A Motion Artifact Correction Procedure for fNIRS Signals Based on Wavelet Transform and Infrared Thermography Video Tracking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. IRT Instrumentation
2.3. fNIRS Instrumentation
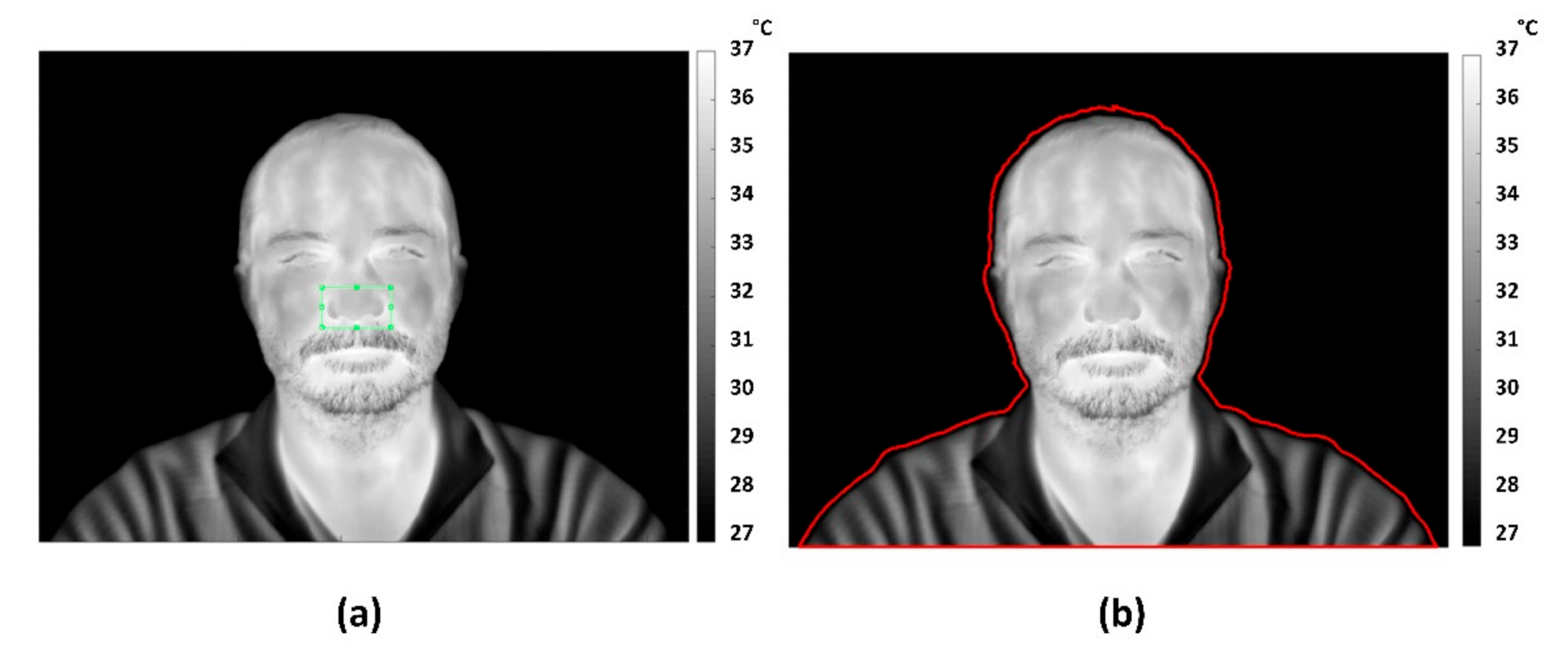
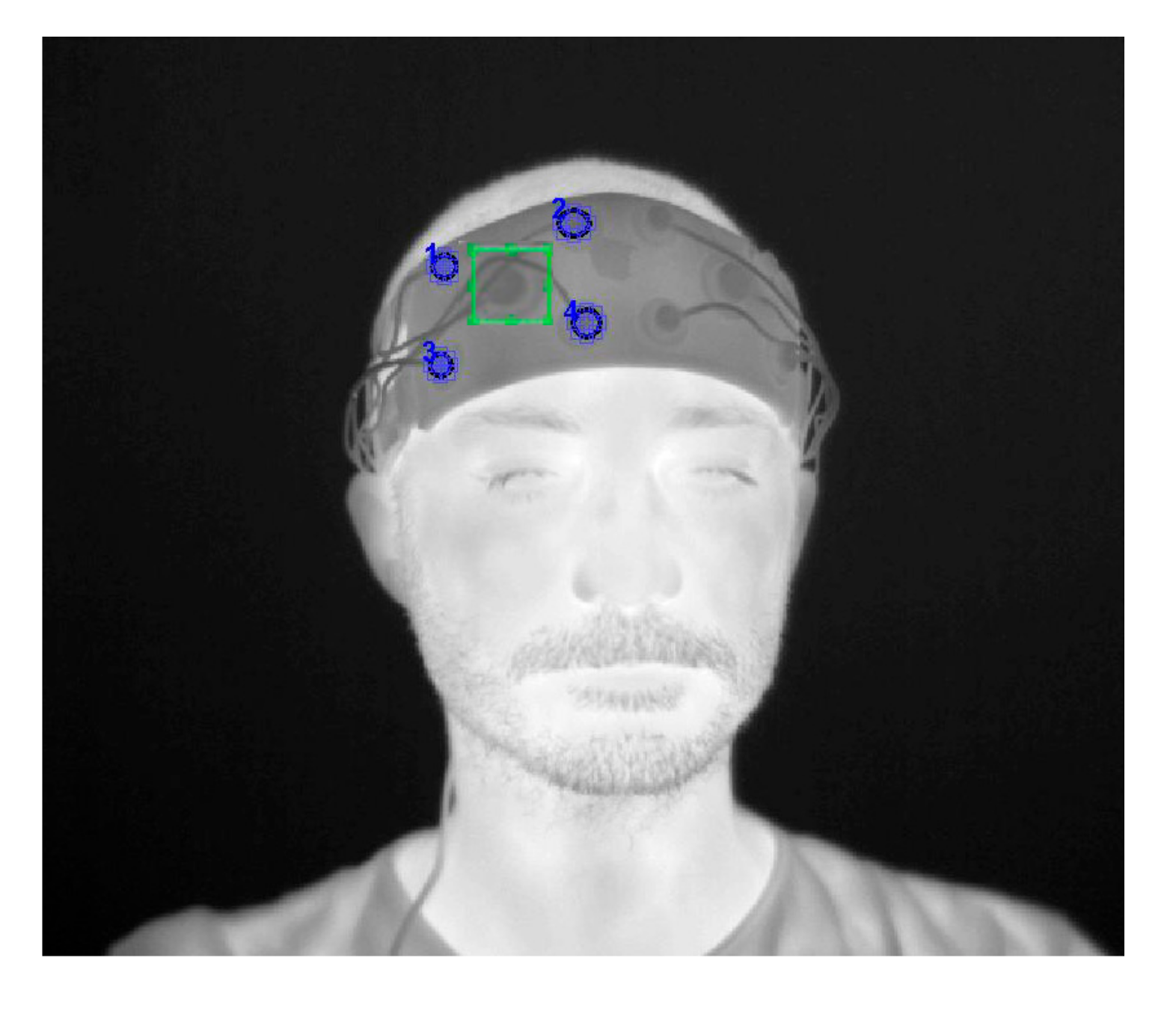
2.4. IRT Tracking Procedure
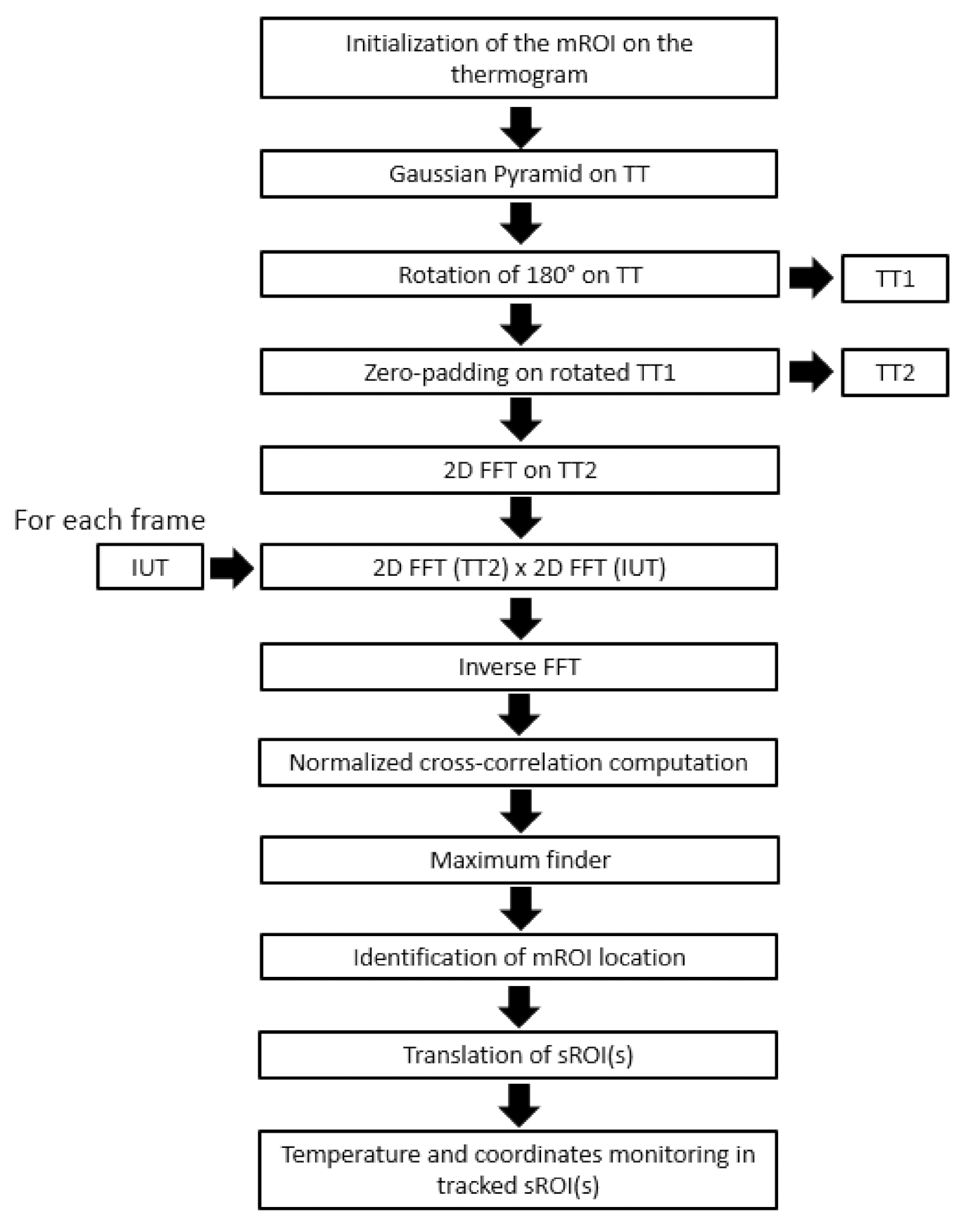
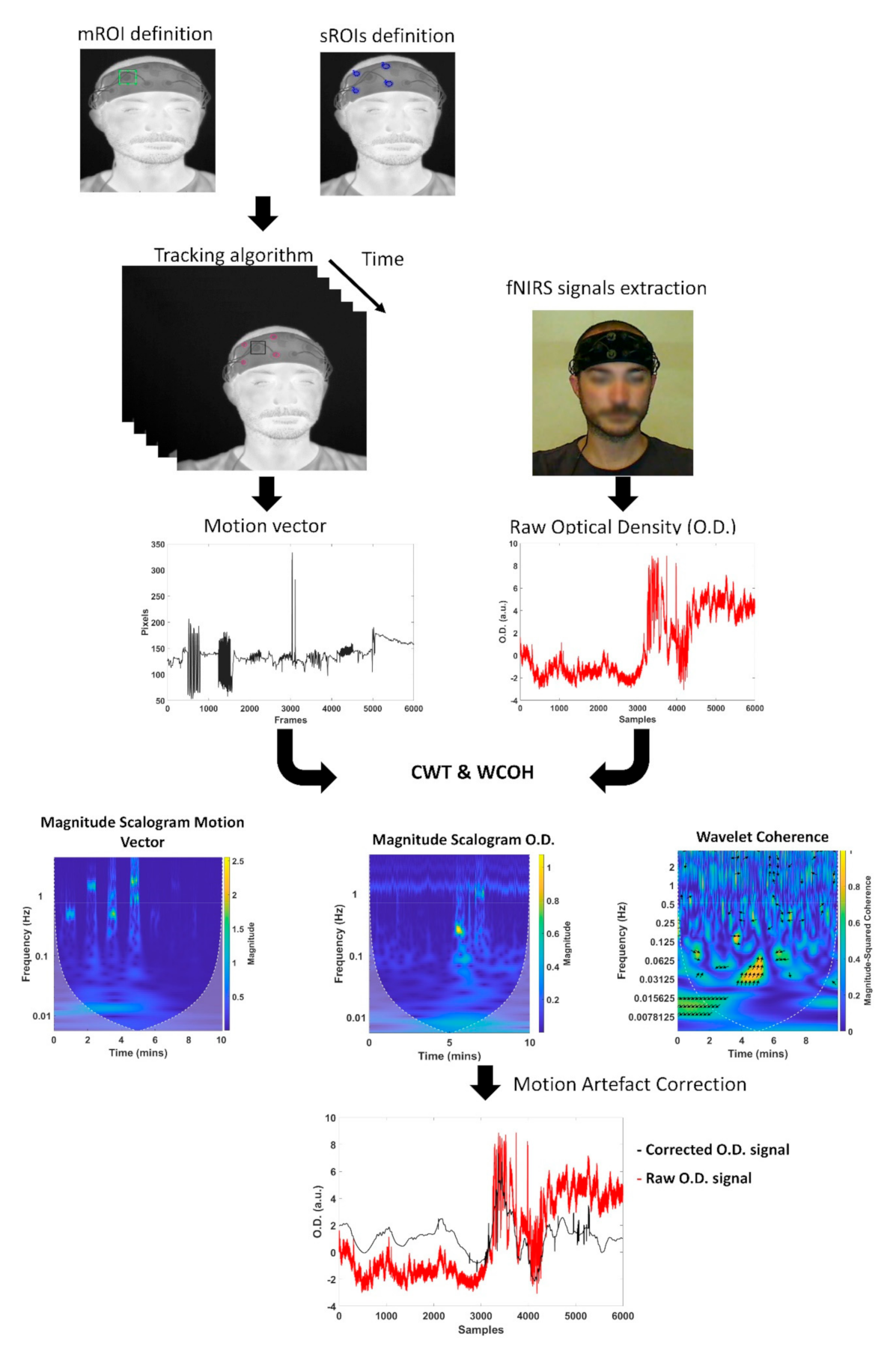
2.5. fNIRS Motion Artefacts Correction Algorithm
2.6. Validation of the fNIRS Motion Artifacts Removal Algorithm
3. Results
3.1. IR Tracking Performances
3.2. Statistical Validation of the Motion Artifacts Removal Algorithm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinti, P.; Tachtsidis, I.; Hamilton, A.; Hirsch, J.; Aichelburg, C.; Gilbert, S.; Burgess, P.W. The Present and Future Use of Functional Near-infrared Spectroscopy (FNIRS) for Cognitive Neuroscience. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1464, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A Brief Review on the History of Human Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (FNIRS) Development and Fields of Application. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaresima, V.; Ferrari, M. A Mini-Review on Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (FNIRS): Where Do We Stand, and Where Should We Go? Photonics 2019, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Perpetuini, D.; Croce, P.; Greco, G.; Mistretta, L.; Rizzo, R.; Vinciguerra, V.; Romeo, M.F.; Zappasodi, F.; Merla, A. Fiberless, Multi-Channel FNIRS-EEG System Based on Silicon Photomultipliers: Towards Sensitive and Ecological Mapping of Brain Activity and Neurovascular Coupling. Sensors 2020, 20, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawangjai, P.; Hompoonsup, S.; Leelaarporn, P.; Kongwudhikunakorn, S.; Wilaiprasitporn, T. Consumer Grade EEG Measuring Sensors as Research Tools: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 3996–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, P.; Aichelburg, C.; Gilbert, S.; Hamilton, A.; Hirsch, J.; Burgess, P.; Tachtsidis, I. A Review on the Use of Wearable Functional Near-infrared Spectroscopy in Naturalistic Environments. Jpn. Psychol. Res. 2018, 60, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perpetuini, D.