A Dual-Band Polarization-Insensitive Frequency Selective Surface for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Unit Cell Design Configurations
2.1. Modified Jerusalem Crossed Loop (MJCL) FSS
2.2. Corner-Modified Square Loop (MJCL) FSS
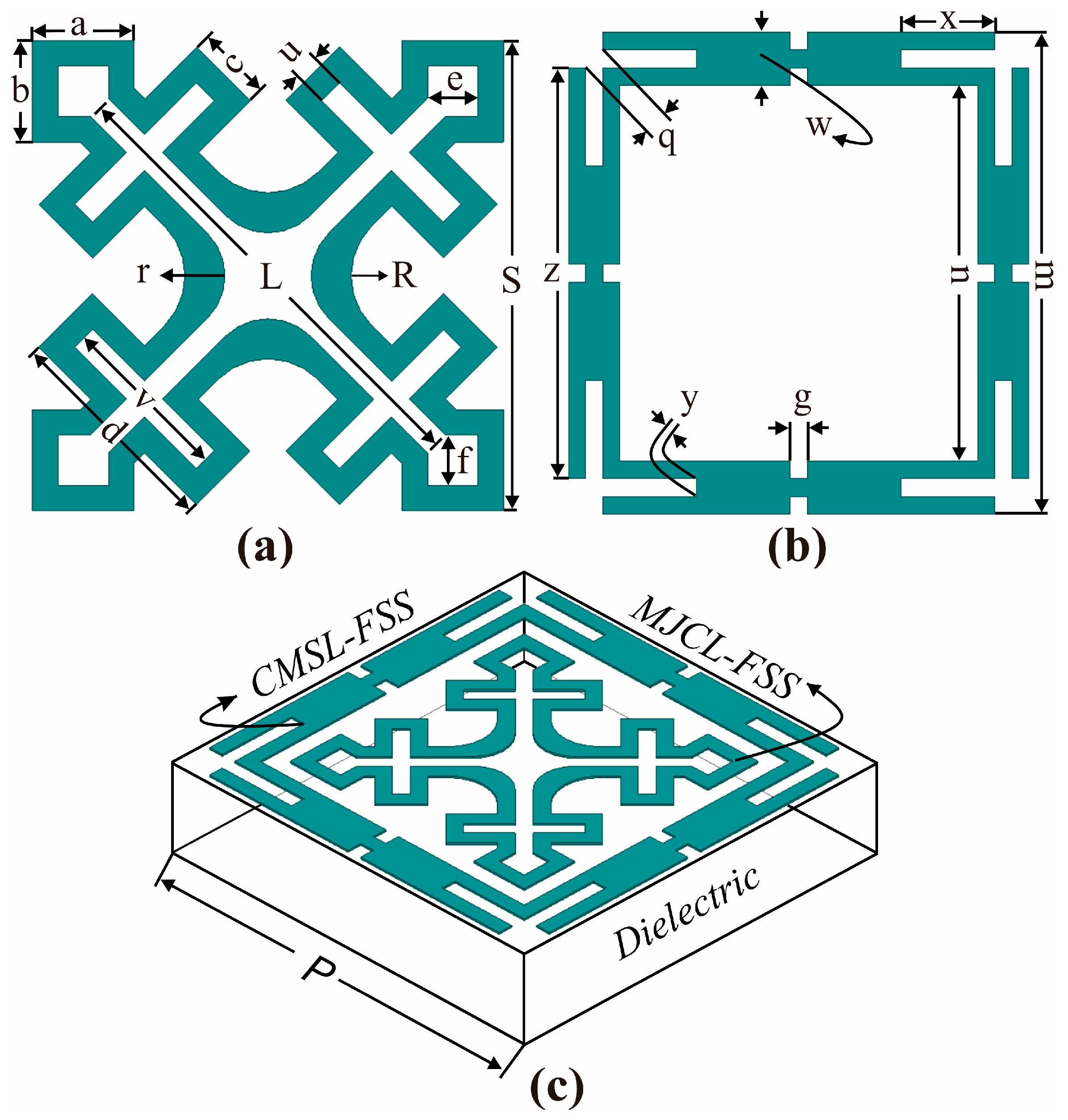
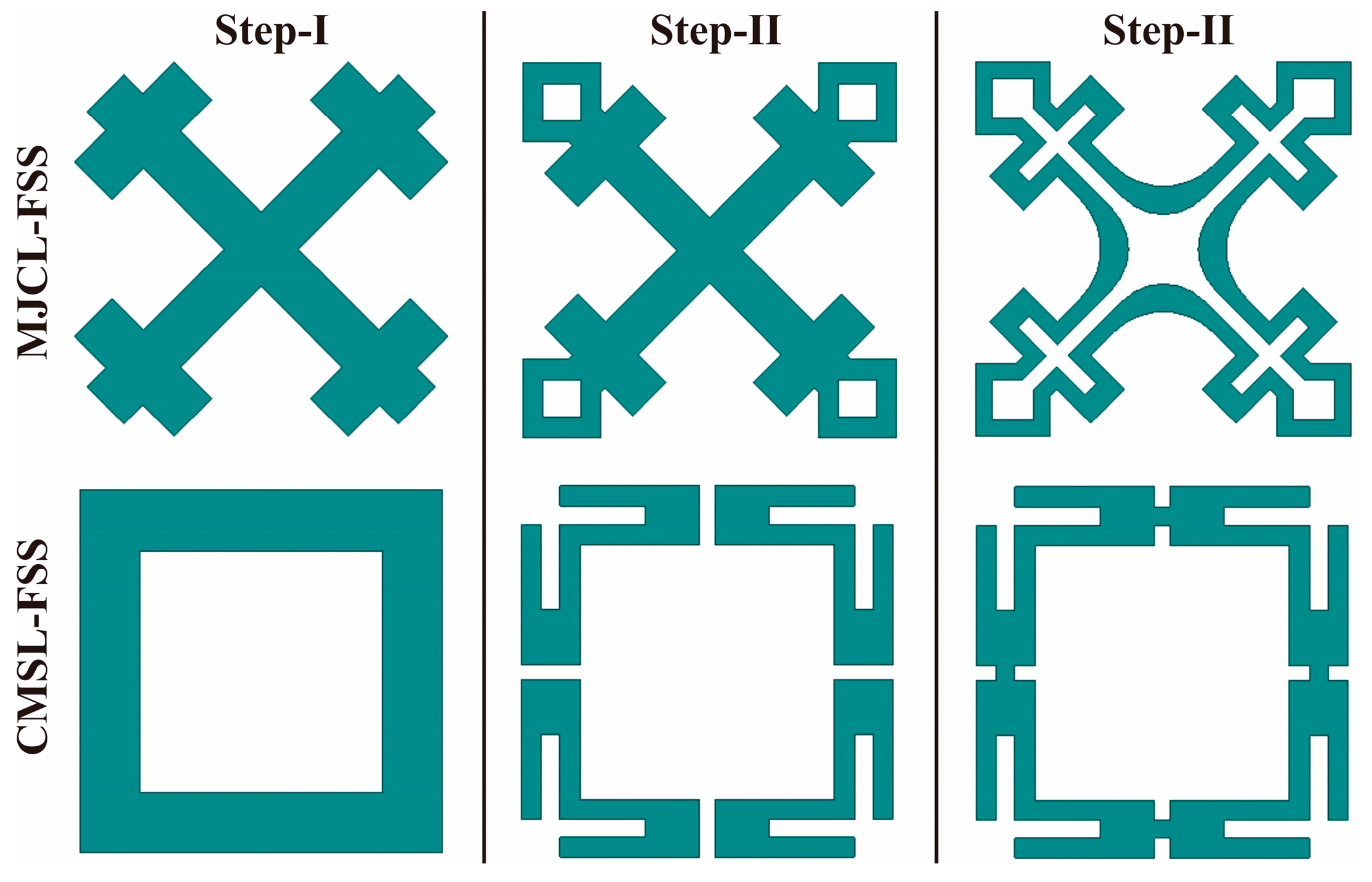
2.3. Co-Planner Design Configuration
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Simulation of the Proposed Unit Cell
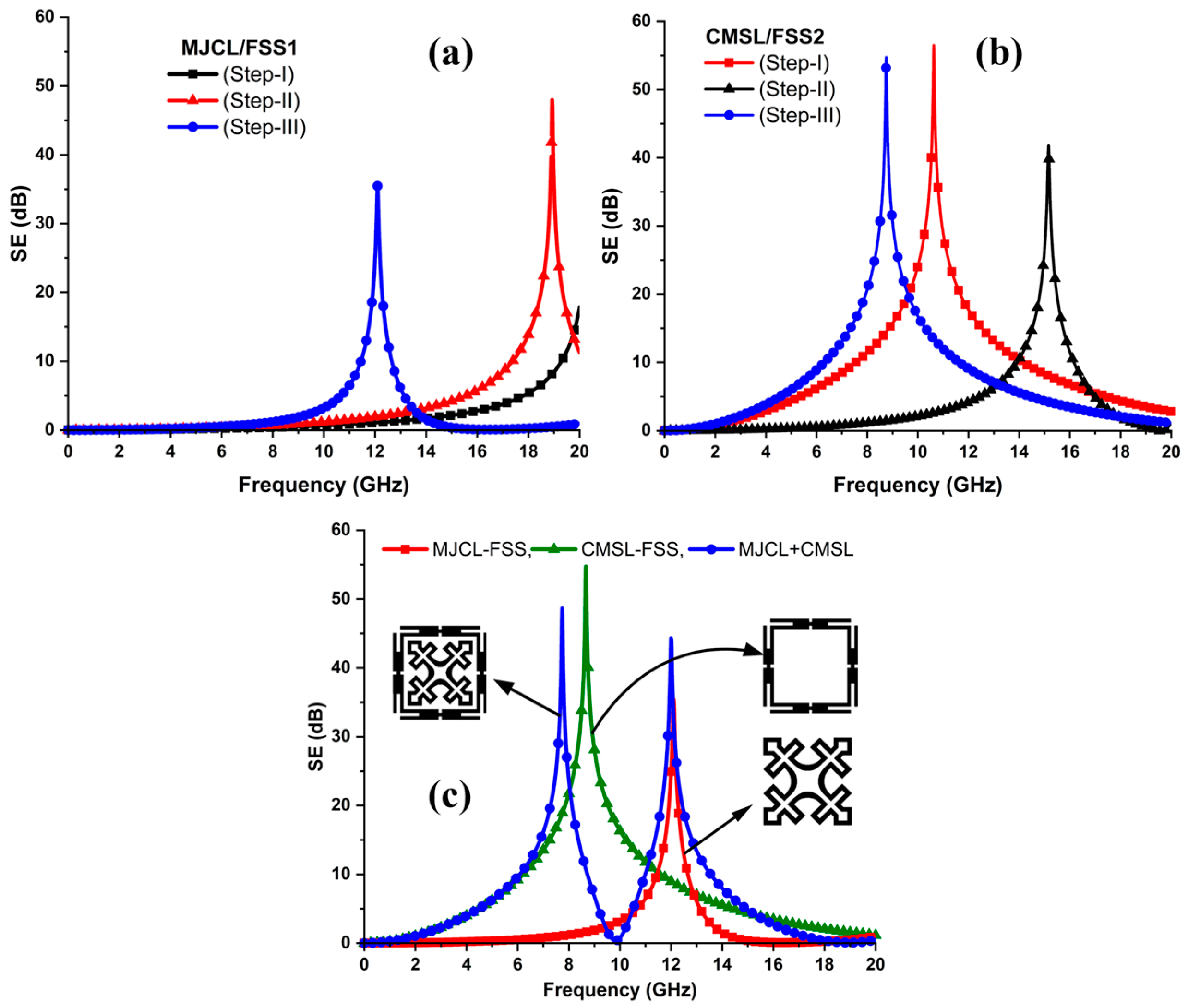
3.2. Shielding Effectiveness
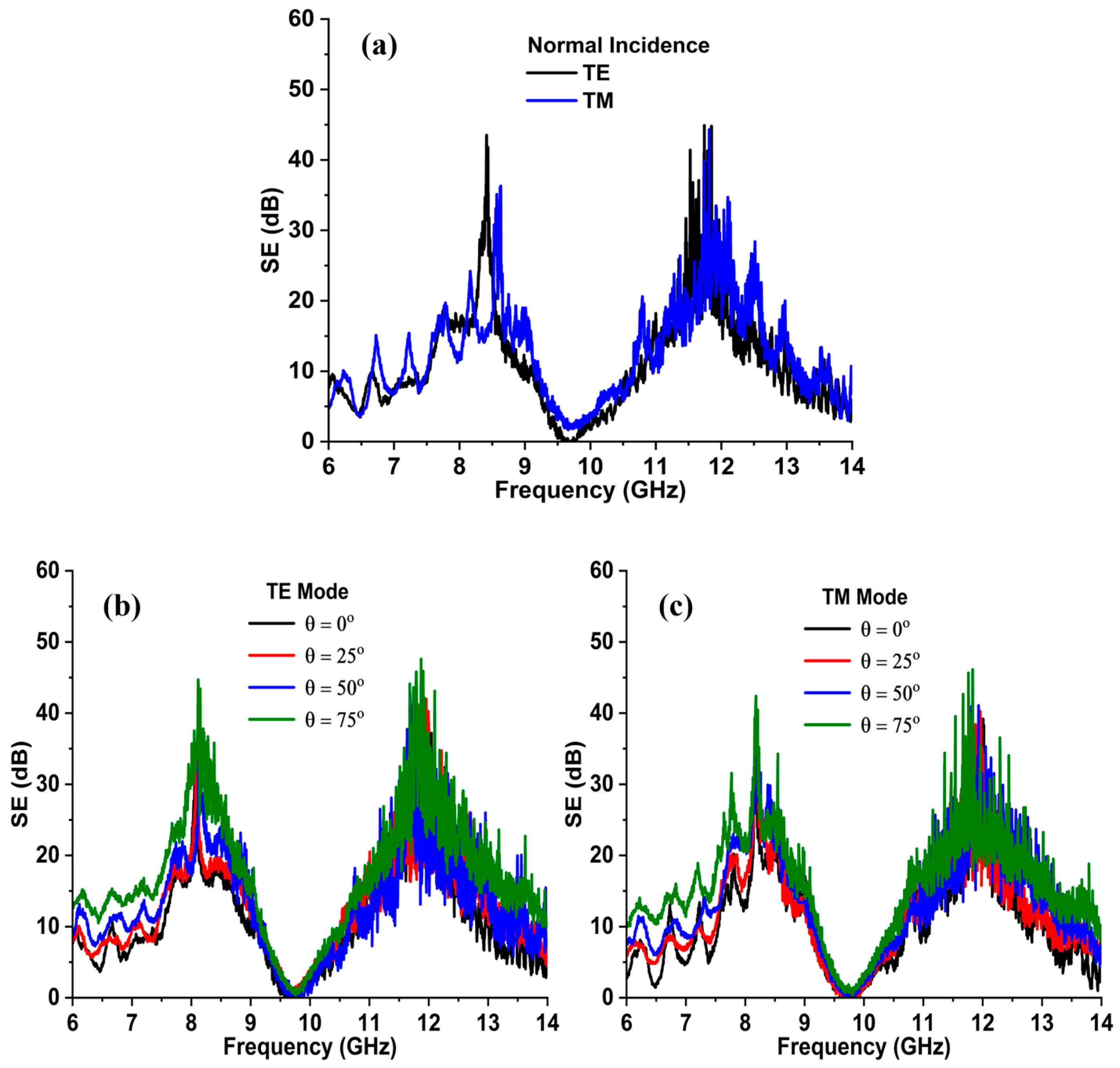
3.3. Angular Stability Analysis
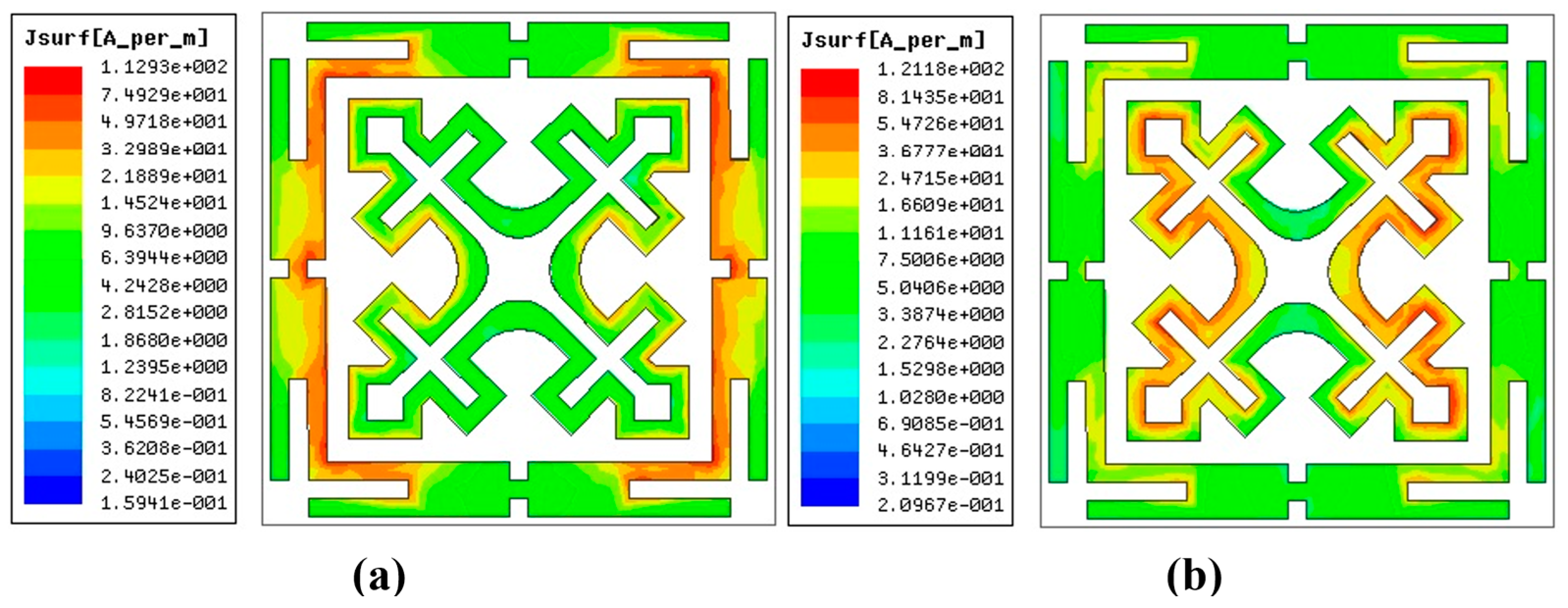
3.4. Surface Current Density
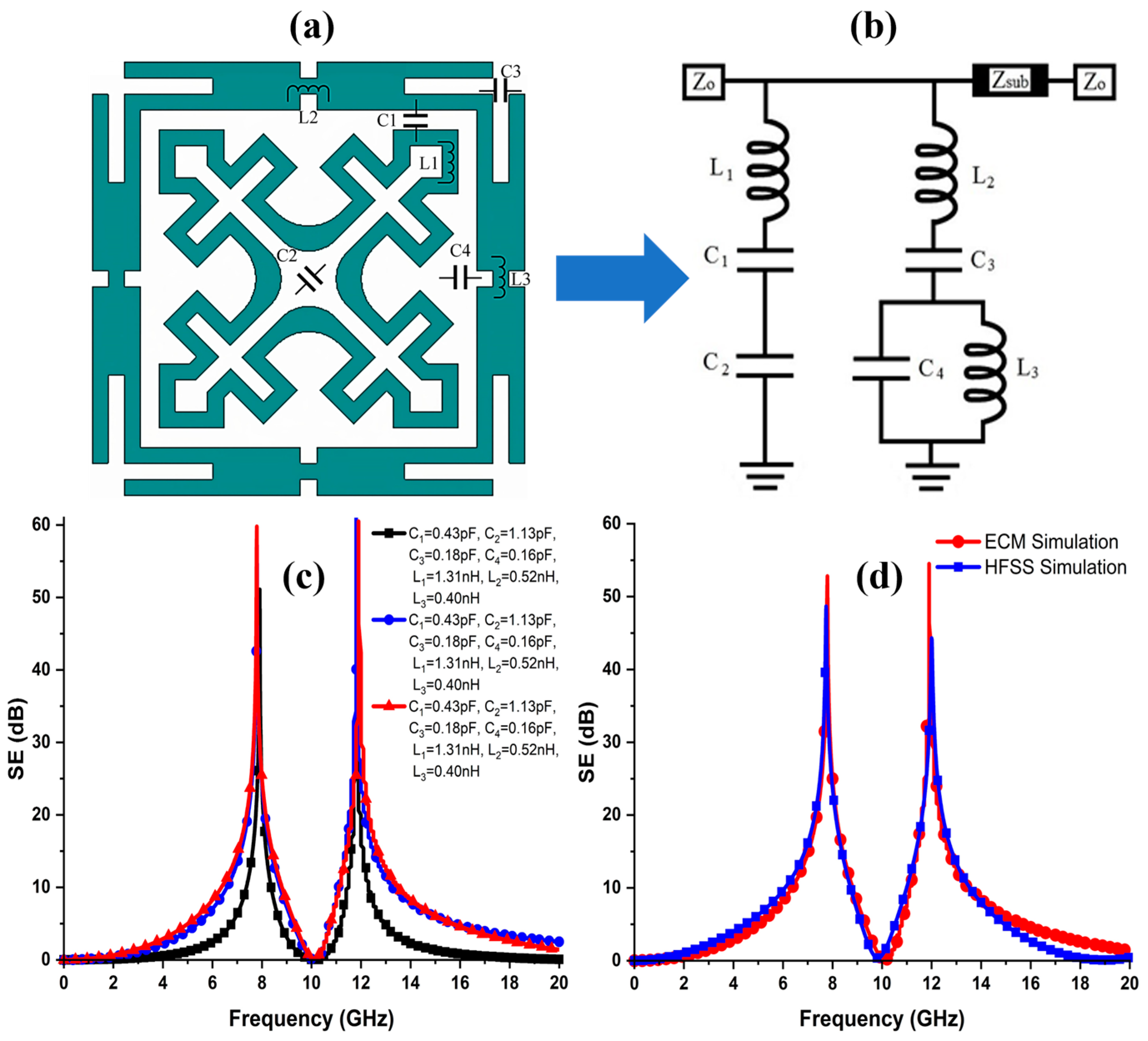
3.5. Equivalent Circuit Model
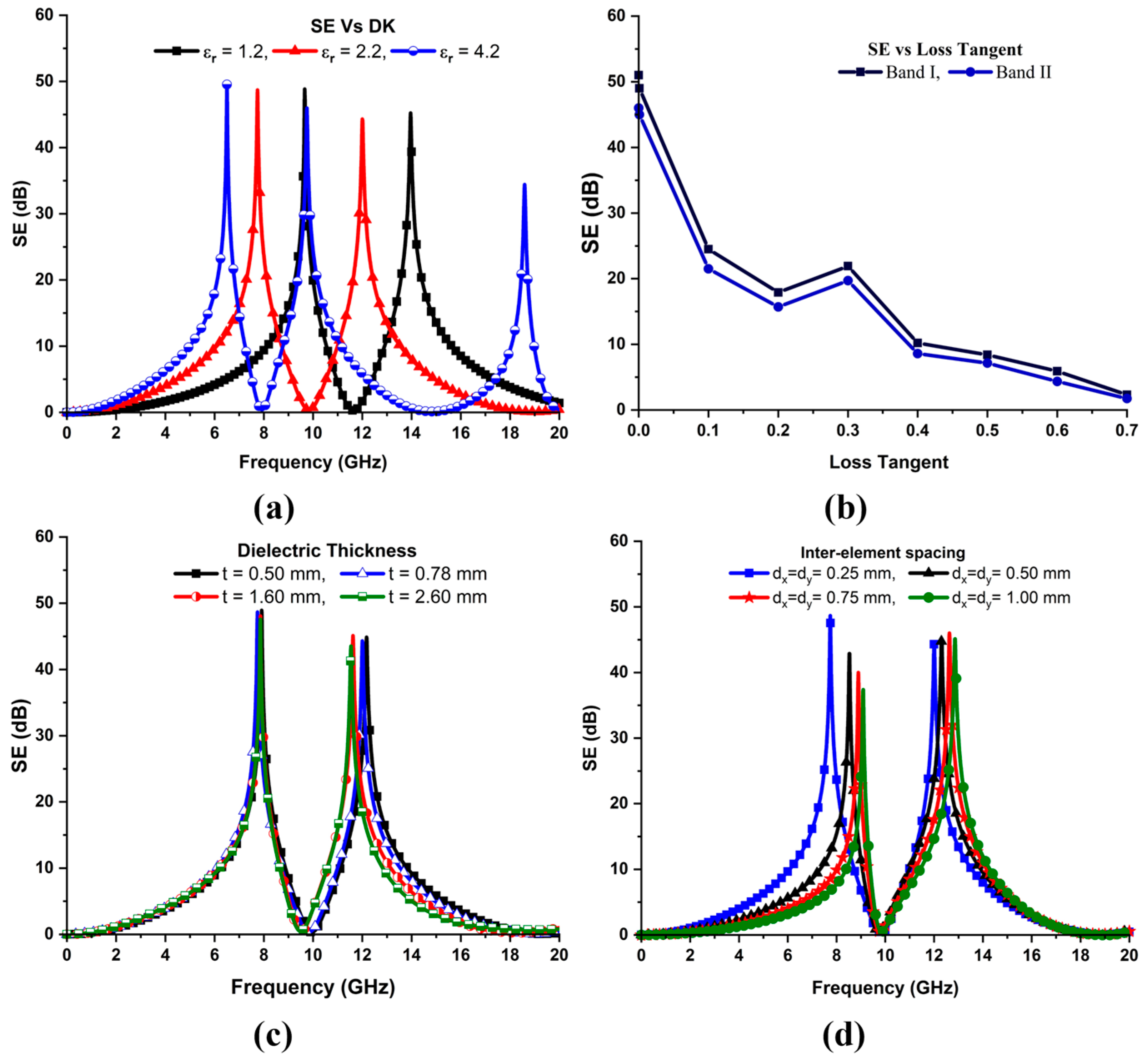
4. Parametric Analysis
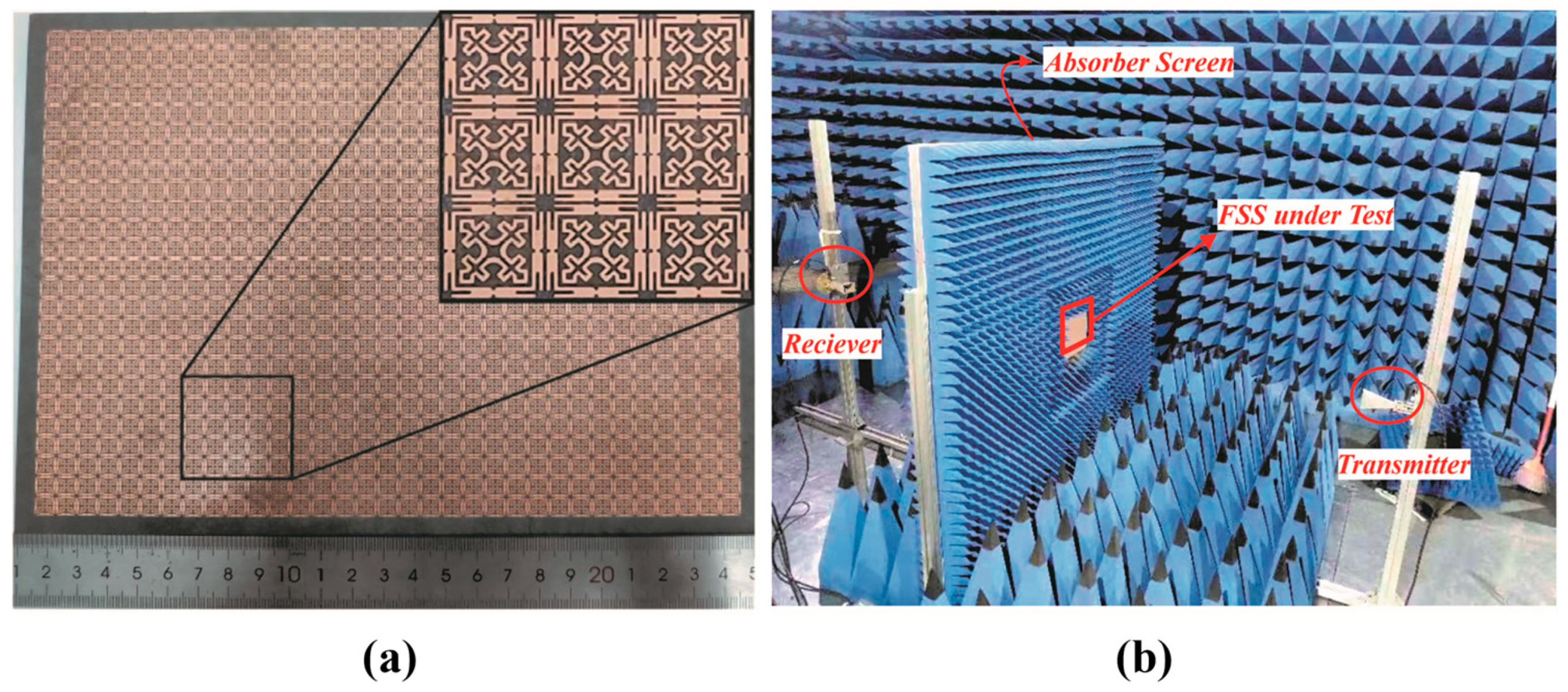
5. Experimental Setup and Measurements
5.1. Normal Angle of Incidence
5.2. Oblique Angle Incidence
