Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor to Detect Adulteration of Ewe, Goat, and Donkey Milk with Cow Milk through Bovine κ-Casein Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Milk Samples
2.3. Photonic Silicon Chip Fabrication, Principle of Operation, and Instrumentation
2.4. Chemical and Biological Functionalization of the Photonic Chip
2.5. Assay for Detection of Bovine Milk in Milk from Other Species with the Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Modification of the Chip
3.2. Assay Optimization
3.3. Matrix Effect
3.4. Analytical Evaluation of the Developed Immunosensor
3.5. Stability and Regeneration of the Immunosensor
3.6. Comparison with Other Immunosensors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Handford, C.E.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T. Impacts of Milk Fraud on Food Safety and Nutrition with Special Emphasis on Developing Countries. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, G.B.; Wani, S.P.; Bafna, P.S.; Bagul, V.S.; Kalaskar, M.G.; Mutha, R.E. Milk adulteration: From detection to health impact. Food Human. 2024, 3, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.F.; Santos, P.M.; Rodrigues Pereira-Filho, E.; Fábio, R.P.; Rocha, F.R.P. Recent advances on determination of milk adulterants. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagraik, R.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, D.; Chawla, P.; Kumar, A.P. Milk adulterant detection: Conventional and biosensor based approaches: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 33, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.F.; Laíño, R.B.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Soldado, A. Progress and Challenge of Sensors for Dairy Food Safety Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garhwal, R.; Sangwan, K.; Mehra, R.; Kumar, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Pal, Y.; Buttar, H.S.; Kumar, H. A Systematic Review of the Bioactive Components, Nutritional Qualities and Potential Therapeutic Applications of Donkey Milk. J. Equine Vet Sci. 2022, 115, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.M.; Venkatesh, K.; Reddy, C.V.S. Adulteration of milk and its detection: A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On Behalf of European Commission. EC 213/2001, Methods for the analysis and quality evaluation of milk and milk products. Off. J. Eur. Comm. 2001, 44, L37/31–L37/99. [Google Scholar]
- Vlasiou, M.C. Cheese and Milk Adulteration: Detection with Spectroscopic Techniques and HPLC: Advantages and Disadvantages. Dairy 2023, 4, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Miao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, J. Detection of the adulteration of camel milk powder with cow milk by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). Int. Dairy J. 2021, 121, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.K.; Chang, L.W.; Chung, Y.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Ling, Y.C. Quantification of cow milk adulteration in goat milk using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rap. Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, P.; Murgia, A.; Pirisi, F.M.; Caboni, P. A gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomic approach for the characterization of goat milk compared with cow milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6057–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesic, M.; Barac, M.; Vrvic, M.; Ristic, N.; Macej, O.; Stanojevic, S. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of bovine milk adulteration in caprine and ovine milks using native-PAGE. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvano, C.D.; de Ceglie, C.; Monopoli, A.; Zambonin, C.G. Detection of sheep and goat milk adulterations by direct MALDI-TOF MS analysis of milk tryptic digests. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysova, L.; Cejnar, P.; Hanus, O.; Legarova, V.; Havlik, J.; Nejeschlebova, H.; Nemeckova, I.; Jedelska, R.; Bozik, M. Use of MALDI-TOF MS technology to evaluate adulteration of small ruminant milk with raw bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 4882–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, C.; Hale, O.J.; Reynolds, C.K.; Jones, A.K.; Taylor, N.; Morris, M.; Cramer, R. Speciation and milk adulteration analysis by rapid ambient liquid MALDI mass spectrometry profiling using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglioti, R.; Polli, H.; Tainá Azevedo, B.; Morita Katiki, L.; Vercesi Filho, A.E. Detection and quantification of adulteration in milk and dairy products: A novel and sensitive qPCR-based method. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 4, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakali, E.; Agkastra, C.; Koliaki, C.; Livanios, D.; Boutris, G.; Christopoulou, M.I.; Koulouris, S.; Koussissis, S.; Van Impe, J.F.M.; Houhoula, D. Milk Adulteration: Detection of Bovine Milk in Caprine Dairy Products by Real Time PCR. J. Food Res. 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourkouli, A.; Thomaidis, N.; Dasenaki, M.; Markou, A. Novel and Sensitive Touchdown Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays for the Detection of Goat and Sheep Milk Adulteration with Cow Milk. Molecules 2024, 29, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xue, H.; Han, Y. Detection of cow’s milk in Shaanxi goat’s milk with an ELISA assay. Food Control 2011, 22, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.P.; Zakaria, S.N.A.; Ahmed, M.U. Trends in the development of immunoassays for mycotoxins and food allergens using gold and carbon nanostructured material. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, B.; Sun, X.; Huang, F.; Chen, A. Disposable and instrument-free nucleic acid lateral flow cassette for rapid and on-site identification of adulterated goat milk. Talanta 2024, 267, 125205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.R.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H.Y.; Jiang, L.; Tian, M.; Ren, F.Z. Detection of cow milk adulteration in yak milk by ELISA. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6000–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Si, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Li, T. Rapid detection of cow milk adulteration/contamination in goat milk by a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Wu, J. Review of Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Safety Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Advances in interferometric sensors for the detection of food contaminants. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 175, 117714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skládal, P. Piezoelectric biosensors: Shedding light on principles and applications. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakti, S.P.; Chabibah, N.; Ayu, S.P.; Padaga, M.C.; Aulanni’Am, A. Development of QCM biosensor with specific cow milk protein antibody for candidate milk adulteration detection. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 1807647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Povedano, E.; Benedé, S.; Mata, L.; Galán-Malo, P.; Gamella, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the detection of adulteration in milk through single or multiplexed determination of bovine, ovine, or caprine immunoglobulins G. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11266–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddaoui, N.; Attaallah, R.; Amine, A. Development of an optical immunoassay based on peroxidase-mimicking Prussian blue nanoparticles and a label-free electrochemical immunosensor for accurate and sensitive quantification of milk species adulteration. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.A.; Peres, A.M.; Veloso, A.C.A.; Reis, F.S.; Vilas-Boas, M.; Machado, A.A.S.C. An electronic tongue taste evaluation: Identification of goat milk adulteration with bovine milk. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2009, 136, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, W.; Smits, N.G.E.; Kemmers-Voncken, A.E.M.; Bremer, M.G.E.G. Fast biosensor immunoassays for the detection of cows’ milk in the milk of ewes and goats. J. Dairy Res. 2004, 71, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haasnoot, W.; Marchesini, G.; Koopal, K. Spreeta-Based Biosensor Immunoassays to Detect Fraudulent Adulteration in Milk and Milk Powder. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Botsialas, A.; Salapatas, A.; Petrou, P.; Haasnoot, W.; Makarona, E.; Jobst, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Siafaka-Kapadai, A.; Raptis, I.; et al. Assessment of goat milk adulteration with a label-free monolithically integrated optoelectronic biosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3995–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Makarona, E.; Haasnoot, W.; Moser, I.; Jobst, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Lees, M.; Kalatzi, K.; Raptis, I.; et al. Ultrafast multiplexed-allergen detection through advanced fluidic design and monolithic interferometric silicon chips. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9559–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.; Raptis, I.; Misiakos, K.; Livaniou, E.; Makarona, E.; Kakabakos, S. Rapid detection of mozzarella and feta cheese adulteration with cow milk through a silicon photonic immunosensor. Analyst 2021, 146, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Pagkali, V.; Makarona, E.; Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S.; Peters, J.; Jobst, G.; Goustouridis, D.; et al. Multiplexed detection of food contaminants with a portable reader based on all-in-one monolithic photonic chips. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 177, 111192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Makarona, E.; Salapatas, A.; Misiakos, K.; Synolaki, E.; Ioannidis, A.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Ritvos, M.A.; Pasternack, A.; Ritvos, O.; et al. Directly immersible silicon photonic probes: Application to rapid SARS-CoV-2 serological testing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022, 215, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourti, D.; Angelopoulou, M.; Misiakos, K.; Makarona, E.; Economou, A.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S. Detection of adulteration of milk from other species with cow milk through an immersible photonic immunosensor. Eng. Proc. 2023, 35, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livas, D.; Trachioti, M.; Banou, S.; Angelopoulou, M.; Economou, A.; Prodromidis, M.; Petrou, P.; Kakabakos, S.; Kokkinos, C. 3D printed microcell featuring a disposable nanocomposite Sb/Sn immunosensor for quantum dot-based electrochemical determination of adulteration of ewe/goat’s cheese with cow’s milk. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2021, 334, 129614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



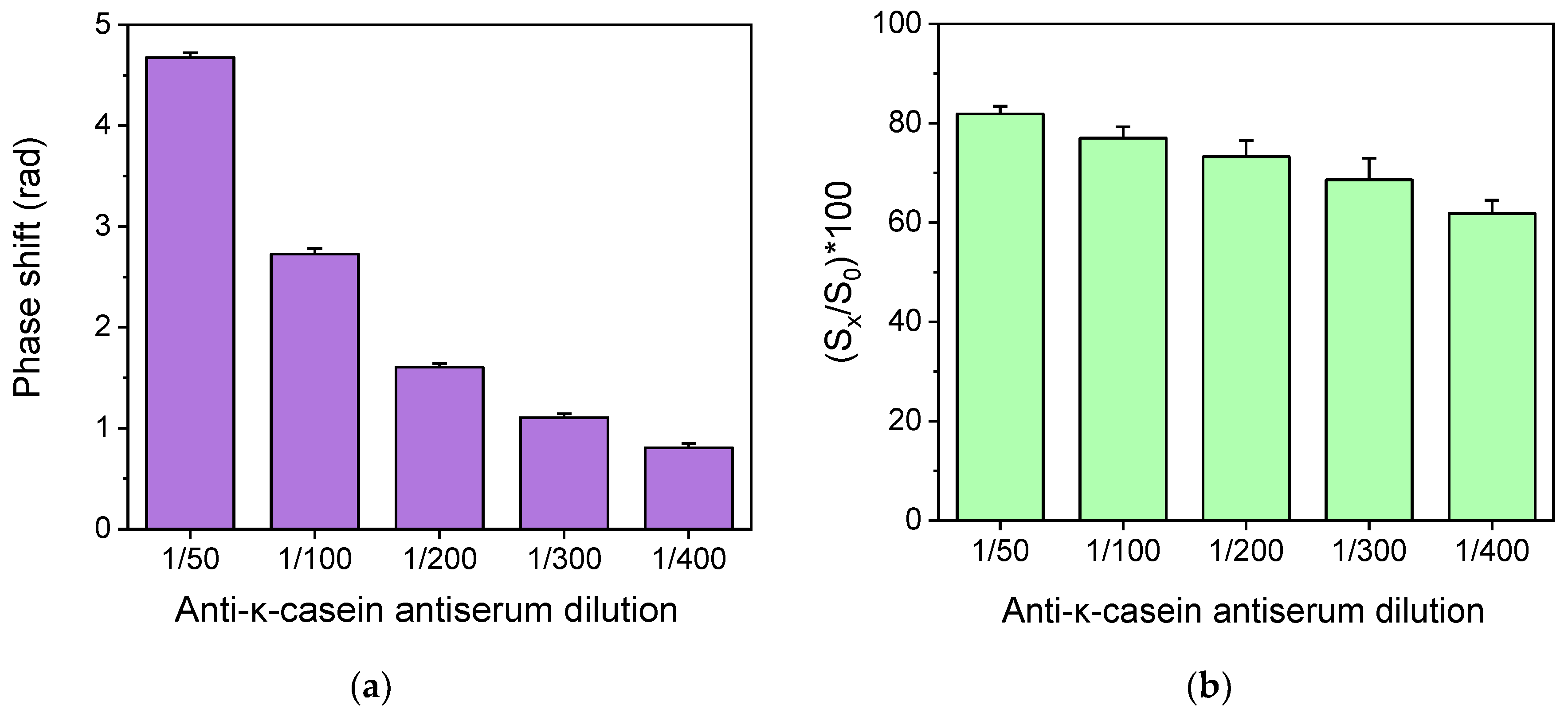
 ,
,  ) and 0.02 % v/v cow milk (
) and 0.02 % v/v cow milk ( ,
,  ) in centrifuged (
) in centrifuged ( ,
,  ) and untreated (non-centrifuged) ewe milk (
) and untreated (non-centrifuged) ewe milk ( ,
,  ). Each value corresponds to the mean of 3 measurements ± SD.
