Laser-Assisted Printed Flexible Sensors: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanocomposite-Based Printed Flexible Sensors
2.1.1. Carbon Elements-Filled Nanocomposite-Based Printed Sensors
2.1.2. Metal-Filled Nanocomposite-Based Printed Sensors
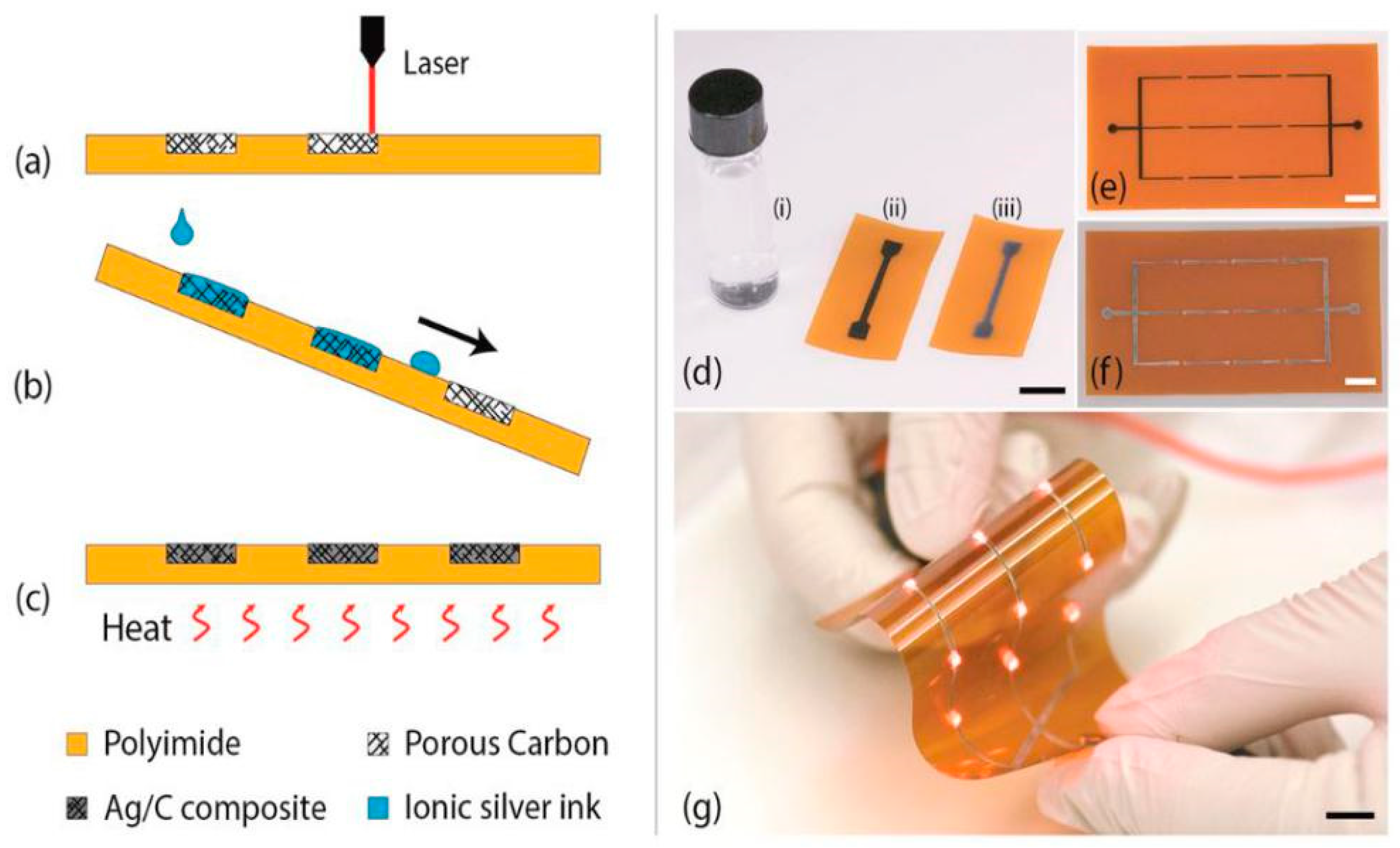
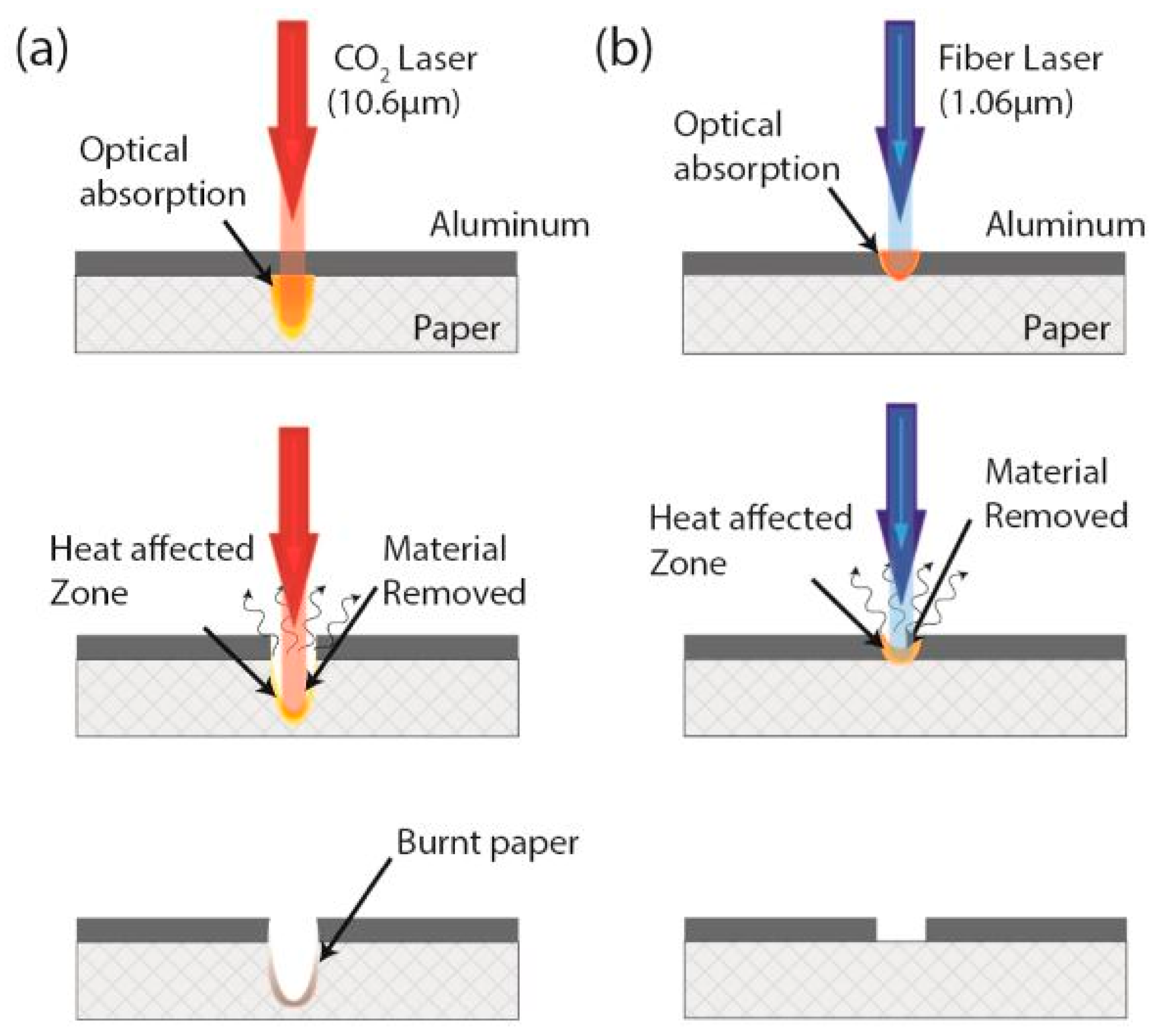
2.2. Laser-Ablated Printed Flexible Sensors
2.3. 3D-Printed Sensors
3. Current Challenges and Future Opportunities
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Flexible carbon nanotube nanocomposite sensor for multiple physiological parameter monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 251, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Tactile Sensing From Laser-Ablated Metallized PET Films. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 17, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Zia, A.I.; Li, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Novel Sensing Approach for LPG Leakage Detection—Part II: Effects of Particle Size, Composition, and Coating Layer Thickness. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Smart Home: Recognition of activities of elderly for 24/7; Coverage issues. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Sensing Technology, Liverpool, UK, 2–4 September 2014; pp. 480–489. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Yu, P.-L.; Goicoechea, J.; Matias, I.R.; Gooneratne, C.P.; Kosel, J. Detection of bacterial endotoxin in food: New planar interdigital sensors based approach. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Zia, A.I.; Li, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Novel Sensing Approach for LPG Leakage Detection: Part I—Operating Mechanism and Preliminary Results. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, S.M. Semiconductor Sensors; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 55. [Google Scholar]
- Beebe, D.J.; Denton, D.D.; Radwin, R.G.; Webster, J.G. A silicon-based tactile sensor for finger-mounted applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 45, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R.S. Technologies for printing sensors and electronics over large flexible substrates: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3164–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassi, S.; Cauda, V.; Canavese, G.; Pirri, C.F. Flexible tactile sensing based on piezoresistive composites: A review. Sensors 2014, 14, 5296–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Wearable Flexible Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, T.H.; Choi, J.-W. A flexible two dimensional force sensor using PDMS nanocomposite. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 174, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Paydar, O.H.; Candler, R.N. 3D printed molds for non-planar PDMS microfluidic channels. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 226, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-C.; Moon, J.-H.; Baek, D.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-Y.; Hong, J.-S.; Lee, S.-H. CNT/PDMS composite flexible dry electrodesfor long-term ECG monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, U.; Phan, D.-T.; Uddin, A.I.; Chung, G.-S. Highly flexible room temperature NO2 sensor based on MWCNTs-WO 3 nanoparticles hybrid on a PET substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.-X.; Han, C.; Li, M.; Shen, X.-Q. High performance of carbon nanotubes/silver nanowires-PET hybrid flexible transparent conductive films via facile pressing-transfer technique. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saftawy, A.; Elfalaky, A.; Ragheb, M.; Zakhary, S. Electron beam induced surface modifications of PET film. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 102, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Peng, Q.; Ding, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; He, X. Lightweight, superelastic, and mechanically flexible graphene/polyimide nanocomposite foam for strain sensor application. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8933–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Guan, B.-O.; Lu, C.; Tam, H.-Y. Salinity sensor based on polyimide-coated photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 20003–20008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, K.-P.; Lim, L.-T.; Min, N.-K.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.J.; Park, C.-W. Novel resistive-type humidity sensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube/polyimide composite films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, L.A.; Facure, M.H.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.; Correa, D.S. One-pot preparation of PEDOT: PSS-reduced graphene decorated with Au nanoparticles for enzymatic electrochemical sensing of H2O2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 407, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, R.S.; Lu, Y.-J.; Fu, Y.; Wei, K.-C.; Chan, S.-H.; Wu, M.-C.; Lee, J.-W.; Lin, T.-K.; Wang, J.-C. Cross-Talk Immunity of PEDOT: PSS Pressure Sensing Arrays with Gold Nanoparticle Incorporation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Aw, K.C.; Gao, W. Skin force sensor using piezoresistive PEDOT: PSS with arabitol on flexible PDMS. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, Busan, Korea, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, P.B.; Alam, B.; Sharma, D.S.; Mandal, S.; Agarwal, A. Flexible NO2 gas sensor based on single walled carbon nanotubes on PTFE substrate. Flex. Print. Electron. 2018, 3, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, C. Imperceptible and Ultraflexible P-Type Transistors and Macroelectronics Based on Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Nano 2015, 10, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, M.; del Río, J.S.; Blondeau, P.; Ortuño, J.A.; Rius, F.X.; Andrade, F.J. Rubber-based substrates modified with carbon nanotubes inks to build flexible electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 827, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Ziaie, B. Direct laser writing of porous-carbon/silver nanocomposite for flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16907–16913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiu, J.; Nogi, M.; Sugahara, T.; Nagao, S.; Koga, H.; He, P.; Suganuma, K. A highly sensitive and flexible pressure sensor with electrodes and elastomeric interlayer containing silver nanowires. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2926–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Song, W. Preparation of solid silver nanoparticles for inkjet printed flexible electronics with high conductivity. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaltin, C.; Basarir, F. Preparation of flexible VOC sensor based on carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiohara, A.; Langer, J.; Polavarapu, L.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Solution processed polydimethylsiloxane/gold nanostar flexible substrates for plasmonic sensing. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9817–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, D.; Niroui, F.; Leung, K. High-performance, flexible enzymatic glucose biosensor based on ZnO nanowires supported on a gold-coated polyester substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2409–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Cheng, M.-Y.; Chang, W.-Y.; Tsao, L.-C.; Yang, S.-A.; Shih, W.-P.; Chang, F.-Y.; Chang, S.-H.; Fan, K.-C. An integrated flexible temperature and tactile sensing array using PI-copper films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 143, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. A flexible and disposable hybrid electrode based on Cu nanowires modified graphene transparent electrode for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayousse, C.; Celle, C.; Carella, A.; Simonato, J.-P. Synthesis and purification of long copper nanowires. Application to high performance flexible transparent electrodes with and without PEDOT: PSS. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Zhou, J.; Dong, S.; Feng, B.; Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Milne, W.; Yang, C. Deposition of c-axis orientation aluminum nitride films on flexible polymer substrates by reactive direct-current magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 520, 4863–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.; Morofuji, Y.; Kamohara, T.; Nishikubo, K.; Tsubai, M.; Fukuda, O.; Ueno, N. Flexible piezoelectric pressure sensors using oriented aluminum nitride thin films prepared on polyethylene terephthalate films. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 114318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, N.; Akiyama, M.; Ikeda, K.; Tateyama, H. A Foil Type Flexible Pressure Sensor Using Nitelide Aluminum Thin Film. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 2002, 38, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Liang, T.; Wei, Z.; Run, M.; Yan, X.; Liu, X. Flexible Graphene Electrodes for Prolonged Dynamic ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Park, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Das, T.; Kim, M.S.; Ahn, J.H. Graphene-Based Flexible and Stretchable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4184–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mitra, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Graphene and its sensor-based applications: A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 270, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Jia, L.; Thomas, E.L. Hierarchically ordered topographic patterns via plasmonic mask photolithography. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuwaysir, E.F.; Huang, W.; Albert, T.J.; Singh, J.; Nuwaysir, K.; Pitas, A.; Richmond, T.; Gorski, T.; Berg, J.P.; Ballin, J. Gene expression analysis using oligonucleotide arrays produced by maskless photolithography. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.K.; Azdast, T.; Shabgard, M.R.; Navidfar, A.; Shishavan, S.M. Effect of carbon nanotubes on laser cutting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/poly methyl methacrylate nanocomposites. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 67, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Garner, S. Laser cutting of flexible glass. In Proceedings of the CLEO: Applications and Technology, San Jose, CA, USA, 8–13 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Huang, N.; Xu, F.; Tong, J.; Chen, Z.; Gui, X.; Fu, Y.; Lao, C. 3D printing technologies for flexible tactile sensors toward wearable electronics and electronic skin. Polymers 2018, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Dang, W.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R. Printing of high concentration nanocomposites (MWNTs/PDMS) using 3D-printed shadow masks. In Proceedings of the AISEM Annual Conference, Trento, Italy, 3–5 February 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K.U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, Skin-Mountable, and Wearable Strain Sensors and Their Potential Applications: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1678–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Hussain, M.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Das, A.K. Direct metal laser sintering of TiN reinforced Ti6Al4V alloy based metal matrix composite: Fabrication and characterization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 2635–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.C.; Phillips, S.T.; Dickey, M.D.; Lu, N.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Foldable printed circuit boards on paper substrates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jeerapan, I.; You, J.