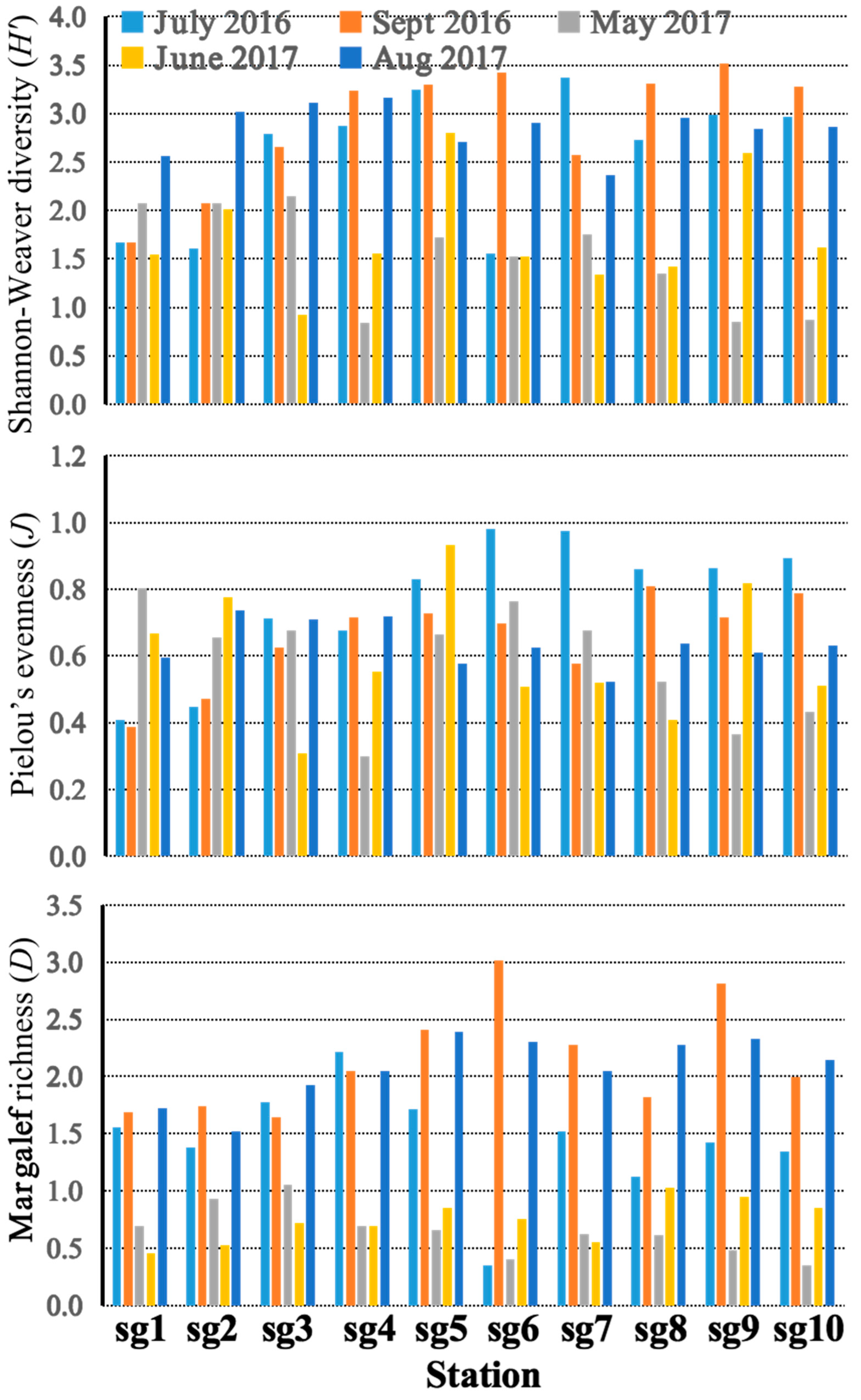
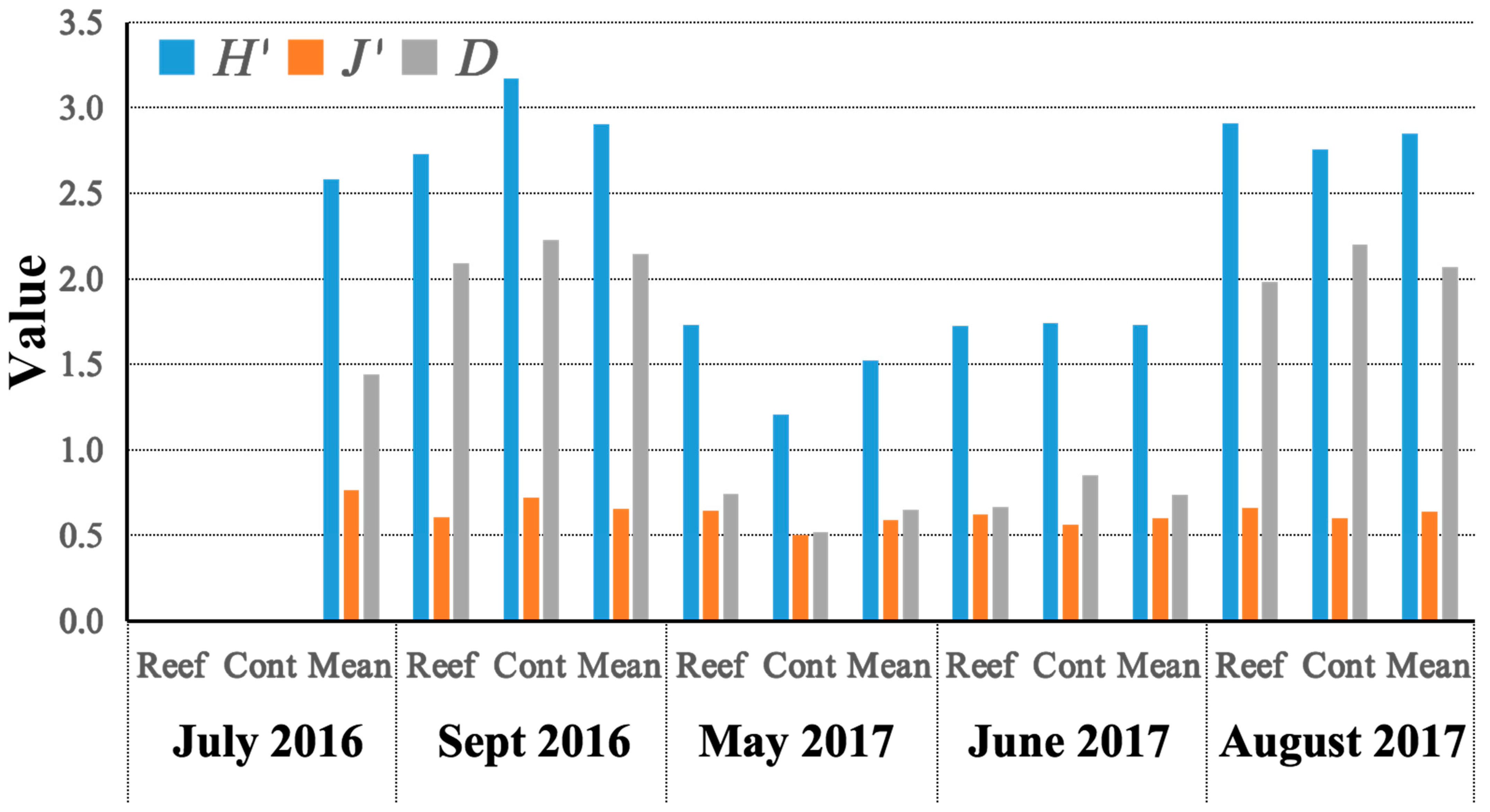
3.2. Diversity, Niche Width, Niche Overlap, and Interspecific Connection
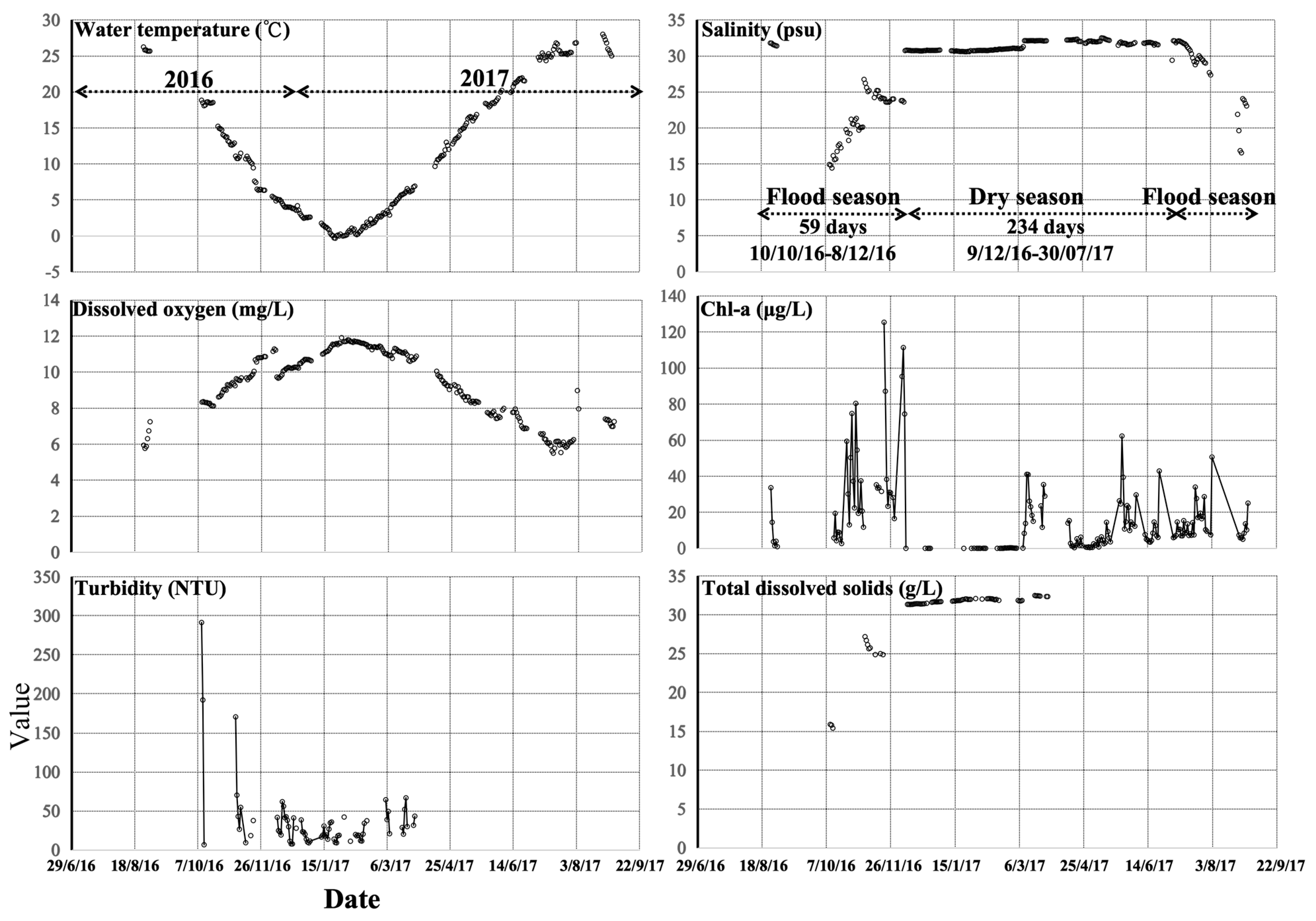
3.3. Temporal Variations in Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, R.J.; Reed, D.C.; Brzezinski, M.A. Partitioning of primary production among giant kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera), understory macroalgae, and phytoplankton on a temperate reef. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, S.T.; Fleeger, J.W.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; Pascal, P.Y. What is the relative importance of phytoplankton and attached macroalgae and epiphytes to food webs on offshore oil platforms? Mar. Coast. Fish. 2013, 5, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthi, M.G.; Prend, C.J.; Aumont, O.; Lévy, M. Annual variations in phytoplankton biomass driven by small-scale physical processes. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E. Effects of Mississippi river water on phytoplankton growth and composition in the upper Barataria Estuary, Louisiana. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1831–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Justic, D.; White, J.R.; Lane, R.; Day, J.; Paerl, H.; Raynie, R. Mississippi River diversions and phytoplankton dynamics in deltaic Gulf of Mexico estuaries: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 221, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, C.A.; Revilla, M.; Glibert, P.M.; Murasko, S. Nutrient quality drives differential phytoplankton community composition on the southwest Florida shelf. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, X.Y.; Song, X.J.; Xu, K.D.; Yang, L.L. Seasonal analysis of artificial oyster reef ecosystems: Implications for sustainable fisheries management. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, Z.L.; Liu, Z.L.; Quan, W.M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.L. Coastal aquaculture farms for the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus provide spawning and first year nursery grounds for wild black rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii: A case study from the Luanhe River estuary, Bohai Bay, the Bohai Sea, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 911399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, H.P.; Xu, K.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Otaki, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Seasonal variations in the diversity and benthic community structure of subtidal artificial oyster reefs adjacent to the Luanhe River Estuary, Bohai Sea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.H.C.d.; Silva-Cunha, M.d.G.G.; Santiago, M.F.; Passavante, J.Z.d.O. Characterization of phytoplankton biodiversity in tropical shipwrecks off the coast of Pernambuco, Brazil. Acta Bot. Bras. 2010, 24, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matisson, J.; Olof, L. Benthic macrofauna succession under mussels, Mytilus edulis L. (Bivalvia), cultured on hanging long-lines. Sarsia 1983, 68, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Zhang, G.T.; Wang, S.W.; Wan, A.Y.; Liu, Q. Distinguishing nutrient-depleting effects of scallop farming from natural variabilities in an offshore sea ranch. