Metagenomic Analysis of the Rhizosphere Microbiome of Poa alpigena in the Qinghai Lake Basin Grasslands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
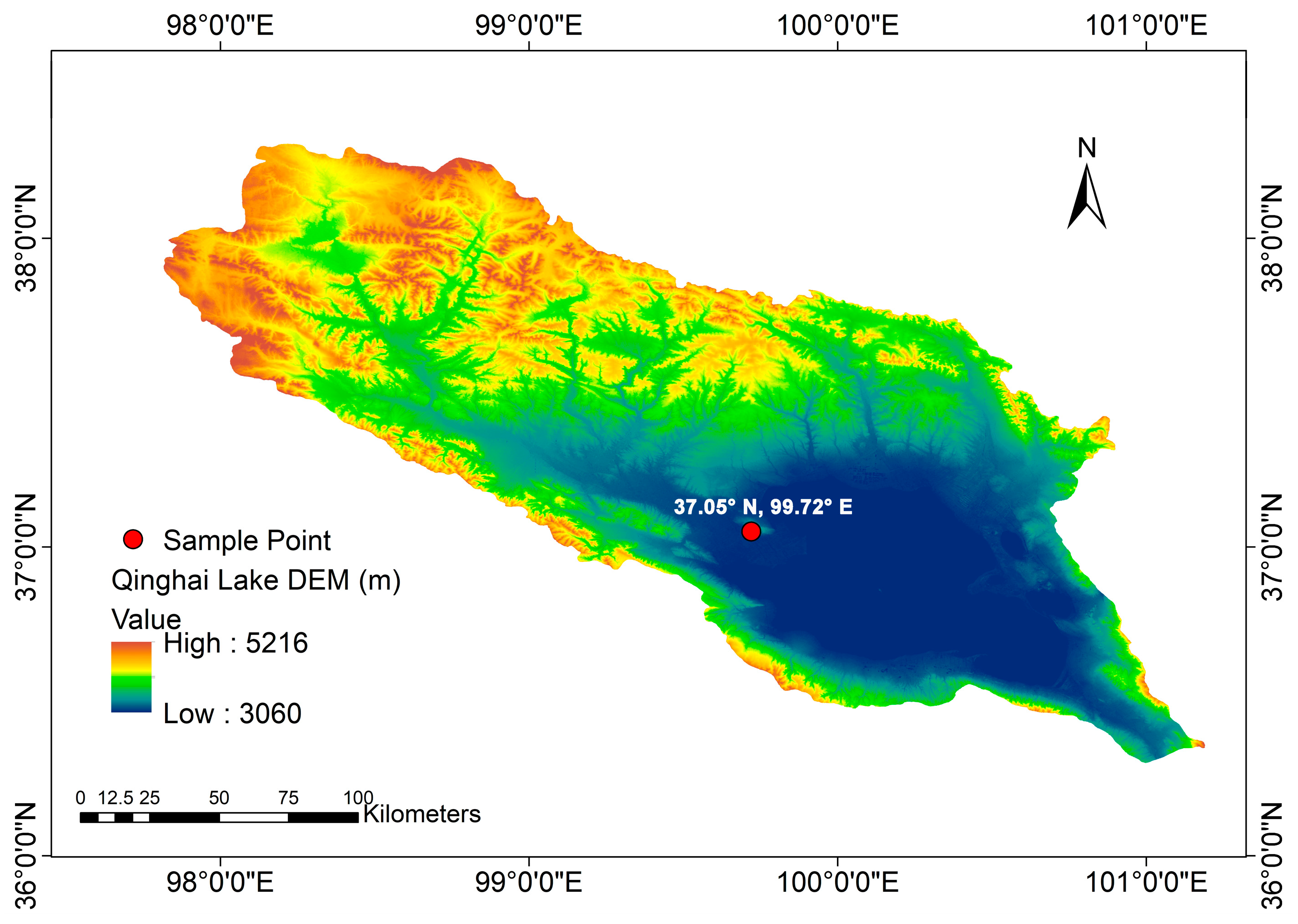
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Method and Treatment
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Quality Control of Sequencing Reads
2.3.2. Microbial Taxonomic Classification
2.3.3. Diversity Analysis
2.3.4. Metagenomic Assembly
2.3.5. Dominant Microorganisms and Metabolic Pathway Analysis
2.3.6. Data Upload and Sequencing Accession
2.3.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
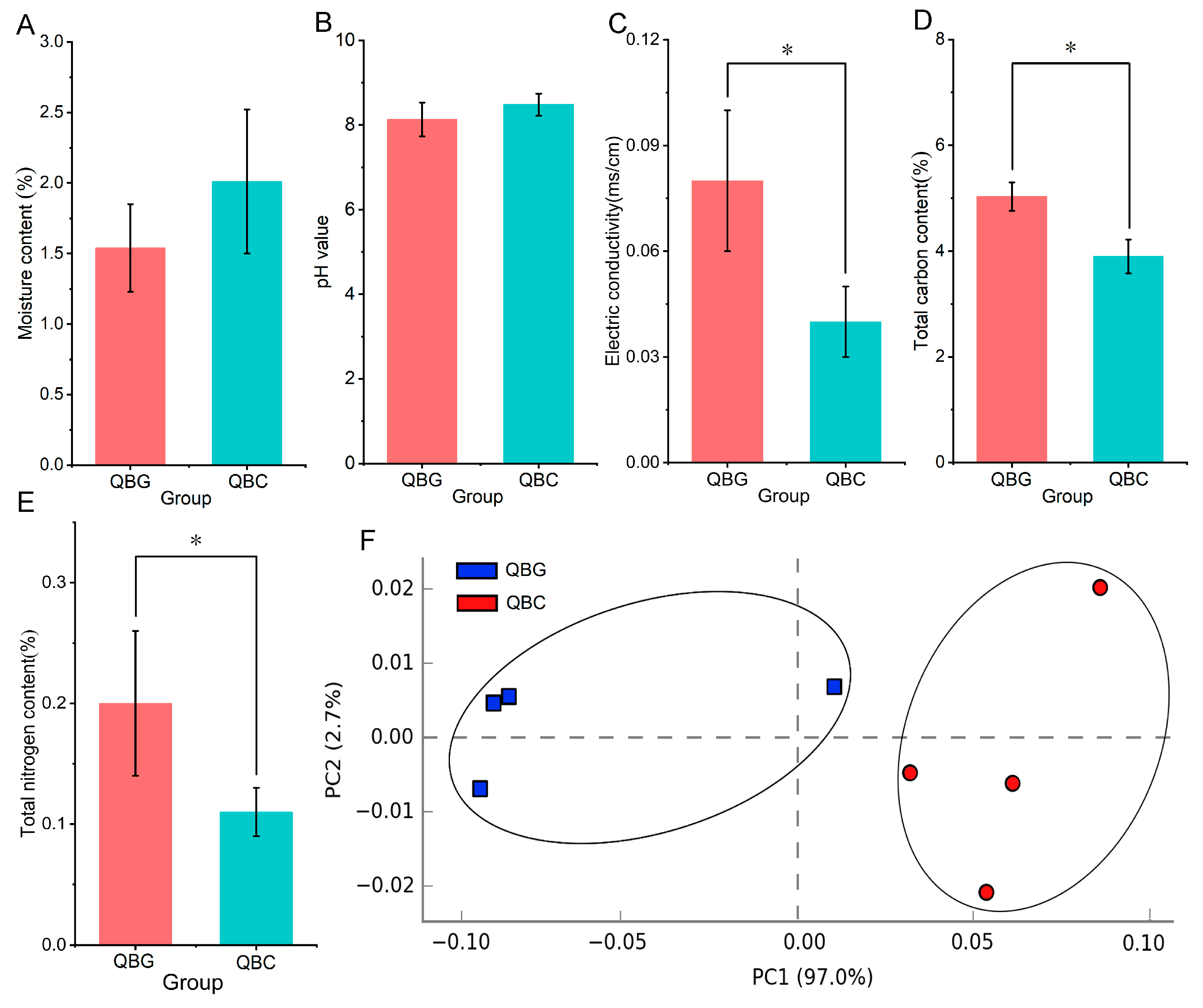
3.1. Heterogeneity Analysis of Physicochemical Indices in the Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil of Temperate Grassland
3.2. The Microbial Composition of Soil in Temperate Grassland Alpine Poa Pratensis
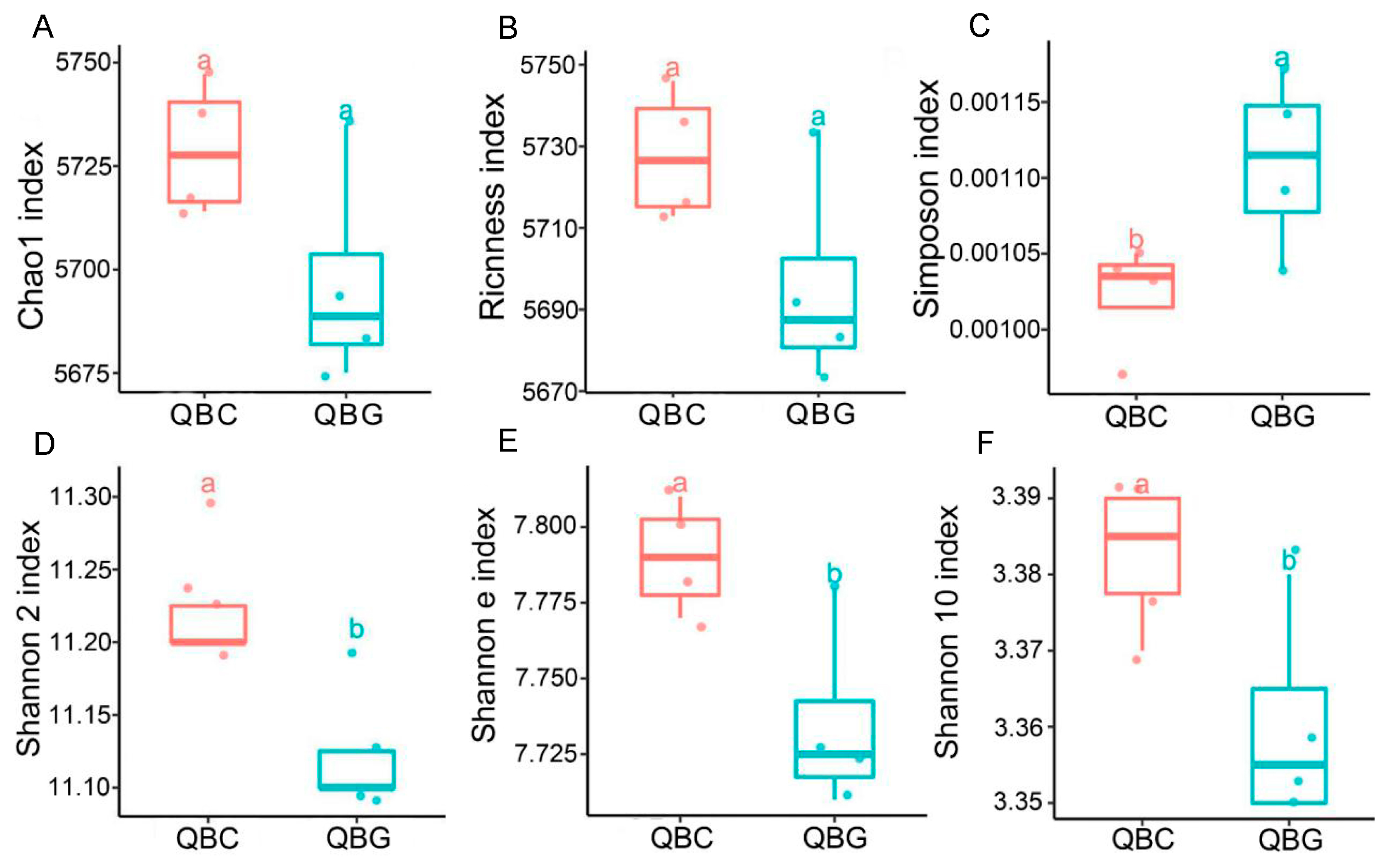
3.3. Analysis of α-Diversity of Microorganisms in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils of Temperate Grassland
3.4. Analysis of β-Diversity of Microorganisms in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils
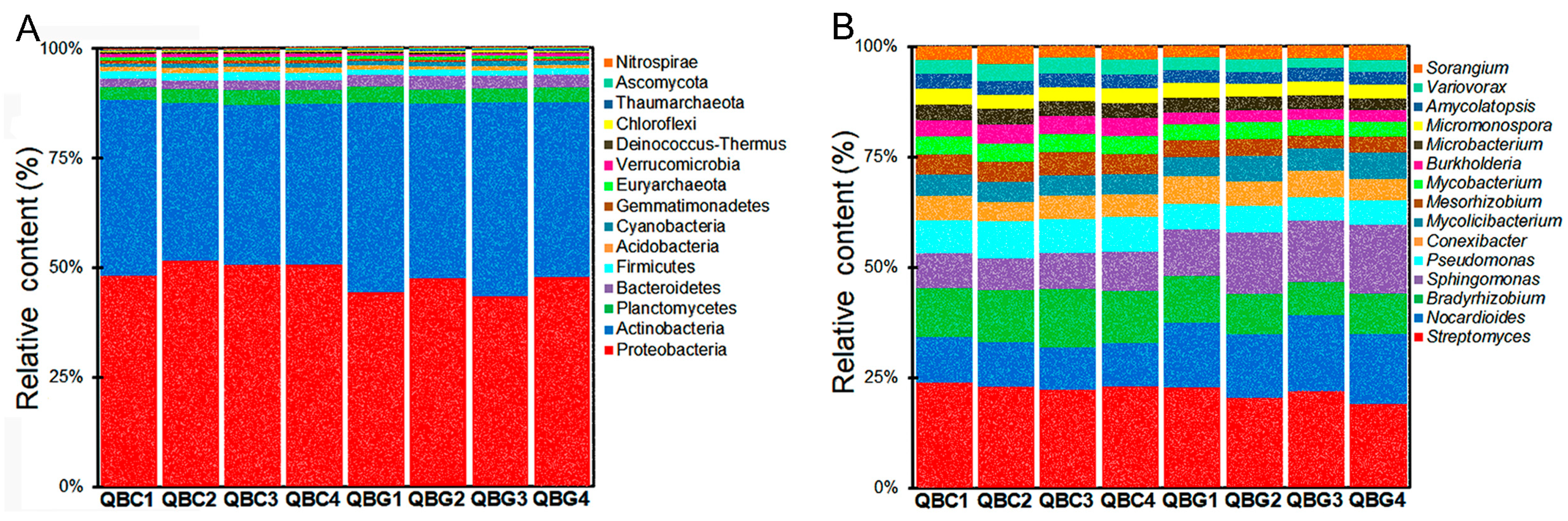
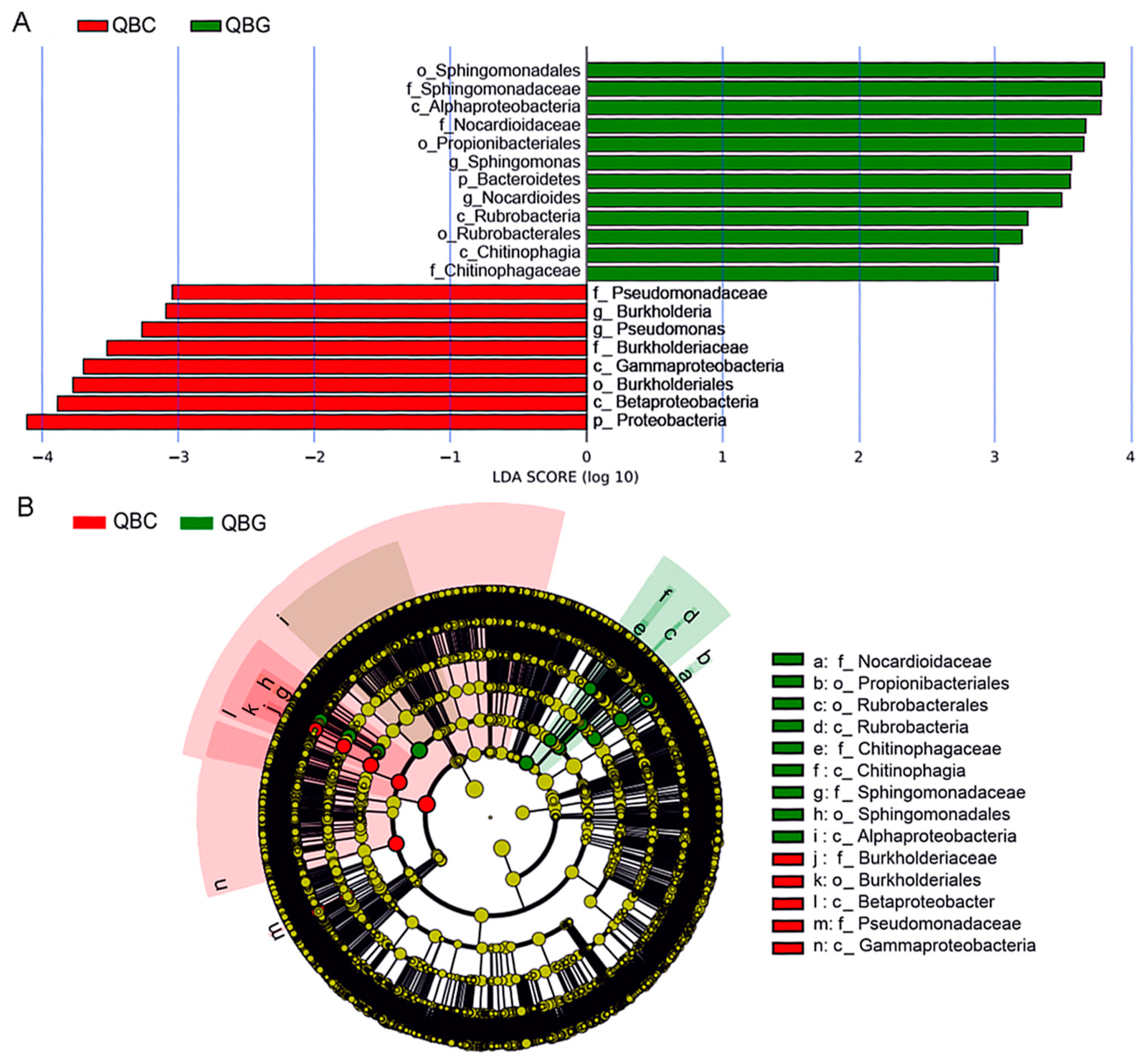
3.5. Dominant Microorganisms in Rhizosphere and Bulk Soils of Temperate Grassland
3.6. Dominant Microbial Taxa in Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils
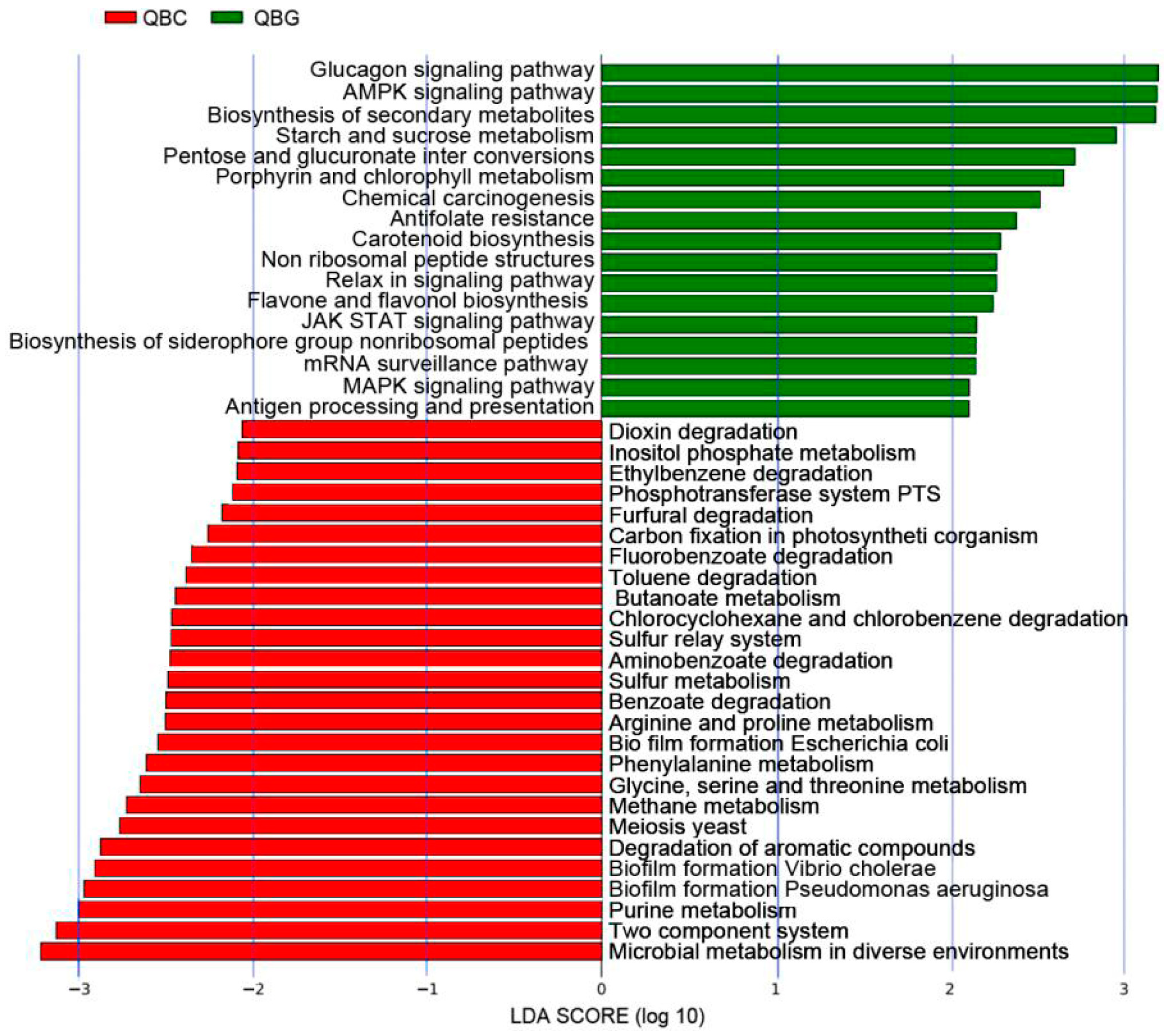
3.7. Differential Metabolic Pathways Between Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil Microorganisms
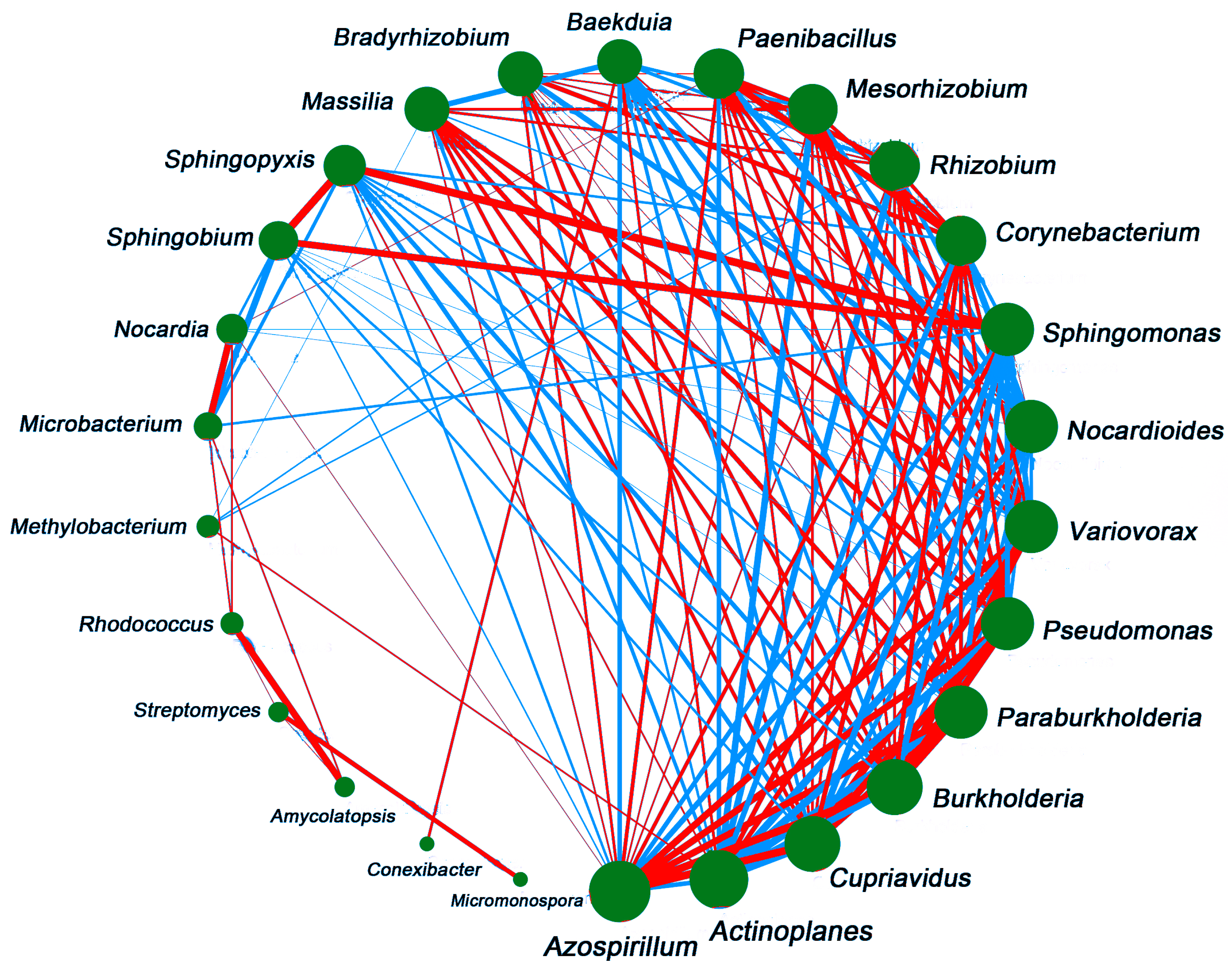
3.8. Correlation Analysis of Rhizosphere and Bulk Soil Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Differential Analysis of Rhizosphere Microorganisms of P. alpigena in the Temperate Grassland of Qinghai Lake
