Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
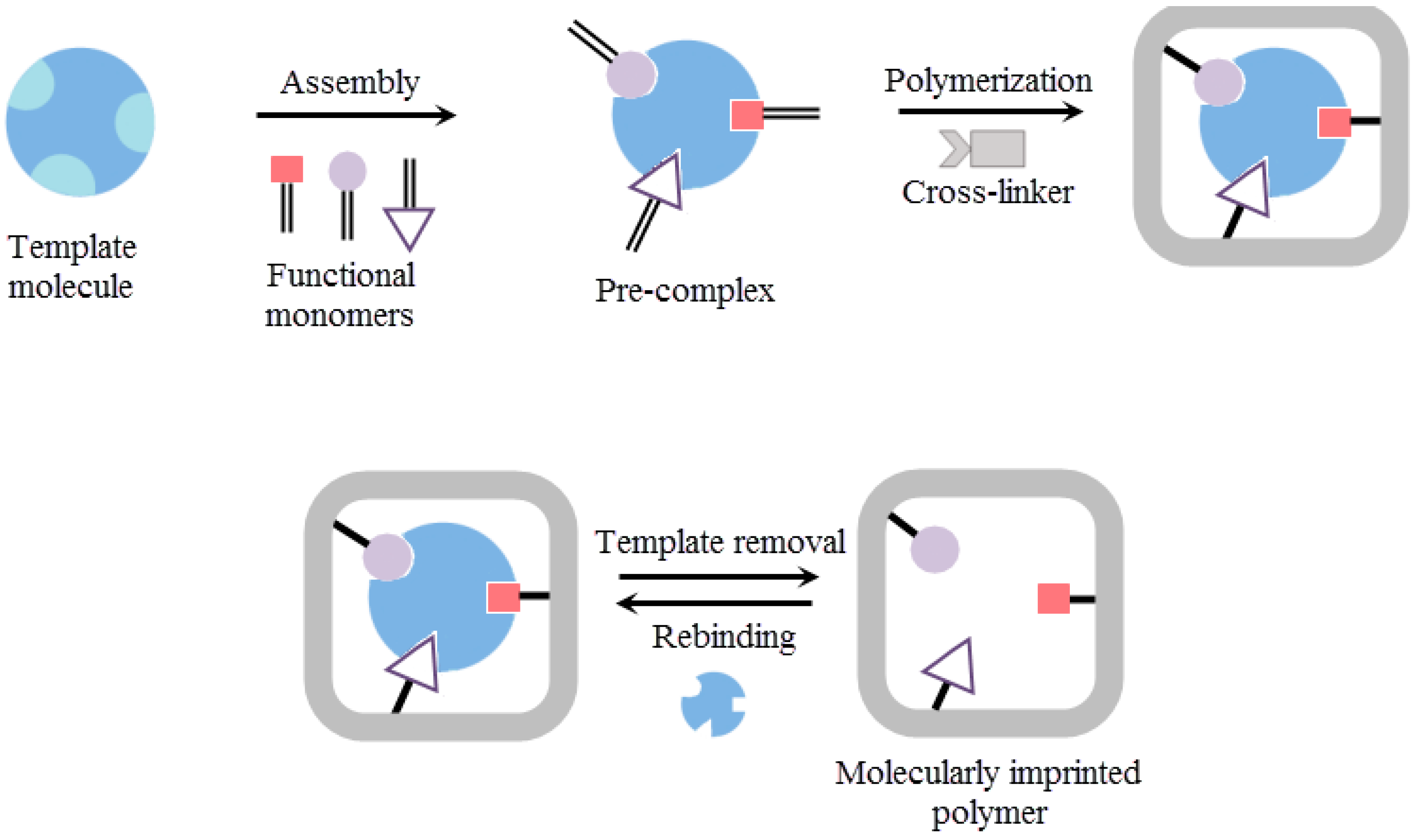
2. Molecular Imprinting Method
3. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors
4. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors
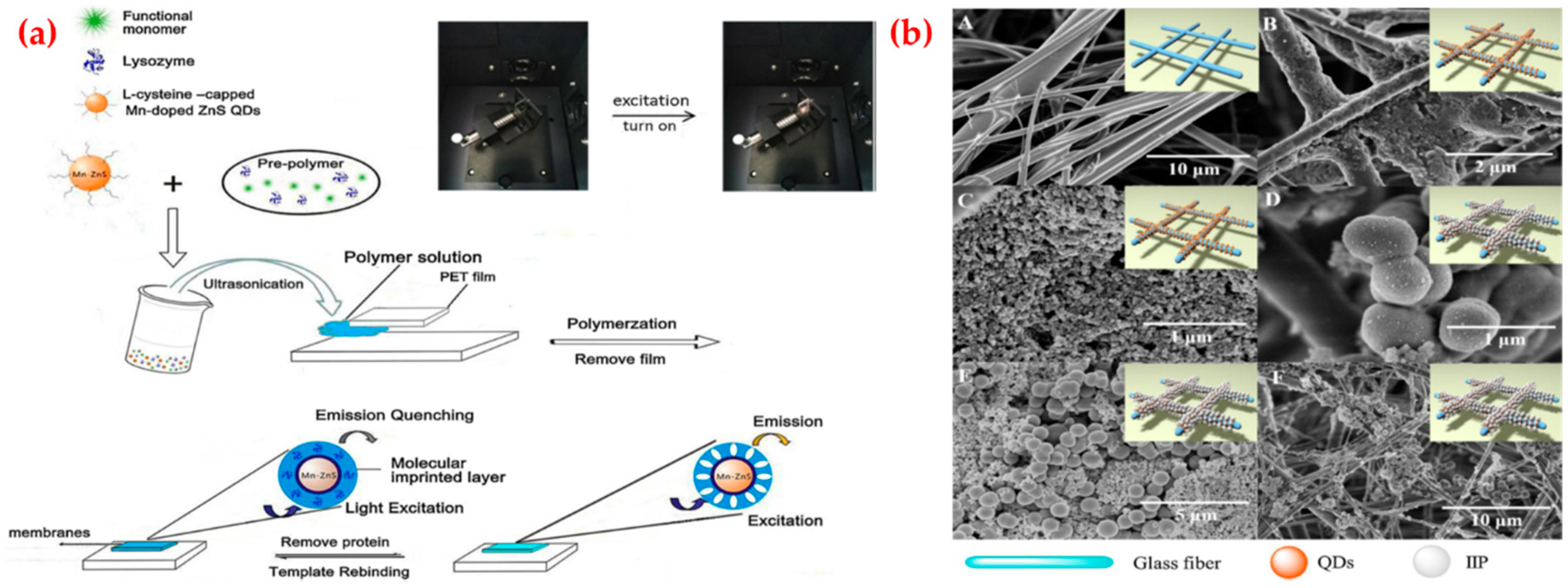
4.1. Optical Sensors
4.2. Electrochemical Sensors
4.3. Piezoelectric Sensors
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acquired immune deficiency syndrome | AIDS |
| Acrylamide | AAM |
| Activated protein C | APC |
| Aminophenyl- boronic acid | APBA |
| 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane | APTES |
| Chitosan | CS |
| Copper | Cu |
| Counter electrode | CE |
| Cytochrome c | Cyt c |
| Dioctyl sulfosuccinate sodium salt | AOT |
| Dopamine | DA |
| Electrogenerated chemiluminescence | ECL |
| Glucose-imprinted polymer | GIP |
| Glutaraldehyde | GA |
| Gold nanoparticles | AuNPs |
| Graphene oxide | GO |
| Human immunodeficiency virus p24 | HIV-p24 |
| Ion-imprinted polymer | IIP |
| Limit of detection | LOD |
| Limit of quantification | LOQ |
| Lysozyme | Lys |
| N,N′-Methylenebisacrylamide | MBA |
| N-Methacryloyl-L-cysteine | MAC |
| Mercury | Hg |
| Molecularly imprinted polymers | MIPs |
| Molecular imprinting technology | MIT |
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes | MWCNTs |
| Myoglobin | Myo |
| Non-imprinted polymers | NIPs |
| Poly(terthiophene) | pTBA |
| Quantum dots | QDs |
| Quartz crystal microbalance | QCM |
| Reference electrode | RE |
| Scanning electron microscope | SEM |
| screen printed carbon electrode | SPCE |
| Surface imprinted polymers | SIPs |
| Surface plasmon resonance | SPR |
| Synthetic cannabinoids | SCs |
| Ultraviolet | UV |
| Working electrode | WE |
| Zika virus | ZIKV |
References
- Lv, Y.Q.; Tan, T.W.; Svec, F. Molecular imprinting of proteins in polymers attached to the surface of nanomaterials for selective recognition of biomacromolecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Gálvez, A.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterials connected to antibodies and molecularly imprinted polymers asbio/receptors for bio/sensor applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, L.; Dai, Y.; Kan, X. Recognition and determination of bovine hemoglobin using a gold electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted self-polymerized dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A. Use of polymers with enzyme analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 1972, 11, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Saylan, Y.; Denizli, A. Advances in molecularly imprinted systems: materials, characterization methods and analytical applications. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Gross, T.; Schonfeld, R. Enzyme models based on molecularly imprinted polymers with strong esterase activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 1997, 36, 1962–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Nakade, H.; Simard, J.M.; Rotello, V.M. Recognition and stabilization of peptide α-helices using templatable nanoparticle receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10806–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin-Tam, M.E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Gold nanoparticle-cytochrome c complexes: the effect of nanoparticle ligand charge on protein structure. Langmuir 2005, 21, 12080–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro-Lago, C.; Quinlan-Pluck, F.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Minogue, A.M.; Thulin, E.; Walsh, D.M.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Inhibition of amyloid β protein fibrillation by polymeric nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15437–15443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Urakami, T.; Kodama, T.; Koide, H.; Oku, N.; Okahata, Y.; Shea, K.J. Design of synthetic polymer nanoparticles that capture and neutralize a toxic peptide. Small 2009, 5, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers: the next generation. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 376A–383A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.C.; Lemcoff, N.G. Synthetic hosts via molecular imprinting-are universal synthetic antibodies realistically possible? Chem. Commun. 