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G. Current status and future development suggestions of marine fisheries resources in Hebei Province. Hebei Fish. 1980, 3, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.C.; Zhou, E.M.; Song, W.X. Distribution characteristics of surface temperature, salinity in the mouth of Luanhe River. Adv. Mar. Sci. 1986, 3, 126–133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, L.; Jia, D. Picophytoplankton from Qinhuangdao coastal waters in spring and summer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 42, 106–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luan, Q.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J. Long-term changes on phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea (1959~2015). Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 9–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.T.; Sun, J.; Wei, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.S.; Xin, Y.H.; Guo, Y.; Gu, T. Seasonal shift of a phytoplankton (>5 μm) community in Bohai Sea and the adjacent Yellow Sea. Diversity 2021, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Q.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J. Long-term changes of phytoplankton community and diversity in adjoining waters of the Yellow River estuary (1960–2010). J. Fish. Sci. China 2017, 24, 913–921. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Gong, G.C.; Shiah, F.K. Hypoxia in the East China Sea: One of the largest coastal low-oxygen areas in the world. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lu, Y.Y.; Yang, W.; Song, G.S. Summer hypoxia in Bohai Sea caused by changes in phytoplankton community. Anthr. Coasts 2021, 4, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Zang, J.; Wei, Q.; Guo, J.; Yi, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. Hypoxia and its cause of formation in the adjacent waters of Rushan Bay. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2012, 30, 347–356. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Liu, T.T.; Li, X.J.; Ai, B.H.; Li, B.Q.; Chen, L.L. Characteristics of macrobenthic communities at the Muping marine ranch of Yantai in summer. Mar. Sci. 2017, 41, 134–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.M.; Dong, S.G. Zhongguohaiyuchangjianfuyouguizaotupu (Atlas of Common Plankton Diatoms in China Seas); China Ocean University Press: Qingdao, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Sun, J. Marine Phycology; China Ocean University Press: Qingdao, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.J.; Qian, S.B. Bacillariophyta; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- State Oceanic Administration. Specifications of Oceanographic Survey: GB12763.6-2007[S]; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 34–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton, S.J. Relationships among functional properties of Californian grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communications; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Information theory in ecology. Gen. Syst. 1958, 3, 