A Bio-Inspired Polarization Sensor with High Outdoor Accuracy and Central-Symmetry Calibration Method with Integrating Sphere
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bio-Sensor for Navigation
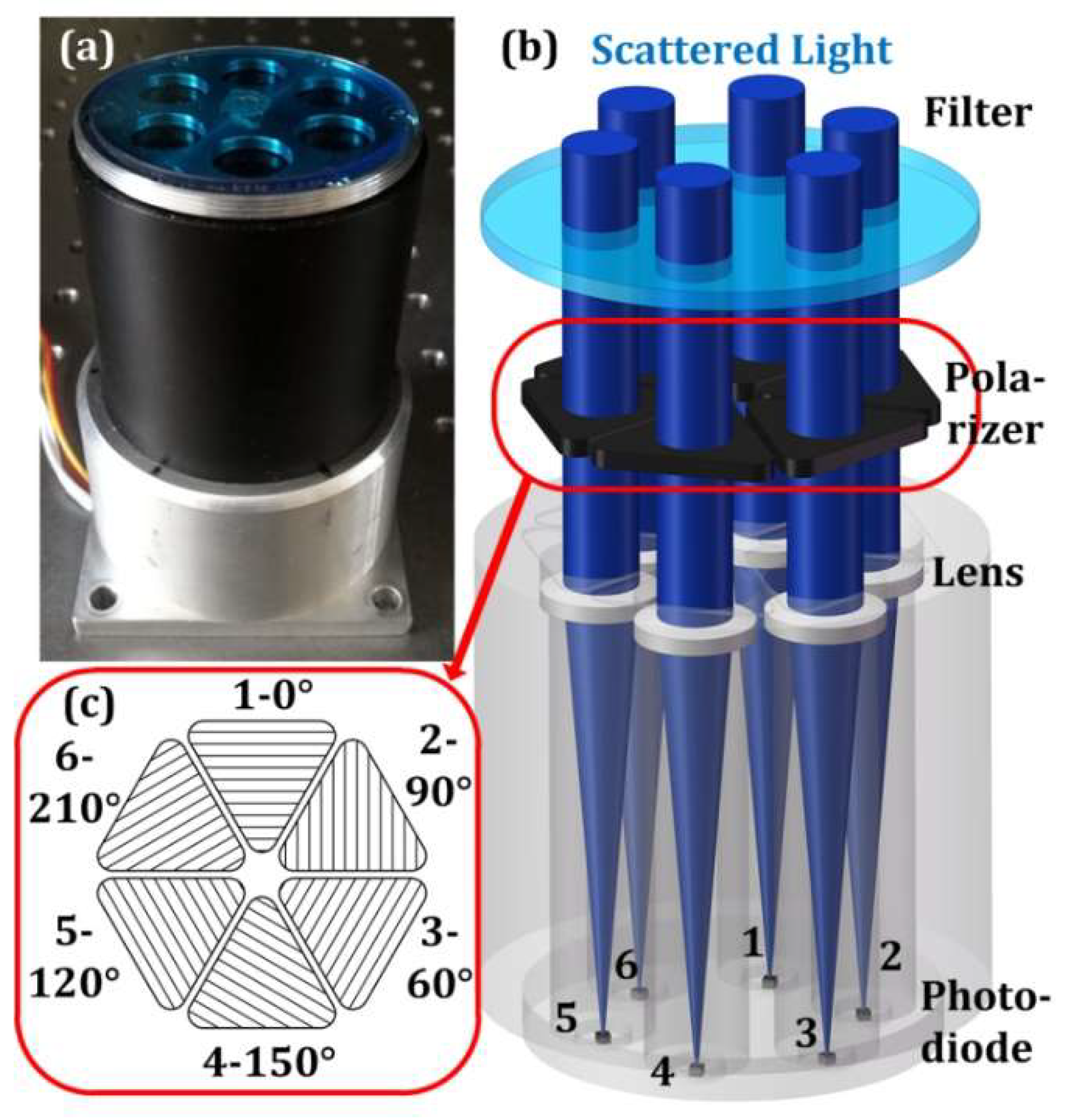
2.1. Structure
2.2. Polarization Angle Calculation
2.3. Section Algorithm
2.4. Accuracy Limit for Different d Values
3. Calibration Method
3.1. Central-Symmetry Method with Integrating Sphere
3.2. Simulation of the Central-Symmetry Method
3.3. Noncontinuous Method
3.4. Calibration Parameters
3.5. Decoupling Method for Calibration Parameters
4. Indoor Results
4.1. Calibration Device
4.2. Section-Only Algorithm
4.3. Adding the (Integrating-Sphere) Central-Symmetry Method
4.4. Adding the Noncontinuous Method
4.5. Comparison of Three Calibration Methods
4.6. Analysis of Four Calibration Parameters
5. Outdoor Results
5.1. Static Outdoor Experiments
5.2. Dynamic Outdoor Experiments
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cochran, W.W.; Mouritsen, H.; Wikelski, M. Migrating songbirds recalibrate their magnetic compass daily from twilight cues. Science 2004, 304, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muheim, R.; Phillips, J.B.; Akesson, S. Polarized light cues underlie compass calibration in migratory songbirds. Science 2006, 313, 837–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, I.M.; How, M.J.; Partridge, J.C.; Temple, S.E.; Marshall, N.J.; Cronin, T.W.; Roberts, N.W. Dynamic polarization vision in mantis shrimps. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, S.; Mangan, M.; Zeil, J.; Webb, B.; Wystrach, A. How Ants Use Vision When Homing Backward. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrinos, D.; Moller, R.; Labhart, T.; Pfeifer, R.; Wehner, R. A mobile robot employing insect strategies for navigation. Rob. Auton. Syst. 2000, 30, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Zhao, K. Study of Angle Measure Optoelectronic Model on Emulating Polarization-Sensitive Compound Eye of Insect. Nanoelectron. Device Technol. 2005, 12, 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T. Construction and performance test of a novel polarization sensor for navigation. Sens. Actuators A 2008, 148, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labhart, T.; Meyer, E.P. Detectors for polarized skylight in insects: A survey of ommatidial specializations in the dorsal rim area of the compound eye. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 1999, 47, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Z.; Hu, X.; Lian, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T. A Novel Angle Computation and Calibration Algorithm of Bio-Inspired Sky-Light Polarization Navigation Sensor. Sensors 2014, 14, 17068–17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; He, X. Calibration of a polarization navigation sensor using the NSGA-II algorithm. Opt. Commun. 2016, 376, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, W. A Bionic Polarization Navigation Sensor and Its Calibration Method. Sensors 2016, 16, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Du, T.; Niu, B.; Li, C.; Qian, J.; Guo, L. A Bionic Polarization Navigation Sensor Based on Polarizing Beam Splitter. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11472–11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupeyroux, J.; Diperi, J.; Boyron, M.; Viollet, S.; Serres, J. A novel insect-inspired optical compass sensor for a hexapod walking robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 3439–3445. [Google Scholar]
