AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for the Sensitive Detection of Trace Lead (II) in Water Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles
2.3. Fabrication of AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion/GCE
2.3.1. Electrode Pre-Treatment
2.3.2. Modification with CeO2/Nafion Composite
2.3.3. Electrodeposition of AgNPs
2.4. Electrochemical Testing
2.5. Water Sample Preparation
3. Results
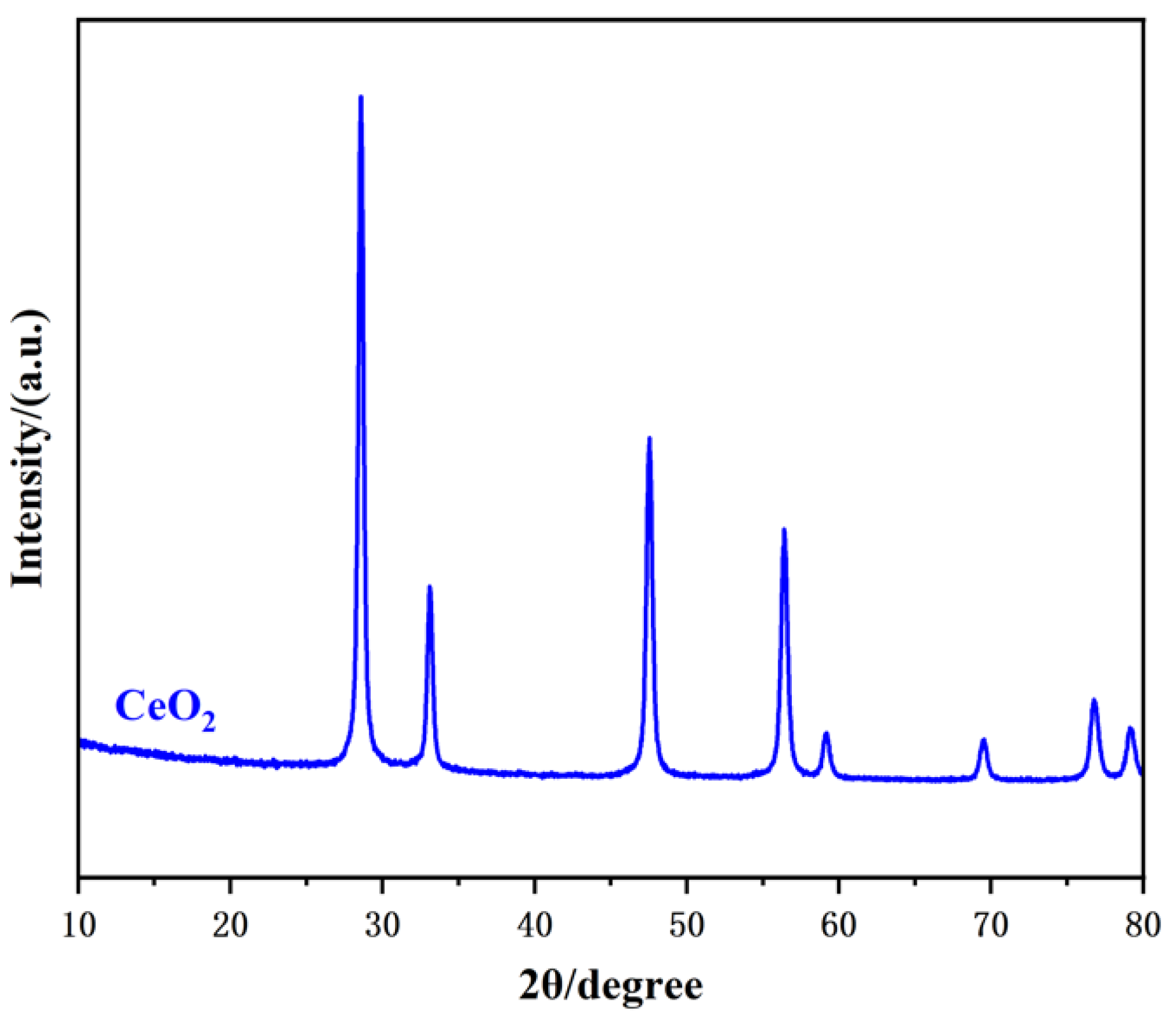
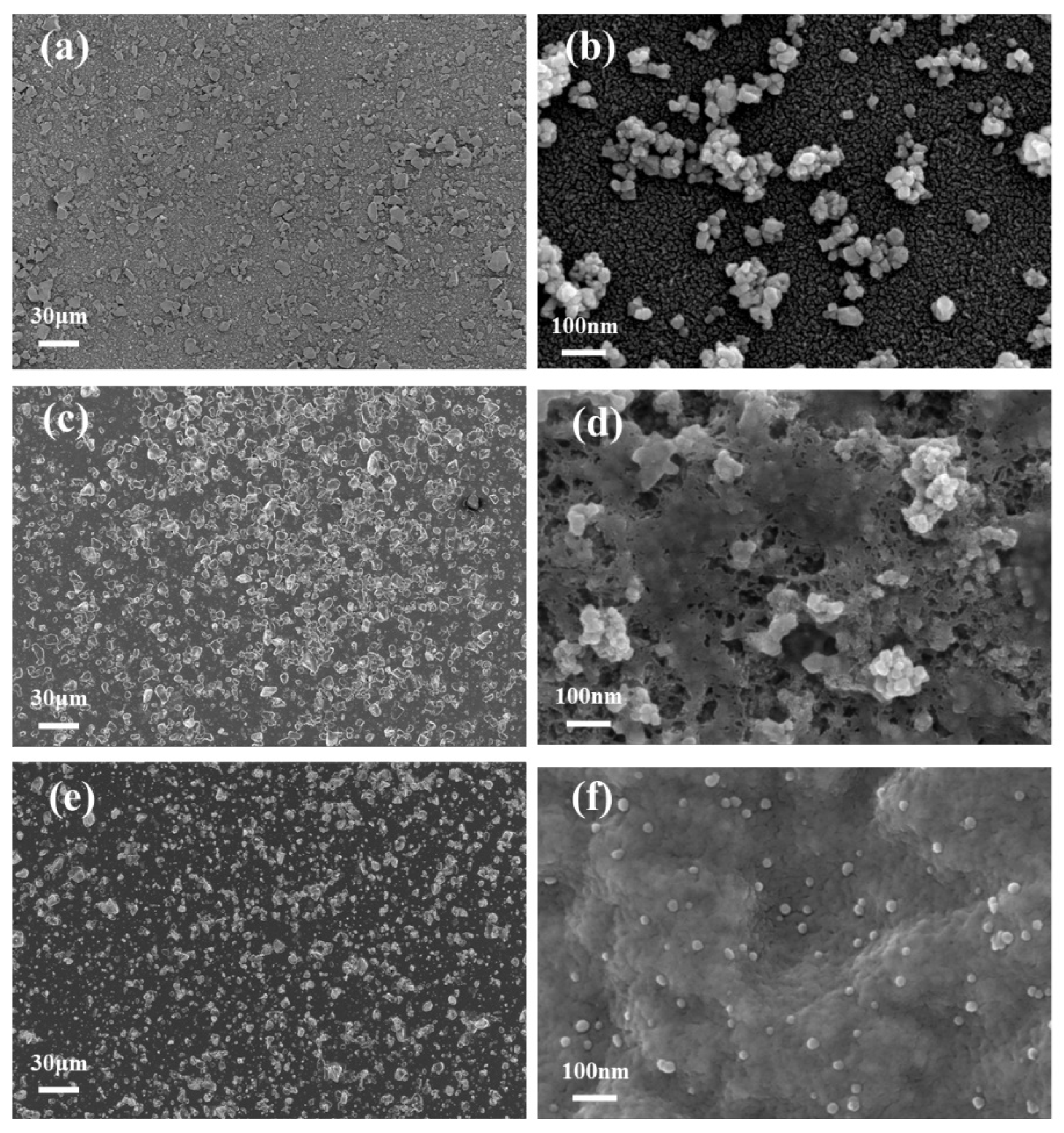
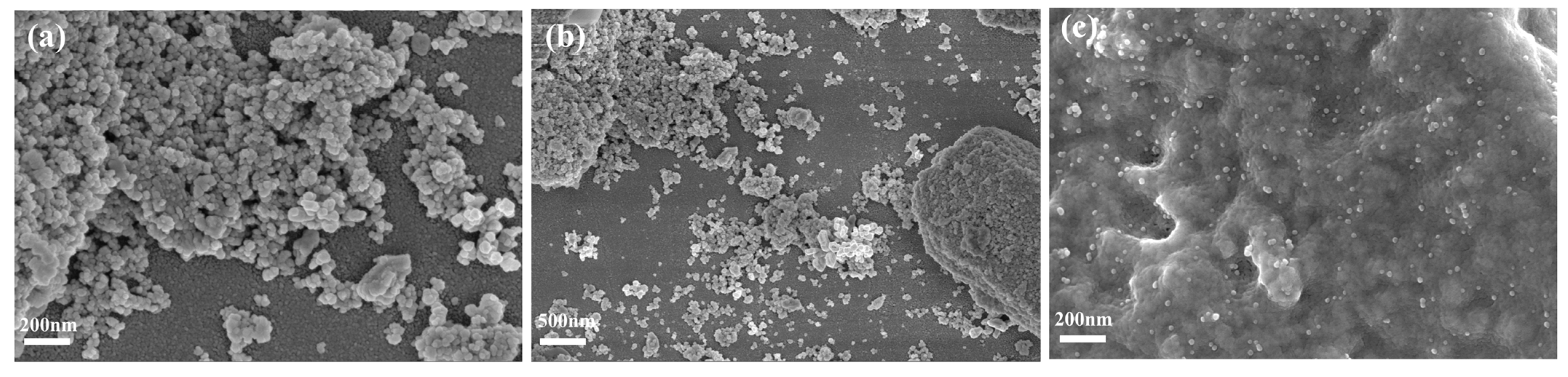
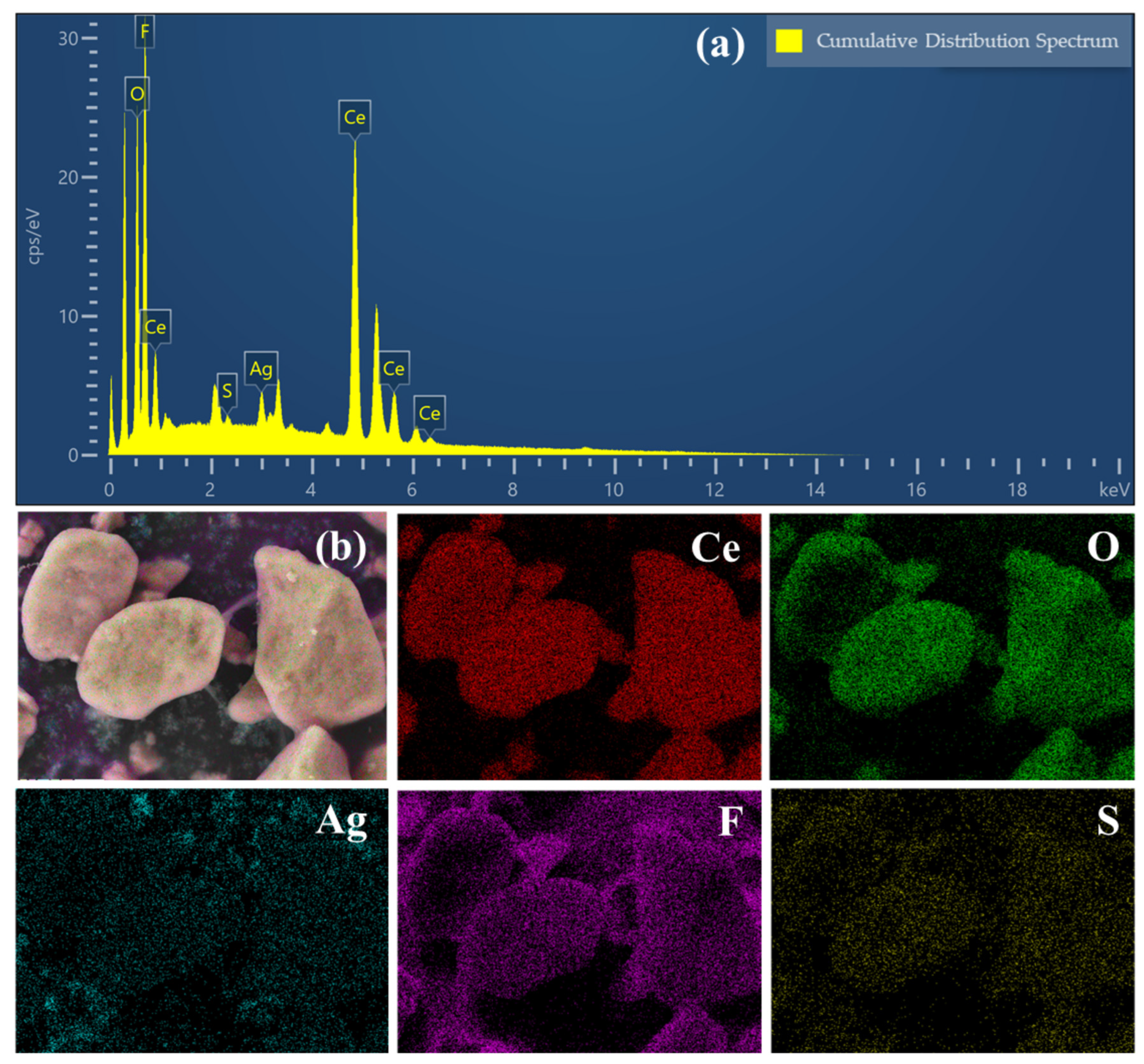
3.1. Characterization of Electrode Materials
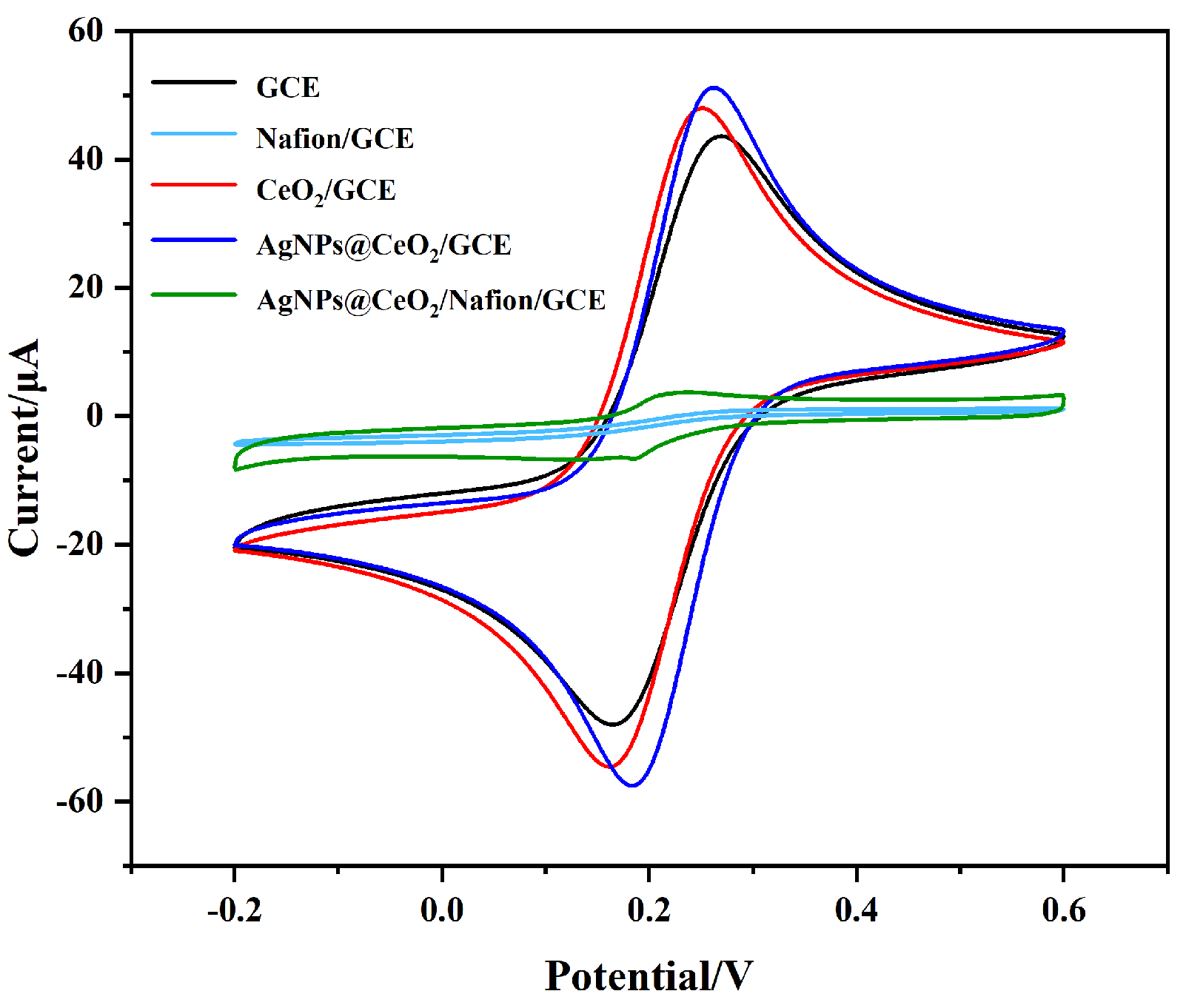
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Modified Electrodes
3.3. Detection of Pb2+ with Modified Electrodes
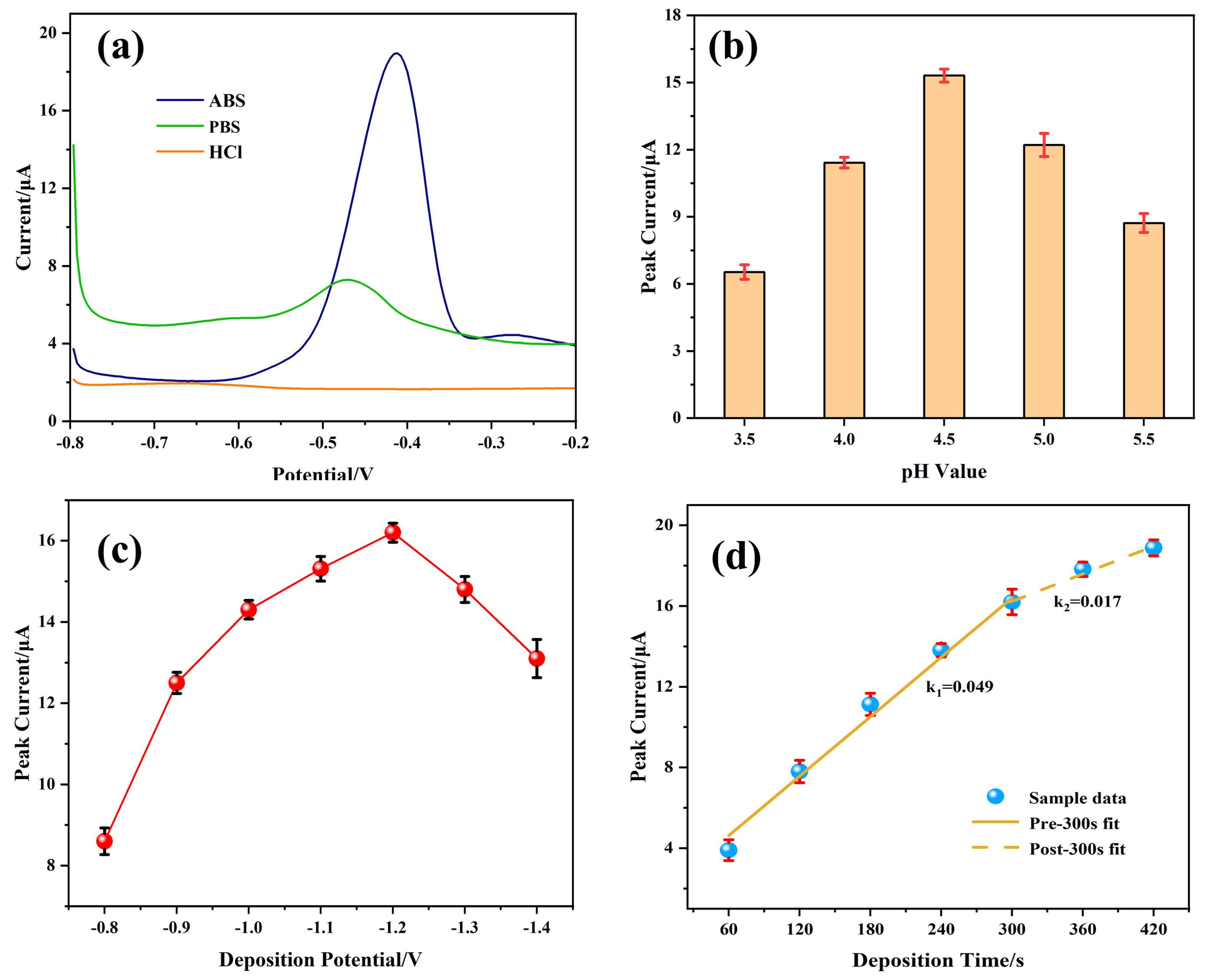
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.4.1. Preparation Conditions of the Modified Electrode
3.4.2. Testing Conditions of the Modified Electrode
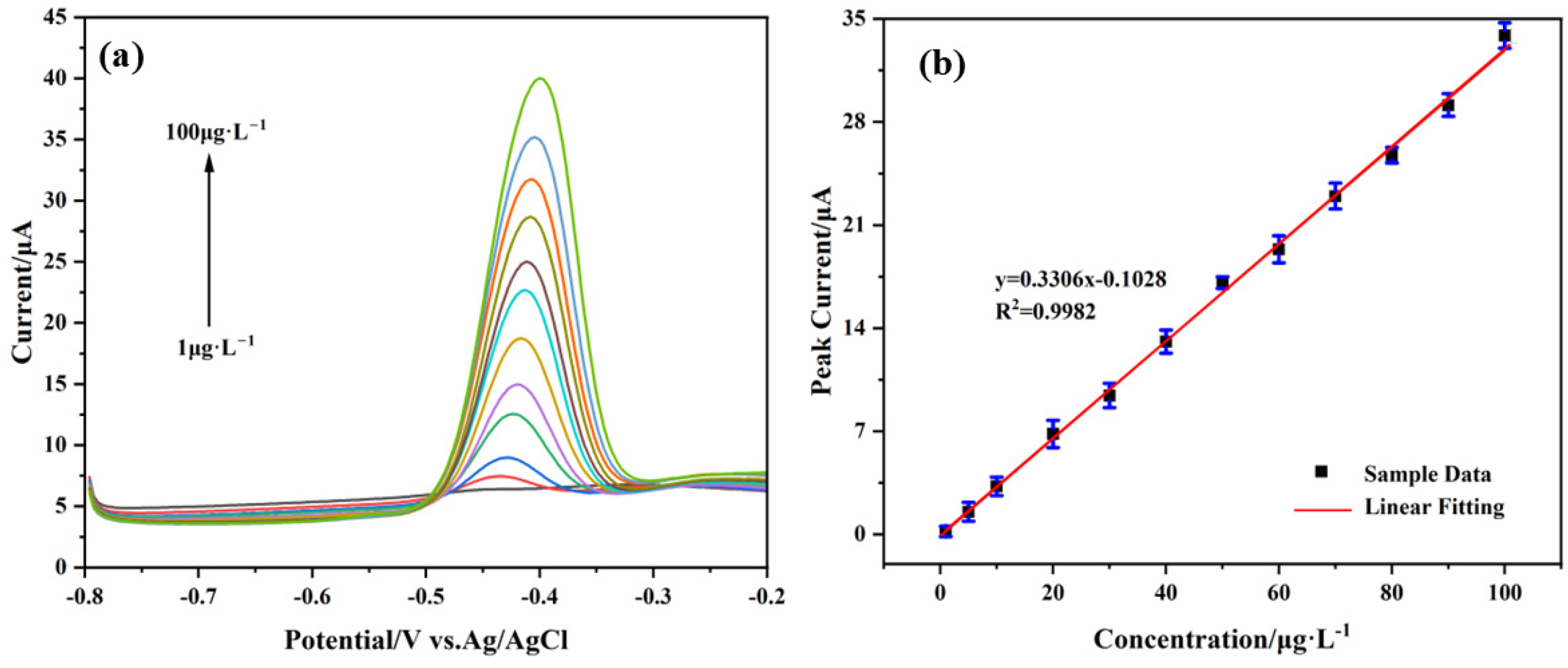
3.5. Analytical Performance
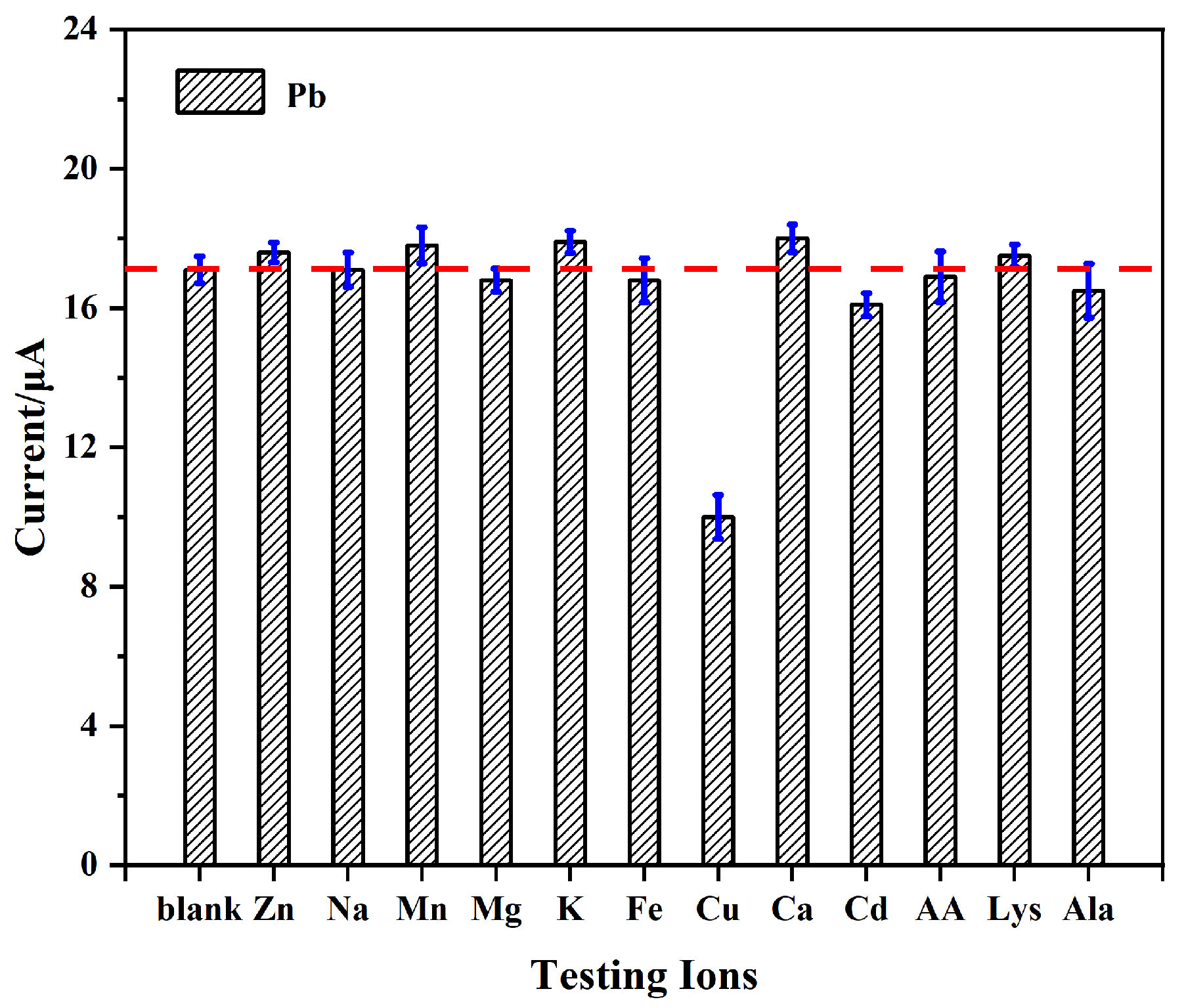
3.6. Anti-Interference, Repeatability, and Reproducibility Studies
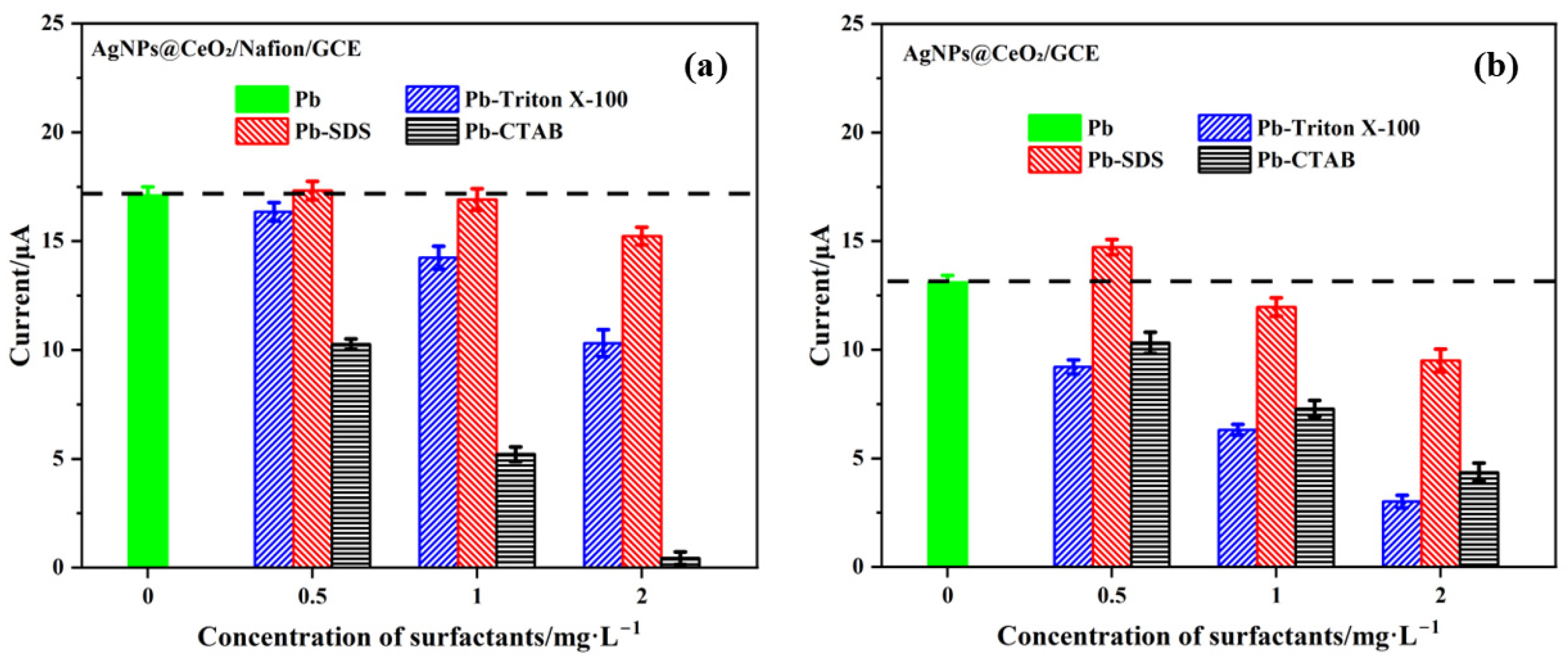
3.6.1. Anti-Interference Capability
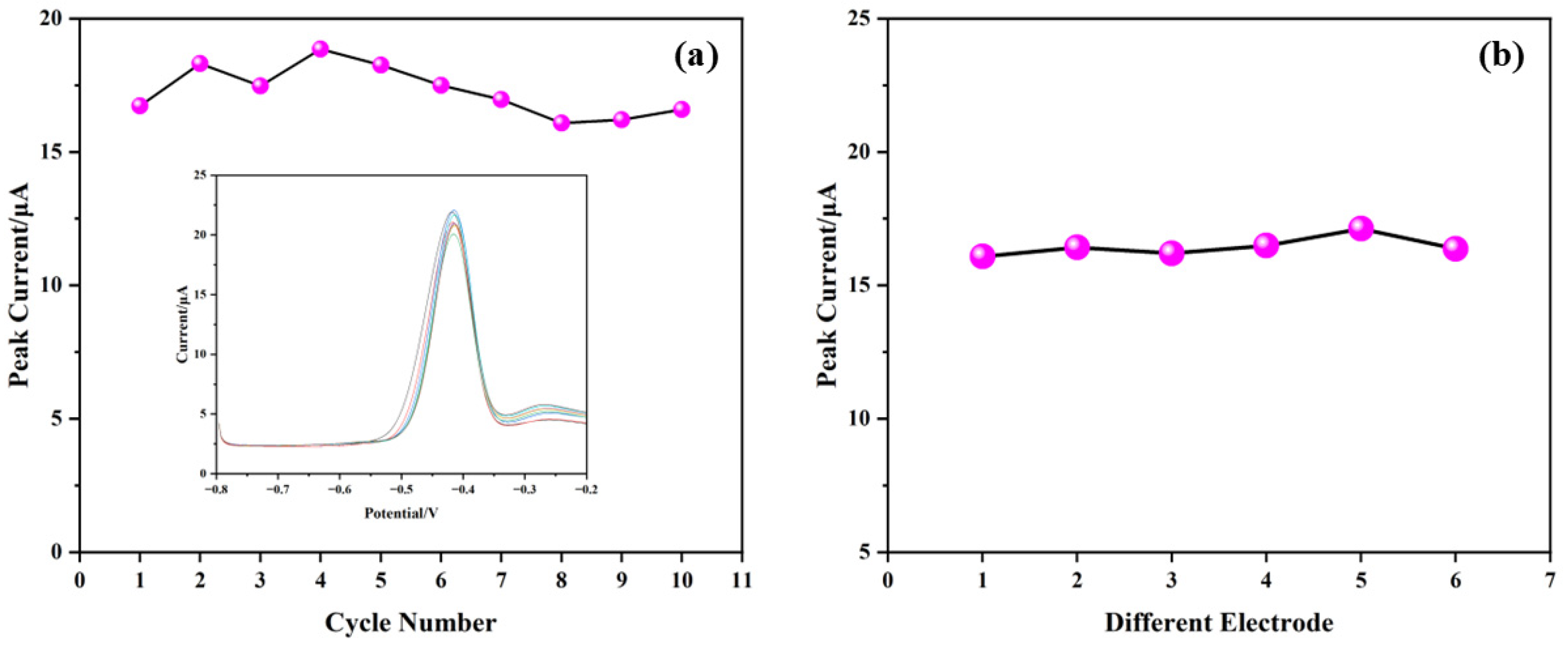
3.6.2. Repeatability and Reproducibility
3.7. Analysis of Real Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luby, S.P.; Forsyth, J.E.; Fatmi, Z.; Rahman, M.; Sultana, J.; Plambeck, E.L.; Miller, N.G.; Bendavid, E.; Winch, P.J.; Hu, H.; et al. Removing lead from the global economy. Lancet Planet. Health 2024, 8, e966–e972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmich, F.; Lock, G. Burton’s Line from Chronic Lead Intoxication. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, J.; Landrigan, D.B. It’s Time to End Lead Poisoning in the United States. