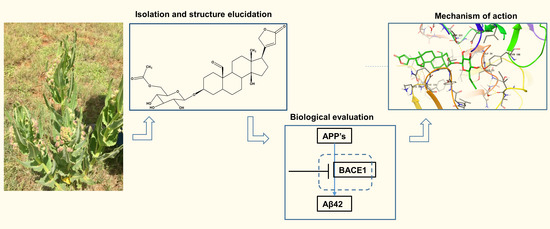
A Novel Cardenolide Glycoside Isolated from Xysmalobium undulatum Reduces Levels of the Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Peptides Aβ42 In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
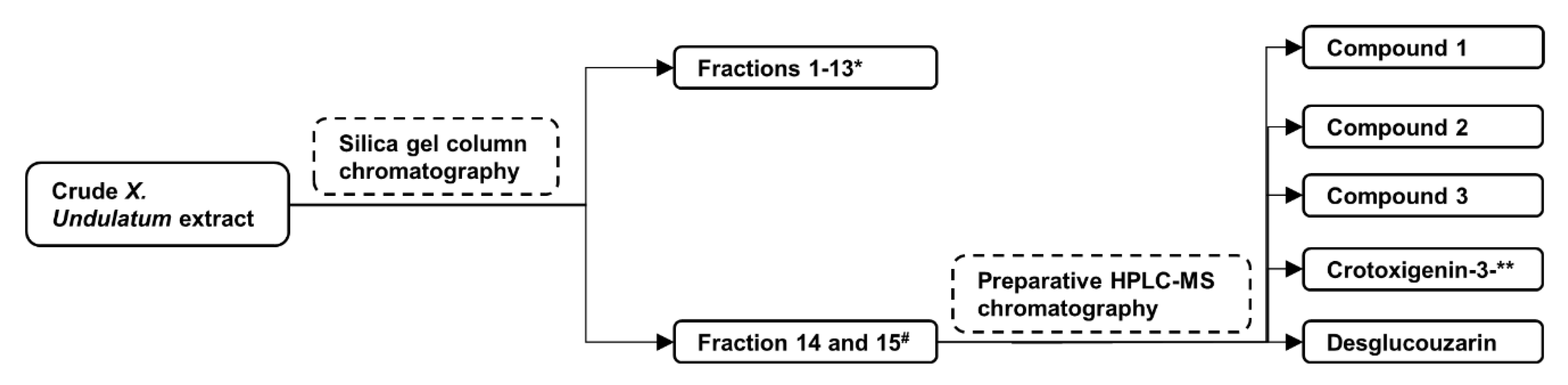
2.1. Isolation of Compounds from X. Undulatum Using Bioassay-Guided Strategy
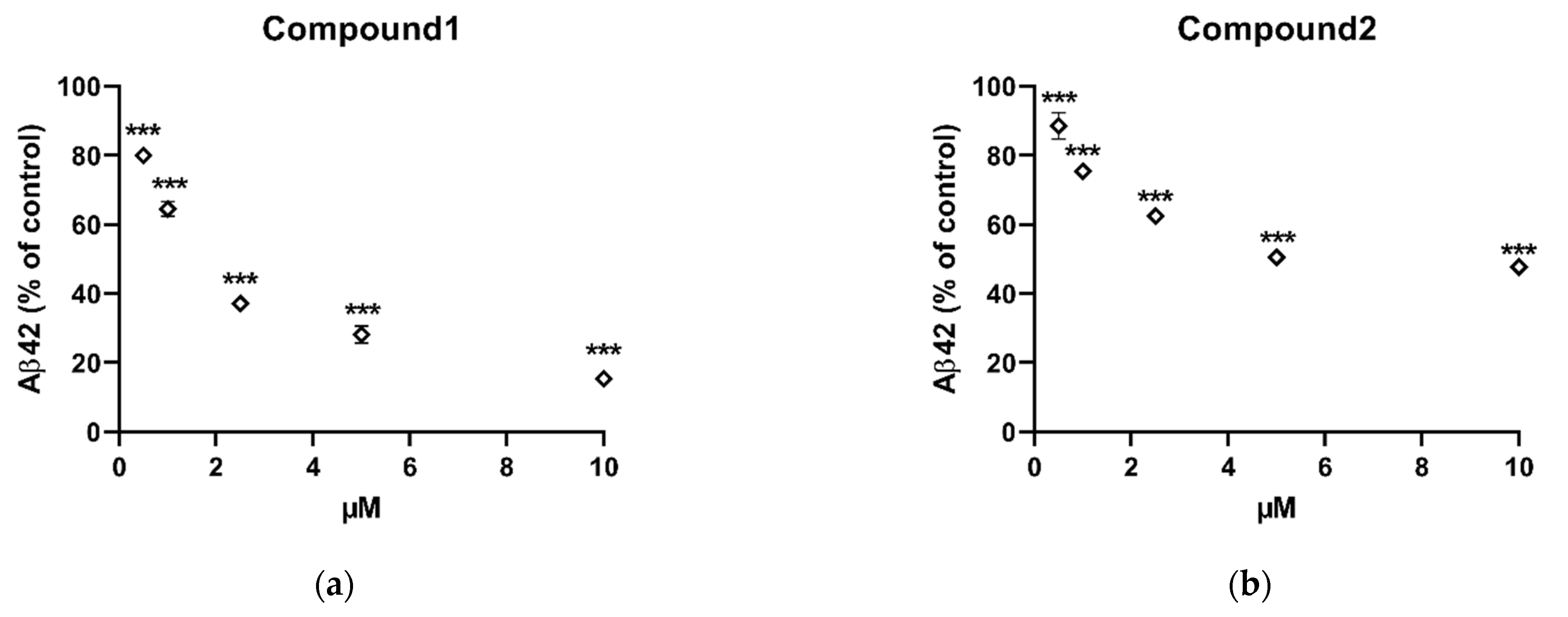
2.2. In Vitro Inhibition of Aβ42 Production by Compounds Isolated from X. Undulatum
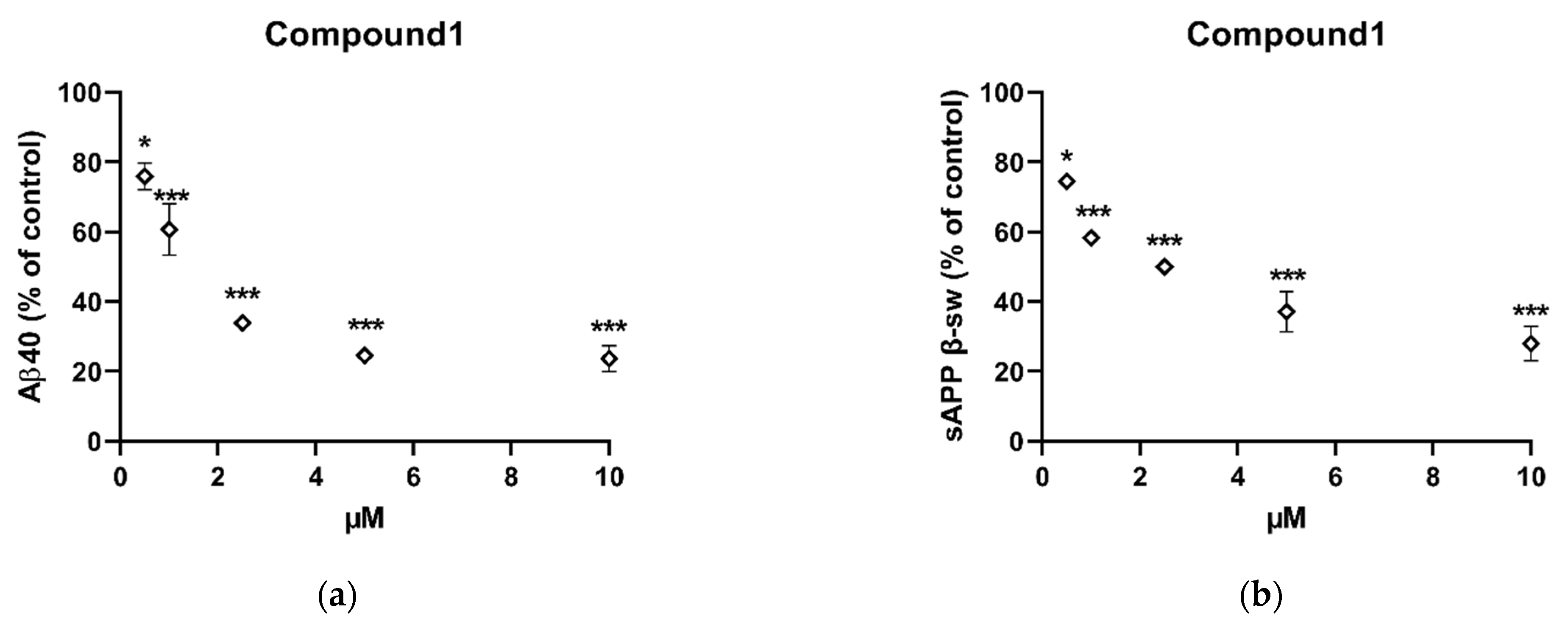
2.3. In Vitro Inhibition of Aβ40 and Sappβ-Sw Production by Compound 1
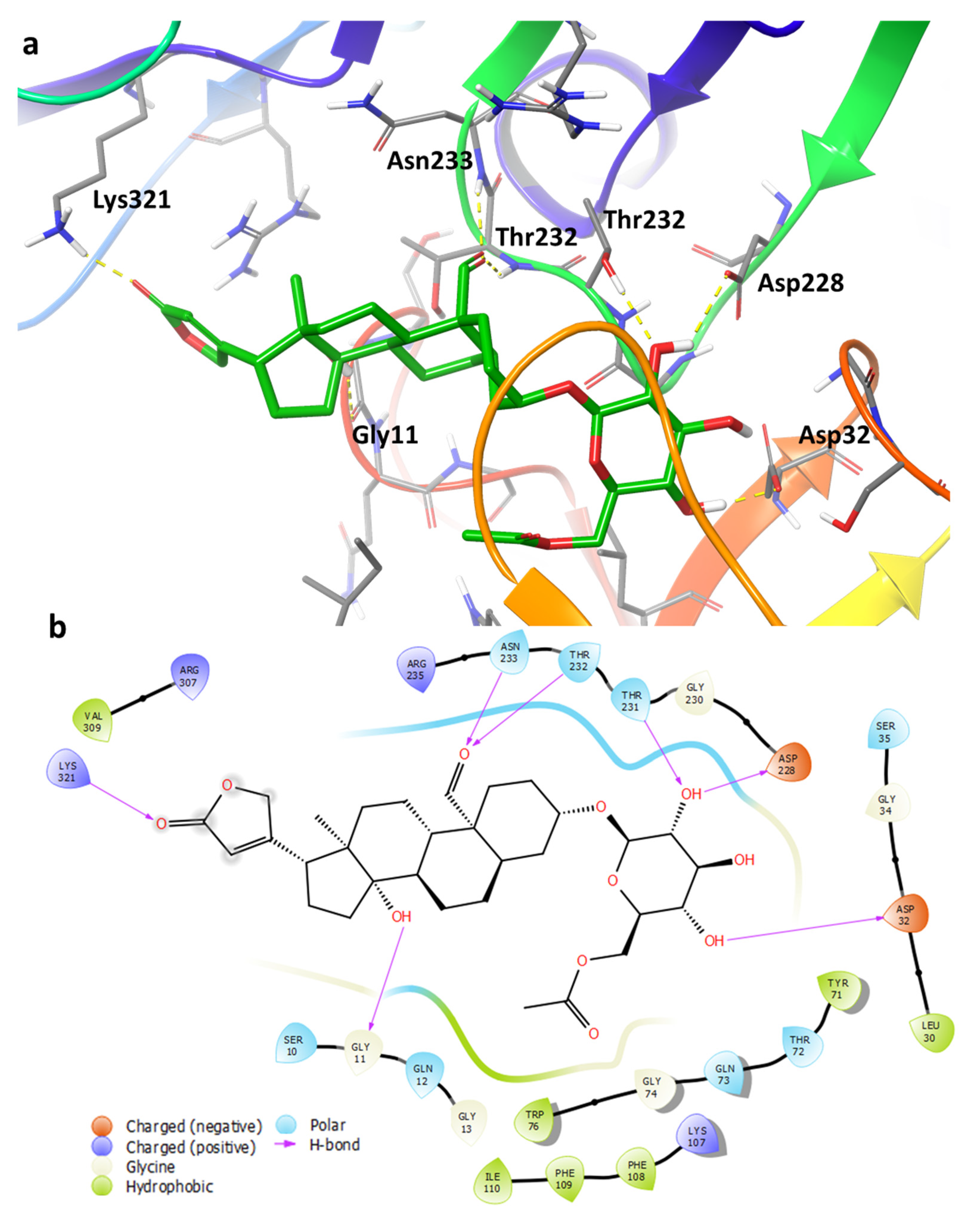
2.4. Binding Pose Analysis of Compound 1 in Β-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein Cleaving Enzyme 1 Active Site
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Extraction, Fractionation, and Isolation of Compounds
4.2. Aβ Peptide Assay
4.3. MS and NMR Analysis
4.4. Target and Ligand Preparation
4.4.1. Molecular Docking
4.4.2. Induced Fit Docking
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaz, M.; Silvestre, S. Alzheimer’s disease: Recent treatment strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Lee, G.; Ritter, A.; Sabbagh, M.; Zhong, K. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2019. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2019, 5, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U. S. Food & Drug Administration, USA. Content Current as of: 07/08/2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/aducanumab-marketed-aduhelm-information (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- Fink, H.A.; Linskens, E.J.; MacDonald, R.; Silverman, P.C.; McCarten, J.R.; Talley, K.M.C.; Forte, M.L.; Desai, P.J.; Nelson, V.A.; Miller, M.A.; et al. Benefits and Harms of Prescription Drugs and Supplements for Treatment of Clinical Alzheimer-Type Dementia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Chun, Y.S.; October, N.; Yang, H.O.; Maharaj, V. Potential of South African medicinal plants targeting the reduction of A$\beta$42 protein as a treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 231, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wyk, B.