Handwriting Evaluation Using Deep Learning with SensoGrip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The SensoGrip System
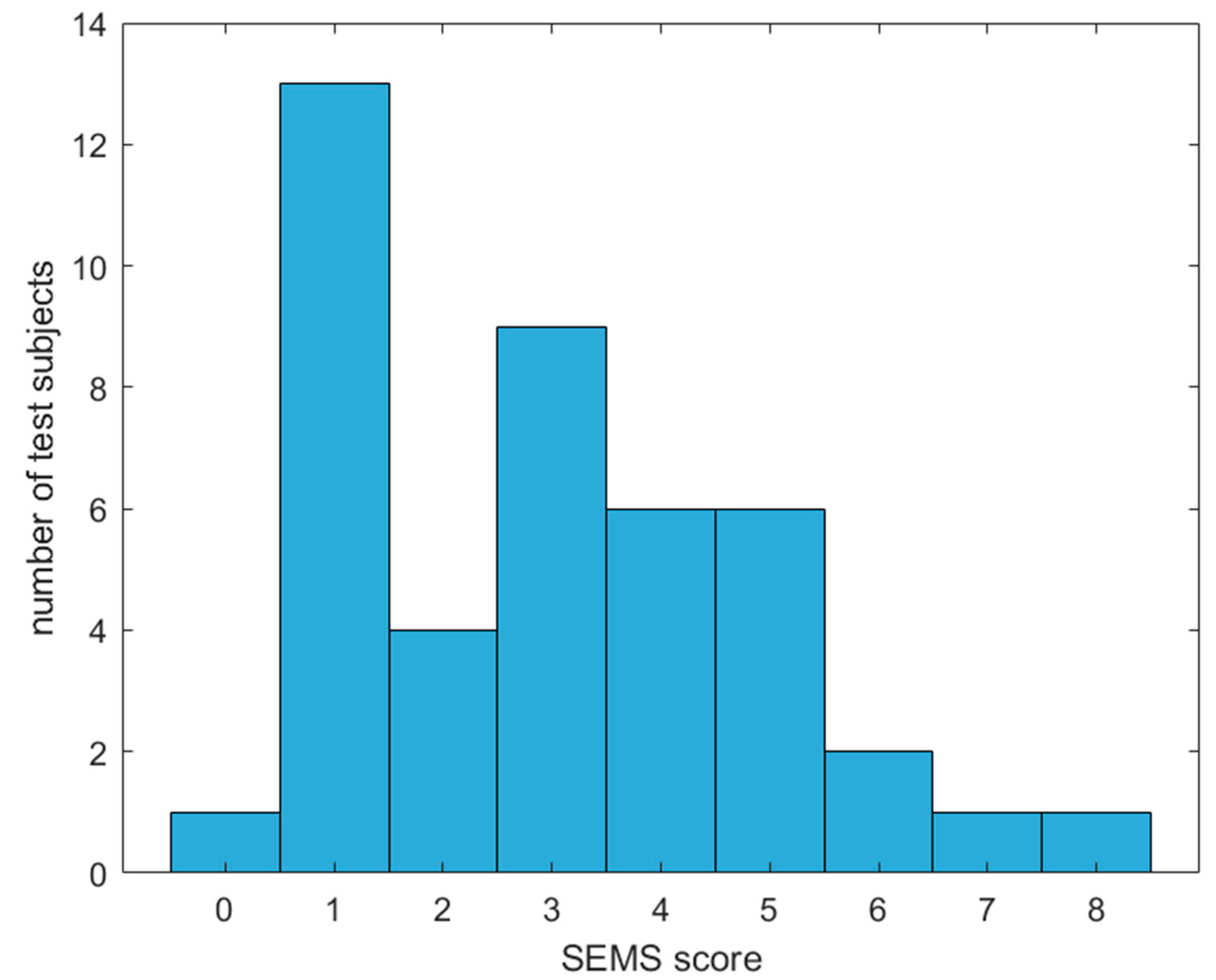
2.2. Data Collection
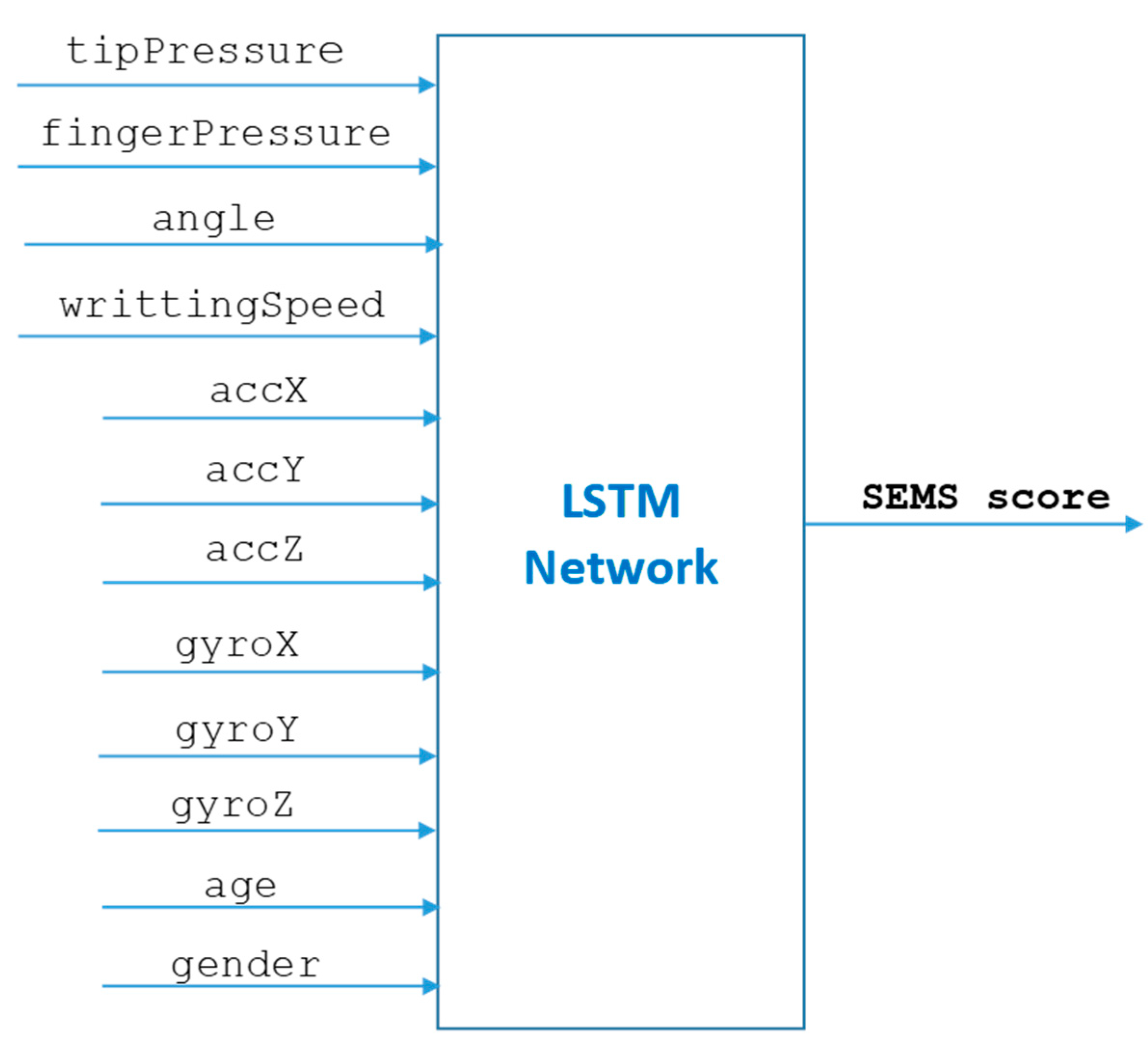
2.3. Machine Learning Methods
3. Results
3.1. Performance Measures
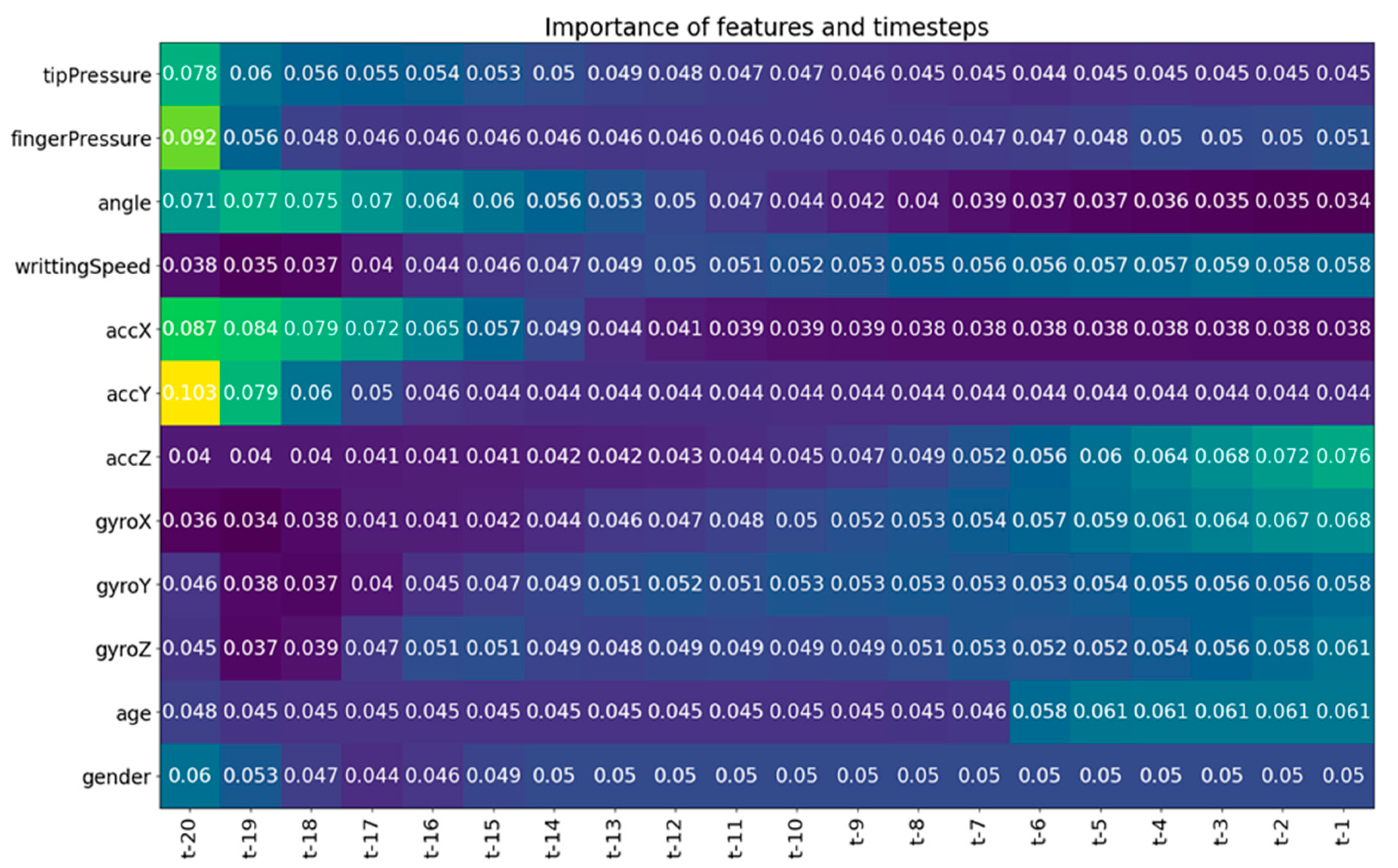
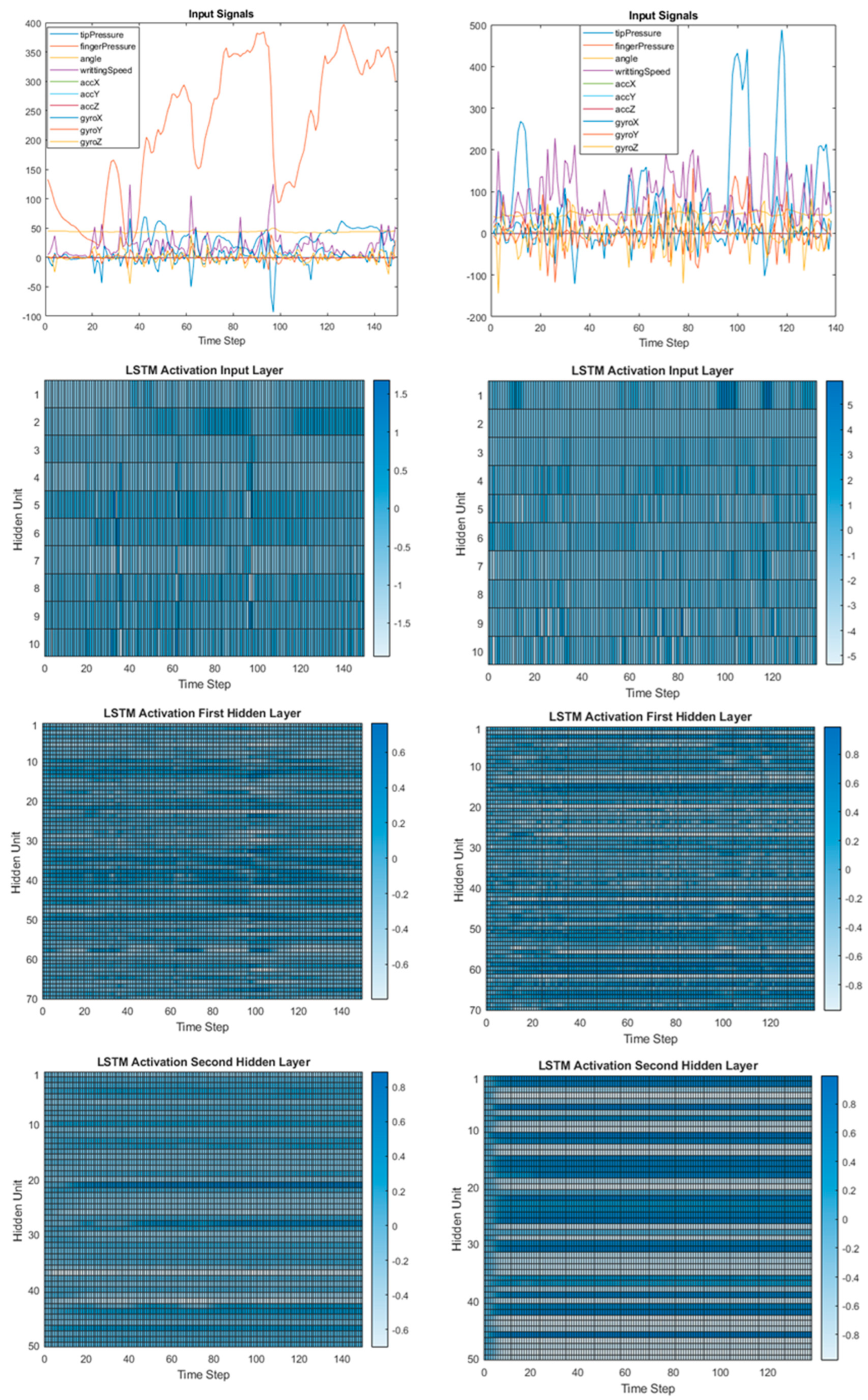
3.2. Numerical Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sampling frequency | 100 Hz |
| ADC resolution | 10 bits |
| Tip pressure | Sensor type: HSFPAR004A Gain: 13.46 dB Force range: 0–8 N |
| Finger pressure | Sensor type: FSR 406 Gain: 0 dB Force range 0.1–10.0 N |
| Inertial measurement unit (IMU) | Sensor type: MPU5060 Gain: 0 dB (connected directly over I2C) Angular velocity range: ±250, ±500, ±1000 and ±2000 dps Accelerator sensor in the range: ±2 g, ±4 g, ±8 g and ±16 g |

| Subject ID | Age | Gender | SEMS Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| KL22 | 9 | f | 0 |
| KL15 | 9 | m | 1 |
| KL15_2 | 9 | m | 1 |
| KL14 | 8 | f | 1 |
| KB5 | 8 | f | 1 |
| KB5_2 | 8 | f | 1 |
