Development of a MEMS Piezoresistive High-g Accelerometer with a Cross-Center Block Structure and Reliable Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure Design and Optimization
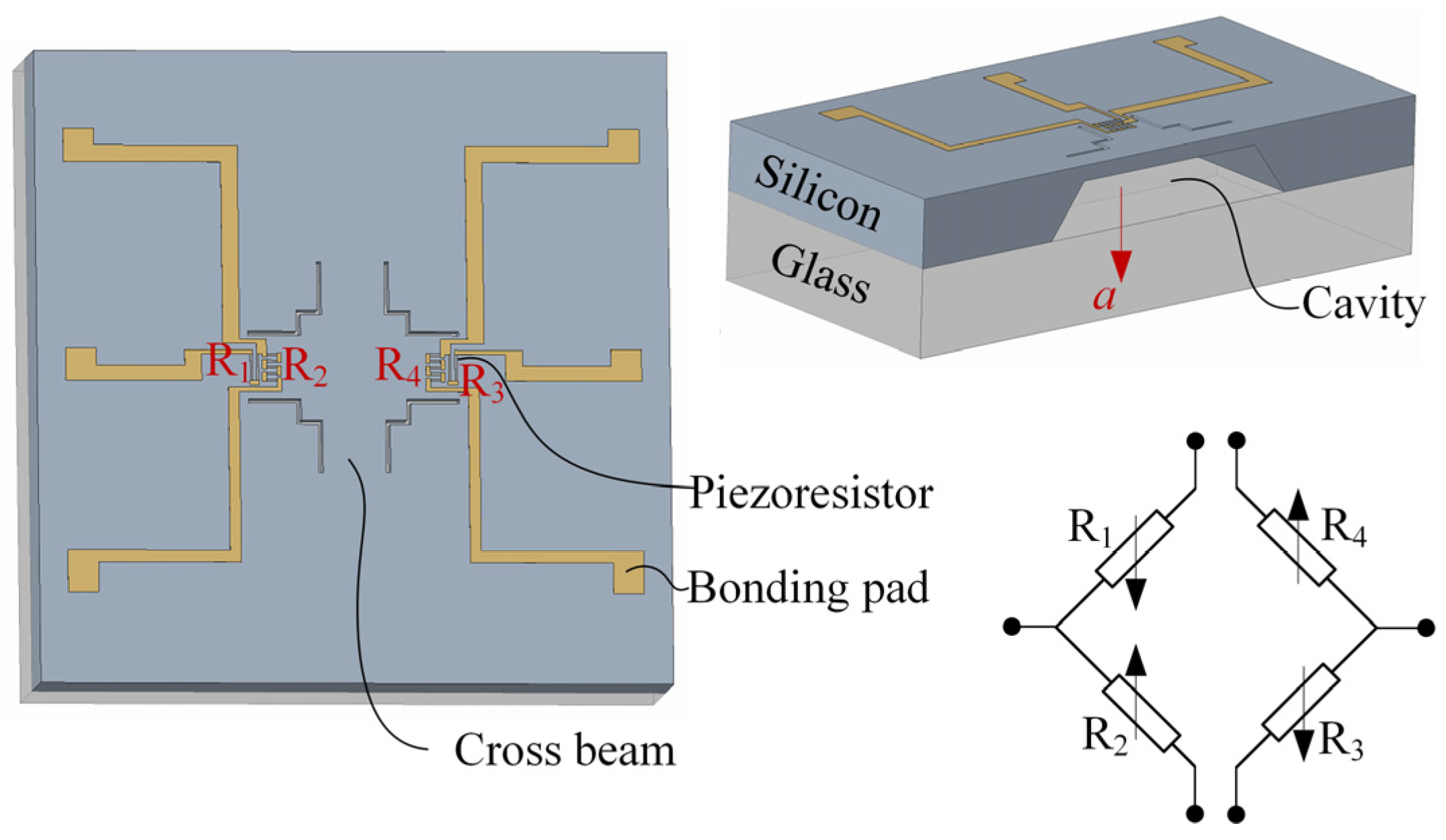
2.1. Structure Design
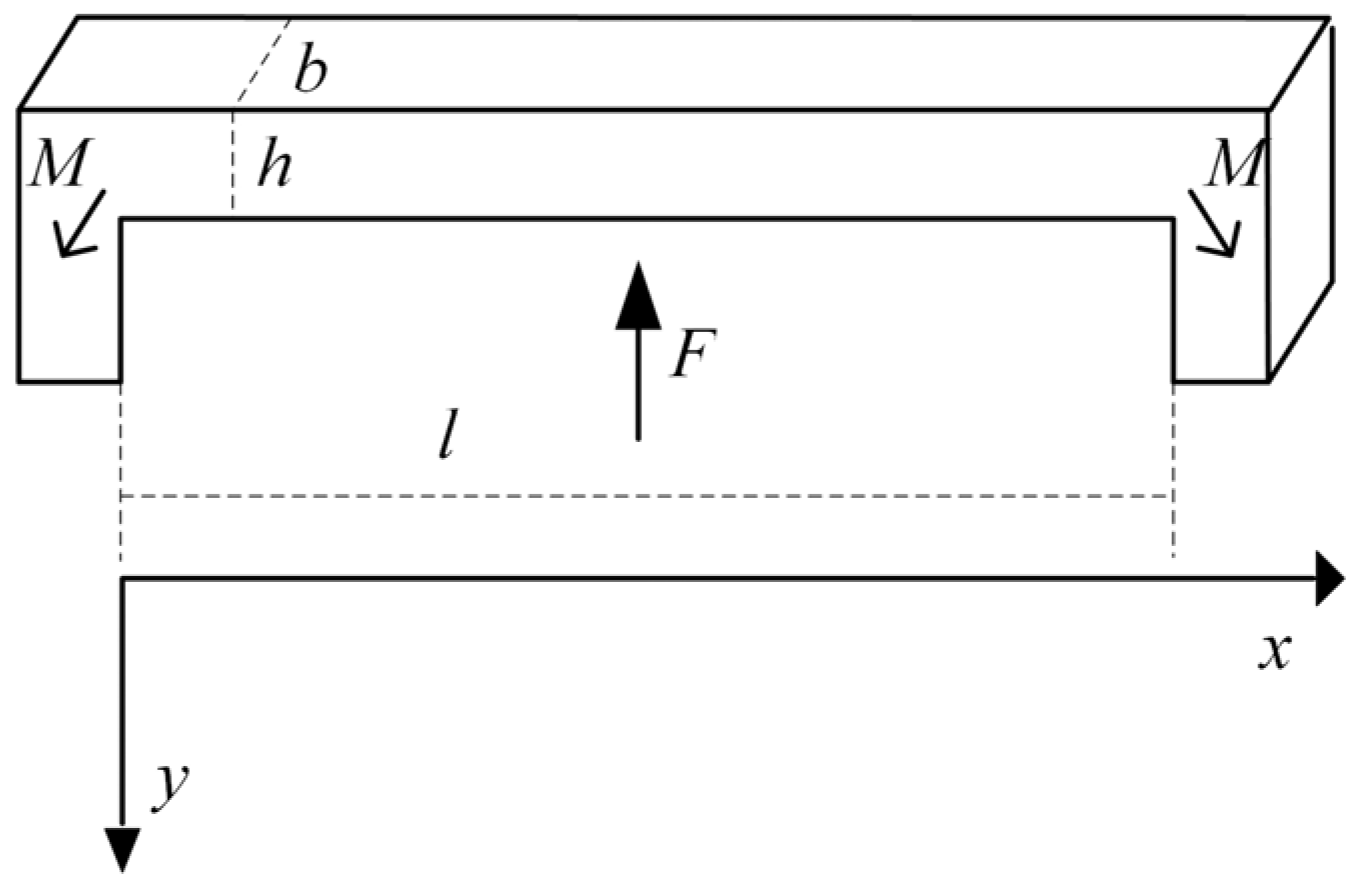
2.2. Theoretical Analysis
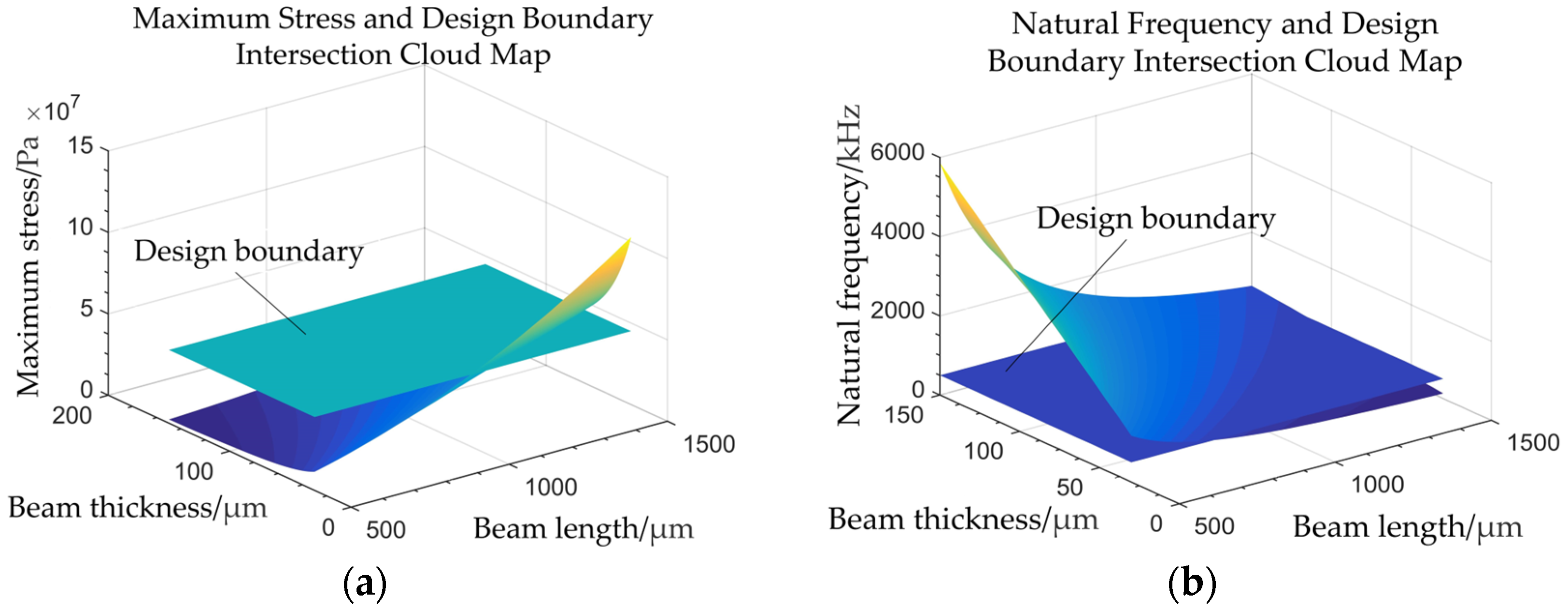
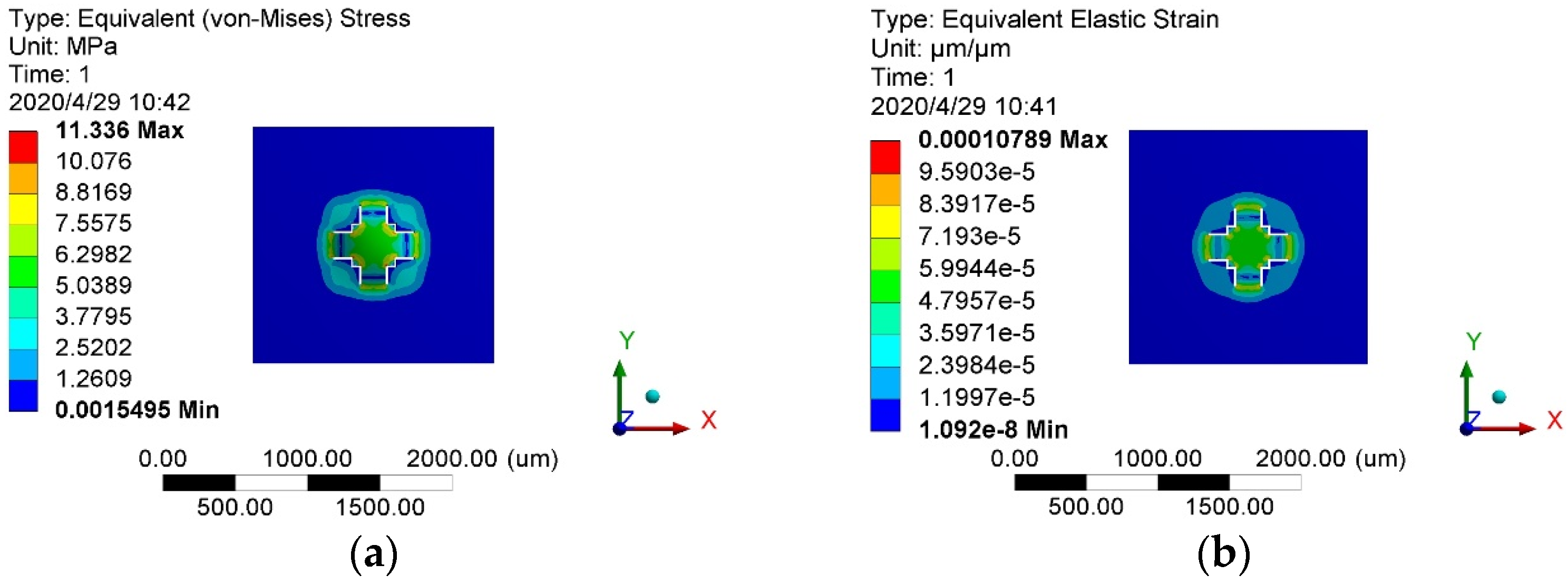
2.3. Static and Modal Analysis
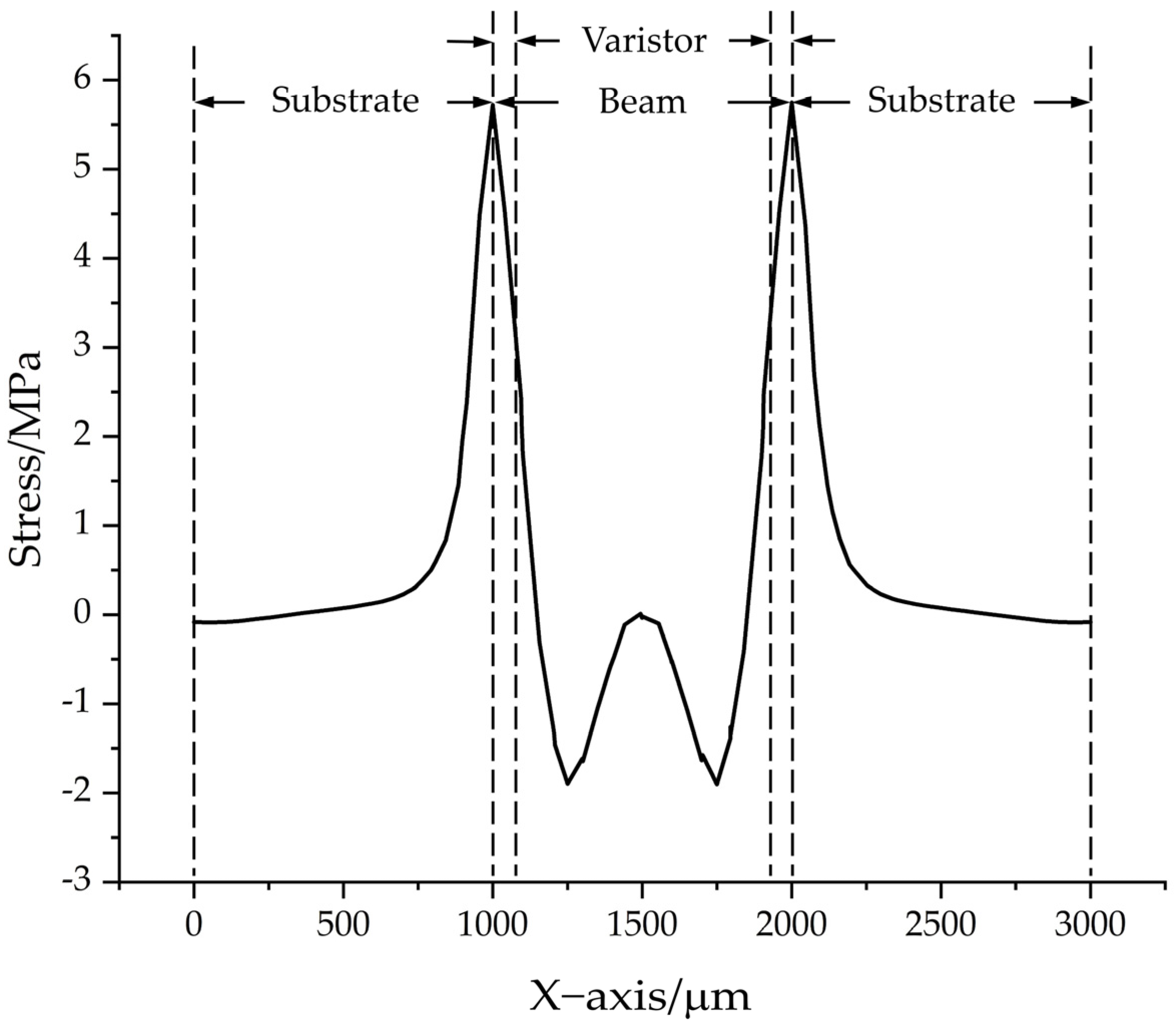
2.4. Arrangement of Piezoresistors
3. Fabrication, Package, and Improved Electrodes
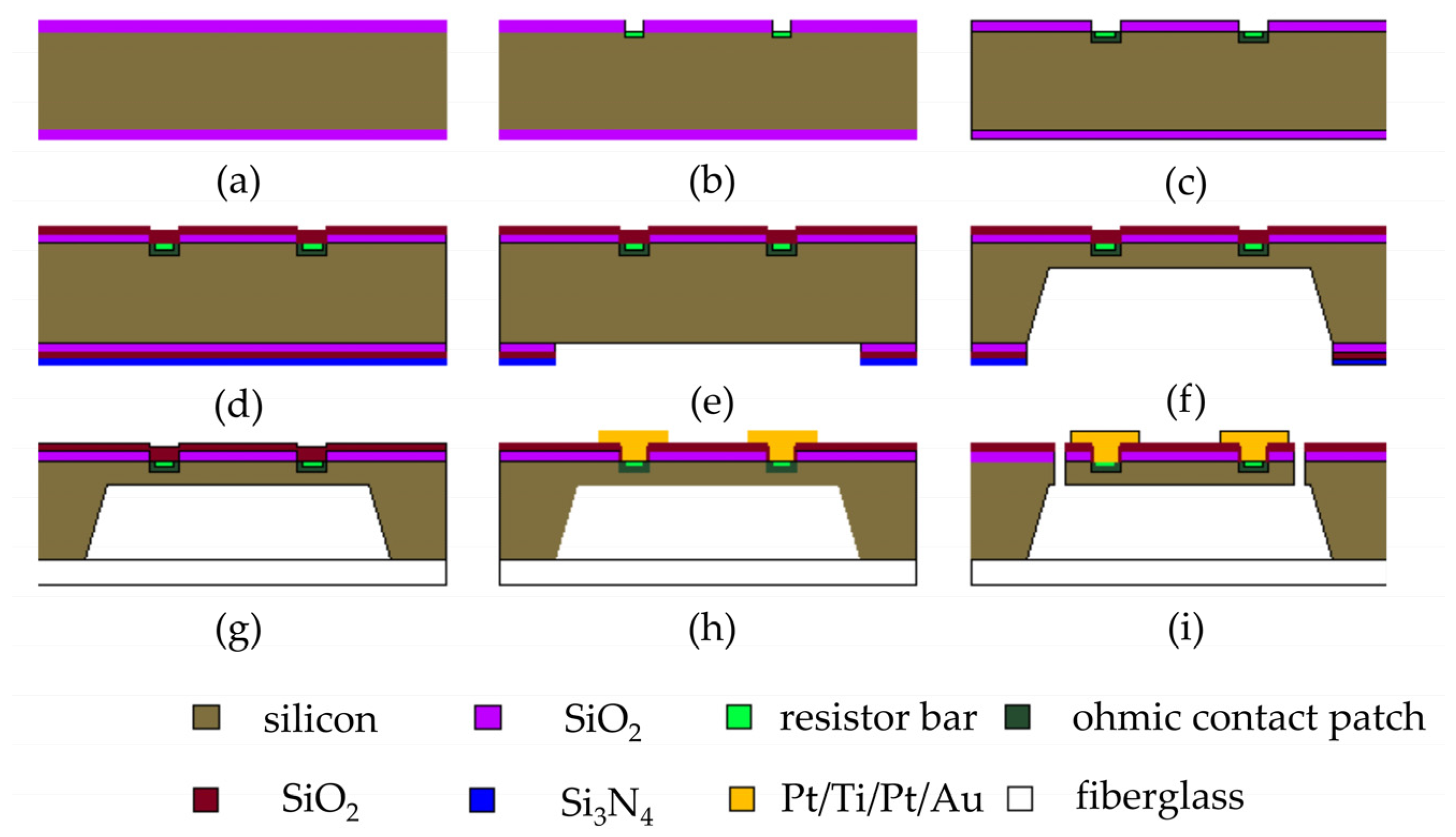
3.1. Fabrication
- (a)
- Prepare and cleanse the chip;
- (b)
- Perform photolithography and patterning of the piezoresistor, and then etch the silica layer in the patterned region, followed by light doping;
- (c)
- Execute photolithography in the ohmic contact area and proceed with heavy doping;
- (d)
- Conduct rapid annealing to activate the introduced elements, and deposit the SiO2 layer as an insulating layer on the prototype’s surface using the PECVD technique;