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Davis, K.P.; Bogen, D.L.; Watkins, S.M. Blood Lead Testing and Follow-up Testing Among Children Hospitalized for Lead Poisoning. Pediatrics 2024, 154, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ye, X.; Zheng, X. Analysis of Blood Lead Levels and Risk Factors for Lead Poisoning in Children Aged 1–7 Years in Wenzhou City from 2018 to 2022. Chin. J. Public Health Manag. 2023, 39, 560–564. [Google Scholar]
- Londonio, A.; Morzán, E.; Smichowski, P. Determination of toxic and potentially toxic elements in rice and rice-based products by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 284, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Qian, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z. Direct Ultratrace Detection of Lead in a Single Hair Using Portable Electromagnetic Heating Vaporization-Atmospheric Pressure Glow Discharge-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14701–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, B.; He, M.; Hu, B. Switchable solvent based liquid phase microextraction of trace lead and cadmium from environmental and biological samples prior to graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry detection. Microchem. J. 2018, 139, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytlakowska, K.; Kocot, K.; Hachuła, B.; Pilch, M.; Wrzalik, R.; Zubko, M. Determination of heavy metal ions by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry using reduced graphene oxide decorated with molybdenum disulfide as solid adsorbent. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2020, 167, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Chen, L.; Haijun, W.; Chuanlai, X.; Hua, K. Electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions in water. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 7215–7231. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, H. Enhancing Trace Pb2+ Detection via Novel Functional Materials for Improved Electrocatalytic Redox Processes on Electrochemical Sensors: A Short Review. Catalysts 2024, 14, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, Z.; Abid, K.; Iannazzo, D.; Montazerozohori, M.