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Filippini, C.; Cardone, D.; Croce, P.; Rotunno, L.; Anzoletti, N.; Zito, M.; Zappasodi, F.; Merla, A. Working Memory Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease Is Detected by Complexity Analysis of Multimodal EEG-FNIRS. Entropy 2020, 22, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.A.; Pinti, P. Wearables and the Brain. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2019, 18, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Nam, C.S. Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS) in Neuroergonomics. In Neuroergonomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, M.M. Statistical Analysis of FMRI Time-Series: A Critical Review of the GLM Approach. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brigadoi, S.; Ceccherini, L.; Cutini, S.; Scarpa, F.; Scatturin, P.; Selb, J.; Gagnon, L.; Boas, D.A.; Cooper, R.J. Motion Artifacts in Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: A Comparison of Motion Correction Techniques Applied to Real Cognitive Data. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cooper, R.; Selb, J.; Gagnon, L.; Phillip, D.; Schytz, H.W.; Iversen, H.K.; Ashina, M.; Boas, D.A. A Systematic Comparison of Motion Artifact Correction Techniques for Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Seghouane, A.-K. Motion Artefact Removal in Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Signals Based on Robust Estimation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 1145–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Brooks, D.H.; Franceschini, M.A.; Boas, D.A. Eigenvector-Based Spatial Filtering for Reduction of Physiological Interference in Diffuse Optical Imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 011014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yücel, M.A.; Selb, J.; Cooper, R.J.; Boas, D.A. Targeted Principle Component Analysis: A New Motion Artifact Correction Approach for near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2014, 7, 1350066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Spichtig, S.; Muehlemann, T.; Wolf, M. How to Detect and Reduce Movement Artifacts in Near-Infrared Imaging Using Moving Standard Deviation and Spline Interpolation. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molavi, B.; Dumont, G.A. Wavelet-Based Motion Artifact Removal for Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, A.; Phillips, D.; Lloyd-Fox, S.; Koh, P.H.; Elwell, C.E. Automatic detection of motion artifacts in infant functional optical topography studies. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXXI; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, J.; Kotilahti, K.M.; Ilmoniemi, R.; Noponen, T.E.; Virtanen, J. Accelerometer-Based Method for Correcting Signal Baseline Changes Caused by Motion Artifacts in Medical Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 087005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, A.J.; Wolf, M.; Achermann, P.; Scholkmann, F. A New Approach for Automatic Removal of Movement Artifacts in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Time Series by Means of Acceleration Data. Algorithms 2015, 8, 1052–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Baker, J.M.; Liu, N.; Reiss, A.L. Sensitivity of FNIRS Measurement to Head Motion: An Applied Use of Smartphones in the Lab. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 245, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiquee, M.R.; Marquez, J.S.; Atri, R.; Ramon, R.; Mayrand, R.P.; Bai, O. Movement Artefact Removal from NIRS Signal Using Multi-Channel IMU Data. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiquee, M.R.; Xue, T.; Marquez, J.S.; Atri, R.; Ramon, R.; Mayrand, R.P.; Leung, C.; Bai, O. Sensor Fusion in Human Cyber Sensor System for Motion Artifact Removal from Nirs Signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th International Conference on Human System Interaction (HSI), Richmond, VA, USA, 25–27 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Izzetoglu, M.; Chitrapu, P.; Bunce, S.; Onaral, B. Motion Artifact Cancellation in NIR Spectroscopy Using Discrete Kalman Filtering. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, F.C.; Douglas, T.S.; Meintjes, E.M. Motion Artifact Removal for Functional near Infrared Spectroscopy: A Comparison of Methods. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, L.; Yücel, M.A.; Boas, D.A.; Cooper, R.J. Further Improvement in Reducing Superficial Contamination in NIRS Using Double Short Separation Measurements. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Robinson, P.; Morency, L.