-E.; Gericke, N. People’s Plants: A Guide to Useful Plants of Southern Africa; Briza Publications: Pretoria, South Africa, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, A.; van Staden, J. Plants used for stress-related ailments in traditional Zulu, Xhosa and Sotho medicine. Part 1: Plants used for headaches. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 43, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmstädter, A. Xysmalobium undulatum (Uzara) research–how everything began. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaak, I.; Enslin, G.M.; Idowu, T.O.; Viljoen, A.M. Xysmalobium undulatum (uzara)–review of an antidiarrhoeal traditional medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Isobiflorin, a chromone C-glucoside from cloves (Eugenia caryophyllata). Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Kumar, Y.; Singh, S.; Ahad, K. Biflorin, a chromone-C-glucoside from Pancratium biflorum. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2591–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascn-Valenzuela, L.; Velzquez, C.; Garibay-Escobar, A.; Medina-Jurez, L.A.; Vilegas, W.; Robles-Zepeda, R.E. Antiproliferative activity of cardenolide glycosides from Asclepias subulata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 171, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Qu, D.H.; Wang, K. Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease through stimulating of non-amyloidogenic processing of amyloid precursor protein. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 2389–2403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, D.; Stankiewicz, A.M.; Mocan, A.; Sah, A.N.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Huminiecki, L.; Horbańczuk, J.O.; Atanasov, A.G. Ethnopharmacological approaches for dementia therapy and significance of natural products and herbal drugs. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V. Potential medicinal plants for CNS disorders: An overview. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2006, 20, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.M.; Buckley, N. Antidotes for acute cardenolide (cardiac glycoside) poisoning. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 4, CD005490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G.; Wolfling, J. Synthetic Cardenolides and Related Compounds. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 8, 1381–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P.; Glupczynski, Y.; Tulkens, P.M. Aminoglycosides: Activity and resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.Y.; Jannat, S.; Edraki, N.; Das, S.; Chang, W.K.; Kim, H.C.; Park, S.K.; Chang, M.S. Flavanone glycosides inhibit β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 and cholinesterase and reduce Aβ aggregation in the amyloidogenic pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 309, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.; Portbury, S.; Thomas, M.B.; Barney, S.; Ricca, D.J.; Morris, D.L.; Warner, D.S.; Lo, D.C. Cardiac glycosides provide neuroprotection against ischemic stroke: Discovery by a brain slice-based compound screening platform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10461–10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storstein, L.; Nore, A.; Sjaastad, O. Studies on digitalis. 23. Blood-brain barrier of digitoxin in humans. Clin. Cardiol. 