Assessing the Diagnostic Validity of Torsobarography in Scoliosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Details
2.2. Instrumentation and Data Acquisition
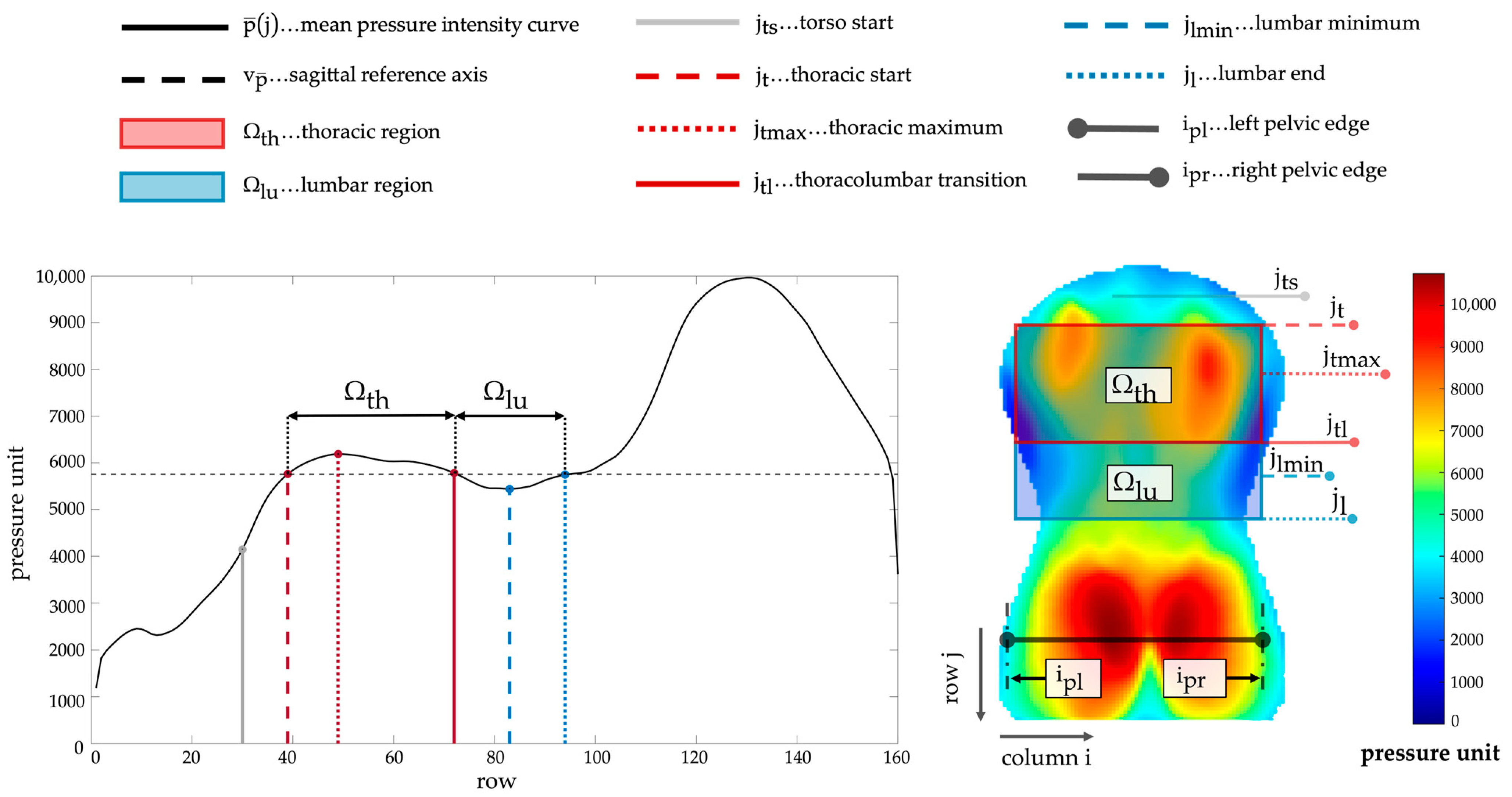
2.3. Preprocessing and Landmark Identification
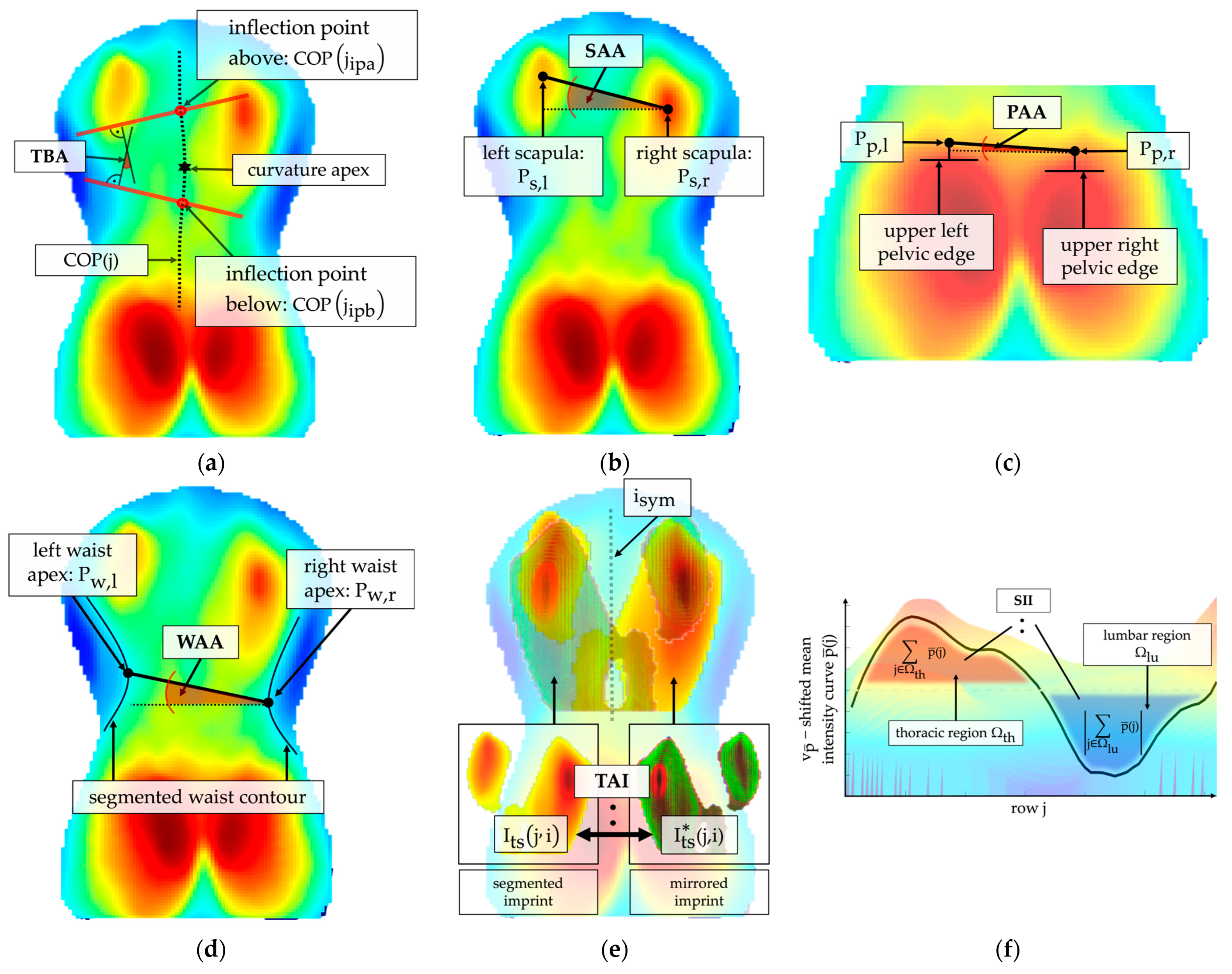
2.4. Index Extraction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Significance Analysis
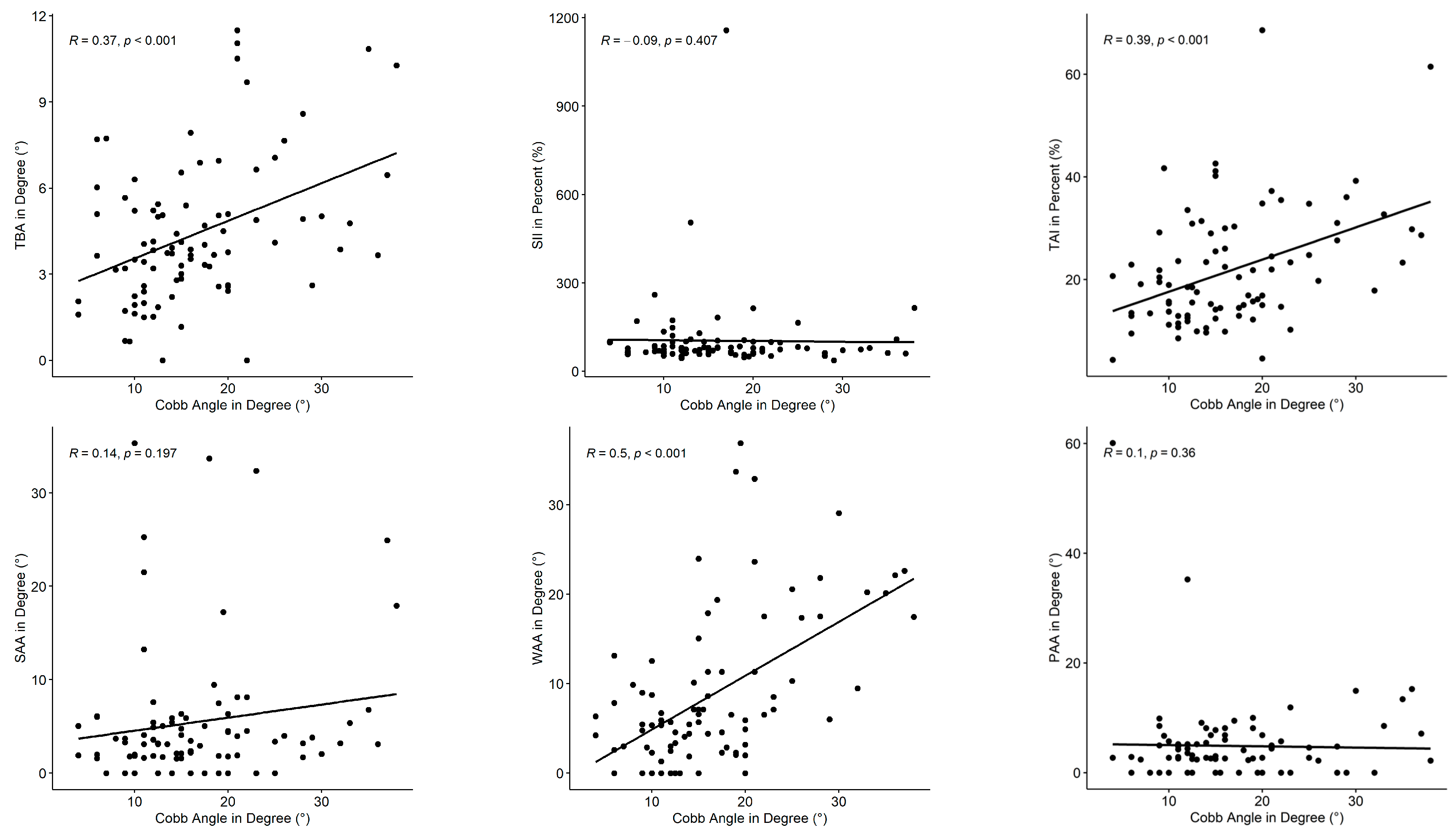
3.2. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Interpretation and Discussion of Implications
4.3. Further Limitations and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis |
| TBA | Torsobarography Angle |
| SII | Sagittal Imbalance Index |
| TAI | Torso Asymmetry Index |
| SAA | Shoulder Asymmetry Angle |
| WAA | Waist Asymmetry Angle |
| PAA | Pelvis Asymmetry Angle |
| COP | Center Of Pressure |
| ES | Effect Size |
References
- Kan, M.M.P.; Negrini, S.; Di Felice, F.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; Donzelli, S.; Zaina, F.; Samartzis, D.; Cheung, E.T.C.; Wong, A.Y.L. Is impaired lung function related to spinal deformities in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? A systematic review and meta-analysis-SOSORT 2019 award paper. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, D.H.R.; Heemskerk, J.L.; Kaçmaz, G.; Altena, M.C.; Reesink, H.J.; Vanhommerig, J.W.; Willigenburg, N.W. Pulmonary function in children and adolescents with untreated idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review with meta-regression analysis. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, C.J.; Kaliszer, M.; Moore, D.P.; Fogarty, E.E.; Dowling, F.E. Surface Topography, Cobb Angles, and Cosmetic Change in Scoliosis. Spine 2001, 26, E55–E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Aulisa, A.G.; Czaprowski, D.; Schreiber, S.; de Mauroy, J.C.; Diers, H.; Grivas, T.B.; Knott, P.; Kotwicki, T.; et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, M.R.; Senyurt, H.; Krauspe, R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, Y.P.; Daures, J.-P.; de Rosa, V.; Diméglio, A. Progression risk of idiopathic juvenile scoliosis during pubertal growth. Spine 2006, 31, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucacos, P.N.; Zacharis, K.; Gelalis, J.; Soultanis, K.; Kalos, N.; Beris, A.; Xenakis, T.; Johnson, E.O. Assessment of curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 1998, 7, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, T.B.; Wade, M.H.; Negrini, S.; O’Brien, J.P.; Maruyama, T.; Hawes, M.C.; Rigo, M.; Weiss, H.R.; Kotwicki, T.; Vasiliadis, E.S.; et