-P. OpenFace: An Open Source Facial Behavior Analysis Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Richmond, VA, USA, 25–27 June 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Vardasca, R.; Magalhaes, C.; Mendes, J. Biomedical Applications of Infrared Thermal Imaging: Current State of Machine Learning Classification. In Proceedings of the Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings, Firenze, Italy, 17–19 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pinti, P.; Cardone, D.; Merla, A. Simultaneous FNIRS and Thermal Infrared Imaging during Cognitive Task Reveal Autonomic Correlates of Prefrontal Cortex Activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, A.; Brigadoi, S.; Giorgi, G.; Sparacino, G.; Narduzzi, C. Accurate Hemodynamic Response Estimation by Removal of Stimulus-Evoked Superficial Response in FNIRS Signals. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 036019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Lühmann, A.; Li, X.; Müller, K.-R.; Boas, D.A.; Yücel, M.A. Improved Physiological Noise Regression in FNIRS: A Multimodal Extension of the General Linear Model Using Temporally Embedded Canonical Correlation Analysis. NeuroImage 2020, 208, 116472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Methods and Applications: A Survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Mei, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X. Automatic Visible and Infrared Face Registration Based on Silhouette Matching and Robust Transformation Estimation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 69, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y.; Tian, J. Non-Rigid Visible and Infrared Face Registration via Regularized Gaussian Fields Criterion. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ross, A. Matching Thermal to Visible Face Images Using Hidden Factor Analysis in a Cascaded Subspace Learning Framework. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2016, 72, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leykin, A.; Ran, Y.; Hammoud, R. Thermal-Visible Video Fusion for Moving Target Tracking and Pedestrian Classification. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. On Pedestrian Detection and Tracking in Infrared Videos. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.