1979, 2, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and blood–brain barrier drug delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, H.; Nakayama, T.; Shimoda, K.; Matsuura, N.; Hamada, H.; Iwaki, T.; Kiriake, Y.; Saikawa, T. Curcumin Oligosaccharides (Gluco-oligosaccharides) Penetrate the Blood-Brain Barrier in Mouse Brain: Glycoside (Polysaccharide) Modification Approach for Brain Drug Delivery Across the Blood-Brain Barrier and Tumor Drug Delivery. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20953653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, M.; Polt, R. New prospects for glycopeptide based analgesia: Glycoside-induced penetration of the blood-brain barrier. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R. Physiological functions of the β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 and 2. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-2; Maestro; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Schrödinger Release 2021-2: LigPrep; Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein−Ligand Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Yang, Q.; Du, Y.; Feng, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. Comparative Assessment of Scoring Functions: The CASF-2016 Update. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 895–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.; Beard, H.S.; Farid, R. Use of an induced fit receptor structure in virtual screening. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.J.; Tiwary, P.; Borrelli, K.; Feng, S.; Miller, E.B.; Abel, R.; Friesner, R.A.; Berne, B.J. Prediction of Protein-Ligand Binding Poses via a Combination of Induced Fit Docking and Metadynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 2990–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
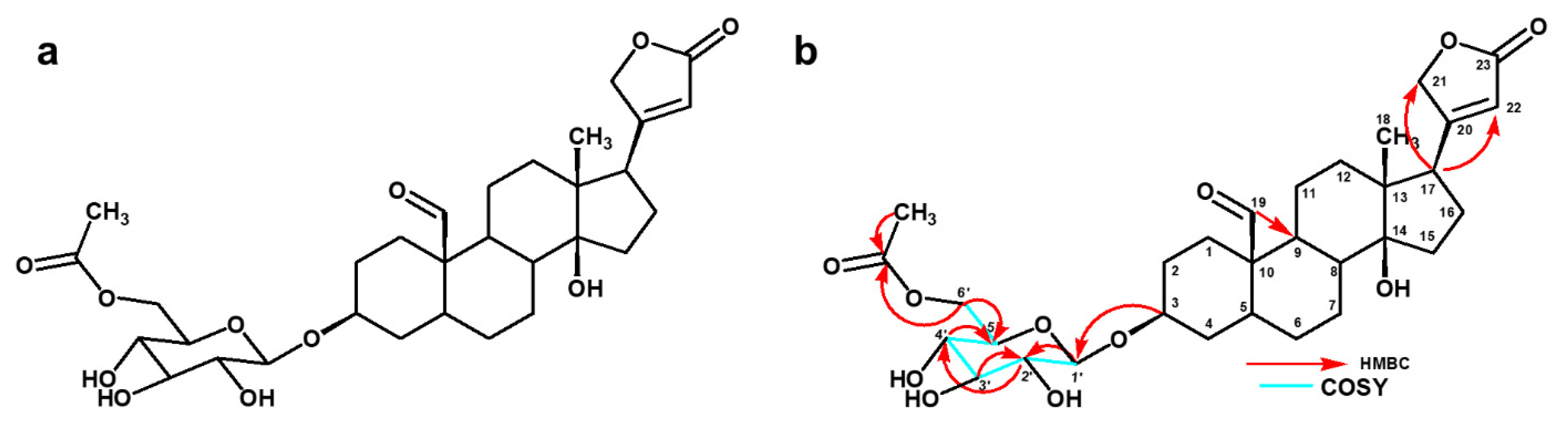



| Position | 13C (ppm) | 1H (ppm), J (Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 28.1 | 1.62, m | C-9 | |
| 1b | 1.51, m | |||
| 2a | 33.0 | 1.96, m | C-3, C-10 | |