-M.; Nuñez-Flores, R.; Wang, J. Highly stretchable fully-printed CNT-based electrochemical sensors and biofuel cells: Combining intrinsic and design-induced stretchability. Nano Lett. 2015, 16, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, J.F.; Aliheidari, N.; Ameli, A.; Pötschke, P. 3D printed highly elastic strain sensors of multiwalled carbon nanotube/thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.H.; Takei, K.; Wang, C.; Ju, Y.; Kim, J.; Yu, Z.; Takahashi, T.; Cho, G.; Javey, A. Fully printed, high performance carbon nanotube thin-film transistors on flexible substrates. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3864–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Kiriya, D.; Ota, H.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Takei, K.; Javey, A. Printed carbon nanotube electronics and sensor systems. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4397–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Post-CMOS and post-MEMS compatible flexible skin technologies: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3962–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Lorenzelli, L. Recent advances of conductive nanocomposites in printed and flexible electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y.; Obata, K.; Machida, M.; Hohnholz, A.; Koch, J.; Suttmann, O.; Terakawa, M. Femtosecond-laser-based fabrication of metal/PDMS composite microstructures for mechanical force sensing. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 4203–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, D.; McGill, R.; Horwitz, J.; Fitz-Gerald, J.; Houser, E.; Stroud, R.; Wu, P.; Ringeisen, B.; Piqué, A.; Chrisey, D. Laser-based processing of polymer nanocomposites for chemical sensing applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 5739–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Isawi, N.A.; Aadim, K.A.; Yousif, A.A. Gas sensitivity properties of TiO2/Ag nanocomposite films prepared by pulse laser deposition. Iraqi J. Phys. 2017, 15, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Dosi, M.; Lau, I.; Zhuang, Y.; Simakov, D.S.; Fowler, M.W.; Pope, M.A. Ultra-Sensitive Electrochemical Methane Sensors based on Solid Polymer Electrolyte-Infused Laser-Induced Graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Peng, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Deng, L.; Tai, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhao, Y. A Simple Graphene NH3 Gas Sensor via Laser Direct Writing. Sensors 2018, 18, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, S.; Goh, G.L.; Dinh Le, T.-S.; An, J.; Peh, Z.K.; Yeong, W.Y.; Kim, Y.-J. Wearable Bandage-Based Strain Sensor for Home Healthcare: Combining 3D Aerosol Jet Printing and Laser Sintering. ACS Sens. 2018, 4, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroso, M.A.; Negri, L.H.; Kamizi, M.A.; Fabris, J.L.; Muller, M. Tactile Sensor Array with Fiber Bragg Gratings in Quasi-Distributed Sensing. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 6506239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Gray, E.; Chen, B. A self-healing, adaptive and conductive polymer composite ink for 3D printing of gas sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6200–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruna, A. Advances in carbon nanotube technology for corrosion applications. In Handbook of Polymer Nanocomposites. Processing, Performance and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 335–359. [Google Scholar]
- Okpala, C.C. The benefits and applications of nanocomposites. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Tech. 2014, 12, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Massaro, A.; Spano, F.; Missori, M.; Malvindi, M.A.; Cazzato, P.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Flexible nanocomposites with all-optical tactile sensing capability. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2820–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, A.; Hilbich, D.; Drewbrook, C.; Chung, D.; Gray, B. Large scale micropatterning of multi-walled carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane nanocomposite polymer on highly flexible 12 × 24 inch substrates. In Proceedings of the Micromachining and Microfabrication Process Technology XVI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 January 2011; p. 79260L. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, R.D.; Dalir, H.; Le Borgne, V.; Gautier, L.A.; El Khakani, M.A.; Lévesque, M.; Therriault, D. Direct-write fabrication of freestanding nanocomposite strain sensors. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 085502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Keating, T.; Todoroki, A.; Hiraoka, N. Rubber-based strain sensor fabricated using photolithography for intelligent tires. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthi, A.; Narakathu, B.; Reddy, A.; Eshkeiti, A.; Bohra, H.; Atashbar, M. A novel flexible strain gauge sensor fabricated using screen printing. In Proceedings of the 2012 Sixth International Conference on Sensing Sensing Technology (ICST), Kolkata, West Bengal, India, 18–21 December 2012; pp. 765–768. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, M.H.; Namdar, N.; Mashayekhi, A.; Ghasemi, F.; Sanaee, Z.; Mohajerzadeh, S. Flexible micro supercapacitors based on laser-scribed graphene/ZnO nanocomposite. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Ramaprabhu, S. Functionalized graphene-based nanocomposites for supercapacitor application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 14006–14013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Han, Q.; Wang, X. Graphene oxide− MnO2 nanocomposites for supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-X.; Choi, J.-W. Precision patterning of conductive polymer nanocomposite using a laser-ablated thin film. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 045014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Yao, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. Ultrafast self-healing nanocomposites via infrared laser and their application in flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araromi, O.A.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. High-resolution, large-area fabrication of compliant electrodes via laser ablation for robust, stretchable dielectric elastomer actuators and sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18046–18053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Zhu, C.; Li, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, J. Rehealable, fully recyclable, and malleable electronic skin enabled by dynamic covalent thermoset nanocomposite. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq0508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Hong, J.; Lee, Y.; Ha, M.; Jung, Y.; Lim, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, H. Tactile-direction-sensitive and stretchable electronic skins based on human-skin-inspired interlocked microstructures. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12020–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, D.P.; Graz, I.M.; Lacour, S.P. A multifunctional capacitive sensor for stretchable electronic skins. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 2008–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Ma, D.; Ma, Y.; Joshi, P.; Hu, A. Laser-assisted reduction of highly conductive circuits based on copper nitrate for flexible printed sensors. Nano-Micro Lett. 2017, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kravchuk, O.; Bobitski, Y.; Reichenberger, M. Laser curing of inkjet printed strain gauge structures. In Proceedings of the 2016 MIXDES-23rd International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, Lodz, Poland, 23–25 June 2016; pp. 343–345. [Google Scholar]