- Dupeyroux, J.; Viollet, S.; Serres, J. Polarized skylight-based heading measurements: A bio-inspired approach. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20180878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupeyroux, J.; Serres, J.; Viollet, S. AntBot: A six-legged walking robot able to home like desert ants in outdoor environments. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaau0307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, T.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Multiple Disturbance Analysis and Calibration of an Inspired Polarization Sensor. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58507–58518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serres, J.R.; Viollet, S. Insect-inspired vision for autonomous vehicles. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2018, 30, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suhai, B.; Horvath, G. How well does the Rayleigh model describe the E-vector distribution of skylight in clear and cloudy conditions? A full-sky polarimetric study. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2004, 21, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. A novel autonomous real-time position method based on polarized light and geomagnetic field. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, R.; Shi, C. Orthogonal vector algorithm to obtain the solar vector using the single-scattering Rayleigh model. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Chu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. A Novel Attitude Determination System Aided by Polarization Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaz, D.; Farkas, A.; Barta, A.; Kretzer, B.; Blaho, M.; Egri, A.; Szabo, G.; Horvath, G. Accuracy of the hypothetical sky-polarimetric Viking navigation versus sky conditions: Revealing solar elevations and cloudinesses favourable for this navigation method. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 473, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, G.; Takacs, P.; Kretzer, B.; Szilasi, S.; Szaz, D.; Farkas, A.; Barta, A. Celestial polarization patterns sufficient for Viking navigation with the naked eye: Detectability of Haidinger’s brushes on the sky versus meteorological conditions. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 160688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Száz, D.; Horváth, G. Success of sky-polarimetric Viking navigation: Revealing the chance Viking sailors could reach Greenland from Norway. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 172187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, K.; You, Z.; Huang, K. Angle algorithm based on Hough transform for imaging polarization navigation sensor. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 7248–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Hu, X.; Lian, J.; Zhang, L.; He, X. Design and Calibration of a Novel Camera-Based Bio-Inspired Polarization Navigation Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 3640–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, K.; You, Z.; Huang, K. Real-time polarization imaging algorithm for camera-based polarization navigation sensors. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3199–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ning, Y. Angle of sky light polarization derived from digital images of the sky under various conditions. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Hu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Lian, J. Integrated Polarized Skylight Sensor and MIMU With a Metric Map for Urban Ground Navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Lin, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. Design and realization of bionic polarized light navigation sensor based on MSP430. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2012, 31, 107–110, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Pust, N.J.; Shaw, J.A. Digital all-sky polarization imaging of partly cloudy skies. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, T.; Manea, V. Symmetry between partially polarised light and partial polarisers in the vectorial Pauli algebraic formalism. J. Mod. Optic. 2011, 58, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




























| Variable | Annotation |
|---|---|
| Vi_ideal | Theoretical voltages, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| Vi_AD | Theoretical voltages of 16-bit ADC, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| Vref | Reference voltage for logarithmic amplifier |
| Vi | Voltages, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| Vimr | Voltages obtained using the central-symmetry method, also mean values of Vibr and Viar, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| Vinc | Voltages obtained using the noncontinuous method, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| Vbr | Voltage before 180° rotation |
| Var | Voltage after 180° rotation |
| Vicf | Theoretical voltages calculated by the calibration parameters in Equation (21) |
| θ | Polarization angle |
| θ12, θ13, θ23 | Polarization angles from three voltages |
| θR | Rotational angle of precise rotary table in simulation |
| θsec | Polarization angle obtained using the section algorithm |
| d | Polarization degree |
| dcm | Polarization degree obtained using the iterative least-squares estimation method, m ∈ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] |
| da | Polarization degree determined by the authors |
| OIS | Center of integrating sphere |
| OS | Center of polarization sensor |
| OR | Center of rotary table |
| Lo | Length between the port and the photosensitive surface |
| Eo | Irradiance at the center |
| Ee | Irradiance at the off-axis edge |
| E1, E2, E’1, E’2 | Irradiance at Point 1, 2, 1’, 2’ |
| Lphoto | Length between OS and the photosensitive surface |
| αIS | Eccentric angle between OR and OIS |
| αS | Eccentric angle between OR and OS |
| LIS | Eccentric distance between OR and OIS |
| LS | Eccentric distance between OR and OS |
| LR1 | Eccentric distance between OR and Point 1 |
| LR2 | Eccentric distance between OR and Point 2 |
| L1, L2, L1’, L2’ | Off-axis distance between OIS and Point 1, 2, 1’, 2’ |
| BSD | Standard deviation of a 360° range before the central-symmetry method is used |
| ASD | Standard deviation of a 360° range after the central-symmetry method is used |
| gup | Gain of unpolarized light |
| gtp | Gain of totally polarized light |
| τM | Transmittance when the reference angle and main polarization angle of incident light are parallel |