- (e)
- Engage in etching of the design in the back cavity area and etch the SiO2 layer within the graphic region;
- (f)
- Protect the chip’s front side with a specialized fixture for wet etching, then wet etch the back cavity, ensuring that the thickness aligns with the design value;
- (g)
- Protect the front of the sample, eradicate the SiO2 layer from the chip’s backside, and employ the silicon-glass anode bonding process to fuse the silicon and glass;
- (h)
- Perform lithography in the lead hole region, corrode the silicon dioxide layer’s graphic region, deposit Pt metal through the sputtering process, and strip to reveal the lead hole with the deposited Pt layer. Utilize a tube furnace for high-temperature annealing of the prototype, establishing a local ohmic contact inside the lead hole. Execute photolithography of the metal lead region, deposit the metal Ti/Pt/Au onto the prototype’s surface through magnetron sputtering, and strip to display the metal lead;
- (i)
- Perform photolithography on the beam and release holes, and then etch the release holes utilizing the ICP dry etching method, resulting in the sensing beam structure.
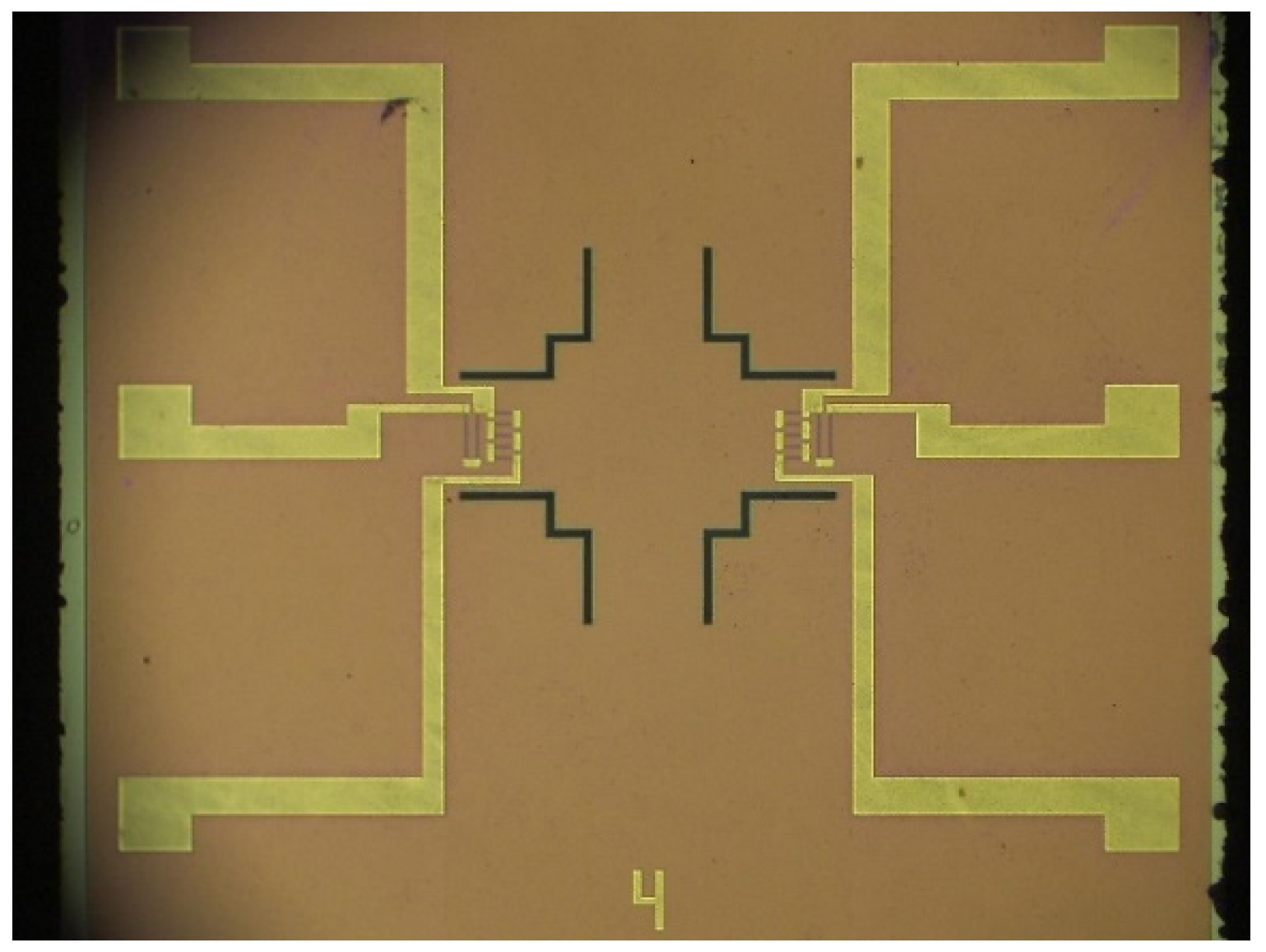
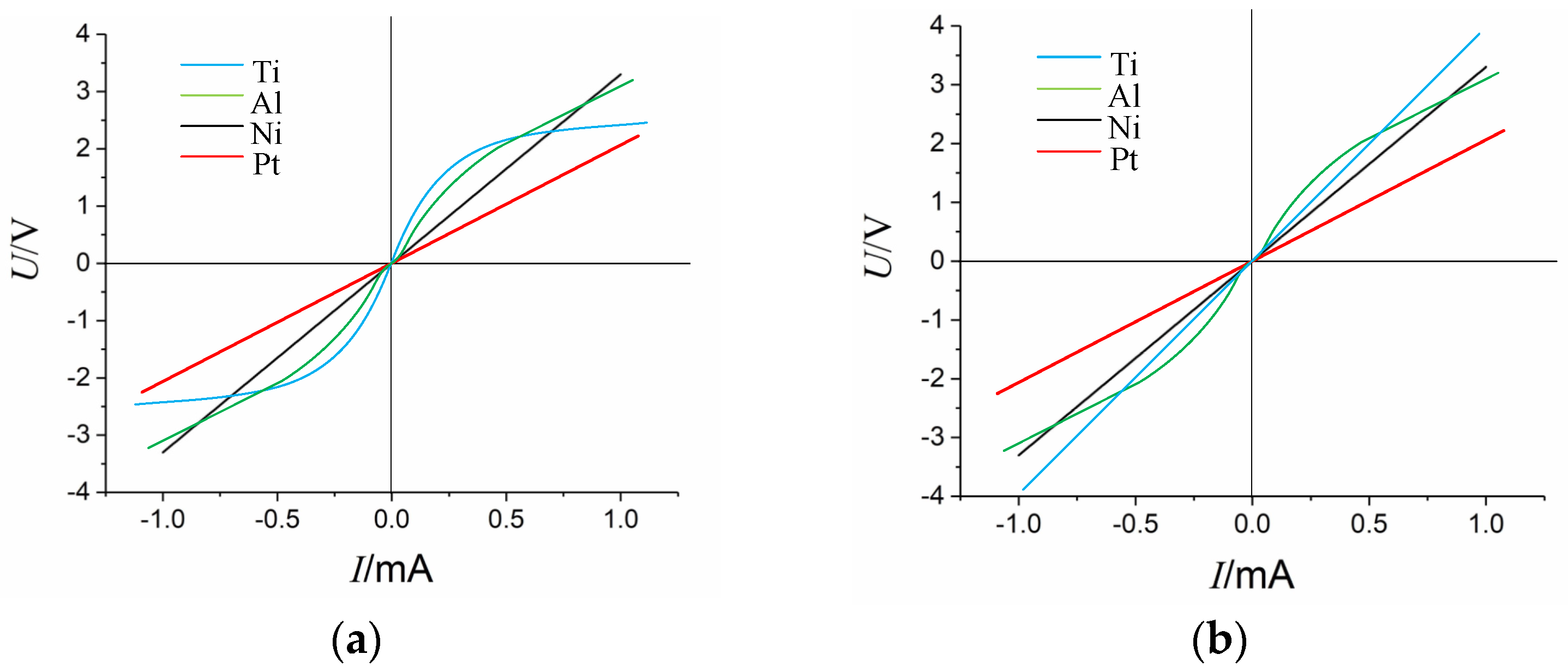
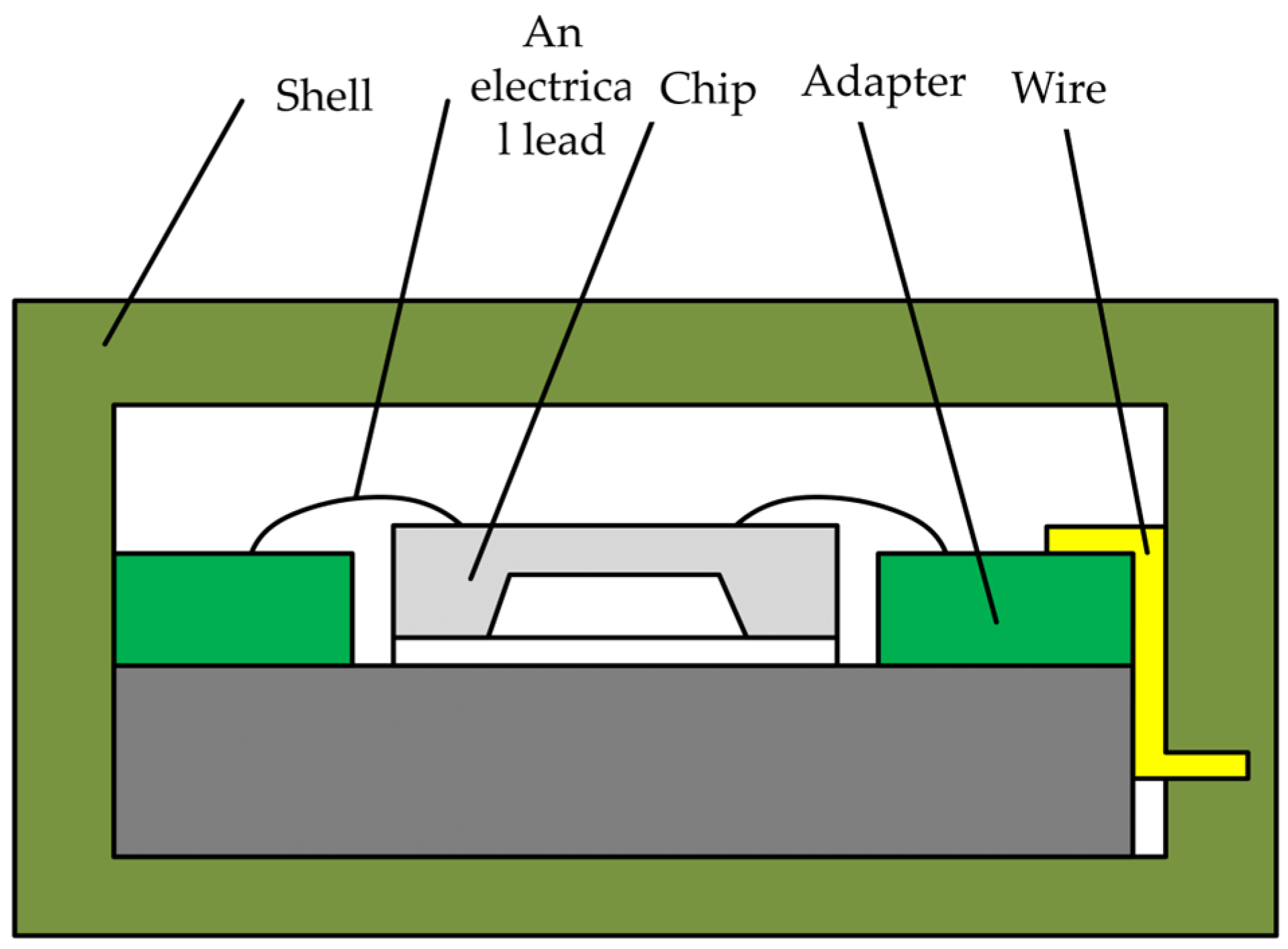
3.2. Improved Reliable Electrodes
3.3. Package
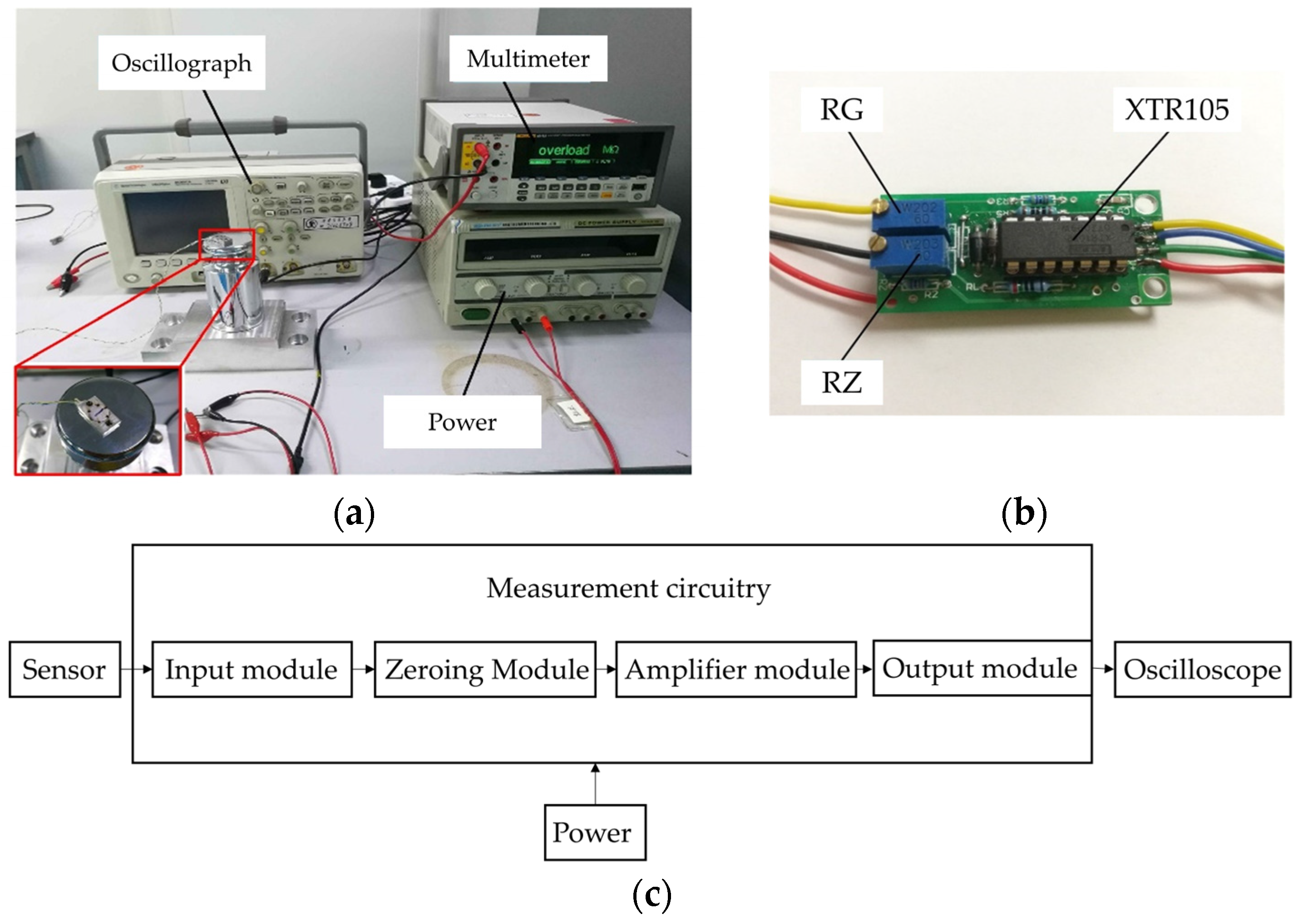
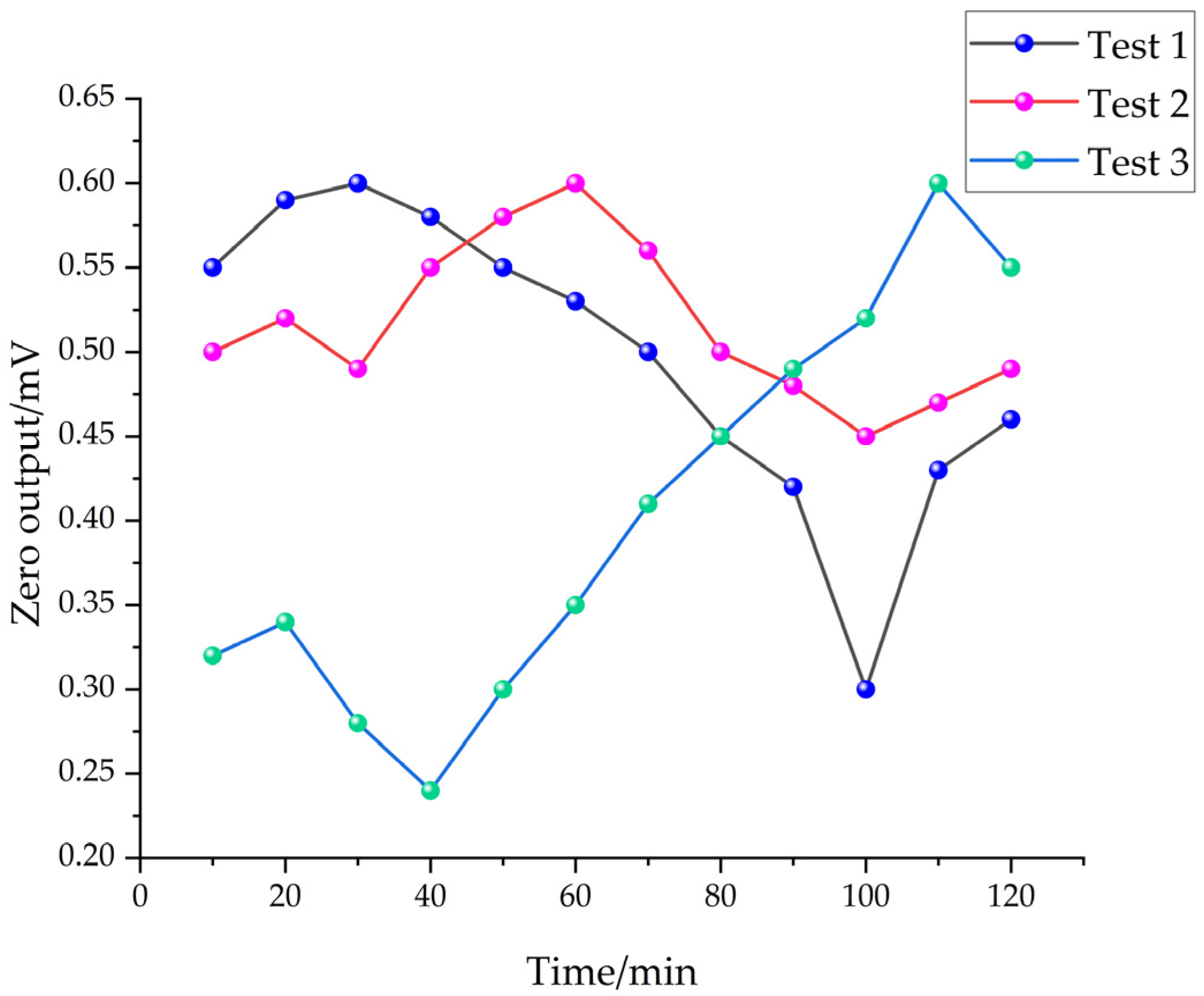
4. Testing and Analysis
4.1. Hammering Test
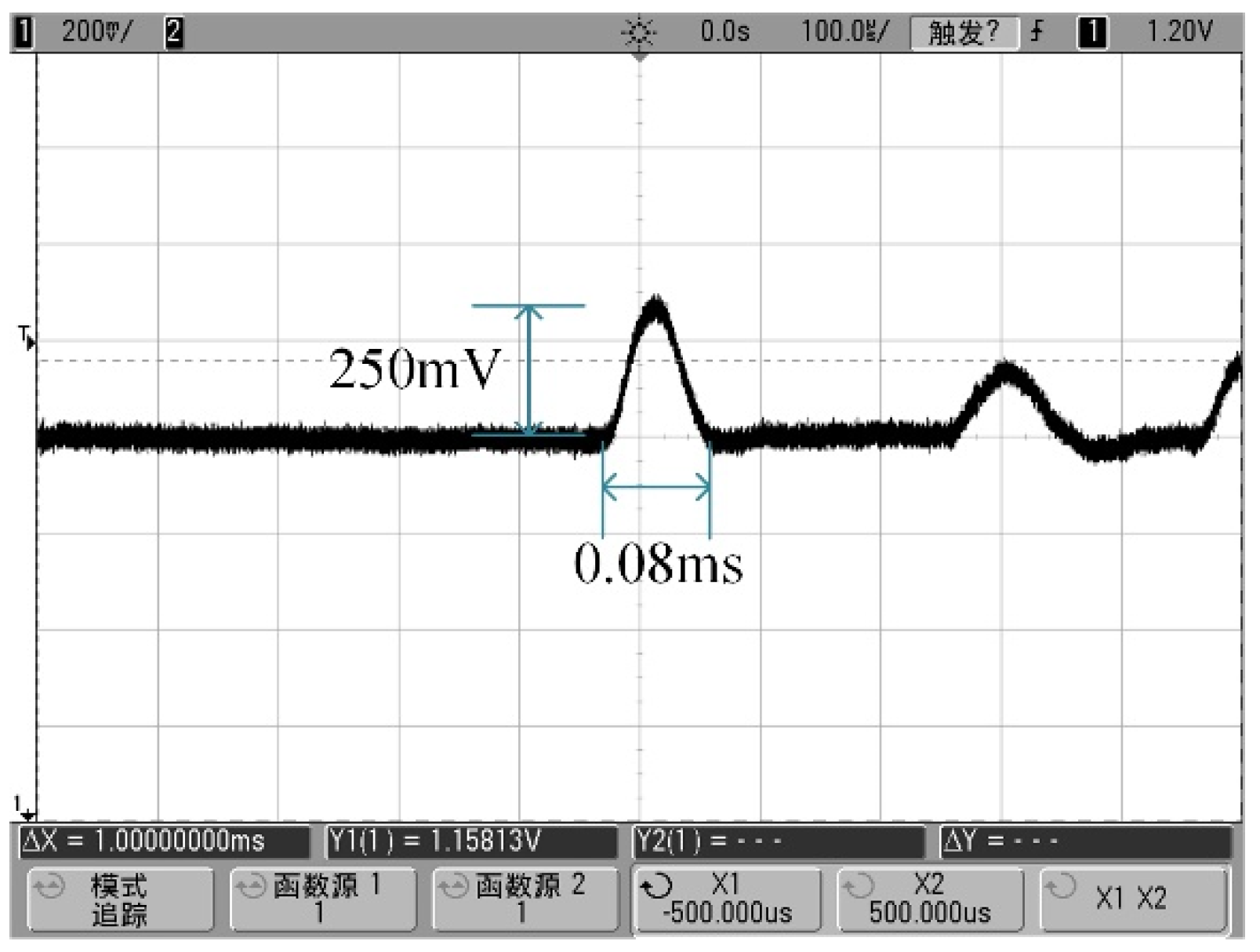
4.2. Impact Table Calibration Test
4.3. Hopkinson Bar Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Gao, S.; Niu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, P. Optimal design of high-g MEMS piezoresistive accelerometer based on Timoshenko beam theory. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, V.; Li, H.; Jianmin, M. Micromachined high-g accelerometers: A review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Yunbo, S.; Zhen, Z.; Yongfeng, R. High-g accelerometer based on MEMS and in projectile penetrating double-layer steel target test application. J. Vib. Shock. 