Investigating Visual Perception Impairments through Serious Games and Eye Tracking to Anticipate Handwriting Difficulties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Game Design
2.1.1. Game Overview
2.1.2. Levels
2.2. Apparatus
2.2.1. iPad and Apple Pencil
2.2.2. Eye Tracker
2.2.3. System Usability Scale
2.2.4. Characterization Questionnaire
2.2.5. Custom Satisfaction Questionnaire
- Was the game fun?
- Are you satisfied with this experience?
- Was the Apple Pencil comfortable?
- Was the Apple Pencil light?
- Do you prefer the Apple Pencil or a normal pen?
- What did you like the most?
- What did you like the least?
- Would you change something?
2.2.6. BVSCO-2
- Writing the letters “le”, in cursive, for a minute;
- Writing the word “uno”, in cursive or in block, for a minute;
- Writing number words, in cursive or in block, for a minute.
2.2.7. Protocol
2.3. Data Analysis
- Tract discontinuity.
- Percentage of discontinuous tracts.
- Length of tracts, both discontinuous and not.
- x and y of centroid.
- Distance from the center (which was computed as the centroid of all children).
- Dispersion from the centroid.
- Dispersion from the start.
- Length of tracts out of trace.
- Percentage of points out of trace.
- Total number of gaze positions and fixations.
- Average duration of fixations.
- Percentage of gaze positions on the target image.
- Percentage of gaze positions on the correct and on the wrong options.
- Indecision, computed as the number of times the gaze position bounced between the target image and the options.
- Indecision, computed as the number of times subsequent fixations bounced between the target image and the options.
- Dispersion of the gaze positions, computed as the Standard Distance.
- Gaussian Naive Bayes;
- Random forest;
- Support Vector Machine (SVM);
- CatBoost.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Exploratory Data Analysis
3.3. System Usability Score and Satisfaction Questionnaire
3.4. Evaluation of Game Difficulties
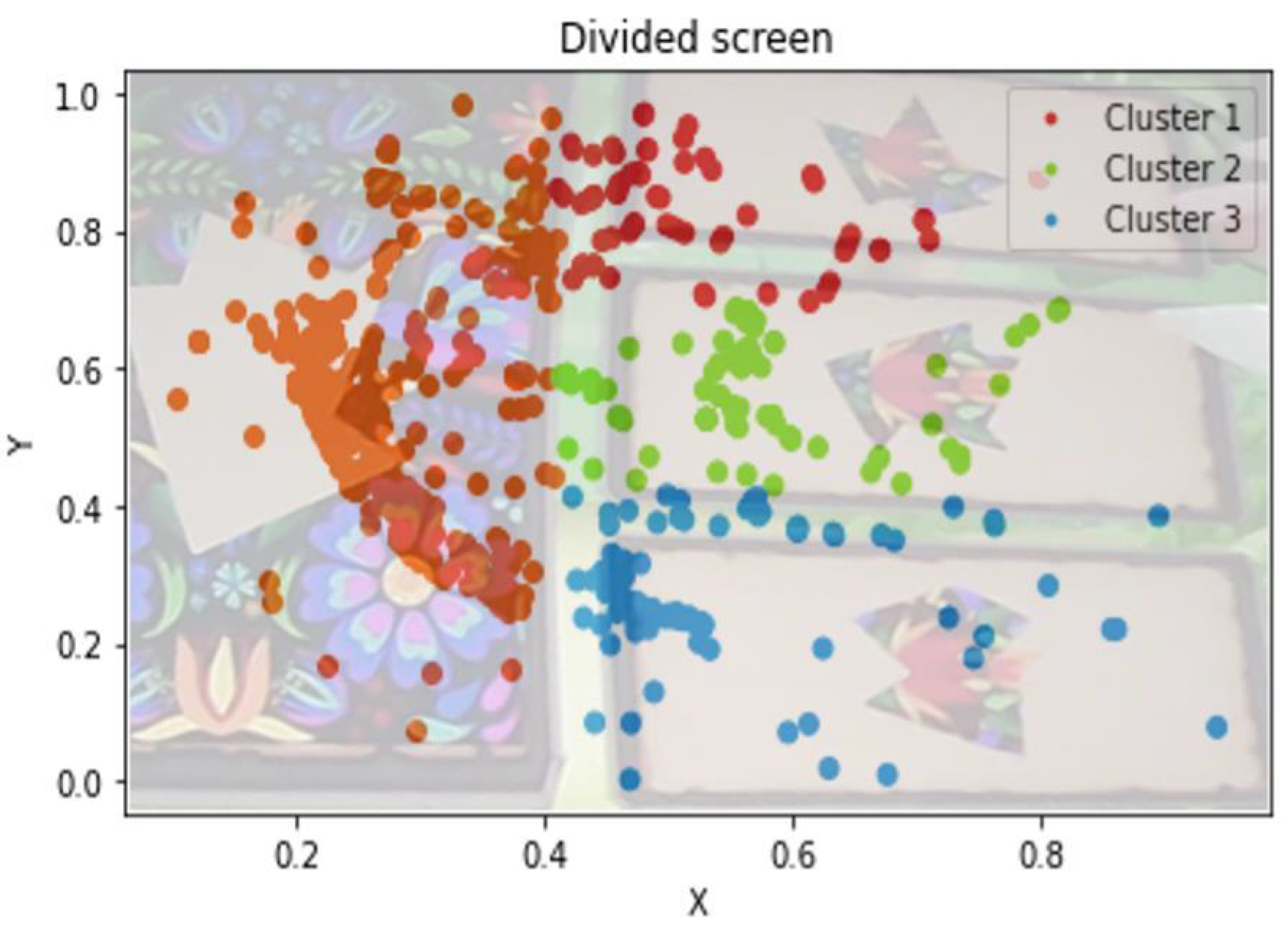
3.5. Eye-Tracking Results
3.6. Classification
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLD | Specific Learning Disorder |
| SUS | System Usability Scale |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| BVSCO | Batteria per la Valutazione della Scrittura e della Competenza Ortografica |
| VMI | Visual Motor Integration |
Appendix A. Game’s Story, Setting, and Characters
Appendix B. Characterization Questionnaire
- Subject ID
- Month and year of birth
- Dominant hand
- Right
- Left
- Ambidextrous
- Gender
- Male
- Female
- Do you have any eye defects?
- Yes
- No
- If yes, specify which ones
- Do you wear glasses?
- Yes
- No
- Is Italian your first language?
- Yes
- No
- If no, how many years of education have you completed in Italy?
- Do you speak Italian at home?
- Yes
- No
- Have you ever used a tablet?
- Yes
- No
- How frequently do you use a tablet?
- Everyday
- At least once a week
- Less than once a week
- Other (specify)
- What do you use a tablet for?
- Gaming
- Watching videos
- Drawing
- Other (specify)
- Have you ever used a stylus pen?
- Yes
- No
- If yes, what have you used the pen for?
- Have you ever used an eye tracker?
- Yes
- No
- If yes, what have you used the eye tracker for?
- How long have you been writing in cursive?
- Which style of writing do you prefer?
- Cursive
- Print
Appendix C. Protocol Additional Information
References
- Berninger, V.W.; Wolf, B. Understanding Dysgraphia. Available online: https://dyslexiaida.org/understanding-dysgraphia/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Berninger, V. Teaching Students with Dyslexia and Dysgraphia: Lessons from Teaching and Science; Paul H. Brookes Pub. Co.: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA; Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, N.; Henderson, S.E. Two Sides of the Same Coin: Variations in Teaching Methods and Failure to Learn to Write. Br. J. Spec. Educ. 2007, 9, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsdottir, R.; Stefansson, T. Problems in Developing Functional Handwriting. