Early Postoperative Gait Analysis in Elderly Patients Following Hip Fracture Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Protocol
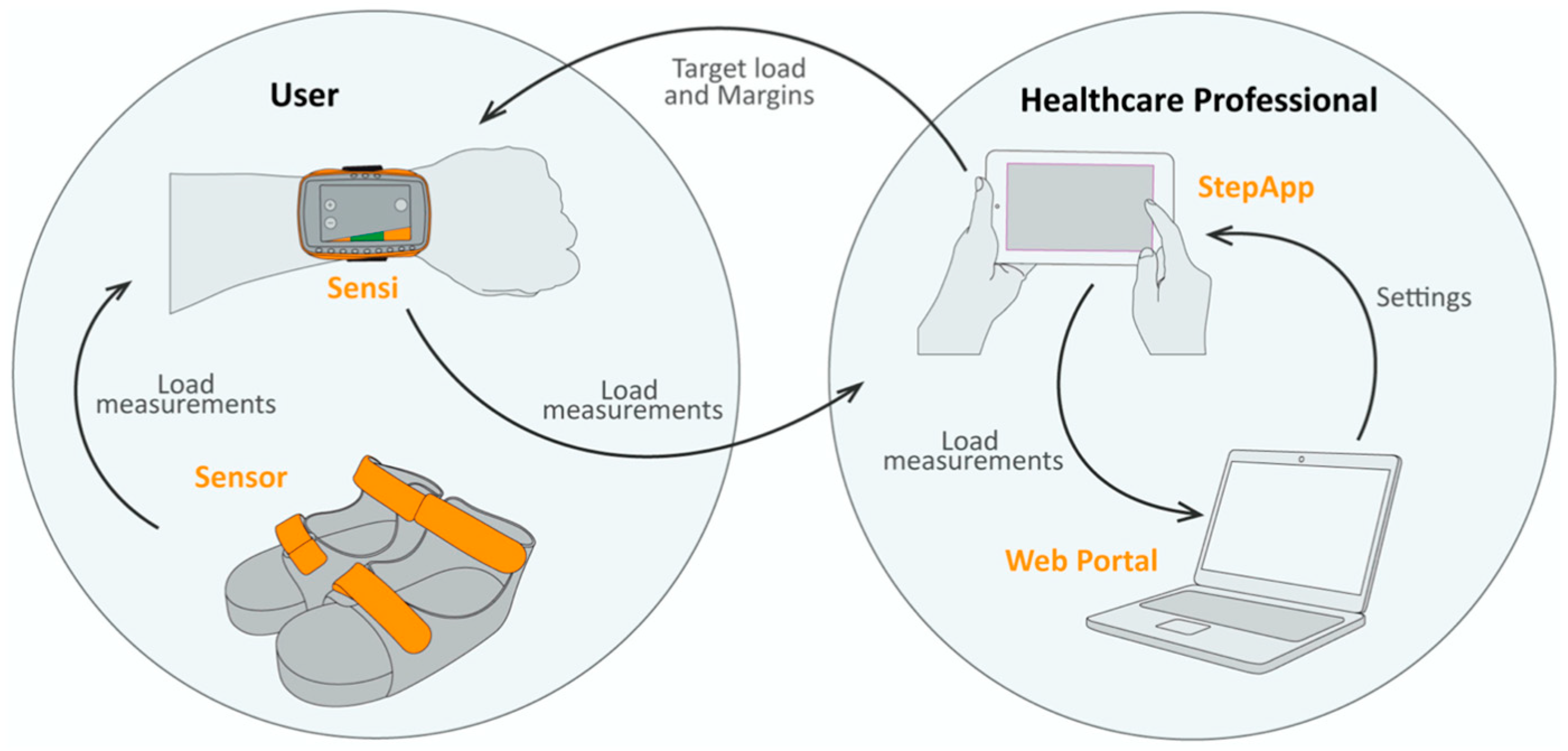
Biofeedback Measurements
2.3. 3D Gait Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
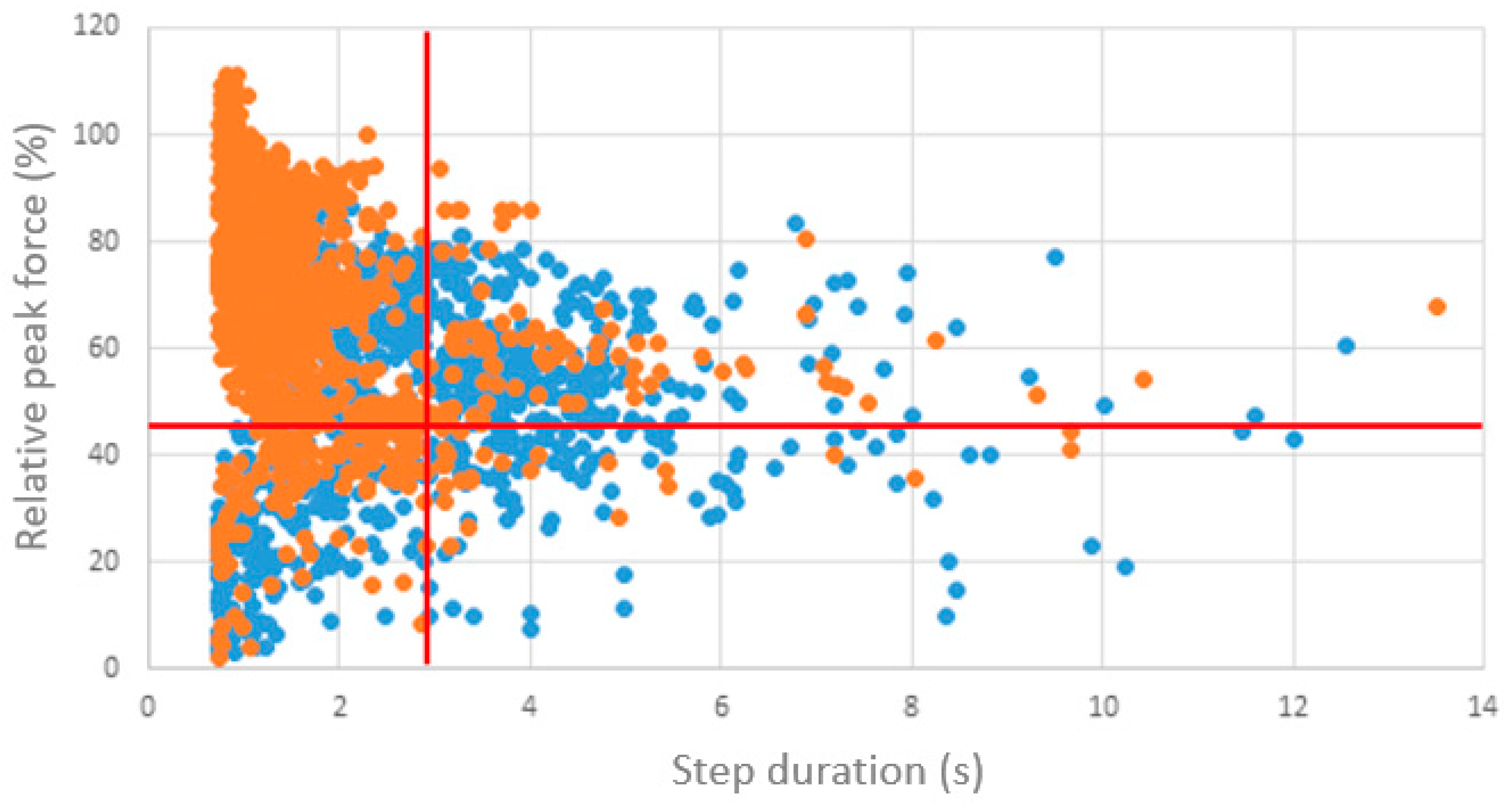
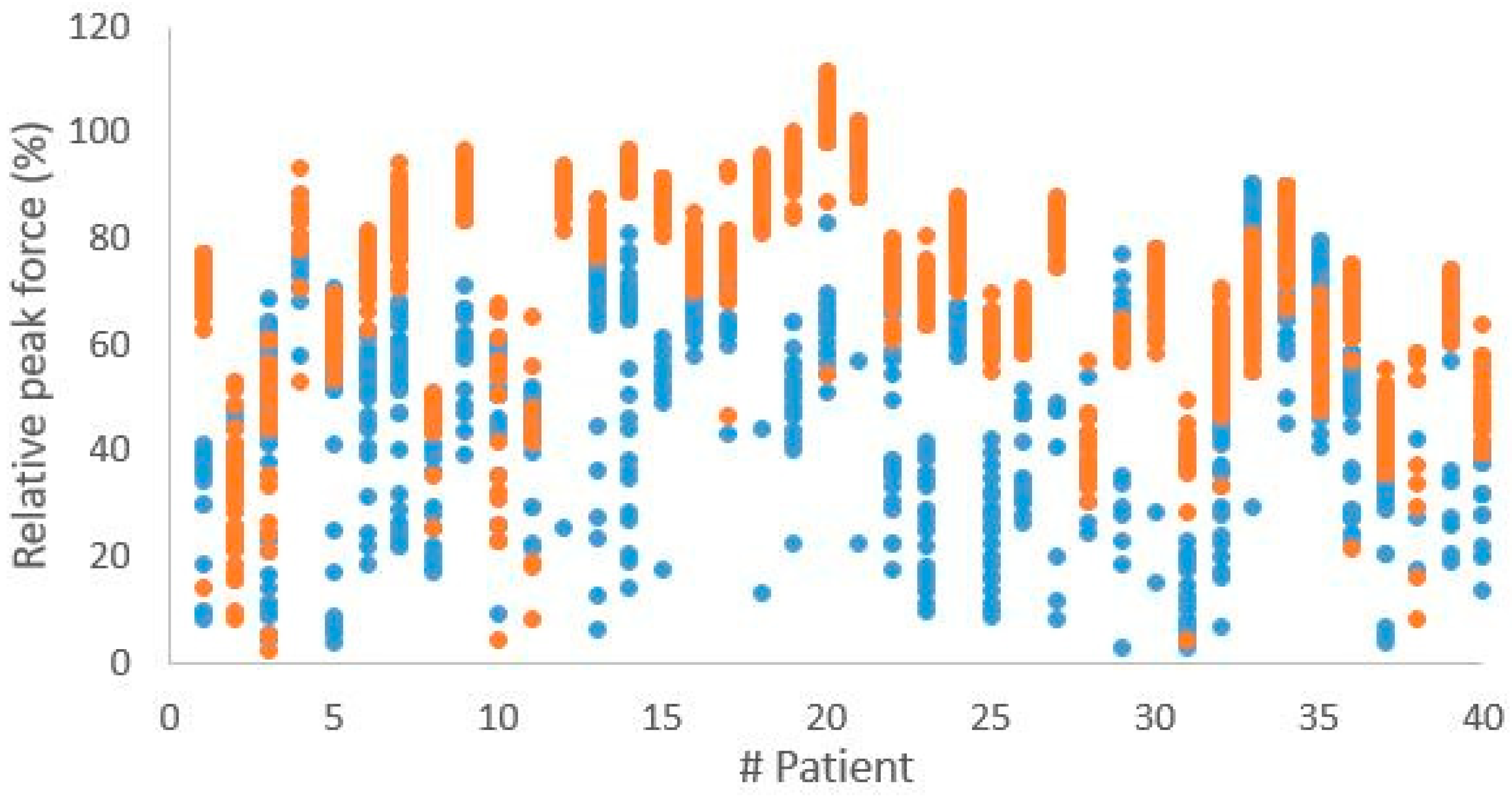
3.2. Biofeedback Measurements During Hospitalization
3.3. Surgical Procedures and Biofeedback Measurements
3.4. Three-Dimensional Gait Analysis: Operated Versus Healthy Leg
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| QoL | Quality of life |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MUMC+ | Maastricht University Medical Centre+ |
| AHFS | Almelo Hip Fracture Score |
| SPM | Statistical parametric mapping |
| PiG | Plug-In Gait |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| Hz | Hertz |
| AMTI | Advanced Mechanical Technology, Inc. |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| IBM | International Business Machines |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
References
- Fernandez, M.; Griffin, X.; Costa, M. Management of hip fracture. Br. Med. Bull. 2015, 115, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-J.; Um, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-H. Postoperative rehabilitation after hip fracture: A literature review. Hip Pelvis 2020, 32, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, H.K.; Iqbal, M.A.; Mogallapu, R.; Maas, D.; Hoffmann, R.G. Time to ambulation after hip fracture surgery: Relation to hospitalization outcomes. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, M1042–M1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmet, P.H.S.; Van Horn, Y.Y.; Sanduleanu, S.; Seelen, H.A.; Brink, P.R.; Poeze, M. Patient-reported quality of life and pain after permissive weight bearing in surgically treated trauma patients with tibial plateau fractures: A retrospective cohort study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2019, 139, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmet, P.H.S.; Meys, G.; YY, V.H.; Evers, S.; Seelen, H.A.M.; Hustinx, P.; Janzing, H.; Vd Veen, A.; Jaspars, C.; Sintenie, J.B.; et al. Permissive weight bearing in trauma patients with fracture of the lower extremities: Prospective multicenter comparative cohort study. BMC Surg. 2018, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, O.P. Interventions for improving mobility after hip fracture surgery in adults. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2011, 129, 435. [Google Scholar]