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Corsaro, C.; Neri, G. Lead ion (Pb2+) electrochemical sensors based on novel Schiff base ligands. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2024, 10, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Karimi-Maleh, H. In situ synthesis of label-free electrochemical aptasensor-based sandwich-like AuNPs/PPy/Ti3C2Tx for ultrasensitive detection of lead ions as hazardous pollutants in environmental fluids. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, A.; Mansha, M.; Ullah, N. Nanomaterials-based electrochemical detection of heavy metals in water: Current status, challenges and future direction. Trends Anal. Chem. TrAC 2018, 105, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthiraj, K.; Karthikeyan, B. Synthesis and characterization of cerium oxide nanoparticles using different solvents for electrochemical applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2020, 126, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, F.; Wei, Y.; Yang, M. Ruthenium-loaded cerium dioxide nanocomposites with rich oxygen vacancies promoted the highly sensitive electrochemical detection of Hg(II). Sens. Actuators B 2020, 320, 128355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Dai, R.; Liu, X.; Weerasooriya, R.; Hong, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y. New strategy for fabricating Cd(II) sensing electrochemical interface based on enhanced adsorption followed by redox processes: Ferro-cerium oxide nanocomposite as an example. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 829, 154551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.H.; Rahale, C.S.; Prasanthrajan, M.; Girija, S.; Wilson, J.; Sharmila, D.J.; Saranya, N.; Maragatham, S. Eco-friendly synthesis of nanoceria using orange peel extract for electrochemical detection of selective cadmium ions. Microchem. J. 2024, 202, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Pankaj, A.; Mishra, S.; Tewari, K.; Singh, S.P. Cerium oxide-catalyzed chemical vapor deposition grown carbon nanofibers for electrochemical detection of Pb(II) and Cu(II). