Temporal Shifts in Biological Community Structure in Response to Wetland Restoration: Implications for Wetland Biodiversity Conservation and Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
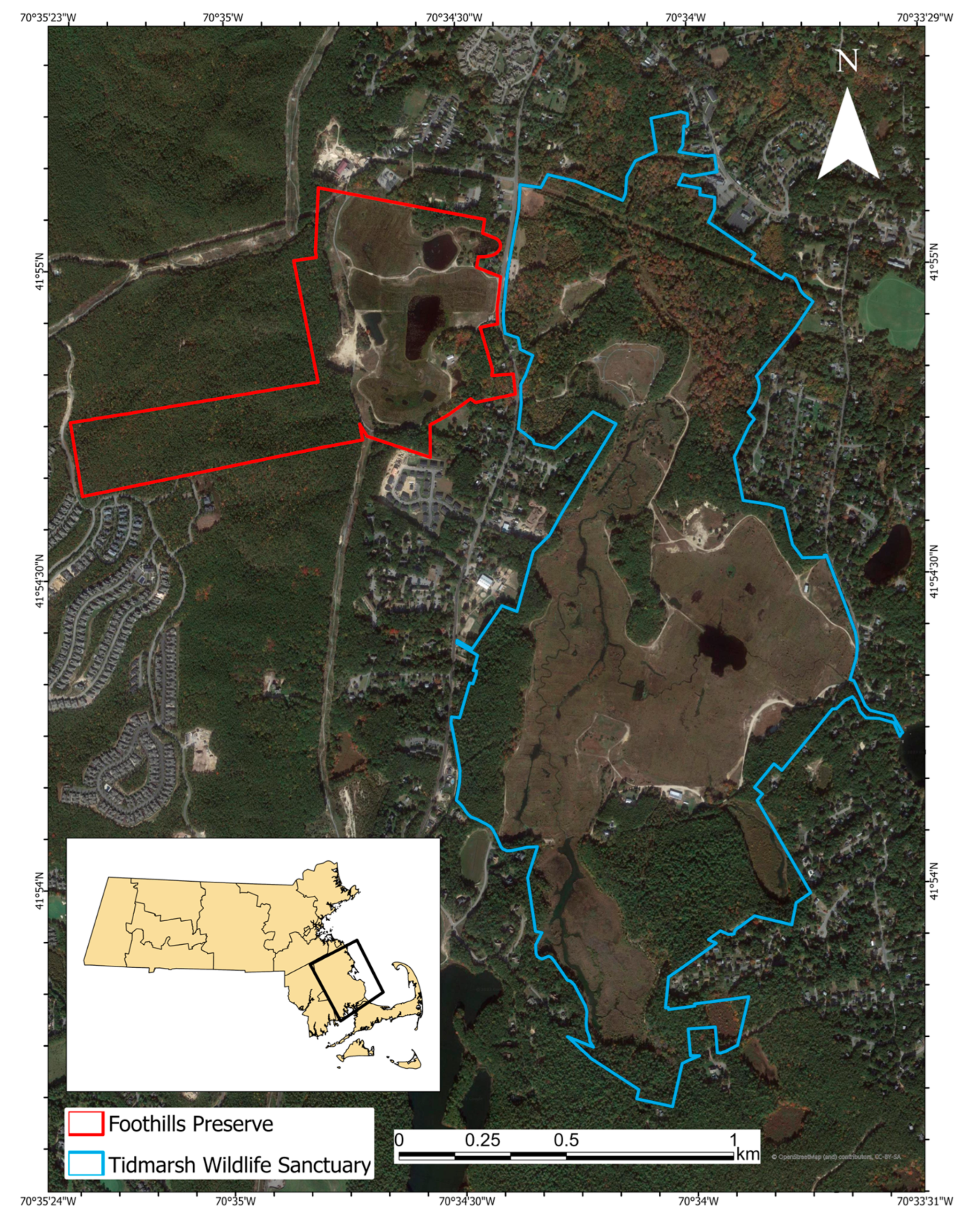
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Field Surveys
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.3.1. Compare Species Richness and Abundance Through Univariate Tests
night)/(Number of traps deployed at the site)
2.3.2. Explore Variations in Community Composition Through Multivariate Ordinations
2.3.3. Explore Species-Specific Responses Through Indicator Species Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Overview
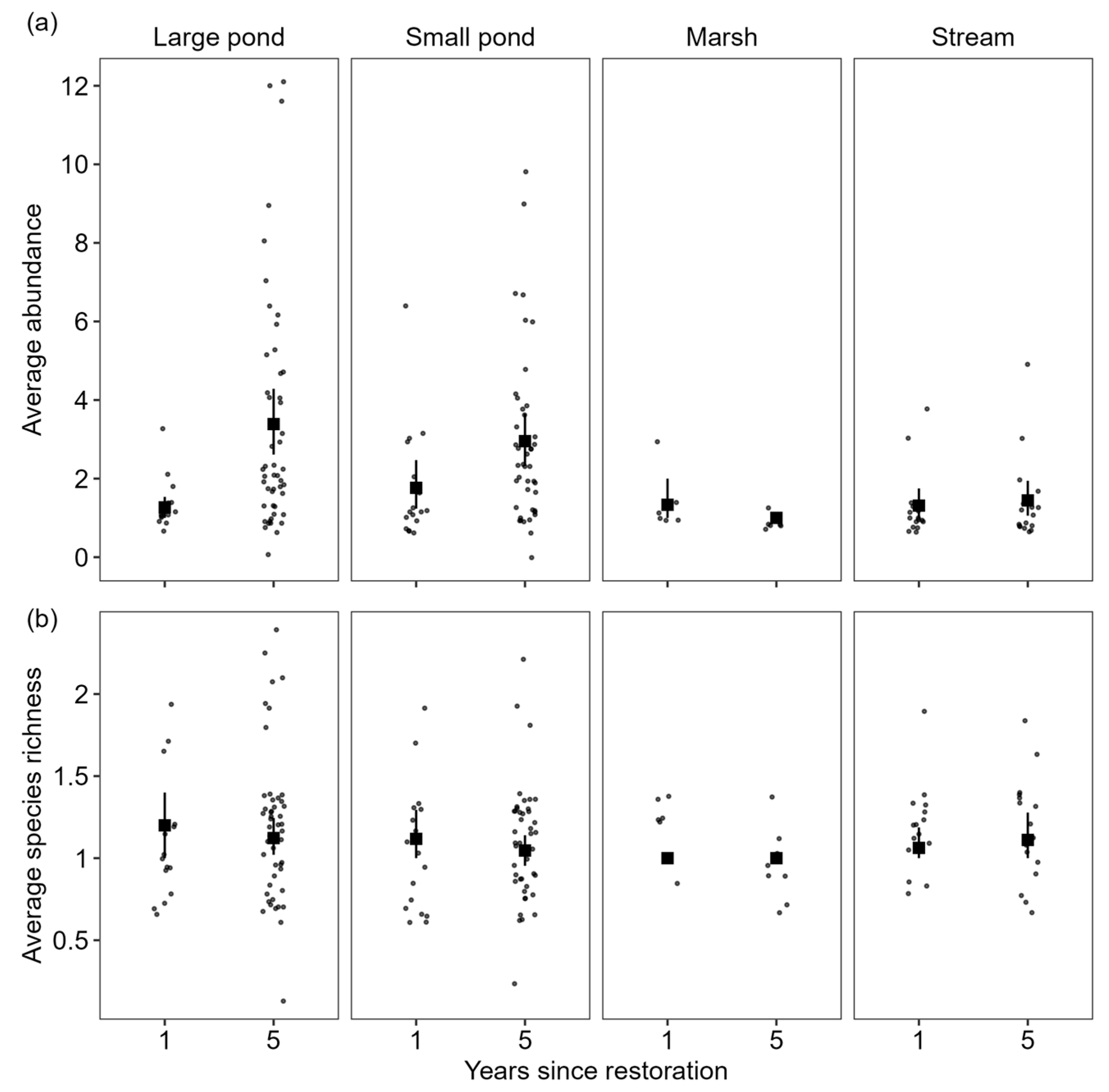
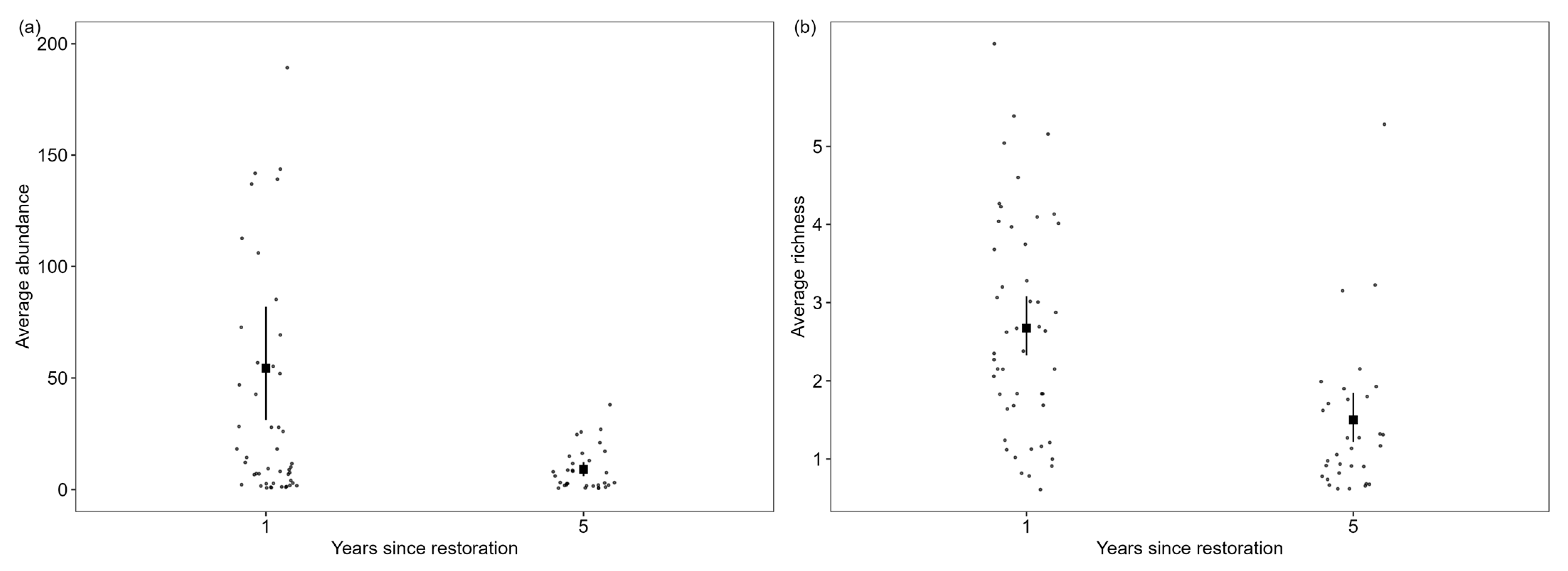
3.2. Variation in Species Richness and Abundance Among Herpetofauna in Response to Restoration
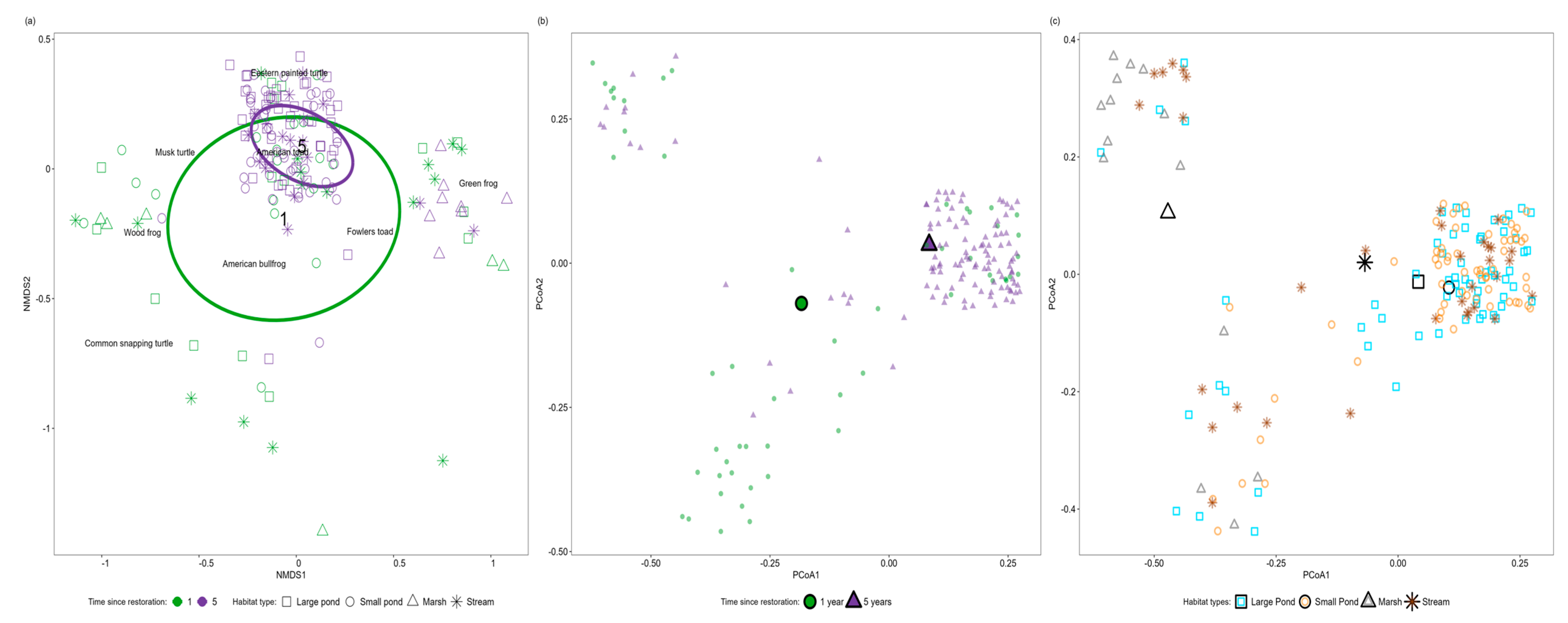
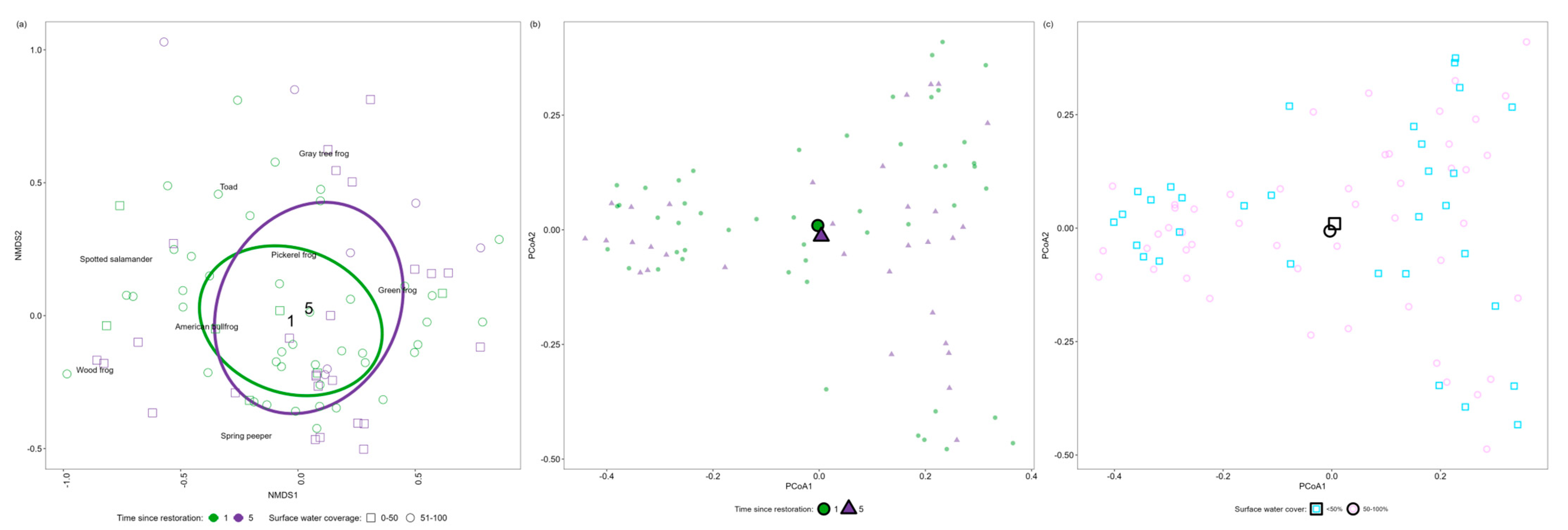
3.3. Variations in Community Composition in Response to Restoration
3.4. Species-Specific Responses to Restoration
4. Discussion
Future Directions and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analyses of Variance |
| ISA | Indicator Species Analyses |
| NMDS | Non-Metric Multidimensional Scaling |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinate Analyses |
| PermMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analyses of Variance |
| Ss | Sums of Squares |
| UN | United Nations |
| YSR | Years Since Restoration |
References
- Tiner, R.W. The concept of a hydrophyte for wetland identification. Bioscience 1991, 41, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B.; Kercher, S. Wetland resources: Status, trends, ecosystem services, and restorability. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2005, 30, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.P. Wetland loss and biodiversity conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbink, R.; Whigham, D.F.; Beltman, B.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. Wetland Functioning in Relation to Biodiversity Conservation and Restoration. In Wetlands: Functioning, Biodiversity Conservation, and Restoration; Bobbink, R., Beltman, B., Verhoeven, J.T.A., Whigham, D.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Geramny, 2006; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, R.T.; Wui, Y.-S. The economic value of wetland services: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 37, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, S.S.K.; Todorova, M.; van Teeffelen, A.J.A.; Verburg, P.H. Public Support for Wetland Restoration: What is the Link with Ecosystem Service Values? Wetlands 2016, 36, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.; Brander, L.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Change 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N.C.; van Dam, A.A.; Finlayson, C.M.; McInnes, R.J. Worth of wetlands: Revised global monetary values of coastal and inland wetland ecosystem services. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, N.C. How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 65, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, B.R.; Ausseil, A.E.; Gerbeaux, P. Wetland ecosystem services. In Ecosystem Services in New Zealand: Conditions and Trends; Dymond, J.R., Ed.; Manaaki Whenua Press: Lincoln, New Zealand, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, J.S.; Destouni, G.; Duke-Sylvester, S.M.; Magurran, A.E.; Oberdorff, T.; Reis, R.E.; Winemiller, K.O.; Ripple, W.J. Scientists’ warning to humanity on the freshwater biodiversity crisis. Ambio 2021, 50, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B. Progress in wetland restoration ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Harris, J.A. Restoration ecology: Repairing the earth’s ecosystems in the new millennium. Restor. Ecol. 2001, 9, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsch, W.J. Wetland Creation and Restoration. In Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Levin, S.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, V.; Hermoso, V.; Hamilton, S.K.; Ward, D.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Lehner, B.; Linke, S. A Global Assessment of Inland Wetland Conservation Status. Bioscience 2017, 67, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, J.; Salcedo, J.-P.; Silva, L.N.; Alekseeva, N.; Neureuther, A.-K.; Li, X.; Gonzalez, L.; Christophersen, T.; Searle, G. Action Plan for the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, 2021–2030 Version April 2023; United Nations Environment Programme and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: 2023. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/42095 (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Fischer, J.; Riechers, M.; Loos, J.; Martin-Lopez, B.; Temperton, V.M. Making the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration a Social-Ecological Endeavour. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zedler, J.B.; Doherty, J.M.; Miller, N.A. Shifting restoration policy to address landscape change, novel ecosystems, and monitoring. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, E.; Falk, D.A.; Guerrini, A.; Hall, M.; Harris, J.; Hobbs, R.J.; Jackson, S.T.; Rhemtulla, J.M.; Throop, W. The changing role of history in restoration ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohr, J.R.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Cadotte, M.W.; Clements, W.H. The ecology and economics of restoration. Ecol. Soc. 2018, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, P.S.; Bond, N.; Reich, P. Linking ecological theory with stream restoration. FreshWater Biol. 2007, 52, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reillo, W.G.; Truchon, A.; Blanchard, J.L.; Pierce, E.A.; Ballantine, K.A. Rewilding the small stuff: The effect of ecological restoration on prokaryotic communities of peatland soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suding, K.N. Toward an era of restoration in ecology: Successes, failures, and opportunities ahead. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 42, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Carstensen, J.; Carvalho, L.; Elliott, M.; Feld, C.K.