). Each value corresponds to the mean of 3 measurements ± SD.
 ,
,  ) and 0.02 % v/v cow milk (
) and 0.02 % v/v cow milk ( ,
,  ) in centrifuged (
) in centrifuged ( ,
,  ) and untreated (non-centrifuged) ewe milk (
) and untreated (non-centrifuged) ewe milk ( ,
,  ). Each value corresponds to the mean of 3 measurements ± SD.
). Each value corresponds to the mean of 3 measurements ± SD.
 ), goat (
), goat ( ), and donkey milk (
), and donkey milk ( ). Each point is the mean value of 3 measurements ± SD.
). Each point is the mean value of 3 measurements ± SD.
 ), goat (
), goat ( ), and donkey milk (
), and donkey milk ( ). Each point is the mean value of 3 measurements ± SD.
). Each point is the mean value of 3 measurements ± SD.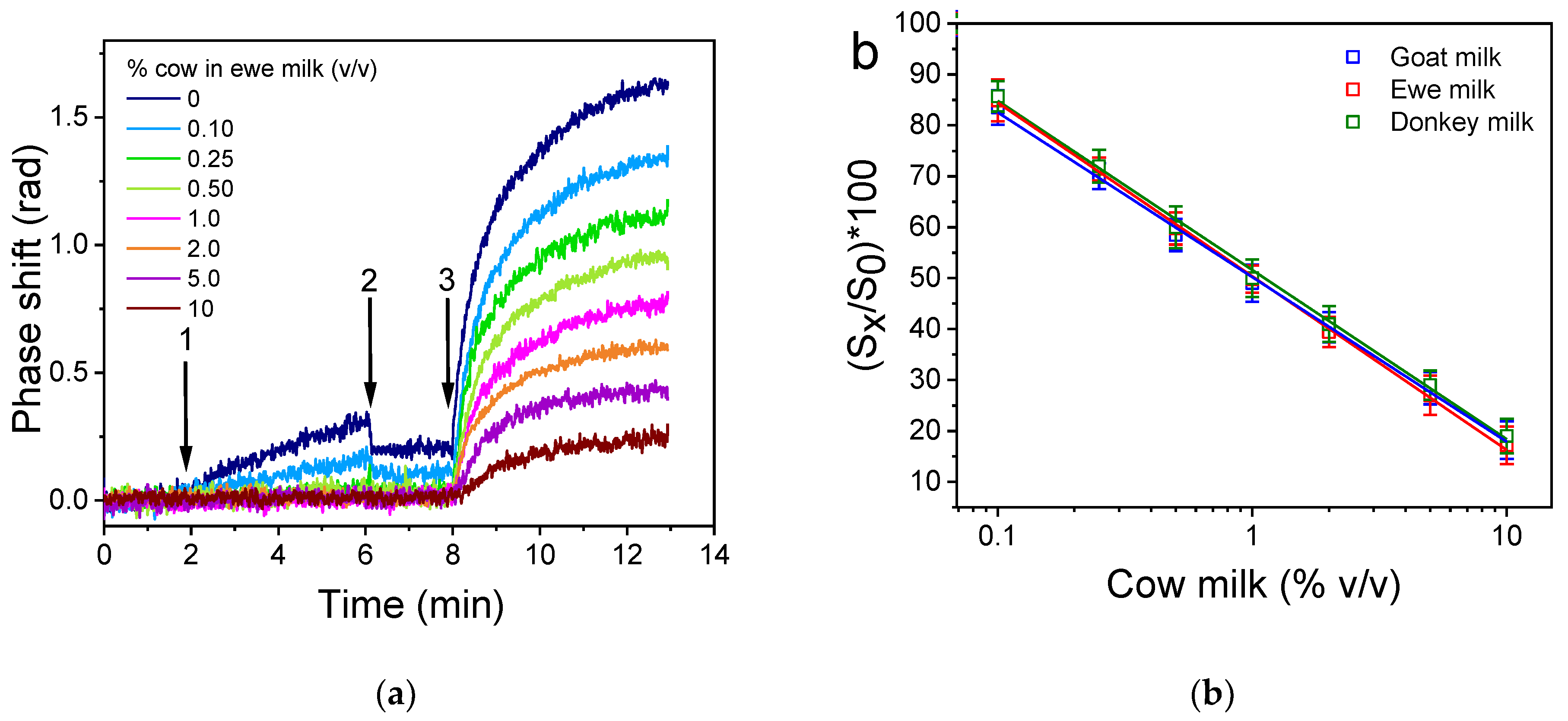
| Immunosensor Type | Sample | Assay Time (min) | LOD (% v/v Cow Milk) | Working Range (% v/v Cow Milk) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPR | Ewe milk Goat milk | 5 | <0.1 | 0.1–10 | [32] |
| Portable SPR | Ewe milk Goat milk | 7 | 0.17 | 0.17–1.35 | [33] |
| Amperometric | Ewe milk Goat milk Buffalo milk | 30 | 0.1 | not defined | [29] |
| Voltametric | Goat milk | 60 | 0.01 | 0.1–100 | [30] |
| QD-based voltametric | Ewe cheese Goat cheese | 15 | 0.07 | 0.14–1.0 | [40] |
| MZI | Ewe Goat milk | 10 | 0.04 | 0.1–1.0 | [34] |
| MZI | Mozzarella Feta cheese | ~9 | 0.5 0.25 | 1.0–50 0.5–25 | [36] |