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanišević, I. The Role of Silver Nanoparticles in Electrochemical Sensors for Aquatic Environmental Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Ahmed, F.M.; Mohamed, L.Z.; Selim, A.M. Mechanochemical enhancement in electrode materials via silver-embedded reduced graphene oxide and cobalt oxide nanostructure for supercapacitor applications. Ionics 2024, 30, 1735–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płócienniczak, P.; Rȩbiś, T.; Nowicki, M.; Milczarek, G. A green approach for hybrid material preparation based on carbon nanotubes/lignosulfonate decorated with silver nanostructures for electrocatalytic sensing of H2O2. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 880, 114896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Tan, Q.; Li, C.; Shang, L.; Zhang, D.; Lu, X.; Qiu, F. Silver/silver halide supported on mesoporous ceria particles and photo-CWPO degradation under visible light for organic compounds in acrylonitrile wastewater. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26791–26799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, A.A.; Labis, J.P.; Alam, M.; Ramay, S.M.; Ahmed, N.; Mahmood, A. Preparation and Spectroscopic, Microscopic, Thermogravimetric, and Electrochemical Characterization of Silver-Doped Cerium(IV) Oxide Nanoparticles. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Balani, K.; Dhami, N.K. Atomic force microscopic investigations of transient early-stage bacterial adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver and ceria modified bioactive glass. J. Mater. Res. 2024, 39, 2415–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzaij, J.M. A Novel Room-Temperature Nitrogen Dioxide Gas