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Johnson, R.K.; Moe, J.; Pont, D. The European Water Framework Directive at the age of 10: A critical review of the achievements with recommendations for the future. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddle, J.H. Use of Amphibians as Ecosystem Indicator Species. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Severns, P.M.; Sykes, E.M. Indicator Species Analysis: A Useful Tool for Plant Disease Studies. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1860–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.A. Amphibians as models for studying environmental change. ILAR J. 2007, 48, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodie, J. Stream and riparian management for freshwater turtles. J. Environ. Manage. 2001, 62, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, K.A.; Davenport, G.; Deegan, L.; Gladfelter, E.; Hatch, C.E.; Kennedy, C.; Klionsky, S.; Mayton, B.; Neil, C.; Surasinghe, T.D.; et al. Learning from the Restoration of Wetlands on Cranberry Farmland: Preliminary Benefits Assessment; Massachusetts Division of Ecological Restoration, Cranberry Bog Program; Living Observatory: Plymouth, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Christen, R.A.; Dewey, A.K.; Gouthro, A.N.; Surasinghe, T.D. Diversity of herpetofauna at restored cranberry bogs: A comparative survey of herpetofaunal diversity at a restored wetland in comparison to a retired cranberry bog to assess the restoration success. Herpetol. J. 2022, 32, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorsa, N.; Johnson-Cicalese, J. American cranberry. In Handbook of Plant Breeding—Fruit Breeding; Badenes, M.L., Bryne, D.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 191–223. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, M. A Rapid Assessment for Cranberry Farm Wetland Restoration Potential in Southeastern and Cape Cod Massachusetts. Master’s Thesis, Antioch University New England, Keene, NH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, B.R.; Neill, C.; Kennedy, C.D. Trends in the Massachusetts cranberry industry create opportunities for the restoration of cultivated riparian wetlands. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwood, E.R.; Playfair, S.R.; Polgar, C.A.; Primack, R.B. Cranberry flowering times and climate change in southern Massachusetts. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA Department of Agricultural Resources. The Massachusetts Cranberry Revitalization Task Force, Final Report; MA Department of Agricultural Resources: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mayton, B.D. Sensor Networks for Experience and Ecology. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Demoranville, C.J. Cranberry Best Management Practice Adoption and Conservatiion Farm Planning in Massachusetts. HortTechnology 2016, 16, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdigian-Boone, R.R. Restoration and Recreation A Cranberry Bog’s Return to Wetland for Water Quality and Recreation, Masters of Landscape Architecture Final Project. Master’s Thesis, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, C.K. Amphibian Ecology and Conservation: A Handbook of Techniques; Oxford University Press New York: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McDiarmid, R.W. Reptile Biodiversity: Standard Methods for Inventory and Monitoring; University of California Press: Berkeley and Loss Angeles, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, J.W. Amphibian Survey and Monitoring Handbook; Pelagic Publishing: Exeter, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, C.K. Reptile ecology and Conservation: A Handbook of Techniques; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.; Ronchetti, E. Robust Statistics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maronna, R.A.; Martin, R.D.; Yohai, V.J.; Salibián-Barrera, M. Robust Statistics: Theory and Methods (with R); John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Potvin, C.; Roff, D.A. Distribution-free and robust statistical methods: Viable alternatives to parametric statistics. Ecology 1993, 74, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurečková, J.; Picek, J.; Schindler, M. Robust Statistical Methods with R.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Team, P. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; Posit Software, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2024; Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Mair, P.; Wilcox, R. Robust statistical methods in R using the WRS2 package. Behav. Res. Methods 2020, 52, 464–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, I. statsExpressions: R package for tidy dataframes and expressions with statistical details. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J. Multidimensional scaling and regression. Stat. Appl. Ital. J. Appl. Stat. 1992, 4, 577–586. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.; Prentice, I.C. A theory of gradient analysis. In Advances in Ecological Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 18, pp. 271–317. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical ecology, Third English Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.; Stafford, S. Multivariate Statistics for Wildlife and Ecology Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 200. [Google Scholar]
- McCune, B.; Grace, J.B.; Urban, D.L. Analysis of Ecological Communities; MjM Software Design: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2002; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Dexter, E.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M. The trouble with stress: A flexible method for the evaluation of nonmetric multidimensional scaling. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2018, 16, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P.; Minchin, P.R.; Belbin, L. Compositional dissimilarity as a robust measure of ecological distance. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, P. An evaluation of relative robustness of techniques for ecological orderings. Vegetatio 1987, 71, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package_. R package version 2.6-4. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 7 March 2025).