4.2. The Influence of Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soils on Microbial Metabolism
4.3. Soil Microbial Correlation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, M.; Geng, L. Monitoring the Recent Trend of Aeolian Desertification Using Landsat TM and Landsat 8 Imagery on the Northeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1753–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; He, K.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Wen, J. Trends, Abrupt Changes, and Periodicity of Streamflow in Qinghai Province, the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Guo, D.; Liang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, W.; Ma, H.; Yu, H.; Si, R. Shrinkage Deformation Law of Portland Cement in Tibetan Plateau Environment and Its Relationship with Standard Shrinkage and Calculation Model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 460, 139823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Moorsel, S.J.; Hahl, T.; Petchey, O.L.; Ebeling, A.; Eisenhauer, N.; Schmid, B.; Wagg, C. Co-Occurrence History Increases Ecosystem Stability and Resilience in Experimental Plant Communities. Ecology 2021, 102, e03205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, S.; Cao, G.; Lan, Y. Effects of Vegetation Phenology on Vegetation Productivity in the Qinghai Lake Basin of the Northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Ganjurjav, H.; Wang, X. Climate Change and Human Activities Altered the Diversity and Composition of Soil Microbial Community in Alpine Grasslands of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Yi, J.; Du, Y.; Wang, N.; Qian, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Human Digital Footprints and Exposure to Human Activities on Grassland Biomass in the Qinghai Lake Nature Reserve. Biodiversity 2022, 30, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, H.; Wu, F.