| KL16 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KL16_2 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KL21 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KL21_2 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KB11 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KB11_2 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KB20 | 9 | f | 1 |
| KB10_2 | 9 | m | 1 |
| KL14_2 | 8 | f | 2 |
| KB20_2 | 9 | f | 2 |
| KL23 | 8 | m | 2 |
| KB7 | 9 | f | 2 |
| KL22_2 | 9 | f | 3 |
| KL23_2 | 8 | m | 3 |
| KB3 | 8 | m | 3 |
| KB10 | 9 | m | 3 |
| KL12 | 8 | f | 3 |
| KL12_2 | 8 | f | 3 |
| KB15 | 9 | f | 3 |
| KB15_2 | 9 | f | 3 |
| KB6_2 | 8 | f | 3 |
| KB3_2 | 8 | m | 4 |
| KL13 | 7 | m | 4 |
| KL13_2 | 7 | m | 4 |
| KB12 | 9 | m | 4 |
| KB22 | 9 | m | 4 |
| KB17 | 7 | f | 4 |
| KB12_2 | 9 | m | 5 |
| KB22_2 | 9 | m | 5 |
| KB17_2 | 7 | f | 5 |
| KL17 | 9 | m | 5 |
| KL20 | 9 | m | 5 |
| KL20_2 | 9 | m | 5 |
| KB7_2 | 9 | f | 6 |
| KL17_2 | 9 | m | 6 |
| KL19 | 7 | m | 7 |
| KL19_2 | 7 | m | 8 |
References
- Chung, P.J.; Patel, D.R.; Nizami, I. Disorder of written expression and dysgraphia: Definition, diagnosis, and management. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9, S46–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feder, K.P.; Majnemer, A. Handwriting development, competency and intervention. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneck, C.M.; Case-Smith, J. Prewriting and Handwriting Skills. In Case Review. Occupational Therapy for Children; Case-Smith, J., O’Brien, C., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 498–524. [Google Scholar]
- Asselborn, T.; Gargot, T.; Kidziński, Ł.; Johal, W.; Cohen, D.; Jolly, C.; Dillenbourg, P. Automated human-level diagnosis of dysgraphia using a consumer tablet. Npj Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits-Engelsman, B.C.M.; Niemeijer, A.S.; van Galen, G.P. Fine motor deficiencies in children diagnosed as DCD based on poor grapho-motor ability. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2001, 20, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, K.P.; Majnemer, A. Children’s handwriting evaluation tools and their psychometric properties. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2003, 23, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselborn, T.; Chapatte, M.; Dillenbourg, P. Extending the Spectrum of Dysgraphia: A Data Driven Strategy to Estimate Handwriting Quality. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotár, P.; Dobeš, M. Dysgraphia detection through machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimauro, G.; Bevilacqua, V.; Colizzi, L.; Di Pierro, D. TestGraphia, a Software System for the Early Diagnosis of Dysgraphia. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 19564–19575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillaine, L.; Lambert, R.; Boutet, J.; Aloui, S.; Brault, V.; Jolly, C.; Labyt, E. Analysis of Graphomotor Tests with Machine Learning Algorithms for an Early and Universal Pre-Diagnosis of Dysgraphia. Sensors 2021, 21, 7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouse, F.; Paranjothi, K.; Vaithiyanathan, R. Dysgraphia Classification based on the Non-Discrimination Regularization in Rotational Region Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2022, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zolna, K.; Asselborn, T.; Jolly, C.; Casteran, L.; Johal, W.; Dillenbourg, P. The dynamics of handwriting improves the automated diagnosis of dysgraphia. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07576 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Franken, A.M.; Harris, S.R. Teachers’ Perceptions of Handwriting Legibility Versus the German Systematic Screening for Motoric-Handwriting Difficulties (SEMS). OTJR Occup. Particip. Health 2021, 41, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettinger, L.; Klupper, C.; Hauser, C.; Schönthaler, E.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Werner, K.; Werner, F. Participatory design and needs assessment for a pressure-sensitive pen and mobile application (SensoGrip) for children with handwriting problems. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhofer, K.; Lehner, K. Under Pressure?-SensoGrip, ein Stift zur Messung des Finger- und Minendrucks von Kindern beim Schreiben. Bachelor Thesis, University of Applied Sciences, Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vinçon, S.; Blank, R.; Jenetzky, E. SEMS: Systematischen Erfassung Motorischer Schreibstörungen [Systematic Screening for Motor-Based Handwriting Difficulties] [Unpublished Measurement Instrument]; Klinik für Kinderneurologie und Sozialpädiatrie Kinderzentrum Maulbronn Gmbh: Maulbronn, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géron, A. Hands-on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems, 3rd ed.; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Lin, T.; Antulov-Fantulin, N. Exploring interpretable lstm neural networks over multi-variable data. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 2494–2504. [Google Scholar]
- IMV-LSTM. Available online: https://github.com/KurochkinAlexey/IMV_LSTM (accessed on 24 May 2023).


