EEG-Based Engagement Monitoring in Cognitive Games
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Are there differences in the (self-reported) levels of engagement across the game levels?
- (2)
- Are there any differences in the EEG engagement indices across the game difficulty levels?
- (3)
- How accurately can the reported engagement be classified from the EEG data using the within-subject and cross-subject approaches?
- (3.1)
- Do the older adults’ and young adults’ EEG data compare with each other in terms of performance reports?
- (3.2)
- Which classifier is better in performance?
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
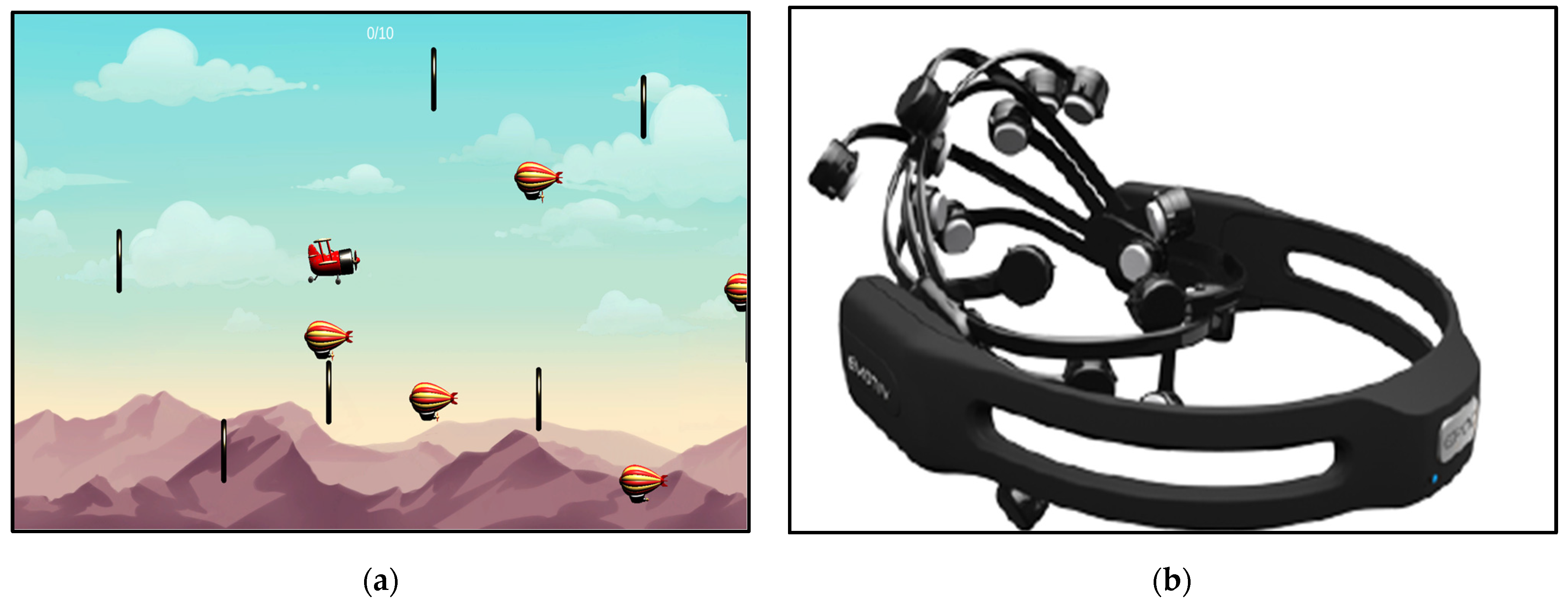
3.1.1. Game and Wearable Device
3.1.2. Flow State Scale of Occupational Tasks
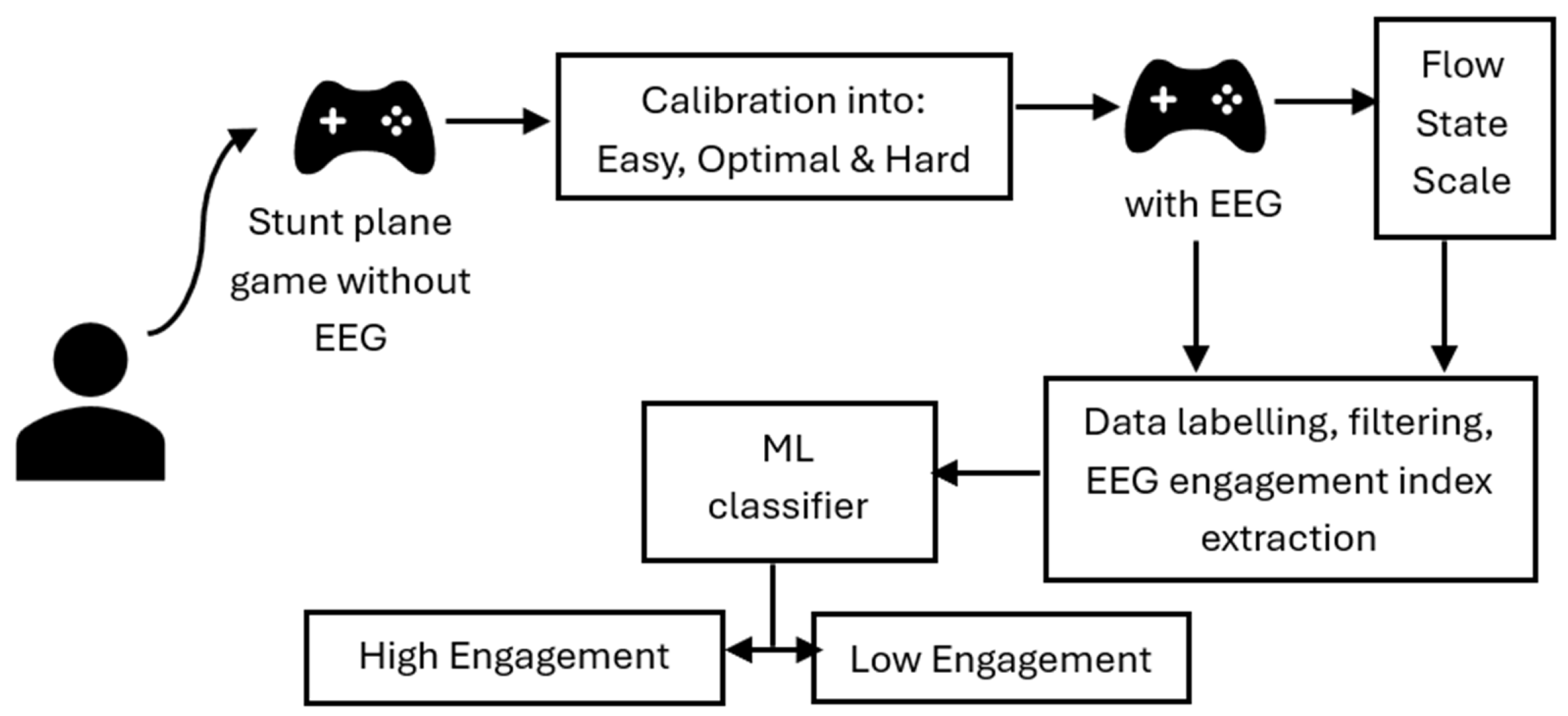
3.2. Design of Experiment
3.2.1. Performance Index Development
3.2.2. Experimental Procedure
3.3. Signal Preprocessing
Data Quality Analysis
3.4. Participants’ Description
3.5. Statistical Analysis
3.6. Machine Learning Analysis
4. Results
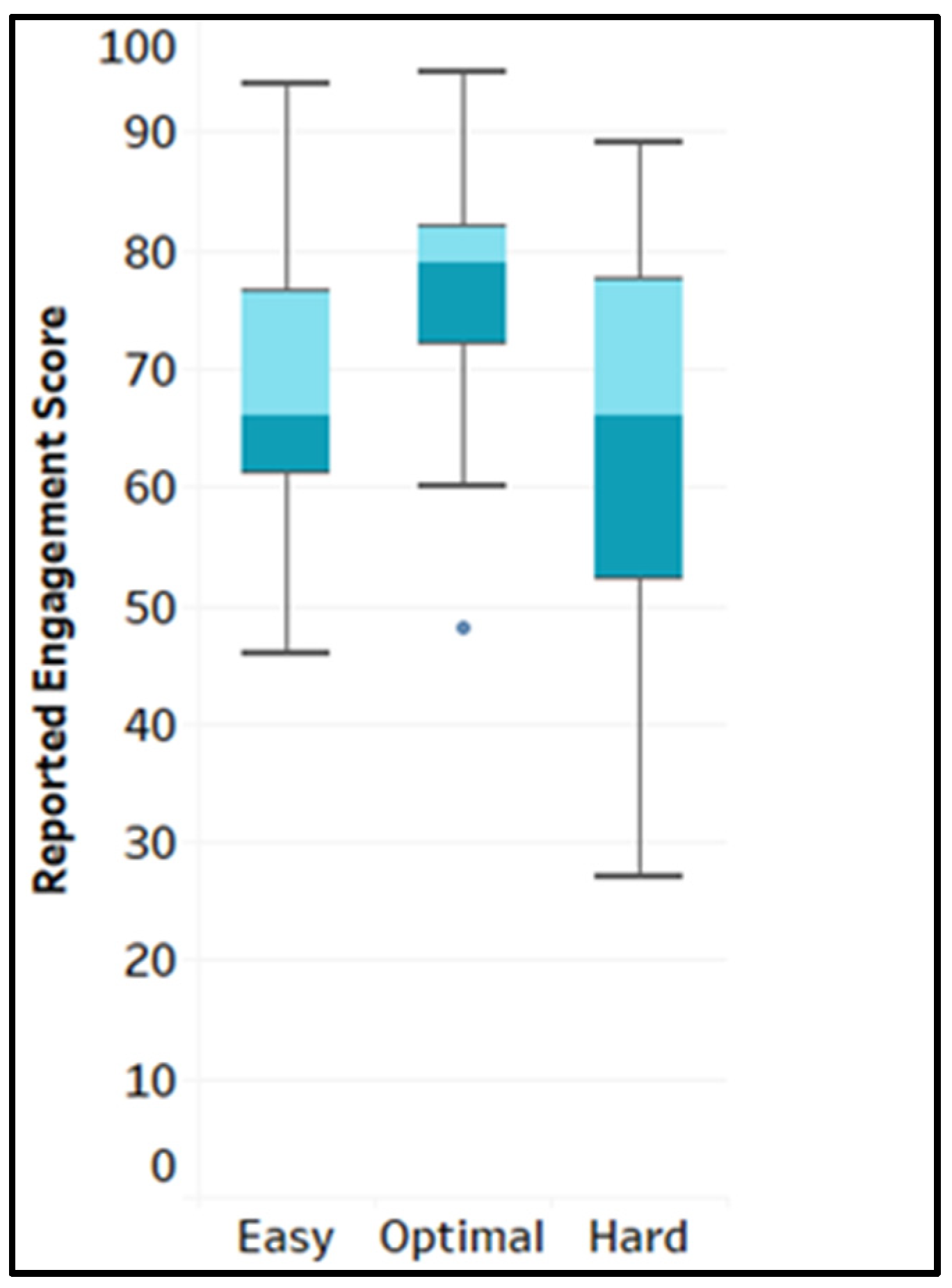
4.1. Reported Engagement Score Across Game Levels (RQ1)
4.2. EEG Engagement Indices Across Game Levels (RQ2)
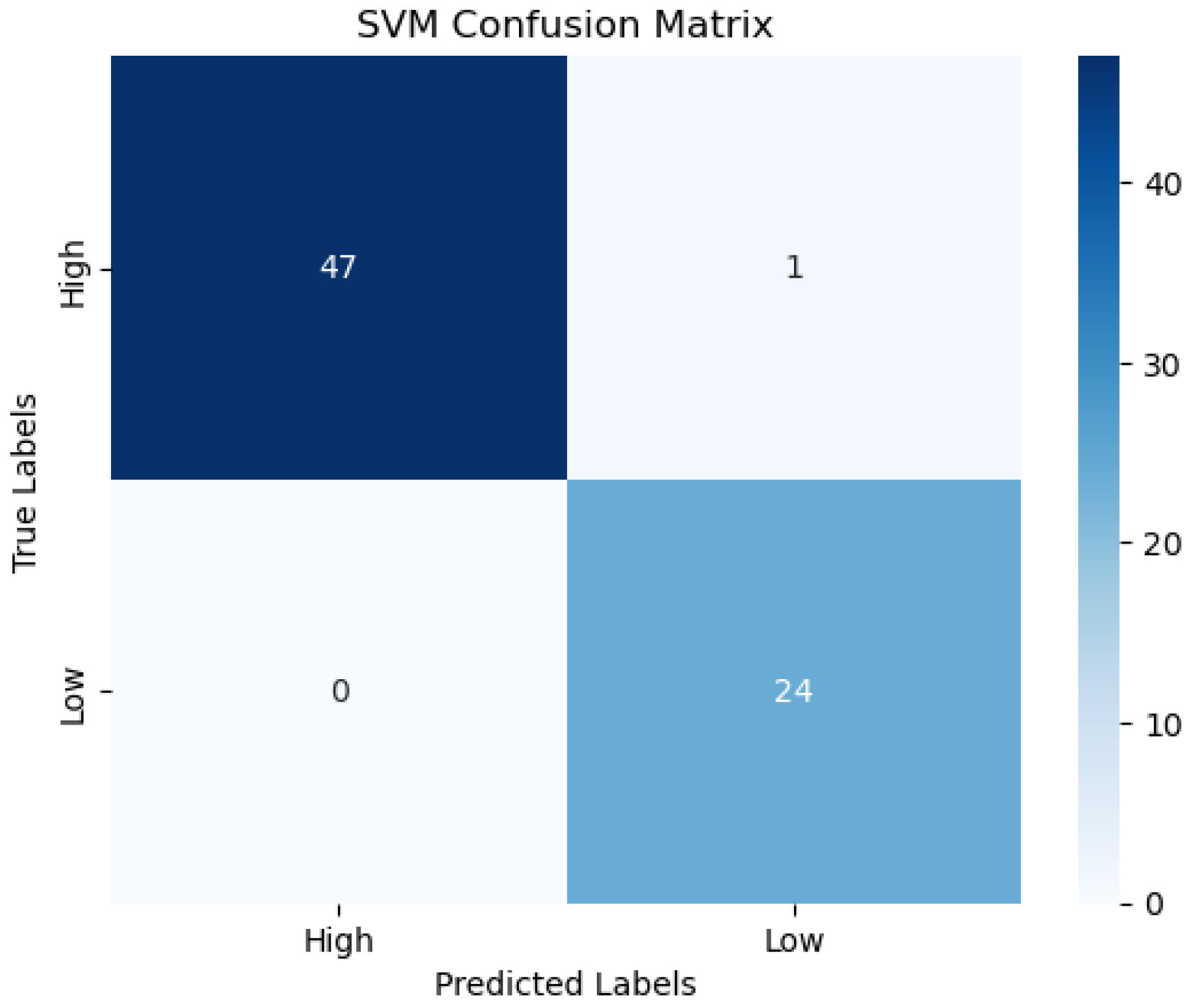
4.3. Machine Learning Analysis (RQ3)
5. Discussion
5.1. Clinical Implications
5.2. Limitation
5.3. Recommendations for Future Research
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ML | Machine learning |
| GEQ | Game Engagement Questionnaire |
| PwD | People living with dementia |
| RF | Random forest |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| UES | User Engagement Scale |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| EOG | Electrooculography |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| GSR | Galvanic skin response |
| SAM | self-assessment manikin |
| BCI | Brain–Computer interface |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| CCT | Computerised cognitive training |
| POSM | partially ordered set masterI |
| DOL | increment/decrement one level |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| ERD/ERS | Desynchronization and Event-Related Synchronisation |
| GAAM | Genetic Algorithm with Aggressive Mutation GAAM |
References
- Bonnechère, B.; Langley, C.; Sahakian, B.J. The Use of Commercial Computerised Cognitive Games in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, C.A.; Anderson, S.D.; Parmar, J. A Biopsychosocial-Ecological Framework for Family-Framed Dementia Care. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 744806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimler, R.; Maresova, P.; Kuhnova, J.; Kuca, K. Predictions of Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment and Care Costs in European Countries. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza, P.; Miller-Petrie, M.K.; Chen, C.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chapin, A.; Hay, S.; Tsakalos, G.; Wimo, A.; Dieleman, J.L. Global and Regional Spending on Dementia Care from 2000–2019 and Expected Future Health Spending Scenarios from 2020–2050: An Economic Modelling Exercise. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 45, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navigating the Path Forward for Dementia in Canada: The Landmark Study Report #1. Available online: http://alzheimer.ca/en/research/reports-dementia/landmark-study-report-1-path-forward (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Alzheimer Society of Canada. The Many Faces of Dementia in Canada. Available online: https://alzheimer.ca/en/the-many-faces-of-dementia-in-canada-landmark-study-volume-2 (accessed on 11 August 2024).
- Wilson, J.; Heinsch, M.; Betts, D.; Booth, D.; Kay-Lambkin, F. Barriers and Facilitators to the Use of E-Health by Older Adults: A Scoping Review. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Cruz, A.; Rincon, A.M.R.; Daum, C.; Torres, D.A.Q.; De Jesus, R.; Liu, L.; Stroulia, E. Predicting Engagement in Older Adults With and Without Dementia While Playing Mobile Games. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2021, 24, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos Rincón, A.M.; Daum, C.; Miguel Cruz, A.; Liu, L.; Stroulia, E. Feasibility and Acceptability of a Serious Mobile-Game Intervention for Older Adults. Phys. Occup. Ther. Geriatr. 2022, 40, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharek, D.; Wiebe, E. Measuring Video Game Engagement Through the Cognitive and Affective Dimensions. Simul. Gaming 2014, 45, 569–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranha, R.V.; Cordeiro, L.N.; Sales, L.M.; Nunes, F.L.S. Engagement and Discrete Emotions in Game Scenario: Is There a Relation Among Them? In Human-Computer Interaction–INTERACT 2021. INTERACT 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12934, pp. 22–42. [Google Scholar]
- Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow and the Foundations of Positive Psychology: The Collected Works of Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-94-017-9087-1. [Google Scholar]
- Balducci, F.; Grana, C.; Cucchiara, R. Affective Level Design for a Role-Playing Videogame Evaluated by a Brain–Computer Interface and Machine Learning Methods. Vis. Comput. 2017, 33, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, B.; Charles, D.; Black, M.; Hickey, R. Toward an Understanding of Flow in Video Games. Comput. Entertain. 2008, 6, 20:1–20:27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, K.; Doherty, G. Engagement in HCI: Conception, Theory and Measurement. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 99:1–99:39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, A.; Egglefield, D.A.; Schiff, S.; Motter, J.N.; Sneed, J.R. Computerized Cognitive Training: A Review of Mechanisms, Methodological Considerations, and Application to Research in Depression. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2021, 5, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hookham, G.; Nesbitt, K. A Systematic Review of the Definition and Measurement of Engagement in Serious Games. In Proceedings of the Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 29–31 January 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Brockmyer, J.H.; Fox, C.M.; Curtiss, K.A.; McBroom, E.; Burkhart, K.M.; Pidruzny, J.N. The Development of the Game Engagement Questionnaire: A Measure of Engagement in Video Game-Playing. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 45, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Asakawa, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Sakuraba, S.; Sawamura, D.; Murakami, Y.; Sakai, S. The Flow State Scale for Occupational Tasks: Development, Reliability, and Validity. Hong Kong J. Occup. Ther. 2013, 23, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, H.L.; Toms, E.G. The Development and Evaluation of a Survey to Measure User Engagement. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.Z.; Ting, D.H.; Hlavacs, H. Engagement in Games: Developing an Instrument to Measure Consumer Videogame Engagement and Its Validation. Int. J. Comput. Games Technol. 2017, 2017, e7363925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimo, S.; Cropano, M.; Gaita, M.; Maggi, G.; Cavallo, N.D.; Roldan-Tapia, M.D.; Santangelo, G. The Efficacy of Cognitive Training on Neuropsychological Outcomes in Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brinke, L.F.; Best, J.R.; Chan, J.L.C.; Ghag, C.; Erickson, K.I.; Handy, T.C.; Liu-Ambrose, T. The Effects of Computerized Cognitive Training With and Without Physical Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: An 8-Week Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Gallegos, R.; Mayer, R.E. Learning Cognitive Skills by Playing Video Games at Home: Testing the Specific Transfer of General Skills Theory. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2022, 6, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, S.A.; Henry, J.D.; Phillips, L.H.; Vanman, E.J.; Allen, R. Age Deficits in Facial Affect Recognition: The Influence of Dynamic Cues. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2017, 72, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson Kakulla, B. Gaming Attitudes and Habits of Adults Ages 50-Plus; AARP Research: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylski, A.K.; Rigby, C.S.; Ryan, R.M. A Motivational Model of Video Game Engagement. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2010, 14, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkul, F.; Palaska, Y.; Masazade, E.; Erol-Barkana, D. Exploring Dynamic Difficulty Adjustment Mechanism for Rehabilitation Tasks Using Physiological Measures and Subjective Ratings. IET Signal Process. 2019, 13, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, A.; Apostolakis, K.C.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Daras, P. Multimodal Student Engagement Recognition in Prosocial Games. IEEE Trans. Games 2018, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhang, X.-H.; Dang, X.; Li, G.