The Protective Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) on Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
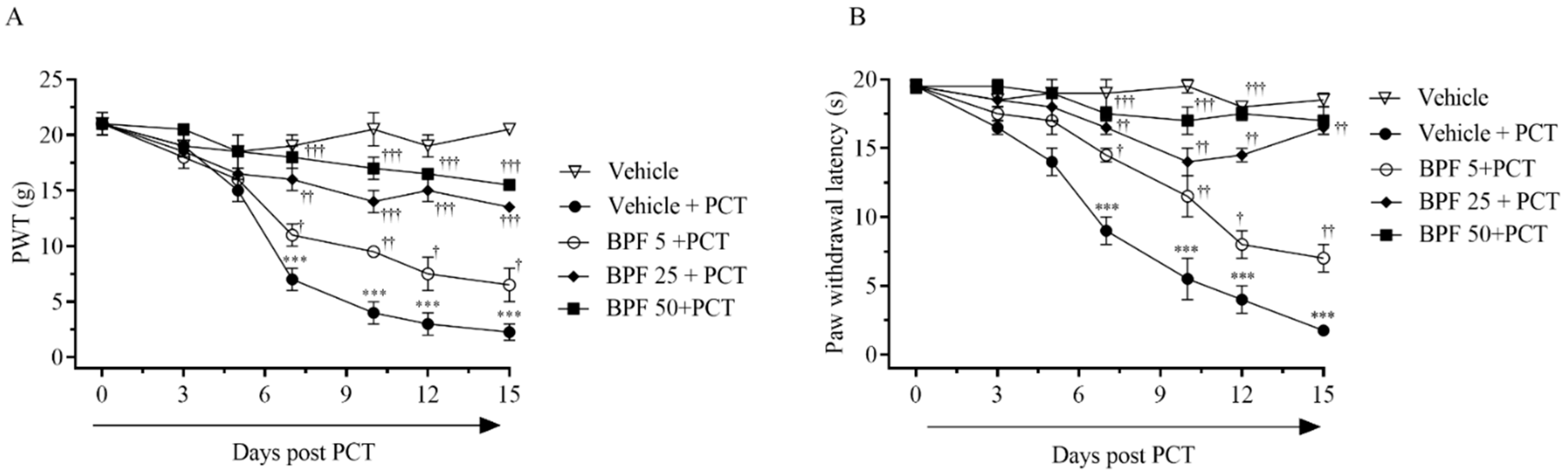
2.1. BPF Effects on Paclitaxel-Induced Thermal Hyperalgesia and Allodynia
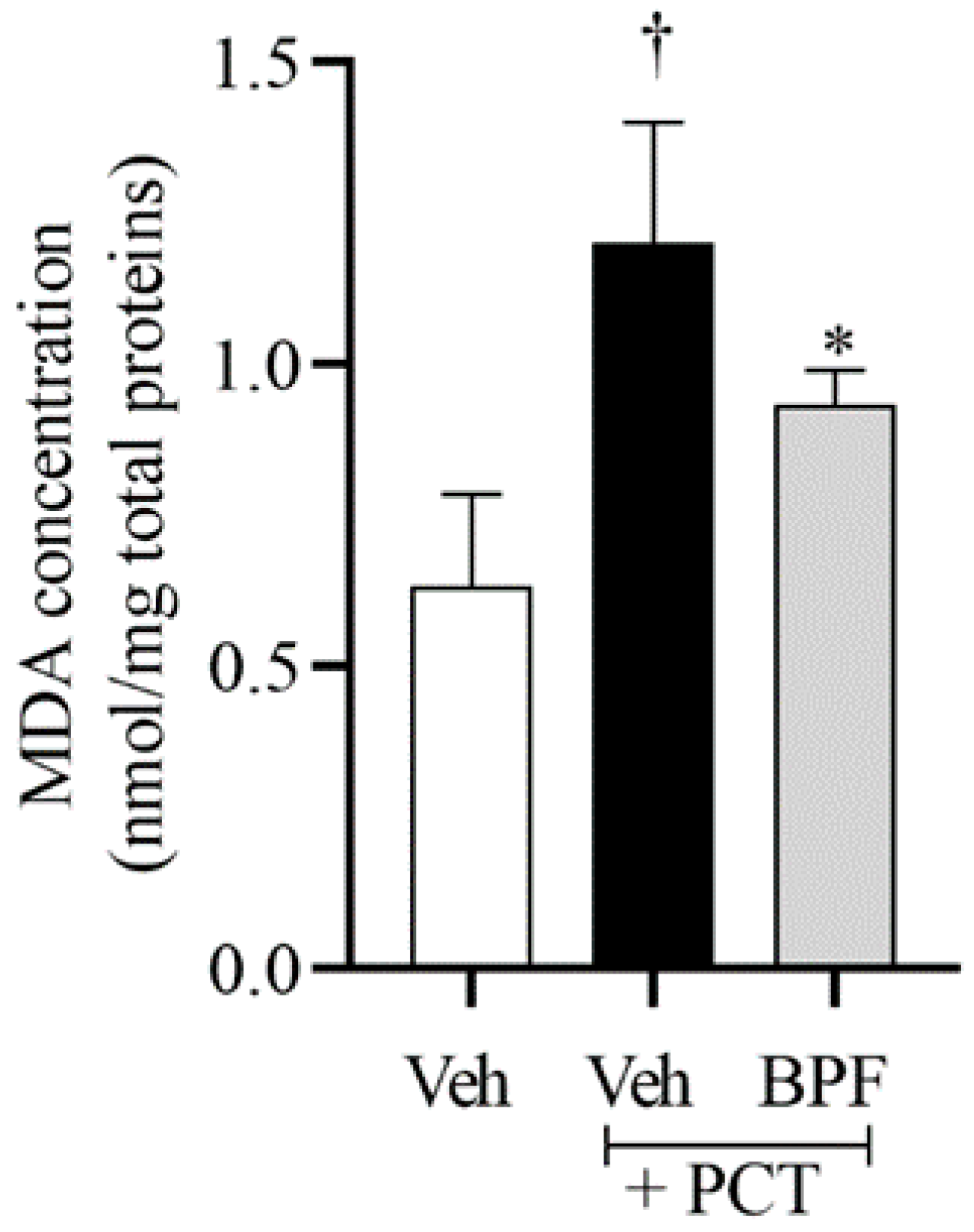
2.2. BPF Effects on Spinal Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels during Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain
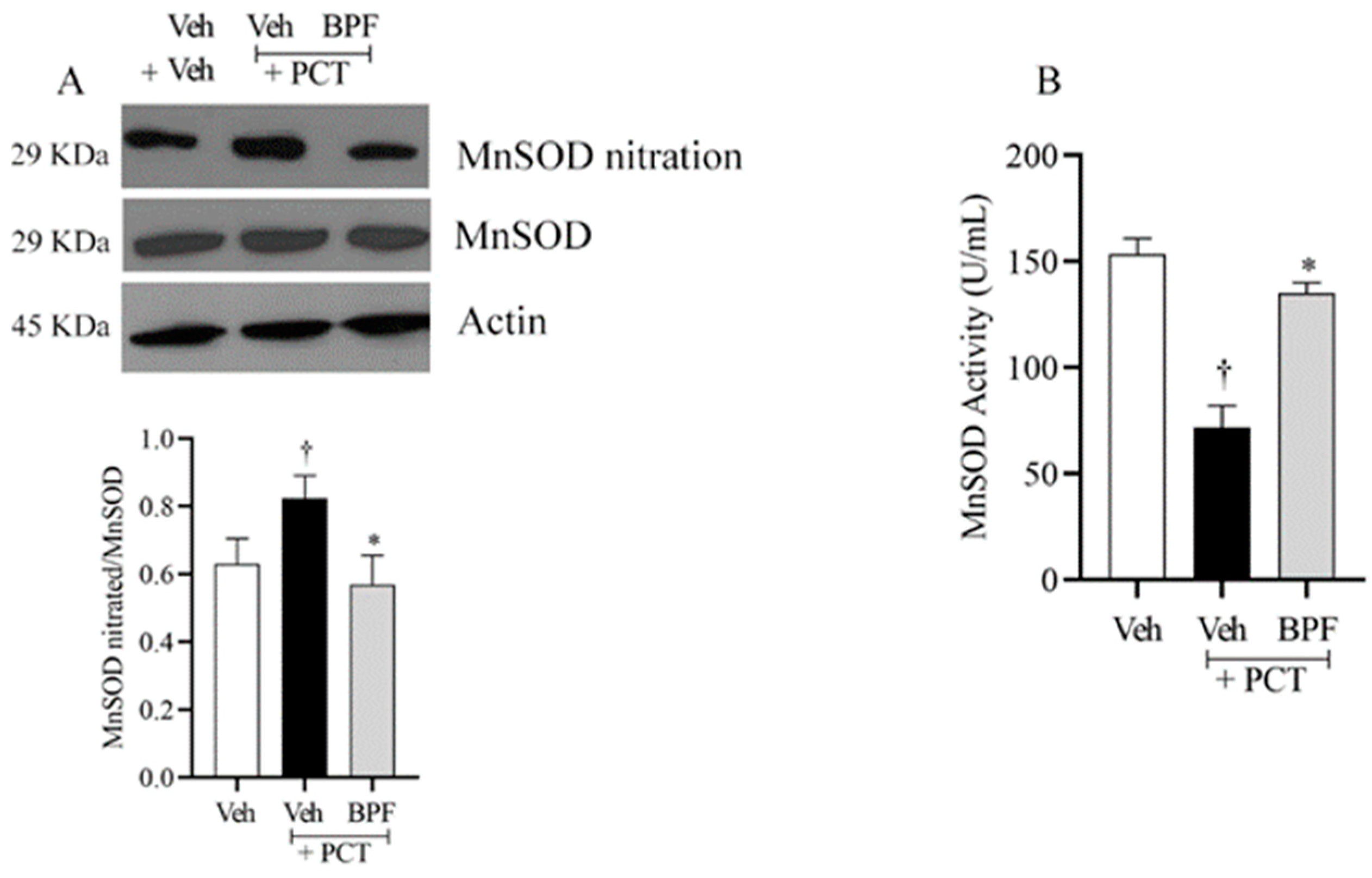
2.3. BPF and Post-Translational Modification of MnSOD during Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain
2.4. BPF and Post-Translational Modification of Gs and Glt-1 during Paclitaxel-Induced Neuropathic Pain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Natural Drugs
4.3. Experimental Group
4.4. Behavioral Test
4.5. Tissue Preparation for Protein Extraction
4.6. Western Blotting e Immunoprecipitation
4.7. MnSOD Activity
4.8. Malonylaldehyde Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colvin, L.A. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Where are we now? Pain 2019, 160 (Suppl. 1), S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajaczkowska, R.; Kocot-Kepska, M.; Leppert, W.; Wrzosek, A.; Mika, J.; Wordliczek, J. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.Y.; Mi, W.L.; Wu, G.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Mao-Ying, Q.L. Prevention and Treatment for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Therapies Based on CIPN Mechanisms. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Jara, J.; Lozano-Terol, G.; Sola-Martinez, R.A.; Canovas-Diaz, M.; de Diego Puente, T. A Compressive Review about Taxol((R)): History and Future Challenges. Molecules 2020, 25, 5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marupudi, N.I.; Han, J.E.; Li, K.W.; Renard, V.M.; Tyler, B.M.; Brem, H. Paclitaxel: A review of adverse toxicities and novel delivery strategies. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2007, 6, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, S.; Stahl, M.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Lordick, F. Influence of Taxanes on Treatment Sequence in Gastric Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2020, 43, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, J.C.; Camdessanche, J.P. Peripheral nervous system involvement in patients with cancer. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintao, N.L.M.; Santin, J.R.; Stoeberl, L.C.; Correa, T.P.; Melato, J.; Costa, R. Pharmacological Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain: PPARgamma Agonists as a Promising Tool. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen Hammond, E.; Pitz, M.; Shay, B. Neuropathic Pain in Taxane-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Evidence for Exercise in Treatment. Neurorehabil. Neural. Repair 2019, 33, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, N.P.; Fehrenbacher, J.C.; Caillaud, M.; Damaj, M.I.; Segal, R.A.; Rieger, S. Pathogenesis of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review of in vitro and in vivo findings using rodent and human model systems. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 324, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.S.; Bae, C.; Wang, J.; Lee, K.H.; Hankerd, K.M.; Kim, H.K.; Chung, J.M.; La, J.H. Peripheral and central oxidative stress in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919840098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huehnchen, P.; van Kampen, A.; Boehmerle, W.; Endres, M. Cognitive impairment after cytotoxic chemotherapy. Neurooncol. Pract. 2020, 7, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Georgieva, M.G.; Ognyanov, I.V.; Kordos, K.; Jozwik, A.; Kuhl, T.; Perry, G.; Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; et al. Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Impact in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Literature Landscape Analysis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 34, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.Q.; Guo, Y.; Chu, X.Y. Neuropathic Pain: The Dysfunction of Drp1, Mitochondria, and ROS Homeostasis. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, S.; Dagostino, C.; Malafoglia, V.; Lauro, F.; Giancotti, L.A.; Spila, A.; Proietti, S.; Ventrice, D.; Rizzo, M.; Gliozzi, M.; et al. Protective Effect of Antioxidants in Nitric Oxide/COX-2 Interaction during Inflammatory Pain: The Role of Nitration. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazhappilly, C.G.; Ansari, S.A.; Al-Jaleeli, R.; Al-Azawi, A.M.; Ramadan, W.S.; Menon, V.; Hodeify, R.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Merheb, M.; Matar, R.; et al. Role of flavonoids in thrombotic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, C.; Di Giacomo, G.; Rizza, S.; Cardaci, S.; Ferraro, E.; Grumati, P.; De Zio, D.; Maiani, E.; Muscoli, C.; Lauro, F.; et al. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase deficiency-induced S-nitrosylation results in neuromuscular dysfunction. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, R.; Lazcano, P.; Ferrari, F.; Pinto-Pardo, N.; Gonzalez-Billault, C.; Utreras, E. TNF-alpha Increases Production of Reactive Oxygen Species through Cdk5 Activation in Nociceptive Neurons. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrasco, C.; Naziroglu, M.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. Neuropathic Pain: Delving into the Oxidative Origin and the Possible Implication of Transient Receptor Potential Channels. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, C.; Liu, T. Oxidative stress induced by NOX2 contributes to neuropathic pain via plasma membrane translocation of PKCepsilon in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qadri, Y.J.; Serhan, C.N.; Ji, R.R. Microglia in Pain: Detrimental and Protective Roles in Pathogenesis and Resolution of Pain. Neuron 2018, 100, 1292–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghavendra, V.; Tanga, F.; Rutkowski, M.D.; DeLeo, J.A. Anti-hyperalgesic and morphine-sparing actions of propentofylline following peripheral nerve injury in rats: Mechanistic implications of spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines. Pain 2003, 104, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.; Chen, Z.; Muscoli, C.; Bryant, L.