6. Comparative Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheng, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Wang, K. A Conformal Miniaturized Band-Pass Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Frequency Response for Radome Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Sun, D.; Zeng, Q.; Song, M.; Denidni, T.A. UWB Frequency-Selective Surface Absorber Based on Graphene Featuring Wide-Angle Stability. Sensors 2023, 23, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, Y.F.C. Enhancing broadband terahertz absorption via a graphene-based metasurface absorber featuring a rectangular ring and triple crossbars. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 055905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaruddin, N.R.; Tan, Y.M.; Chen, S.H.; Chou Chao, C.T.; Lim, C.M.; Thotagamuge, R.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Chou Chau, Y.F. Designing a Broadband Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber Through Bi-Layer Hybridization of Metal and Graphene. Plasmonics 2024, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Xue, Z.; Ren, W.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, B.; Jin, C. High roll-off rate ultra-thin polarization rotating frequency selective surface. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ud Din, I.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Virdee, B.S.; Jayanthi, R.K.R.; Ullah, S.; Khan, S.; See, C.H.; Golunski, L.; Koziel, S. Frequency-Selective Surface-Based MIMO Antenna Array for 5G Millimeter-Wave Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkmen, F.; Omar, M.R. A scalable, dual-polarized absorber surface for electromagnetic energy harvesting and wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 4021–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahvand, M.; Keyvan, F.; Jose, A.E.; Zahra, A.; Eduardo, M.d.R. A 20/30 GHz reflectarray backed by FSS for shared aperture Ku/Ka-band satellite communication antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Dey, S. Conformal miniaturized angular stable triband frequency selective surface for EMI shielding. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2022, 64, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.L.; Islam, M.T.; Alam, T. Incident Angle Stable Broadband Conformal mmWave FSS for 5G (n257, n258, n260, and n261) band EMI Shielding Application. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 23, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rac-Rumijowska, O.; Pokryszka, P.; Rybicki, T.; Suchorska-Woźniak, P.; Woźniak, M.; Kaczkowska, K.; Karbownik, I. Influence of Flexible and Textile Substrates on Frequency-Selective Surfaces (FSS). Sensors 2024, 24, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sabata, A.; Matekovits, L.; Buta, A.; Dassano, G.; Silaghi, A. Frequency Selective Surface for Ultra-Wide Band Filtering and Shielding. Sensors 2022, 22, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Salama, K.N.; Shamim, A. Polarization insensitive and transparent frequency selective surface for dual band GSM shielding. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 69, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Shafique, F.M.; Mughal, J.M. Polarization insensitive dual band frequency selective surface for RF shielding through glass windows. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2019, 62, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, N.; Loïc, M. A single-layer frequency selective surface with dual wideband band-stop response. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Huang, C.; Cai, Y.; Lin, X. Dual-Band Frequency Selective Surface with Different Polarization Selectivity for Wireless Communication Application. Sensors 2023, 23, 4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ren, P.; Xiang, Z.; Xu, B.; Chen, R. Design of dual-stopband FSS with tightly spaced frequency response characteristics. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2022, 32, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Eibert, T.F. A multifunctional metamaterial-based dual-band isotropic frequency-selective surface. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, G.; Thottappan, M.; Singh, S.P. Highly angularly stable dual-band stop FSS for blocking satellite downlink frequencies. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2022, 64, 2055–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, K.; Jaglan, N.; Gupta, S.D. Analysis and design of a simple and