SNR-Dependent Environmental Model: Application in Real-Time GNSS Landslide Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Models
2.1. DD Measurement Model
2.2. SNR-Dependent Environment Model
2.3. Using the Environmental Model
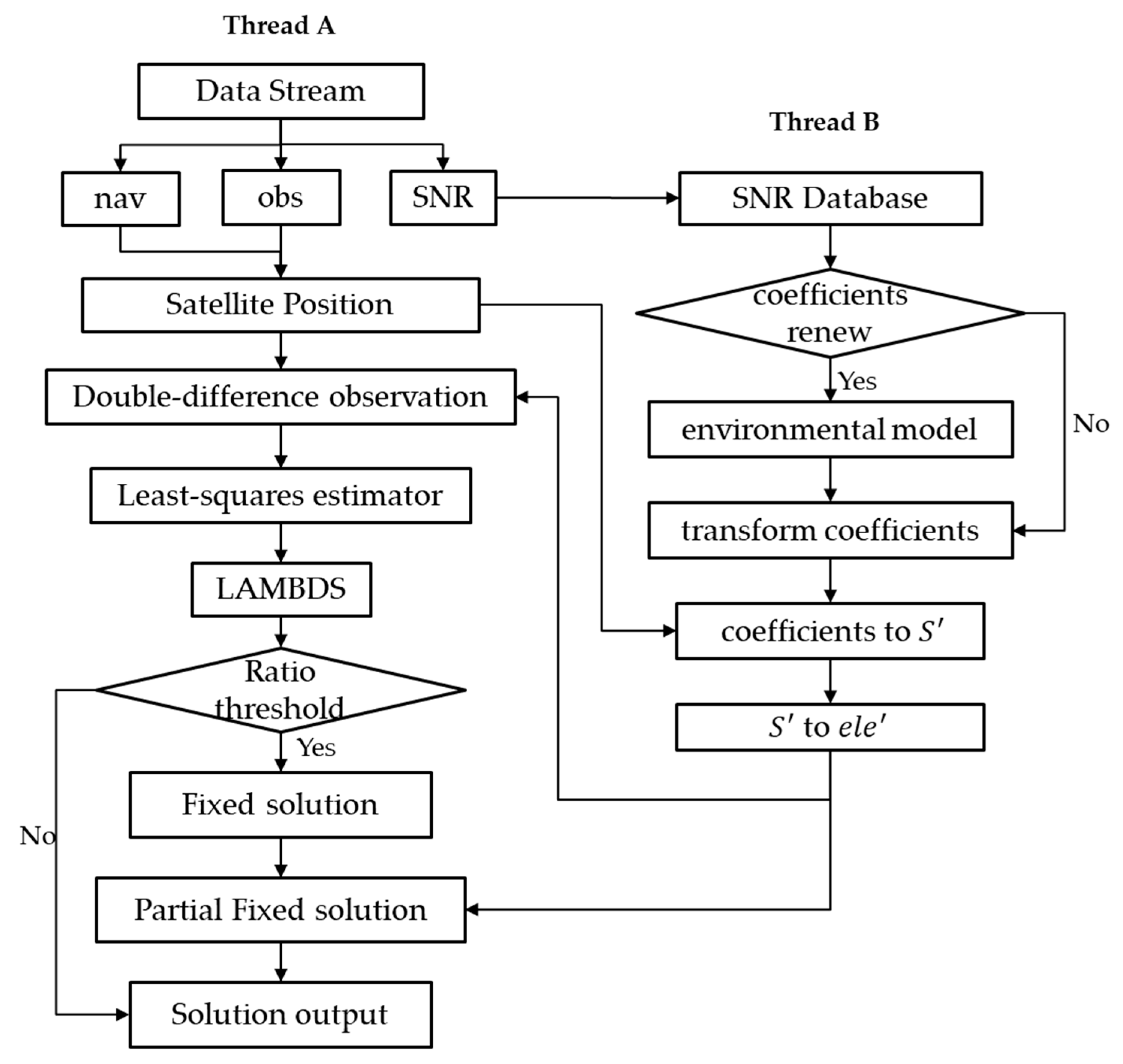
2.4. Processing Flowchart
3. Experiments and Results
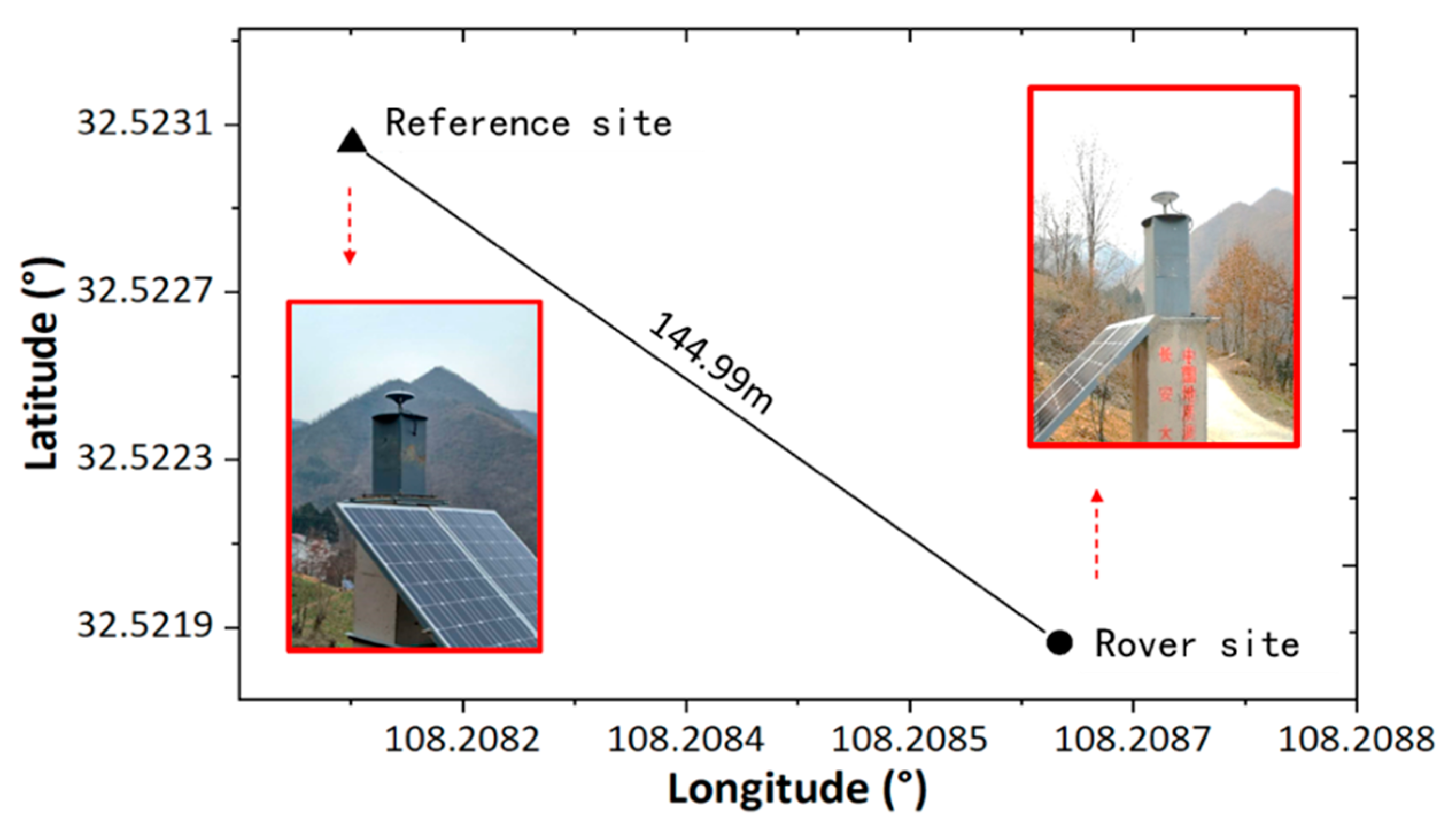
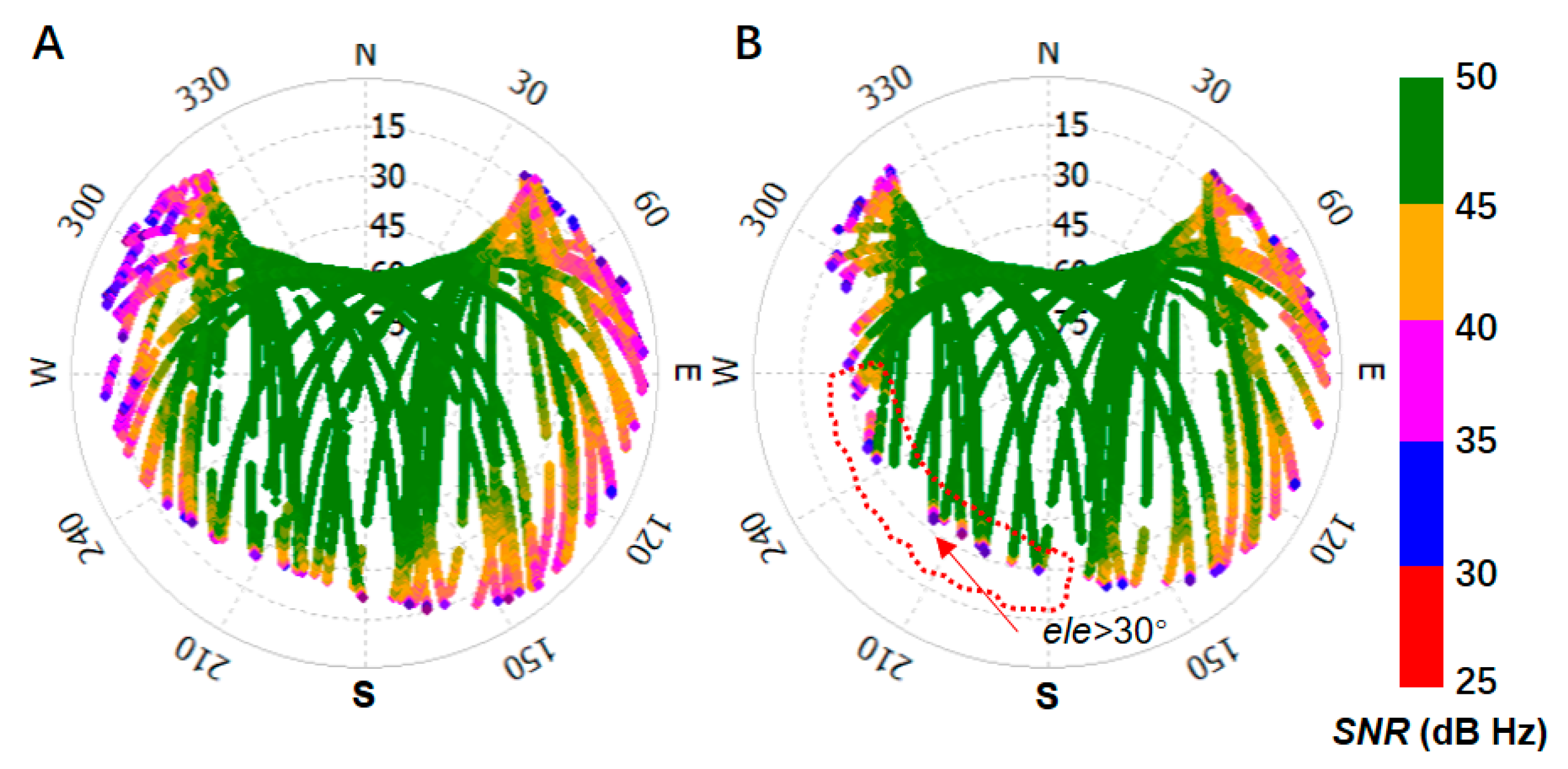
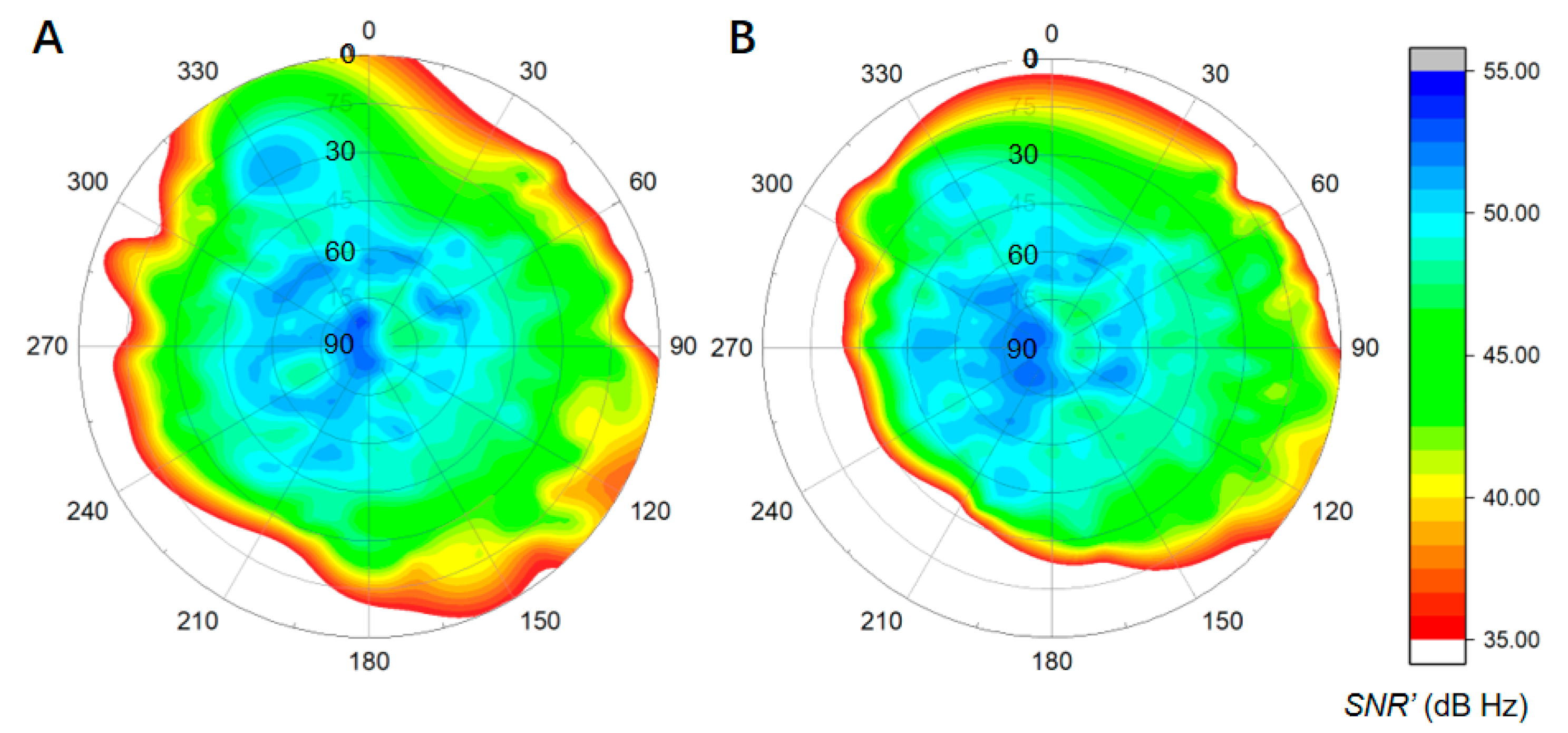
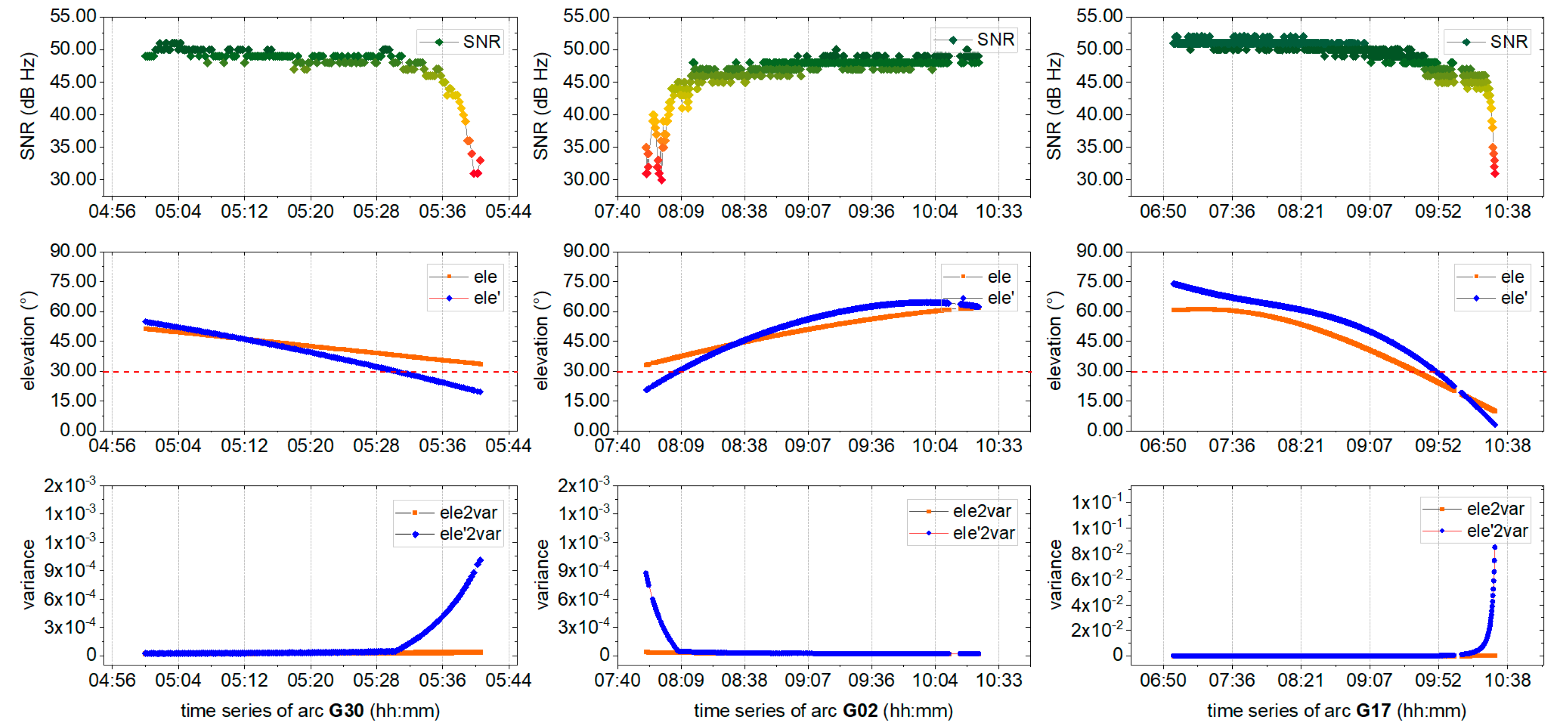
3.1. Data and Environmental Model
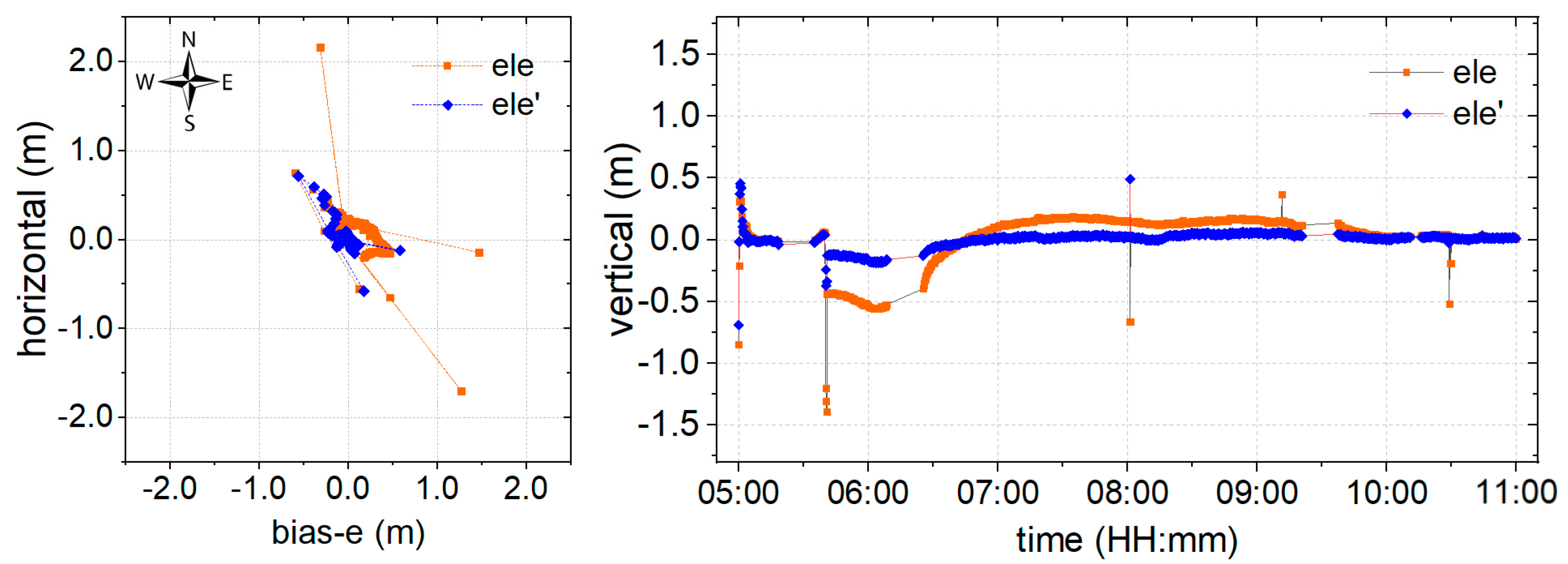
3.2. Performance Evaluation of the Float Solution
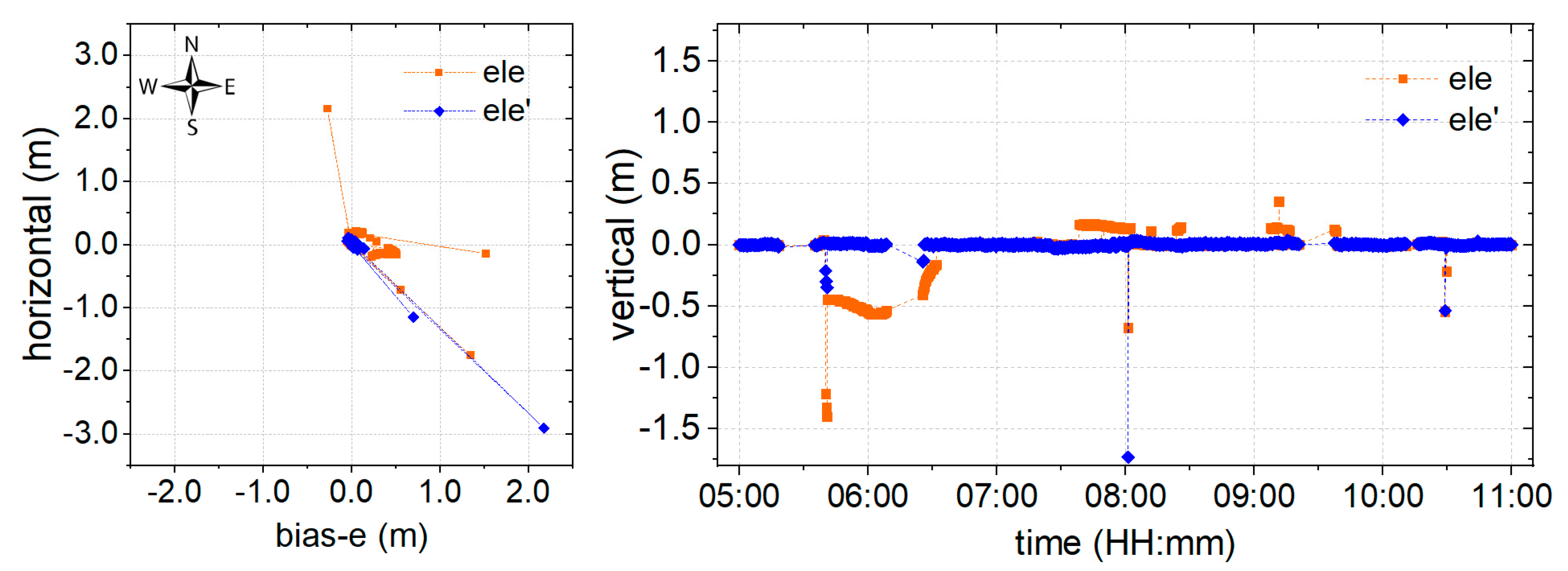
3.3. Performance Evaluation of the Ambiguity-Fixed Solution
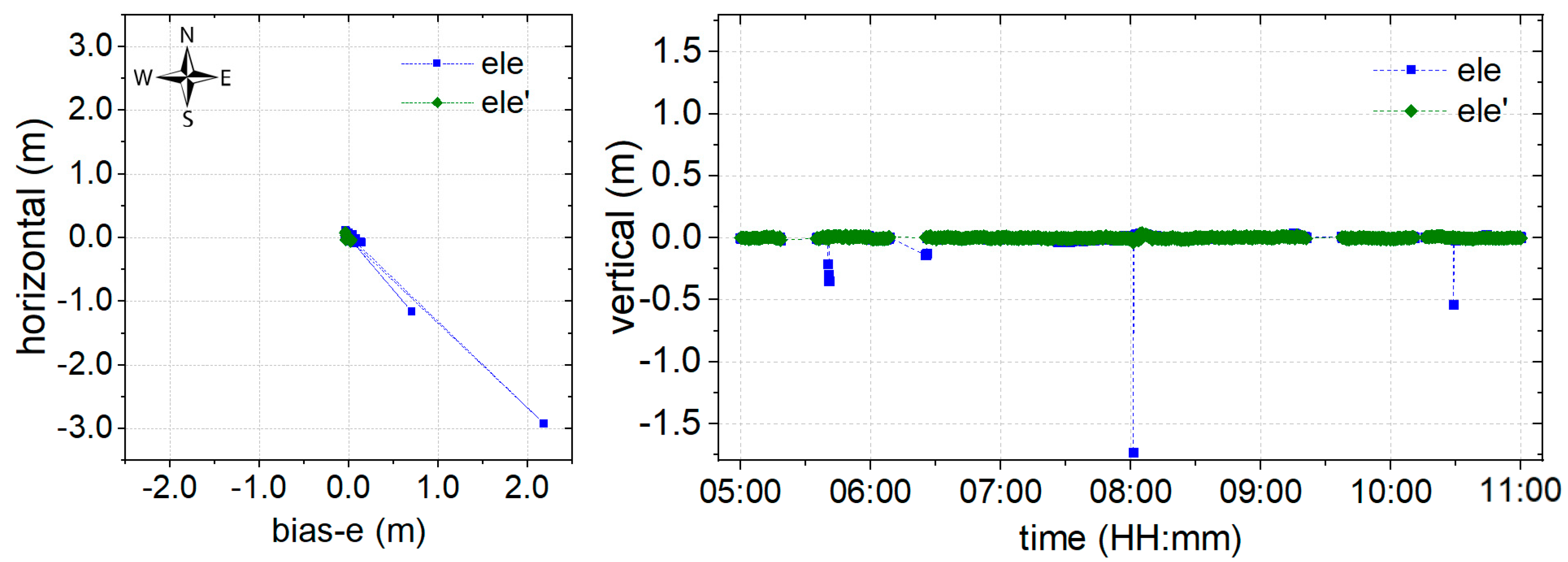
3.4. Performance of Partial Ambiguity-Fixed Solution
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Weighting using the proposed environmental model could effectively lessen the influence of poor signals, and provide an improved RMS and convergence time compared to that obtained using elevation angle. However, certain abnormal epochs caused by poor signals at higher elevation angles cannot be resolved.