- Robling, A.G.; Castillo, A.B.; Turner, C.H. Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 8, 455–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein-Nulend, J.; Bacabac, R.; Mullender, M. Mechanobiology of bone tissue. Pathol. Biol. 2005, 53, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Nulend, J.; Bakker, A.D.; Bacabac, R.G.; Vatsa, A.; Weinbaum, S. Mechanosensation and transduction in osteocytes. Bone 2013, 54, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailón-Plaza, A.; Van Der Meulen, M.C. Beneficial effects of moderate, early loading and adverse effects of delayed or excessive loading on bone healing. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, L.E.; Heigele, C.A.; Neidlinger-Wilke, C.; Kaspar, D.; Seidl, W.; Margevicius, K.J.; Augat, P. Effects of mechanical factors on the fracture healing process. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. (1976–2007) 1998, 355, S132–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, M.J.; van der Meulen, M.C.; Demetrakopoulos, D.; Wright, T.M.; Myers, E.R.; Bostrom, M.P. In vivo cyclic axial compression affects bone healing in the mouse tibia. J. Orthop. Res. 2006, 24, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaben, M.; Holtslag, H.R.; Augustine, R.; Van Merkerk, R.O.; Koopman, B.F.; Blokhuis, T.J. Technical aspects and validation of a new biofeedback system for measuring lower limb loading in the dynamic situation. Sensors 2017, 17, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtenberg, E.M.; Kalmet, P.H.; De Krom, M.A.; Blokhuis, T.J.; Seelen, H.A.; Poeze, M. Feasibility and validity of ambulant biofeedback devices to improve weight-bearing compliance in trauma patients with lower extremity fractures: A narrative review. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52, jrm00092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaben, M.; Redzwan, S.M.S.; Augustine, R.; Blokhuis, T.J. (Eds.) Innovative measurement of rehabilitation progress in elderly with a hip fracture: A new endpoint. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Antenna Measurements & Applications (CAMA), Västerås, Sweden, 3–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bogunovic, L.; Cherney, S.M.; Rothermich, M.A.; Gardner, M.J. Biomechanical considerations for surgical stabilization of osteoporotic fractures. Orthop. Clin. 2013, 44, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, N.; Kristensen, M.; Palm, H.; Kehlet, H. Postoperative pain after hip fracture is procedure specific. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.G.; Sutherland, D.H. A practical guide to gait analysis. JAAOS J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2002, 10, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoeve, S.; Houben, M.; Verbruggen, J.P.; Willems, P.; Meijer, K.; Poeze, M. Gait analysis related to functional outcome in patients operated for ankle fractures. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.K.; Andersen, N.T.; Mogensen, P.; Voight, M.; Søballe, K. Gait analysis after total hip replacement with hip resurfacing implant or Mallory-head Exeter prosthesis: A randomised controlled trial. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulet, C.; Hurwitz, D.; Andriacchi, T.; Galante, J.; Vielpeau, C. Functional gait adaptations in patients with painful hip. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice L’appareil Mot. 2000, 86, 581–589. [Google Scholar]
- Vereniging, N.O. Proximale Femurfracturen. 2017. Available online: https://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/proximale_femurfracturen/nabehandeling_proximale_femurfractuur.html (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Fountoulakis, K.N.; Tsolaki, M.; Chantzi, H.; Kazis, A. Mini mental state examination (MMSE): A validation study in Greece. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2000, 15, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijmeijer, W.; Folbert, E.; Vermeer, M.; Slaets, J.; Hegeman, J. Prediction of early mortality following hip fracture surgery in frail elderly: The Almelo Hip Fracture Score (AHFS). Injury 2016, 47, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, A.; Blokhuis, T.J.; Meeks, M.; Hermens, H.J.; Holtslag, H.R. Dynamic weight loading in older people with hip fracture. J. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 46, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Ilg, W.; Giese, M.A.; Ludolph, N. Validation of enhanced kinect sensor based motion capturing for gait assessment. PloS ONE 2017, 12, e0175813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaben, M.; Holtslag, H.R.; Leenen, L.P.; Augustine, R.; Blokhuis, T.J. Real-time visual biofeedback during weight bearing improves therapy compliance in patients following lower extremity fractures. Gait Posture 2018, 59, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senden, R.; Marcellis, R.; Willems, P.; Vermeulen, J.; Witlox, A.; Meijer, K. Protocol 3D Gait Analysis Using Overground Approach-MUMC+. 2022. Available online: https://www.protocols.io/view/protocol-3d-gait-analysis-using-overground-approac-14egn7b86v5d/v1 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Morrison, R.S.; Magaziner, J.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Orosz, G.; Silberzweig, S.B.; Koval, K.J.; Siu, A.L. The impact of post-operative pain on outcomes following hip fracture. Pain 2003, 103, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, R.; Lanting, B.; Marsh, J.; Al-Jurayyan, A.; Churchill, L.; Howard, J.; Somerville, L. Postoperative gait mechanics after total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JBJS Rev. 2018, 6, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, G.; Walsh, M.; Bennett, D.; Rice, J.; O’Brien, T. Gait analysis and hip extensor function early post total hip replacement. J. Orthop. 2016, 13, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, J.; Rosental, D.; Classen, T.; Krebs, S.; Jäger, M. A Retrospective Single-Center Study of 23 Patients to Compare Gait Before and After Total Hip Arthroplasty Using the S-ROM Modular Hip System. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2021, 27, e934558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, C.A.; Fukuchi, R.K.; Duarte, M. Effects of walking speed on gait biomechanics in healthy participants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, M.; Batista, J.P.; Markert, B.; Bollheimer, C.; Laurentius, T. Walking with rollator: A systematic review of gait parameters in older persons. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All Patients | Proximal Femur Nail vs. Hemiarthroplasty | Gait Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intramedullary Femur Nail | Hemiarthroplasty | |||