compact bandstop Frequency Selective Surface at mobile WiMAX and satellite communication X-band. J. Electromag. Waves Appl. 2021, 35, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MJCL-FSS | Parameter | a = b | c | d | e = f | r | R | u | v | S | L |
| Values | 1.00 | 0.75 | 2.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.25 | 2.00 | 4.65 | 4.70 | |
| CMSL-FSS | Parameter | g | m | n | q | x | y | z | P | - | - |
| Values | 0.50 | 6.75 | 5.25 | 0.35 | 1.35 | 0.50 | 5.75 | 7 | - | - |
| Angle (θ) | Resonant Frequency (GHz) | Attenuation (dB) | Fractional Bandwidth (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band I | Band II | Band I | Band II | Band I | Band II | |||||||
| TE | TM | TE | TM | TE | TM | TE | TM | TE | TM | TE | TM | |
| 0° | 7.90 | 7.70 | 11.94 | 12.08 | 48.72 | 45.02 | 49.21 | 43.82 | 35.27 | 34.76 | 21.62 | 20.37 |
| 30° | 7.91 | 7.76 | 11.92 | 12.01 | 48.99 | 45.22 | 49.65 | 44.39 | 39.10 | 40.45 | 22.45 | 21.63 |
| 45° | 7.95 | 7.79 | 11.90 | 12.00 | 50.09 | 46.62 | 50.21 | 45.65 | 45.01 | 46.25 | 23.77 | 23.44 |
