Pharmacology, Physiology and Genetics of the Neuropeptide S System
Abstract
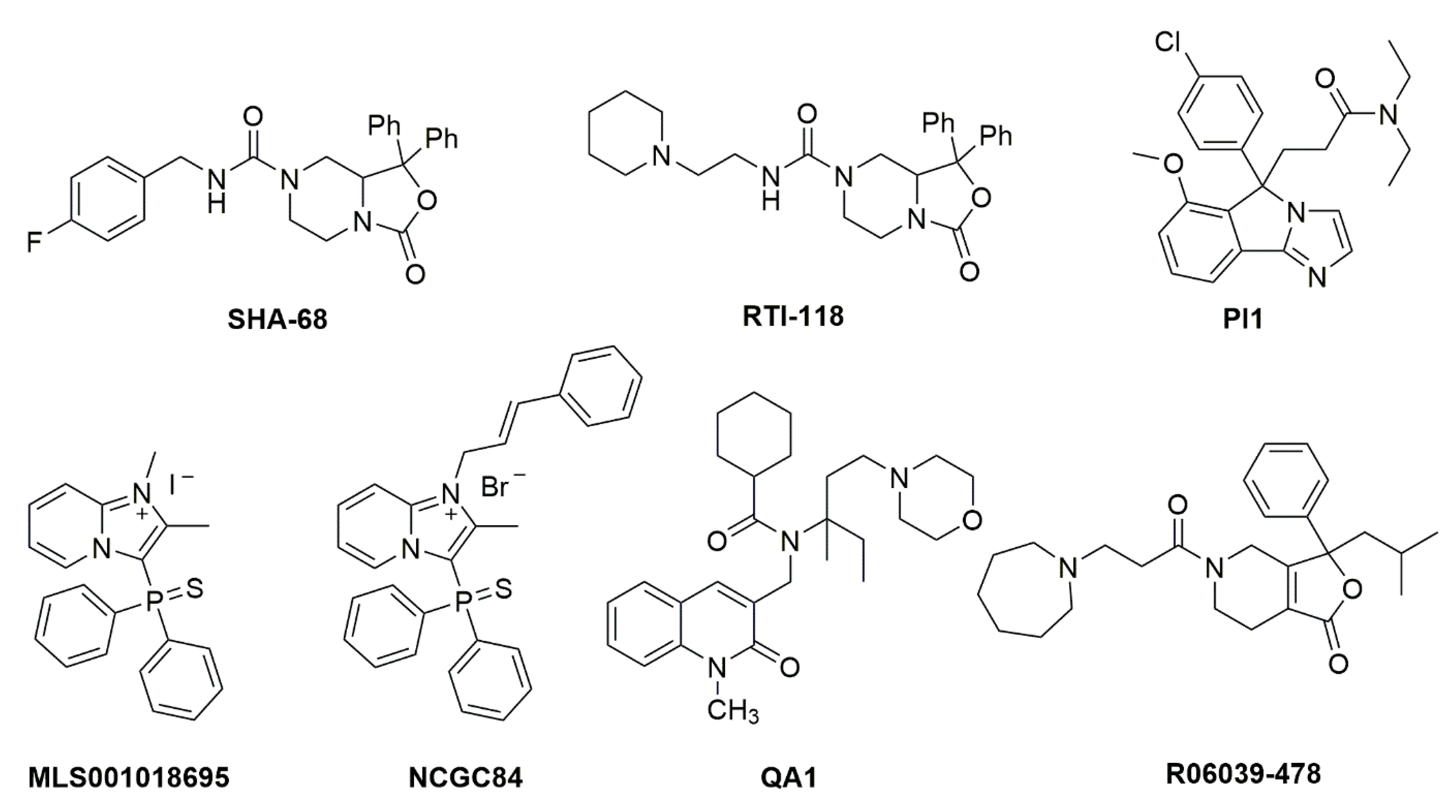
1. NPS and the Orphan Receptor Strategy
2. General Pharmacology
3. Anatomical Distribution of the NPS System
4. Physiological and Behavioral Effects of NPS
4.1. Modulation of Animal Behavior
4.2. NPS and Immune Functions
5. Genetics of the Human NPS System and Associations with Disease and Behavior
6. Therapeutic Potential
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Civelli, O.; Saito, Y.; Wang, Z.; Nothacker, H.-P.; Reinscheid, R.K. Orphan GPCRs and their ligands. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 110, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Shintani, Y.; Miyajima, N.; Yoshimura, K. Novel G protein-coupled receptor protein and DNA thereof. World Patent WO 02/31145 A1, 18 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.-L.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Clark, S.D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.H.; Brucher, F.A.; Zeng, J.; Ly, N.K.; Henriksen, S.J.; et al. Neuropeptide S: A neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects. Neuron 2004, 43, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinscheid, R.K. Phylogenetic appearance of neuropeptide S precursor proteins in tetrapods. Peptides 2007, 28, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, M.R. NG peptides: A novel family of neurophysin-associated neuropeptides. Gene 2010, 458, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mirabeau, O.; Joly, J.S. Molecular evolution of peptidergic signaling systems in bilaterians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2028–E2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitti, T.; Manoj, N. Molecular evolution of the neuropeptide S receptor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinscheid, R.K.; Xu, Y.-L.; Okamura, N.; Zeng, J.; Chung, S.; Pai, R.; Wang, Z.; Civelli, O. Pharmacological characterization of human and murine neuropeptide S receptor variants. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, V.; Ezer, S.; Sundman, L.; Hagström, J.; Remes, S.; Söderhäll, C.; Dario, G.; Haglund, C.; Kere, J.; Arola, J. Neuropeptide S receptor 1 (NPSR1) activates cancer-related pathways and is widely expressed in neuroendocrine tumors. Virchows Arch. 2014, 465, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, F.; Kügler, S.; Blaesse, P.; Lange, M.D.; Skryabin, B.V.; Pape, H.C.; Jüngling, K. Neuronal expression of the human neuropeptide S receptor NPSR1 identifies NPS-induced calcium signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.L.; Marzola, E.; Rizzi, A.; Arduin, M.; Trapella, C.; Corti, C.; Vergura, R.; Martinelli, P.; Salvadori, S.; Regoli, D.; et al. Structure-activity studies on neuropeptide S: Identification of the amino acid residues crucial for receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20809–20816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, V.; Trapella, C.; Caló, G.; Guerrini, R.; Rizzi, A.; Ruzza, C.; Fiorini, S.; Marzola, E.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Regoli, D.; et al. Synthesis and biological activity of human neuropeptide S analogues modified in position 2. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, V.; Trapella, C.; Calo’, G.; Guerrini, R.; Rizzi, A.; Ruzza, C.; Fiorini, S.; Marzola, E.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Regoli, D.; et al. Structure-activity study at positions 3 and 4 of human neuropeptide S. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 8841–8845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, R.; Camarda, V.; Trapella, C.; Calò, G.; Rizzi, A.; Ruzza, C.; Fiorini, S.; Marzola, E.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Regoli, D.; et al. Synthesis and biological activity of human neuropeptide S analogues modified in position 5: Identification of potent and pure neuropeptide S receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, R.; Camarda, V.; Trapella, C.; Caló, G.; Rizzi, A.; Ruzza, C.; Fiorini, S.; Marzola, E.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Regoli, D.; et al. Further studies at neuropeptide S position 5: Discovery of novel neuropeptide S receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4068–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ruzza, C.; Rizzi, A.; Camarda, V.; Pulga, A.; Marzola, G.; Filaferro, M.; Novi, C.; Ruggieri, V.; Marzola, E.; Vitale, G.; et al. [tBu-D-Gly5]NPS, a pure and potent antagonist of the neuropeptide S receptor: In vitro and in vivo studies. Peptides 2012, 34, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, V.; Rizzi, A.; Ruzza, C.; Zucchini, S.; Marzola, G.; Marzola, E.; Guerrini, R.; Salvadori, S.