Sensor Based on Silver-Doped Cerium Oxide Thin Film. Sens. Actuators A 2023, 363, 114748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, F.B.; Rafique, S.; Akram, R.A.; Hussain, M.; Bashir, S.; Nasir, R.; Khan, J. A simple, sensitive, label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on the chitosan-coated silver/cerium oxide (CS@Ag/CeO2) nanocomposites for the detection of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 265501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Alam, M.; Ali, M.A. Nanostructured CeO2:Ag platform for electrochemically sensitive detection of nitrophenol. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2021, 613, 126116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, B.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X. Electrochemical sensor construction based on Nafion/calcium lignosulphonate functionalized porous graphene nanocomposite and its application for simultaneous detection of trace Pb2+ and Cd2+. Sens. Actuators B. 2018, 259, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, J. Simultaneous determination of trace Cd(II) and Pb(II) based on Bi/Nafion/reduced graphene oxide-gold nanoparticle nanocomposite film-modified glassy carbon electrode by one-step electrodeposition. Ionics 2017, 23, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Dubovyk, V.; Guo, M.; Zhu, G.; Ran, Q.; Zhao, H. Electrochemical sensing platform based on graphitized and carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with cerium oxide nanoparticles for sensitive detection of methyl parathion. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 3738–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Xiang, X.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Zong, E. Cerium oxide nanoparticle functionalized lignin as a nano-biosorbent for efficient phosphate removal. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, L.; Dong, S. Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of horseradish peroxidase immobilized in Nafion-RTIL composite film. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 9, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, P.; Liu, J.; Jin, L. Sensitive Voltammetric Detection of Trace Heavy Metals in Real Water Using Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes/Nafion Composite Film Electrode. Chin. J. Chem. 2011, 29, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jia, J.; Wang, J. Simultaneous determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry based on graphite nanofibers-Nafion composite modified bismuth film electrode. Talanta 2010, 83, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, G. A carbon-supported BiSn nanoparticles based novel sensor for sensitive electrochemical determination of Cd (II) ions. Talanta 2019, 202, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J. Preparation and Application of Bismuth/MXene Nano-Composite as Electrochemical Sensor for Heavy Metal Ions Detection. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y. A Fe-OSA/Nafion composite film-decorated glassy carbon electrode as a sensor for detection of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II). Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5618–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Wang, R.; Bai, X.; Li, S.; Meng, P.; Luo, L. Research on Improvement of Detection of Pb2+ in Environment Waters by Graphene/Nafion Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. ECS Adv. 2023, 2, 030505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Luo, Z.; Peng, X.; Fang, J.; Zhao, J. Leaf-Like ZIF-Derived Zinc-Cobalt Layered Double Hydroxide@Cerium Dioxide Nanosphere Heterostructure/Nickel Foam Composite Electrode for the Detection of Lead Ions in the Environment. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 037519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, P.; Chen, J.; Senthil Kumar, A.; Feng, S.P.T. High index facets-Ag nanoflower enabled efficient electrochemical detection of lead in blood serum and cosmetics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 878, 114657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antil, M.; Bansod, B.S. An innovative strategy for the quantification of the lead ions using platinum nanoparticles combined with gold substrate electrochemical sensor. Microchem. J. 2025, 212, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I.; Efstathiou, C.E. Lithographically fabricated disposable bismuth-film electrodes for the trace determination of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta. 2008, 53, 5294–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colozza, N.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Effects of Humidity, Temperature and Bismuth Electrodeposition on Electroanalytical Performances of Nafion-coated Printed Electrodes for Cd2+ and Pb2+ Detection. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeng, L.; Xing, S.; Xian, Y.; Shi, G. Ultrasensitive voltammetric detection of trace lead(II) and cadmium(II) using MWCNTs-nafion/bismuth composite electrodes. Electroanalysis 2009, 20, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia-Caridade, C.; Pauliukaite, R.; Brett, C.M.A. Influence of Nafion coatings and surfactant on the stripping voltammetry of heavy metals at bismuth-film modified carbon film electrodes. Electroanalysis 2007, 18, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrodes | Technique | Linear Range (μg·L−1) | Detection Limit (μg·L−1) | Repeatability (RSD%) | Reproducibility (RSD%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene/Nafion/GCE | DPASV | 4.14–5000 | 1.06 | 2.0 (n a = 5) | N/A b | [39] |
| Bi/Nafion/RGO-GNPs/GCE | SWASV | 1–90 | 0.12 | 1.25 (n = 6) | N/A | [30] |
| Fe-OSA/Nafion GCE | DPASV | 8.3–2776 | 1.5 | N/A | N/A | [38] |
| ZnCo ZLDH@CeO2/NF | DPASV | 21–6200 | 1.9 | N/A | N/A | [40] |
| AgNF@GCE | SWASV | 10–700 | 0.74 | 2.8 (n = 8) | N/A | [41] |