-H. Classification for Motion Game Based on EEG Sensing. ITM Web Conf. 2017, 11, 05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejer, I.; Twardochleb, M. Gamers’ Involvement Detection from EEG Data with cGAAM–A Method for Feature Selection for Clustering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 101, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, T.; Saeed, S.M.U.; Arsalan, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Ashraf, M.U.; Alsubhi, K. EEG in Game User Analysis: A Framework for Expertise Classification during Gameplay. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Arpaia, P.; Frosolone, M.; Improta, G.; Moccaldi, N.; Pollastro, A. EEG-Based Measurement System for Monitoring Student Engagement in Learning 4.0. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.R.; Rajavenkatanarayanan, A.; Brady, J.R.; Makedon, F. Multimodal Approach for Cognitive Task Performance Prediction from Body Postures, Facial Expressions and EEG Signal. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Modeling Cognitive Processes from Multimodal Data, Boulder, CO, USA, 16 October 2018; ACM: Boulder, CO, USA, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Hui, Z.; Li, Y.; Guan, J. Research on Learning Concentration Recognition with Multi-Modal Features in Virtual Reality Environments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Kim, J.; Jang, D.-P.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, S.-P. Investigation of Engagement of Viewers in Movie Trailers Using Electroencephalography. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2015, 2, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Kim, S. Pleasure-Arousal-Outlier Model for Quantitative Evaluation of Game Experiences. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 19459–19477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterman, S.L.; Estepp, J.R. Investigating Ensemble Learning and Classifier Generalization in a Hybrid, Passive Brain-Computer Interface for Assessing Cognitive Workload. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 3543–3546. [Google Scholar]
- Natalizio, A.; Sieghartsleitner, S.; Schreiner, L.; Walchshofer, M.; Esposito, A.; Scharinger, J.; Pretl, H.; Arpaia, P.; Parvis, M.; Solé-Casals, J.; et al. Real-Time Estimation of EEG-Based Engagement in Different Tasks. J. Neural Eng. 2024, 21, 016014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, L.; Schultze-Kraft, M.; Dähne, S.; Blankertz, B. Prediction of Difficulty Levels in Video Games from Ongoing EEG. In Proceedings of the Symbiotic Interaction; Gamberini, L., Spagnolli, A., Jacucci, G., Blankertz, B., Freeman, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- DeFalco, J.A.; Rowe, J.P.; Paquette, L.; Georgoulas-Sherry, V.; Brawner, K.; Mott, B.W.; Baker, R.S.; Lester, J.C. Detecting and Addressing Frustration in a Serious Game for Military Training. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2018, 28, 152–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente, C.D.L.; Castellanos, F.J.; Valero-Mas, J.J.; Calvo-Zaragoza, J. Multimodal Recognition of Frustration during Game-Play with Deep Neural Networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 13617–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Romero, D.; Ríos-Rincón, A.M.; Cruz, A.; Yee, N.; Stroulia, E. Recognizing Emotional States With Wearables While Playing A Serious Game. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2506312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimardani, M.; van den Braak, S.; Jouen, A.-L.; Matsunaka, R.; Hiraki, K. Assessment of Engagement and Learning During Child-Robot Interaction Using EEG Signals. In Proceedings of the Social Robotics; Li, H., Ge, S.S., Wu, Y., Wykowska, A., He, H., Liu, X., Li, D., Perez-Osorio, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 671–682. [Google Scholar]
- Karimah, S.N.; Hasegawa, S. Automatic Engagement Estimation in Smart Education/Learning Settings: A Systematic Review of Engagement Definitions, Datasets, and Methods. Smart Learn. Environ. 2022, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbaryhosseinabadi, S.; Kamavuako, E.N.; Jiang, N.; Farina, D.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N. Classification of EEG Signals to Identify Variations in Attention during Motor Task Execution. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 284, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle-Rodriguez, D.; de Oliveira, H.L.; da Silva, J.C.; de Souza, M.L.; Bastos, T.; Nakamura-Palacios, E.M.; Frizera-Neto, A. Multi-Channel EEG-Based BCI Using Regression and Classification Methods for Attention Training by Serious Game. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 85, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Barroso, A.; Siugzdaite, R.; Guerrero-Cubero, J.; Molina-Cantero, A.J.; Gomez-Gonzalez, I.M.; Lopez, J.C.; Vargas, J.P. Detecting Attention Levels in ADHD Children with a Video Game and the Measurement of Brain Activity with a Single-Channel BCI Headset. Sensors 2021, 21, 3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun Seo, J.; Hong Noh, Y.; Un Jeong, D. Development of Smartphone Contents to Improve Concentration Based on EEG. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andujar, M.; Ekandem, J.I.; Gilbert, J.E.; Morreale, P. Evaluating Engagement Physiologically and Knowledge Retention Subjectively through Two Different Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction. Applications and Services; Kurosu, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Ghergulescu, I.; Muntean, C.H. ToTCompute: A Novel EEG-Based TimeOnTask Threshold Computation Mechanism for Engagement Modelling and Monitoring. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2016, 26, 821–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, V.; Wai, A.A.P.; Ho, C.Y. Evaluation of Learning Performance by Quantifying User’s Engagement Investigation through Low-Cost Multi-Modal Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Orange Technologies (ICOT), Singapore, 8–10 December 2017; IEEE: Singapore, 2017; pp. 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Amprimo, G.; Rechichi, I.; Ferraris, C.; Olmo, G. Measuring Brain Activation Patterns from Raw Single-Channel EEG during Exergaming: A Pilot Study. Electronics 2023, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, S.; Sclocco, R.; Barbieri, R.; Reni, G.; Zucca, C.; Bianchi, A. EEG-Based Index for Engagement Level Monitoring during Sustained Attention; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ezell, B.; Lynch, C.J.; Hester, P.T. Methods for Weighting Decisions to Assist Modelers and Decision Analysts: A Review of Ratio Assignment and Approximate Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saminu, S.; Xu, G.; Shuai, Z.; Abd El Kader, I.; Jabire, A.H.; Ahmed, Y.K.; Karaye, I.A.; Ahmad, I.S. A Recent Investigation on Detection and Classification of Epileptic Seizure Techniques Using EEG Signal. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, C.; Moontaha, S.; Real, S.; Arnrich, B. Unobtrusive Measurement of Cognitive Load and Physiological Signals in Uncontrolled Environments. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urigüen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG Artifact Removal-State-of-the-Art and Guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apicella, A.; Arpaia, P.; Frosolone, M.; Moccaldi, N. High-Wearable EEG-Based Distraction Detection in Motor Rehabilitation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, F.G.; Mikulka, P.J.; Prinzel, L.J.; Scerbo, M.W. Evaluation of an Adaptive Automation System Using Three EEG Indices with a Visual Tracking Task. Biol. Psychol. 1999, 50, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada-Quintero, H.F.; Reljin, N.; Bolkhovsky, J.B.; Orjuela-Cañón, A.D.; Chon, K.H. Brain Activity Correlates With Cognitive Performance Deterioration During Sleep Deprivation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, S.; Barbieri, R.; Reni, G.; Zucca, C.; Bianchi, A.M. EEG Indices Correlate with Sustained Attention Performance in Patients Affected by Diffuse Axonal Injury. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, A.T.; Bogart, E.H.; Bartolome, D.S. Biocybernetic System Evaluates Indices of Operator Engagement in Automated Task. Biol. Psychol. 1995, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislov, A.; Gorin, A.; Konstantinovsky, N.; Klyuchnikov, V.; Bazanov, B.; Klucharev, V. Central EEG Beta/Alpha Ratio Predicts the Population-Wide Efficiency of Advertisements. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radüntz, T. Signal Quality Evaluation of Emerging EEG Devices. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanza, V.; Avilés-Mendoza, K.; Trivino-Gonzalez, H.; Rosales-Uribe, F.; Torres-Brunes, J.; Loayza, F.R.; Peláez, E.; Cajo, R.; Tinoco-Egas, R. SSVEP-EEG Signal Classification Based on Emotiv EPOC BCI and Raspberry Pi⁎. IFAC-Pap. 2021, 54, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbaryhosseinabadi, S.; Kamavuako, E.N.; Jiang, N.; Farina, D.