36–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert, S.H. The measurement of niche overlap and some relatives. Ecology 1978, 59, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Q. Guidelines for Investigation of River Hydrobiology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 172–286. ISBN 978-7-03-039429-3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations; Princeton University Press: Priceton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Pianka, E.R. The structure of lizard communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, K. Ecological Methodology; Harper Collins Publishers: Now York, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 0321021738. [Google Scholar]
- Schluter, D. A variance test for detecting species associations, with some example applications. Ecology 1984, 65, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T. Quantitative Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004; ISBN 9787030309372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, F. Spatial and temporal distribution and factors influencing the phytoplankton community structure in the Bohai Sea. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 10–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.Y.; Zhang, C.X. Data Processing System (DPS) sofware with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q. The Study of Phytoplankton Sinking Rate in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University of Science & Technology, Tianjin, China, 2016; pp. 1–61. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Delesalle, B.; Pichon, M.; Frankignoulle, M.; Gattuso, J. Effects of a cyclone on coral reef phytoplankton biomass, primary production and composition (Moorea island, French polynesia). J. Plankton Res. 1993, 15, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.S.; Allen, D.M. Zooplankton of the Atlantic and Gulf Coasts: A Guide to Their Identification and Ecology; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013; pp. 1–452. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.S.; Huang, H.L. Advances in the study of biodiversity of phytoplankton and red tide species in China (1):Bohai Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2021, 52, 346–395. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Shang, H.X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.S.; Xu, Y. Community Structure and Correlations of Phytoplankton with Environmental factors in Coastal Aquaculture area in Dalian, Liaoning Province, China. Chin. J. Fish. 2023, 36, 60–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, S. Phytoplankton community structure and its seasonal variation in the Bohai Sea in 2021. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2024, 42, 337–348. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Yi, C.L.; Xu, Y.S.; Shi, H.M. The Phytoplankton Community Sampled by Nets in the Dominant Area Monitoring Red Tide in Bohai Bay in Summer, 2006. J. Tianjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 3, 19–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, W.