- Cottam, G.; Goff, F.G.; Whittaker, R.H. Ordination and Classification of Communities. In Wisconsin Comparative Ordination. Handbook of Vegetation Science, Vol. 5; Whittaker, R.H., Ed.; Junk: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1973; pp. 193–221. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B. Nonmetric multidimensional scaling: A numerical method. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel test in the face of heterogeneous dispersions: What null hypothesis are you testing? Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Legendre, P. An empirical comparison of permutation methods for tests of partial regression coefficients in a linear model. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 1999, 62, 271–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Ellingsen, K.E.; McArdle, B.H. Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, M.D.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.P. Two-phase species–time relationships in North American land birds. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzyna, M.A.; Norman, K.E.A.; LaMontagne, J.M.; Helmus, M.R.; Li, D.; Parker, S.M.; Perez Rocha, M.; Record, S.; Sokol, E.R.; Zarnetske, P.L.; et al. Community stability is related to animal diversity change. Ecosphere 2022, 13, e3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.J.; Soininen, J.; Hillebrand, H. A quantitative analysis of temporal turnover in aquatic species assemblages across ecosystems. Ecology 2010, 91, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magurran, A.E.; Henderson, P.A. Temporal turnover and the maintenance of diversity in ecological assemblages. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, E.M.; de Andrade-Tubino, M.F.; Franco, T.P.; Neves, L.M.; dos Santos, L.N.; dos Santos, A.F.G.N.; Araújo, F.G. Temporal dimensions of taxonomic and functional fish beta diversity: Scaling environmental drivers in tropical transitional ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 1911–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, R.M.; Galatowitsch, S.M. Colonization of restored wetlands by amphibians in Minnesota. Am. Midl. Nat. 2001, 145, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.J.; Street, G.M.; Nairn, R.W.; Forstner, M.R.J. A Place to Call Home: Amphibian Use of Created and Restored Wetlands. Int. J. Ecol. 2012, 2012, 989872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.A.; Pierce, C.L.; Smalling, K.L.; Klaver, R.W.; Vandever, M.W.; Battaglin, W.A.; Muths, E. Restored agricultural wetlands in central Iowa: Habitat quality and amphibian response. Wetlands 2016, 36, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannap, R.; Lõhmus, A.; Briggs, L. Restoring ponds for amphibians: A success story. Hydrobiologia 2009, 634, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, S.C.; Hardin Waddle, J.; Barichivich, W.J.; Bartoszek, I.A.; Brown, M.E.; Hefner, J.M.; Schuman, M.J. Anuran site occupancy and species richness as tools for evaluating restoration of a hydrologically-modified landscape. Wetlands Ecol. Manage. 2014, 22, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, J.M.; Noss, R.F. Specialist and generalist amphibians respond to wetland restoration treatments. J. Wildl. Manage. 2016, 80, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, R.D. Principles for Management of Aquatic-Breeding Amphibians. J. Wildl. Manage. 2000, 64, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, R.D. Critical Elements for Biologically Based Recovery Plans of Aquatic-Breeding Amphibians. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, L.R.; McGarigal, K.; Compton, B.W. Fidelity and dispersal in the pond-breeding amphibian, Ambystoma opacum: Implications for spatio-temporal population dynamics and conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 139, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechmann, J.H.K.; Estes, R.A.; Scott, D.E.; Gibbons, J.W. Amphibian colonization and use of ponds created for trial mitigation of wetland loss. Wetlands 2001, 21, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.M.; Haas, C.A.; Harpole, D.N.; Kirkpatrick, R.L. Initial effects of clearcutting and alternative silvicultural practices on terrestrial salamander abundance. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazerolle, M.J.; Desrochers, A.; Rochefort, L. Landscape characteristics influence pond occupancy by frogs after accounting for detectability. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buskirk, J. Local and landscape influence on amphibian occurrence and abundance. Ecology 2005, 86, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baber, M.J.; Fleishman, E.; Babbitt, K.J.; Tarr, T.L. The relationship between wetland hydroperiod and nestedness patterns in assemblages of larval amphibians and predatory macroinvertebrates. Oikos 2004, 107, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eterovick, P.C.; Carnaval, A.C.O.d.Q.; Borges-Nojosa, D.M.; Silvano, D.b.L.; Segalla, M.V.; Sazima, I. Amphibian Declines in Brazil: An Overview. Biotropica 2005, 37, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, J.B.; Callaway, J.C. Tracking wetland restoration: Do mitigation sites follow desired trajectories? Restor. Ecol. 1999, 7, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, A.; Langel, R.; Scheu, S.; Himstedt, W.; Maraun, M. Trophic ecology of a tropical aquatic and terrestrial food web: Insights from stable isotopes (15N). J. Trop. Ecol. 2006, 22, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashpole, S.L.; Bishop, C.A.; Murphy, S.D. Reconnecting Amphibian Habitat through Small Pond Construction and Enhancement, South Okanagan River Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Diversity 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, K.; Schneider, R. Fifty-five years of soil development in restored freshwater depressional wetlands. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, K.; Schneider, R.; Groffman, P.; Lehmann, J. Soil properties and vegetative development in four restored freshwater depressional wetlands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, N.N.; Anderson, T.R.; Ballantine, K.A. Restoration of retired agricultural land to wetland mitigates greenhouse gas emissions. Restor. Ecol. 2021, 29, e13314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, C.; Megonigal, P.; Broome, S.; Stevenson, J.; Freese, R.; Cornell, J.; Zheng, L.; Sacco, J. The pace of ecosystem development of constructed Spartina alterniflora marshes. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, K.A.; Anderson, T.R.; Pierce, E.A.; Groffman, P.M. Restoration of denitrification in agricultural wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCanty, S.T.; Dimino, T.F.; Christian, A.D. Near-Term Changes to Reach Scale Habitat Features Following Headwater Stream Restoration in a Southeastern Massachusetts Former Cranberry Bog. Diversity 2021, 13, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranka, J.W.; Murray, S.S.; Kennedy, C.A. Responses of amphibians to restoration of a southern Appalachian wetland: Perturbations confound post-restoration assessment. Wetlands 2003, 23, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, L.J.; Marsden, T.; Duffy, D.; Horta, A.; Ning, N. Optimizing efforts to restore aquatic ecosystem connectivity requires thinking beyond large dams. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 17, 014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ickes, B.S.; Vallazza, J.; Kalas, J.; Knights, B. River Floodplain Connectivity and Lateral Fish Passage: A Literature Review; US Fish and Wildlife Service, Mark Twain Wildlife Refuge Complex: Quincy, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Baecher, J.A.; Vogrinc, P.N.; Guzy, J.C.; Kross, C.S.; Willson, J.D. Herpetofaunal communities in restored and unrestored remnant tallgrass prairie and associated wetlands in northwest Arkansas, USA. Wetlands 2018, 38, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmore, J.R.; Pess, G.R.; Duda, J.J.; O’Connor, J.E.; East, A.E.; Foley, M.M.; Wilcox, A.C.; Major, J.J.; Shafroth, P.B.; Morley, S.A.; et al. Conceptualizing Ecological Responses to Dam Removal: If You Remove It, What’s to Come? Bioscience 2019, 69, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanski, I. Dynamics of regional distribution: The core and satellite species hypothesis. Oikos 1982, 38, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L. Landscape filters and species traits: Towards mechanistic understanding and prediction in stream ecology. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 1997, 16, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.M.; Aronson, J.; Newton, A.C.; Pywell, R.F.; Rey-Benayas, J.M. Restoration of ecosystem services and biodiversity: Conflicts and opportunities. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2011, 26, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, J.; Kelemen, A.; Valkó, O.; Deák, B.; Kiss, R.; Tóth, K.; Miglécz, T.; Tóthmérész, B.; Török, P. Both mass ratio effects and community diversity drive biomass production in a grassland experiment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.W. Interpreting the ‘selection effect’of biodiversity on ecosystem function. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Allan, J.D.; Lake, P.S.; Alexander, G.; Brooks, S.; Carr, J.; Clayton, S.; Dahm, C.N.; Follstad Shah, J.; et al. Standards for ecologically successful river restoration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suding, K.N.; Gross, K.L.; Houseman, G.R. Alternative states and positive feedbacks in restoration ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.P.; Jones, P.C.; Barbier, E.B.; Blackburn, R.C.; Rey Benayas, J.M.; Holl, K.D.; McCrackin, M.; Meli, P.; Montoya, D.; Mateos, D.M. Restoration and repair of Earth’s damaged ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20172577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Mateos, D.; Power, M.E.; Comín, F.A.; Yockteng, R. Structural and functional loss in restored wetland ecosystems. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography; Princeton University Press Princeton: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Soberón, J. Grinnellian and Eltonian niches and geographic distributions of species. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merovich, C.E.; Howard, J.H. Amphibian use of constructed ponds on Maryland’s eastern shore. J. Iowa Acad. Sci. 2000, 107, 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Klee, R.J.; Zimmerman, K.I.; Daneshgar, P.P. Community succession after cranberry bog abandonment in the New Jersey pinelands. Wetlands 2019, 39, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, E. Establishment of Baseline Physical, Chemical, and Biological Stream Conditions at a Passive Cranberry Bog Restoration. Master’s Thesis, University of Massachusetts, Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.T.; Hobbs, R.J. Ecological Restoration in the Light of Ecological History. Science 2009, 325, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, M.E.; Franklin, J.F.; Beschta, R.L.; Crisafulli, C.M.; DellaSala, D.A.; Hutto, R.L.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Swanson, F.J. The forgotten stage of forest succession: Early-successional ecosystems on forest sites. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinn, K.M.; Marks, P.L. Agricultural legacies in forest environments: Tree communities, soil properties, and light availability. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham-Cheatham, S.M.; Freund, S.M.; Uselman, S.M.; Leger, E.A.; Sullivan, B.W. Persistent Agricultural Legacy in Soil Influences Plant Restoration Success in a Great Basin Salt Desert Ecosystem. Ecol. Restor. 2020, 38, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddington, K. Legacy Effects: The Persistent Impact of Ecological Interactions. Biol. Theory 2011, 6, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, J.C.; Garcia, T.S. Impacts of Wetland Restoration Efforts on an Amphibian Assemblage in a Multi-invader Community. Wetlands 2014, 34, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodman, R.; Parrish, M.; Kraus, H.; Cortwright, S. Amphibian Biodiversity Recovery in a Large-Scale Ecosystem Restoration. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 1, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bartelt, P.E.; Klaver, R.W. Response of Anurans to Wetland Restoration on a Midwestern Agricultural Landscape. J. Herpetol. 2017, 51, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southwood, T.R. Habitat, the templet for ecological strategies? J. Anim. Ecol. 1977, 46, 337–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H.; Slatyer, R.O. Mechanisms of succession in natural communities and their role in community stability and organization. Am. Nat. 1977, 111, 1119–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.P.; Adler, P.B.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Gill, R.A.; Greenberg, D.; Kaufman, D.M.; Rassweiler, A.; Rusak, J.A.; Smith, M.D.; Steinbeck, J.R. A comparison of the species–time relationship across ecosystems and taxonomic groups. Oikos 2006, 112, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferren, W.; Hubbard, D.M.; Wiseman, S.; Parikh, A.K.; Gale, N. Review of ten years of vernal pool restoration and creation in Santa Barbara, California. In Ecology, Conservation, and Management of Vernal Pool Ecosystems–Proceedings from a 1996 Conference; Witham, C.W., Bauder, E.T., Belk, D., Ferren, W.R., Jr., Ornduff, R., Eds.; California Native Plant Society: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 206–216. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, C.E.; Ito, E.T. Recovering groundwater for wetlands from an anthropogenic aquifer. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 945065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, C.L.; Hatch, C.E.; Wicks, R. Mapping groundwater discharge seeps by thermal UAS imaging on a wetland restoration site. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.; Ruhi, A. Linkages between flow regime, biota, and ecosystem processes: Implications for river restoration. Science 2019, 365, eaaw2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, C.H.; Lovich, J.E. Turtles of the United States and Canada; John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoza, J.E.; Jones, G.; French, T.; Halliwell, D. Exotic and Translocated Vertebrates of Massachusetts, 2nd ed.; Fauna of Massachusetts Series 6; Massachusetts Division of Fisheries and Wildlife: Westborough, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Christen, R.; Dewey, A.; Gouthro, A.; Tocchio, K.; Sheehan, B.; Venuto, D.; Dobeib, Y.; McCulley, T.; Surasinghe, T. Comparison of reptile diversity between restored and unrestored freshwater wetlands: An assessment of restoration success of New England cranberry farms. In Proceedings of the American Fisheries Society & The Wildlife Society 2019 Joint Annual Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Surasinghe, T.D.; Tochhio, T.; Sheehan, B.; Venuto, D.; Montanaro, N.; Schneider, V.; Deguire, A.; Zimmerman, A.; Albanese, G. Amphibian and reptile diversity at Tidmarsh Mass Audubon Sanctuary. In Proceedings of the Connecting Communities and Ecosystems in Restoration Practice. Regional Conference of the Society for Ecological Restoration, New Endgland Chapter, Southern Connecticut State University, New Haven, CT, USA, 11–13 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.S.; Richardson, C.J.; Urban, D.L.; Romanowicz, E.A. Spatial Dependency of Vegetation–Environment Linkages in an Anthropogenically Influenced Wetland Ecosystem. Ecosystems 2004, 7, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, F.; Devaux, B.; Dupré, A. Turtles of the World; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, J.M. Community assembly: When should history matter? Oecologia 2003, 136, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonesh, J.R.; De la Cruz, O. Complex life cycles and density dependence: Assessing the contribution of egg mortality to amphibian declines. Oecologia 2002, 133, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, B.A. Wetland Restoration, Flood Pulsing, and Disturbance Dynamics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, D.J.; Bruland, G.L.; Zedler, J.B. Heterogeneity Theory and Ecological Restoration. In Foundations of Restoration Ecology; Palmer, M.A., Zedler, J.B., Falk, D.A., Eds.; Island Press/Center for Resource Economics: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, R.J.; Heino, J.; Ryder, D.S.; Chessman, B.C.; Growns, I.O.; Thompson, R.M.; Gido, K.B. Scaling biodiversity responses to hydrological regimes. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 971–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.P.; Bradshaw, A.D.; Baker, A.J. Hopes for the future: Restoration ecology and conservation biology. Science 1997, 277, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylecraine, K.A.; Zimmermann, G.L.; Williams, R.R.; Kuser, J.E. Atlantic white-cedar wetland restoration on a former agricultural site in the New Jersey Pinelands. Ecol. Restor. 2004, 22, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, R.D.; Muths, E.; Noon, B.R. The importance of local and landscape-scale processes to the occupancy of wetlands by pond-breeding amphibians. Popul. Ecol. 2012, 54, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyderski, M.K.; Czapiewska, N.; Zajdler, M.; Tyborski, J.; Jagodziński, A.M. Functional diversity, succession, and human-mediated disturbances in raised bog vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzell, B.M.; DeVito, E.D.; Shebitz, D.J. Effects of restoration strategies on vegetation establishment in retired cranberry bogs. Plant Ecol. 2021, 222, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolka, R.K.; Nelson, E.A.; Trettin, C.C. Conceptual assessment framework for forested wetland restoration: The Pen Branch experience. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 15, S17–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.; Clewell, A.; Moreno-Mateos, D. Ecological restoration and ecological engineering: Complementary or indivisible? Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mateos, D.; Alberdi, A.; Morriën, E.; van der Putten, W.H.; Rodríguez-Uña, A.; Montoya, D. The long-term restoration of ecosystem complexity. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranka, J.W.; Harp, E.M.; Holbrook, C.T.; Hamel, J.A. Long-term persistence of amphibian populations in a restored wetland complex. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 138, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulse, C.D.; Semlitsch, R.D.; Trauth, K.M.; Williams, A.D. Influences of Design and Landscape Placement Parameters on Amphibian Abundance in Constructed Wetlands. Wetlands 2010, 30, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petranka, J.W.; Holbrook, C.T. Wetland Restoration for Amphibians: Should Local Sites Be Designed to Support Metapopulations or Patchy Populations? Restor. Ecol 2006, 14, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittenhouse, T.A.; Semlitsch, R.D. Distribution of amphibians in terrestrial habitat surrounding wetlands. Wetlands 2007, 27, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.F.; Calhoun, A.J.K.; deMaynadier, P.G. Conservation planning for amphibian species with complex habitat requirements: A case study using movements and habitat selection of the Wood Frog Rana sylvatica. J. Herpetol. 2006, 40, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, R.D.; Bodie, J.R. Biological criteria for buffer zones around wetlands and riparian habitats for amphibians and reptiles. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, A.L.; Nickerson, M.A. Reassessment of the Turtle Community in the North Fork of White River, Ozark County, Missouri. Copeia 2012, 2012, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; MacKenzie, D.I.; Wintle, B.A.; McCarthy, M.A. Ignoring imperfect detection in biological surveys is dangerous: A response to ‘fitting and interpreting occupancy models’. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, D.I.; Nichols, J.D.; Lachman, G.B.; Droege, S.; Andrew Royle, J.; Langtimm, C.A. Estimating site occupancy rates when detection probabilities are less than one. Ecology 2002, 83, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienentreu, J.