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Regoli, D.; et al. In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of the neuropeptide S receptor antagonist [D-Cys(tBu)5]neuropeptide S. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Habay, S.A.; Zeng, J.; Chamberlin, A.R.; Reinscheid, R.K. Synthesis and pharmacological in vitro and in vivo profile of 3-oxo-1,1-diphenyl-tetrahydro-oxazolo[3,4-a]pyrazine-7-carboxylic acid 4-fluoro-benzylamide (SHA 68), a selective antagonist of the neuropeptide S receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 325, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzza, C.; Rizzi, A.; Trapella, C.; Pela’, M.; Camarda, V.; Ruggieri, V.; Filaferro, M.; Cifani, C.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Vitale, G.; et al. Further studies on the pharmacological profile of the neuropeptide S receptor antagonist SHA 68. Peptides 2010, 31, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapella, C.; Pela, M.; Del Zoppo, L.; Calo, G.; Camarda, V.; Ruzza, C.; Cavazzini, A.; Costa, V.; Bertolasi, V.; Reinscheid, R.K.; et al. Synthesis and separation of the enantiomers of the neuropeptide S receptor antagonist (9 R/S)-3-Oxo-1,1-diphenyl-tetrahydro-oxazolo[3,4-a]pyrazine-7-carboxylic Acid 4-fluoro-benzylamide (SHA 68). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2738–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gilmour, B.; Graf, T.; Fennell, T.; Snyder, R.; Deschamps, J.R.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Garau, C.; Runyon, S.P. Identification of neuropeptide s antagonists: Structure-Activity relationship studies, x-ray crystallography, and in vivo evaluation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, V.; Ruzza, C.; Marzola, E.; Bernadi, T.; Fabbri, M.; Fantinati, A.; Trapella, C.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Ferrari, F.; Sturaro, C.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on Oxazolo[3,4-a]pyrazine Derivatives Leading to the Discovery of a Novel Neuropeptide S Receptor Antagonist with Potent In Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsell, A.; Tapocik, J.D.; Liu, K.; Zook, M.; Bell, L.; Flanigan, M.; Patnaik, S.; Marugan, J.; Damadzic, R.; Dehdashti, S.J.; et al. A novel brain penetrant NPS receptor antagonist, NCGC00185684, blocks alcohol-induced ERK-phosphorylation in the central amygdala and decreases operant alcohol self-administration in rats. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10132–10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batran, R.Z.; Dawood, D.H.; El-Seginy, S.A.; Maher, T.J.; Gugnani, K.S.; Rondon-Ortiz, A.N. Coumarinyl pyranopyrimidines as new neuropeptide S receptor antagonists; design, synthesis, homology and molecular docking. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 75, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzza, C.; Calò, G.; Di Maro, S.; Pacifico, S.; Trapella, C.; Salvadori, S.; Preti, D.; Guerrini, R. Neuropeptide S receptor ligands: A patent review (2005–2016). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-L.; Gall, C.M.; Jackson, V.R.; Civelli, O.; Reinscheid, R.K. Distribution of neuropeptide S receptor mRNA and neurochemical characteristics of neuropeptide S-expressing neurons in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 500, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.D.; Duangdao, D.M.; Schulz, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.L.; Reinscheid, R.K. Anatomical characterization of the neuropeptide S system in the mouse brain by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1867–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, A.; Theodorsson, E.; Fahrenkrug, J.; Reinscheid, R.K. Molecular fingerprint of neuropeptide s-producing neurons in the mouse brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 1847–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, K.; Rjabokon, A.; Pape, H.C.; Singewald, N. Increased in vivo release of neuropeptide S in the amygdala of freely moving rats after local depolarisation and emotional stress. Amino Acids 2011, 41, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adori, C.; Barde, S.; Vas, S.; Ebner, K.; Su, J.; Svensson, C.; Mathé, A.A.; Singewald, N.; Reinscheid, R.R.; Uhlén, M.; et al. Exploring the role of neuropeptide S in the regulation of arousal: A functional anatomical study. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 3521–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palasz, A.; Rojczyk, E.; Golyszny, M.; Filipczyk, L.; Worthington, J.J.; Wiaderkiewicz, R. Long-term treatment with haloperidol affects neuropeptide S and NPSR mRNA levels in the rat brain. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2016, 28, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałasz, A.; Rojczyk, E. Neuroleptics Affect Neuropeptide S and NPSR mRNA Levels in the Rat Brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 57, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, P.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Ubaldi, M. Morphine dependence is associated with changes in neuropeptide S receptorexpression and function in rat brain. Peptides 2013, 46, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adori, C.; Barde, S.; Bogdanovic, N.; Uhlén, M.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Kovacs, G.G.; Hökfelt, T. Neuropeptide S-and Neuropeptide S receptor-expressing neuron populations in the human pons. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, T.; Polvi, A.; Rydman, P.; Vendelin, J.; Pulkkinen, V.; Salmikangas, P.; Mäkelä, S.; Rehn, M.; Pirskanen, A.; Rautanen, A.; et al. Characterization of a Common Susceptibility Locus for Asthma-Related Traits. Science 2004, 304, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendelin, J.; Pulkkinen, V.; Rehn, M.; Pirskanen, A.; Räisänen-Sokolowski, A.; Laitinen, A.; Laitinen, L.A.; Kere, J.; Laitinen, T. Characterization of GPRA, a novel G protein-coupled receptor related to asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, L.; Saarialho-Kere, U.; Vendelin, J.; Lindfors, K.; Assadi, G.; Kaukinen, K.; Westerholm-Ormio, M.; Savilahti, E.; Mäki, M.; Alenius, H.; et al. Neuropeptide S receptor 1 expression in the intestine and skin—Putative role in peptide hormone secretion. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.K.; Ring, R.H. Immunohistochemical localization of the neuropeptide S receptor in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 2011, 172, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzi, A.; Vergura, R.; Marzola, G.; Ruzza, C.; Guerrini, R.; Salvadori, S.; Regoli, D.; Calo, G. Neuropeptide S is a stimulatory anxiolytic agent: A behavioural study in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, S.K.; Dwyer, J.M.; Sukoff Rizzo, S.J.; Platt, B.; Logue, S.F.; Neal, S.J.; Malberg, J.E.; Beyer, C.E.; Schechter, L.E.; Rosenzweig-Lipson, S.; et al. Pharmacology of neuropeptide S in mice: Therapeutic relevance to anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacology 2008, 197, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, I.A.; Dine, J.; Yen, Y.C.; Buell, D.R.; Herrmann, L.; Holsboer, F.; Eder, M.; Landgraf, R.; Schmidt, U. Intranasally administered neuropeptide S (NPS) exerts anxiolytic effects following internalization into NPS receptor-expressing neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dine, J.; Ionescu, I.A.; Avrabos, C.; Yen, Y.C.; Holsboer, F.; Landgraf, R.; Schmidt, U.; Eder, M. Intranasally applied neuropeptide S shifts a high-anxiety electrophysiological endophenotype in the ventral hippocampus towards a “normal”-anxiety one. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, D.A.; Naik, R.R.; Grund, T.; Yen, Y.C.; Sartori, S.B.; Füchsl, A.; Finger, B.C.; Elfving, B.; Nordemann, U.; Guerrini, R.; et al. Selective breeding for high anxiety introduces a synonymous SNP that increases Neuropeptide S receptor activity. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4599–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoicas, I.; Menon, R.; Neumann, I.D. Neuropeptide S reduces fear and avoidance of con-specifics induced by social fear conditioning and social defeat, respectively. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Garau, C.; Duangdao, D.M.; Clark, S.D.; Jüngling, K.; Pape, H.-C.; Reinscheid, R.K. Neuropeptide S enhances memory during the consolidation phase and interacts with noradrenergic systems in the brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukas, M.; Neumann, I.D. Nasal application of neuropeptide S reduces anxiety and prolongs memory in rats: Social versus non-social effects. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.W.; Zhang, R.S.; Xu, H.J.; Chang, M.; Peng, Y.L.; Wang, R. Neuropeptide S enhances memory and mitigates memory impairment induced by MK801, scopolamine or Aβ1-42 in mice novel object and object location recognition tasks. Neuropharmacology 2013, 70, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüngling, K.; Seidenbecher, T.; Sosulina, L.; Lesting, J.; Sangha, S.; Clark, S.D.; Okamura, N.; Duangdao, D.M.; Xu, Y.-L.; Reinscheid, R.K.; et al. Neuropeptide S-Mediated Control of Fear Expression and Extinction: Role of Intercalated GABAergic Neurons in the Amygdala. Neuron 2008, 59, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, S.B.; Maurer, V.; Murphy, C.; Schmuckermair, C.; Muigg, P.; Neumann, I.D.; Whittle, N.; Singewald, N. Combined neuropeptide S and D-cycloserine augmentation prevents the return of fear in extinction-impaired rodents: Advantage of dual versus single drug approaches. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Reinscheid, R.K.; Ohgake, S.; Iyo, M.; Hashimoto, K. Neuropeptide S attenuates neuropathological, neurochemical and behavioral changes induced by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Patterson, M.; Dhillo, W.S.; Patel, S.R.; Semjonous, N.M.; Gardiner, J.V.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Neuropeptide S stimulates the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and inhibits food intake. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3510–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Mingler, M.K.; McBride, M.L.; Murphy, A.J.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Williams, M.T.; Vorhees, C.V.; Rothenberg, M.E. Abnormal response to stress and impaired NPS-induced hyperlocomotion, anxiolytic effect and corticosterone increase in mice lacking NPSR1. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010, 35, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Aluisio, L.; Okamura, N.; Clark, S.D.; Fraser, I.; Sutton, S.W.; Bonaventure, P.; Reinscheid, R.K. Neuropeptide S stimulates dopaminergic neurotransmission in the medial prefrontal cortex. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Chang, M.; Peng, Y.L.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhang, J.N.; Han, R.W.; Wang, R. Neuropeptide S produces antinociceptive effects at the supraspinal level in mice. Regul. Pept. 2009, 156, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.L.; Zhang, J.N.; Chang, M.; Li, W.; Han, R.W.; Wang, R. Effects of central neuropeptide S in the mouse formalin test. Peptides 2010, 31, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor Holanda, A.D.; Asth, L.; Santos, A.R.; Guerrini, R.; Soares-Rachetti, V.D.P.; Calo’, G.; André, E.; Gavioli, E.C. Central adenosine A1 and A2A receptors mediate the antinociceptive effects of neuropeptide S in the mouse formalin test. Life Sci. 2015, 120, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, V.A.D.; Oliveira, M.C.; Souza, L.S.; Lobão-Soares, B.; André, E.; Da Silva Junior, E.D.; Guerrini, R.; Calo, G.; Ruzza, C.; Gavioli, E.C. Dopamine D1 and D2 receptors mediate neuropeptide S-induced antinociception in the mouse formalin test. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 859, 172557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Chiu, Y.T.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hor, C.C.; Lee, H.J.; Guerrini, R.; Calo, G.; Chiou, L.C. Neuropeptide S-initiated sequential cascade mediated by OX1, NK1, mGlu5 and CB1 receptors: A pivotal role in stress-induced analgesia. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinushi, K.; Kushikata, T.; Kudo, T.; Calo, G.; Guerrini, R.; Hirota, K. Central noradrenergic activity affects analgesic effect of Neuropeptide S. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.L.; Han, R.W.; Chang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.S.; Li, W.; Han, Y.F.; Wang, R. Central Neuropeptide S inhibits food intake in mice through activation of Neuropeptide S receptor. Peptides 2010, 31, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifani, C.; Di Bonaventura, M.V.M.; Cannella, N.; Fedeli, A.; Guerrini, R.; Calo, G.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Ubaldi, M. Effect of neuropeptide S receptor antagonists and partial agonists on palatable food consumption in the rat. Peptides 2011, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didonet, J.J.; Cavalcante, J.C.; Souza, L.D.; Costa, M.S.; André, E.; Soares-Rachetti, V.D.; Guerrini, R.; Gavioli, E.C. Neuropeptide S counteracts 6-OHDA-induced motor deficits in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 266, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, N.; Economidou, D.; Kallupi, M.; Stopponi, S.; Heilig, M.; Massi, M.; Ciccocioppo, R. Persistent Increase of Alcohol-Seeking Evoked by Neuropeptide S: An Effect Mediated by the Hypothalamic Hypocretin System. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, N.; Kallupi, M.; Li, H.W.; Stopponi, S.; Cifani, C.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Ubaldi, M. Neuropeptide S differently modulates alcohol-related behaviors in alcohol-preferring and non-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pañeda, C.; Huitron-Resendiz, S.; Frago, L.M.; Chowen, J.A.; Picetti, R.; De Lecea, L.; Roberts, A.J. Neuropeptide S reinstates cocaine-seeking behavior and increases locomotor activity through corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 in mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4155–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kallupi, M.; Cannella, N.; Economidou, D.; Ubaldi, M.; Ruggeri, B.; Weiss, F.; Massi, M.; Marugan, J.; Heilig, M.; Bonnavion, P.; et al. Neuropeptide S facilitates cue-induced relapse to cocaine seeking through activation of the hypothalamic hypocretin system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19567–19572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallupi, M.; De Guglielmo, G.; Cannella, N.; Li, H.W.; Caló, G.; Guerrini, R.; Ubaldi, M.; Renger, J.J.; Uebele, V.N.; Ciccocioppo, R. Hypothalamic Neuropeptide S receptor blockade decreases discriminative cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2013, 226, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoutz, C.D.; Zhang, Y.; Runyon, S.P.; Goeders, N.E. Antagonism of the neuropeptide S receptor with RTI-118 decreases cocaine self-administration and cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 103, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannella, N.; Kallupi, M.; Ruggeri, B.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Ubaldi, M. The role of the neuropeptide S system in addiction: Focus on its interaction with the CRF and hypocretin/orexin neurotransmission. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 100, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubaldi, M.; Giordano, A.; Severi, I.; Li, H.; Kallupi, M.; De Guglielmo, G.; Ruggeri, B.; Stopponi, S.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Cannella, N. Activation of hypocretin-1/orexin-a neurons projecting to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and paraventricular nucleus is critical for reinstatement of alcohol seeking by neuropeptide S. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, G.; Finger, B.C.; Elfving, B.; Keller, K.; Liebenberg, N.; Fischer, C.W.; Singewald, N.; Slattery, D.A.; Neumann, I.D.; Mathé, A.A. Neuropeptide S alters anxiety, but not depression-like behaviour in Flinders Sensitive Line rats: A genetic animal model of depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirayama, Y.; Ishima, T.; Oda, Y.; Okamura, N.; Iyo, M.; Hashimoto, K. Opposite roles for neuropeptide S in the nucleus accumbens and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in learned helplessness rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 291, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangdao, D.M.; Clark, S.D.; Okamura, N.; Reinscheid, R.K. Behavioral phenotyping of Neuropeptide S receptor knockout mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fendt, M.; Buchi, M.; Bürki, H.; Imobersteg, S.; Ricoux, B.; Suply, T.; Sailer, A.W. Neuropeptide S receptor deficiency modulates spontaneous locomotor activity and the acoustic startle response. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 217, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Si, W.; Garau, C.; Jüngling, K.; Pape, H.-C.; Schulz, S.; Reinscheid, R.K. Neuropeptide S precursor knockout mice display memory and arousal deficits. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzza, C.; Pulga, A.; Rizzi, A.; Marzola, G.; Guerrini, R.; Calo’, G. Behavioural phenotypic characterization of CD-1 mice lacking the neuropeptide S receptor. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, I.C.; Pace, A.J.; Jania, L.A.; Ledford, J.G.; Latour, A.M.; Snouwaert, J.N.; Bernier, V.; Stocco, R.; Therien, A.G.; Koller, B.H. Expression and function of NPSR1/GPRA in the lung before and after induction of asthma-like disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L1005–L1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Perkins, C.; Mingler, M.K.; Finkelman, F.