Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
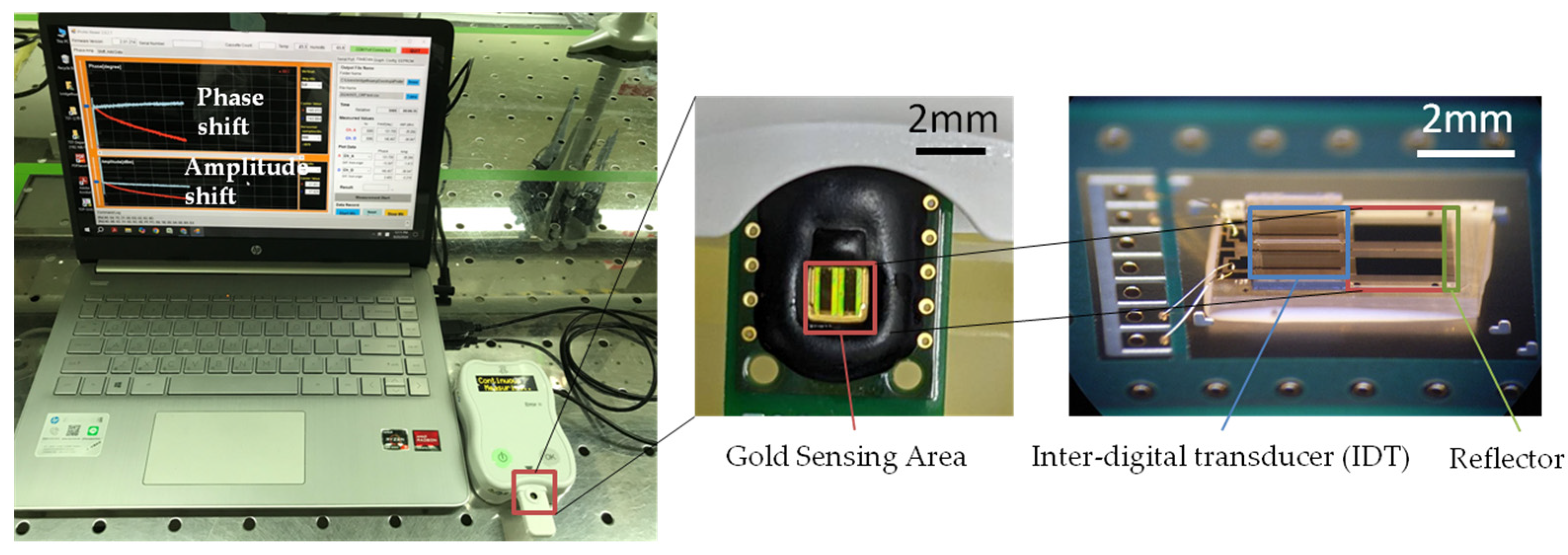
2.2. Fabrication of ApoB SH-SAW Biosensor
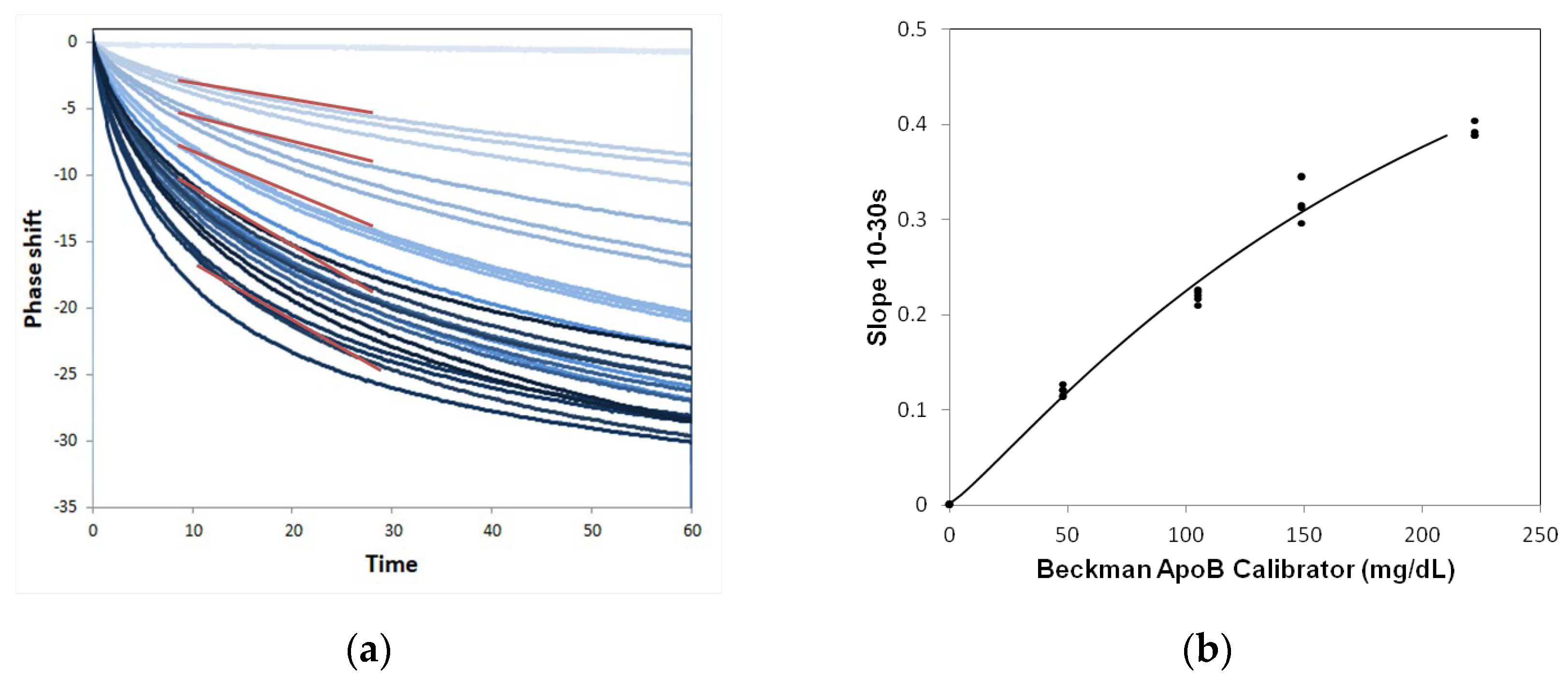
2.3. Performance of ApoB SH-SAW Biosensor
2.4. Measurement of ApoB by SH-SAW Biosensor
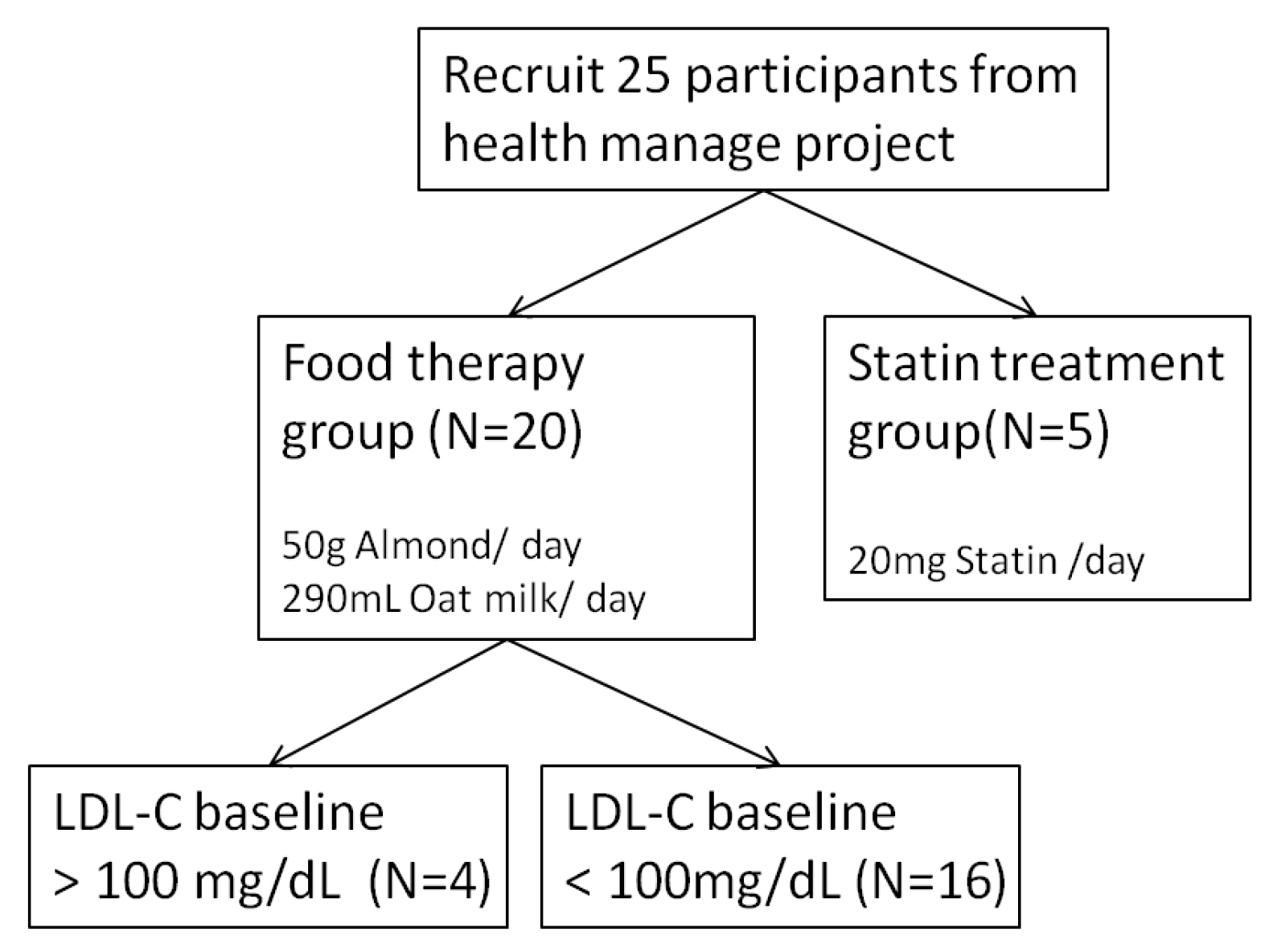
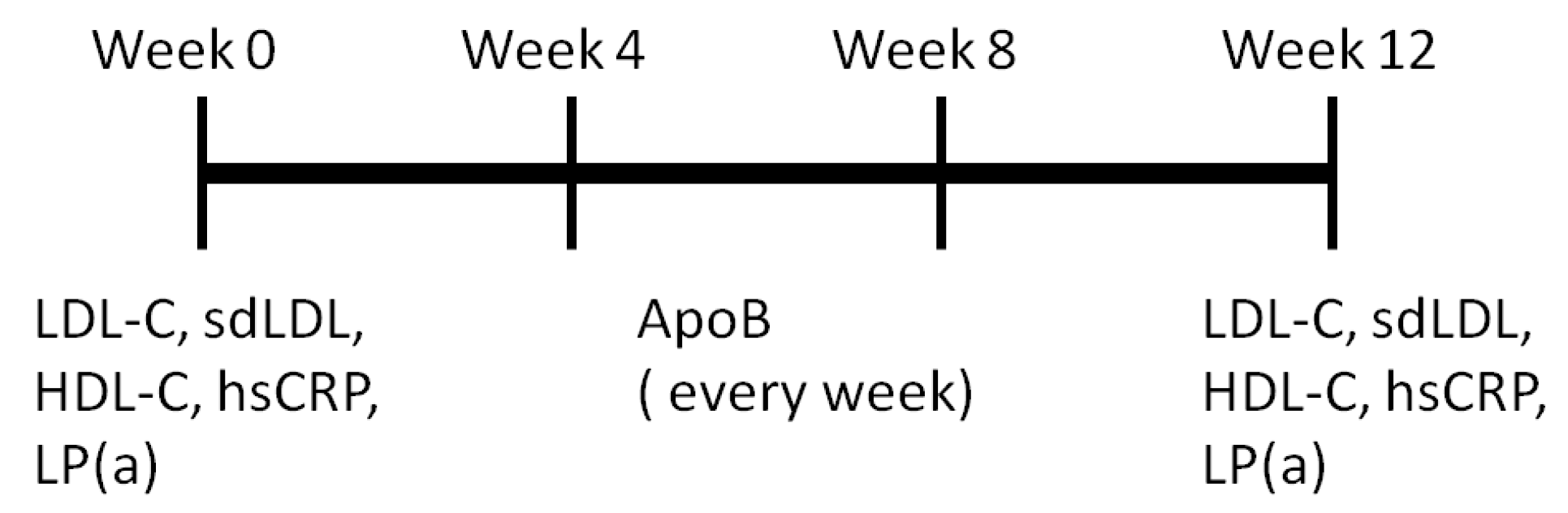
2.5. Study Design and Participant
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar]
- Celermajer David, S.; Chow Clara, K.; Marijon, E.; Anstey Nicholas, M.; Woo Kam, S. Cardiovascular Disease in the Developing World: Prevalences, patterns, and the potential of early disease detection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, J.N.; Hoke, L.; Whitwam, W.; Sommers, P.A.; Taylor, A.L.; Duprez, D.; Roessler, R.; Florea, N. Screening for early detection of cardiovascular disease in asymptomatic individuals. Am. Heart. J. 2003, 146, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.Y.; Marcu, L.G.; Bezak, E.; Parange, N.A. Review of Health Economics of Point-of-Care Testing Worldwide and Its Efficacy of Implementation in the Primary Health Care Setting in Remote Australia. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2020, 13, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istvan, E. Statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase: A 3-dimensional view. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2003, 4, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesti, L.; Mengozzi, A.; Natali, A. Statins, LDL Cholesterol Control, Cardiovascular Disease Prevention, and Atherosclerosis Progression: A Clinical Perspective. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, J.W.; Weiss, S.R.; Davidson, M.H.; Sprecher, D.L.; Schwartz, S.L.; Lupien, P.-J.; Jones, P.H.; Haber, H.E.; Black, D.M. Reduction of LDL Cholesterol by 25% to 60% in Patients With Primary Hypercholesterolemia by Atorvastatin, a New HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berryman, C.E.; Preston, A.G.; Karmally, W.; Deckelbaum, R.J.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Effects of almond consumption on the reduction of LDL-cholesterol: A discussion of potential mechanisms and future research directions. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Marchie, A.; Parker, T.L.; Connelly, P.W.; Qian, W.; Haight, J.S.; Faulkner, D.; Vidgen, E.; Lapsley, K.G.; et al. Dose Response of Almonds on Coronary Heart Disease Risk Factors: Blood Lipids, Oxidized Low-Density Lipoproteins, Lipoprotein(a), Homocysteine, and Pulmonary Nitric Oxide. Circulation 2002, 106, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onning, G.; Wallmark, A.; Persson, M.; Akesson, B.; Elmståhl, S.; Oste, R. Consumption of oat milk for 5 weeks lowers serum cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in free-living men with moderate hypercholesterolemia. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 1999, 43, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.V.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Zurbau, A.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Jovanovski, E.; Au-Yeung, F.; Jenkins, A.L.; Vuksan, V. The effect of oat β-glucan on LDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol and apoB for CVD risk reduction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised-controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.Z.; Zhang, H.; Sreejith, V.S.; Naghdi, M.; Ju, S. Advances in the surface acoustic wave sensors for industrial applications: Potentials, challenges, and future directions: A review. Measurement 2023, 222, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Das, P.K.; Bhethanabotla, V.R. Surface acoustic waves in biosensing applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2021, 3, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Yatsuda, H.; Goto, M.; Kondoh, J.; Liu, S.-H.; Wang, R.Y.L. Application of Shear Horizontal Surface Acoustic Wave (SH-SAW) Immunosensor in Point-of-Care Diagnosis. Biosensors 2023, 13, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, K.; Yatsuda, H.; Kondoh, J. Evaluation of Shear Horizontal Surface Acoustic Wave Biosensors Using “Layer Parameter” Obtained from Sensor Responses during Immunoreaction. Sensors 2021, 21, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuda, H.; Kogai, T.; Goto, M.; Yoshimura, N. Shear-Horizontal Surface Acoustic Wave Biosensors for POCT. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (FCS), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–22 May 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, J.T.; Li, R.C.; Sniderman, A.; Chan, C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M. Discordance Between Apolipoprotein B and LDL-Cholesterol in Young Adults Predicts Coronary Artery Calcification: The CARDIA Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson-Perry, J.F.; Vaks, J.E.; Vore, T.; Durham, A.; Fischer, C.; Gutenbrunner, C.; Hillyard, D.; Kondratovich, M.; Ladwig, P.; Middleberg, R. Evaluation of Detection Capability for Clinical Laboratory Measurement Procedures; Approved Guideline, 2nd ed.; CLSI Document EP17-A2; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Peeling, R.W.; Mabey, D. Point-of-care tests for diagnosing infections in the developing world. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppa, P.B.; Bietenbeck, A.; Beaudoin, C.; Giannetti, A. Clinically relevant analytical techniques, organizational concepts for application and future perspectives of point-of-care testing. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, M.; Agostini, M.; Lunardelli, F.; Miranda, A.; Luminare, A.G.; Cervelli, F.; Gambineri, F.; Cecchini, M. A surface acoustic wave (SAW)-based lab-on-chip for the detection of active α-glycosidase. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, B.; O’Kennedy, R.; Collins, D. Advances in point-of-care testing for cardiovascular diseases. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 104, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plüddemann, A.; Thompson, M.; Price, C.P.; Wolstenholme, J.; Heneghan, C. Point-of-care testing for the analysis of lipid panels: Primary care diagnostic technology update. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2012, 62, e224–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmali, K.N.; Brown, T.; Sanchez, T.; Long, T.; Persell, S.D. Point-of-care testing to promote cardiovascular disease risk assessment: A proof of concept study. Prev. Med. Rep. 2017, 7, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, M.J.; Sharma, M.; Li, Y.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Yu, C.Y.; Tsai, C.L.; Huang, S.F.; Chang, L.B.; Lai, C.S. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor for C-Reactive Protein Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Peng, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-M.; Yatsuda, H.; Szu-Heng, L.; Liu, S.-J.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Wang, R.Y.L. Measurements of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels after Vaccination Using a SH-SAW Biosensor. Biosensors 2022, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-C.; Cheng, C.-H.; Yatsuda, H.; Liu, S.-H.; Liu, S.-J.; Kogai, T.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Wang, R.Y.L. A Novel Rapid Test to Detect Anti-SARS-CoV-2 N Protein IgG Based on Shear Horizontal Surface Acoustic Wave (SH-SAW). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-H.; Cheng, C.-H.; Lo, C.-J.; Young, G.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Wang, R.Y.-L. New Advances in Rapid Pretreatment for Small Dense LDL Cholesterol Measurement Using Shear Horizontal Surface Acoustic Wave (SH-SAW) Technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbodikhah, J.; Ahmed, S.; Elyasi, A.; Kasselman, L.J.; De Leon, J.; Glass, A.D.; Reiss, A.B. Apolipoprotein B and Cardiovascular Disease: Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target. Metabolites 2021, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, F.; Casula, M.; Olmastroni, E. Apolipoprotein B compared with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk assessment. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 2023, 195, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniderman, A.D.; Thanassoulis, G.; Glavinovic, T.; Navar, A.M.; Pencina, M.; Catapano, A.; Ference, B.A. Apolipoprotein B Particles and Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, S.; Khandelwal, S.; Madan, J.; Pandya, H.; Sesikeran, B.; Krishnaswamy, K. Almonds and Cardiovascular Health: A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruisinger, J.F.; Gibson, C.A.; Backes, J.M.; Smith, B.K.; Sullivan, D.K.; Moriarty, P.M.; Kris-Etherton, P. Statins