-F.; Lesbarrères, D. Amphibian disease ecology: Are we just scratching the surface? Herpetologica 2020, 76, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, R.A.; Wilber, M.Q.; Joseph, M.B.; Smith, T.C.; Grasso, R.L. Reintroduction of resistant frogs facilitates landscape-scale recovery in the presence of a lethal fungal disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloegel, L.; Ferreira, C.; James, T.; Hipolito, M.; Longcore, J.; Hyatt, A.; Yabsley, M.; Martins, A.; Mazzoni, R.; Davies, A. The North American bullfrog as a reservoir for the spread of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Brazil. Anim. Conserv. 2010, 13, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-García, J.M.; López-Barrera, F.; Pineda, E.; Toledo-Aceves, T.; Andresen, E. Comparing the success of active and passive restoration in a tropical cloud forest landscape: A multi-taxa fauna approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreika, N.; Pärtel, M.; Öckinger, E. Community completeness as a measure of restoration success: Multiple-study comparisons across ecosystems and ecological groups. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 3807–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašových, A.; Kidwell, S.M. The effects of temporal resolution on species turnover and on testing metacommunity models. Am. Nat. 2010, 175, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.M.; Whitmore, S.A.; Gutiérrez, R.J.; Sawyer, S.C.; Keane, J.J.; Peery, M.Z. Using metapopulation models to assess species conservation–ecosystem restoration trade-offs. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 224, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, M.; Fletcher, M.S.; Powell, A.; Dobson, M.K. The Feasibility of Developing Multi-Taxa Indicators for Landscape Scale Assessment of Freshwater Systems. Freshw. Rev. 2011, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carignan, V.; Villard, M.-A. Selecting Indicator Species to Monitor Ecological Integrity: A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess 2002, 78, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, V.H.; Beyeler, S.C. Challenges in the development and use of ecological indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2001, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, J.W.; Gordon, A.; Law, E.A.; Suttle, K.B.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. Importance of Baseline Specification in Evaluating Conservation Interventions and Achieving No Net Loss of Biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2014, 28, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Frempong-Manso, A.; Piczak, M.L.; Karathanou, E.; Clavijo, C.; Ajagbe, S.O.; Akeredolu, E.; Strauch, A.M.; Piccolo, J. A freshwater perspective on the United Nations decade for ecosystem restoration. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, e12787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, D.; Brander, L.; Finlayson, C.M. Wetland Ecosystem Services. In The Wetland Book: I: Structure and Function, Management, and Methods; Finlayson, C.M., Everard, M., Irvine, K., McInnes, R.J., Middleton, B.A., van Dam, A.A., Davidson, N.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, G.W. Ecological research for aquatic science and environmental restoration in south Florida. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.D. Theories for ecological restoration in changing environment: Toward ‘futuristic’ restoration. Ecol. Res. 2004, 19, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Niu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H. Global wetlands: Potential distribution, wetland loss, and status. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 586, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scientific Name | Vernacular Name | Years Since Restoration | Large Pond | Marsh | Small Pond | Stream | Life-History Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphibians | |||||||
| Ambystoma maculatum | Spotted salamander | B | x | E, L | |||
| Anaxyrus americanus | American toad | B | x | x | E, L, A | ||
| Anaxyrus fowleri | Fowler’s toad | B | x | E, L, A | |||
| Dryophytes versicolor | Gray tree frog | B | x | L | |||
| Lithobates catesbeianus | American Bullfrog | B | x | x | x | x | L, A |
| Lithobates clamitans | Green Frog | B | x | x | x | x | L, A |
| Lithobates palustris | Pickerel frog | B | x | L, A | |||
| Lithobates sylvaticus | Wood frog | B | x | E, L, A | |||
| Pseudacris crucifer | Spring peeper | B | x | E, L, A | |||
| Reptiles | |||||||
| Chelydra serpentina | Common snapping turtle | B | x | x | x | A | |
| Chrysemys picta | Eastern painted turtle | B | x | x | x | x | A |
| Sternotherus odoratus | Eastern musk turtle | 5 | x | x | A | ||
| Thamnophis sauritus | Eastern ribbon snake | 5 | x | A | |||
| Thamnophis sirtalis | Common garter snake | B | x | A | |||
| Species | 1-YSR | 5-YSR | Test Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American bullfrog | x | 0.336 | 0.000 *** | |
| American toad | x | 0.097 | 0.307 | |
| Common snapping turtle | x | 0.284 | 0.000 *** | |
| Fowler’s toad | x | 0.097 | 0.000 *** | |
| Green frog | x | 0.161 | 0.061 | |
| Wood frog | x | 0.097 | 0.307 | |
| Eastern painted turtle | x | 0.506 | 0.000 *** | |
| Musk turtle | x | 0.170 | 0.014 * |
| Species | 1-YSR | 5-YSR | Test Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American bullfrog | x | 0.206 | 0.028 * | |
| Green frog | x | 0.023 | 0.844 | |
| Spotted salamander | x | 0.221 | 0.050 | |
| Spring peeper | x | 0.004 | 0.974 | |
| Toad | x | 0.018 | 0.867 | |
| Wood frog | x | 0.016 | 0.892 | |
| Gray tree frog | x | 0.206 | 0.071 | |
| Pickerel frog | x | 0.138 | 0.280 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keith, K.M.; Potvin, M.K.; Saad, S.R.; Surasinghe, T.D. Temporal Shifts in Biological Community Structure in Response to Wetland Restoration: Implications for Wetland Biodiversity Conservation and Management. Diversity 2025, 17, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030198
Keith KM, Potvin MK, Saad SR, Surasinghe TD. Temporal Shifts in Biological Community Structure in Response to Wetland Restoration: Implications for Wetland Biodiversity Conservation and Management. Diversity. 2025; 17(3):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030198
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeith, Kayla M., Matthew K. Potvin, Summer R. Saad, and Thilina D. Surasinghe. 2025. "Temporal Shifts in Biological Community Structure in Response to Wetland Restoration: Implications for Wetland Biodiversity Conservation and Management" Diversity 17, no. 3: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030198
APA StyleKeith, K. M., Potvin, M. K., Saad, S. R., & Surasinghe, T. D. (2025). Temporal Shifts in Biological Community Structure in Response to Wetland Restoration: Implications for Wetland Biodiversity Conservation and Management. Diversity, 17(3), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17030198