al. SOSORT consensus paper: School screening for scoliosis. Where are we today? Scoliosis 2007, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Wright, J.G.; Dobbs, M.B. Effects of bracing in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J.R. Outline for the Study of Scoliosis. In Instructional Course Lectures; The American Academy of Orthopaedics Surgeons: Rosemont, IL, USA, 1948; Volume 5, pp. 261–275. [Google Scholar]
- Patias, P.; Grivas, T.B.; Kaspiris, A.; Aggouris, C.; Drakoutos, E. A review of the trunk surface metrics used as Scoliosis and other deformities evaluation indices. Scoliosis 2010, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznia, A.L.; Hernandez, A.K.; Lee, L.U. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horng, M.-H.; Kuok, C.-P.; Fu, M.-J.; Lin, C.-J.; Sun, Y.-N. Cobb Angle Measurement of Spine from X-Ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019, 2019, 6357171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, P.; Pappo, E.; Cameron, M.; Demauroy, J.; Rivard, C.; Kotwicki, T.; Zaina, F.; Wynne, J.; Stikeleather, L.; Bettany-Saltikov, J.; et al. SOSORT 2012 consensus paper: Reducing x-ray exposure in pediatric patients with scoliosis. Scoliosis 2014, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, F.-J.; Wan, Y.; Mak, K.-C.; Ma, C.-J.; Wang, H.-Q. Cancer and mortality risks of patients with scoliosis from radiation exposure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 3123–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, D.M.; Bonagamba, G.H.; Oliveira, A.S. Scoliometer measurements of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2013, 17, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachalios, T.; Sofianos, J.; Roidis, N.; Sapkas, G.; Korres, D.; Nikolopoulos, K. Ten-Year Follow-Up Evaluation of a School Screening Program for Scoliosis. Spine 1999, 24, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.-K.; Hui, J.H.P.; Rajan, U.; Chia, H.-P. Idiopathic scoliosis in Singapore schoolchildren: A prevalence study 15 years into the screening program. Spine 2005, 30, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.-W.; Modi, H.N.; Yang, J.-H.; Hong, J.-Y. Idiopathic scoliosis in Korean schoolchildren: A prospective screening study of over 1 million children. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendt, L.E.; Ause-Ellias, K.L.; Eybers, J.L.; Wadsworth, C.T.; Nielsen, D.H.; Weinstein, S.L. Validity and reliability testing of the Scoliometer. Phys. Ther. 1990, 70, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, H.; Kokabu, T.; Abe, Y.; Iwata, A.; Yamada, K.; Ito, Y.M.; Iwasaki, N.; Kanai, S. Automated noninvasive detection of idiopathic scoliosis in children and adolescents: A principle validation study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drerup, B. Rasterstereographic measurement of scoliotic deformity. Scoliosis 2014, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, P.; Sturm, P.; Lonner, B.; Cahill, P.; Betsch, M.; McCarthy, R.; Kelly, M.; Lenke, L.; Betz, R. Multicenter Comparison of 3D Spinal Measurements Using Surface Topography With Those From Conventional Radiography. Spine Deform. 2016, 4, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassani, T.; Stucovitz, E.; Galbusera, F.; Brayda-Bruno, M. Is rasterstereography a valid noninvasive method for the screening of juvenile and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabard-Fougère, A.; Bonnefoy-Mazure, A.; Hanquinet, S.; Lascombes, P.; Armand, S.; Dayer, R. Validity and Reliability of Spine Rasterstereography in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2017, 42, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Dong, R.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Y. Reliability and Validity of Scoliosis Measurements Obtained with Surface Topography Techniques: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, F.; Heitmann, K.; Luceri, F.; Donzelli, S.; Zaina, F.; Mangiavini, L.; Negrini, S. Reliability, repeatability and comparison to normal of a set of new stereophotogrammetric parameters to detect trunk asymmetries. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kokabu, T.; Kawakami, N.; Uno, K.; Kotani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Abe, Y.; Maeda, K.; Inage, F.; Ito, Y.M.; Iwasaki, N.; et al. Three-dimensional depth sensor imaging to identify adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čelan, D.; Jesenšek Papež, B.; Poredoš, P.; Možina, J. Laser triangulation measurements of scoliotic spine curvatures. Scoliosis 2015, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzinger, M.; Bernardini, I.; Thevenin Lemoine, C.; Gallini, A.; Accadbled, F.; Sales de Gauzy, J. Monitoring adolescent idiopathic scoliosis by measuring ribs prominence using surface topography device. Spine Deform. 