Drop Drying on the Sensor: One More Way for Comparative Analysis of Liquid Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Morphological Characteristics of Dried Drops as a Source of Information about the Liquid Quality
1.2. The Dynamic Characteristics of Drying Drops as a Source of Information about the Liquid Quality
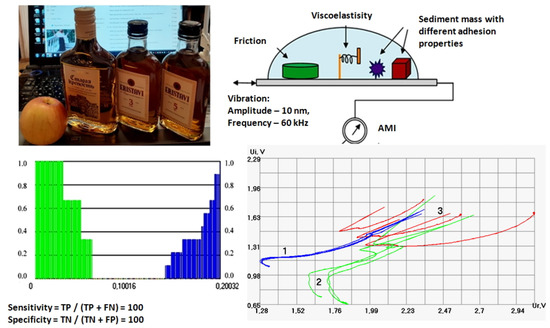
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fundamentals of the Method Used
2.2. Amplitude Curve Parametrization (Shape Indices) as a Tool for Distinguishing between Liquids
3. Next Generation Device
3.1. Technical Features of the Next Generation Device
3.2. Signal Registration
3.3. Signal Processing
3.4. Results of Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolen, L. The blood pattern as a clue to the diagnosis of malignant disease. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1942, 27, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Bolen, H.L. The blood pattern in pre-symptomatic malignancy of the gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1951, 19, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalin, V.N.; Shatokhina, S.N. Morphology of Biological Fluids; Khrisostom: Moscow, Russia, 2001; p. 304. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sadek, C.; Schuck, P.; Fallourd, Y.; Pradeau, N.; Le Floch-Fouéré, C.; Jeantet, R. Drying of a single droplet to investigate process–structure–function relationships: A review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 95, 771–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefiane, K. Patterns from drying drops. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, N.M.; Trybala, A.; Starov, V. Evaporation of sessile droplets. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popov, Y.O. Evaporative deposition patterns: Spatial dimensions of the deposit. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 036313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuncicky, D.M.; Velev, O.D. Surface-Guided Templating of Particle Assemblies inside Drying Sessile Droplets. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Fang, X.; Somasundaran, P.; Attinger, D. Self-Assembly of Colloidal Particles from Evaporating Droplets: Role of DLVO Interactions and Proposition of a Phase Diagram. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7833–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsoumpas, Y.; Dehaeck, S.; Rednikov, A.; Colinet, P. Effect of Marangoni Flows on the Shape of Thin Sessile Droplets Evaporating into Air. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13334–13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brutin, D.; Sobac, B.; Loquet, B.; Sampol, J. Pattern formation in drying drops of blood. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 667, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgiutti-Dauphiné, F.; Pauchard, L. Drying drops. Eur. Phys. J. E 2018, 41, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gutiérrez, J.; Pérez-Isidoro, R.; Ruiz-Suárez, J.C. A technique based on droplet evaporation to recognize alcoholic drinks. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 074101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadeh, L.; Imran, S.; Bencsik, M.; Sharpe, G.R.; Johnson, M.A.; Fairhurst, D. Machine Learning Analysis for Quantitative Discrimination of Dried Blood Droplets. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Li, Z.; Hurth, C.M.; Zenhausern, F.; Chang, S.-F.; Attinger, D. Identification of fluid and substrate chemistry based on automatic pattern recognition of stains. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G.; Levin, G.Y.; Korochkina, O.V.; Buzoverya, M.E. The dynamics of self-organization of biofluids in norm and some diseases. In Proceedings of the Materials of the 4th International conference on mathematical modeling, Moscow, Russia, 27 June–1 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G.; Sanin, A.G.; Sanina, O.; Pelyushenko, A.S.; Egorova, N.; Terentiev, I.G.; Smetanina, S.V.; Korochkina, O.V.; Yashukova, E.V. The informative-capacity phenomenon of drying drops. IEEE Eng. Med. Boil. Mag. 2005, 24, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.; Sanin, A.; Pelyushenko, A.; Kazakov, V.; Shaposhnikova, O.; Chernov, A.V.; Yakhno, V.; Vacca, C.; Falcione, F.; Johnson, B. Uncoated quartz resonator as a universal biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakhno, T.; Sanin, A.; Kazakov, V.; Sanina, O.; Vacca, C.; Falcione, F.; Yakhno, V. Uncoated quartz resonator as a universal biosensor. In Intelligent and Biosensors; Somerset, V.