| 60° | 8.02 | 7.84 | 11.84 | 11.94 | 52.30 | 48.63 | 52.32 | 47.89 | 58.56 | 60.75 | 28.22 | 27.90 |
| 75° | 8.09 | 7.84 | 11.70 | 11.94 | 57.47 | 55.9 | 56.63 | 55.45 | 92.91 | 98.12 | 39.29 | 36.67 |
| Equivalent Circuit Values | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.31 nH | 0.52 nH | 0.40 nH | - | - | |||
| 1.13 pF | 0.16 pF | 0.18 pF | 0.16 pF | ||||
| Ref. No. | Unit Cell Size (mm) | Employed Substrate | Operation Band | Angular Stability | Frequency Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [12] | 0.087λ × 0.087λ | FR-4 | UWB | 0–60° | N/A |
| [13] | 0.194λ × 0.194λ | Polyethylene terephthalate | GSM | 0–60° | 2.11 |
| [14] | 0.163λ × 0.163λ | Glass | WiFi/WLAN | 0–45° | 2.24 |
| [15] | 0.21λ × 0.21λ | Paper and Polymer | WiFi/WLAN | 0–45° | 2.22 |
| [16] | 0.161λ × 0.161λ | Taconic RF-35 | X | 0–50° | N/A |
| [17] | 0.167λ × 0.167λ | FR-4 | C/X | 0–60° | 1.32 |
| [18] | 0.26λ × 0.26λ | RO4350B | X/Ku | 0–45° | 1.91 |
| [19] | 0.149λ × 0.149λ | FR-4 | C/X | 0–60° | 1.87 |
| [20] | 0.082λ × 0.082λ | FR-4 | WiMAX/X | 0–70° | 3.3 |
| This Work | 0.184λ × 0.184λ | RT/duroid 5880 | X/Ku | 0–75° | 1.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idrees, M.; He, Y.; Ullah, S.; Wong, S.-W. A Dual-Band Polarization-Insensitive Frequency Selective Surface for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113333
Idrees M, He Y, Ullah S, Wong S-W. A Dual-Band Polarization-Insensitive Frequency Selective Surface for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Sensors. 2024; 24(11):3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113333
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdrees, Muhammad, Yejun He, Shahid Ullah, and Sai-Wai Wong. 2024. "A Dual-Band Polarization-Insensitive Frequency Selective Surface for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications" Sensors 24, no. 11: 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113333
APA StyleIdrees, M., He, Y., Ullah, S., & Wong, S.-W. (2024). A Dual-Band Polarization-Insensitive Frequency Selective Surface for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Sensors, 24(11), 3333. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24113333