| Photonic dipstick immunosensor | Ewe milk Goat milk Donkey milk | 12 | 0.05 | 0.1–10 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kourti, D.; Angelopoulou, M.; Makarona, E.; Economou, A.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Kakabakos, S. Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor to Detect Adulteration of Ewe, Goat, and Donkey Milk with Cow Milk through Bovine κ-Casein Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175688
Kourti D, Angelopoulou M, Makarona E, Economou A, Petrou P, Misiakos K, Kakabakos S. Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor to Detect Adulteration of Ewe, Goat, and Donkey Milk with Cow Milk through Bovine κ-Casein Detection. Sensors. 2024; 24(17):5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175688
Chicago/Turabian StyleKourti, Dimitra, Michailia Angelopoulou, Eleni Makarona, Anastasios Economou, Panagiota Petrou, Konstantinos Misiakos, and Sotirios Kakabakos. 2024. "Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor to Detect Adulteration of Ewe, Goat, and Donkey Milk with Cow Milk through Bovine κ-Casein Detection" Sensors 24, no. 17: 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175688
APA StyleKourti, D., Angelopoulou, M., Makarona, E., Economou, A., Petrou, P., Misiakos, K., & Kakabakos, S. (2024). Photonic Dipstick Immunosensor to Detect Adulteration of Ewe, Goat, and Donkey Milk with Cow Milk through Bovine κ-Casein Detection. Sensors, 24(17), 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175688