- Mizoshiri, M.; Ito, Y.; Arakane, S.; Sakurai, J.; Hata, S. Direct fabrication of Cu/Cu2O composite micro-temperature sensor using femtosecond laser reduction patterning. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 55, 06GP05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Flexible thermistors: Pulsed laser-induced liquid-phase sintering of spinel Mn–Co–Ni oxide films on polyethylene terephthalate sheets. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3809–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzynska, J.A.; Gijs, M.A. Flexible polyimide-based force sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 173, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Ziaie, B. Comparison of Direct and Indirect Laser Ablation of Metallized Paper for Inexpensive Paper-Based Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 36332–36341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.P.; Ratterman, M.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Hou, L.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Naik, R.R.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I.; Heikenfeld, J.C. Adhesive RFID sensor patch for monitoring of sweat electrolytes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, I.; Cerrada, C.; Cerrada, J.A.; Heradio, R.; Valero, E. Managing RFID sensors networks with a general purpose RFID middleware. Sensors 2012, 12, 7719–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaye, M.; Landry, G. Flexible Capacitive Sensor Array. Google Patents US9459736B2, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gregorio, P. Capacitive Sensor Gloves. Google Patents US9459736B2, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Atalay, A.; Sanchez, V.; Atalay, O.; Vogt, D.M.; Haufe, F.; Wood, R.J.; Walsh, C.J. Batch Fabrication of Customizable Silicone-Textile Composite Capacitive Strain Sensors for Human Motion Tracking. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuautla, M.; Bernardini, S.; Gallais, L.; Bendahan, M. Direct laser patterning of a gas sensor on flexible substrate. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallais, L.; Bergeret, E.; Wang, B.; Guérin, M.; Bènevent, E. Ultrafast laser ablation of metal films on flexible substrates. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 115, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankoco, M.; Bénevent, E.; Bergeret, E.; Gallais, L.; Bendahan, M. Temperature sensor on flexible substrate patterned by laser ablation. In Proceedings of the 2014 10th International Conference on Advanced Semiconductor Devices & Microsystems (ASDAM), Smolenice Castle, Slovakia, 20–22 October 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bellini, N.; Geremia, R.; Norval, S.; Fichet, G.; Karnakis, D. Laser Thin Film Patterning for Rapid Prototyping and Customised Production of Flexible Electronics Devices. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2016, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, J.-H. Graphene-based flexible and stretchable thin film transistors. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4870–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuautla, M.; Bernardini, S.; Gallais, L.; Fiorido, T.; Patout, L.; Bendahan, M. Ozone flexible sensors fabricated by photolithography and laser ablation processes based on ZnO nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Kim, H.; Lone, S.; Jeon, S.; Kwon, Y.W.; Shin, B.; Hong, S.W. One-Step Laser Patterned Highly Uniform Reduced Graphene Oxide Thin Films for Circuit-Enabled Tattoo and Flexible Humidity Sensor Application. Sensors 2018, 18, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Sensing System for Salinity Testing Using Laser-induced Graphene Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 264, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Ye, R.; Samuel, E.L.; Yacaman, M.J.; Yakobson, B.I.; Tour, J.M. Laser-induced porous graphene films from commercial polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahi, M.E.E.; Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Burkitt, L. A temperature-compensated graphene sensor for nitrate monitoring in real-time application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Fabrication and implementation of printed sensors for taste sensing applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.H.; Park, J.B.; Ahn, S.; Grigoropoulos, C.P. Laser-Induced Direct Graphene Patterning and Simultaneous Transferring Method for Graphene Sensor Platform. Small 2013, 9, 4269–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strek, W.; Cichy, B.; Radosinski, L.; Gluchowski, P.; Marciniak, L.; Lukaszewicz, M.; Hreniak, D. Laser-induced white-light emission from graphene ceramics–opening a band gap in graphene. Light: Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-Q.