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N. Classification of Movement Preparation Between Attended and Distracted Self-Paced Motor Tasks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 3060–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centre on Aging Lifelong Learning. Available online: http://umanitoba.ca/centre-on-aging/facts-on-aging/lifelong-learning (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Heerink, M.; Krose, B.; Evers, V.; Wielinga, B. Measuring Acceptance of an Assistive Social Robot: A Suggested Toolkit. In Proceedings of the RO-MAN 2009—The 18th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Toyama, Japan, 27 September 2009–2 October 2009; IEEE: Toyama, Japan, 2009; pp. 528–533. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-C. Acceptability Engineering: The Study of User Acceptance of Innovative Technologies. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2015, 13, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetos, A.; Petrovic, M.; Strandberg, T. Hypertension Management in Older and Frail Older Patients. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.A.; Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. J. Leis. Res. 1992, 24, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katahira, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Yamaoka, C.; Ozaki, H.; Nakagawa, S.; Nagata, N. EEG Correlates of the Flow State: A Combination of Increased Frontal Theta and Moderate Frontocentral Alpha Rhythm in the Mental Arithmetic Task. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, D.V.C.; Esteves, F.; Rajado, A.T.; Silva, N.; Araújo, I.; Bragança, J.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Nóbrega, C. Assessing Cognitive Decline in the Aging Brain: Lessons from Rodent and Human Studies. npj Aging 2023, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berka, C.; Levendowski, D.J.; Lumicao, M.N.; Yau, A.; Davis, G.; Zivkovic, V.T.; Olmstead, R.E.; Tremoulet, P.D.; Craven, P.L. EEG Correlates of Task Engagement and Mental Workload in Vigilance, Learning, and Memory Tasks. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2007, 78, B231–B244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hassib, M.; Schneegaß, S.; Eiglsperger, P.; Henze, N.; Schmidt, A.; Alt, F. EngageMeter: A System for Implicit Audience Engagement Sensing Using Electroencephalography; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM): New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmyna, N.; Maes, P. AttentivU: A Biofeedback Device to Monitor and Improve Engagement in the Workplace; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 2019, p. 1708. [Google Scholar]
- Nuamah, J.; Seong, Y.; Yi, S. Electroencephalography (EEG) Classification of Cognitive Tasks Based on Task Engagement Index. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Cognitive and Computational Aspects of Situation Management (CogSIMA), Savannah, GA, USA, 27–31 March 2017; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- López-Loeza, E.; Rangel-Argueta, A.R.; López-Vázquez, M.Á.; Cervantes, M.; Olvera-Cortés, M.E. Differences in EEG Power in Young and Mature Healthy Adults during an Incidental/Spatial Learning Task Are Related to Age and Execution Efficiency. Age 2016, 38, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.K.-H.; Fong, M.C.-M.; Xie, C.; Lee, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.S. Regularity and Randomness in Ageing: Differences in Resting-State EEG Complexity Measured by Largest Lyapunov Exponent. Neuroimage Rep. 2021, 1, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Tejada, L.; Puertas-Gonzalez, A.; Yoshimura, N.; Koike, Y. Exploring EEG Characteristics to Identify Emotional Reactions under Videogame Scenarios. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richhariya, B.; Tanveer, M. EEG Signal Classification Using Universum Support Vector Machine. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 106, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcello, J.C. Designing and Implementing SVMs for High-Dimensional Knowledge Discovery Using FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rabipour, S.; Davidson, P.S.R. Do You Believe in Brain Training? A Questionnaire about Expectations of Computerised Cogni tive Training. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 295, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braboszcz, C.; Cahn, B.R.; Levy, J.; Fernandez, M.; Delorme, A. Increased Gamma Brainwave Amplitude Compared to Control in Three Different Meditation Traditions. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halderman, L.K.; Finn, B.; Lockwood, J.R.; Long, N.M.; Kahana, M.J. EEG Correlates of Engagement During Assessment. ETS Res. Rep. Ser. 2021, 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Subcategories | Game | Biomarker/Feature | Population/Age | Study | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEG | Smart phone game app | Concentration index | Not specified | Yun Seo et al. [49] | 2018 |
