A Low-Cost Strain Gauge Displacement Sensor Fabricated via Shadow Mask Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
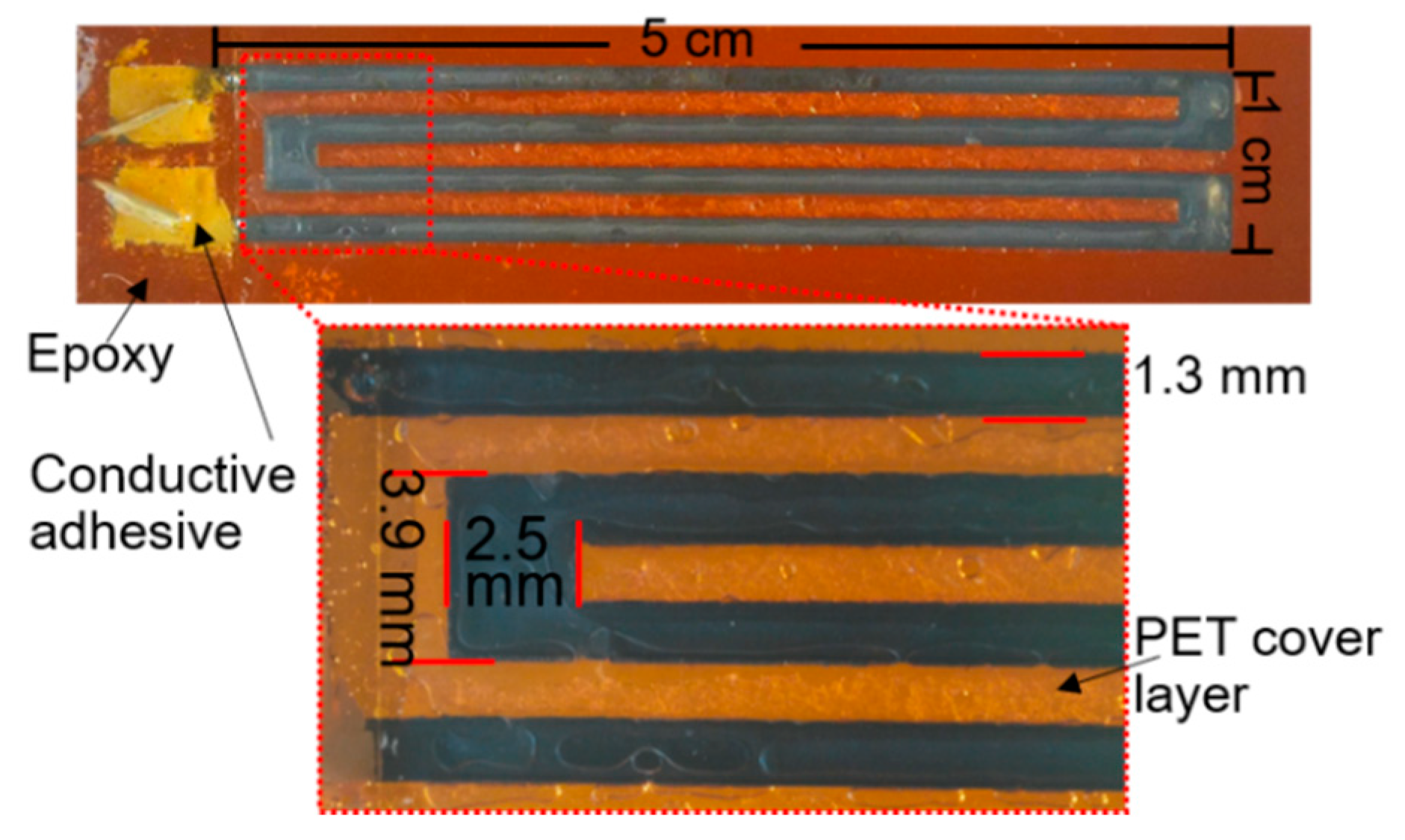
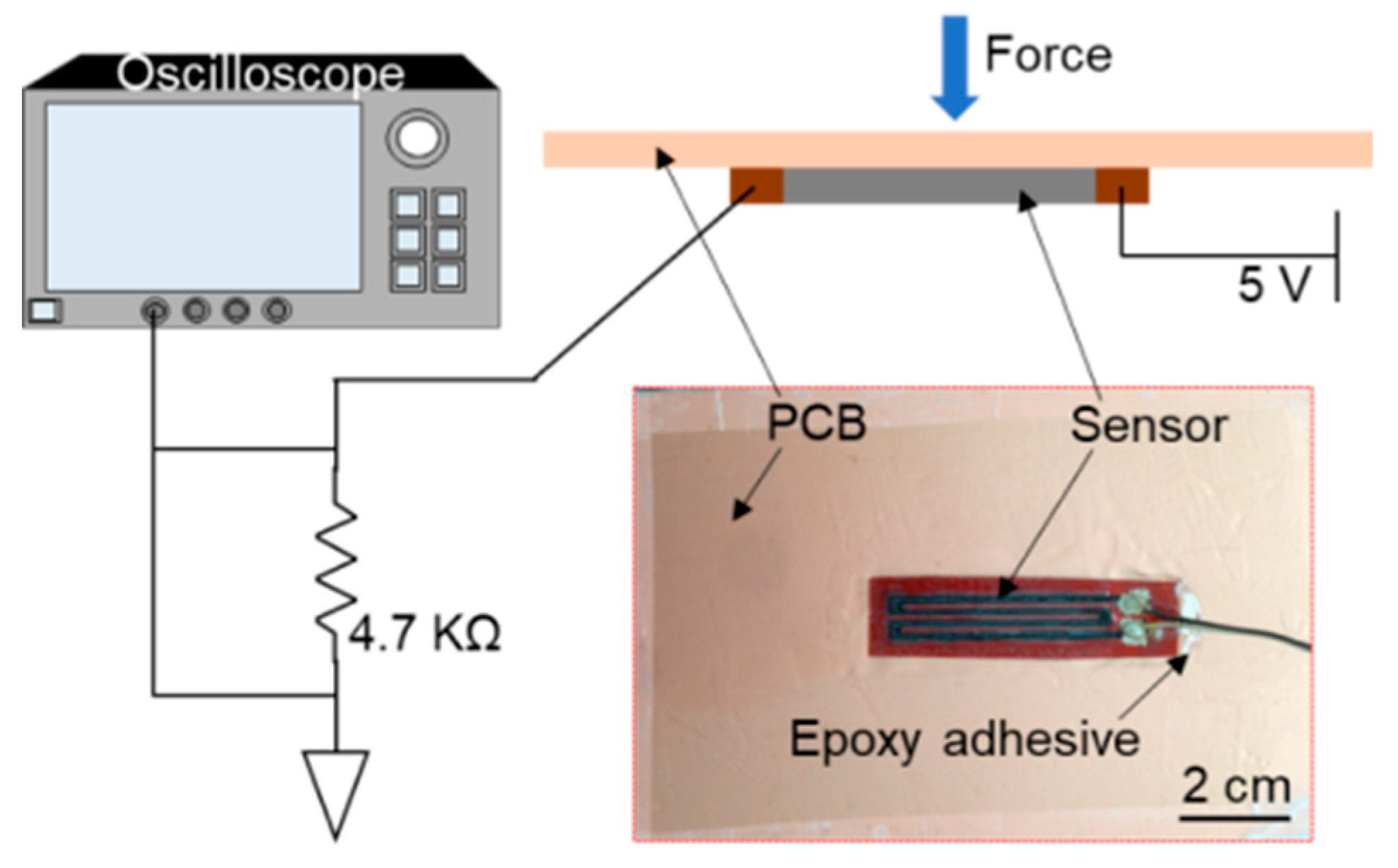
2. Materials and Fabrication
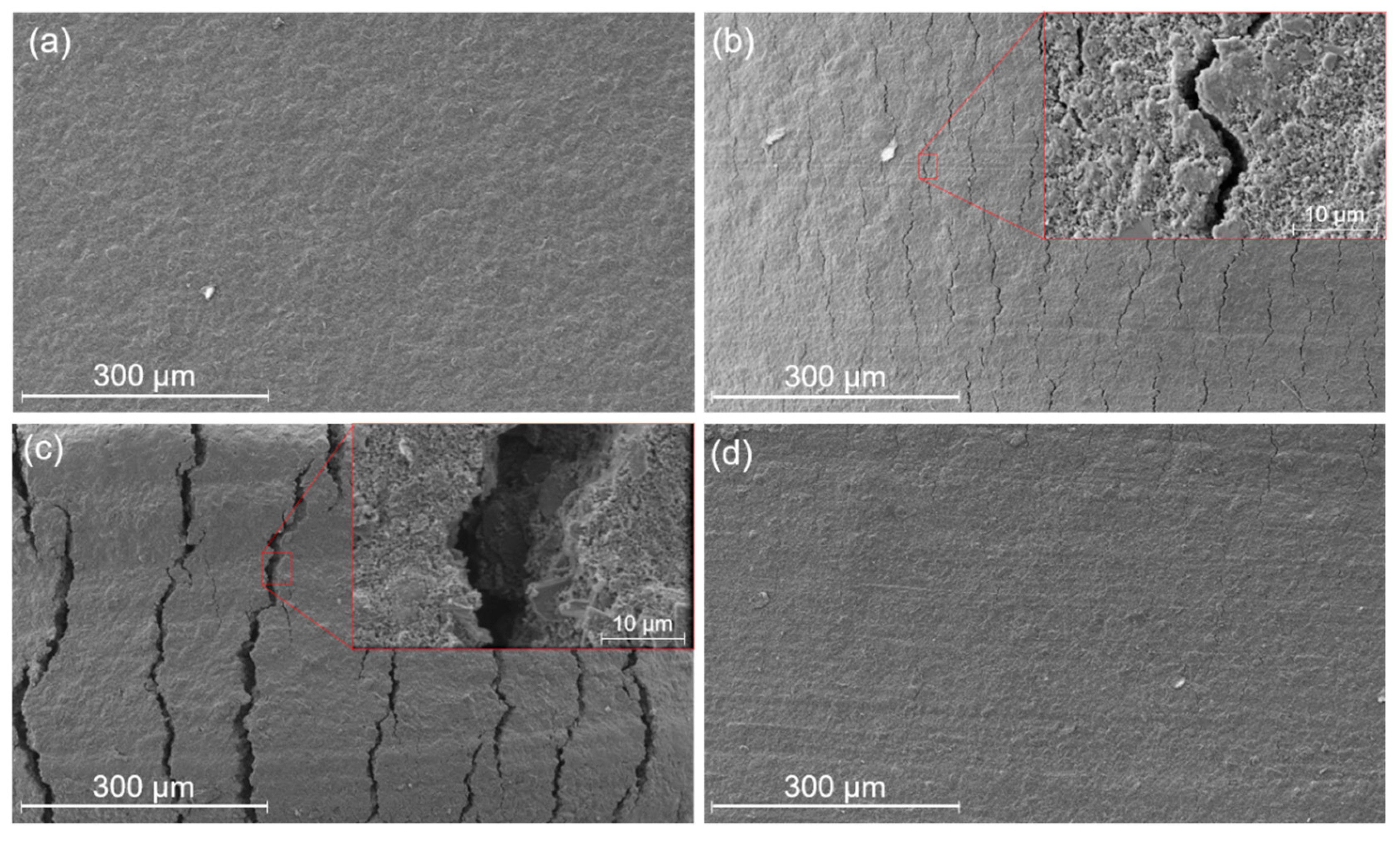
3. Working Principle and Characterization of the Fabricated Sensor
3.1. Working Principle
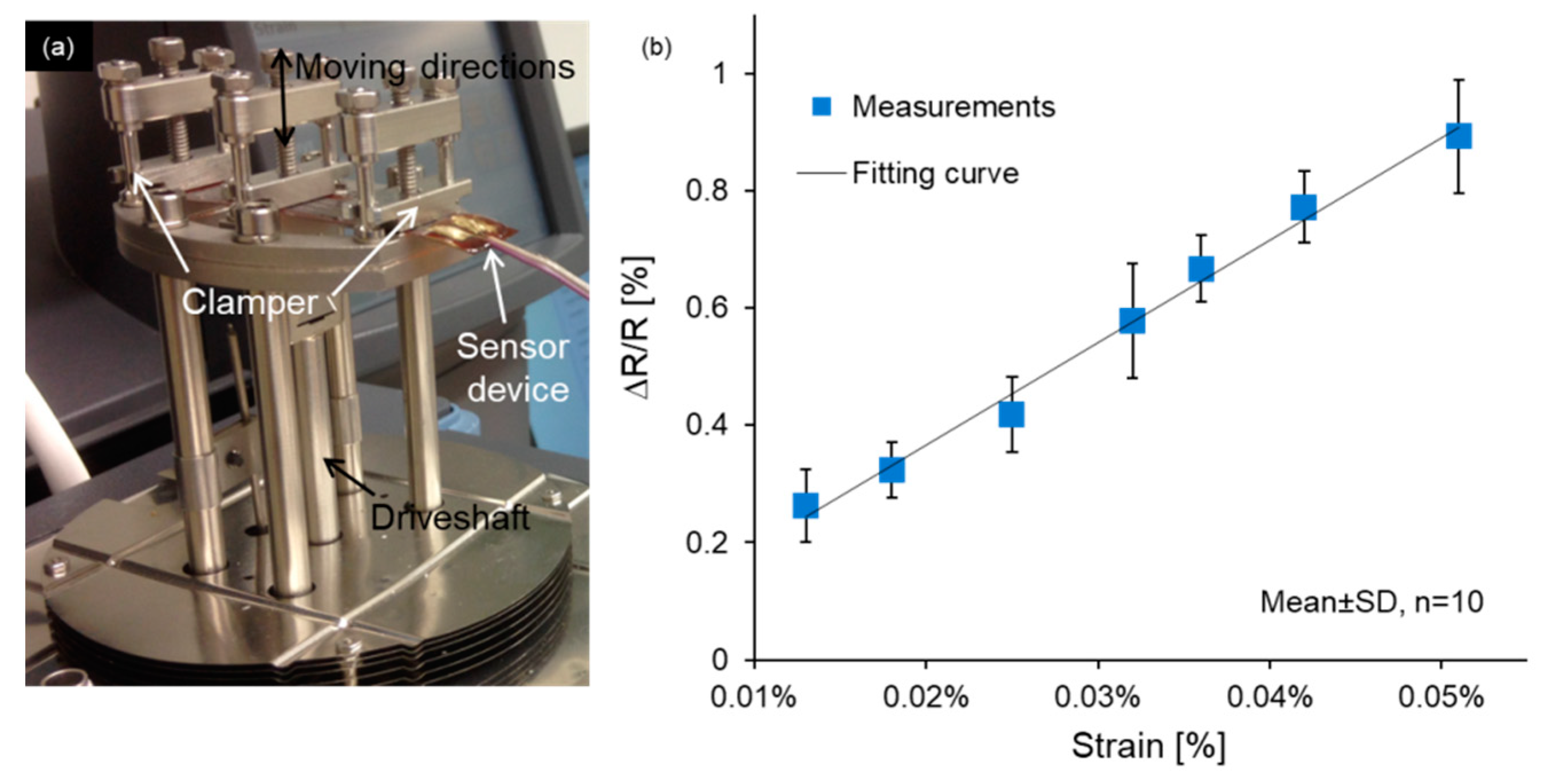
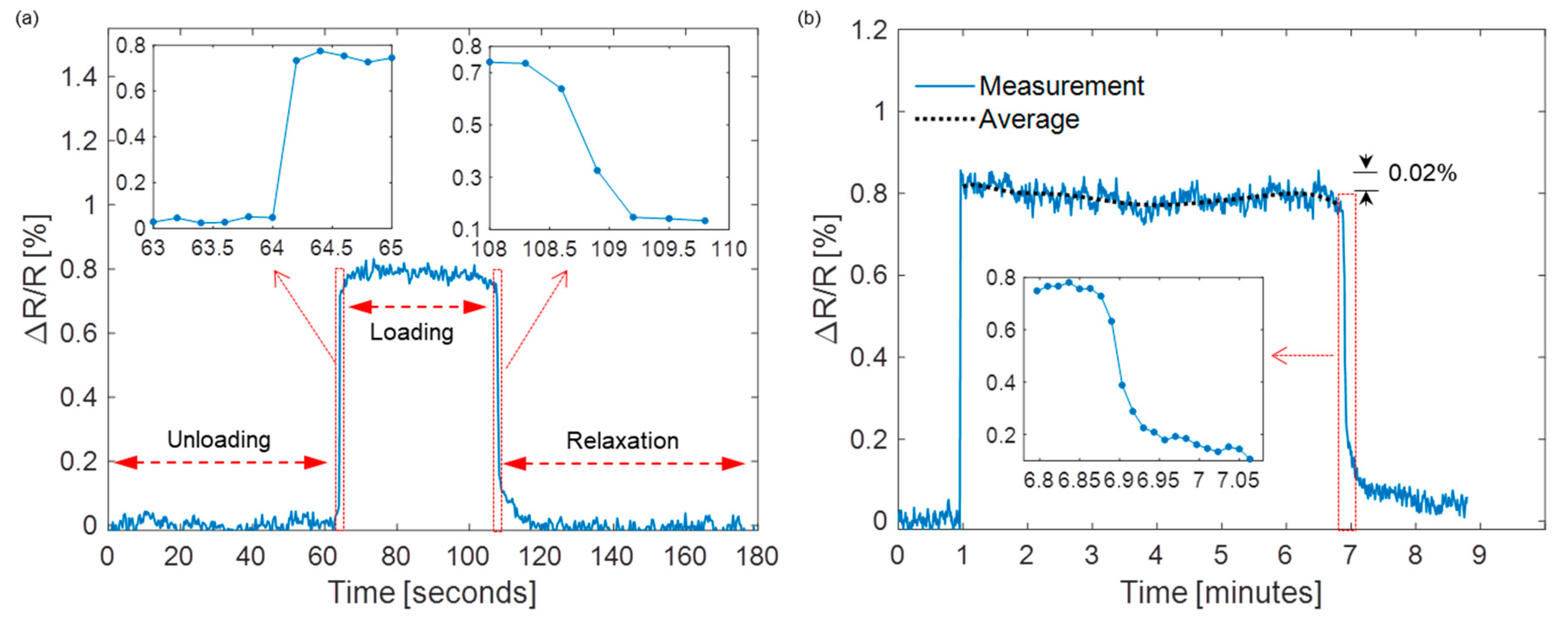
3.2. Device Characterization
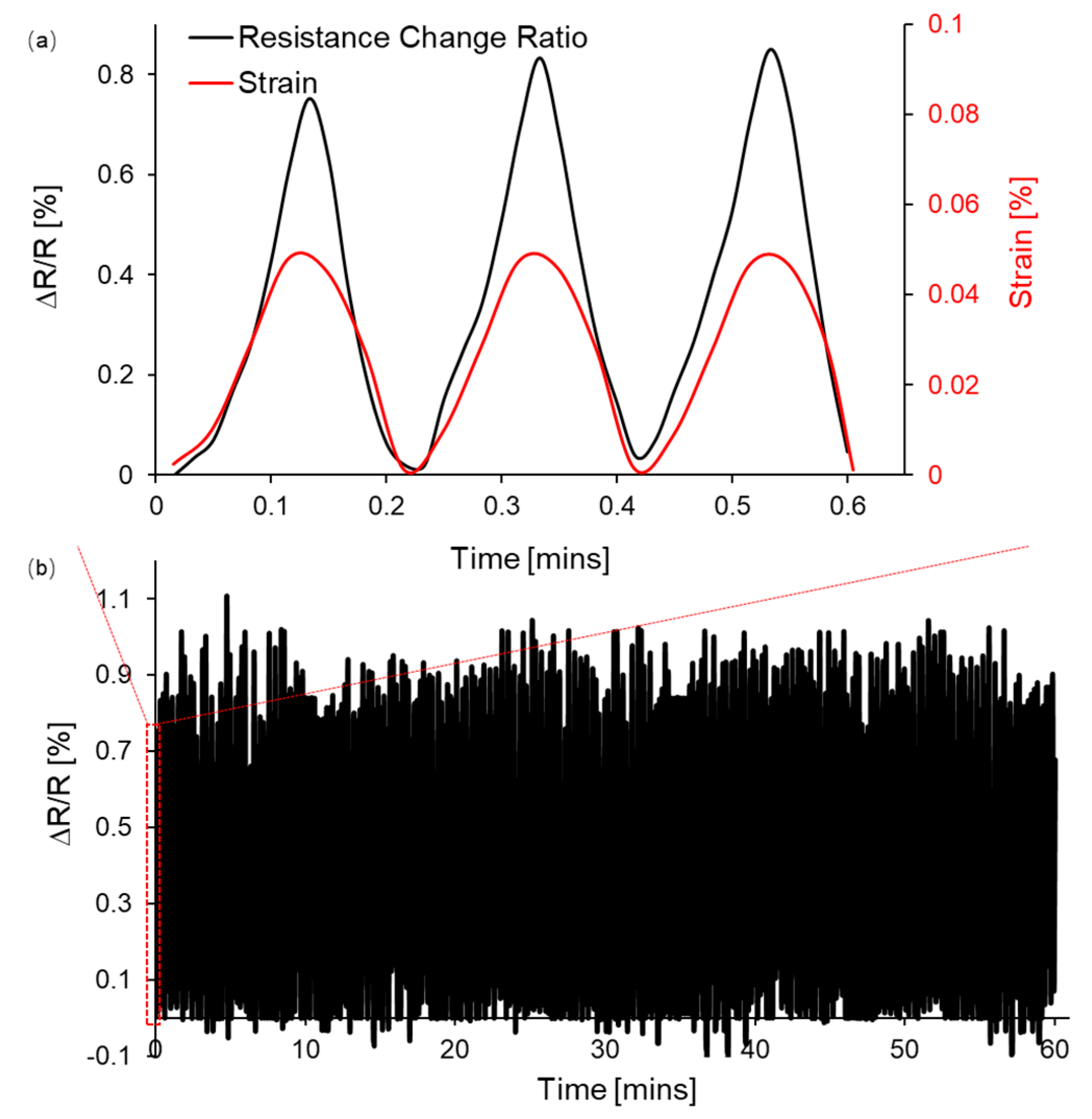
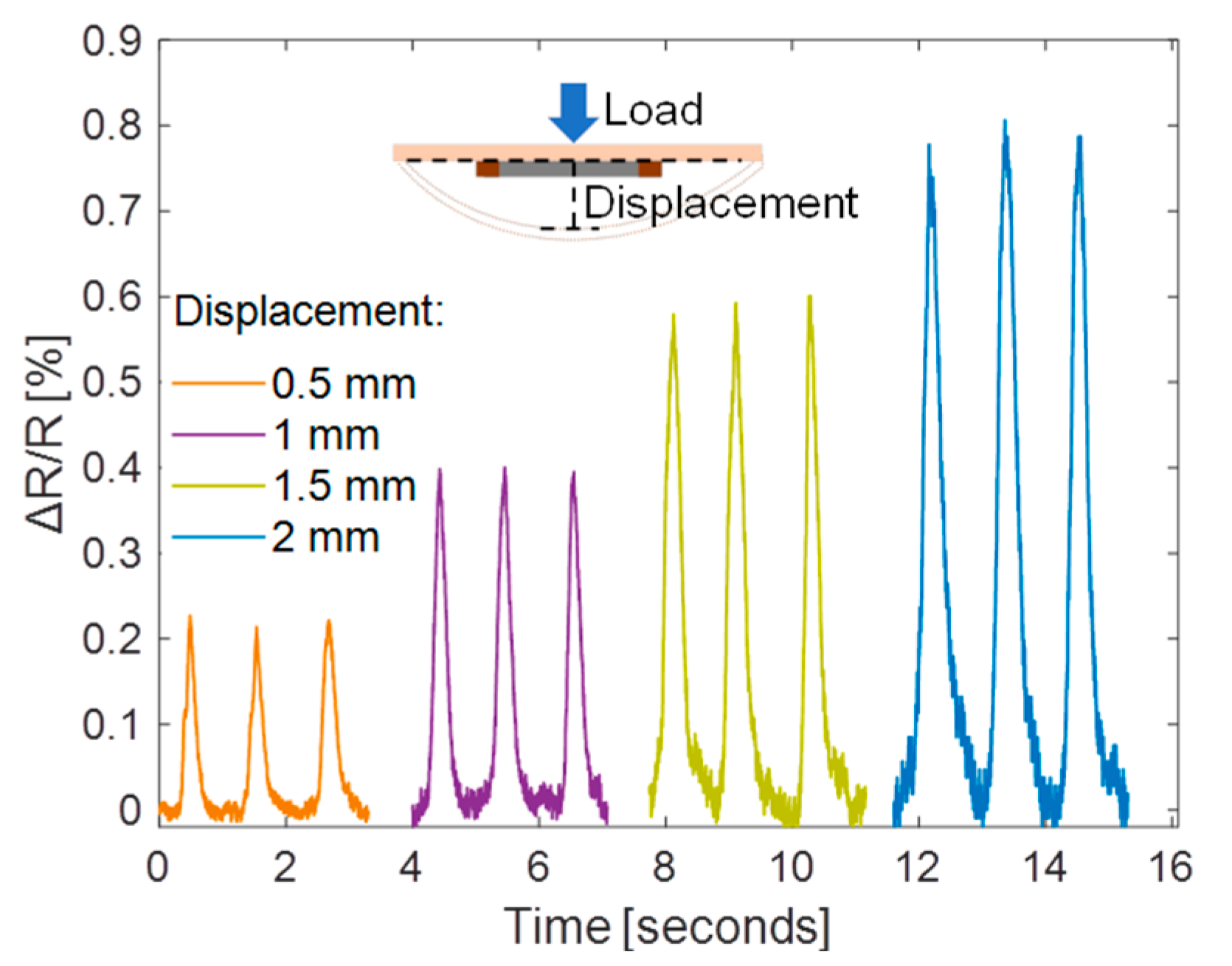
4. Application in Displacement Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, D.; Pikhitsa, P.V.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, C.; Shin, S.S.; Piao, L.; Park, B.; Suh, K.-Y.; Kim, T.-I.; Choi, M. Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system. Nature 2014, 516, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suster, M.; Guo, J.; Chaimanonart, N.; Ko, W.H.; Young, D.J. A high-performance MEMS capacitive strain sensing system. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, R.; Lu, X.; Cheng, M.; He, C.; Xie, G.; Meng, J.; Shi, D.; Zhang, G. Tunable Piezoresistivity of Nanographene Films for Strain Sensing. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeparre, H.; Liu, Q.; Minev, I.R.; Suo, Z.; Lacour, S.P. Localization of folds and cracks in thin metal films coated on flexible elastomer foams. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3117–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Chu, M.; Khine, M. Highly Flexible Wrinkled Carbon Nanotube Thin Film Strain Sensor to Monitor Human Movement. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Liu, T. SWCNT/Graphite Nanoplatelet Hybrid Thin Films for Self-Temperature-Compensated, Highly Sensitive, and Extensible Piezoresistive Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5650–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Honda, W.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Fully Printed, Highly Sensitive Multifunctional Artificial Electronic Whisker Arrays Integrated with Strain and Temperature Sensors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3921–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Mei, J.; Appleton, A.L.; Kim, D.H.; Wang, H.; Bao, Z. Flexible polymer transistors with high pressure sensitivity for application in electronic skin and health monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamil, M.; Hassan, N.; Ingy, B.; Sahour, S.; Ahmed, M.F.; Koichi, N.; Osamu, T.; Ahmed, A.E. Graphene-based strain gauge on a flexible substrate. Sens. Mater. 2014, 26, 699–709. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Ham, S.; Bae, N.; Park, M.; Min, N. A Hydrogen Pressure Sensor based on Bulk-micromachined Silicon Strain Gauges. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.; Pitchon, E.; Bertsch, A.; Renaud, P.; Mermoud, A. Wireless contact lens sensor for intraocular pressure monitoring: Assessment on enucleated pig eyes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009, 87, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Yun, K. Capacitive tactile sensor array for touch screen application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 165, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Lee, C.; Suh, K. Recent advances in flexible