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Ju, Z.-Y.; Pang, Y.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; Tian, X.-G.; Yan, J.-C.; Deng, N.-Q. An intelligent artificial throat with sound-sensing ability based on laser induced graphene. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, A.; Cai, J. On Demand Process Based on Laser Direct Writing and the Sensor Application. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2017, 30, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.-W.; Feng, Q.-P.; Xiao, H.-M.; Li, N.; Fu, S.-Y. Rapid Laser Printing of Paper-Based Multilayer Circuits. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8895–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Yu, W.; Ziaie, B. Highly stretchable and sensitive unidirectional strain sensor via laser carbonization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4463–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Park, J.E.; Lee, J.; Yang, M.; Kang, B. Laser-assisted fabrication of single-layer flexible touch sensor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Rovere, T.; Weerawarne, D.; Osterhoudt, G.; Kang, N.; Joseph, P.; Luo, J.; Shim, B.; Poliks, M.; Zhong, C.-J. Nanoalloy printed and pulse-laser sintered flexible sensor devices with enhanced stability and materials compatibility. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6168–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, D.X.; Subramanian, A.K.; Silva, G.A.L.; Yoon, J.; Cofer, S.; Yang, K.; Owuor, P.S.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Lou, J. Laminated Object Manufacturing of 3D-Printed Laser-Induced Graphene Foams. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, M.J.; Schrandt, M.; Renn, J.; Feng, J.Q. Localized Laser Sintering of Metal Nanoparticle Inks Printed with Aerosol Jet® Technology for Flexible Electronics. J. Microelectron. Electron. Packag. 2017, 14, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Disadvantages of Nanocomposites for Application in Gas Sensors. In Handbook of Gas Sensor Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Julkapli, N.M.; Bagheri, S.; Sapuan, S. Multifunctionalized carbon nanotubes polymer composites: Properties and applications. In Eco-Friendly Polymer Nanocomposites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 155–214. [Google Scholar]
- Warnke, P.H.; Seitz, H.; Warnke, F.; Becker, S.T.; Sivananthan, S.; Sherry, E.; Liu, Q.; Wiltfang, J.; Douglas, T. Ceramic scaffolds produced by computer-assisted 3D printing and sintering: Characterization and biocompatibility investigations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2010, 93, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Printed Image Sensors Market (2018–2023) with Analysis by Printing Technology, End-User Industries, and Region. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180514006024/en/Global-Printed-Image-Sensors-Market-2018-2023-Analysis (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Global Printed Sensors Market 2015–2018 & 2027—Focus on Proximity, Touch, Temperature, Image, Pressure, Gas, Bio and Humidity Sensors. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-printed-sensors-market-2015-2018--2027----focus-on-proximity-touch-temperature-image-pressure-gas-bio-and-humidity-sensors-300758929.html (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Printed Sensors Market: Global Industry Analysis 2012–2016 and Opportunity Assessment; 2017–2027. Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/printed-sensors-market (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- 3D Printing Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/3d-printing-industry-analysis (accessed on 17 March 2019).