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. The role of neuropeptide S and neuropeptide S receptor 1 in regulation of respiratory function in mice. Peptides 2011, 32, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pulkkinen, V.; Majuri, M.L.; Wang, G.; Holopainen, P.; Obase, Y.; Vendelin, J.; Wolff, H.; Rytilä, P.; Laitinen, L.A.; Haahtela, T.; et al. Neuropeptide S and G protein-coupled receptor 154 modulate macrophage immune responses. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Su, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, G.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Kou, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Effects of neuropeptide S on the proliferation of splenic lymphocytes, phagocytosis, and proinflammatory cytokine production of pulmonary alveolar macrophages in the pig. Peptides 2011, 32, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, F.; Lei, Z. Effects of central and peripheral administration of neuropeptide S on the level of serum proinflammatory cytokines in pigs. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmarinen, P.; James, A.; Moilanen, E.; Pulkkinen, V.; Daham, K.; Saarelainen, S.; Laitinen, T.; Dahlén, S.E.; Kere, J.; Dahlén, B.; et al. Enhanced expression of neuropeptide S (NPS) receptor in eosinophils from severe asthmatics and subjects with total IgE above 100 IU/ml. Peptides 2014, 51, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melén, E.; Bruce, S.; Doekes, G.; Kabesch, M.; Laitinen, T.; Lauener, R.; Lindgren, C.M.; Riedler, J.; Scheynius, A.; Van Hage-Hamsten, M.; et al. Haplotypes of G protein-coupled receptor 154 are associated with childhood allergy and asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormann, M.S.D.; Carr, D.; Klopp, N.; Illig, T.; Leupold, W.; Fritzsch, C.; Weiland, S.K.; Von Mutius, E.; Kabesch, M. G-Protein-coupled receptor polymorphisms are associated with asthma in a large German population. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, C.P.; Raby, B.A.; Soto-Quirós, M.E.; Murphy, A.J.; Avila, L.; Lasky-Su, J.; Sylvia, J.S.; Klanderman, B.J.; Lange, C.; Weiss, S.T.; et al. Comprehensive testing of positionally cloned asthma genes in two populations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, S.; Nyberg, F.; Melén, E.; James, A.; Pulkkinen, V.; Orsmark-Pietras, C.; Bergström, A.; Dahlén, B.; Wickman, M.; Von Mutius, E.; et al. The protective effect of farm animal exposure on childhood allergy is modified by NPSR1 polymorphisms. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulkkinen, V.; Haataja, R.; Hannelius, U.; Helve, O.; Pitkänen, O.M.; Karikoski, R.; Rehn, M.; Marttila, R.; Lindgren, C.M.; Hästbacka, J.; et al. G protein-coupled receptor for asthma susceptibility associates with respiratory distress syndrome. Ann. Med. 2006, 38, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerba, G.; Lindgren, C.M.; Xumerle, L.; Kiviluoma, P.; Trabetti, E.; Laitinen, T.; Galavotti, R.; Pescollderungg, L.; Boner, A.L.; Kere, J.; et al. Chromosome 7p linkage and GPR154 gene association in Italian families with allergic asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, M.; Zucchelli, M.; Seddighzadeh, M.; Anedda, F.; Lindblad, S.; Kere, J.; Alfredsson, L.; Klareskog, L.; Padyukov, L. Analysis of neuropeptide S receptor gene (NPSR1) polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, C.; Jiménez, S.; Acevedo, N.; Martínez, B.; Mercado, D.; Gusmão, L.; Rafaels, N.; Hand, T.; Barnes, K.C.; Caraballo, L. Association of G-protein-coupled receptor 154 with asthma and total IgE in a population of the Caribbean coast of Colombia. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, M.; Bruce, S.; Bresso, F.; Zucchelli, M.; Ezer, S.; Pulkkinen, V.; Lindgren, C.; Astegiano, M.; Rizzetto, M.; Gionchetti, P.; et al. Neuropeptide S Receptor 1 Gene Polymorphism Is Associated With Susceptibility to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Giner, F.; De Cid, R.