sensors for wearable and implantable devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Keating, T.; Todoroki, A.; Hiraoka, N. Rubber-based strain sensor fabricated using photolithography for intelligent tires. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, K.; Niu, S.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Superfast and high-sensitivity printable strain sensors with bioinspired micron-scale cracks. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, E.; Meitl, M.A.; Sun, Y.; Park, J.-U.; Shir, D.J.-L.; Nam, Y.-S.; Jeon, S.; Rogers, J.A. Micro-and Nanopatterning Techniques for Organic Electronic and Optoelectronic Systems. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1117–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempien, Z.; Khalid, M.; Kozicki, M.; Kozanecki, M.; Varela, H.; Filipczak, P.; Pawlak, R.; Korzeniewska, E.; Sąsiadek, E. In-situ deposition of reduced graphene oxide layers on textile surfaces by the reactive inkjet printing technique and their use in supercapacitor applications. Synth. Met. 2019, 256, 116144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessing, J.; Glavan, A.; Walker, S.; Keplinger, C.; Lewis, J.; Whitesides, G. Inkjet Printing of Conductive Inks with High Lateral Resolution on Omniphobic RFPaper for Paper-Based Electronics and MEMS. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4677–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, T.; Cacovich, S.; Divitini, G.; Ren, J.; Mansouri, A.; Kim, J.M.; Wang, C.; Ducati, C.; Sordan, R.; Torrisi, F. Fully inkjet-printed two-dimensional material field-effect heterojunctions for wearable and textile electronics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Bu, N.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y. Inkjet printing for flexible electronics: Materials, processes and equipments. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 3383–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Choi, Y.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.; Kang, D.; Choi, M. Crack-based strain sensor with diverse metal films by inserting an inter-layer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 