2021, 9, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino-Almero, L.; Mínguez-Rey, M.F.; de Anda, R.M.C.O.; Salvador-Palmer, M.R.; Sentamans-Segarra, S. Correlation between Topographic Parameters Obtained by Back Surface Topography Based on Structured Light and Radiographic Variables in the Assessment of Back Morphology in Young Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2017, 11, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, L.; Durdle, N.G.; Raso, V.J.; Hill, D.L. A support vector machines classifier to assess the severity of idiopathic scoliosis from surface topography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2006, 10, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Hong, Q.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, M. A comparison of foot posture and walking performance in patients with mild, moderate, and severe adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Xie, L.; Xu, J.; Xia, N.; Ma, C.Z.-H. A feasibility study of applying two-dimensional photogrammetry for screening and monitoring of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in clinical practice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecher, N.; Heinke, A.; Żurawski, A.Ł.; Harder, M.R.; Schumann, P.; Jochim, T.; Malberg, H. Torsobarography: Intra-Observer Reliability Study of a Novel Posture Analysis Based on Pressure Distribution. Sensors 2024, 24, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, 8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwicki, T.; Negrini, S.; Grivas, T.B.; Rigo, M.; Maruyama, T.; Durmala, J.; Zaina, F. Methodology of evaluation of morphology of the spine and the trunk in idiopathic scoliosis and other spinal deformities—6th SOSORT consensus paper. Scoliosis 2009, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac-Thiong, J.-M.; Labelle, H.; Charlebois, M.; Huot, M.-P.; de Guise, J.A. Sagittal plane analysis of the spine and pelvis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis according to the coronal curve type. Spine 2003, 28, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlén, G.; Aaro, S.; Bylund, P. The Sagittal Configuration and Mobility of the Spine in Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 1988, 13, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, I.A. Axial rotation component of thoracic scoliosis. J. Orthop. Res. 1989, 7, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabjek, K.F.; Leroux, M.A.; Coillard, C.; Prince, F.; Rivard, C.H. Postural characteristics of adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2008, 28, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, S.; Aubin, C.-E.; Sangole, A.P.; Labelle, H.; Parent, S.; Mac-Thiong, J.