and almonds to lower lipoproteins (the STALL Study). J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 9, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Bravatti, M.A.; Wang, J.; Avendano, E.E.; King, L.; Johnson, E.J.; Raman, G. Almond Consumption and Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Ryu, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, H. The effects of daily intake timing of almond on the body composition and blood lipid profile of healthy adults. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, M.L. A Comprehensive Review of Almond Clinical Trials on Weight Measures, Metabolic Health Biomarkers and Outcomes, and the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

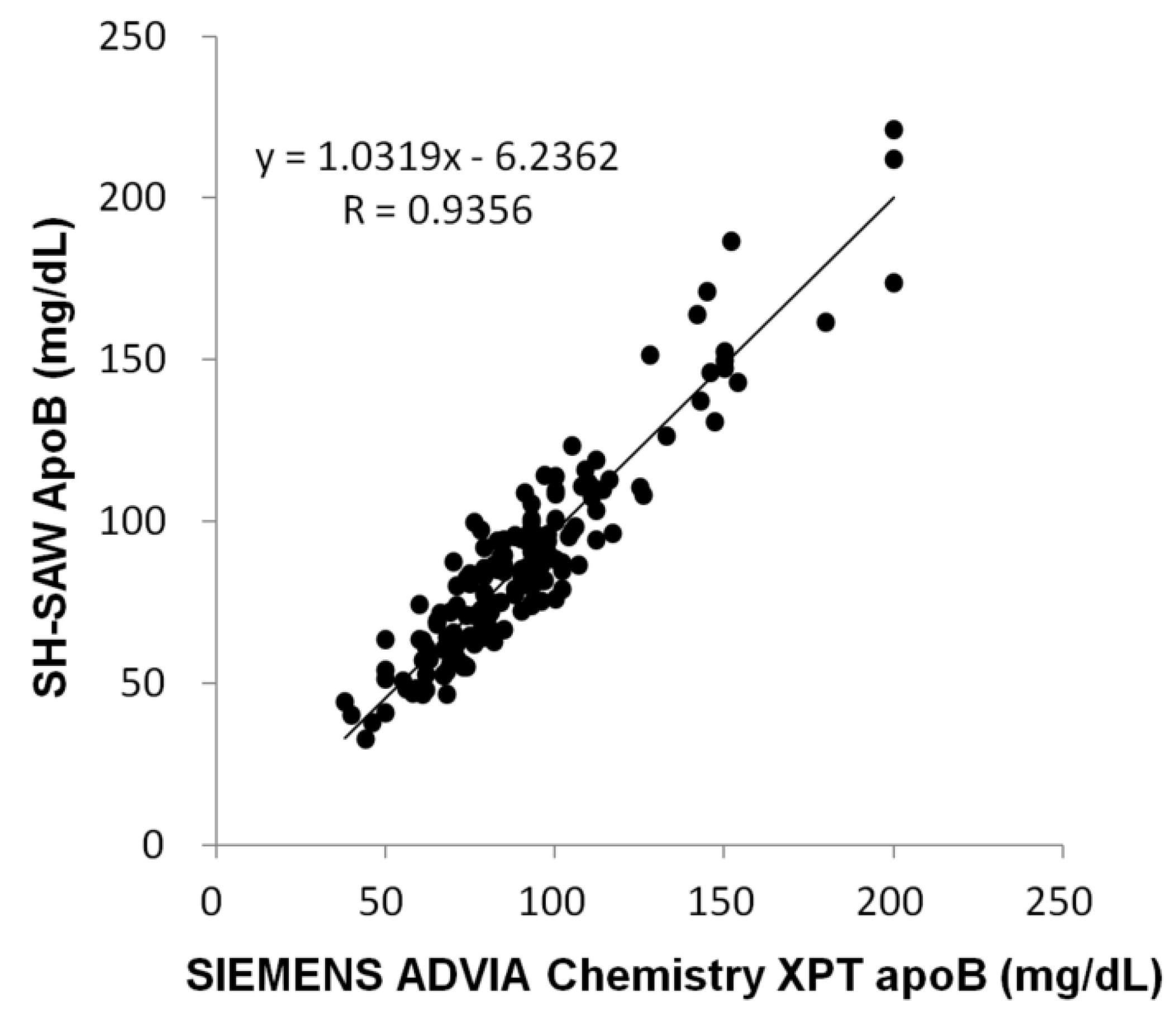
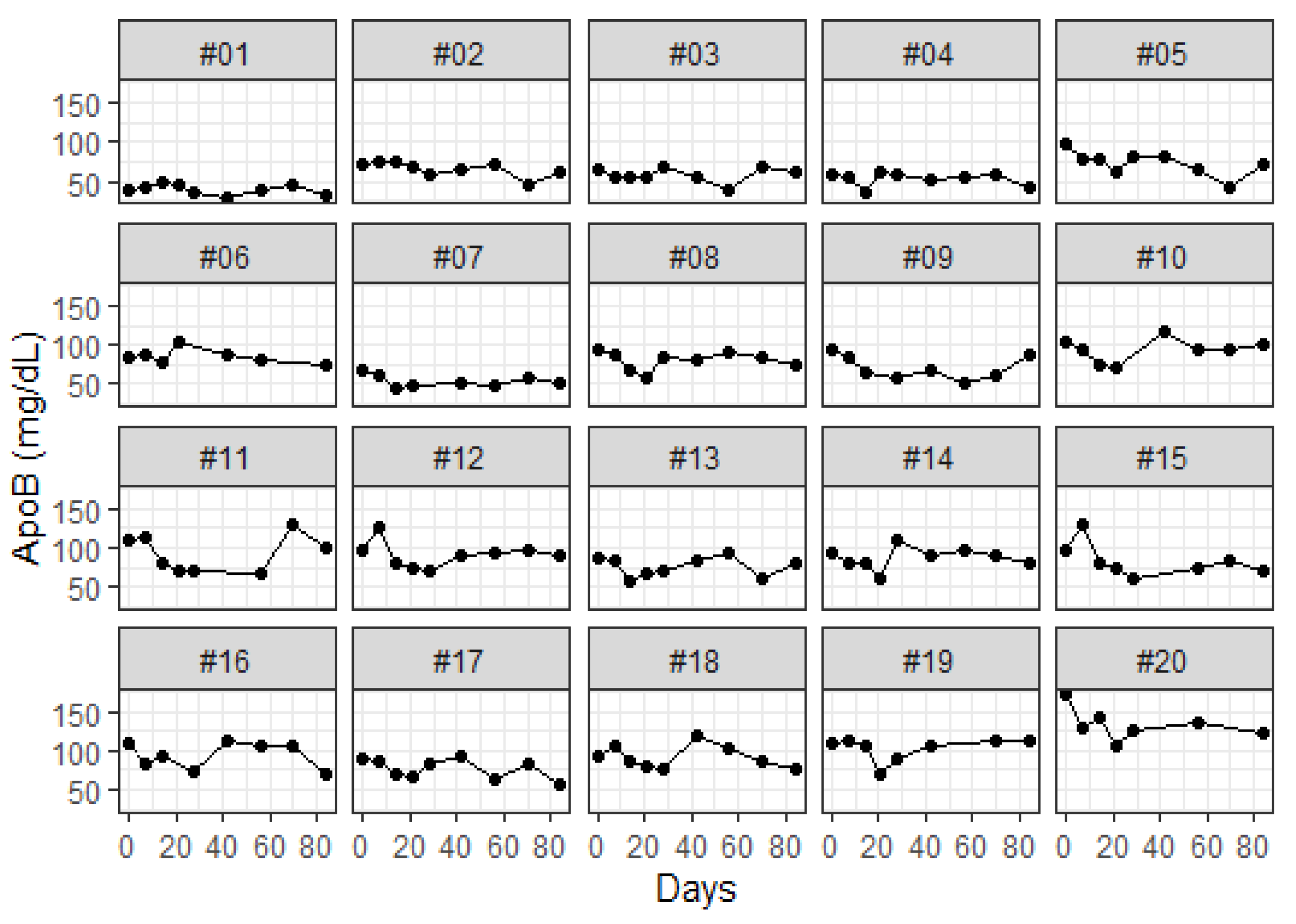
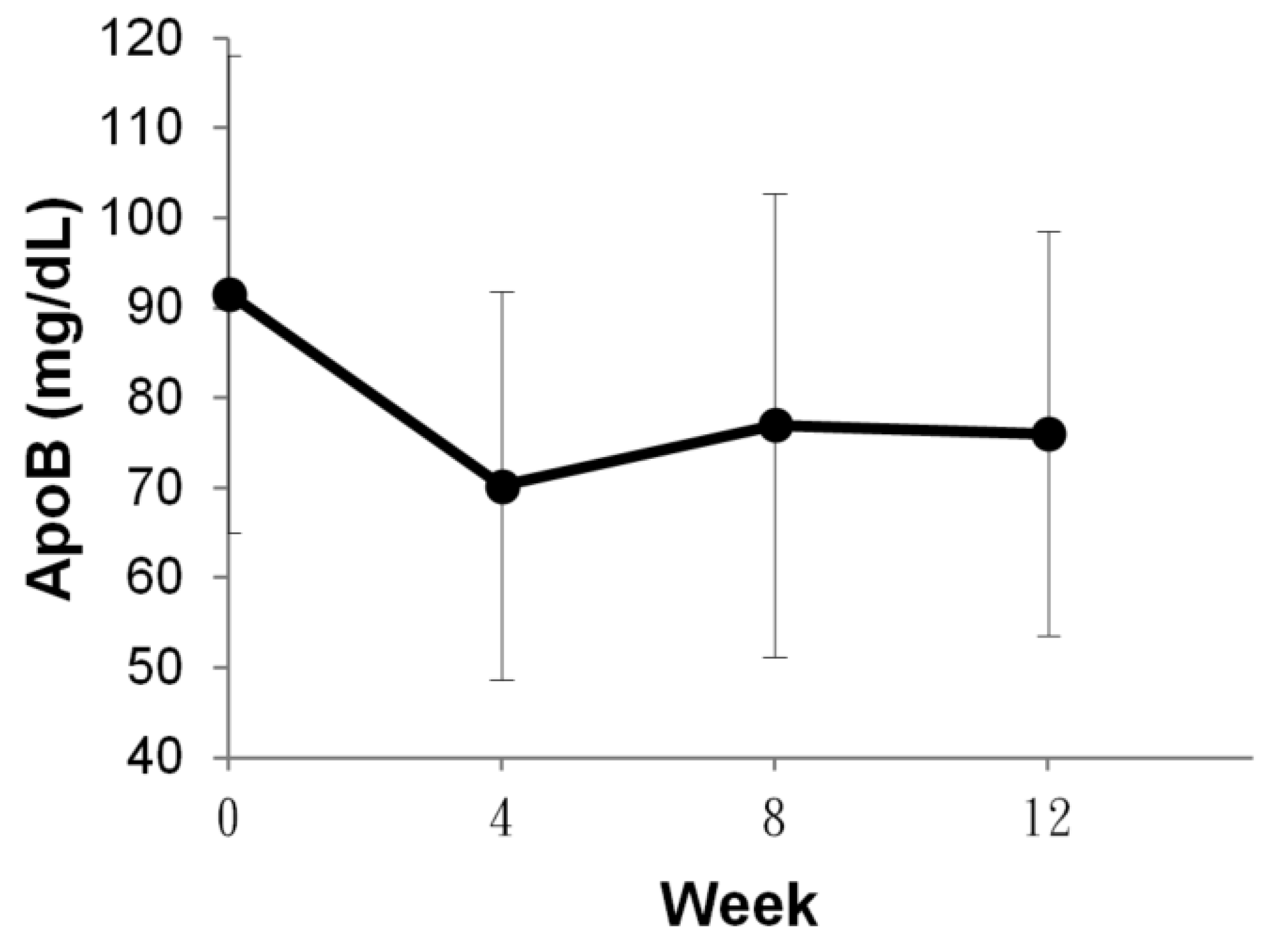


| Group | ||
|---|---|---|
| Food Therapy | Statin Treatment | |
| Subject | 20 | 5 |
| Gender | 10 Male; 10 Female | 5 Male |
| Intervene | Almond (50 g/day) & oat milk (290 mL/day) | Statin (20 mg/day) |
| Baseline | ||
| ApoB | 91.56 ± 26.49 | 85.83 ± 13.82 |
| HDL-C | 59.60 ± 19.58 | 46.80 ± 6.87 |
| LDL-C | 135.9 ± 39.38 | 167.8 ± 45.60 |
| sdLDL | 38.85 ± 23.42 | 63.76 ± 21.85 |
| hsCRP | 0.34 ± 0.40 | 0.16 ± 0.20 |
| Lp(a) | 33.08 ± 42.47 | 20.47 ± 23.05 |
