Adenosine Receptor Agonists Increase the Inhibition of Platelet Function by P2Y12 Antagonists in a cAMP- and Calcium-Dependent Manner
Abstract
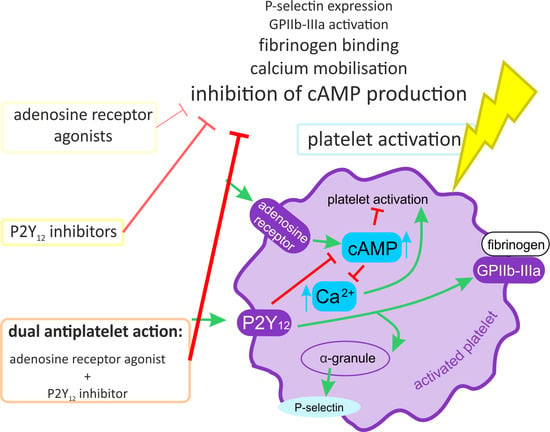
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Combined Effect of Adenosine Receptor Agonists and P2Y12 Antagonists Increases the Inhibition of P-Selectin Expression
2.2. The Combined Action of Adenosine Receptor Agonists and P2Y12 Antagonists Increases the Inhibition of GPIIb-IIIa Activation and the Inhibition of Fibrinogen Binding
2.3. The Combined Action of Adenosine Receptor Agonists and P2Y12 Antagonists Increases the Inhibition of Calcium Flux
2.4. The Combined Action of Adenosine Receptor Agonists and P2Y12 Antagonists on cAMP Level
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Chemical Solutions Preparation
4.3. Blood Donors
4.4. Platelet Viability Assay
4.5. P-Selectin Expression and GPIIb-IIIa Activation
4.6. Binding of Exogenous Fibrinogen
4.7. VASP-P Measurement
4.8. Calcium Mobilization
4.9. cAMP
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaplan, Z.S.; Jackson, S.P. The role of platelets in atherothrombosis. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2011, 2011, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patrono, C.; Morais, J.; Baigent, C.; Collet, J.P.; Fitzgerald, D.; Halvorsen, S.; Rocca, B.; Siegbahn, A.; Storey, R.F.; Vilahur, G. Antiplatelet agents for the treatment and prevention of coronary atherothrombosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1760–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozalski, M.; Boncler, M.; Luzak, B.; Watala, C. Genetic factors underlying differential blood platelet sensitivity to inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kupka, D.; Sibbing, D. P2Y12 receptor inhibitors: An evolution in drug design to prevent arterial thrombosis. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqi, Y.; Müller, C.E. Antithrombotic P2Y12 receptor antagonists: Recent developments in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Johnston, S.C.; Bath, P.M.; Grotta, J.C.; Pan, Y.; Amarenco, P.; Wang, Y.; Simon, T.; Kim, J.S.; Jeng, J.-S.; et al. Acute dual antiplatelet therapy for minor ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack. BMJ 2019, 364, l895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serebruany, V.L.; Pokov, A.N.; Fortmann, S.D.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. Disbalance between mortality and non-fatal vascular events in the champion-phoenix trial: The cangrelor efficacy challenge. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 111, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watala, C.; Ulicna, O.; Golanski, J.; Nocun, M.; Waczulikova, I.; Markuszewski, L.; Drzewoski, J. High glucose contributes to aspirin insensitivity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: A multiparametric aggregation study. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2006, 17, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.F.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine receptors as drug targets--what are the challenges? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine receptors as drug targets. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston-Cox, H.A.; Ravid, K. Adenosine and blood platelets. Purinergic Signal 2011, 7, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, E.; Pereira, J.; Mezzano, D.; Alarcon, M.; Caballero, J.; Palomo, I. Inhibition of platelet activation and thrombus formation by adenosine and inosine: Studies on their relative contribution and molecular modeling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolska, N.; Rozalski, M. Blood platelet adenosine receptors as potential targets for anti-platelet therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A. Recent developments in adenosine receptor ligands and their potential as novel drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 1290–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Born, G.V.R. Strong inhibition by 2-chloroadenosine of the aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Nature 1964, 202, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristalli, G.; Vittori, S.; Thompson, R.D.; Padgett, W.L.; Shi, D.; Daly, J.W.; Olsson, R.A. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by adenosine receptor agonists. N-S Arch. Pharmacol. 1994, 349, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristalli, G.; Volpini, R.; Vittori, S.; Camaioni, E.; Monopoli, A.; Conti, A.; Dionisotti, S.; Zocchi, C.; Ongini, E. 2-alkynyl derivatives of adenosine-5′-n-ethyluronamide: Selective a2 adenosine receptor agonists with potent inhibitory activity on platelet aggregation. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Fuentes, M.; Caballero, J.; Palomo, I.; Hinz, S.; El-Tayeb, A.; Müller, C.E. Adenosine a2a receptor agonists with potent antiplatelet activity. Platelets 2018, 29, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncler, M.; Wzorek, J.; Wolska, N.; Polak, D.; Watala, C.; Rozalski, M. Adenosine receptor agonists deepen the inhibition of platelet aggregation by P2Y12 antagonists. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2019, 113, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, S.; Mittal, A.; Kumar, P.; Alhayani, D.M.; Al-Aboudi, A. Therapeutic potential of agonists and antagonists of a1, a2a, a2b and a3 adenosine receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, N.; Boncler, M.; Polak, D.; Wzorek, J.; Przygodzki, T.; Gapinska, M.; Watala, C.; Rozalski, M. Adenosine receptor agonists exhibit anti-platelet effects and the potential to overcome resistance to P2Y12 receptor antagonists. Molecules 2019, 25, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rywaniak, J.; Luzak, B.; Podsedek, A.; Dudzinska, D.; Rozalski, M.; Watala, C. Comparison of cytotoxic and anti-platelet activities of polyphenolic extracts from arnica montana flowers and juglans regia husks. Platelets 2015, 26, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, M.R.; Vance, C.O.; Morschl, E.; Wilson, C.N. Adenosine receptors and inflammation. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 193, 215–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero, M.E. Purinoceptors in inflammation: Potential as anti-inflammatory therapeutic targets. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 2172–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasko, G.; Linden, J.; Cronstein, B.; Pacher, P. Adenosine receptors: Therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and immune diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.; Gao, Z.-G. Adenosine receptors as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valgimigli, M.; Bueno, H.; Byrne, R.A.; Collet, J.P.; Costa, F.; Jeppsson, A.; Juni, P.; Kastrati, A.; Kolh, P.; Mauri, L.; et al. 2017 esc focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with eacts: The task force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the european society of cardiology (esc) and of the european association for cardio-thoracic surgery (eacts). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 213–260. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, N.A.; McIntosh, M.; Garofolo, F.; Wong, E.; Shwajch, A.; Kennedy, M.; Young, M.; Sarkar, P.; Kawabata, K.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Determination of the active and inactive metabolites of prasugrel in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Scior, T. Adenosine receptors and their modulators. Pharm. Acta Helv. 1993, 68, 77–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Feoktistov, I.; Hollister, A.S.; Robertson, D.; Biaggioni, I. Adenosine inhibits the rise in intracellular calcium and platelet aggregation produced by thrombin: Evidence that both effects are coupled to adenylate cyclase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1990, 37, 870–875. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, S.; Brito, R.; Mukherjea, D.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Adenosine receptors: Expression, function and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2024–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deuther, C.; Peter, B.; Martin, E.L.; Matthias, J.B.; Sven, E.; Jürgen, S.; Gennady, G.Y.; Christa, E.M.; Alexander Pfeifer, T.G.; Saskia, S.; et al. Adenosine activates brown adipose tissue and recruits beige adipocytes via a2a receptors. Nature 2014, 516, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Van Calker, D.; Muller, M.; Hamprecht, B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic amp in cultured brain cells. J. Neurochem. 1979, 33, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpini, R.; Dal Ben, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Taffi, S.; Vittori, S.; Klotz, K.-N.; Cristalli, G. N6 -methoxy-2-alkynyladenosine derivatives as highly potent and selective ligands at the human a3 adenosine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Theoret, J.F.; Yacoub, D.; Hachem, A.; Gillis, M.A.; Merhi, Y. P-selectin ligation induces platelet activation and enhances microaggregate and thrombus formation. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullard, J.F. The role of the platelet glycoprotein iib/iiia in thrombosis and haemostasis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.S. Platelet-fibrinogen interactions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 936, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davlouros, P.; Xanthopoulou, I.; Mparampoutis, N.; Giannopoulos, G.; Deftereos, S.; Alexopoulos, D. Role of calcium in platelet activation: Novel insights and pharmacological implications. Med. Chem. 2016, 12, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Noe, L.; Peeters, K.; Izzi, B.; Van Geet, C.; Freson, K. Regulators of platelet camp levels: Clinical and therapeutic implications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2897–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S.; Ongini, E.; Borea, P.A. A(2a) adenosine receptors in human peripheral blood cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aszodi, A.; Pfeifer, A.; Ahmad, M.; Glauner, M.; Zhou, X.H.; Ny, L.; Andersson, K.E.; Kehrel, B.; Offermanns, S.; Fassler, R. The vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (vasp) is involved in cgmp- and camp-mediated inhibition of agonist-induced platelet aggregation, but is dispensable for smooth muscle function. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawicki, D.D.; Agarwal, K.C.; Parks, R.E., Jr. Potentiation of the antiplatelet action of adenosine in whole blood by dipyridamole or dilazep and the camp phosphodiesterase inhibitor, ra 233. Thromb. Res. 1986, 43, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Gupta, M. Adenosine and its receptors as therapeutic targets: An overview. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolska, N.; Kassassir, H.; Luzak, B.; Watala, C.; Rozalski, M. Adenosine Receptor Agonists Increase the Inhibition of Platelet Function by P2Y12 Antagonists in a cAMP- and Calcium-Dependent Manner. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080177
Wolska N, Kassassir H, Luzak B, Watala C, Rozalski M. Adenosine Receptor Agonists Increase the Inhibition of Platelet Function by P2Y12 Antagonists in a cAMP- and Calcium-Dependent Manner. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(8):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080177
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolska, Nina, Hassan Kassassir, Boguslawa Luzak, Cezary Watala, and Marcin Rozalski. 2020. "Adenosine Receptor Agonists Increase the Inhibition of Platelet Function by P2Y12 Antagonists in a cAMP- and Calcium-Dependent Manner" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 8: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080177
APA StyleWolska, N., Kassassir, H., Luzak, B., Watala, C., & Rozalski, M. (2020). Adenosine Receptor Agonists Increase the Inhibition of Platelet Function by P2Y12 Antagonists in a cAMP- and Calcium-Dependent Manner. Pharmaceuticals, 13(8), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080177