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, K.F. The net-phytoplankton community structure in the Bohai Sea in autumn 2014. Haiyangxuebao 2020, 42, 89–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F. Community characteristics of phytoplankton in artificial reef area around Nanri islands in spring. J. Fish. Res. 2016, 38, 210–218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.D.; Yi, J.; Guo, X.F.; Tang, Y.L.; Huang, L.Y. Phytoplankton community structure in artificial reef area around Lidao, Rongcheng, and its relationship with environmental factors. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2016, 46, 50–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.B.; Chen, Q.Z.; Shou, L.; Ling, Y.B.; Zhu, X.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, J.N.; Zhang, Y.X. Community composition of net-phytoplankton and its relationship with the environmental factors at artificial reef area in Xiangshan Bay. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 5813–5824. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.L.; Chen, P.M.; Ma, S.W.; Chen, H.G. Community structure of phytoplankton and its relationship with environmental factors before and after construction of artificial reefs in Yangmeikeng, Daya Bay. S. China Fish. Sci. 2013, 9, 109–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, K.W.; Sun, M.C. Species composition and biomass variation in phytoplankton in artificial reef area in Haizhou Bay. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2006, 21, 134–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Einbinder, S.; Perelberg, A.; Ben-Shaprut, O.; Foucart, M.; Shashar, N. Effects of artificial reefs on fish grazing in their vicinity: Evidence from algae presentation experiments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 61, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Wang, J. Effects of Artificial Reefs on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water 2021, 13, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.P.; Gao, W.B.; Wang, S.Z.; Hu, B.C.; Liu, S.J. Evaluation index system and case applications of ecological restoration effect in artificial fish (Macroalgae) reef areas. Hebei Fish. 2017, 1, 42–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.D.; Zhao, J.B.; You, K.; Zhang, P. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of net-collected phytoplankton Community Structure and its relationship with key environmental factors in the artificial reef area of Xiangyun Bay, Hebei Province. Haiyang Xuebao 2024, 46, 52–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Leon, L.F.; Smith, R.E.; Hipsey, M.R.; Bocaniov, S.A.; Higgins, S.N.; Hecky, R.E.; Antenucci, J.P.; Imberger, J.A.; Guildford, S.J. Application of a 3D hydrodynamic–biological model for seasonal and spatial dynamics of water quality and phytoplankton in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, C.J.; Lane, R.R.; Day, J.W. Spatial and temporal variations in nutrients and water-quality parameters in the Mississippi River-influenced Breton Sound estuary. J. Coast. Res. Int. Forum 2014, 30, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, H.M.; Lastra, M. Diet of intertidal bivalves in the Rıa de Arosa (NW Spain): Evidence from stable C and N isotope analysis. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.C.M.; Dubois, S.; Orvain, F.; Galois, R.; Blin, J.L.; Ropert, M.; Bataille, M.P.; Ourry, A.; Lefebvre, S. Stable isotopes (δ13C, δ15N) and modelling as tools to estimate the trophic ecology of cultivated oysters in two contrasting environments. Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.M.; Humphries, A.T.; Shi, L.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Determination of trophic transfer at a created intertidal oyster (Crassostrea ariakensis) reef in the Yangtze River estuary using stable isotope analyses. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumori, K.; Oi, M.; Doi, H.; Okuda, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kuwae, M.; Miyasaka, H.; Yoshino, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Omori, K.; et al. Food sources of the pearl oyster in coastal ecosystems of Japan: Evidence from diet and stable isotope analysis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; D’Elia, C.F.; Schaffner, L.C. Limits to top-down control of phytoplankton by oysters in Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 325, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lv, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L. Seasonal changes of phytoplankton community structure and its influencing factors in waters adjacent to Huanghua port. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 46, 134–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Seaman, W.; Seaman, W., Jr. Artificial Reef Evaluation with Application to Natural Marine Habitats; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.; Palma, S.; Oliveira, P.B.; Moita, M.T. Composition and interannual variability of phytoplankton in a coastal upwelling region (Lisbon Bay, Portugal). J. Sea Res. 2009, 62, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Cable, J.E.; Cowan, J.H., Jr.; DeLaune, R.; de Mutsert, K.; Fry, B.; Mashriqui, H.; Justic, D.; Kemp, P.; Lane, R.R.; et al. The impacts of pulsed reintroduction of river water on a Mississippi Delta coastal basin. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 54, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekenberg, J.; Bargu, S.; Twilley, R. Phytoplankton community shifts and harmful algae presence in a diversion influenced estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 2213–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael Beman, J.; Arrigo, K.R.; Matson, P.A. Agricultural runoff fuels large phytoplankton blooms in vulnerable areas of the ocean. Nature 2005, 434, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.E. Temperature effects on steady-state growth, phosphorus uptake, and the chemical composition of a marine phytoplankton. Microb. Ecol. 1979, 5, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Effects of Temperature on Growth of Phytoplankton in the Changjiang Estuary and Adjacent Coastal Waters; Ocean University of China: Shandong, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Species Name | Before | After | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flood | Dry | Dry | Flood | ||
| July 2016 | September 2016 | May 2017 | June 2017 | August 2017 | |
| Diatoms | |||||
| 1. Actinoptychus sp. | 135 | 45 | 45 | ||