| N = 40 | N = 19 | N = 10 | N = 9 | |
| Gender (female/male) | 26/14 | 12/7 | 5/5 | 9/0 |
| Age (years) | 79.00 (12.75) | 83.00 (16.00) | 81.50 (7.00) | 77.00 (8.50) |
| Body height (cm) | 167.50 (14.50) | 165.00 (13.00) | 171.50 (17.00) | 167.00 (13.50) |
| Body weight (kg) | 66.50 (15.50) | 65.00 (15.00) | 77.00 (26.75) * | 62.50 (17.50) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.70 (4.75) | 24.10 (2.80) | 24.50 (8.83) | 22.60 (4.20) |
| AHFS | 6.00 (4.00) | 7.00 (3.00) | 8.00 (6.25) | 6.00 (3.50) |
| MMSE | 27.00 (4.00) | 26.00 (5.00) | 26.50 (5.25) | 26.00 (4.00) |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 8.50 (3.00) | 9.00 (2.00) | 8.00 (3.25) | 9.00 (4.00) |
| Days till first SensiStep measurement | 3.00 (2.00) | 3.00 (2.00) | 2.50 (2.00) | 3.00 (1.50) |
| Days between first and last SensiStep measurement | 3.00 (3.00) | 4.00 (3.00) | 3.50 (1.00) | 4.00 (2.50) |
| Surgical procedure (n): | ||||
| Proximal femur nail | 19 | 4 | ||
| Sliding/dynamic hip screw | 2 | 0 | ||
| Hemiarthroplasty | 10 | 2 | ||
| Total hip replacement | 5 | 1 | ||
| Femoral neck system | 4 | 2 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hecht, G.A.; Senden, R.; Marcellis, R.; Mertes, M.; Willems, P.; Meijer, K.; Poeze, M.; Blokhuis, T.J. Early Postoperative Gait Analysis in Elderly Patients Following Hip Fracture Surgery. Sensors 2025, 25, 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061888
Hecht GA, Senden R, Marcellis R, Mertes M, Willems P, Meijer K, Poeze M, Blokhuis TJ. Early Postoperative Gait Analysis in Elderly Patients Following Hip Fracture Surgery. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061888
Chicago/Turabian StyleHecht, Gereon Anton, Rachel Senden, Rik Marcellis, Matthias Mertes, Paul Willems, Kenneth Meijer, Martijn Poeze, and Taco J. Blokhuis. 2025. "Early Postoperative Gait Analysis in Elderly Patients Following Hip Fracture Surgery" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061888
APA StyleHecht, G. A., Senden, R., Marcellis, R., Mertes, M., Willems, P., Meijer, K., Poeze, M., & Blokhuis, T. J. (2025). Early Postoperative Gait Analysis in Elderly Patients Following Hip Fracture Surgery. Sensors, 25(6), 1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061888