-M. Three-dimensional spinopelvic relative alignment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2014, 39, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, I.J.R.L.; Da Rosa, B.N.; Candotti, C.T. Anatomical reference marks, evaluation parameters and reproducibility of surface topography for evaluating the adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Gait Posture 2019, 69, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamalas, A.; Bagó, J.; D Agata, E.; Pellisé, F. Validity and reliability of photographic measures to evaluate waistline asymmetry in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3170–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S. A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, C.O.; Morris, P.E.; Richler, J.J. Effect size estimates: Current use, calculations, and interpretation. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2012, 141, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.-S.; Moon, B.G.; Kang, H.I.; Kim, J.H.; Jwa, C.; Kim, D.R. Difference in the Cobb Angle Between Standing and Supine Position as a Prognostic Factor After Vertebral Augmentation in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Neurospine 2022, 19, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, G. Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: Can Cobb Angle on a Supine Posteroanterior Radiograph Be Used to Predict the Cobb Angle in a Standing Position? Medicine 2016, 95, e2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klos, S.S.; Liu, X.-C.; Lyon, R.M.; Tassone, J.C.; Thometz, J.G. Reliability of a functional classification system in the monitoring of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2007, 32, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, I.A.; Armstrong, J.G.; Moreland, M.S. Spinal deformity and back surface asymmetry in idiopathic scoliosis. J. Orthop. Res. 1988, 6, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrani, M.; Kirdeikis, R.; Igwe, P.; Hill, D.; Adeeb, S. Surface reconstruction of torsos with and without scoliosis. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2200–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlösser, T.P.C.; Castelein, R.M.; Grobost, P.; Shah, S.A.; Abelin-Genevois, K. Specific sagittal alignment patterns are already present in mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Ou, W.; Gao, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Kang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Digital