2004, 1, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Yılmaz, F.; Özgür, E.; Derazshamshir, A.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinting of macromolecules for sensors applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, B.; Uzun, L.; Beşirli, N.; Denizli, A. Microcontact imprinted surface plasmon resonance sensor for myoglobin detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3609–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, D.; Thomasa, B.; Devaky, K.S. Biomimetic recognition and peptidase activities of transition state analogue imprinted chymotrypsin mimics. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toorisakaa, E.; Uezua, K.; Gotoa, M.; Furusaki, S. A molecularly imprinted polymer that shows enzymatic activity. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 14, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Razavi, N. Application of molecularly-imprinted polymers in solid-phase microextraction techniques. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2015, 73, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, K.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z. A molecularly imprinted polymer as an antibody mimic with affinity for lysine acetylated peptides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskierko, Z.; Checinska, A.; Sharma, P.S.; Golebiewska, K.; Noworyta, K.; Borowicz, P.; Fronc, K.; Bandi, V.; D’Souza, F.; Kutne, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer based extended-gate field-effect transistor chemosensors for phenylalanine enantioselective sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, G.; Ozgur, E.; Rad, A.Y.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Rapid real-time detection of procalcitonin using a microcontact imprinted surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Analyst 2013, 138, 6422–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyüktiryaki, S.; Say, R.; Denizli, A.; Ersöz, A. Phosphoserine imprinted nanosensor for detection of Cancer Antigen 125. Talanta 2017, 167, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, Y.; Isomura, M. Gas-stimuli-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer particles with switchable affinity for target protein. Chem. Comm. 2018, 54, 2538–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Regulation of protein-binding activities of molecularly imprinted polymers via post-imprinting modifications to exchange functional groups within the imprinted cavity. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Su, X.; Wang, T. Advancements of molecularly imprinted polymers in the food safety field. Analyst 2016, 141, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, X. Molecular imprinting technology for microorganism analysis. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Recent configurations and progressive uses of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for drug analysis. Talanta 2017, 167, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Novel developments and trends of analytical methods for drug analysis in biological and environmental samples by molecularly imprinted polymers. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, E.; Üzek, R.; Duman, M.; Denizli, A. Detection of ciprofloxacin through surface plasmon resonance nanosensor with specific recognition sites. J. Biomat. Sci-Polym. E 2018, 11, 1302–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Temperature and magnetism bi-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers: Preparation, adsorption mechanism and properties as drug delivery system for sustained release of 5-fluorouracil. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, E.; Üzek, R.; Duman, M.; Yavuz Alagöz, H.; Denizli, A. Prism coupler-based sensor system for simultaneous screening of synthetic glucocorticosteroid as doping control agent. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2018, 260, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S. Application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as a versatile and highly selective tool in food and environmental analysis: Recent developments and trends. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goradel, N.H.; Mirzaei, H.; Sahebkar, A.; Poursadeghiyan, M.; Masoudifar, A.; Malekshai, V.Z.; Negahdari, B. Biosensors for the detection of enviromental and urban pollutions. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introductions to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koedrith, P.; Thasiphu, T.; Weon, J.I.; Boonprasert, R.; Tuitemwong, K.; Tuitemwong, P. Recent trends in rapid environmental monitoring of pathogens and toxicants: Potential of nanoparticle-based biosensor and applications. Sci. World J. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, E.; Özgür, E.; Bereli, N.; Türkmen, D.; Denizli, A. Plastic antibody based surface plasmon resonance nanosensors for selective atrazine detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; de Alda, M.J.L.; Barcelo, D. Biosensors as useful tools for environmental analysis and monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1025–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Nucleic acid biosensors for environmental pollution monitoring. Analyst 2008, 133, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskierko, Z.; Sharma, P.S.; Bartold, K.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; Noworyta, K.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymers for separating and sensing of macromolecular compounds and microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 30–46. [Google Scholar]
- Göktürk, I.; Tamahkar, E.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. Protein depletion with bacterial cellulose nanofibers. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1099, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, R.; Keçili, R.; Denizli, A.; Ersöz, A. Biomimetic Imprinted Polymers: Theory, Design Methods, and Catalytic Applications. Molecularly Imprinted Catalysts Principles, Syntheses, and Applications; Li, S., Cao, S., Piletsky, S.A., Turner, A.P.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 103–120. [Google Scholar]
- Algieri, C.; Drioli, E.; Guzzo, L.; Donato, L. Bio-mimetic sensors based on molecularly imprinted membranes. Sensors 2014, 14, 13863–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.S.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsh, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahany, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular imprinting science and technology: a survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2003. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Preparation of imprinted cryogel cartridge for chiral separation of l-phenylalanine. Artif. Cell. Nanomed. B 2016, 45, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battista, E.; Scognamiglio, P.L.; Luise, N.D.; Raucci, U.; Donati, G.; Rega, N.; Netti, P.A.; Causa, F. Turn-on fluorescence detection of protein by molecularly imprinted hydrogels based on supramolecular assembly of peptide multi-functional blocks. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhai, X.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. Highly selective fluorescent sensing of proteins based on a fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanosensor. Sensors 2013, 13, 12994–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andac, M.; Galaev, I.Y.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted cryogels for protein purification. Biomater. Nat. Adv. Dev. Ther. 2016, 401–428. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, J. Molecular imprinting on inorganic nanozymes for hundred-fold enzyme specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5412–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czulak, J.; Guerreiro, A.; Metran, K.; Canfarotta, F.; Goddard, A.; Cowan, R.H.; Trochimczuk, A.W.; Piletsky, S. Formation of target-specific binding sites in enzymes: solid-phase molecular imprinting of HRP. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11060–11066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, J.G.; Rebelo, P.; Cagide, F.; Gonçalvesc, M.L.; Borges, F.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical sensing of the thyroid hormone thyronamine (T0AM) via molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs). Talanta 2019, 194, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, S.L.; Fajardo, L.M.; Cunha, L.A.