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Jarvis, D.; Heinrich, J.; Janson, C.; Omenaas, E.R.; Matheson, M.C.; Pin, I.; Antó, J.M.; et al. Positionally cloned genes and age-specific effects in asthma and atopy: An international population-based cohort study (ECRHS). Thorax 2010, 65, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Robledo, G.; González-Gay, M.A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, B.; Lamas, J.R.; Balsa, A.; Pascual-Salcedo, D.; Castañeda, S.; Blanco, R.; González-Alvaro, I.; García, A.; et al. NPSR1 gene is associated with reduced risk of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Ezer, S.; Merid, S.K.; Gaertner, V.D.; Söderhäll, C.; D’Amato, M.; Kabesch, M.; Melén, E.; Kere, J.; Pulkkinen, V. Neuropeptide S (NPS) variants modify the signaling and risk effects of NPS Receptor 1 (NPSR1) variants in asthma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.D.; Park, K.S.; Park, C.S. Lack of association of GPRA (G protein-coupled receptor for asthma susceptibility) haplotypes with high serum IgE or asthma in a Korean population. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1226–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veal, C.D.; Reynolds, N.J.; Meggitt, S.J.; Allen, M.H.; Lindgren, C.M.; Kere, J.; Trembath, R.C.; Barker, J.N. Absence of association between asthma and high serum immunoglobulin E associated GPRA haplotypes and adult atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Romieu, I.; Sienra-Monge, J.J.; del Rio-Navarro, B.E.; Burdett, L.; Yuenger, J.; Li, H.; Chanock, S.J.; London, S.J. Lack of association between genetic variation in G-protein-coupled receptor for asthma susceptibility and childhood asthma and atopy. Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakey, J.D.; Sayers, I.; Ring, S.M.; Strachan, D.P.; Hall, I.P. Positionally cloned asthma susceptibility gene polymorphisms and disease risk in the British 1958 Birth Cohort. Thorax 2009, 64, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, V.; Stocco, R.; Bogusky, M.J.; Joyce, J.G.; Parachoniak, C.; Grenier, K.; Arget, M.; Mathieu, M.C.; O’Neill, G.P.; Slipetz, D.; et al. Structure-function relationships in the neuropeptide S receptor: Molecular consequences of the asthma-associated mutation N107I. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 24704–24712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Iyo, M.; Shimizu, E.; Dempfle, A.; Friedel, S.; Reinscheid, R.K. Gender-specific association of a functional coding polymorphism in the Neuropeptide S receptor gene with panic disorder but not with schizophrenia or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, D.J.; O’Connor, G.T.; Wilk, J.B. Genome-wide association of sleep and circadian phenotypes. BMC Med. Genet. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 1), S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laas, K.; Eensoo, D.; Paaver, M.; Lesch, K.P.; Reif, A.; Harro, J. Further evidence for the association of the NPSR1 gene A/T polymorphism (Asn107Ile) with impulsivity and hyperactivity. J. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 29, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laas, K.; Reif, A.; Kiive, E.; Domschke, K.; Lesch, K.P.; Veidebaum, T.; Harro, J. A functional NPSR1 gene variant and environment shape personality and impulsive action: A longitudinal study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczka, K.A.; Gartmann, N.; Mechias, M.L.; Reif, A.; Büchel, C.; Deckert, J.; Kalisch, R. A neuropeptide S receptor variant associated with overinterpretation of fear reactions: A potential neurogenetic basis for catastrophizing. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Donner, J.; Haapakoski, R.; Ezer, S.; Meln, E.; Pirkola, S.; Gratacs, M.; Zucchelli, M.; Anedda, F.; Johansson, L.E.; Sderhll, C.; et al. Assessment of the neuropeptide S system in anxiety disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domschke, K.; Reif, A.; Weber, H.; Richter, J.; Hohoff, C.; Ohrmann, P.; Pedersen, A.; Bauer, J.; Suslow, T.; Kugel, H.; et al. Neuropeptide S receptor gene converging evidence for a role in panic disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannlowski, U.; Kugel, H.; Franke, F.; Stuhrmann, A.; Hohoff, C.; Zwanzger, P.; Lenzen, T.; Grotegerd, D.; Suslow, T.; Arolt, V.; et al. Neuropeptide-S (NPS) receptor genotype modulates basolateral amygdala responsiveness to aversive stimuli. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotzbach-Schoon, E.; Andreatta, M.; Reif, A.; Ewald, H.; Tröger, C.; Baumann, C.; Deckert, J.; Mühlberger, A.; Pauli, P. Contextual fear conditioning in virtual reality is affected by 5httlpr and npsr1 polymorphisms: Effects on fear-potentiated startle. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tupak, S.V.; Reif, A.; Pauli, P.; Dresler, T.; Herrmann, M.J.; Domschke, K.; Jochum, C.; Haas, E.; Baumann, C.; Weber, H.; et al. Neuropeptide S receptor gene: Fear-specific modulations of prefrontal activation. Neuroimage 2013, 66, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauke, B.; Deckert, J.; Zwanzger, P.; Baumann, C.; Arolt, V.; Pauli, P.; Reif, A.; Domschke, K. Neuropeptide S receptor gene (NPSR) and life events: G × e effects on anxiety sensitivity and its subdimensions. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 15, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laas, K.; Reif, A.; Akkermann, K.; Kiive, E.; Domschke, K.; Lesch, K.P.; Veidebaum, T.; Harro, J. Interaction of the neuropeptide S receptor gene Asn107Ile variant and environment: Contribution to affective and anxiety disorders, and suicidal behaviour. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennertz, L.; Quednow, B.B.; Schuhmacher, A.; Petrovsky, N.; Frommann, I.; Schulze-Rauschenbach, S.; Landsberg, M.W.; Steinbrecher, A.; Höfels, S.; Pukrop, R.; et al. The functional coding variant Asn107Ile of the neuropeptide S receptor gene (NPSR1) is associated with schizophrenia and modulates verbal memory and the acoustic startle response. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gechter, J.; Liebscher, C.; Geiger, M.J.; Wittmann, A.; Schlagenhauf, F.; Lueken, U.; Wittchen, H.U.; Pfleiderer, B.; Arolt, V.; Kircher, T.; et al. Association of NPSR1 gene variation and neural activity in patients with panic disorder and agoraphobia and healthy controls. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 24, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinscheid, R.K.; Mafessoni, F.; Lüttjohann, A.; Jüngling, K.; Pape, H.-C.; Schulz, S. Neandertal introgression and accumulation of hypomorphic mutations in the neuropeptide S (NPS) system promote attenuated functionality. Peptides 2021, 138, 170506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Shi, G.; Mostovoy, Y.; Gentry, N.W.; Fan, Z.; McMahon, T.B.; Kwok, P.Y.; Jones, C.R.; Ptáček, L.J.; Fu, Y.H. Mutant neuropeptide S receptor reduces sleep duration with preserved memory consolidation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; He, X.; Hsueh, A.J.W. A single-nucleotide polymorphism of human neuropeptide S gene originated from Europe shows decreased bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bonano, J.S.; Runyon, S.P.; Hassler, C.; Glennon, R.A.; Stevens Negus, S. Effects of the neuropeptide S receptor antagonist RTI-118 on abuse-related facilitation of intracranial self-stimulation produced by cocaine and methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 743, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, B.W.; Nanda, K.K.; Manley, P.J.; Uebele, V.N.; Condra, C.L.; Gotter, A.L.; Menzel, K.; Henault, M.; Stocco, R.; Renger, J.J.; et al. Tricyclic imidazole antagonists of the Neuropeptide S Receptor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4704–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, S.; Marugan, J.J.; Liu, K.; Zheng, W.; Southall, N.; Dehdashti, S.J.; Thorsell, A.; Heilig, M.; Bell, L.; Zook, M.; et al. Structure-activity relationship of imidazopyridinium analogues as antagonists of neuropeptide s receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9045–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, J.Y.; Zartman, A.E.; Kett, N.R.; Gotter, A.L.; Uebele, V.N.; Reiss, D.R.; Condra, C.L.; Fandozzi, C.; Lubbers, L.S.; Rowe, B.A.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a new series of Neuropeptide S receptor antagonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4700–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runyon, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hassler, C.; Gilmour, B. Composition and method for Neuropeptide S receptor (NPSR) antagonists. World Patent WO/2013/086200, 13 June 2013. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reinscheid, R.K.; Ruzza, C. Pharmacology, Physiology and Genetics of the Neuropeptide S System. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050401
Reinscheid RK, Ruzza C. Pharmacology, Physiology and Genetics of the Neuropeptide S System. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050401
Chicago/Turabian StyleReinscheid, Rainer K., and Chiara Ruzza. 2021. "Pharmacology, Physiology and Genetics of the Neuropeptide S System" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050401
APA StyleReinscheid, R. K., & Ruzza, C. (2021). Pharmacology, Physiology and Genetics of the Neuropeptide S System. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050401