2013, 32, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Baginsky, I.L.; Kostsov, E.G. Capacitive MEMS accelerometers for measuring high-g accelerations. Optoelectron. Instrum. Data Process. 2017, 53, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, C.; Zhao, B. Design of an In-Plane High-g Value MEMS Accelerometer Based on the Micro Beam. J. Sens. Actuators 2014, 27, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, H.; Cao, H.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, R.; Liu, J. Design, fabrication and calibration of a high-G MEMS accelerometer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 279, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Mao, Q.; Luo, G.; Zhao, L.; Lu, D.; Yang, P.; Yu, M.; Li, C.; Chang, B.; Jiang, Z. Novel high-performance piezoresistive shock accelerometer for ultra-high-g measurement utilizing self-support sensing beams. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Hou, X.; He, J.; Chou, X. Design and Implementation of a Novel Membrane-Island Structured MEMS Accelerometer with an Ultra-High Range. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 20246–20256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Che, L.; Xiong, B.; Wang, Y. A silicon micromachined high-shock accelerometer with a bonded hinge structure. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.D.; Mackowiak, P.; Bäuscher, M.; Ehrmann, O.; Lang, K.D.; Schneider-Ramelow, M.; Linke, S.; Ngo, H.D. Design and Application of a High-G Piezoresistive Acceleration Sensor for High-Impact Application. Micromachines 2018, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuells, R.; Nau, S.; Salk, M.; Thoma, K. Novel piezoresistive high-g accelerometer geometry with very high sensitivity-bandwidth product. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 182, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Jiang, Z. Design, fabrication and experiment of a MEMS piezoresistive high-g accelerometer. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S. High-g Accelerometer in MEMS for Penetrator Weapon. Ordnace Ind. Autom. 2002, 21, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, P.; Tang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H. Experimental study on the package of high-g accelerometer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 173, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liao, N.; Liu, Y.; Meng, C. Fabrication and Structural Design of Micro Pressure Sensors for Tire Pressure Measurement Systems (TPMS). Sensors 2009, 9, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.; Denison, T.; Kuang, J. A Monolithic High-g SOI-MEMS Accelerometer for measuring Projectile Launch and Flight Accelerations. Shock. Vib. 2006, 13, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Song, Z.; Lu, D.; Li, X. A simple estimation of transverse response of high-g accelerometers by a free-drop-bar method. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z. Micro and Nano Sensor Technology; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kuells, R.; Bruder, M.; Nau, S.; Salk, M.; Thoma, K.; Hansch, W. Design of a 1D and 3D Monolithically Integrated Piezoresistive MEMS High-G Accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (INERTIAL), Laguna Beach, CA, USA, 25–26 February 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]



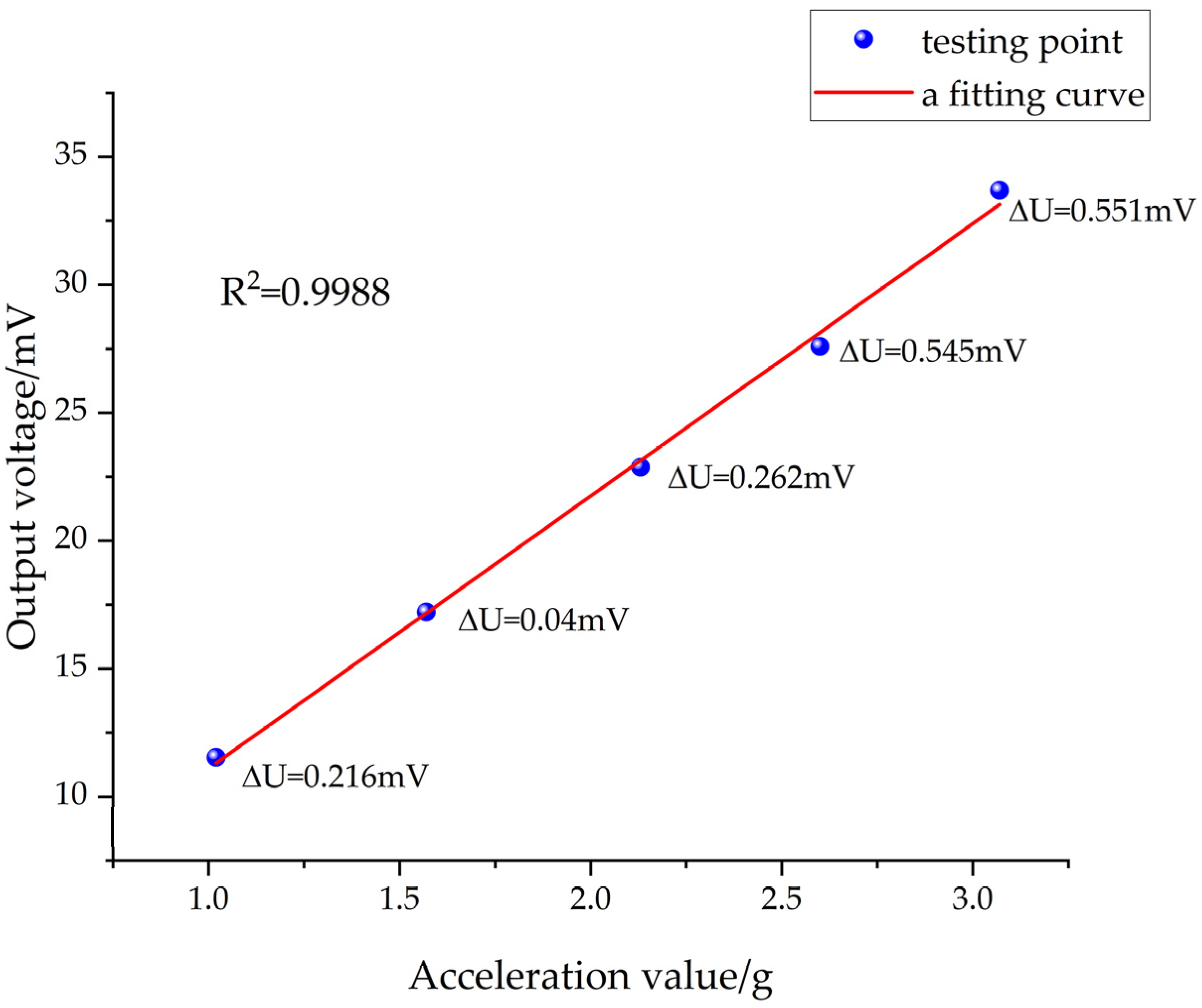


| Impact Acceleration × 104 (g) | Accelerometer Output Voltage (mV) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | Fifth | Average | |
| 1.02 | 13.02 | 11.44 | 12.16 | 10.22 | 10.84 | 11.53 |
| 1.57 | 16.82 | 18.04 | 16.52 | 18.20 | 16.46 | 17.21 |
| 2.13 | 23.68 | 22.06 | 22.88 | 23.18 | 22.56 | 22.87 |
| 2.60 | 27.14 | 28.28 | 28.16 | 27.38 | 26.98 | 27.59 |
| 3.07 | 32.92 | 34.38 | 35.18 | 35.48 | 30.48 | 33.69 |
| Zero Drift | Sensitivity | Linearity | Range | Overload | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0.29% | 1.06/μV∙g−1 | 1.95% | 100,000/g | >150,000/g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Hao, L.; Zhao, Y. Development of a MEMS Piezoresistive High-g Accelerometer with a Cross-Center Block Structure and Reliable Electrode. Sensors 2024, 24, 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175540
Li C, Zhang R, Hao L, Zhao Y. Development of a MEMS Piezoresistive High-g Accelerometer with a Cross-Center Block Structure and Reliable Electrode. Sensors. 2024; 24(17):5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175540
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Cun, Ran Zhang, Le Hao, and Yulong Zhao. 2024. "Development of a MEMS Piezoresistive High-g Accelerometer with a Cross-Center Block Structure and Reliable Electrode" Sensors 24, no. 17: 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175540
APA StyleLi, C., Zhang, R., Hao, L., & Zhao, Y. (2024). Development of a MEMS Piezoresistive High-g Accelerometer with a Cross-Center Block Structure and Reliable Electrode. Sensors, 24(17), 5540. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175540