| τm | Transmittance when the reference angle and main polarization angle of incident light are orthogonal |
| τf | Transmittance of blue filter |
| Ein | Irradiance of incident light |
| Ep | Irradiance at photodiode |
| sr | Spectral responsivity of photodiode |
| Ar | Active area size of photodiode |
| kci | Constant value generated by the integrating sphere method, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| ki | Additive coefficient of calibration, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| kvi | Deviation parameter of reference voltage of logarithmic amplifier, i ∈ [1, 2, 3] |
| kdm | Coefficient of non-ideal polarizer, m ∈ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] |
| αm | Installation angles of polarizer, m ∈ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] |
| Parameter | Theory | Indoor | Outdoor1 | Outdoor2 | Sun1 | Sun2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α1 (°) | 0 | 0.7554 | 0.7813 | 0.9189 | 0.7887 | 0.9344 |
| α2 (°) | 0 | 0.5500 | 0.8017 | 0.4385 | 0.8236 | 0.4540 |
| α3 (°) | −120 | −117.6462 | −117.8128 | −118.0658 | −117.7964 | −118.0503 |
| α4 (°) | −120 | −116.5699 | −116.3585 | −116.3233 | −116.3421 | −116.3078 |
| α5 (°) | 120 | 123.0730 | 123.3667 | 122.9320 | 123.3727 | 122.9510 |
| α6 (°) | 120 | 120.6994 | 120.6410 | 120.6542 | 120.6634 | 120.6634 |
| k1 (mV) | 0 | −10.1519 | −7.4487 | −7.8456 | −7.4461 | −7.8455 |
| k2 (mV) | 0 | 7.9230 | 8.8675 | 9.3682 | 8.8674 | 9.3681 |
| k3 (mV) | 0 | −9.4542 | −18.5845 | −18.7583 | −18.5778 | −18.7604 |
| kd1 | 0 | −0.0438 | −0.0229 | −0.0277 | −0.0203 | −0.0246 |
| kd2 | 0 | −0.0365 | −0.0074 | −0.0153 | −0.0100 | −0.0158 |
| kd3 | 0 | −0.0457 | −0.0118 | −0.0050 | −0.0127 | −0.0086 |
| kd4 | 0 | −0.0492 | −0.0255 | −0.0163 | −0.0217 | −0.0166 |
| kd5 | 0 | −0.0555 | −0.0151 | −0.0179 | −0.0136 | −0.0140 |
| kd6 | 0 | −0.0166 | −0.0137 | −0.0217 | −0.0134 | −0.0172 |
| kv1 | 1 | 1.0224 | 1.0064 | 1.0119 | 1.0066 | 1.0119 |
| kv2 | 1 | 1.0081 | 1.0135 | 1.0029 | 1.0135 | 1.0029 |
| kv3 | 1 | 1.0183 | 1.0070 | 1.0125 | 1.0054 | 1.0073 |
| da | ----- | 0.5500 | 0.6550 | 0.7100 | 0.6600 | 0.7150 |
| Origin-Accuracy (°) | ----- | ±0.0088 | ±0.0177 | ±0.0140 | ±0.0207 | ±0.0119 |
| Accuracy (°) | ----- | ±0.009 | ±0.018 | ±0.014 | ±0.021 | ±0.012 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Lin, M. A Bio-Inspired Polarization Sensor with High Outdoor Accuracy and Central-Symmetry Calibration Method with Integrating Sphere. Sensors 2019, 19, 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163448
Wang Y, Chu J, Zhang R, Li J, Guo X, Lin M. A Bio-Inspired Polarization Sensor with High Outdoor Accuracy and Central-Symmetry Calibration Method with Integrating Sphere. Sensors. 2019; 19(16):3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163448
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yinlong, Jinkui Chu, Ran Zhang, Jinshan Li, Xiaoqing Guo, and Muyin Lin. 2019. "A Bio-Inspired Polarization Sensor with High Outdoor Accuracy and Central-Symmetry Calibration Method with Integrating Sphere" Sensors 19, no. 16: 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163448
APA StyleWang, Y., Chu, J., Zhang, R., Li, J., Guo, X., & Lin, M. (2019). A Bio-Inspired Polarization Sensor with High Outdoor Accuracy and Central-Symmetry Calibration Method with Integrating Sphere. Sensors, 19(16), 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163448