| Marker | Week 0 | Week 12 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApoB | 91.56 ± 26.49 | 76.02 ± 22.52 | p < 0.001 |
| HDL-C | 59.60 ± 19.58 | 59.20 ± 18.70 | N.S |
| LDL-C | 135.90 ± 39.38 | 124.20 ± 35.22 | p < 0.01 |
| sdLDL | 38.85 ± 23.42 | 27.68 ± 16.58 | p < 0.001 |
| hsCRP | 0.34 ± 0.40 | 0.20 ± 0.23 | N.S |
| Lp(a) | 33.08 ± 42.47 | 26.63 ± 25.37 | N.S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-H.; Yatsuda, H.; Chen, H.-H.; Young, G.-H.; Liu, S.-H.; Wang, R.Y. Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform. Sensors 2024, 24, 6517. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206517
Cheng C-H, Yatsuda H, Chen H-H, Young G-H, Liu S-H, Wang RY. Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform. Sensors. 2024; 24(20):6517. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206517
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chia-Hsuan, Hiromi Yatsuda, Han-Hsiang Chen, Guang-Huar Young, Szu-Heng Liu, and Robert YL Wang. 2024. "Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform" Sensors 24, no. 20: 6517. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206517
APA StyleCheng, C.-H., Yatsuda, H., Chen, H.-H., Young, G.-H., Liu, S.-H., & Wang, R. Y. (2024). Tracking the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease after Almond and Oat Milk Intervene or Statin Medication with a Powerful Reflex SH-SAW POCT Platform. Sensors, 24(20), 6517. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24206517







