Printed Directional Bending Sensor with High Sensitivity and Low Hysteresis for Human Motion Detection and Soft Robotic Perception
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ink Preparation
2.3. Fabrication of the Printed Sensors
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
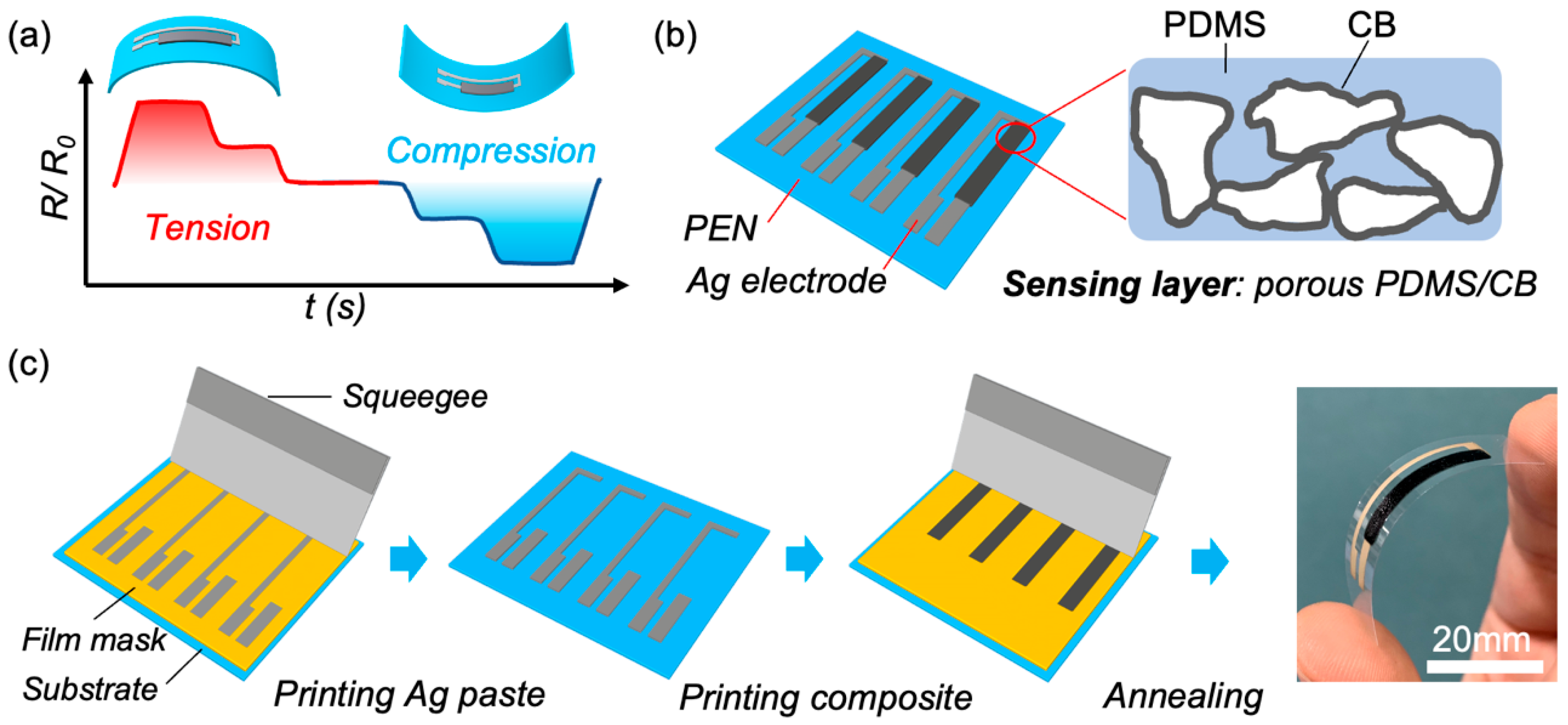
3.1. Design and Fabrication of Flexible Bending Sensor
3.2. Characterization of Printed Conductive Composite Films
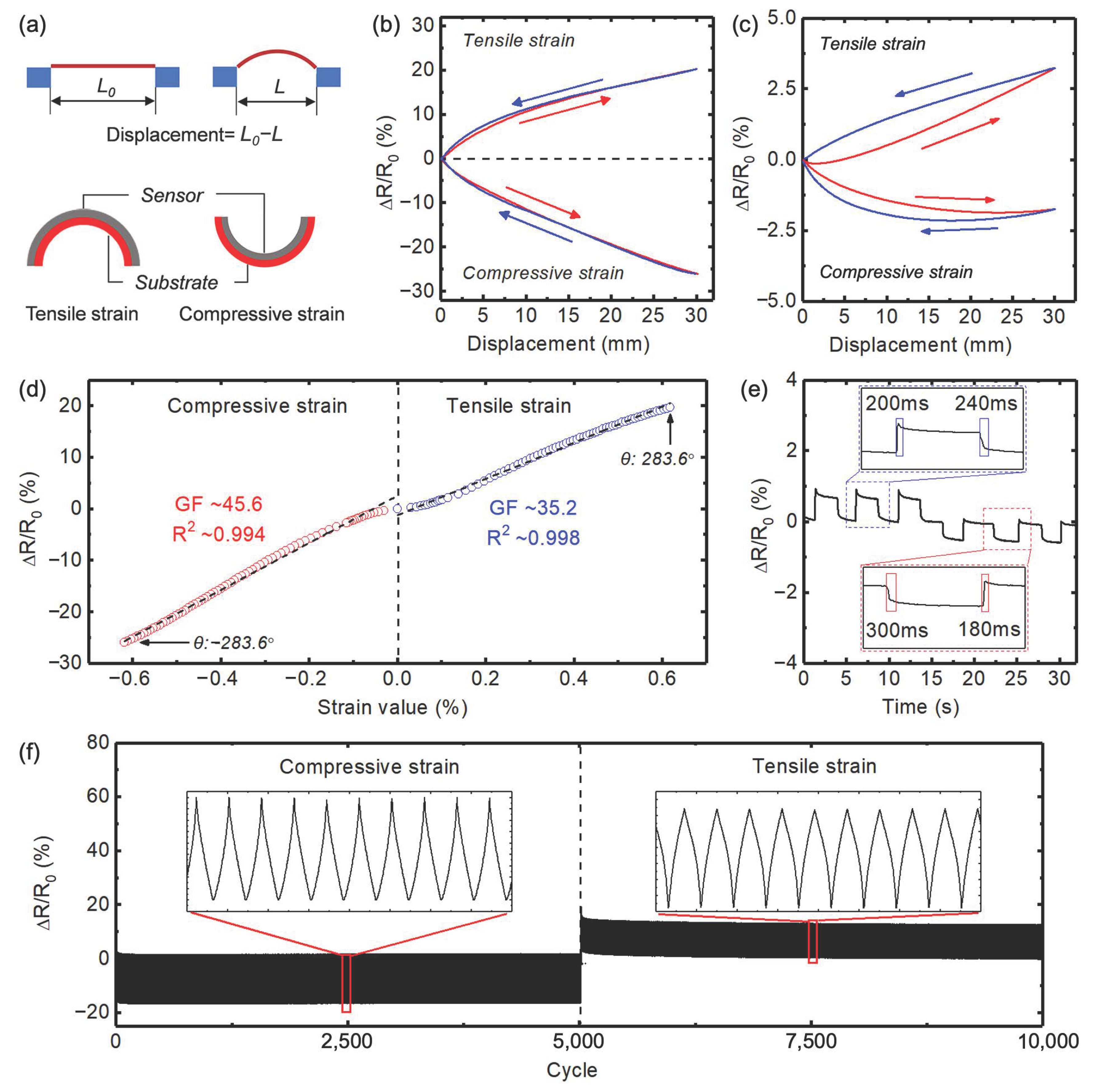
3.3. Directional Bending Sensing Performances
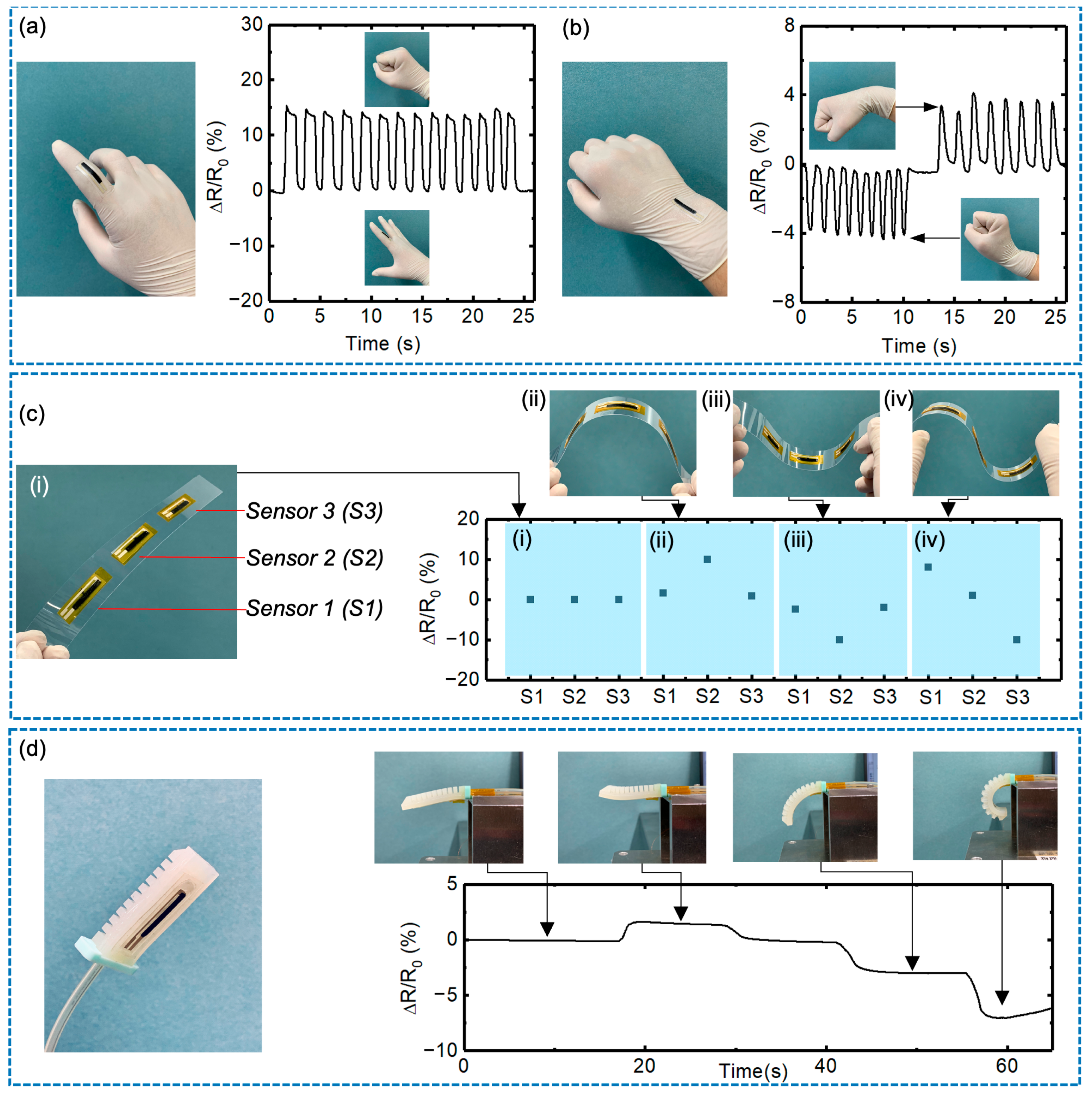
3.4. Multifunctional Mechanosensory Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.E. Flexible and stretchable physical sensor integrated platforms for wearable human-activity monitoring and personal healthcare. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K.U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, skin-mountable, and wearable strain sensors and their potential applications: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Cao, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jin, Y.; Sun, R.; et al. Recent Advancements in Flexible and Stretchable Electrodes for Electromechanical Sensors: Strategies, Materials, And Features. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12147–12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, B.; Shah, D.; Li, J.; Thuruthel, T.; Park, Y.; Iida, F.; Bao, Z.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R.; Tolley, M. Electronic Skins and Machine Learning for Intelligent Soft Robots. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eaaz9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, G.; Yang, G.; Pang, Z. Review of robot skin: A potential enabler for safe collaboration, immersive teleoperation, and affective interaction of future collaborative robots. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2021, 3, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Wan, C.; Pan, L.; Pan, S.; He, K.; Neo, A.; Chen, X. Artificial skin perception. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, W.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Pan, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, Z. Highly anisotropic and flexible piezoceramic kirigami for preventing joint disorders. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf0795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, J.; Ma, X.; Yang, L.; Lee, K.M.; Xiong, C. Flexible capacitive curvature sensor with one-time calibration for amphibious gait monitoring. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Fan, B.; Wu, B.; Guo, X. Printed flexible strain sensor array for bendable interactive surface. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Sekine, T.; Yi-Fei, W.; Takeda, Y.; Matsui, H.; Kumaki, D.; Dos Santos, F.D.; Miyabo, A.; Tokito, S. Ferroelectric polymer-based fully printed flexible strain rate sensors and their application for human motion capture. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 295, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, J.; Zhang, M. Unidirectional sensitive flexible sensor for bending measurements. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2021, 23, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Highly sensitive printed crack-enhanced strain sensor as dual-directional bending detector. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 045023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hu, F.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, R.; Wei, M.; Lao, K.; Hu, J.; Zheng, J.; et al. Fiber-junction design for directional bending sensors. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y. Adhesion-Free Thin-Film-Like Curvature Sensors Integrated on Flexible and Wearable Electronics for Monitoring Bending of Joints and Various Body Gestures. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Yin, R.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Dai, K.; Shan, C.; Guo, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Electrically Conductive Polymer Composites for Smart Flexible Strain Sensors: A Critical Review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12121–12141. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Swetha, P.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-Enabled Wearable Sensors for Healthcare. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 7, 1700889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, C.; Khan, U.; Ryan, G.; Barwich, S.; Charifou, R.; Harvey, A.; Backes, C.; Li, Z.; Ferreira, M.; Mobius, M.; et al. Sensitive Electromechanical Sensors Using Viscoelastic Graphene-Polymer Nanocomposites. Science 2016, 354, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alamusi; Hu, N.; Fukunaga, H.; Atobe, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Piezoresistive Strain Sensors Made from carbon Nanotubes Based Polymer Nanocomposites. Sensors 2011, 11, 10691–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Vinciguerra, V.