-S.; Jeon, E.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Le, T.T.; Shin, K.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Park, K.R. Robust Pedestrian Detection by Combining Visible and Thermal Infrared Cameras. Sensors 2015, 15, 10580–10615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardone, D.; Spadolini, E.; Perpetuini, D.; Filippini, C.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Merla, A. Automated Warping Procedure for Facial Thermal Imaging Based on Features Identification in the Visible Domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 112, 103595. [Google Scholar]
- Eveland, C.K.; Socolinsky, D.A.; Wolff, L.B. Tracking Human Faces in Infrared Video. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdall, J.; Pavlidis, I.T.; Tsiamyrtzis, P. Coalitional Tracking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2007, 106, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarian, N.; Venetsanopoulos, A.N.; Chau, T. Infrared Thermography as an Access Pathway for Individuals with Severe Motor Impairments. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2009, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Tsiamyrtzis, P.; Lindner, P.; Timofeyev, I.; Pavlidis, I. Spatiotemporal Smoothing as a Basis for Facial Tissue Tracking in Thermal Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 60, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burt, P.J. Fast Filter Transform for Image Processing. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1981, 16, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, D. The Discrete Fourier Transform, Part 6: Cross-Correlation. J. Object Technol. 2010, 9, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wachowiak, M.P.; Wachowiak-Smolíková, R.; Johnson, M.J.; Hay, D.C.; Power, K.E.; Williams-Bell, F.M. Quantitative Feature Analysis of Continuous Analytic Wavelet Transforms of Electrocardiography and Electromyography. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2018, 376, 20170250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Holmes, A.P.; Worsley, K.J.; Poline, J.