| EEG | Video game and handout | Emotiv’s proprietary engagement algorithm | 32 participants, no age record | Andujar et al. [50] | 2013 |
| EEG | Neverwinter Nights 2 | Emotiv’s proprietary engagement algorithm | 19 students, no age record | Balducci et al. [13] | 2017 |
| EEG | Fire Protocol game | Emotiv’s proprietary engagement algorithm | 50 participants, 18–55 years Average: 27 7 | Ghergulescu & Muntean [51] | 2016 |
| EEG+Eye tracker + Motion tracker | Whack-a-Mole game | PSD, standard deviation (Std) of bands, Delta/Theta, Delta/Alpha, Delta/Beta, Theta/Alpha, Theta/Beta, and Alpha/Beta. | 21 participants, >18 years | Diaz et al. [43] | 2021 |
| EEG + HRV + GSR+ Eye tracker | Conjunctive Continuous Performance Test | absolute band power, Interbeat (R-R) Interval, eye motion velocity | 10 participants, 17–22 years | Sandhu et al. [52] | 2017 |
| EEG | Grab-Drag-Drop Exergame | Concentration index, Engagement index ( and event-related desynchronization/synchronisation | 50 participants, 26 ± 4.5 years | Amprimo et al. [53] | 2023 |
| EEG | Continuous Performance Test | Engagement index (, Filter banks, Domain adaptation, Butterworth Principal Component Analysis | 21 participants, 23.7 ± 4.1 years | Apicella et al. [33] | 2022 |
| Non physiological signal | Multimodal Game Frustration | Audiovisual data | 67 students, 12–16 years | Fuente et al. [42] | 2023 |
| Other physiological signal | Fruit picking game | blood volume pulse, skin temperature, and skin conductance | 20–37 years | Ozkul et al. [28] | 2019 |
| EEG | continuous performance test | Engagement index ( | 9 participants, 18–28 | Coelli et al. [54] | 2015 |
| EEG | D2 test, video and Tetris game | Filter bank and Engagement index ( | 23 participants, 34 ± 7 years | Natalizio et al. [39] | 2024 |
| Level | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51.21027 |
| 2 | 54 | 6 | 3 | 0.245098 | 0.037267 | 0 | 0.086603 | 77.83074 |
| 3 | 76 | 10 | 8 | 0.460784 | 0.062112 | 0.092593 | 0.150701 | 97.5334 |
| 4 | 91 | 27 | 11 | 0.607843 | 0.167702 | 0.148148 | 0.158725 | 100 |
| 5 | 98 | 44 | 20 | 0.676471 | 0.273292 | 0.314815 | 0.115556 | 86.73052 |
| 6 | 115 | 57 | 21 | 0.843137 | 0.354037 | 0.333333 | 0.148275 | 96.7876 |
| 7 | 115 | 89 | 31 | 0.843137 | 0.552795 | 0.518519 | 0.0346 | 61.8459 |
| 8 | 111 | 119 | 34 | 0.803922 | 0.73913 | 0.574074 | −0.06864 | 30.11069 |
| 9 | 128 | 139 | 42 | 0.970588 | 0.863354 | 0.722222 | −0.07564 | 27.9604 |
| 10 | 131 | 161 | 57 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −0.1666 | 0 |
| S/N | AF3 | F7 | F3 | FC5 | T7 | P7 | O1 | O2 | P8 | T8 | FC6 | F4 | F8 | AF4 | AVG EEG (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 10.23 | 8.57 | 10.44 | 8.54 | 4.86 | 6.63 | 7.51 | 8.98 | 10.97 | 11.90 | 13.57 | 10.66 | 13.27 | 14.37 | 10.04 |
| #2 | 13.11 | 9.98 | 11.08 | 7.19 | 6.80 | 6.89 | 9.23 | 9.20 | 7.74 | 5.88 | 11.31 | 14.36 | 12.47 | 14.23 | 9.96 |
| #3 | 10.57 | 4.31 | 6.20 | 2.92 | 6.94 | 6.12 | 5.78 | 5.49 | 5.61 | 4.53 | 5.41 | 6.16 | 7.43 | 13.58 | 6.50 |
| #4 | 9.94 | 9.89 | 9.43 | 9.59 | 10.20 | 10.47 | 11.21 | 11.16 | 10.48 | 8.89 | 10.51 | 11.65 | 11.61 | 10.78 | 10.42 |
| #5 | 7.69 | 4.38 | 3.78 | 3.00 | 2.18 | 1.84 | 2.82 | 3.29 | 2.60 | 2.82 | 3.71 | 3.85 | 7.13 | 5.29 | 3.88 |
| #6 | 6.68 | 4.46 | 4.22 | 3.12 | 1.68 | 1.71 | 2.40 | 2.91 | 3.59 | 8.21 | 3.97 | 4.25 | 6.61 | 5.54 | 4.24 |
| #7 | 11.39 | 9.39 | 12.51 | 9.57 | 5.26 | 6.79 | 9.04 | 9.35 | 5.82 | 9.93 | 11.95 | 12.59 | 12.59 | 12.51 | 9.91 |
| #8 | 4.94 | 4.10 | 4.88 | 3.95 | 2.24 | 3.36 | 3.76 | 3.60 | 3.17 | 3.87 | 4.87 | 4.38 | 6.30 | 6.24 | 4.26 |
| #9 | 16.50 | 9.34 | 12.37 | 8.21 | 4.16 | 5.60 | 7.09 | 7.80 | 8.17 | 6.87 | 13.25 | 13.03 | 12.28 | 16.19 | 10.06 |
| #10 | 5.37 | 5.56 | 4.98 | 4.02 | 14.88 | 3.13 | 2.98 | 4.20 | 3.25 | 5.56 | 5.43 | 4.99 | 9.17 | 6.00 | 5.68 |
| #11 | 9.72 | 8.97 | 11.29 | 7.82 | 2.93 | 5.87 | 7.89 | 8.35 | 7.39 | 4.49 | 10.76 | 10.94 | 11.62 | 10.15 | 8.44 |
| #12 | 9.97 | 4.63 | 6.95 | 4.47 | 4.96 | 4.56 | 6.87 | 6.93 | 5.70 | 6.73 | 5.62 | 7.06 | 6.99 | 5.60 | 6.22 |
| #13 | 6.01 | 8.97 | 8.62 | 6.77 | 4.30 | 5.37 | 8.02 | 8.18 | 7.86 | 5.89 | 7.87 | 8.23 | 7.03 | 7.39 | 7.18 |