measurement and correlation analysis of coronal and sagittal anatomic parameters in the radiographs of adolescent patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevillotte, T.; Coudert, P.; Cawley, D.; Bouloussa, H.; Mazas, S.; Boissière, L.; Gille, O. Influence of posture on relationships between pelvic parameters and lumbar lordosis: Comparison of the standing, seated, and supine positions. A preliminary study. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-A.; Kwak, D.-S.; Cho, H.-J.; Min, D.-U. Changes of spinopelvic parameters in different positions. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohndorf, J.; Stecher, N.; Heinke, A.; Malberg, H. Experimental determination of the transmission behavior of a pressure sensor array for torsobarography in posture analysis. In Proceedings of the AUTOMED 2024 Proceedings, Villingen-Schwenningen, Germany, 11–13 September 2024; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No Scoliosis | Mild Scoliosis | Moderate Scoliosis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cobb < 10° | 10° ≤ Cobb < 20° | 20° ≤ Cobb < 40° | |||||
| UNIT | MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | |
| Age | Years | 12.5 | 1.8 | 13.8 | 2.7 | 14.2 | 2.3 |
| Weight | kg | 46.8 | 12.8 | 53.1 | 13.4 | 52.3 | 12.8 |
| Height | cm | 158 | 15 | 164 | 13 | 164 | 11 |
| BMI | 18.5 | 2.4 | 19.5 | 3.4 | 19.1 | 3.0 | |
| Cobb angle | ° | 7.1 | 1.9 | 14.0 | 2.9 | 26.2 | 6.0 |
| Sex | Total Female:male | 13 (8:5) | 49 (27:22) | 25 (16:9) | |||
| Index | Symbol | Unit | Description | Corresponding Clinical Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torsobarography angle | TBA | ° | Maximum angle between the two tangents at the inflection points of the frontal curve | Abnormal lateral spinal curvature |
| Sagittal imbalance index | SII | % | Ratio of summed pressure in the thoracic region to summed pressure in the lumbar region | Sagittal imbalance |
| Torso asymmetry index | TAI | % | Summation of the percentage differences between the torso imprint and the mirrored torso imprint | Torso asymmetry induced by muscle tone asymmetry or structural changes (e.g., rib hump, lumbar bulge) |
| Shoulder asymmetry angle | SAA | ° | Angle between the localized scapula centers | Asymmetric shoulders |
| Waist asymmetry angle | WAA | ° | Angle between both waist apices | Asymmetric waist |
| Pelvis asymmetry angle | PAA | ° | Angle between both midpoints of the detected upper pelvic edges | Pelvic obliquity |