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Dagostino, C.; Ryerse, J.; Rausaria, S.; Kamadulski, A.; et al. Targeting the overproduction of peroxynitrite for the prevention and reversal of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6149–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gwak, Y.S.; Hulsebosch, C.E.; Leem, J.W. Neuronal-Glial Interactions Maintain Chronic Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 2480689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Anjaneyulu, M.; Choi, J.; Kumar, P.; Salimian, M.; Ho, C.Y.; Russell, J.W. Role of mitochondria in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Influencing the NAD(+)-dependent SIRT1-PGC-1alpha-TFAM pathway. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 145, 177–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauro, F.; Giancotti, L.A.; Ilari, S.; Dagostino, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Morabito, C.; Malafoglia, V.; Raffaeli, W.; Muraca, M.; Goffredo, B.M.; et al. Inhibition of Spinal Oxidative Stress by Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction Attenuates the Development of Morphine Induced Tolerance and Hyperalgesia in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nistico, S.; Ventrice, D.; Dagostino, C.; Lauro, F.; Ilari, S.; Gliozzi, M.; Colica, C.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Strongoli, M.C.; et al. Effect of MN (III) tetrakis (4-benzoic acid) porphyrin by photodynamically generated free radicals on SODs keratinocytes. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2013, 27, 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.S.; DeNicola, G.M. The Complex Interplay between Antioxidants and ROS in Cancer. Trends. Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free radicals: Properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Floyd, R.A.; Hensley, K. Oxidative stress in brain aging. Implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chuang, C.C.; Kandaswamy, E.; Zhou, T.; Zuo, L. Role of ROS and Nutritional Antioxidants in Human Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleem, U.; Sabir, S.; Niazi, S.G.; Naeem, M.; Ahmad, B. Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2020, 30, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandolini, L.; d’Angelo, M.; Antonosante, A.; Allegretti, M.; Cimini, A. Chemokine Signaling in Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loprinzi, C.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Hertz, D.L.; Kelley, M.R.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; Paice, J.A.; et al. Prevention and Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Survivors of Adult Cancers: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3325–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilari, S.; Giancotti, L.A.; Lauro, F.; Dagostino, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Malafoglia, V.; Sansone, L.; Palma, E.; Tafani, M.; Russo, M.A.; et al. Antioxidant modulation of sirtuin 3 during acute inflammatory pain: The ROS control. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, S.; Giancotti, L.A.; Lauro, F.; Gliozzi, M.; Malafoglia, V.; Palma, E.; Tafani, M.; Russo, M.A.; Tomino, C.; Fini, M.; et al. Natural Antioxidant Control of Neuropathic Pain-Exploring the Role of Mitochondrial SIRT3 Pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, J.S.K.; Selakovic, D.; Mihailovic, V.; Rosic, G. Antioxidant Supplementation in the Treatment of Neurotoxicity Induced by Platinum-Based Chemotherapeutics—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, C.; Facchiano, F.; Bartoli, M.; Pieretti, S.; Facchiano, A.; D’Arcangelo, D.; Norelli, S.; Valle, G.; Nisini, R.; Beninati, S.; et al. Beneficial Role of Phytochemicals on Oxidative Stress and Age-Related Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8748253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Russa, D.; Giordano, F.; Marrone, A.; Parafati, M.; Janda, E.; Pellegrino, D. Oxidative Imbalance and Kidney Damage in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Rat Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomino, C.; Ilari, S.; Solfrizzi, V.; Malafoglia, V.; Zilio, G.; Russo, P.; Proietti, S.; Marcolongo, F.; Scapagnini, G.; Muscoli, C.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia: The Role of Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761((R))). Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, C.; Valentao, P.; Ferreres, F.; Andrade, P.B. The use of flavonoids in central nervous system disorders. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 4694–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade Teles, R.B.; Diniz, T.C.; Costa Pinto, T.C.; de Oliveira Junior, R.G.; Gama, E.S.M.; de Lavor, E.M.; Fernandes, A.W.C.; de Oliveira, A.P.; de Almeida Ribeiro, F.P.R.; da Silva, A.A.M.; et al. Flavonoids as Therapeutic Agents in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Evidences. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 7043213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, K.A.; Qaiser, M.Z.; Begley, D.J.; Rice-Evans, C.A.; Abbott, N.J. Flavonoid permeability across an in situ model of the blood-brain barrier. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.L.; Shih, P.H.; Yen, G.C. Neuroprotective effects of citrus flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ikram, M.; Hahm, J.R.; Kim, M.O. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Citrus Flavonoid Hesperetin: Special Focus on Neurological Disorders. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curro, M.; Risitano, R.; Ferlazzo, N.; Cirmi, S.; Gangemi, C.; Caccamo, D.; Ientile, R.; Navarra, M. Citrus bergamia Juice Extract Attenuates beta-Amyloid-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Activation of THP-1 Cells Through MAPK and AP-1 Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nauman, M.C.; Johnson, J.J. Clinical application of bergamot (Citrus bergamia) for reducing high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease markers. Integr. Food Nutr. Metab. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musolino, V.; Gliozzi, M.; Bombardelli, E.; Nucera, S.; Carresi, C.; Maiuolo, J.; Mollace, R.; Paone, S.; Bosco, F.; Scarano, F.; et al. The synergistic effect of Citrus bergamia and Cynara cardunculus extracts on vascular inflammation and oxidative stress in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2020, 10, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Spadaccini, D.; Botteri, L.; Girometta, C.; Riva, A.; Allegrini, P.; Petrangolini, G.; Infantino, V.; Rondanelli, M. Efficacy of bergamot: From anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms to clinical applications as preventive agent for cardiovascular morbidity, skin diseases, and mood alterations. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Resveratrol inhibits paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain by the activation of PI3K/Akt and SIRT1/PGC1alpha pathway. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Recalde, M.D.; Miguel, C.A.; Noya-Riobo, M.V.; Gonzalez, S.L.; Villar, M.J.; Coronel, M.F. Resveratrol exerts anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory actions and prevents oxaliplatin-induced mechanical and thermal allodynia. Brain Res. 2020, 1748, 147079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscoli, C.; Lauro, F.; Dagostino, C.; Ilari, S.; Giancotti, L.A.; Gliozzi, M.; Costa, N.; Carresi, C.; Musolino, V.; Casale, F.; et al. Olea Europea-derived phenolic products attenuate antinociceptive morphine tolerance: An innovative strategic approach to treat cancer pain. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2014, 28, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, T.; Katsuyama, S.; Uezono, Y.; Sakurada, C.; Tsuzuki, M.; Hamamura, K.; Bagetta, G.; Sakurada, S.; Sakurada, T. Possible involvement of the peripheral Mu-opioid system in antinociception induced by bergamot essential oil to allodynia after peripheral nerve injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 686, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggett, N.A.; Griffiths, L.A.; McKenna, O.E.; de Santis, V.; Yongsanguanchai, N.; Mokori, E.B.; Flatters, S.J. Oxidative stress in the development, maintenance and resolution of paclitaxel-induced painful neuropathy. Neuroscience 2016, 333, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Hiraoka, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Tanaka, K. Region-specific deletions of the glutamate transporter GLT1 differentially affect nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in mice. Glia 2018, 66, 1988–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, K.; Esposito, E.; Doyle, T.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Tosh, D.K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Salvemini, D. A3 adenosine receptor agonist prevents the development of paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain by modulating spinal glial-restricted redox-dependent signaling pathways. Pain 2014, 155, 2560–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malafoglia, V.; Ilari, S.; Vitiello, L.; Tenti, M.; Balzani, E.; Muscoli, C.; Raffaeli, W.; Bonci, A. The Interplay between Chronic Pain, Opioids, and the Immune System. Neuroscientist 2021, 16, 10738584211030493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Presynaptic NMDA receptors control nociceptive transmission at the spinal cord level in neuropathic pain. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gegelashvili, G.; Bjerrum, O.J. Glutamate transport system as a key constituent of glutamosome: Molecular pathology and pharmacological modulation in chronic pain. Neuropharmacology 2019, 161, 107623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y. Hydrogen enriched saline alleviates morphine tolerance via inhibiting neuroinflammation, GLT-1, GS nitration and NMDA receptor trafficking and functioning in the spinal cord of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 755, 135847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal, F.J.; Mattison, H.A.; Cerpa, W. Role of NMDA Receptor-Mediated Glutamatergic Signaling in Chronic and Acute Neuropathologies. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 2701526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckhauser, T.F.; Francis-Oliveira, J.; De Pasquale, R. Reactive Oxygen Species: Physiological and Physiopathological Effects on Synaptic Plasticity. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafoglia, V.; Tenti, M.; Ilari, S.; Balzani, E.; Fanelli, A.; Muscoli, C.; Raffaeli, W.; Bonci, A. Opportunities and challenges for nonaddictive interventions in chronic pain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 57, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.Y.; Liu, C.T.; Su, Y.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Tsai, M.Y. A review of complementary therapies with medicinal plants for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 42, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.J.; Xie, Y.K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 1988, 33, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.; Dubner, R.; Brown, F.; Flores, C.; Joris, J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988, 32, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polomano, R.C.; Mannes, A.J.; Clark, U.S.; Bennett, G.J. A painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat produced by the chemotherapeutic drug, paclitaxel. Pain 2001, 94, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilari, S.; Lauro, F.; Giancotti, L.A.; Malafoglia, V.; Dagostino, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Condemi, A.; Maiuolo, J.; Oppedisano, F.; Palma, E.; et al. The Protective Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) on Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14100975
Ilari S, Lauro F, Giancotti LA, Malafoglia V, Dagostino C, Gliozzi M, Condemi A, Maiuolo J, Oppedisano F, Palma E, et al. The Protective Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) on Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(10):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14100975
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlari, Sara, Filomena Lauro, Luigino Antonio Giancotti, Valentina Malafoglia, Concetta Dagostino, Micaela Gliozzi, Antonia Condemi, Jessica Maiuolo, Francesca Oppedisano, Ernesto Palma, and et al. 2021. "The Protective Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) on Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 10: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14100975








