Coffee Bean Characterization Using Terahertz Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
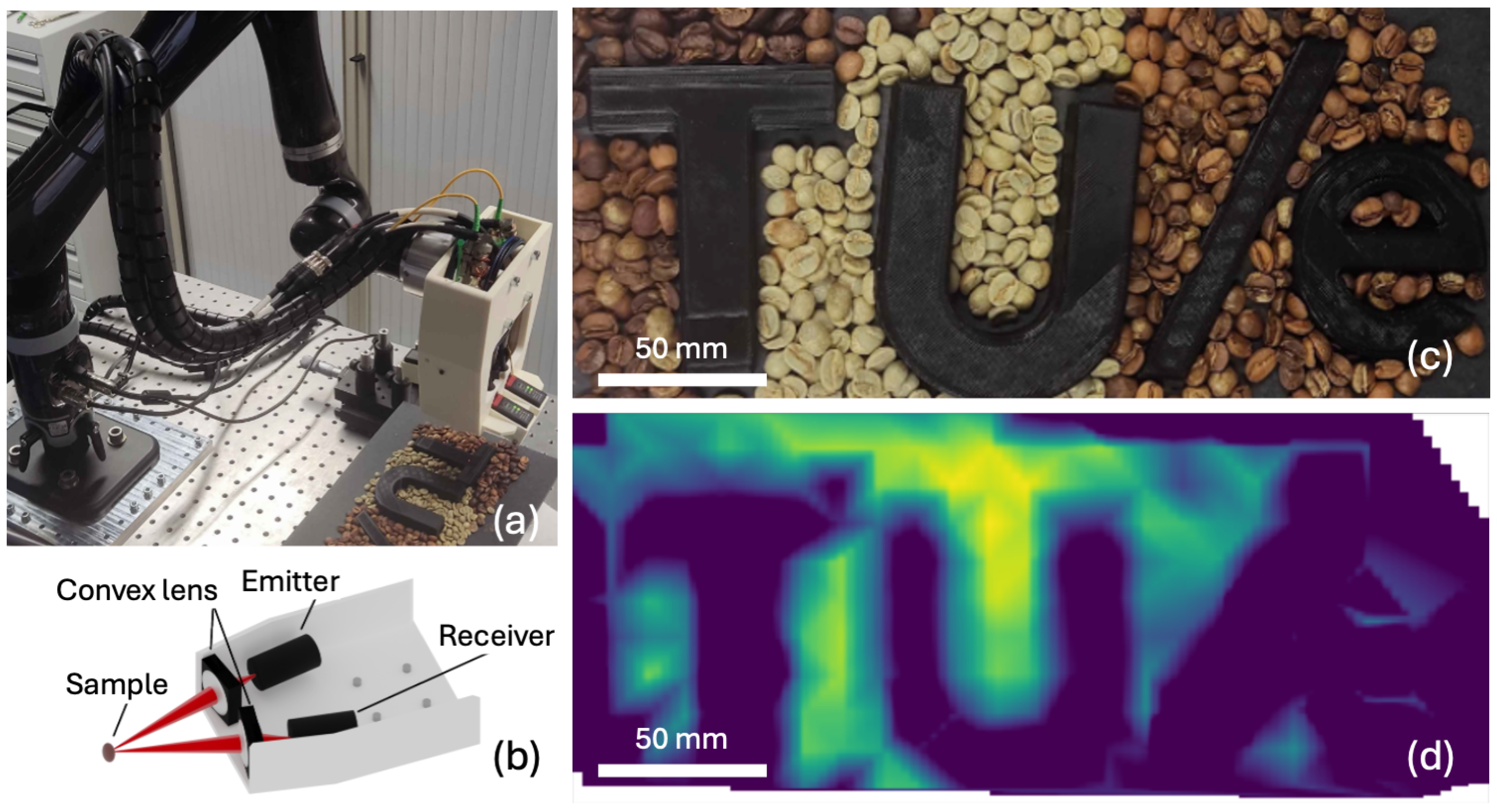
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Optical Properties of Coffee Beans
3.1.1. Time-Domain Transmission
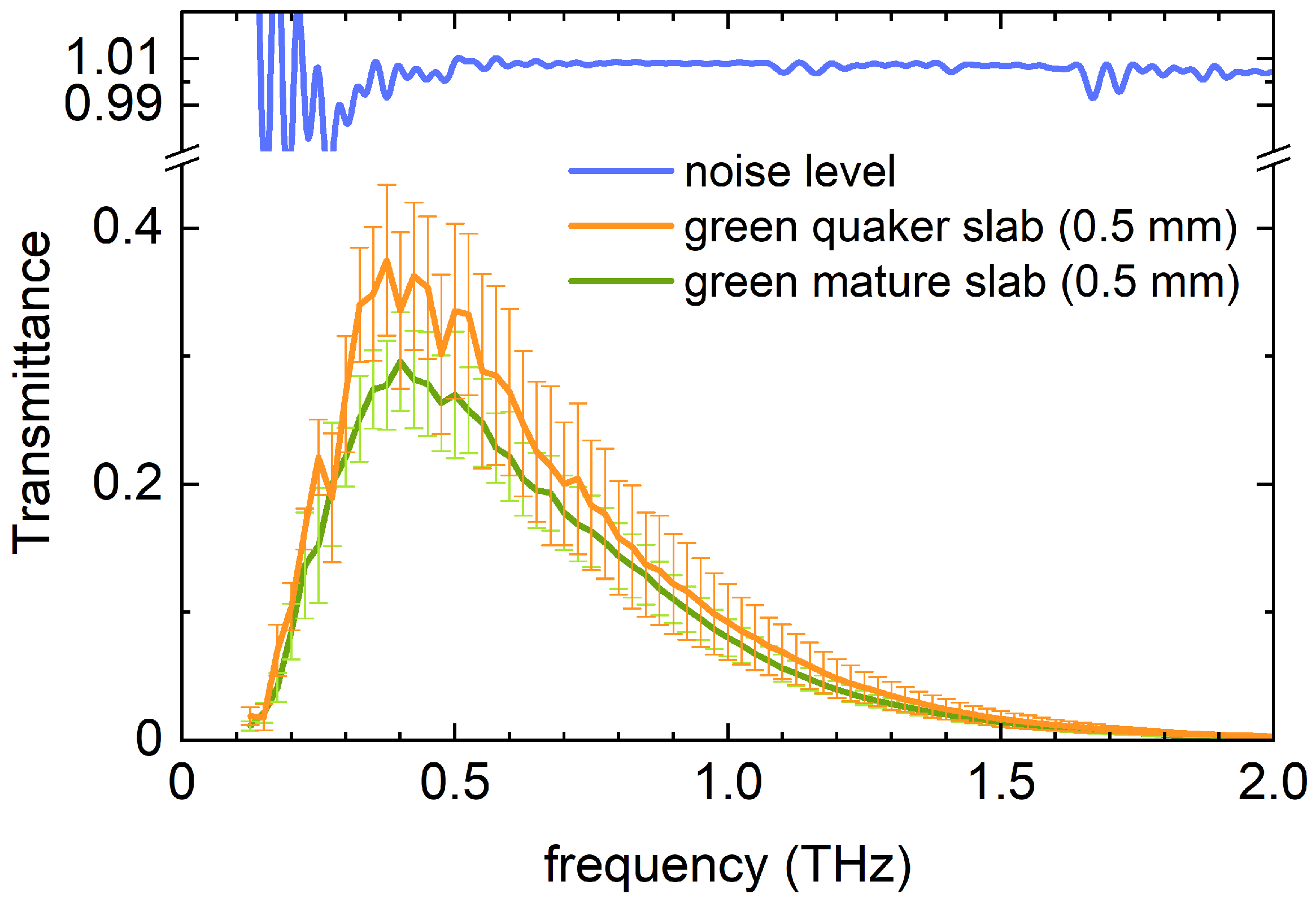
3.1.2. Transmission of Coffee Bean Slabs
3.1.3. Transmission Profile Correlated to Coffee Bean Constituents
3.1.4. Transmission Modeled Using Transfer Matrix Method
3.1.5. Transmission of Whole Coffee Beans
3.1.6. Reflectivity of Coffee Beans
3.1.7. Relevance of Optical Properties of Coffee Beans for Industrial Applications
3.2. Optical Properties of Quaker Beans
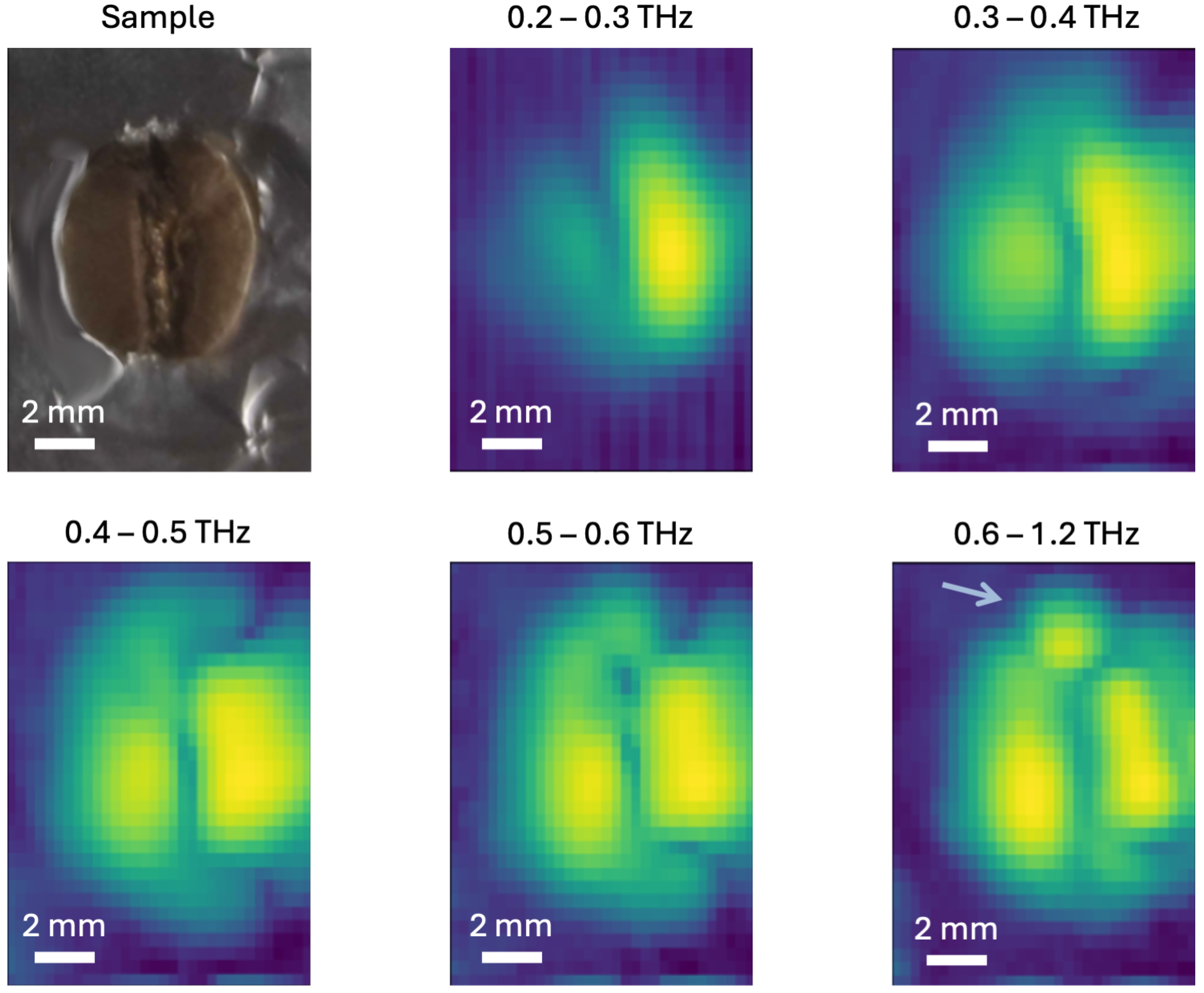
3.3. Terahertz Tomography of Coffee Beans
3.4. Toward the Industrial Sorting of Coffee Beans Using THz Spectroscopy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, E.M.; Leme, D.S.; Barbosa, B.H.G.; Rodarte, M.P.; Pereira, R.G.F.A. A computer vision system for coffee beans classification based on computational intelligence techniques. J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.; Furukawa, J.; Fukai, H.; Tamura, S. Classification of Green Coffee Bean Images Based on Defect Types Using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advanced Informatics, Concepts, Theory, and Applications (ICAICTA), Denpasar, Indonesia, 16–18 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reh, C.; Gerber, A.; Prodolliet, J.; Vuataz, G. Water content determination in green coffee—Method comparison to study specificity and accuracy. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbin, D.F.; Felicio, A.L.D.S.M.; Sun, D.W.; Nixdorf, S.L.; Hirooka, E.Y. Application of infrared spectral techniques on quality and compositional attributes of coffee: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- We recorded zero transmission in the range 400–8000 cm−1 for a green coffee bean slab polished to 0.1 mm using a Vertex 70 FTIR spectrometer. Calibration measurements indicate that T < 10−3, leading to an estimated penetration depth of less than 40 μm.