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, X. Spatial Differentiation Patterns and Driving Forces of Ecosystem Services in the Qinghai Lake Basin. J. Ecol. Environ. 2024, 33, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, N.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, C.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Peñuelas, J.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Antibiotic-Resistance Genes and Viruses Released from Glaciers into Downstream Habitats. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Yan, W.; Wang, K. Interplanting Leguminous Shrubs Boosts the Trophic Interactions of Soil Micro-Food Web in a Karst Grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 188, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.; Cardoso, P.; Figueira, E.; Lopes, I.; Venâncio, C. Forward-Looking on New Microbial Consortia: Combination of Rot Fungi and Rhizobacteria on Plant Growth-Promoting Abilities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, A.M.; Anderson, J.L.; Meece, J.K. Detection of Blastomyces gilchristii via Metagenomic Sequencing in Outbreak-Associated Soils. Med. Mycol. 2024, 62, myad140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhuo, Z.; Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J. Response of Soil Microorganisms to Soil Fertility in the Process of Vegetation Rehabilitation of Degraded Pinus massoniana Forest. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 3477–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, M.R.; Badr, K.; Hassan, Z.U.; Al-Thani, R.; Jaoua, S. Metagenomic Approaches and Opportunities in Arid Soil Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.K.; Rahayu, F.; Alkahtani, A.M.; Alreshidi, M.A.; Yadav, K.K.; Parnidi, L.; Fauziah, L.; Murianingrum, M.; Akhtar, N.; Mufidah, E.; et al. Metagenomic Profiling of Rhizosphere Microbiota: Unraveling the Plant–Soil Dynamics. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 133, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Rincon, N.; Wood, D.E.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Pockrandt, C.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Steinegger, M. Metagenome analysis using the Kraken software suite. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 2815–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Huang, H.; Lv, J.; Xu, X.; Cao, D.; Rao, Z.; Geng, F.; Kang, Y. Unique dissolved organic matter molecules and microbial communities in rhizosphere of three typical crop soils and their significant associations based on FT-ICR-MS and high-throughput sequencing analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrone, A.; Lopez-Guerrero, M.; Yadav, P.; Meier, M.A.; Russo, S.E.; Weber, K.A. Interactions between root hairs and the soil microbial community affect the growth of maize seedlings. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Chakraborty, J.; Das, S. Underlying mechanism of plant–microbe crosstalk in shaping microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Dong, C.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Long, X.; Han, Y. Seed endophytes reshape rhizosphere microbiota to promote the growth of Eucommia ulmoides seedlings. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 201, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Y.; He, C.; Xiao, L.; Wang, N.; Jiang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Gu, Y.; et al. Diversity and composition of microbial communities in Jinsha earthen site under different degree of deterioration. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-J.; Nuerhamanti, N.; Bai, X.-Y.; Wang, H.-N.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Zhang, W. The composition and diversity of the rhizosphere bacterial community of Ammodendron bifolium growing in the Takeermohuer Desert are different from those in the nonrhizosphere. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 87, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laassami, A.; Yekkour, A.; Meklat, A.; Djemouai, N.; Zitouni, A.; Mokrane, S.; Lecomte, P.; Rey, P.; Berraf-Tebbal, A. Actinobacteria associated with vineyard soils of Algeria: Classification, antifungal potential against grapevine trunk pathogens and plant growth-promoting features. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2831–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Yu, M.; Shabala, S.; Shi, W. Nitrogen-loss and carbon-footprint reduction by plant-rhizosphere exudates. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiya, L.; Kumla, J.; Suwannarach, N.; Kiatsiriroat, T.; Lumyong, S. Isolation, characterization, and efficacy of actinobacteria associated with arbuscular mycorrhizal spores in promoting plant growth of chili (Capsicum flutescens L.). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubiec-Krzesniak, K.; Rajnisz-Mateusiak, A.; Guspiel, A.; Ziemska, J.; Solecka, J. Secondary metabolites of actinomycetes and their antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral properties. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Yang, M.; He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, H.; et al. α-Terpineol fumigation alleviates negative plant-soil feedbacks of Panax notoginseng via suppressing Ascomycota and enriching antagonistic bacteria. Phytopathol. Res. 2021, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.-I.