Detecting Small Size and Minimal Thermal Signature Targets in Infrared Imagery Using Biologically Inspired Vision
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We perform extensive evaluation and compare the robustness of the BIV target detector with 10 conventional state-of-the-art target detectors using our newly collected infrared imagery. To the best of our knowledge, the BIV target detector analysis for the detection of small size and minimal thermal signature targets is new.
- (2)
- The BIV target detector was previously tested mostly using simulated visible spectrum imagery. As the infrared imagery is generated by a process having a fundamentally different distribution (heat distribution) than the visible spectrum imagery (light distribution), the signal and noise characteristics of the two are significantly different. Our results also confirm that the BIV target detector is just as applicable to inputs from different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum with different data distributions.
- (3)
- Our results show that the spatial-only methods are less reliable for detecting long range, small size and minimal thermal signature targets and that temporal information is beneficial for solving such a problem robustly.
- (4)
- The BIV target detector utilizes highly nonlinear processing stages. Our processing times investigation show that these stages do not come at an increased cost of processing efficiency when compared to the previous existing methods.
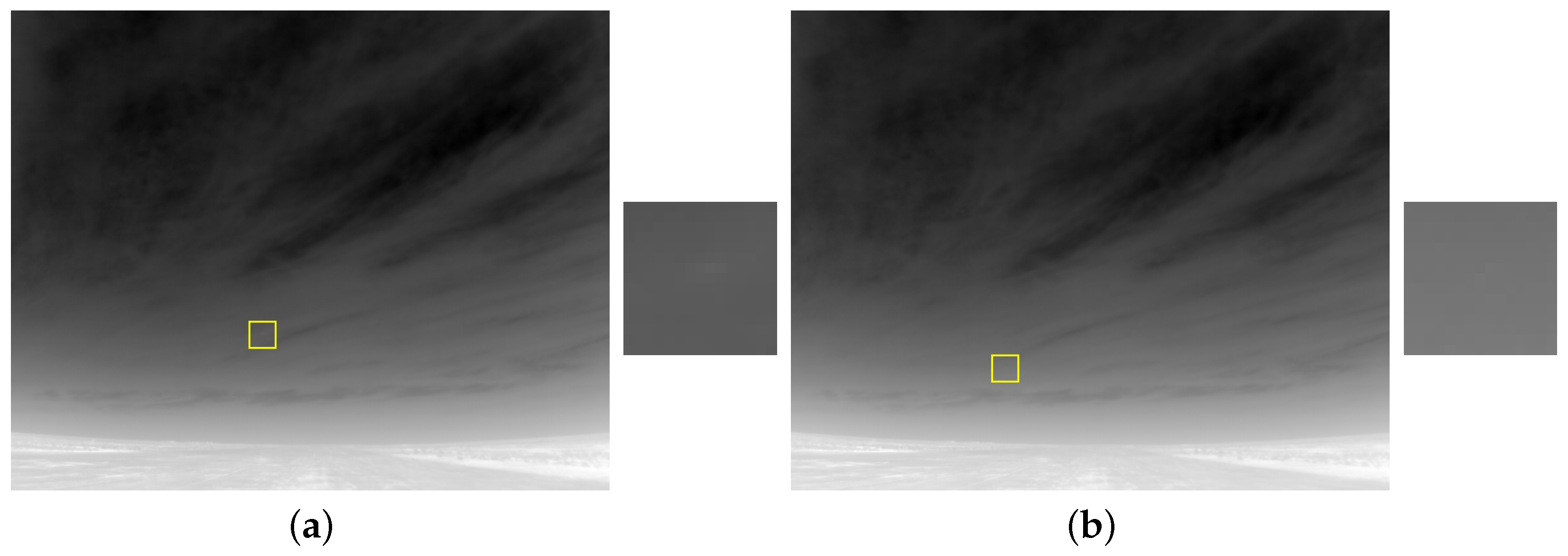
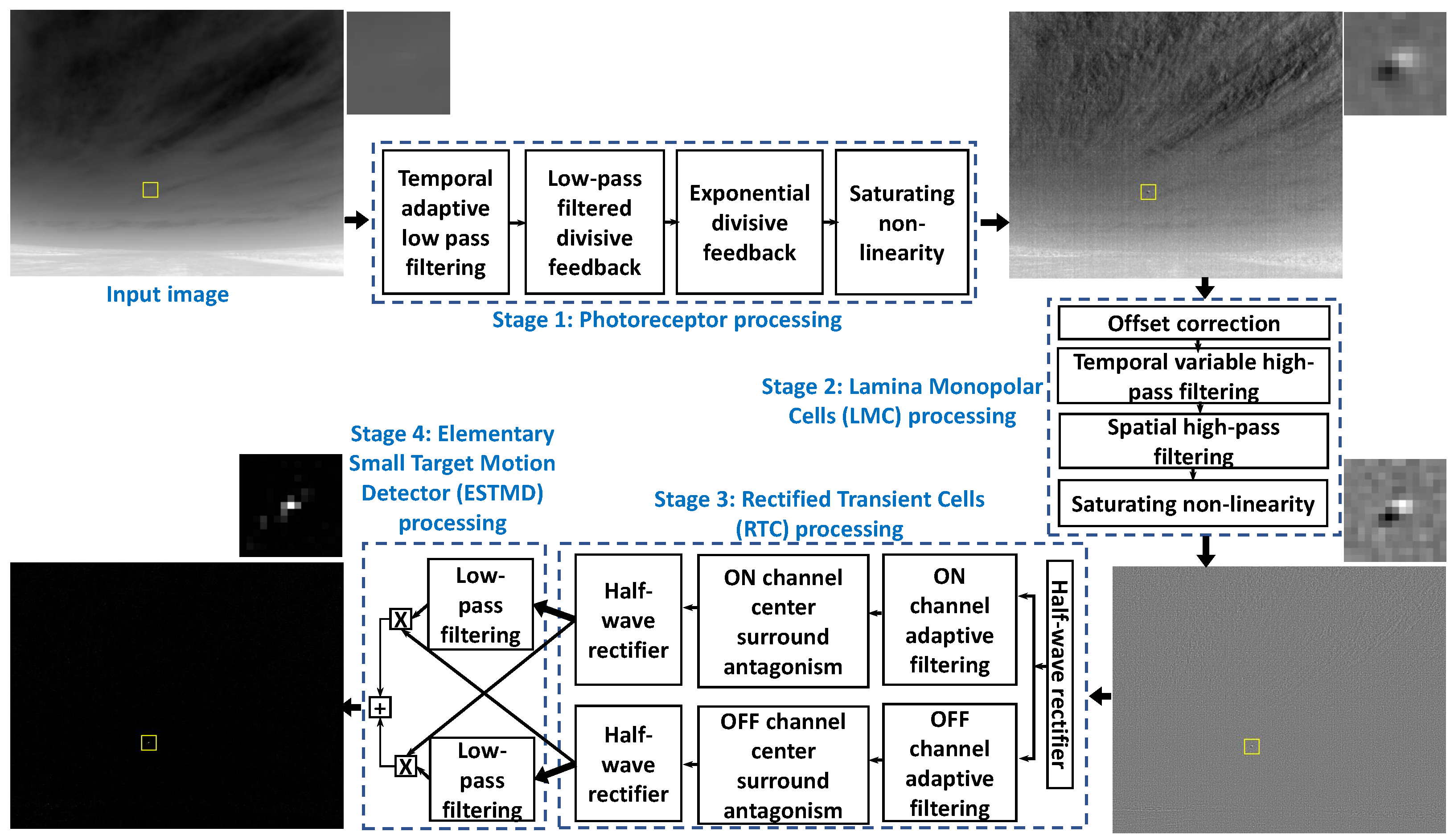
2. Bio-Inspired Vision Based Target Detector
3. Performance Evaluation
3.1. Infrared Image Data
3.2. Existing Conventional Methods for Comparison
3.2.1. Spatiotemporal Methods
3.2.2. Spatial-Only Methods
3.3. Performance Assessment Metrics
3.4. Experimental Setup
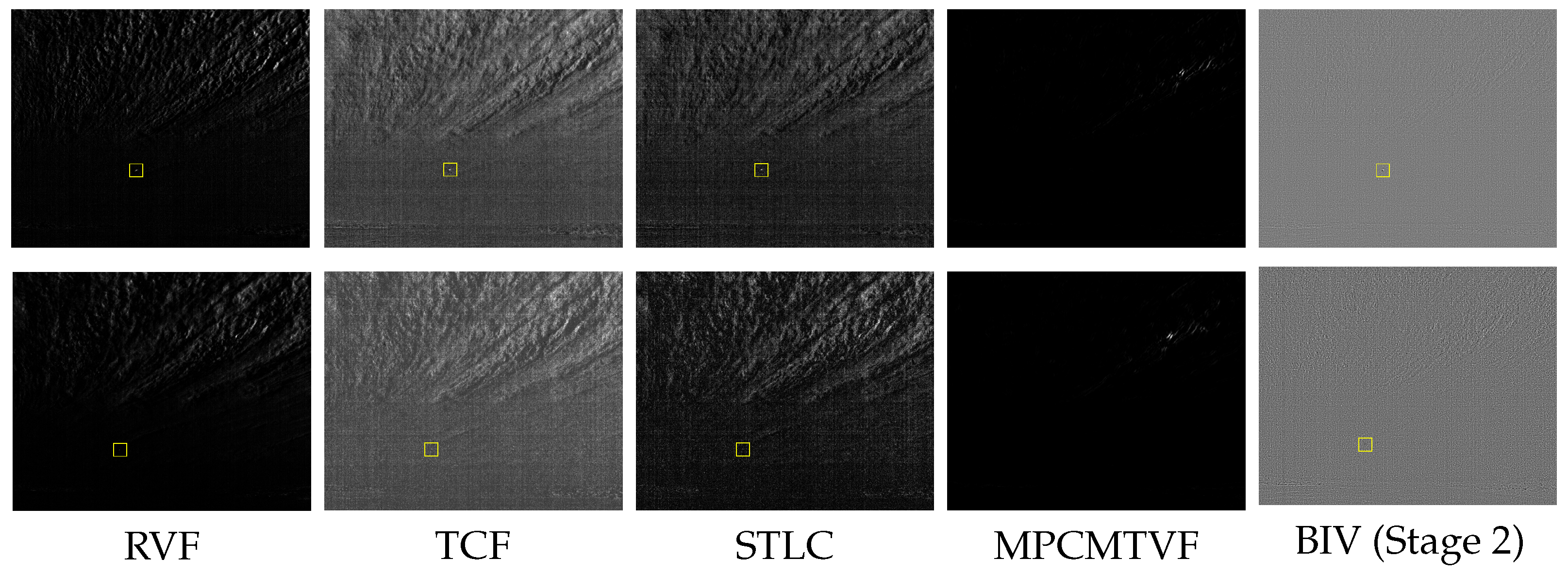
3.5. Target Enhancement Comparison (Temporal)
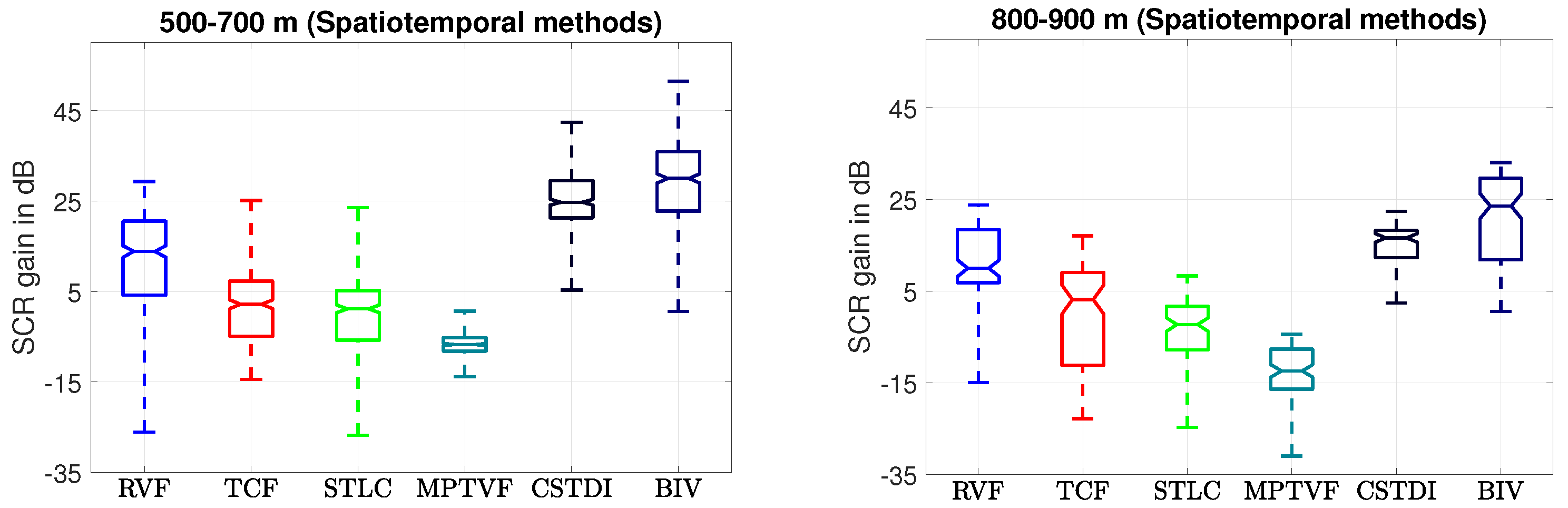
3.6. Target Enhancement Comparison (Spatiotemporal)