| 2b | 1.78, m | |||
| 3 | 77.8 | 3.74, m | ||
| 4a | 25.9 | 1.87, m | ||
| 4b | 1.37, m | |||
| 5 | 41.6 | 1.89, m | C-9 | |
| 6a | 25.1 | 1.92, m | C-5 | |
| 6b | 1.35, m | |||
| 7a | 21.2 | 1.80, m | C-6, C-8 | |
| 7b | 1.34, m | |||
| 8 | 35.0 | 1.98, m | C-5 | |
| 9 | 35.1 | 1.83, m | ||
| 10 | 50.5 | - | ||
| 11a | 20.3 | 1.79, m | C-9, C-10 | |
| 11b | 1.51, m | |||
| 12 | 39.3 | 1.88, m | C-9 | |
| 12b | 1.57, m | |||
| 13 | 49.6 | - | ||
| 14 | 84.5 | - | ||
| 15a | 31.3 | 2.21, m | ||
| 15b | 1.72, m | |||
| 16a | 26.5 | 2.17, m | C-14 | |
| 16b | 1.61, m | |||
| 17 | 50.4 | 2.80 (q, 14.6) | C-13, C-14, C-21, C-22 | |
| 18 | 14.8 | 0.97, s | C-12, C-13, C-14 | |
| 19 | 206.5 | 9.57, s | C-9 | |
| 20 | 175.8 | - | ||
| 21a | 73.9 | 5.03 (dd, 18.5, 1.57) | C-22 | |
| 21b | 4.96 (dd, 18.1, 1.73) | |||
| 22 | 116.4 | 5.92, s | C-17, C-21, C-23 | |
| 23 | 176.9 | - | ||
| 1′ | 101.3 | 4.40 (d, 7.57) | H-2′ | C-3 |
| 2′ | 73.6 | 3.17, m | H-1′, H-3′ | C-1′ |
| 3′ | 70.2 | 3.36, m | H-2′ | |
| 4′ | 73.7 | 3.30, m | H-5′ | |
| 5′ | 76.4 | 3.47, m | H-4′ | |
| 6′a | 63.4 | 4.20 (dd, 11.6, 5.14) | H-5′ | C-2, C-5, -OCOCH3 |
| 6′b | 4.30 (dd, 11.6, 1.84) | |||
| 5′- OCO | 171.2 | - | ||
| 5′- CH3 | 19.3 | 2.08, s | C-5′-OCO |
| Position | 13C (ppm) | 1H (ppm), J (Hz) | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.9 | 2.27, m | C-3, C-5, C-6 | |
| 2a | 30.5 | 1.92, m | ||
| 2b | 1.62, m | |||
| 3 | 79.6 | 3.60, m | ||
| 4 | 40.1 | 1.52, m | ||
| 5 | 140.8 | - | ||
| 6 | 122.7 | 5.44, m | H-7 | C-8 |
| 7a | 27.4 | 2.26, m | H-6 | C-5, C-6 |
| 7b | 2.22, m | |||
| 8 | 38.3 | 1.72, m | ||
| 9 | 47.7 | 1.24, m | ||
| 10 | 38.3 | |||
| 11 | 22.0 | 1.53, m | ||
| 12 | 39.4 | 2.44, m | ||
| 13 | 50.7 | - | ||
| 14 | 86.3 | - | ||
| 15 | 33.8 | 1.74, m | ||
| 16 | 28.1 | 1.73, m | C-14, C-15 | |
| 17 | 52.1 | 2.86, (q, 14.62) | C-12, C-21, C-22, C-23 | |
| 18 | 16.1 | 0.92, s | C-12, C-13, C-14 | |