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R. Printable Stretchable Interconnects. Flex. Print. Electron. 2017, 2, 013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Pichitpajongkit, A.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Park, I. Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensor Based on Silver Nanowire–Elastomer Nanocomposite. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5154–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Ji, M.; Deng, H.; Fu, Q. Towards Tunable Sensitivity of Electrical Property to Strain for Conductive Polymer Composites Based on Thermoplastic Elastomer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5815–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Deng, H.; Valenca, R.; Jin, J.; Fu, Q.; Bilotti, E.; Peijs, T. Strain Sensing Behaviour of Elastomeric Composite Films Containing Carbon Nanotubes under Cyclic Loading. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 74, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Chortos, A.; Lian, F.; Pop, E.; Linder, C.; Bao, Z.; Cai, W. Microstructural Origin of Resistance-Strain Hysteresis in Carbon Nanotube Thin Film Conductors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1986–1991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yeung, C.; Wu, W.; Venkatesh, S.; Xu, Z.; Wylie, J.; Li, W.; Roy, V. Fingertip-Skin-Inspired Highly Sensitive and Multifunctional Sensor with Hierarchically Structured Conductive graphite/Polydimethylsiloxane Foams. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, T.; Onyilagha, O.; Fong, H.; Zhu, Z. Recent Advances in Flexible and Wearable Pressure Sensors Based on Piezoresistive 3D Monolithic Conductive Sponges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6685–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, W.; Jia, L.; Xu, L.; Dai, K.; Yan, D.; Li, Z. Highly Stretchable and Sensitive Strain Sensor with Porous Segregated Conductive Network. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37094–37102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Feng, J. Mass-Produced SEBS/graphite Nanoplatelet Composites with A Segregated Structure for Highly Stretchable and Recyclable Strain Sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 9423–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; D’hooge, D.; Spoerk, M.; Cornillie, P.; Cardon, L. Facile and Low-Cost Route for Sensitive Stretchable Sensors by Controlling Kinetic and Thermodynamic Conductive Network Regulating Strategies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22678–22691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Wang, Y.F.; Sekine, T.; Takeda, Y.