| 2. Amphora lineolata | 180 | 225 | 90 | 3105 [0.0837] (0.03) | 1850 |
| 3. Asterionella glacialis | 200 | ||||
| 4. Bacillaria paxillifera | 450 | ||||
| 5. Bacteriastrum sp. | 100 | ||||
| 6. Bellerochea malleus | 90 | ||||
| 7. Chaetoceros decipiens | 5220 | ||||
| 8. Chaetoceros atlanticus | 1620 | ||||
| 9. Chaetoceros curvisetus | 80,658 [0.0364] (0.21) | 136,000 0.0131 (0.38) | |||
| 10. Chaetoceros debilis | 270 | ||||
| 11. Chaetoceros densus | 2385 | 1500 | |||
| 12. Chaetoceros eibenii | 225 | 1170 | |||
| 13. Chaetoceros lorenzianus | 6255 | 9150 [0.0121] (0.03) | |||
| 14. Chaetoceros peruvianus | 270 | 540 | |||
| 15. Chaetoceros sp. | 135 | 62,865 [0.0259] (0.14) | 400 | ||
| 16. Climacodium frauenfeldianum | 90 | ||||
| 17. Corethron hystrix | 45 | ||||
| 18. Coscinodiscus gigas | 45 | ||||
| 19. Coscinodiscus granii | 150 | ||||
| 20. Coscinodiscus radiatus | 135 | 135 | 4275 [0.0205] (0.11) | 270 | 75 |
| 21. Coscinodiscus sp. | 810 | 2790 | 6615 [0.0148] (0.19) | 5310 [0.0186] (0.04) | 9600 [0.0109] (0.03) |
| 22. Cyclotella sp. | 360 | 45 | 360 | 1200 | |
| 23. Detonula pumila | 315 | 35,118 [0.0908] (0.08) | |||
| 24. Ditylum brightwellii | 90 | 90 | 1700 | ||
| 25. Entomoneis alata | 585 | ||||
| 26. Eucampia zodiacus | 81,675 [0.0713] (0.14) | 31,100 [0.0281] (0.07) | |||
| 27. Guinardia delicatula | 90 | 1080 | 450 | ||
| 28. Guinardia striata | 315 | 585 | 1700 | ||
| 29. Helicotheca tamesis | 180 | 50 | |||
| 30. Hemiaulus sinensis | 90 | ||||
| 31. Leptocylindrus danicus | 180 | 6570 | 5100 | ||
| 33. Meuniera membranacea | 45 | ||||
| 34. Navicula sp. | 675 | 135 | 472.5 | 630 | 50 |
| 35. Nitzschia closterium | 1550 | ||||
| 36. Nitzschia longissma | 1395 | 540 | 3285 [0.0593] (0.02) | 50 | |
| 37. Nitzschia lorenziana | 315 | 2970 [0.0203] (0.02) | 100 | ||
| 38. Nitzschia sp. | 360 | 2880 | 45 | 5085 [0.059] (0.03) | 2850 |
| 39. Odontella sinensis | 450 | 13,650 [0.0123] (0.04) | |||
| 40. Paralia sulcata | 4995 [0.0396] (0.08) | 315 | 21,105 [0.0156] (0.62) | 5895 [0.0443] (0.04) | 950 |
| 41. Pinnularia sp. | 630 | 180 | 225 | 45 | |
| 42. Planktoniella blanda | 45 | ||||
| 43. Pleurosigma angulatum | 1170 [0.023] (0.02) | 2250 | 540 | 2385 | |
| 44. Pleurosigma pelagicum | 100 | ||||
| 45. Pleurosigma sp. | 1800 | ||||
| 46. Proboscia alata | 45 | 990 | 75 | ||
| 47. Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima | 17,415 [0.3084] (0.11) | 225 | |||
| 48. Pseudo-nitzschia pungens | 11,790 [0.104] (0.18) | 14,130 [0.0167] (0.04) | 630 | ||
| 49. Rhizosolenia setigera | 517.5 | 45 | 1225 | ||
| 50. Skeletonema costatum | 76,150 [0.0113] (0.21) | ||||
| 51. Skeletonema sp. | 180 [0.0397] (0.03) | 135 | 66,375 [0.0141] (0.68) | ||
| 52. Stephanopyxis palmeriana | 1620 | 21,250 [0.014] (0.06) | |||
| 53. Surirella sp. | 270 | 45 | |||
| 54. Thalassionema frauenfeldii | 45 | 855 | |||
| 55. Thalassionema nitzschioides | 90 | 585 | 1035 | ||
| 56. Thalassiosira rotula | 1755 | 29,350 [0.0113] (0.08) | |||
| 57. Thalassiosira sp. | 180 | 135 | 135 | 3500 | |
| 58. Thalassiothrix franuenfeldii | 50 | ||||
| Dinoflagellates | |||||
| 59. Akashiwo sanguinea | 90 | ||||
| 60. Alexandrium catenella | 270 | 4140 | |||
| 61. Ceratium furca | 180 [0.0315] (0.02) | ||||