| Nafion/CLS/PGR/GCE | DPASV | 10–1000 | 2.1 | 3.63 (n = 8) | 3.85 (n = 8) | [29] |
| PtNPs/Au | SWV | 21~104 | 10 | 0.6 | N/A | [42] |
| AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion/GCE | SWASV | 1–100 | 0.17 | 5.46 (n = 10) | 2.2 (n = 6) | This work |
| Samples | Added (μg·L−1) | Found by Proposed Method a (μg·L−1) | Found by ICP-MS a (μg·L−1) | Recovery b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 0 | N.D. | N.D. | — |
| 10 | 11.03 ± 0.57 | 9.89 ± 0.42 | 110.3 | |
| 20 | 21.26 ± 0.69 | 20.79 ± 0.31 | 106.3 | |
| Xiangjiang River | 0 | 3.73 ± 0.36 | 3.54 ± 0.16 | — |
| 10 | 13.89 ± 0.51 | 14.07 ± 0.29 | 101.6 | |
| 20 | 22.57 ± 0.42 | 23.98 ± 0.24 | 94.2 | |
| Rainwater | 0 | 1.85 ± 0.76 | 2.01 ± 0.39 | — |
| 10 | 12.64 ± 0.42 | 12.33 ± 0.23 | 107.9 | |
| 20 | 21.03 ± 0.53 | 22.17 ± 0.27 | 95.9 | |
| Mineral water | 0 | N.D. | N.D. | — |
| 10 | 10.06 ± 0.43 | 9.91 ± 0.38 | 100.6 | |
| 20 | 18.73 ± 0.64 | 21.02 ± 0.26 | 93.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Xu, P.; Zhou, S.; Wu, R. AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for the Sensitive Detection of Trace Lead (II) in Water Samples. Sensors 2025, 25, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092655
Guo Z, Xu P, Zhou S, Wu R. AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for the Sensitive Detection of Trace Lead (II) in Water Samples. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092655
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhengying, Peng Xu, Shiqing Zhou, and Ruoxi Wu. 2025. "AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for the Sensitive Detection of Trace Lead (II) in Water Samples" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092655
APA StyleGuo, Z., Xu, P., Zhou, S., & Wu, R. (2025). AgNPs@CeO2/Nafion Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode for the Sensitive Detection of Trace Lead (II) in Water Samples. Sensors, 25(9), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092655