34810–34815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, I.; Schulz, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shanov, V.; Shi, D. A carbon nanotube strain sensor for structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, B.; Saraswathi, R.; Kumar, A.S. Water based homogenous carbon ink modified electrode as an efficient sensor system for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 233, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Ali, S.; Wang, B. An Inkjet-printed Strain Sensor with a Carbon-SilverPolyimide Topology. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Glasgow, UK, 8–10 July 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Yi, Y.; Foulds, I. PMMA to Polystyrene bonding for polymer based microfluidic systems. Microsyst. Technol. 2013, 20, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Radha, B.; Chan, J.Y.; Saifullah, M.S.; Kulkarni, G.U.; Ho, G.W. Flexible palladium-based H2 sensor with fast response and low leakage detection by nanoimprint lithography. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7274–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, V.; Caparros, C.; Casellas, C.; Francesch, L.; Rocha, J.G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Development of inkjet printed strain sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Hayamizu, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yomogida, Y.; Izadi-Najafabadi, A.; Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K. A stretchable carbon nanotube strain sensor for human-motion detection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattmann, C.; Clemens, F.; Tröster, G. Sensor for Measuring Strain in Textile. Sensors 2008, 8, 3719–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, H.; Fan, K.; Brownjohn, J. Development and application of a relative displacement sensor for structural health monitoring of composite bridges. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2015, 22, 726–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Yang, D.; Park, B.C.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. A stretchable strain sensor based on a metal nanoparticle thin film for human motion detection. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11932–11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Yoon, Y.J.; Park, I. Ultra-stretchable and skin-mountable strain sensors using carbon nanotubes–Ecoflex nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 375501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, Y.; Wang, B.; Bermak, A. A Low-Cost Strain Gauge Displacement Sensor Fabricated via Shadow Mask Printing. Sensors 2019, 19, 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19214713
Yi Y, Wang B, Bermak A. A Low-Cost Strain Gauge Displacement Sensor Fabricated via Shadow Mask Printing. Sensors. 2019; 19(21):4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19214713
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Ying, Bo Wang, and Amine Bermak. 2019. "A Low-Cost Strain Gauge Displacement Sensor Fabricated via Shadow Mask Printing" Sensors 19, no. 21: 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19214713
APA StyleYi, Y., Wang, B., & Bermak, A. (2019). A Low-Cost Strain Gauge Displacement Sensor Fabricated via Shadow Mask Printing. Sensors, 19(21), 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19214713