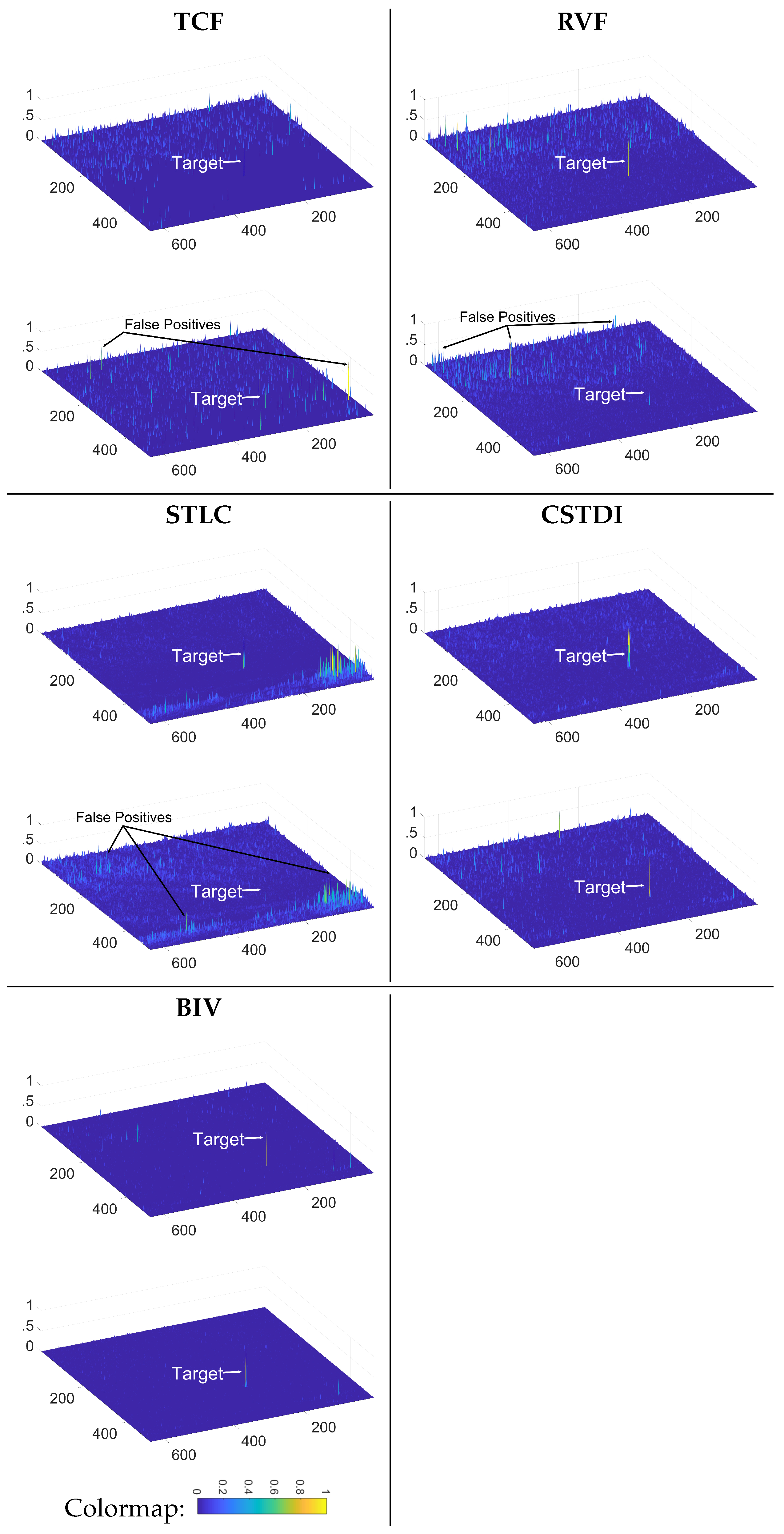
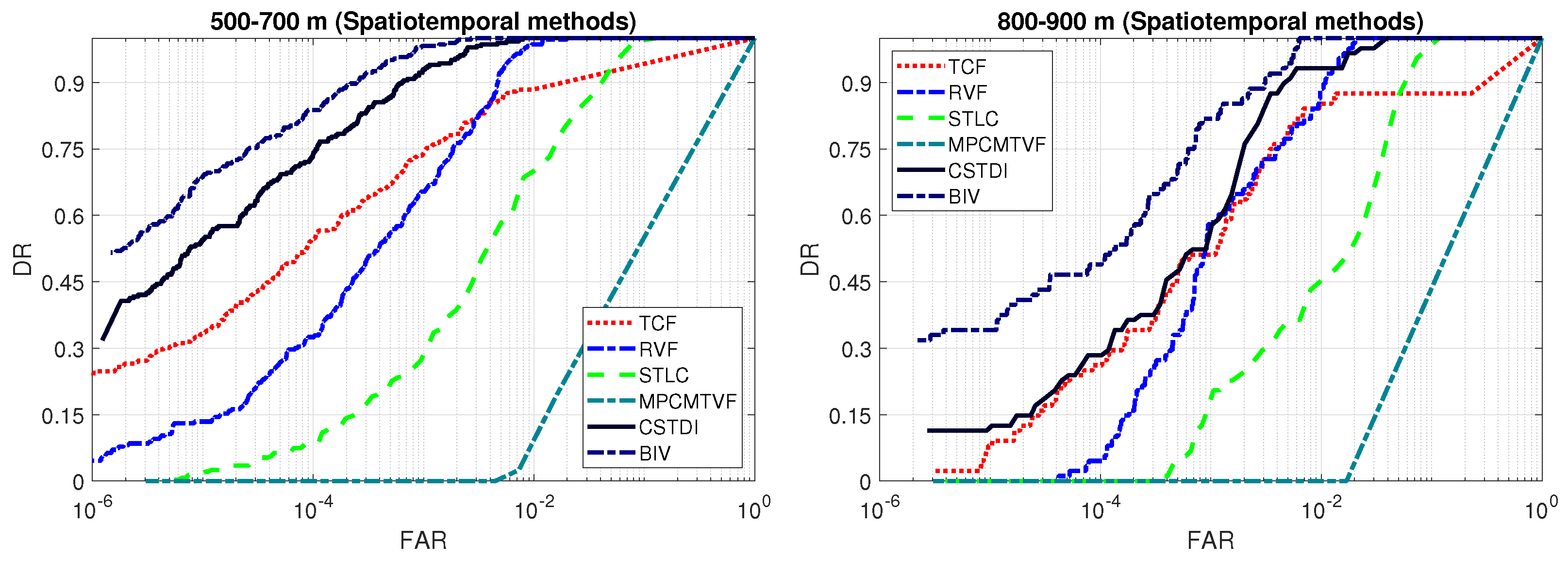
3.7. Detection Performance Comparison: Spatiotemporal Methods
3.8. Detection Performance Comparison: Spatial-Only Methods
3.9. Compute Time
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dedrone. Available online: https://www.dedrone.com/resources/incidents/all (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Gettinger, D.; Michel, A.H. Drone Sightings and Close Encounters: An Analysis; Center for the Study of the Drone, Bard College: Annandale-on-Hudson, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.P.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y.Y. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hauptmann, A.G. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Gao, C.; Li, B. Infrared small target detection based on facet kernel and random walker. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 22, 7104–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J. Small infrared target detection by region-adaptive clutter rejection for sea-based infrared search and track. Sensors 2014, 14, 13210–13242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Huang, S. A two-dimensional adaptive target detection algorithm in the compressive domain. Sensors 2019, 19, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, W. A robust detection algorithm for infrared maritime small and dim targets. Sensors 2020, 20, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, S.; Er, M.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small-targets. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3809, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. The design of top-hat morphological filter and application to infrared target detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2006, 48, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Infrared small target detection utilizing the multiscale relative local contrast measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, N. A local contrast method combined with adaptive background estimation for infrared small target detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Ma, J.; Tao, C.; Yang, C.; Tian, J. A robust directional saliency-based method for infrared small-target detection under various complex backgrounds. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Shi, J. A robust infrared dim target detection method based on template filtering and saliency extraction. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 73, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; You, X.; Li, H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection. Patt. Recognit. 2016, 58, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Shu, R. Infrared small target detection based on multiscale local contrast measure using local energy factor. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ni, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, G.; Deng, L. Tnlrs: Target-aware non-local low-rank modeling with saliency filtering regularization for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9546–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzair, M.; Brinkworth, R.; Finn, A. Insect-inspired small moving target enhancement in infrared videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Perth, Australia, 2–4 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, M.; Brinkworth, R.S.; Finn, A. A bio-inspired spatiotemporal contrast operator for small and low-heat-signature target detection in infrared imagery. In Neural Computing and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.; Caefer, C.E.; DiSalvo, S.; Vickers, V.E. Temporal filtering for point target detection in staring ir imagery: Ii. recursive variance filter. In Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1998; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Volume 3373, pp. 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tartakovsky, A.G.; Brown, J. Adaptive spatial-temporal filtering methods for clutter removal and target tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2008, 44, 1522–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-L.; Wen, C.-L.; Bao, Z.-J.; Liu, M.-Q. Detecting slowly moving infrared targets using temporal filtering and association strategy. Front. Inform. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2016, 17, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. High-speed incoming infrared target detection by fusion of spatial and temporal detectors. Sensors 2015, 15, 7267–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Sun, S.-G.; Kim, K.-T. Highly efficient supersonic small infrared target detection using temporal contrast filter. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Motai, Y.; Dong, L.; Xu, W. Detecting infrared maritime targets overwhelmed in sun glitters by antijitter spatiotemporal saliency. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5159–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, W. Target recognition in infrared circumferential scanning system via deep convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohacs, J.; Jankovics, I.; Gal, I.; Bakunowicz, J.; Mingione, G.; Carozza, A. Small aircraft infrared radiation measurements supporting the engine airframe aero-thermal integration. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2019, 47, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederman, S.; Brinkworth, R.; O’Carroll, D. Performance of a bio-inspired model for the robust detection of moving targets in high dynamic range natural scenes. J. Comput. Theoret. Nanosci. 2010, 7, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkworth, R.; O’Carroll, D. Robust models for optic flow coding in natural scenes inspired by insect biology. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melville-Smith, A.; Finn, A.; Brinkworth, R.S. Enhanced micro target detection through local motion feedback in biologically inspired algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2019 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Perth, Australia, 2–4 December 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nordström, K.; Barnett, P.D.; O’Carroll, D.C. Insect detection of small targets moving in visual clutter. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederman, S.; Shoemaker, P.; O’Carroll, D. A model for the detection of moving targets in visual clutter inspired by insect physiology. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, Z.; Wiederman, S.; Cazzolato, B.; Grainger, S.; O’Carroll, D. Performance of an insect-inspired target tracker in natural conditions. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederman, S.; Brinkworth, R.; O’Carroll, D. Bio-inspired target detection in natural scenes: Optimal thresholds and ego-motion. SPIE Biosens. 2008, 7035, 70350Z. [Google Scholar]
- Hateren, J.V. Processing of natural time series of intensities by the visual system of the blowfly. Vis. Res. 1997, 37, 3407–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hateren, J.V.; Snippe, H. Information theoretical evaluation of parametric models of gain control in blowfly photoreceptor cells. Vis. Res. 2001, 41, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinkworth, R.; Mah, E.-L.; Gray, J.P.; O’Carroll, D.C. Photoreceptor processing improves salience facilitating small target detection in cluttered scenes. J. Vis. 2008, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Hateren, J.H. Theoretical predictions of spatiotemporal receptive fields of fly lmcs, and experimental validation. J. Comparat. Physiol. A 1992, 171, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hateren, J.H. A theory of maximizing sensory information. Biol. Cybernet. 1992, 68, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, D. Feature-detecting neurons in dragonflies. Nature 1993, 362, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassenstein, B.; Reichardt, W. Systemtheoretische analyse der zeit-, reihenfolgen-und vorzeichenauswertung bei der bewegungsperzeption des rüsselkäfers chlorophanus. Z. Naturforschung B 1956, 11, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Zhu, H.; Tao, C.; Wei, Y. Infrared moving point target detection based on spatial—Temporal local contrast filter. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, Z.; An, W. Infrared small target detection using a temporal variance and spatial patch contrast filter. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 32217–32226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, T.; Wei, L.; Sang, N. Efficient method for multiscale small target detection from a natural scene. Opt. Eng. 1996, 35, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, L. Random Walks for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard, C.I. Selection of a clutter rejection algorithm for real-time target detection from an airborne platform. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2000, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–27 April 2000; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; Volume 4048, pp. 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P.; Sun, S.; Lin, C.; Liu, G. A method for weak target detection based on human visual contrast mechanism. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to roc analysis. Patt. Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matić, T.; Laughlin, S. Changes in the intensity-response function of an insect’s photoreceptors due to light adaptation. J. Comparat. Physiol. 1981, 145, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, P.S.; Finn, A.; Brinkworth, R.S. Consistent estimation of rotational optical flow in real environments using a biologically-inspired vision algorithm on embedded hardware. Imag. Vis. Comput. 2019, 92, 103814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkworth, R.; O’Carroll, D. Bio-inspired model for robust motion detection under noisy conditions. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Barcelona, Spain, 18–23 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- McGill, R.; Tukey, J.; Larsen, W. Variations of box plots. Am. Stat. 1978, 32, 12–16. [Google Scholar]






| Method | Parameters |
|---|---|
| MTH | Structuring element scales = {3,5,7,15,31,61} |
| MLCM | window scales = {5,7,9,11} |
| AADG | outer window scale = {9,13,17}, inner window scale={1,3,5} |
| IPI | patch size = 80 × 80, solver = APG |
| Random Walker | top level segmentation threshold = 4 |
| TCF | history buffer = 30, seed segmentation threshold = 40%, 8NN clustering |
| RVF | history buffer = 30 |
| STLC | history buffer = 30, spatial window extent = 5 |
| MPCMTVF | history buffer = 30, same filter as in RVF |
| CSTDI | scales = {8,16,24}, medium scale fusion |
| Spatial-only methods | ||||||
| Method | IPI | MLCM | Random Walker | MTH | AADG | |
| Compute time (s/frame) | 320 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.05 | |
| Spatiotemporal methods | ||||||
| Method | TCF | RVF | MPCMTVF | STLC | CSTDI | BIV |
| Compute time (s/frame) | 3.7 | 3.6 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uzair, M.; Brinkworth, R.S.A.; Finn, A. Detecting Small Size and Minimal Thermal Signature Targets in Infrared Imagery Using Biologically Inspired Vision. Sensors 2021, 21, 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051812
Uzair M, Brinkworth RSA, Finn A. Detecting Small Size and Minimal Thermal Signature Targets in Infrared Imagery Using Biologically Inspired Vision. Sensors. 2021; 21(5):1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051812
Chicago/Turabian StyleUzair, Muhammad, Russell S. A. Brinkworth, and Anthony Finn. 2021. "Detecting Small Size and Minimal Thermal Signature Targets in Infrared Imagery Using Biologically Inspired Vision" Sensors 21, no. 5: 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051812
APA StyleUzair, M., Brinkworth, R. S. A., & Finn, A. (2021). Detecting Small Size and Minimal Thermal Signature Targets in Infrared Imagery Using Biologically Inspired Vision. Sensors, 21(5), 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051812






