Investigation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Effect of Cycas thouarsii R.Br. Extract against Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
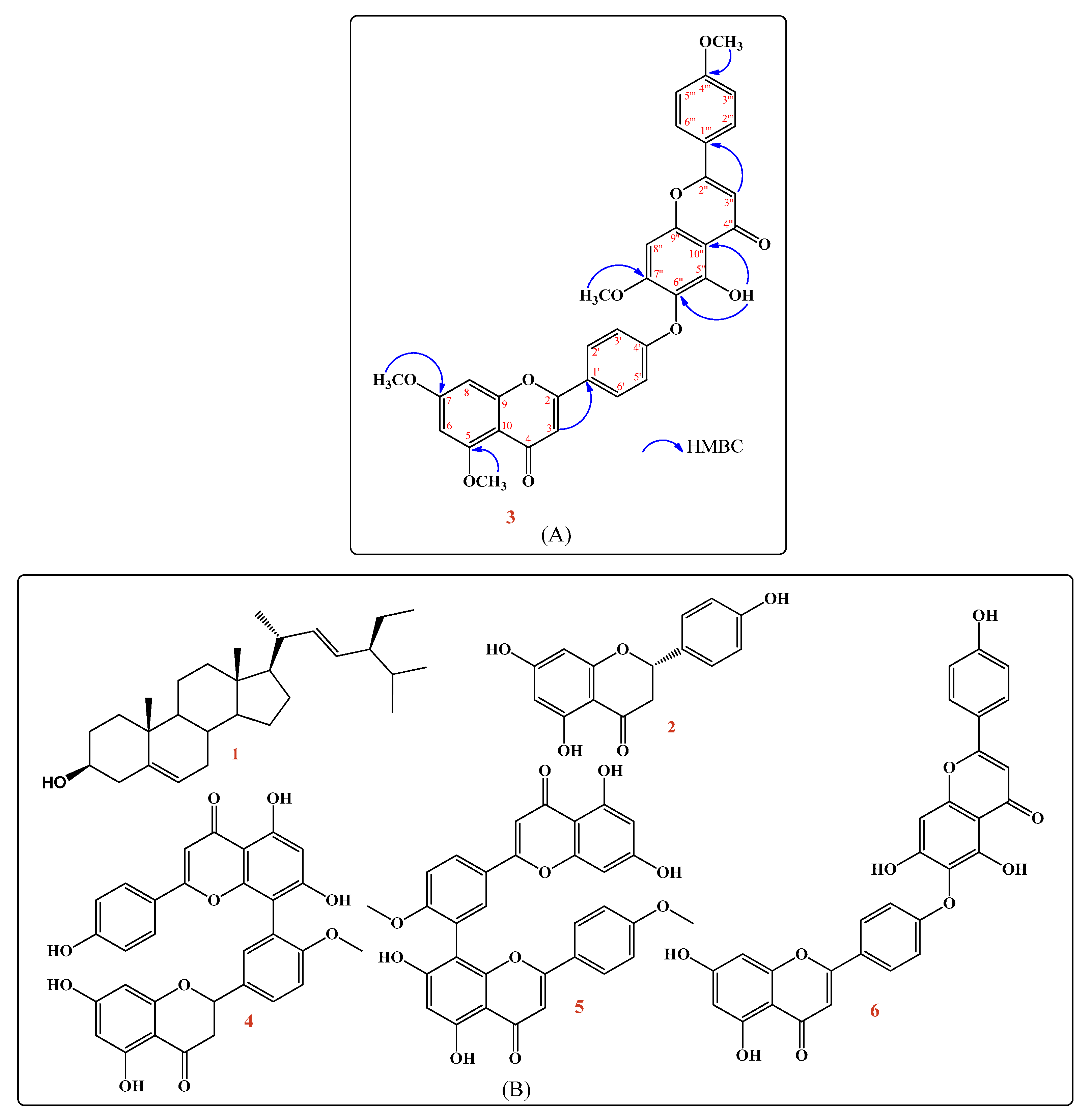
2.1. Phytochemical Investigation
2.1.1. Spectroscopic Data
2.1.2. Structure Elucidation of the Isolated New Compound (3)