-P.; Frith, C.D.; Frackowiak, R.S. Statistical Parametric Maps in Functional Imaging: A General Linear Approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1994, 2, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.C.; Tak, S.; Jang, K.E.; Jung, J.; Jang, J. NIRS-SPM: Statistical Parametric Mapping for near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Bray, S.; Reiss, A.L. Functional near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Signal Improvement Based on Negative Correlation between Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Hemoglobin Dynamics. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagemann, D.; Waldstein, S.R.; Thayer, J.F. Central and Autonomic Nervous System Integration in Emotion. Brain Cogn. 2003, 52, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Cardone, D.; Bucco, R.; Zito, M.; Merla, A. Assessment of the Autonomic Response in Alzheimer’s Patients During the Execution of Memory Tasks: A Functional Thermal Imaging Study. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eysenck, M.W.; Derakshan, N.; Santos, R.; Calvo, M.G. Anxiety and Cognitive Performance: Attentional Control Theory. Emotion 2007, 7, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachtsidis, I.; Scholkmann, F. False Positives and False Negatives in Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: Issues, Challenges, and the Way Forward. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 031405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zohdi, H.; Egli, R.; Guthruf, D.; Scholkmann, F.; Wolf, U. Color-Dependent Changes in Humans during a Verbal Fluency Task under Colored Light Exposure Assessed by SPA-FNIRS. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohdi, H.; Scholkmann, F.; Wolf, U. Individual Differences in Hemodynamic Responses Measured on the Head Due to a Long-Term Stimulation Involving Colored Light Exposure and a Cognitive Task: A SPA-FNIRS Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadev, P.; Giri, L.I. Non-Contact Monitoring of Human Respiration Using Infrared Thermography and Machine Learning. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 104, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadev, P.; Giri, L.I. Human Respiration Monitoring Using Infrared Thermography and Artificial Intelligence. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2020, 6, 035007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Harford, M.; Villarroel, M.; Chaichulee, S.; Davidson, S.; Finnegan, E.; Clark, S.H.; Young, J.D.; Watkinson, P.J.; Tarassenko, L. Non-Contact Assessment of Peripheral Artery Haemodynamics Using Infrared Video Thermography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandi, S.; Yusuf, S.; Kaelan, C.; Mukhtar, M. Evaluation Risk of Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs) Using Infrared Thermography Based on Mobile Phone as Advanced Risk Assessment Tool in the Community Setting: A Multisite Cross-Sectional Study. Enfermería Clínica 2020, 30, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hu, M.; Gao, Z.; Fan, L.; Dai, R.; Pan, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhai, G.; Lu, Y. Detection of Respiratory Infections Using RGB-Infrared Sensors on Portable Device. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13674–13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhai, G. Portable Health Screening Device of Respiratory Infections. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), London, UK, 6–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, K.P. Design and Development of Low Cost Humanoid Robot with Thermal Temperature Scanner for COVID-19 Virus Preliminary Identification. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 3485–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, D.; Perpetuini, D.; Filippini, C.; Spadolini, E.; Mancini, L.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Merla, A. Driver Stress State Evaluation by Means of Thermal Imaging: A Supervised Machine Learning Approach Based on ECG Signal. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Cardone, D.; Filippini, C.; Spadolini, E.; Mancini, L.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Merla, A. Can Functional Infrared Thermal Imaging Estimate Mental Workload in Drivers as Evaluated by Sample Entropy of the FNIRS Signal? In Proceedings of the 8th European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference, Portorož, Slovenia, 29 November–3 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Burgholzer, P.; Mayr, G.; Thummerer, G.; Haltmeier, M. Linking Information Theory and Thermodynamics to Spatial Resolution in Photothermal and Photoacoustic Imaging. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 171102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