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2010; pp. 345–362. ISBN 978-953-7619-58-9. Available online: http://www.sciyo.com/articles/show/title/uncoated-quartz-resonator-as-a-universal-biosensor (accessed on 25 December 2010). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Sanin, A.G.; Yahno, V.G. Dynamics of phase transitions in drying drops of biological fluids: Physicochemical fundamentals, a method for recording and extracting diagnostic information. In Medicine in the Mirror of Computer Science; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 2008; pp. 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G. Structural evolution of drying drops of biological fluids. Tech. Phys. 2009, 54, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Kazakov, V.V.; Sanin, A.G.; Shaposhnikova, O.B.; Chernov, A.V. Mechanical properties of adsorption layers in solutions of human blood serum proteins: A comparative assessment. Tech. Phys. 2007, 52, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Kazakov, V.V.; Sanin, A.G.; Shaposhnikova, O.B.; Chernov, A.V. Dynamics of phase transitions in drying drops of human serum protein solutions. Tech. Phys. 2007, 52, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Kazakov, V.V.; Sanina, O.A.; Sanin, A.G.; Yakhno, V.G. Drops of biological fluids drying on a hard substrate: Variation of the morphology, weight, temperature, and mechanical properties. Tech. Phys. 2010, 55, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Sanin, A.G.; Sanina, O.A.; Yakhno, V.G. Dynamics of mechanical properties of drying drops of biological liquids as a reflection of the features of self-organization of their components from nano- to microlevel. Biophysics 2011, 56, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanina, O.A.; Yakhno, T.A.; Sanin, A.G. A new rapid test to assess the degree of endogenous intoxication in burn injury. Clin. Lab. Consult. 2011, 3, 52–59. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Sanin, A.G.; Ilyazov, R.G.; Vildanova, G.V.; Khamzin, R.A.; Astascheva, N.P.; Markovsky, M.G.; Bashirov, V.D.; Yakhno, V.G. Drying Drop Technology as a Possible Tool for Detection Leukemia and Tuberculosis in Cattle. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakhno, T.; Sanin, A.; Yakhno, V.; Guguchkina, T.; Markovsky, M. Wine recognition system based on drying drop technology. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 2016, 4, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.; Sanin, A.; Yakhno, V.; Kazakov, V.; Pakhomov, A.; Guguchkina, T.; Markovsky, M. Drying drop technology in wine and hard drinks quality control. In A Handbook of Food Bioengineering, V.16: Food Control and Biosecurity; Holban, A.M., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 451–480. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.; Yakhno, V.; Sanin, A.; Sanina, O.; Pelyushenko, A. Dynamics of Phase Transitions in Drying Drops as an Information Parameter of Liquid Structure. Nonlinear Dyn. 2005, 39, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakhno, T.A.; Sanin, A.G.; Sanina, O.A.; Iakhno, V.G. Method for study of phase transitions in evaporating drop and its application for evaluation of physical-chemical properties of water and water solutions. Biofizika 2012, 57, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- ROC Curve Analysis. Available online: https://www.statsdirect.com/help/nonparametric_methods/roc.htm (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G.; Shmeljov, I.I.; Sanin, A.G.; Krotov, E.V.; Brodsky, Y.Y. Method for studying liquid and device for carrying out said method. U.S. Patent 6,874,357 B2, 5 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G.; Shmeljov, I.I.; Sanin, A.G.; Krotov, E.V.; Brodsky, Y.Y. Method and Apparatus for Determination of Food Quality and Authenticity. U.S. Patent US7350403B2, 3 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G.; Shmeljov, I.I.; Sanin, A.G.; Krotov, E.V.; Brodsky, Y.Y. Method and Apparatus for Determination of Medical Diagnostics Using Biological Fluids. U.S. Patent US7350402B2, 1 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.F.S.; Rocha, F.R. A novel approach to detect milk adulteration based on the determination of protein content by smartphone-based digital image colorimetry. Food Control. 2020, 115, 107299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera-Chiner, L.; Jiménez, Y.; Montoya, Á.; Juan-Borrás, M.; Pascual, N.; Arnau, A.; Escriche, I. High Fundamental Frequency Quartz Crystal Microbalance (HFF-QCMD) Immunosensor for detection of sulfathiazole in honey. Food Control. 2020, 115, 107296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Hard Drinks | Wine | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Georgian brandy Eristavi 5* | 1. | Semi-sweet red table wine Toro de Oro (Spain) |