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Kim, H.S. Paclitaxel suppresses the viability of breast tumor MCF7 cells through the regulation of EF1α and FOXO3a by AMPK signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tang, P.; Li, H.-J.; Hu, N.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Lin, M.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Lu, M.; Lu, X. Serum from Jiao-Tai-Wan treated rats increases glucose consumption by 3T3-L1 adipocytes through AMPK pathway signaling. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Daròs, J.-A. Transient expression systems to rewire plant carotenoid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 66, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; He, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Sun, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Deng, Y.; Hou, C. The expression profile of genes related to carotenoid biosynthesis in pepper under abiotic stress reveals a positive correlation with plant tolerance. Life 2024, 14, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Anoop, C.; Nongthomba, U. What a tangled web we weave: Crosstalk between JAK–STAT and other signalling pathways during development in Drosophila. FEBS J. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Wen, H.; Qi, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; Li, Y. Comprehensive genome-wide identification and functional characterization of mapk gene family in northern snakeheads (Channa argus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 157, 110076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contos, P.; Gibb, H.; Murphy, N.P.; Jellinek, S.; Wood, J.L. Rebuilding microbiomes: Facilitating animal-microbe interactions through ecological restoration and rewilding. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Comparative genomic analysis reveals the environmental impacts on two Arcticibacter strains including sixteen Sphingobacteriaceae species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.-Q.; Lu, G.-N.; Dang, Z.; Yang, C.; Yi, X.-Y. A phenanthrene-degrading strain Sphingomonas sp. GY2B isolated from contaminated soils. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wen, Z.; Li, S.; Ren, Y.; Nan, T.; Li, X. Remediation of aniline-contaminated aquifer by combining in-well Rhizobium borbori and circulated groundwater electrolysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Duan, C.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L. Co-inoculation effect of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and Rhizobium on EDDS-assisted phytoremediation of Cu-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.-G.; Kong, C.-C.; Wang, S.-X.; Xie, Z.-H. Enhanced phytoremediation of uranium-contaminated soils by arbuscular mycorrhiza and Rhizobium. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Lü, H.; Zhao, H.-M.; Xiang, L.; Li, H.; Mo, C.-H.; Li, Y.-W.; Cai, Q.-Y.; et al. Root-associated bacteria strengthen their community stability against disturbance of antibiotics on structure and functions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patani, A.; Patel, M.; Islam, V.K.Y.; Prajapati, D.; Yadav, A.N.; Sahoo, D.K.; Patel, A. Recent advances in Bacillus-mediated plant growth enhancement: A paradigm shift in redefining crop resilience. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizoglu, U. Bacillus thuringiensis as a biofertilizer and biostimulator: A mini-review of the little-known plant growth-promoting properties of Bt. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xu, Q.; Kong, J.; Su, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, H. Metagenomics-based study of rhizospheric microorganisms of Poa alpigena L. in Qinghai Lake, Ganzi River Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1518637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Project | QBC | QBG |