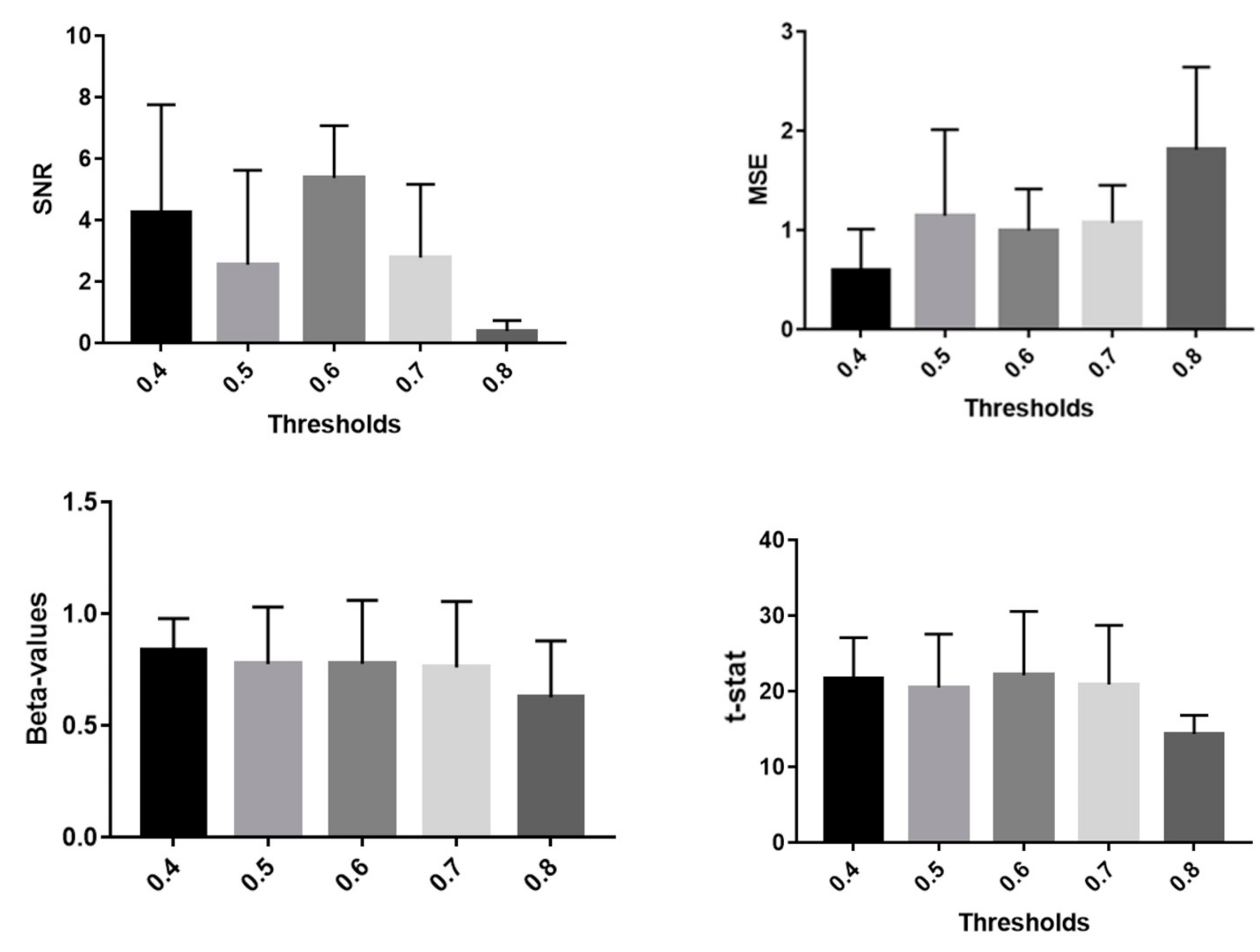
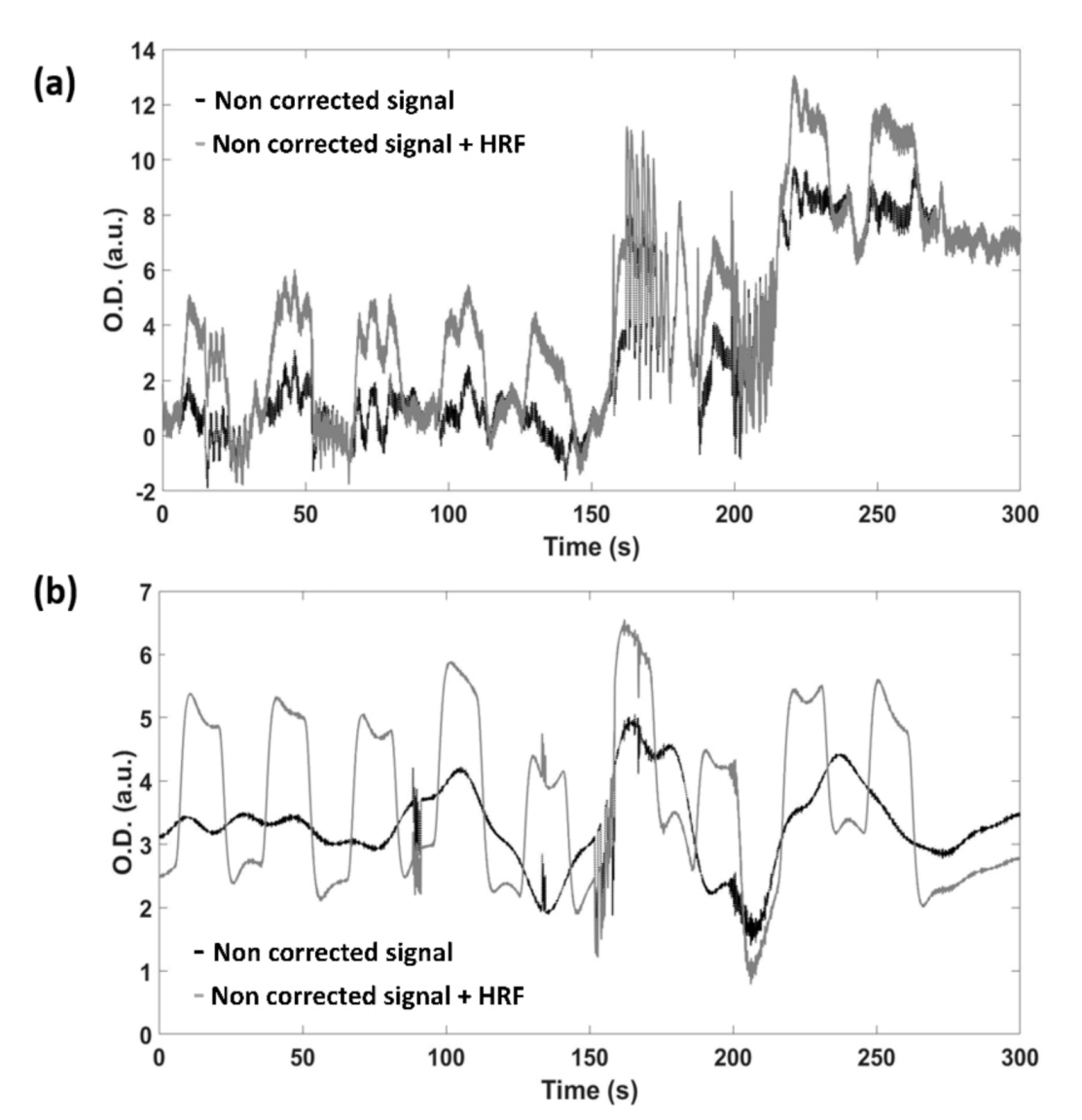

| Metric | t-Score | Degrees of Freedom | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Method vs. Non- corrected | SNR | 5.766 | 7 | 6.87 × 10−4 |
| MSE | −9.352 | 7 | 3.32 × 10−5 | |
| Beta-value | 92.064 | 7 | 4.70 × 10−12 | |
| t-stat | 6.339 | 7 | 3.89 × 10−4 | |
| Proposed Method vs. Wavelet | SNR | 0.249 | 7 | 0.811 |
| MSE | −8.768 | 7 | 5.05 × 10−5 | |
| Beta-value | 6.772 | 7 | 2.60 × 10−4 | |
| t-stat | 6.04 | 7 | 5.21 × 10−4 | |
| Proposed Method vs. PCA | SNR | 5.986 | 7 | 5.50 × 10−4 |
| MSE | −4.827 | 7 | 0.002 | |
| Beta-value | 29.329 | 7 | 1.38 × 10−8 | |
| t-stat | 7.055 | 7 | 2.02 × 10−4 | |
| Proposed Method vs. Spline | SNR | 5.444 | 7 | 9.62 × 10−4 |
| MSE | 0.125 | 7 | 0.904 | |
| Beta-value | 22.537 | 7 | 8.57 × 10−8 | |
| t-stat | 6.937 | 7 | 2.23 × 10−4 | |
| Proposed Method vs. cbsi | SNR | 4.571 | 7 | 0.003 |
| MSE | −6.445 | 7 | 3.51 × 10−4 | |
| Beta-value | 37.351 | 7 | 2.56 × 10−9 | |
| t-stat | 6.862 | 7 | 2.39 × 10−4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perpetuini, D.; Cardone, D.; Filippini, C.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Merla, A. A Motion Artifact Correction Procedure for fNIRS Signals Based on Wavelet Transform and Infrared Thermography Video Tracking. Sensors 2021, 21, 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155117
Perpetuini D, Cardone D, Filippini C, Chiarelli AM, Merla A. A Motion Artifact Correction Procedure for fNIRS Signals Based on Wavelet Transform and Infrared Thermography Video Tracking. Sensors. 2021; 21(15):5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155117
Chicago/Turabian StylePerpetuini, David, Daniela Cardone, Chiara Filippini, Antonio Maria Chiarelli, and Arcangelo Merla. 2021. "A Motion Artifact Correction Procedure for fNIRS Signals Based on Wavelet Transform and Infrared Thermography Video Tracking" Sensors 21, no. 15: 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155117
APA StylePerpetuini, D., Cardone, D., Filippini, C., Chiarelli, A. M., & Merla, A. (2021). A Motion Artifact Correction Procedure for fNIRS Signals Based on Wavelet Transform and Infrared Thermography Video Tracking. Sensors, 21(15), 5117. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21155117