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Printed Low-Hysteresis Stretchable Strain Sensor Based on a Self-Segregating Conductive Composite. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2023, 1, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Sekine, T.; Takeda, Y.; Hong, J.; Yoshida, A.; Kumaki, D.; Shiba, T.; Tokito, S. Deep eutectic solvent induced porous conductive composite for fully printed piezoresistive pressure sensor. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Jeong, K.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Ku, B.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Park, C. Facile Supramolecular Processing of carbon Nanotubes and Polymers for Electromechanical Sensors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 16180–16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J. Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Nanotubes and Graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3680–3695. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Song, Y.; Ding, D.; Ling, Z.; Xu, F. Flexible and Anisotropic Strain Sensor Based on carbonized Crepe Paper with Aligned Cellulose Fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802547. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sekine, T.; Takeda, Y.; Hong, J.; Yoshida, A.; Matsui, H.; Kumaki, D.; Nishikawa, T.; Shiba, T.; Sunaga, T.; et al. Printed Strain Sensor with High Sensitivity and Wide Working Range Using a Novel Brittle–Stretchable Conductive Network. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35282–35290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Hou, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zou, B.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.; Guo, S.; Li, H.; Zheng, B.; et al. Leather-Based Strain Sensor with Hierarchical Structure for Motion Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajahat, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Chang, W.; Pyo, J.; Cho, S.; Seol, S. Flexible Strain Sensors Fabricated by Meniscus-Guided Printing of carbon Nanotube–Polymer Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19999–20005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Mi, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; et al. Superhydrophobic Electrically Conductive Paper for Ultrasensitive Strain Sensor with Excellent Anticorrosion and Self-Cleaning Property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21904–21914. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Weng, M.; Zhou, P.; Huang, F.; Liu, C.; Fan, S.; Zhang, W. Actuators: Graphene-Based Actuator with Integrated-Sensing Function. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1970025. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Han, J.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Flexible conductive Ag nanowire/cellulose nanofibril hybrid nanopaper for strain and temperature sensing applications. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 899–908. [Google Scholar]

| Materials | Tensile GF | Compressive GF | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonized cellulose | 10.1 | 4.45 | creping | [34] |
| Leather/CNT | 5.68 | 12.56 | drop casting | [36] |
| MWCNT | 13. 07 | 12.87 | printing | [37] |
| CNT/CB/paper | 7.5 | 2.6 | dip-coating | [38] |
| RGO/paper | 7.99 | 18.96 | soaking | [39] |
| AgNW/CNF | 10.2 | 1.2 | filtration | [40] |
| PDMS/CB | 35.2 | 45.6 | printing | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-F.; Yoshida, A.; Takeda, Y.; Sekine, T.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Printed Directional Bending Sensor with High Sensitivity and Low Hysteresis for Human Motion Detection and Soft Robotic Perception. Sensors 2023, 23, 5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115041
Wang Y-F, Yoshida A, Takeda Y, Sekine T, Kumaki D, Tokito S. Printed Directional Bending Sensor with High Sensitivity and Low Hysteresis for Human Motion Detection and Soft Robotic Perception. Sensors. 2023; 23(11):5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Fei, Ayako Yoshida, Yasunori Takeda, Tomohito Sekine, Daisuke Kumaki, and Shizuo Tokito. 2023. "Printed Directional Bending Sensor with High Sensitivity and Low Hysteresis for Human Motion Detection and Soft Robotic Perception" Sensors 23, no. 11: 5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115041
APA StyleWang, Y.-F., Yoshida, A., Takeda, Y., Sekine, T., Kumaki, D., & Tokito, S. (2023). Printed Directional Bending Sensor with High Sensitivity and Low Hysteresis for Human Motion Detection and Soft Robotic Perception. Sensors, 23(11), 5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115041