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Machado, F.B.C.L.; Ferrão, F.A.; Pividori, M.I. Theoretical and experimental study for the biomimetic recognition of levothyroxine hormone on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, L.; Andreetto, E.; Vestri, A.; Bovi, M.; Barozzi, M.; Iaco, E.; Busato, M.; Castagna, A.; Girelli, D.; Bossi, A.M. Surface plasmon resonance based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the picomolar detection of the iron regulating hormone Hepcidin-25. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Hepatitis B surface antibody purification with hepatitis B surface antibody imprinted poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate-N-methacryloyl-l-tyrosine methyl ester) particles. J. Chromatog. B 2009, 877, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunath, S.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Maximilien, J.; Marchyk, N.; Sänge, J.; Haupt, K. Cell and tissue imaging with molecularly imprinted polymers as plastic antibody mimics. Ads. Healthcare Mater. 2015, 4, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujahid, A.; Dickert, F.L. Blood group typing: from classical strategies to the application of synthetic antibodies generated by molecular imprinting. Sensors 2016, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmbhatt, H.; Poma, A.; Pendergraff, H.M.; Watts, J.K.; Turner, N.W. Improvement of DNA recognition through molecular imprinting: hybrid oligomer imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (oligoMIP NPs). Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartold, K.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; Golebiewska, K.; Lisowski, W.; Cauteruccio, S.; Licandro, E.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Oligonucleotide determination via peptide nucleic acid macromolecular imprinting in an electropolymerized cg-rich artificial oligomer analogue. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2018, 10, 27562–27569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, Ö.; Saylan, Y.; Cihangir, N.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based plasmonic sensors for real-time Enterococcus faecalis detection. Biosens. Biolectron. 2019, 126, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Chen, C.; Liang, C.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. Highly selective recognition and fluorescent detection of JEV via virus-imprinted magnetic silicon microspheres. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2016, 233, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Luo, M.; Wan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Mei, F.; Wang, Z.; Jin, A.; Shi, Y.; Lu, B. Bio-inspired virus imprinted polymer for prevention of viral infections. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. A virus resonance light scattering sensor based on mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymers for high sensitive and high selective detection of hepatitis A virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Papageorgiou, M.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Preparation of molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction fiber for the selective removal and extraction of the antiviral drug abacavir in environmental and biological matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 913, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumitrăchioaie, A.; Tertiș, M.; Cernat, A.; Săndulescu, R.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical methods based on molecularly imprinted polymers for drug Detection. A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 2556–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Shafik, A.L.; Abdel-Latif, D.A. Synthesis of azo-functionalized ion-imprinted polymeric resin for selective extraction of nickel(II) ions. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Kong, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Z. Preparation and adsorption characteristics of an ion-imprinted polymer for fast removal of Ni(II) ions from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, M.; Mathew, B. Carbon nanotube-based ion imprinted polymer as electrochemical sensor and sorbent for Zn(II) ion from paint industry wastewater. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Chem. 2018, 23, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Zo, T.; Yang, Y.; Xing, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Citric acid capped CdS quantum dots for fluorescence detection of copper ions (II) in aqueous solution. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Yao, M.; Saeger, S.D.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Carbon quantum dots encapsulated molecularly imprinted fluorescence quenching particles for sensitive detection of zearalenone in corn sample. Toxins 2018, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Halder, A.; Sun, Y. Fluorescent nanosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers coated on graphene quantum dots for fast detection of antibiotics. Biosensors 2018, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, J.; Qin, M.; Gu, T. Molecularly imprinted nanocapsule mimicking phosphotriesterase for the catalytic hydrolysis of organophosphorus pesticides. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Çimen, D.; Derazshamshir, A.; Bereli, N.; Yılmaz, F.; Denizli, A. Surface plasmon resonance nanosensors based on molecularly imprinted nanofilm for detection of pesticides. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 241, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eersels, K.; Lieberzeit, P.; Wagner, P. A review on synthetic receptors for bioparticle detection created by surface-imprinting techniques from principles to applications. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1171–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, M.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Electrochemical methods for the analysis of clinically relevant biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9001–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanović, I.; Schasfoort, R.B.M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Analysis of cell surface antigens by surface plasmon resonance imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Yılmaz, F.; Derazshamshir, A.; Yılmaz, E.; Denizli, A. Synthesis of hydrophobic nanoparticles for real-time lysozyme detection using surface plasmon resonance sensor. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, e2631, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Yılmaz, F.; Özgür, E.; Derazshamshir, A.; Bereli, N.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Nanotechnology Characterization Tools for Biosensing and Medical Diagnosis. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors for Medical Diagnosis; Kumar, C.S.S.R., Ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 425–458. [Google Scholar]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, G.V.; Zaitouna, A.J.; Lai, R.Y. Characterization of an electrochemical mercury sensor using alternating current, cyclic, square wave and differential pulse voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 810, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campuzanoa, S.; Kuralay, F.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Bartošík, M.; Vyavaharea, K.; Paleček, E.; Haake, D.A.; Wang, J. Ternary monolayers as DNA recognition interfaces for direct and sensitive electrochemical detection in untreated clinical samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3577–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, M. Molecularly imprinted Au-nanoparticle composite-functionalized EQCM sensor for l-serine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 780, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shang, L.; Yoshioka, H.T.; Chen, B.; Hayashi, K. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer nanobeads for selective sensing of carboxylic acid vapors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sener, G.; Ozgur, E.; Yılmaz, E.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Quartz crystal microbalance based nanosensor for lysozyme detection with lysozyme imprinted nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Magnetoelectrics for magnetic sensor applications: status, challenges and perspectives. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, M.; Karnaushenko, D.; Lin, G.; Baunack, S.; Makarov, D.; Schmidt, O.G. Direct transfer of magnetic sensor devices to elastomeric supports for stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, S. A highly selective magnetic sensor for Cd2+ in living cells with (Zn, Mn)-doped iron oxide nanoparticles. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2015, 207, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiker, P.; Oesterschulze, E. Geometrically tuned wettability of dynamic micromechanical sensors for an improved in-liquid operation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 101903–101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, D.; Melli, M.; Zilio, S.D.; Toffoli, V.; Scoles, G.; Toffoli, G.; Lazzarino, M. How to engineer superhydrophobic micromechanical sensors preserving mass resolution. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2014, 119, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.M.; Zhang, W.M.; Shi, X.; Yan, H.; Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G. Adsorption-induced surface effects on the dynamical characteristics of micromechanical resonant sensors for in situ real-time detection. J. Appl. Mech. 2016, 83, 081009–081020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Romero, D.F.; Behrmann, O.; Dame, G.; Urban, G.A. Dynamic thermal sensor for biofilm monitoring. Sens. Actuat. A-Phys. 2014, 213, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, C.; Raschner, C.; Ammer, K. An overview of recent application of medical infrared thermography in sports medicine in Austria. Sensors 2010, 10, 4700–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chu, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Fan, Z.; Huang, J. Thermally stable, biocompatible, and flexible organic field-effect transistors and their application in temperature sensing arrays for artificial skin. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Li, S. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvolini, G.; Marrazza, G. MIP-based sensors: Promising new tools for cancer biomarker determination. Sensors 2017, 17, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabi, M.; Kuralay, F.; Jager, E.W.H.; Beni, V.; Turner, A.P.F. Electrochemical bacterial detection using poly(3-aminophenylboronicacid)-based imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, H.; Janfaza, S. Medical nanobiosensors: A tutorial review. Nanomed. J. 2015, 2, 74–87. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.P.F. Biosensors: sense and sensibility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3184–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, M.; Yarman, A.; Erdossy, J.; Yildiz, H.B.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Scheller, F.W. MIPs and aptamers for recognition of proteins in biomimetic sensing. Biosensors 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. SPR biosensors: Historical perspectives and current challenges. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2016, 229, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryayeva, E.; Krull, U.J. Localized surface plasmon resonance: Nanostructures, bioassays and biosensing—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caucheteur, C.; Voisin, V.; Albert, J. Near-infrared grating-assisted SPR optical fiber sensors: design rules for ultimate refractometric sensitivity. Opt. Exp. 2015, 23, 2918–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, N.C.; Nagpal, P.; McPeak, K.M.; Norris, D.J.; Oh, S.H. Engineering metallic nanostructures for plasmonics and nanophotonics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 036501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.; Canva, M.; Vo-Dinh, T. Narrow groove plasmonic nano-gratings for surface plasmon resonance sensing. Opt. Exp. 2011, 19, 787–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, K.; Spasic, D.; Delport, F.; Lammertyn, J. Real-time ligation chain reaction for DNA quantification and identification on the FO-SPR. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, B.; François, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Monro, T.M. Multiplexing of radiative-surface plasmon resonance for the detection of gastric cancer biomarkers in a single optical fiber. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2013, 183, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyun, S.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Erdem, A.; Denizli, A. Surface plasmon resonance aptasensor for detection of human activated protein C. Talanta 2019, 194, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylan, Y.; Denizli, A. Molecular fingerprints of hemoglobin on a nanofilm chip. Sensors 2018, 18, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, X.; Song, F.; Wang, C.; Chu, F.; Wu, S. A sensing approach for dopamine determination by boronic acid-functionalized molecularly imprinted graphene quantum dots composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Jiang, R.; Sun, L.; Pang, S.; Luo, A. Fluorescent molecularly imprinted membranes as biosensor for the detection of target protein. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2018, 254, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göçenoğlu Sarıkaya, A.; Osman, B.; Çam, T.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor for uric acid determination. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 251, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Han, J.; Chen, L. Three-dimensional paper-based microfluidic chip device for multiplexed fluorescence detection of Cu2+ and Hg2+ ions based on ion imprinting technology. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 251, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibekkaya, H.; Saylan, Y.; Yılmaz, F.; Derazshamshir, A.; Denizli, A. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for real-time detection of cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2016, 53, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Özen, H.; Tümer, M.A.; Mattiasson, B.; Denizli, A. Microcontact imprinting based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for real-time and ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) from clinical samples. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2016, 224, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson-Brown, A.; Acton, A.L.; Preece, J.A.; Fossey, J.S.; Mendes, P.M. Selective glycoprotein detection through covalent templating and allosteric click-imprinting. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5114–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Bastola, P.; Le, L.; Paul, A.M.; Fernandez, E.; Diamond, M.S.; Miao, W.; Bai, F. An ultrasensitive electrogenerated chemiluminescence-based immunoassay for specific detection of Zika virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32227–32238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Thepparit, C.; Jaimipuk, T.; Auewarakul, P.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Sangma, C. An electrochemical biosensor based on surface imprinting for zika virus detection in serum. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Noh, H.B.; Won, M.S.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, K.B.; Shim, Y.B. A selective glucose sensor based on direct oxidation on a bimetal catalyst with a molecular imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Ye, X.; Wu, K.; Wu, T.; Li, C. Voltammetric myoglobin sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a composite film consisting of carbon nanotubes and a molecularly imprinted polymerized ionic liquid. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Tian, L.; Sun, S.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y. Electrochemical microfluidic chip based on molecular imprinting technique applied for therapeutic drug monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.M.; Moon, J.M.; Lee, W.C.; Yoon, J.H.; Choi, C.S.; Shim, Y.B. A potentiometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor using a molecularly imprinted layer bonded on a conducting polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, X.L.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.S.; Wang, L.S. A multi-walled carbon nanotubes based molecularly imprinted polymers electrochemical sensor for the sensitive determination of HIV-p24. Talanta 2017, 164, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Lu, X. An “on-off” electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and recycling amplifications for determination of dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 250, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, A.; Motia, S.; Hassani, N.A.E.; Bari, N.E.; Bouchikhi, B. Development and characterization of an electrochemical biosensor for creatinine detection in human urine based on functional molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 788, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Pacheco, J.G.; Rebelo, P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor prepared on a screen printed carbon electrode for naloxone detection. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 243, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguy, T.P.; Phi, T.V.; Tram, D.T.N.; Eersels, K.; Wagner, P.; Lien, T.T.N. Development of an impedimetric sensor for the label-free detection ofthe amino acid sarcosine with molecularly imprinted polymer receptors. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 246, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Ahmad, O.S.; Guerreiro, A.; Karim, K.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S. New potentiometric sensor based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for cocaine detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, M.A.K.P.; Albano, D.R.B.; Sevilla, F.B. Piezoelectric sensor for ethylene based on silver(I)/polymer composite. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2018, 254, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diltemiz, S.E.; Keçili, R.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Molecular imprinting technology in quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberzeit, P.A.; Chunta, S.; Navakul, K.; Sangma, C.; Jungmann, C. Molecularly imprinted polymers for diagnostics: sensing high density lipoprotein and dengue virus. Pro. Eng. 2016, 168, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maa, X.T.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Epitope molecularly imprinted polymer coated quartz crystal microbalance sensor for the determination of human serum albumin. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 246, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.T.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Oriented surface epitope imprinted polymer-based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for cytochrome C. Talanta 2019, 191, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, F.; Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for the clinical detection of insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Pan, M.; Fang, G.; Gu, Y.; Wen, W.; Xue, R.; Wang, S. An electrodeposited molecularly imprinted quartz crystal microbalance sensor sensitized with AuNPs and rGO material for highly selective and sensitive detection of amantadine. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6600–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Guo, H. Preparation of a molecularly imprinted sensor based on quartz crystal microbalance for specific recognition of sialic acid in human urine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4387–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunta, S.; Suedee, R.; Lieberzeit, P.A. High-density lipoprotein sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battal, D.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yalcin, M.S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor system for sensitive and label-free detection of synthetic cannabinoids in urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshpour, M.; Özgür, E.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Microcontact imprinted quartz crystal microbalance nanosensor for protein C recognition. Coll. Surf. B 2017, 151, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, Ç.; Yılmaz, F.; Özgür, E.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted quartz crystal microbalance sensor (QCM) for bilirubin detection. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, E.; Yılmaz, E.; Şener, G.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. A new molecular imprinting-based mass-sensitive sensor for real-time detection of 17β-estradiol from aqueous solution. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2013, 32, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061279
Saylan Y, Akgönüllü S, Yavuz H, Ünal S, Denizli A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors. 2019; 19(6):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061279
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaylan, Yeşeren, Semra Akgönüllü, Handan Yavuz, Serhat Ünal, and Adil Denizli. 2019. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications" Sensors 19, no. 6: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061279
APA StyleSaylan, Y., Akgönüllü, S., Yavuz, H., Ünal, S., & Denizli, A. (2019). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors, 19(6), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061279