- (2)
- Based on float ambiguity resolution using the proposed weighting model, the ambiguity-fixed solution is resolved. It can be shown from the results that the proposed environmental model significantly improves the success rate of the ambiguity-fixed solution, which plays an important role in providing a continuous and reliable indication of landslide monitoring and early warnings. However, abnormal epochs are not eliminated in this manner.
- (3)
- Employing the partial AR model, which is derived from the proposed environmental model, positioning precision is further improved and even reaches the millimeter level, both in the horizontal and vertical components. Furthermore, the abnormal epochs are eliminated, which could effectively prevent false alarms during monitoring.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizos, C.; Cranenbroeck, A.J.V.; Geosystems, L. Alternatives to Current GPS-RTK Services. J. Neurocase 2006, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlemann, S.; Smith, A.; Chambers, J.; Dixon, N.; Dijkstra, T.; Haslam, E.; Meldrum, P.; Merritt, D.; Gunn, D.; Mackay, J. Assessment of ground-based monitoring techniques applied to landslide investigations. Geomorphology 2015, 253, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, T.; Yasuda, A. Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on GPS/GNSS, Jeju, Korea, 4–6 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zeybek, M.; Şanlıoğlu, İ.; Özdemir, A. Monitoring landslides with geophysical and geodetic observations. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6247–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Qu, F.; Qu, W. Landslide monitoring by combining of CR-InSAR and GPS techniques. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, L.; Briole, P.; Martin, O.; Thom, C.; Malet, J.P.; Ulrich, P. Monitoring landslide displacements with the Geocube wireless network of low-cost GPS. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cina, A.; Piras, M. Performance of low-cost GNSS receiver for landslides monitoring: Test and results. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2015, 6, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ochieng, W.; Moore, T.; Hill, C.; Hide, C. Carrier phase-based integrity monitoring for high-accuracy positioning. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malet, J.P.; Maquaire, O.; Calais, E. The use of Global Positioning System techniques for the continuous monitoring of landslides: Application to the Super-Sauze earthflow (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence, France). Geomorphology 2002, 43, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, G.; Menge, F.; Völksen, C.; Wübbena, G.; Schmitz, M. Precise GPS Positioning Improvements by Reducing Antenna and Site Dependent Effects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 118. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Cui, X.; Zhao, S.; Lu, M. Mitigating Multipath Bias Using a Dual-Polarization Antenna: Theoretical Performance, Algorithm Design, and Simulation. Sensors 2017, 17, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satirapod, C.; Rizos, C. Multipath mitigation by wavelet analysis for GPS base station applications. Surv. Rev. 2005, 38, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.L. Attitude determination by kalman filtering. Automatica 1970, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, S.J.; Zimbelman, D.F. Spacecraft attitude determination by Kalman filtering of Global Positioning System signals. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1995, 18, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.W.; Zhong, P.; Ding, X.L.; Chen, W. Filtering GPS time-series using a Vondrak filter and cross-validation. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Han, S.; Rizos, C. Multipath Mitigation of Continuous GPS Measurements Using an Adaptive Filter. GPS Solut. 2000, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Mayer, M.; Heck, B. Improving the Stochastic Model of GNSS Observations by Means of SNR-Based Weighting, Observing our Changing Earth; Sideris, M.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 725–734. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Huang, D.; Cai, C. Multipath mitigation via component analysis methods for GPS dynamic deformation monitoring. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Shi, Q.; Cai, C. Characteristics of the BDS Carrier Phase Multipath and Its Mitigation Methods in Relative Positioning. Sensors 2017, 17, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Zeng, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, M.; Cheng, Y.; Lv, J. Mitigation of multipath effect in GNSS short baseline positioning by the multipath hemispherical map. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, S.; Dai, W.; Zeng, F.; Kuang, C. The BDS Multipath Hemispherical Map Based on Double Difference Residuals and Its Application Analysis. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 381–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb, A.E.; Clarke, P.J.; Edwards, S.J. GPS sidereal filtering: Coordinate- and carrier-phase-level strategies. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Ding, X.; Yuan, L.; Xu, Y.; Kwok, K.; Chen, Y. Sidereal filtering based on single differences for mitigating GPS multipath effects on short baselines. J. Geod. 2010, 84, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Tu, R.; Du, Y.; Wang, X. A New Azimuth-Dependent Elevation Weight (ADEW) Model for Real-Time Deformation Monitoring in Complex Environment by Multi-GNSS. Sensors 2018, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, H.; Brunner, F.K. Variances of GPS Phase Observations: The SIGMA-ɛ Model. GPS Solut. 1999, 2, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, A.; Brunner, F.K. An extended weight model for GPS phase observations. Earth Planets Space 2000, 52, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostius, R.; Wieser, A.; Brunner, F.K. Treatment of diffraction effects caused by mountain ridges. In Proceedings of the 3rd IAG/12th FIG Symposium, Baden, Austria, 22–24 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Tang, W.; Liu, J.; Shi, C. Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: A method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J. Geod. 1995, 70, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. GPS Carrier Phase Ambiguity Fixing Concepts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. An optimality property of the integer least-squares estimator. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, T. MLAMBDA: A modified LAMBDA method for integer least-squares estimation. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RTKLIB: An Open Source Program Package for GNSS Positioning. Available online: http://www.rtklib.com/prog/manual_2.4.2.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2013).

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Tu, R.; Zhang, R.; Fan, L.; Zhang, P. SNR-Dependent Environmental Model: Application in Real-Time GNSS Landslide Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19225017
Han J, Tu R, Zhang R, Fan L, Zhang P. SNR-Dependent Environmental Model: Application in Real-Time GNSS Landslide Monitoring. Sensors. 2019; 19(22):5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19225017
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Junqiang, Rui Tu, Rui Zhang, Lihong Fan, and Pengfei Zhang. 2019. "SNR-Dependent Environmental Model: Application in Real-Time GNSS Landslide Monitoring" Sensors 19, no. 22: 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19225017
APA StyleHan, J., Tu, R., Zhang, R., Fan, L., & Zhang, P. (2019). SNR-Dependent Environmental Model: Application in Real-Time GNSS Landslide Monitoring. Sensors, 19(22), 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19225017