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2002, 94, 623–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, K.P.; Majnemer, A. Handwriting development, competency, and intervention. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V.W.; May, M.O. Evidence-Based Diagnosis and Treatment for Specific Learning Disabilities Involving Impairments in Written and/or Oral Language. J. Learn. Disabil. 2011, 44, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Dyslexia, dysgraphia, procedural learning and the cerebellum. Cortex 2011, 47, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapcsak, S.Z.; Beeson, P.M.; Henry, M.L.; Leyden, A.; Kim, E.; Rising, K.; Andersen, S.; Cho, H. Phonological dyslexia and dysgraphia: Cognitive mechanisms and neural substrates. Cortex 2009, 45, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohare, A.E.; Brown, J.K. Childhood dysgraphia. Part 1. An illustrated clinical classification. Child Care Health Dev. 1989, 15, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeland, A.F. Handwriting and Perceptual-Motor Skills in Clumsy, Dysgraphic, and ‘Normal’ Children. Percept. Mot. Ski. 1992, 75, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamstra-Bletz, L.; Blöte, A.W. A Longitudinal Study on Dysgraphic Handwriting in Primary School. J. Learn. Disabil. 1993, 26, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidlitz, M. The Nature of Dysgraphic Handwriting in Grade-1 Children; Faculty of Graduate Studies, University of Western Ontario: London, ON, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, S.; Aloni, T.; Josman, N. Relationships between handwriting performance and organizational abilities among children with and without dysgraphia: A preliminary study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2010, 31, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DÁmico, A.; Cardaci, M. Relations among Perceived Self-Efficacy, Self-Esteem, and School Achievement. Psychol. Rep. 2003, 92, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, M.; Srivastava, S.K. To Study the Effect of Academic Achievement on the Level of Self-confidence. Int. J. Yoga Allied Sci. 2012, 1, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.; Patel, D.R. Dysgraphia. In Pediatrics, Child and Adolescent Health; Nova Biomedical Books: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- McHale, K.; Cermak, S.A. Fine Motor Activities in Elementary School: Preliminary Findings and Provisional Implications for Children with Fine Motor Problems. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1992, 46, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, D.; Maiorana, F. A Mobile Web Game Approach for Improving Dysgraphia. In Proceedings of the CSEDU 2015—7th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Lisbon, Portugal, 23–25 May 2015; Volume 1, pp. 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, J.H. Self-esteem in Dyslexic Children. Acad. Ther. 1973, 9, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neef, S.; José Dijck, V.; Ketelaar, E. (Eds.) Sign Here: Handwriting in the Age of New Media; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, E. The Story of Handwriting: Is Handwriting as a Practice Still Used in Swedish Schools? 2018. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1239050/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- De Ajuriaguerra, J. L’écriture de L’énfant; Delachaux et Niestle: Paris, France, 1989; pp. 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Hamstra-Bletz, L.; Bie, H.D.; Brinker, B.D. BHK—Concise Assessment Scale for Children’s Handwriting; Erickson: Portland, OR, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tressoldi, P. BVSCO-2: Batteria per la Valutazione della Scrittura e della Competenza Ortografica-2: Manuale e Materiali per le Prove; Giunti EDU: Via Fra Paolo Sarpi, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Overvelde, A.; Hulstijn, W. Handwriting development in grade 2 and grade 3 primary school children with normal, at risk, or dysgraphic characteristics. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselborn, T.; Gargot, T.; Kidziński, Ł.; Johal, W.; Cohen, D.; Jolly, C.; Dillenbourg, P. Automated human-level diagnosis of dysgraphia using a consumer tablet. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.M.; Silvers, G. Functions of vision in the control of handwriting. Acta Psychol. 1987, 65, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, R.R.; Keuss, P.J. The role of vision in the temporal and spatial control of handwriting. Acta Psychol. 1992, 81, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneck, C.M. Occupational Therapy Intervention: Performance Areas. 2009. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Occupational-Therapy-Intervention-%3A-Performance-Schneck/06770379840be86b1aa754613c844811529c08a4 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Garje, M.P.; Vishnu, D.; Rashmi, Y.; Arpita, A.; Maninder, S. Study of visual perceptual problems in children with learning disability. Indian J. Basic Appl. Med. Res. 2015, 4, 492–497. [Google Scholar]
- Noton, D.; Stark, L. Scanpaths in saccadic eye movements while viewing and recognizing patterns. Vis. Res. 1971, 11, 929-IN8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Monty, R.; Senders, J. Eye Movements: Cognition and Visual Perception. In Psychology Library Editions: Perception; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ditchburn, R. Eye-Movements and Visual Perception; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Wong, M.; Umali, M.; Pomplun, M. Using Eye-Tracking to Study Audio—Visual Perceptual Integration. Perception 2007, 36, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, A.C.; Braun, D.I.; Gegenfurtner, K.R. Eye movements and perception: A selective review. J. Vis. 2011, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, K.E.; Buktenica, N.A.; Beery, N.A. The Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration: VMI, with Supplemental Developmental Tests of Visual Perception and Motor Coordination: Administration, Scoring and Teaching Manual; Modern Curriculum Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hammill, D.D.; Pearson, N.A.; Voress, J.K. DTVP-3: Developmental Test of Visual Perception, 3rd ed.; PRO-ED: Austin, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N.A. Test of Visual Perception Skills, 4th ed.; ATP Assessments: Novato, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Panicker, A.S.; Chelliah, A. Resilience and Stress in Children and Adolescents with Specific Learning Disability. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 25, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, M.; Pulina, F.; Lanfranchi, S.; Jiménez, R. Video games and Intellectual Disabilities: A literature review—IRCCS Life Span and Disability. Life Span Disabil. 2015, 2, 147–165. [Google Scholar]
- Abt, C. Serious Games; G-Reference, Information and Interdisciplinary Subjects Series; University Press of America: Lanham, MD, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Susi, T.; Johannesson, M.; Backlund, P. Serious Games: An Overview. 2007. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220017759_Serious_Games_-_An_Overview (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- El-Nasr, M.S.; Yan, S. Visual attention in 3D video games. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGCHI International Conference on Advances in Computer Entertainment Technology—ACE, Hollywood, CA, USA, 14–16 June 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, W.R.; Blakely, D.P.; Simons, D.J. Do Action Video Games Improve Perception and Cognition? Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, D. Videogames and spatial skills: An exploratory study. ECTJ 1985, 33, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, I.; Feng, J. Video games and spatial cognition. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2010, 14, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, E.H.; Wilkinson, K.M.; Hickerson, B.D. Social Referencing Gaze Behavior During a Videogame Task: Eye Tracking Evidence from Children With and Without ASD. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tsai, M.J. Eye-hand coordination strategies during active video game playing: An eye-tracking study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 51, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Bertoni, S.; Ronconi, L.; Molteni, M.; Gori, S.; Facoetti, A. “Shall We Play a Game?”: Improving Reading Through Action Video Games in Developmental Dyslexia. Curr. Dev. Disord. Rep. 2015, 2, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, S.; Gori, S.; Ruffino, M.; Viola, S.; Molteni, M.; Facoetti, A. Action video games make dyslexic children read better. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulina, F.; Carretti, B.; Lanfranchi, S.; Mammarella, I.C. Improving spatial-simultaneous working memory in Down syndrome: Effect of a training program led by parents instead of an expert. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilg, W.; Schatton, C.; Schicks, J.; Giese, M.A.; Schols, L.; Synofzik, M. Video game-based coordinative training improves ataxia in children with degenerative ataxia. Neurology 2012, 79, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dui, L.G.; Toffoli, S.; Speziale, C.; Termine, C.; Matteucci, M.; Ferrante, S. Can Free Drawing Anticipate Handwriting Difficulties? A Longitudinal Study. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE—EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Ioannina, Greece, 27–30 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.; Simon, R. Bias in error estimation when using cross-validation for model selection. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstajic, D.; Buturovic, L.J.; Leahy, D.E.; Thomas, S. Cross-validation pitfalls when selecting and assessing regression and classification models. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C. Visual Perceptual Skills as Predictors of Handwriting Skills of Children Grades 1-3. J. Occup. Ther. Sch. Early Interv. 2022, 15, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavale, K. Meta-Analysis of the Relationship Between Visual Perceptual Skills and Reading Achievement. J. Learn. Disabil. 1982, 15, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Slattery, T.J.; Bélanger, N.N. Eye movements, the perceptual span, and reading speed. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2010, 17, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, E.; Barrett, M.; Davis, A. The effect of affective characterizations on the size of children’s drawings. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 2003, 21, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dui, L.G.; Lunardini, F.; Termine, C.; Matteucci, M.; Stucchi, N.A.; Borghese, N.A.; Ferrante, S. A Tablet App for Handwriting Skill Screening at the Preliteracy Stage: Instrument Validation Study. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8, e20126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, M.; Gey, F. The relationship between Recall and Precision. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1994, 45, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, B.; Keller, J.B.; Billard, A. A wearable gaze tracking system for children in unconstrained environments. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2011, 115, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dui, L.G.; Calogero, E.; Malavolti, M.; Termine, C.; Matteucci, M.; Ferrante, S. Digital Tools for Handwriting Proficiency Evaluation in Children. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Athens, Greece, 27–30 July 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunick, K.L.; Putnam, M.M.; McGarry, L.E.; Richards, M.N.; Calvert, S.L. Children’s future parasocial relationships with media characters: The age of intelligent characters. J. Child. Media 2016, 10, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, M.; Hofmann, O.; Brosius, H.B.; Carter, C.; Chan, K.; Donald, S.; Fisherkeller, J.; Frenette, M.; Kolbjørnsen, T.; Lemish, D.; et al. Gender in children’s television worldwide: Results from a media analysis in 24 countries. Televizion 2008, 21, 4–9. [Google Scholar]








| Screenshot | Tested Ability | Game Mechanics | Collected Data |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Form constancy: the ability to recognize a shape when size, color or orientation changes. | The player must locate the correct shape and drag it to the center of the white outline. When the difficulty rises, the shapes are rotated, thus changing not only color and size but also orientation. |