| 2. | Georgian brandy Eristavi 3* | 2. | Port wine 777 (Russia) |
| 3. | Russian brandy Staraya Krepost | 3. | Vermouth Martini Bianco (Italy) |
| 4. | Russian brandy Lezginka | 4. | Semi-sweet grape natural red wine Khvanchkara (Georgia) |
| 5. | Russian drink Three old men | 5. | Dry white table wine Chardonnay (Fanagoria, Russia) |
| 6. | Irish whiskey Jameson | 6. | Dry white table wine Sauvignon (Fanagoria, Russia) |
| 7. | Macallan Whiskey (Scotland) | 7. | Dry white table wine Aligote-Riesling of Fanagoria (Fanagoria, Russia) |
| 8. | Mordovian balm (Russia) | 8. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) |
| 9. | Brandy Stareishina (Russia) | 9. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (3 g/100 mL) |
| 10. | Vodka Khlebnaya Sleza (Russia) | 10. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (6 g/100 mL) |
| 11. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (9 g/100 mL) | ||
| Milk | |||
| 1. | Whole powdered milk, 6 g/100 mL distilled water | 3. | Whole powdered milk, 10 g/100 mL distilled water |
| 2. | Whole powdered milk, 8 g/100 mL distilled water | 4. | Whole powdered milk, 14 g/100 mL distilled water |
| Compared Samples | Recognition Statistics (EER—Equal Error Rate) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard drinks | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
| 1. | Georgian brandy Eristavi 5* and Georgian brandy Eristavi 3* | 93 | 99 |
| 2. | Georgian brandy Eristavi 5* and Russian brandy Staraya Krepost | 97 | 100 |
| 3. | Georgian brandy Eristavi 3* and Russian brandy Staraya Krepost | 20 | 99 |
| 4. | Russian brandy Lezginka and Russian drink Three old men | 100 | 100 |
| 5. | Russian brandy Lezginka and Irish whiskey Jameson | 100 | 100 |
| 6. | Macallan Whiskey (Scotland) and Mordovian balm (Russia) | 100 | 100 |
| 7. | Vodka Khlebnaya Sleza (Russia) and Brandy Stareishina (Russia) | 100 | 100 |
| Wine | |||
| 8. | Semi-sweet red table wine Toro de Oro (Spain) and Port wine 777 (Russia) | 100 | 100 |
| 9. | Port wine 777 (Russia) and Vermouth Martini Bianco (Italy) | 100 | 100 |
| 10. | Semi-sweet red table wine Toro de Oro (Spain) and Semi-sweet grape natural red wine Khvanchkara (Georgia) | 100 | 100 |
| 11. | Dry white table wine Chardonnay (Fanagoria, Russia) and Dry white table wine Sauvignon (Fanagoria, Russia) | 100 | 100 |
| 12. | Dry white table wine Sauvignon (Fanagoria, Russia) and Dry white table wine Aligote -Riesling of Fanagoria (Russia) | 100 | 100 |
| 13. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) and Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (3 g/100 mL) | 100 | 100 |
| 14. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (3 g/100 mL) and Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (6 g/100 mL) | 100 | 100 |
| 15. | Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (6 g/100 mL) and Semi-dry red wine Pirosmani (Georgia) + sugar (9 g/100 mL) | 100 | 100 |
| Milk | |||
| 16. | Whole powdered milk, 6 g/100 mL distilled water and Whole powdered milk, 8 g/100 mL distilled water | 99 | 85 |
| 17. | Whole powdered milk, 6 g/100 mL distilled water and Whole powdered milk, 10 g/100 mL distilled water | 100 | 100 |
| 18. | Whole powdered milk, 10 g/100 mL distilled water and Whole powdered milk, 14 g/100 mL distilled water | 100 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yakhno, T.; Pakhomov, A.; Sanin, A.; Kazakov, V.; Ginoyan, R.; Yakhno, V. Drop Drying on the Sensor: One More Way for Comparative Analysis of Liquid Media. Sensors 2020, 20, 5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185266
Yakhno T, Pakhomov A, Sanin A, Kazakov V, Ginoyan R, Yakhno V. Drop Drying on the Sensor: One More Way for Comparative Analysis of Liquid Media. Sensors. 2020; 20(18):5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185266
Chicago/Turabian StyleYakhno, Tatiana, Alexander Pakhomov, Anatoly Sanin, Vyacheslav Kazakov, Ruben Ginoyan, and Vladimir Yakhno. 2020. "Drop Drying on the Sensor: One More Way for Comparative Analysis of Liquid Media" Sensors 20, no. 18: 5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185266
APA StyleYakhno, T., Pakhomov, A., Sanin, A., Kazakov, V., Ginoyan, R., & Yakhno, V. (2020). Drop Drying on the Sensor: One More Way for Comparative Analysis of Liquid Media. Sensors, 20(18), 5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185266