| Index | No Scoliosis | Mild Scoliosis | Moderate Scoliosis | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNIT | MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | MEAN | SD | ||
| TBA | ° | 3.76 | 2.47 | 3.74 | 1.63 | 6.02 | 3.23 | 0.031 |
| SII | % | 97.44 | 56.70 | 113.01 | 166.55 | 88.56 | 45.23 | n.s. |
| TAI | % | 19.14 | 9.36 | 18.82 | 8.78 | 28.57 | 14.18 | 0.012 |
| SAA | ° | 2.98 | 2.00 | 5.71 | 7.91 | 6.21 | 7.72 | n.s. |
| WAA | ° | 5.31 | 3.87 | 6.84 | 7.93 | 14.32 | 8.87 | 0.002 |
| PAA | ° | 0.92 | 0.86 | 1.04 | 1.47 | 2.04 | 2.67 | n.s. |
| Index | Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Value | ES |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBA | No scoliosis | Mild scoliosis | n.s. | 0.02 |
| No scoliosis | Moderate scoliosis | n.s. | 0.37 | |
| Mild scoliosis | Moderate scoliosis | 0.023 | 0.34 | |
| TAI | No scoliosis | Mild scoliosis | n.s. | −0.03 |
| No scoliosis | Moderate scoliosis | n.s. | 0.36 | |
| Mild scoliosis | Moderate scoliosis | 0.005 | 0.40 | |
| WAA | No scoliosis | Mild scoliosis | n.s. | 0.02 |
| No scoliosis | Moderate scoliosis | 0.026 | 0.46 | |
| Mild scoliosis | Moderate scoliosis | 0.001 | 0.44 |
| Index | Spearman’s ρ | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| TBA | 0.37 | <0.001 |
| SII | −0.09 | 0.407 |
| TAI | 0.39 | <0.001 |
| SAA | 0.14 | 0.197 |
| WAA | 0.50 | <0.001 |
| PAA | 0.10 | 0.360 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stecher, N.; Richter, L.; Żurawski, A.Ł.; Heinke, A.; Harder, M.R.; Jochim, T.; Schumann, P.; Kiebzak, W.P.; Malberg, H. Assessing the Diagnostic Validity of Torsobarography in Scoliosis. Sensors 2025, 25, 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082485
Stecher N, Richter L, Żurawski AŁ, Heinke A, Harder MR, Jochim T, Schumann P, Kiebzak WP, Malberg H. Assessing the Diagnostic Validity of Torsobarography in Scoliosis. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082485
Chicago/Turabian StyleStecher, Nico, Lea Richter, Arkadiusz Łukasz Żurawski, Andreas Heinke, Maximilian Robert Harder, Thurid Jochim, Paula Schumann, Wojciech Piotr Kiebzak, and Hagen Malberg. 2025. "Assessing the Diagnostic Validity of Torsobarography in Scoliosis" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082485
APA StyleStecher, N., Richter, L., Żurawski, A. Ł., Heinke, A., Harder, M. R., Jochim, T., Schumann, P., Kiebzak, W. P., & Malberg, H. (2025). Assessing the Diagnostic Validity of Torsobarography in Scoliosis. Sensors, 25(8), 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082485