| Number of Layers | Number of Hidden Units L1 | Number of Hidden Units L2 | Accuracy (%) | F1-Score (%) | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | - | 98.29 | 71.87 | 0.97 |
| 1 | 100 | - | 98.00 | 63.65 | 1.07 |
| 1 | 120 | - | 98.22 | 67.82 | 1.04 |
| 2 | 70 | 40 | 99.18 | 86.97 | 0.99 |
| 2 | 70 | 50 | 99.80 | 97.78 | 0.68 |
| 2 | 80 | 50 | 99.35 | 94.01 | 0.87 |
| Model | Accuracy | F1-Score | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM only | 99.80 | 97.78 | 0.68 |
| LSTM + SVM | 99.54 | 95.98 | 0.85 |
| LSTM + FCNN | 99.56 | 94.15 | 0.78 |
| LSTM + DT | 99.70 | 97.21 | 0.69 |
| Model | Accuracy Mean +/− Std. Dev. (%) | F1-Score Mean +/− Std (%) | RMSE Mean +/− Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asselborn et al. [4] | - | 97.98 +/− 2.68 | - |
| Drotar and Dobes [8] | 79.50 +/− 3 | - | - |
| Dimauro et al. [9] | 96 | - | - |
| Devillaine et al. [10] | 73.40 +/− 3.4 | - | - |
| Ghouse et al. [11] | 98.2 | 98.16 | - |
| Zolna et al. [12] | 90 | ||
| Our model | 99.80 +/− 0.28 | 97.78 +/− 3.14 | 0.68 +/− 0.07 |
| Model | RMSE | RMSE Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|
| LSTM with all variables | 0.68 | 0.00 |
| LSTM without the gender variable | 1.16 | 70.36 |
| LSTM without the age variable | 1.04 | 52.54 |
| LSTM without gender and age variables | 1.34 | 97.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bublin, M.; Werner, F.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Korak, G.; Geyer, S.; Rettinger, L.; Schönthaler, E.; Schmid-Kietreiber, M. Handwriting Evaluation Using Deep Learning with SensoGrip. Sensors 2023, 23, 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115215
Bublin M, Werner F, Kerschbaumer A, Korak G, Geyer S, Rettinger L, Schönthaler E, Schmid-Kietreiber M. Handwriting Evaluation Using Deep Learning with SensoGrip. Sensors. 2023; 23(11):5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115215
Chicago/Turabian StyleBublin, Mugdim, Franz Werner, Andrea Kerschbaumer, Gernot Korak, Sebastian Geyer, Lena Rettinger, Erna Schönthaler, and Matthias Schmid-Kietreiber. 2023. "Handwriting Evaluation Using Deep Learning with SensoGrip" Sensors 23, no. 11: 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115215
APA StyleBublin, M., Werner, F., Kerschbaumer, A., Korak, G., Geyer, S., Rettinger, L., Schönthaler, E., & Schmid-Kietreiber, M. (2023). Handwriting Evaluation Using Deep Learning with SensoGrip. Sensors, 23(11), 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115215