| #14 | 5.08 | 11.55 | 10.27 | 11.00 | 7.60 | 6.23 | 8.61 | 9.73 | 9.51 | 7.22 | 10.00 | 9.92 | 10.24 | 6.20 | 8.80 |
| #15 | 10.10 | 10.28 | 5.32 | 7.52 | 2.33 | 2.32 | 2.12 | 2.97 | 3.07 | 3.61 | 7.81 | 4.70 | 14.54 | 7.64 | 6.02 |
| #16 | 6.70 | 3.54 | 3.31 | 4.47 | 0.07 | 1.33 | 2.65 | 3.33 | 1.96 | 0.65 | 2.65 | 2.68 | 4.86 | 5.06 | 3.09 |
| #17 | 6.85 | 8.16 | 5.57 | 5.32 | 2.73 | 5.54 | 6.38 | 6.23 | 6.14 | 4.75 | 6.96 | 6.59 | 9.82 | 8.41 | 6.39 |
| #18 | 6.19 | 6.45 | 7.17 | 6.30 | 5.83 | 6.76 | 8.01 | 8.40 | 6.31 | 5.28 | 6.47 | 6.29 | 6.43 | 5.69 | 6.54 |
| #19 | 4.93 | 4.30 | 6.43 | 3.34 | 2.44 | 4.26 | 4.40 | 5.76 | 5.74 | 1.80 | 5.94 | 6.85 | 7.58 | 4.19 | 4.85 |
| #20 | 10.18 | 9.04 | 10.36 | 8.75 | 9.21 | 8.45 | 9.40 | 9.86 | 9.23 | 10.00 | 10.52 | 11.10 | 11.01 | 10.97 | 9.86 |
| #21 | 8.53 | 6.67 | 7.72 | 5.03 | 5.53 | 6.70 | 7.69 | 7.02 | 6.53 | 5.87 | 8.47 | 9.74 | 10.83 | 11.46 | 7.70 |
| #22 | 3.94 | 3.83 | 3.74 | 2.55 | 3.92 | 1.04 | 2.99 | 3.08 | 2.82 | 3.83 | 4.51 | 3.58 | 5.84 | 6.35 | 3.72 |
| #23 | 4.41 | 5.53 | 4.49 | 2.78 | 1.53 | 1.40 | 1.52 | 2.05 | 2.59 | 2.31 | 3.72 | 2.70 | 9.97 | 4.50 | 3.54 |
| #24 | 3.82 | 1.82 | 3.54 | 2.29 | 1.52 | 2.24 | 3.21 | 3.17 | 1.75 | 2.27 | 3.17 | 3.18 | 3.13 | 3.74 | 2.77 |
| #25 | 8.36 | 10.57 | 7.66 | 8.90 | 9.41 | 6.49 | 7.88 | 8.08 | 8.39 | 7.43 | 9.31 | 8.30 | 11.17 | 11.84 | 8.84 |
| #26 | 3.43 | 2.12 | 2.68 | 0.97 | 2.85 | 1.27 | 2.09 | 2.33 | 2.35 | 2.96 | 3.25 | 2.88 | 5.02 | 5.03 | 2.80 |
| #27 | 5.52 | 7.29 | 6.49 | 4.25 | 5.14 | 3.39 | 5.92 | 5.55 | 3.56 | 4.15 | 7.08 | 6.44 | 8.78 | 5.48 | 5.65 |
| Variables | n = 27 | Young Adults = 18 (10 Men and 8 Women) | Older Adults = 9 (5 Men and 4 Women) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean, SD) | 44.77, 19.12 | 33.77, 6.12 | 70.77, 2.85 | ||||
| Sex (% Male) | 65% | 55.55% | 55.55% | ||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Highest degree/Education | Elementary | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Secondary school | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| High school | 2 | 7.40 | 2 | 11.11 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Trade school | 5 | 18.52 | 0 | 0.00 | 5 | 55.56 | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 11 | 40.74 | 8 | 44.44 | 3 | 33.33 | |
| Master’s degree | 8 | 29.63 | 7 | 38.89 | 1 | 11.11 | |
| MD, PhD or higher | 1 | 3.70 | 1 | 5.56 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Residential status | LCA | 3 | 11.11 | 2 | 11.11 | 1 | 11.11 |
| LCWO | 24 | 88.89 | 16 | 88.89 | 8 | 88.89 | |
| RH/AL | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| UR | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Others | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Experience with video games | Daily | 9 | 33.33 | 5 | 27.78 | 4 | 44.44 |
| Twice weekly | 4 | 14.81 | 4 | 22.22 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Weekly | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| 1-2X/month | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| <once/month | 4 | 14.81 | 4 | 22.22 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Few times/year | 6 | 22.22 | 3 | 16.67 | 3 | 33.33 | |
| Never | 4 | 14.81 | 2 | 11.11 | 2 | 22.22 | |
| Duration of video gameplay | <30 min | 6 | 22.22 | 4 | 22.22 | 2 | 22.20 |
| 30 min–1 h | 11 | 40.74 | 7 | 38.89 | 4 | 44.44 | |
| 1–2 h | 2 | 7.41 | 1 | 5.56 | 1 | 11.11 | |
| 2–3 h | 3 | 11.11 | 3 | 16.67 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| ≥4 h | 3 | 11.11 | 3 | 16.67 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Never | 2 | 7.41 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 22.22 | |
| Medical conditions | Cardiovascular | 4 | 14.81 | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 44.44 |
| Haematological | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Musculoskeletal | 1 | 3.70 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 11.11 | |
| Endocrine | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Respiratory | 2 | 7.41 | 2 | 11.11 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Gastrointestinal | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Neurological | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | ||
| Mental, behavioural, or neurodevelopmental disorders | 6 | 22.22 | 6 | 33.33 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Cognitive | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Others | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| None | 9 | 33.33 | 7 | 38.89 | 2 | 22.22 | |
| Not Given | 4 | 14.81 | 3 | 16.67 | 1 | 11.11 | |