2.2. Biological Investigation
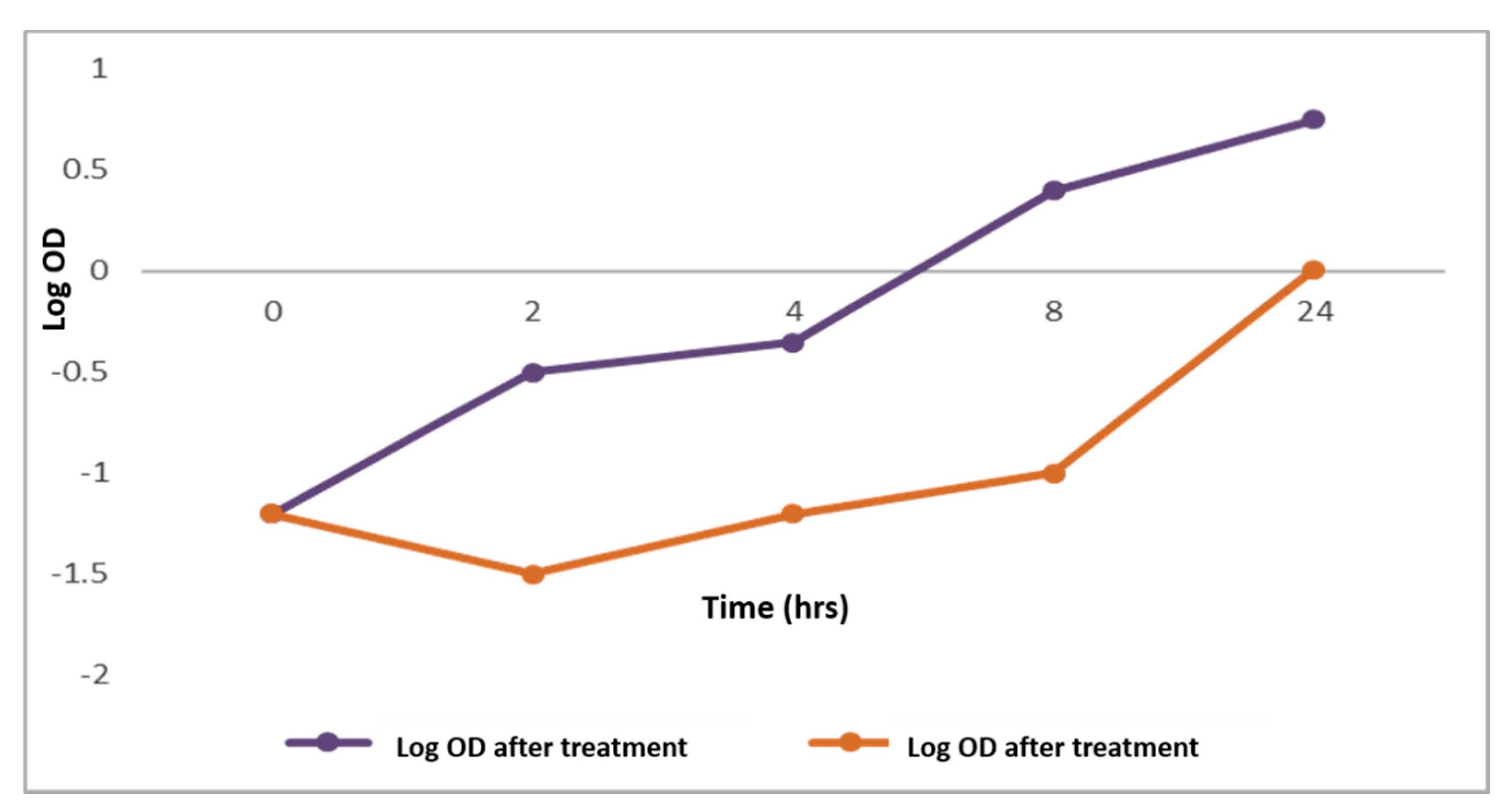
2.2.1. Bacterial Growth Curve
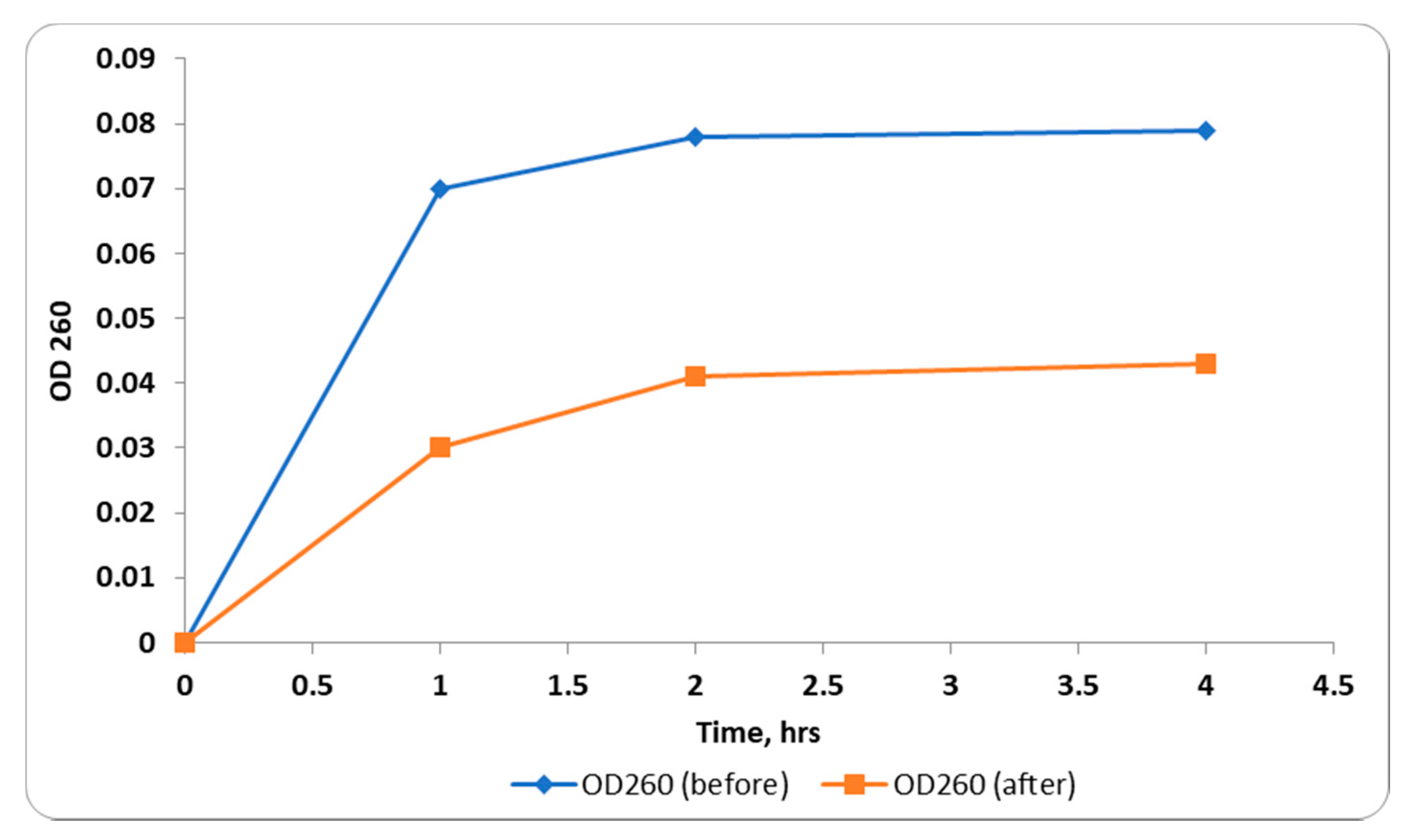
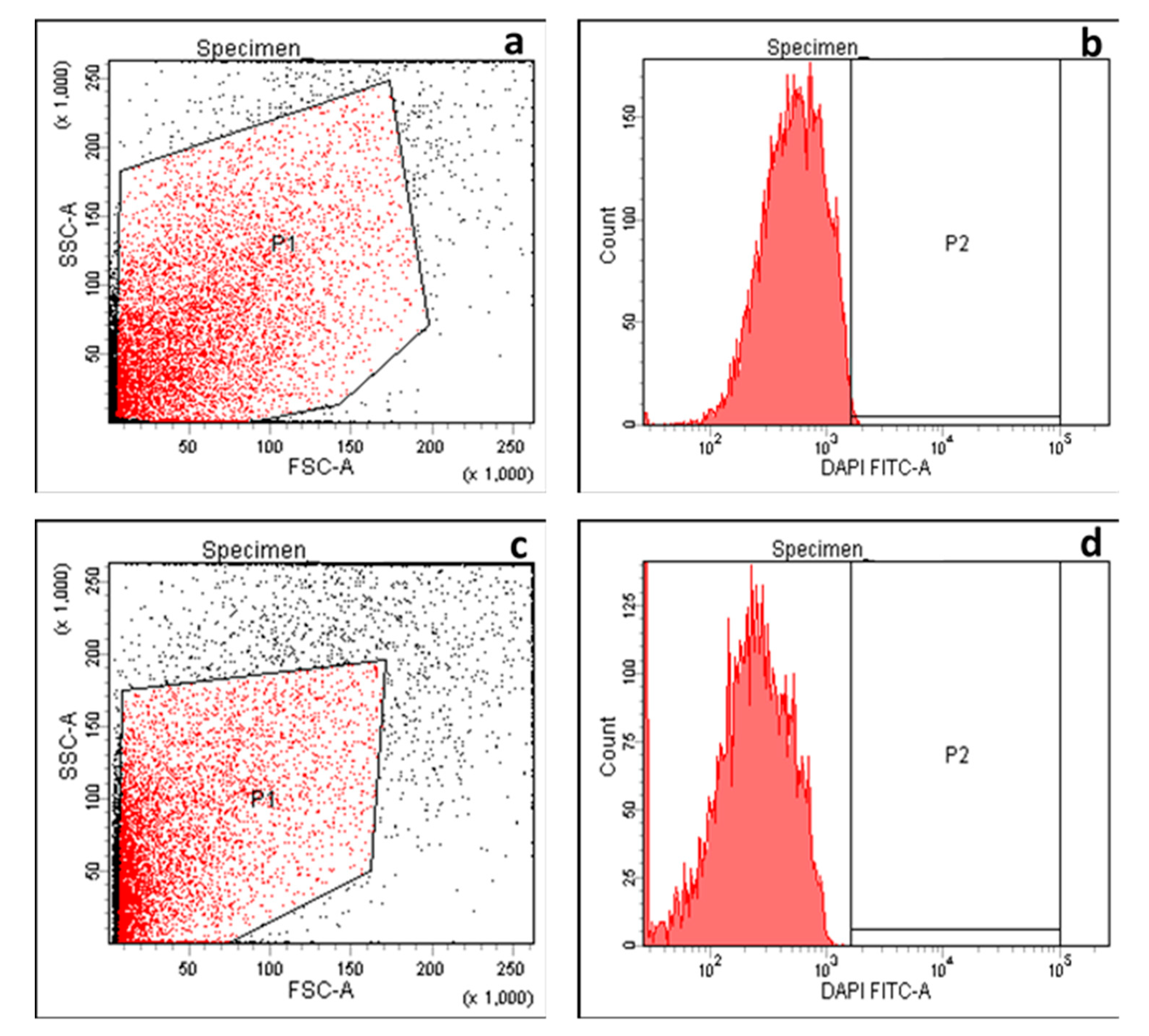
2.2.2. Integrity of Cell Membranes
2.2.3. Inner Membrane Permeability Assay
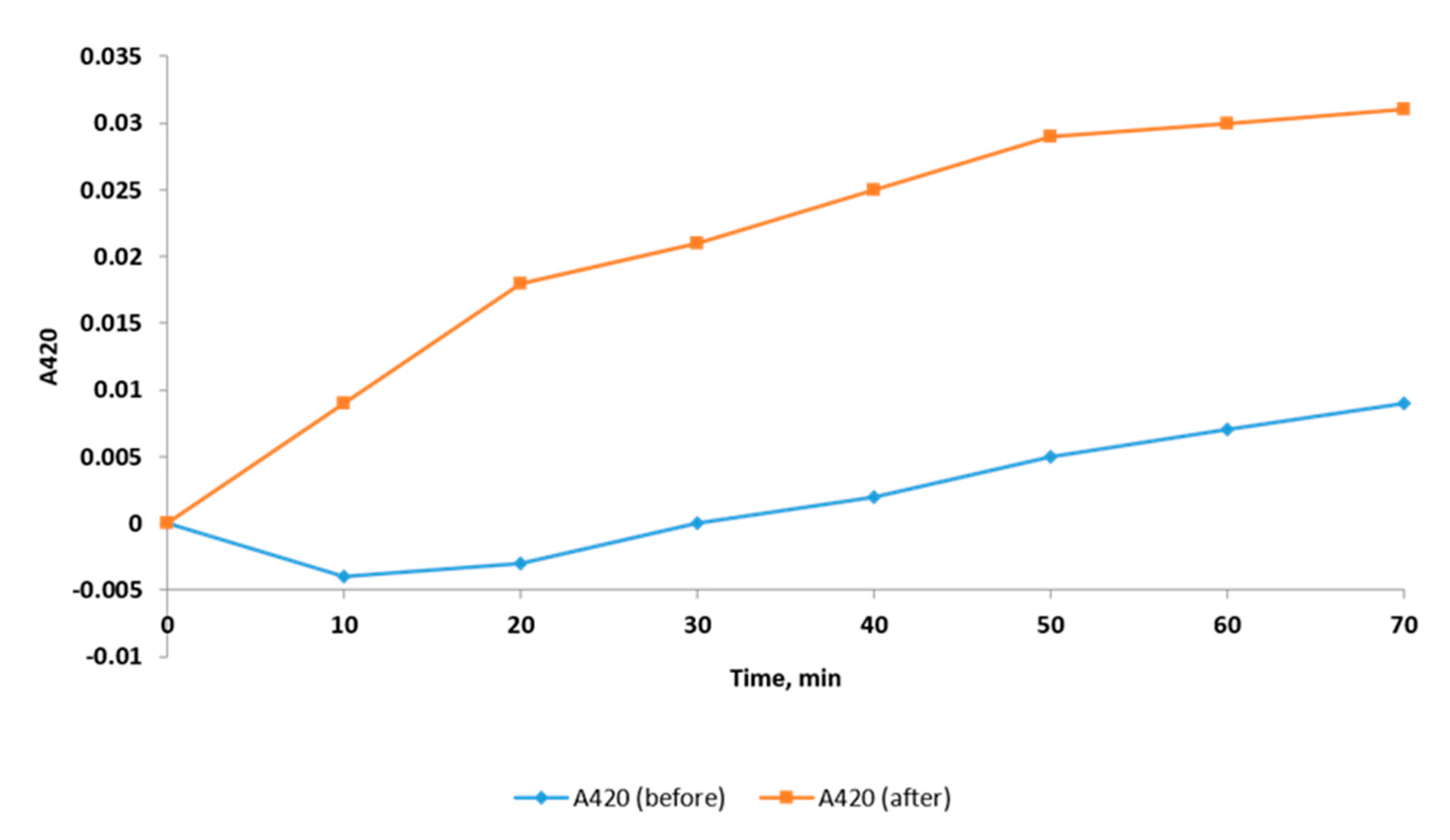