| 62. Ceratium fusus | 45 | ||||
| 63. Ceratium macroceras | 45 | 45 | |||
| 64. Ceratium tripos | 540 | 135 | |||
| 65. Dinophysis caudata | 90 | ||||
| 66. Gymnodinium sp. | 90 | ||||
| 67. Gyrodinium spirale | 585 | ||||
| 68. Noctiluca scientillans | 360 | 585 | 135 | 800 | |
| 69. Ornithocercus steinii | 45 | ||||
| 70. Prorocentrum dentatum | 135 | ||||
| 71. Prorocentrum minimum | 90 | ||||
| 72. Prorocentrum sp. | 990 | ||||
| 73. Protoperidinium divergens | 45 | ||||
| 74. Protoperidinium ovum | 90 | 45 | |||
| 75. Protoperidinium pallidum | 45 | 45 | |||
| 76. Protoperidinium sp. | 90 | 630 | 350 | ||
| 77. Pyrophacus steinii | 45 | 90 | |||
| 78. Scrippsiella trochoidea | 270 | ||||
| Silicoflagellates | |||||
| 79. Dictyocha fibula | 45 | 1215 | 1050 | ||
| July 2016 | ||||||||
| P. sulcata | P. angulatum | P. delicatissima | P. pungens | |||||
| P. sulcata | 1.0000 | |||||||
| P. angulatum | 0.4118 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| P. delicatissima | 0.0046 | 0.1725 | 1.0000 | |||||
| P. pungens | 0.0300 | 0.1917 | 0.9937 | 1.0000 | ||||
| September 2016 | ||||||||
| C. curvisetus | Chaetoceros sp. | D. pumila | E. zodiacus | P. pungens | Skeletonema sp. | C. furca | ||
| C. curvisetus | 1.0000 | |||||||
| Chaetoceros sp. | 0.6453 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| D. pumila | 0.9486 | 0.5241 | 1.0000 | |||||
| E. zodiacus | 0.1875 | 0.8005 | 0.1046 | 1.0000 | ||||
| P. pungens | 0.5720 | 0.7483 | 0.3907 | 0.3528 | 1.0000 | |||
| Skeletonema sp. | 0.1991 | 0.7781 | 0.0290 | 0.7634 | 0.6630 | 1.0000 | ||
| C. furca | 0.1415 | 0.3408 | 0.0630 | 0.0885 | 0.6235 | 0.2497 | 1.0000 | |
| May 2017 | ||||||||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | C. radiatus | P. sulcata | ||||||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | 1.0000 | |||||||
| C. radiates | 0.7474 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| P. sulcate | 0.6684 | 0.4107 | 1.0000 | |||||
| June 2017 | ||||||||
| A. lineolata | Coscinodiscus sp. | Nitzschia sp. | N. longissima | N. lorenziana | P. sulcata | Skeletonema sp. | ||
| A. lineolata | 1.0000 | |||||||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | 0.5447 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| Nitzschia sp. | 0.5878 | 0.7189 | 1.0000 | |||||
| N. longissima | 0.2181 | 0.5899 | 0.8512 | 1.0000 | ||||
| N. lorenziana | 0.3821 | 0.7208 | 0.2063 | 0.2564 | 1.0000 | |||
| P. sulcata | 0.5321 | 0.5144 | 0.8186 | 0.7398 | 0.1646 | 1.0000 | ||
| Skeletonema sp. | 0.6577 | 0.6695 | 0.5849 | 0.5282 | 0.6355 | 0.3895 | 1.0000 | |
| August 2017 | ||||||||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | C. curvisetus | C. lorenzianus | E. zodiacus | O. sinensis | S. costatum | S. palmeriana | C. furca | |
| Coscinodiscus sp. | 1.0000 | |||||||
| C. curvisetus | 0.8680 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| C. lorenzianus | 0.9349 | 0.8980 | 1.0000 | |||||
| E. zodiacus | 0.5811 | 0.6069 | 0.6909 | 1.0000 | ||||
| O. sinensis | 0.8532 | 0.6515 | 0.7596 | 0.6536 | 1.0000 | |||
| S. costatum | 0.8686 | 0.8388 | 0.8621 | 0.6809 | 0.9154 | 1.0000 | ||
| S. palmeriana | 0.8192 | 0.8057 | 0.8528 | 0.9082 | 0.8064 | 0.8217 | 1.0000 | |