|
 | Masked form constancy: similar to form constancy, but the shape that has to be recognized is part of a larger image. | The player must locate the correct shape and drag it to the center of the image on the left, which is missing a piece. When the difficulty rises, the options and the target image rotate. |
|
 | Copying: the ability to reproduce an image. | The player must copy the image proposed on the left in the right panel. When the difficulty rises, the reference images become more complex. |
|
 | Tracing: the ability to reproduce an image on top of a reference. | The player must trace the image proposed, trying to stay inside the line. When the difficulty rises, the reference images become more complex. |
|
 | Figure-ground perception: the ability to recognize a shape on a confusing background. | The player must find a reference image (shown in the lower left corner) among others. In higher difficulty levels, the number and variety of images increase. |
|
 | Visual closure: the ability to recognize a partially hidden shape. | The player has to recognize and select the image that corresponds to the reference one. The game is presented in two modalities: in the first, the reference is partially hidden; in the second, the options are hidden. |
|
| Algorithm | Game Performance (Train) | Game Performance (Test) | Eye Tracking (Train) | Eye Tracking (Test) | Drawing (Train) | Drawing (Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 0.86 (0.032) | 0.68 (0.069) | 0.86 (0.026) | 0.55 (0.091) | 0.78 (0.058) | 0.47 (0.094) |
| CatBoost | 1.00 (0.000) | 0.72 (0.121) | 1.00 (0.000) | 0.43 (0.216) | 1.00 (0.000) | 0.53 (0.125) |
| Random Forest | 1.00 (0.000) | 0.70 (0.115) | 1.00 (0.000) | 0.43 (0.229) | 1.00 (0.000) | 0.47 (0.094) |
| SVM | 0.92 (0.040) | 0.63 (0.125) | 0.95 (0.038) | 0.41 (0.160) | 0.95 (0.034) | 0.52 (0.107) |
| Set of Features | Accuracy (Train) | Precision (Train) | Recall (Train) | F1 Score (Train) | Accuracy (Test) | Precision (Test) | Recall (Test) | F1 Score (Test) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Game performance | 0.72 (0.045) | 0.73 (0.042) | 0.85 (0.061) | 0.77 (0.045) | 0.61 (0.079) | 0.61 (0.036) | 0.86 (0.127) | 0.71 (0.067) |
| Eye tracking | 0.66 (0.051) | 0.74 (0.0.53) | 0.66 (0.144) | 0.64 (0.090) | 0.60 (0.183) | 0.63 (0.245) | 0.70 (0.215) | 0.65 (0.185) |
| Drawing | 0.68 (0.066) | 0.72 (0.103) | 0.72 (0.109) | 0.69 (0.093) | 0.55 (0.115) | 0.59 (0.118) | 0.70 (0.219) | 0.62 (0.119) |
| Game and drawing | 0.77 (0.057) | 0.80 (0.031) | 0.82 (0.092) | 0.79 (0.057) | 0.59 (0.126) | 0.62 (0.074) | 0.77 (0.225) | 0.67 (0.123) |
| All of the above | 0.70 (0.067) | 0.65 (0.125) | 0.66 (0.158) | 0.64 (0.130) | 0.65 (0.112) | 0.64 (0.083) | 0.75 (0.129) | 0.69 (0.093) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piazzalunga, C.; Dui, L.G.; Termine, C.; Bortolozzo, M.; Matteucci, M.; Ferrante, S. Investigating Visual Perception Impairments through Serious Games and Eye Tracking to Anticipate Handwriting Difficulties. Sensors 2023, 23, 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041765
Piazzalunga C, Dui LG, Termine C, Bortolozzo M, Matteucci M, Ferrante S. Investigating Visual Perception Impairments through Serious Games and Eye Tracking to Anticipate Handwriting Difficulties. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041765
Chicago/Turabian StylePiazzalunga, Chiara, Linda Greta Dui, Cristiano Termine, Marisa Bortolozzo, Matteo Matteucci, and Simona Ferrante. 2023. "Investigating Visual Perception Impairments through Serious Games and Eye Tracking to Anticipate Handwriting Difficulties" Sensors 23, no. 4: 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041765
APA StylePiazzalunga, C., Dui, L. G., Termine, C., Bortolozzo, M., Matteucci, M., & Ferrante, S. (2023). Investigating Visual Perception Impairments through Serious Games and Eye Tracking to Anticipate Handwriting Difficulties. Sensors, 23(4), 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23041765