|---|---|---|
| Number of clean reads | 36,920,777.00 ± 8354.47 a | 37,091,595.50 ± 836,079.71 a |
| Unclassified reads (%) | 57.86 ± 0.57 a | 55.37 ± 0.57 b |
| Classified reads (%) | 42.15 ± 0.57 b | 44.63 ± 0.57 a |
| Chordate reads (%) | 5.97 ± 0.03 b | 6.42 ± 0.62 a |
| Microbial reads (%) | 36.03 ± 0.61 b | 38.07 ± 1.15 a |
| Bacterial reads (%) | 28.56 ± 0.59 b | 30.14 ± 1.62 a |
| Fungal reads (%) | 0.15 ± 0.001 a | 0.16 ± 0.004 a |
| Viral reads (%) | 1.33 ± 0.002 a | 1.38 ± 0.045 a |
| Protozoan reads (%) | 0.17 ± 0.002 a | 0.19 ± 0.024 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Ji, W.; Chen, K. Metagenomic Analysis of the Rhizosphere Microbiome of Poa alpigena in the Qinghai Lake Basin Grasslands. Diversity 2025, 17, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040266
Mao Y, Zhu S, Wang H, Ji W, Chen K. Metagenomic Analysis of the Rhizosphere Microbiome of Poa alpigena in the Qinghai Lake Basin Grasslands. Diversity. 2025; 17(4):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040266
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Yahui, Shuchang Zhu, Hengsheng Wang, Wei Ji, and Kelong Chen. 2025. "Metagenomic Analysis of the Rhizosphere Microbiome of Poa alpigena in the Qinghai Lake Basin Grasslands" Diversity 17, no. 4: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040266
APA StyleMao, Y., Zhu, S., Wang, H., Ji, W., & Chen, K. (2025). Metagenomic Analysis of the Rhizosphere Microbiome of Poa alpigena in the Qinghai Lake Basin Grasslands. Diversity, 17(4), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/d17040266