| C. furca | 0.9477 | 0.9397 | 0.9502 | 0.6964 | 0.8206 | 0.8999 | 0.8770 | 1.0000 |
| July 2016 | |||||||
| P. sulcata | P. angulatum | P. delicatissima | |||||
| P. angulatum | 0.21 (0.78) | ||||||
| P. delicatissima | 0.36 (0.25) | 0.21 (0.33) | |||||
| P. pungens | 0.36 (0.56) | 0.21 (0.78) | 0.36 (0.25) | ||||
| September 2016 | |||||||
| C. curvisetus | Chaetoceros sp. | D. pumila | E. zodiacus | P. pungens | Skeletonema sp. | ||
| Chaetoceros sp. | 0.63 (0.70) | ||||||
| D. pumila | 0.63 (0.89) | 0.04 (0.78) | |||||
| E. zodiacus | 0.05 (0.67) | 0.23 (0.56) | 0.28 (0.56) | ||||
| P. pungens | (0.90) | (0.89) | (0.89) | (0.75) | |||
| Skeletonema sp. | 0.21 (0.60) | 0.03 (0.50) | 0.03 (0.50) | 0.18 (0.44) | (0.70) | ||
| C. furca | 0.63 (0.70) | 0.04 (0.60) | 0.04 (0.60) | 0.23 (0.40) | (0.80) | 0.02 (0.73) | |
| May 2017 | |||||||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | C. radiatus | ||||||
| C. radiatus | (0.90) | ||||||
| P. sulcata | (1.00) | (0.90) | |||||
| June 2017 | |||||||
| A. lineolata | Coscinodiscus sp. | Nitzschia sp. | N. longissima | N. lorenziana | P. sulcata | ||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | 0.04 (0.60) | ||||||
| Nitzschia sp. | 1.28 (0.75) | 1.28 (0.75) | |||||
| N. longissima | 0.23 (0.40) | 0.06 (0.56) | 2.1 (0.33) | ||||
| N. lorenziana | 0.04 (0.60) | 0.04 (0.60) | 0.23 (0.40) | 0.23 (0.56) | |||
| P. sulcata | 1.28 (0.75) | 0.23 (0.40) | 0.02 (0.50) | 2.1 (0.33) | 4.4 (0.40) | ||
| Skeletonema sp. | (1.00) | (0.80) | (0.60) | (0.60) | (0.80) | (0.60) | |
| August 2017 | |||||||
| Coscinodiscus sp. | C. curvisetus | C. lorenzianus | E. zodiacus | O. sinensis | S. costatum | S. palmeriana | |
| C. curvisetus | (1.00) | ||||||
| C. lorenzianus | (1.00) | (1.00) | |||||
| E. zodiacus | (0.80) | (0.90) | (0.80) | ||||
| O. sinensis | (1.00) | (1.00) | (1.00) | (0.80) | |||
| S. costatum | (1.00) | (1.00) | (1.00) | (0.80) | (1.00) | ||
| S. palmeriana | (1.00) | (1.00) | (1.00) | (0.80) | (1.00) | (1.00) | |
| T. rotula | (1.00) | (1.00) | (1.00) | (0.80) | (1.00) | (1.00) | (1.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Diversity: A Case Study for a Macroalgae–Oyster Reef Ecosystem. Diversity 2025, 17, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010052
Xu M, Zhao Q, Xu Y, Wang S, Yu Y, Zhang H, Wang Y, Shen J, Yang L, Zhang Y, et al. Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Diversity: A Case Study for a Macroalgae–Oyster Reef Ecosystem. Diversity. 2025; 17(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Min, Qi Zhao, Yufu Xu, Shenzhi Wang, Yingbo Yu, Haipeng Zhang, Yun Wang, Jiabin Shen, Linlin Yang, Yunling Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Diversity: A Case Study for a Macroalgae–Oyster Reef Ecosystem" Diversity 17, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010052
APA StyleXu, M., Zhao, Q., Xu, Y., Wang, S., Yu, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Shen, J., Yang, L., Zhang, Y., Otaki, T., Komatsu, T., & Xu, K. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Diversity: A Case Study for a Macroalgae–Oyster Reef Ecosystem. Diversity, 17(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17010052