| 19 | 19.8 | 1.03, s | C-5, C-9, C-10 | |
| 20 | 177.1 | - | ||
| 21a | 75.2 | 5.02, (dd, 18.44, 1.65) | C-22, C-23 | |
| 21b | 4.92, (dd, 18.44, 1.65) | |||
| 22 | 117.8 | 5.91, s | C-13, C-20, C-21 | |
| 23 | 178.2 | - | ||
| 1′ | 102.3 | 4.38 (dd, 7.68) | H-2′ | C-3 |
| 2′ | 75.1 | 3.14, m | C-1′, C-3′ | |
| 3′ | 78.0 | 3.25, m | ||
| 4′ | 71.5 | 3.25, m | ||
| 5′ | 77.7 | 3.35, m | ||
| 6′a | 63.6 | 3.84, m | H-5′ | C-4′, C-5, |
| 6′b | 3.65, m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thakur, A.; Moyo, P.; van der Westhuizen, C.J.; Yang, H.O.; Maharaj, V. A Novel Cardenolide Glycoside Isolated from Xysmalobium undulatum Reduces Levels of the Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Peptides Aβ42 In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080743
Thakur A, Moyo P, van der Westhuizen CJ, Yang HO, Maharaj V. A Novel Cardenolide Glycoside Isolated from Xysmalobium undulatum Reduces Levels of the Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Peptides Aβ42 In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(8):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080743
Chicago/Turabian StyleThakur, Anuradha, Phanankosi Moyo, Carl Johan van der Westhuizen, Hyun Ok Yang, and Vinesh Maharaj. 2021. "A Novel Cardenolide Glycoside Isolated from Xysmalobium undulatum Reduces Levels of the Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Peptides Aβ42 In Vitro" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 8: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080743
APA StyleThakur, A., Moyo, P., van der Westhuizen, C. J., Yang, H. O., & Maharaj, V. (2021). A Novel Cardenolide Glycoside Isolated from Xysmalobium undulatum Reduces Levels of the Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Peptides Aβ42 In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals, 14(8), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080743