| Classifier | Hyperparameter Optimised/Tuned | Range |
|---|---|---|
| RF | classifier__n_estimators | 100, 200, 300 |
| classifier__max_depth | None, 10, 20, 30 | |
| classifier__min_samples_split | 2, 5, 10 | |
| classifier__min_samples_leaf | 1, 2, 4 | |
| classifier__bootstrap | True, False | |
| SVM | classifier__C | 0.1, 1, 10, 100 |
| classifier__gamma | scale, auto | |
| classifier__kernel | rbf, linear |
| Subjects | Sessions | Trials/Session | Epochs/Trial | Epochs/Subject | Total Epochs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 3 | 1 | 120 | 360 | 5760 |
| Friedman Test | χ² | df | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEG index 1 | 5.63 | 2 | 0.060 |
| EEG index 2 | 3.76 | 2 | 0.153 |
| EEG index 3 | 24.16 | 2 | 0.001 |
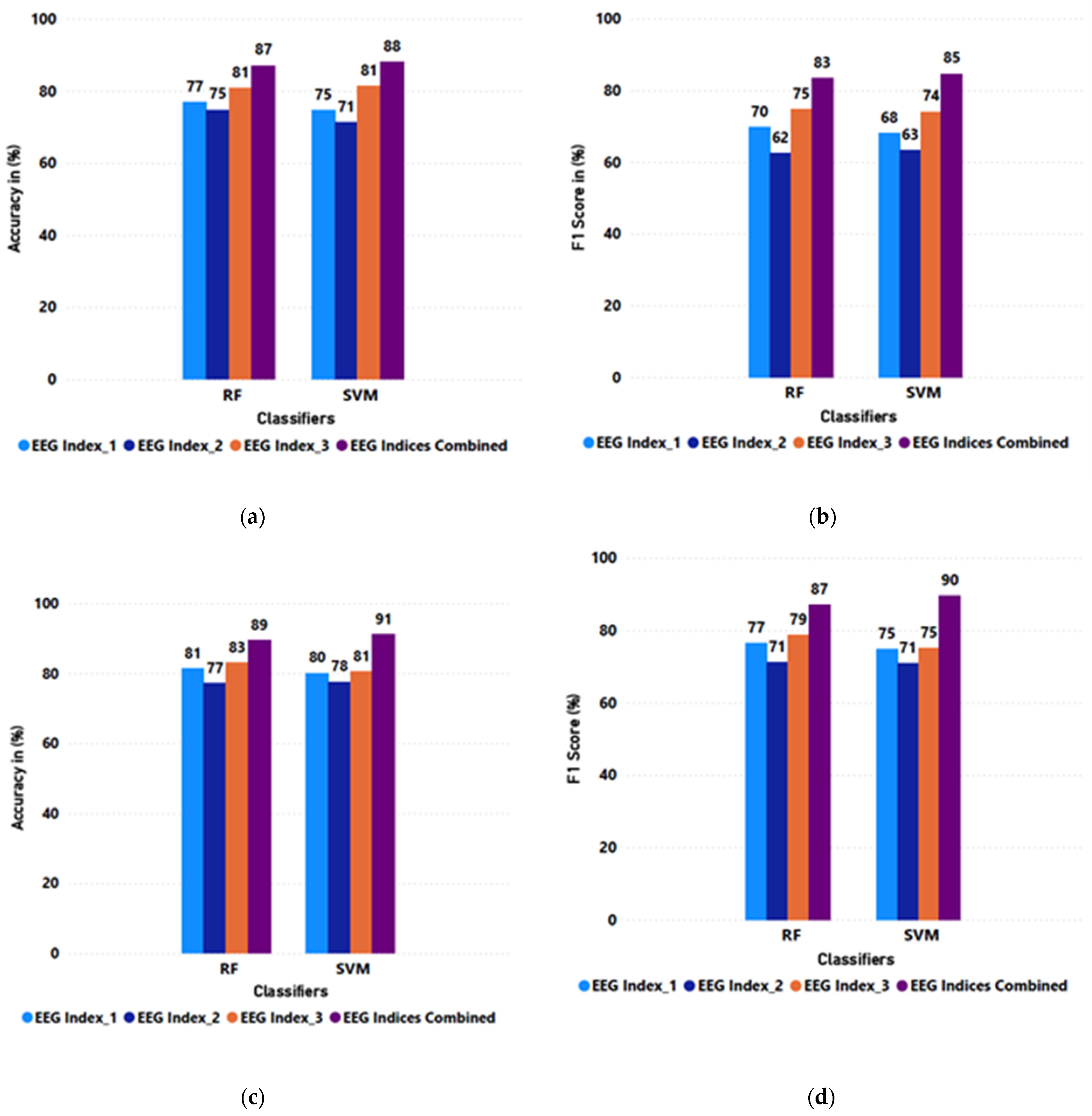
| RF | EEG Index_1 | EEG Index_2 | EEG Index_3 | EEG Indices_ Combined | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject ID | Accuracy | F1 Score | Accuracy | F1 Score | Accuracy | F1 Score | Accuracy | F1 Score |
| #1 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| #2 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| #3 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| #4 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.84 |
| #5 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
| #6 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| #7 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.83 |
| #8 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.80 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| #9 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.69 |
| #10 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 0.78 |
| #11 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.83 |
| #12 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.84 |
| #13 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| #14 | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.86 |
| #15 | 0.83 | 0.8 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| #16 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.74 |
| Mean | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.86 |
| SD | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| SVM | EEG Index_1 | EEG Index_2 | EEG Index_3 | EEG Indices_Combined | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject ID | Accuracy | F1 Score | Accuracy | F1 Score | Accuracy | F1 Score | Accuracy | F1 Score |
| #1 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| #2 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| #3 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
| #4 | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| #5 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
| #6 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| #7 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 0.89 |
| #8 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| #9 | 0.72 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 0.42 | 0.85 | 0.82 |
| #10 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.75 |
| #11 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.91 |
| #12 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| #13 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| #14 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.69 | 0.64 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.90 |
| #15 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.89 |
| #16 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.74 | 0.57 | 0.82 | 0.75 |
| Mean | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.89 |
| SD | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
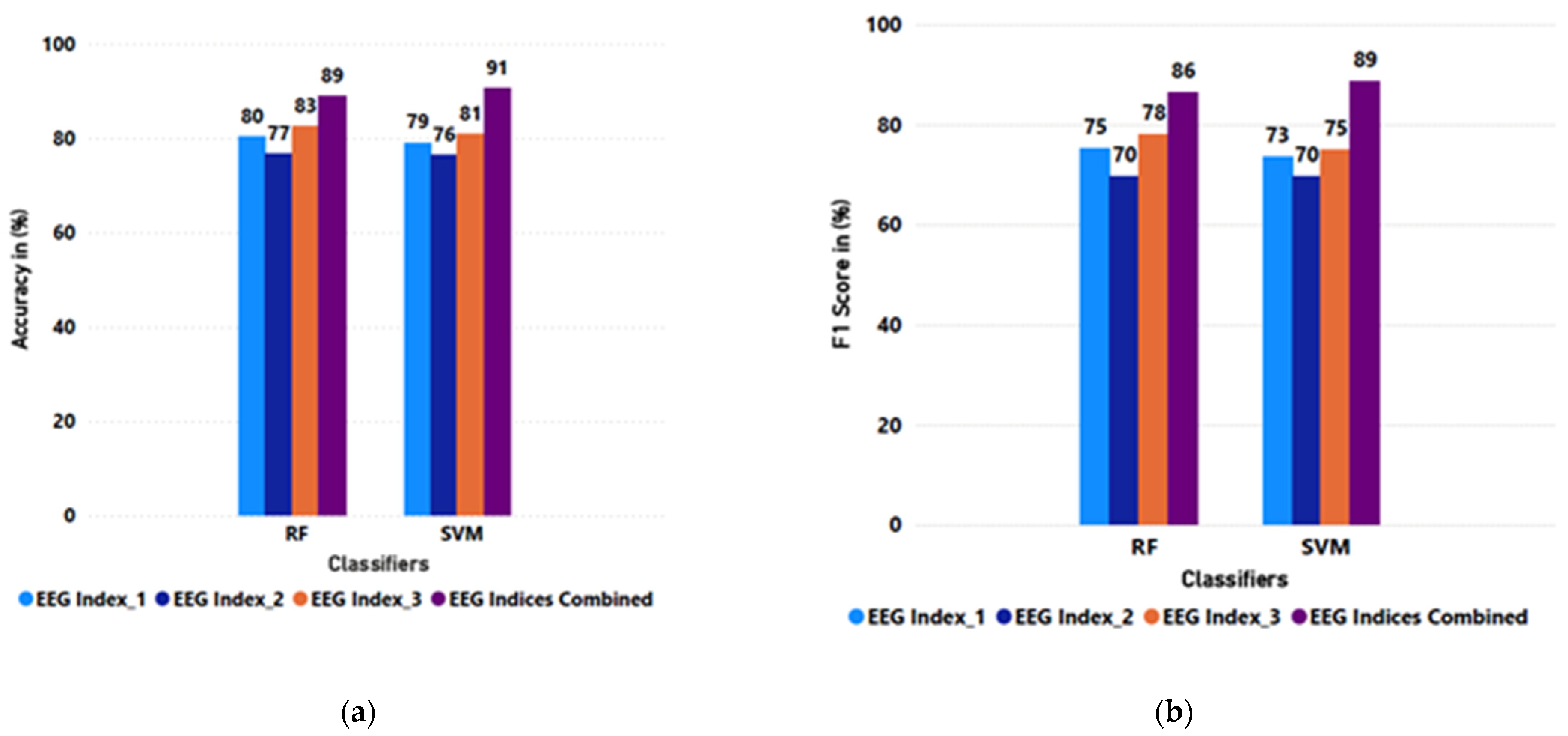
| Accuracy | F1 Score | |
|---|---|---|
| RF | 79 | 78 |
| SVM | 81 | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, Y.; Ferguson-Pell, M.; Adams, K.; Ríos Rincón, A. EEG-Based Engagement Monitoring in Cognitive Games. Sensors 2025, 25, 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072072
Ahmed Y, Ferguson-Pell M, Adams K, Ríos Rincón A. EEG-Based Engagement Monitoring in Cognitive Games. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072072
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Yusuf, Martin Ferguson-Pell, Kim Adams, and Adriana Ríos Rincón. 2025. "EEG-Based Engagement Monitoring in Cognitive Games" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072072
APA StyleAhmed, Y., Ferguson-Pell, M., Adams, K., & Ríos Rincón, A. (2025). EEG-Based Engagement Monitoring in Cognitive Games. Sensors, 25(7), 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072072