| Materials | Type | Sensor Type | Processing Parameters | Res. Time (s) | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTs/PDMS | Nanocomposite-based | Cap. | P:24 W, S: 70 m/min, FD: 1 mm | 1 | Limb movements, respiration | [1] |
| Silver/PDMS | Nanocomposite-based | Res. | P:120 mW, S: 2 m/min, FD: 1 mm | ~5 | Pressure sensing: 50-100 kPa | [57] |
| Polymer/carbon black | Nanocomposite-based | Res. | P: 150-300 mJ/cm2, Pulse duration: 30 ns, FD: 3 cm, F.: 10/20 Hz | 1.2 | Toluene vapor sensing | [58] |
| Titanium dioxide/Ag | Nanocomposite-based | Res. | Nd:YAG: beam wav.:1064 nm, W: 532 nm, repetition rate: 6 Hz, PD: 10ns | 0.2 | Gas-sensing: NO2: 60 ppm, NH3: 200 ppm | [59] |
| Graphene/Polyimide | Laser ablation | Cap. | P: 10%, S: 25mm/s, | 40 | Gas-sensing: CH4, H2O, CO2, CO: 10–100 ppm | [60] |
| Aluminium/PET | Laser ablation | Cap. | P: 24 W, S: 70 m/min, FD: 1 mm | 1 | Tactile-sensing: Pressure: | [2] |
| Graphene/Polyimide | Laser ablation | Res. | W: 10.6 μm, FD: 5 cm | 214 | Gas-sensing: NH3: 75–400 ppm | [61] |
| Silver/PU coated with a layer of acrylic | 3D printed | Res. | P: 120 mW, S: 10-150 mm/s, W: 780 nm, FD: 60 µm | 492.16 | Strain-sensing: 10–30 MPa, 7 N | [62] |
| Silicon elastomer | 3D printed | Optical | Energy: 2.5 mJ, F: 250 Hz, EX: ~1 min, length: 3 mm, SB: 0.21 nm | – | Tactile-sensing: Different loads from 50–250 g | [63] |
| Graphene/PBS | 3D printed | Res. | P: 1mW, SR: 2.5 cm-1, W: 514.5 nm | 1–27 | Gas-sensing: Methanol, Toluene, Hexane, 1,4- Dioxane, Diethyl ether, Dimethyl carbonate | [64] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, T.; Nag, A.; Afsarimanesh, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kundu, S.; Xu, Y. Laser-Assisted Printed Flexible Sensors: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061462
Han T, Nag A, Afsarimanesh N, Mukhopadhyay SC, Kundu S, Xu Y. Laser-Assisted Printed Flexible Sensors: A Review. Sensors. 2019; 19(6):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061462
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Tao, Anindya Nag, Nasrin Afsarimanesh, Subhas Chandra Mukhopadhyay, Sudip Kundu, and Yongzhao Xu. 2019. "Laser-Assisted Printed Flexible Sensors: A Review" Sensors 19, no. 6: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061462
APA StyleHan, T., Nag, A., Afsarimanesh, N., Mukhopadhyay, S. C., Kundu, S., & Xu, Y. (2019). Laser-Assisted Printed Flexible Sensors: A Review. Sensors, 19(6), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19061462