- Yang, S.; Li, C.; Mei, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, W.; Han, D.; Xu, K. Determination of the Geographical Origin of Coffee Beans Using Terahertz Spectroscopy Combined With Machine Learning Methods. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 680627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Li, B.; Chitrakar, B.; Duan, X. Terahertz Spectroscopic Identification of Roast Degree and Variety of Coffee Beans. Foods 2024, 13, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, N.; Whitworth, M.B.; Grebby, S.; Fisk, I.D. Non-destructive analysis of sucrose, caffeine and trigonelline on single green coffee beans by hyperspectral imaging. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, F. Terahertz spectroscopy of thick and diluted water solutions. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, C.; Hun Kim, J.; Lee, T.; Son, J.H.; Park, Q.H.; Seo, M. Highly sensitive and selective sugar detection by terahertz nano-antennas. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Mechelen, J.L.M.; Frank, A.; Maas, D.J.H.C. Thickness sensor for drying paints using THz spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunkenheimer, P.; Emmert, S.; Gulich, R.; Köhler, M.; Wolf, M.; Schwab, M.; Loidl, A. Electromagnetic-radiation absorption by water. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 062607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.; Candelo-Becerra, J.E.; Hoyos, F. Quality and Defect Inspection of Green Coffee Beans Using a Computer Vision System. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumans, M.; Meulendijks, D.; Middeljans, H.; Peeters, D.; Douma, J.C.; Van Mechelen, D. Physics-assisted machine learning for THz time-domain spectroscopy: Sensing leaf wetness. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumans, M.; Van Mechelen, J.L.M. Physics-based AI methodology for Material Parameter Extraction from Optical Data. In Proceedings of the 2025 50th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Espoo, Finland, 17–22 August 2025; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Dohms, A.; Vieweg, N.; Breuer, S.; Heßelmann, T.; Herda, R.; Regner, N.; Keyvaninia, S.; Gruner, M.; Liebermeister, L.; Schell, M.; et al. Fiber-Coupled THz TDS System with mW-Level THz Power and up to 137-dB Dynamic Range. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, J.F. Review of Moisture and Liquid Detection and Mapping using Terahertz Imaging. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2012, 33, 97–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yan, J.; Chu, J.; Qi, H.; Xu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Gao, J. Accurate prediction of wood moisture content using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 227, 120771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gente, R.; Born, N.; Voß, N.; Sannemann, W.; Léon, J.; Koch, M.; Castro-Camus, E. Determination of Leaf Water Content from Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopic Data. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2013, 34, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Pérez-López, A.V.; Simpson, J.; Castro-Camus, E. Three-dimensional water mapping of succulent Agave victoriae-reginae leaves by terahertz imaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merbold, H.; Maas, D.J.H.C.; Van Mechelen, J.L.M. Multiparameter sensing of paper sheets using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy: Caliper, fiber orientation, moisture, and the role of spatial inhomogeneity. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mechelen, D.v.; Meulendijks, D.; Koumans, M. Coffee Bean Characterization Using Terahertz Sensing. Sensors 2025, 25, 2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072096
Mechelen Dv, Meulendijks D, Koumans M. Coffee Bean Characterization Using Terahertz Sensing. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072096
Chicago/Turabian StyleMechelen, Dook van, Daan Meulendijks, and Milan Koumans. 2025. "Coffee Bean Characterization Using Terahertz Sensing" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072096
APA StyleMechelen, D. v., Meulendijks, D., & Koumans, M. (2025). Coffee Bean Characterization Using Terahertz Sensing. Sensors, 25(7), 2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072096