2.2.4. Outer Membrane Permeability
2.2.5. Membrane Depolarization Assay
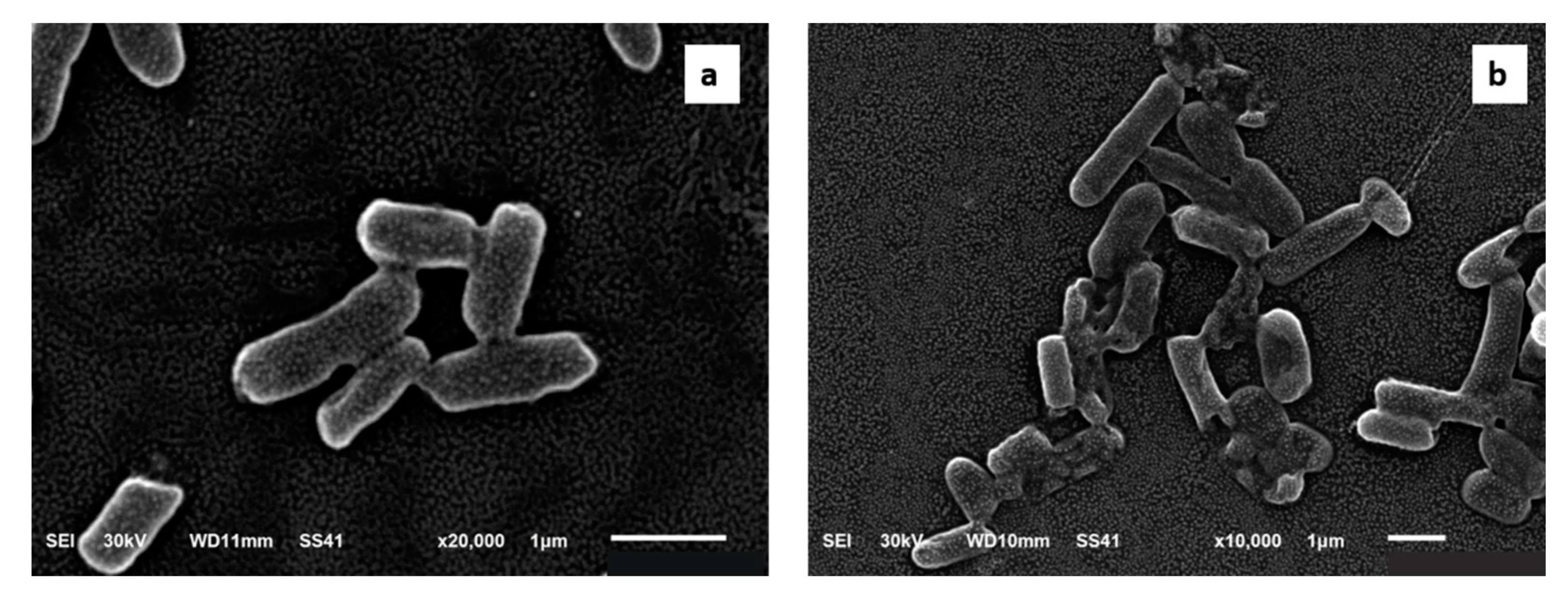
2.2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Examination
2.2.7. Detection of Efflux
2.2.8. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.2.9. Antimicrobial Activity of Different Fractions and Isolated Pure Compounds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Plant Extract and Isolation of Pure Compounds
4.2. Bacterial Isolates
4.3. Chemicals
4.4. Antibacterial Screening
4.5. Determination of the MIC Values
4.6. Bacterial Growth Curve
4.7. Integrity of Cell Membranes
4.8. Inner Membrane Permeability Assay
4.9. Outer Membrane Permeability Assay
4.10. Membrane Depolarization Assay
4.11. SEM Examination
4.12. Evaluation of Efflux Activity Using Cartwheel Method
4.13. qRT-PCR
4.14. General Instruments
4.15. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Effah, C.Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae: An increasing threat to public health. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benthall, G.; Touzel, R.E.; Hind, C.K.; Titball, R.W.; Sutton, J.M.; Thomas, R.J.; Wand, M.E. Evaluation of antibiotic efficacy against infections caused by planktonic or biofilm cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Galleria mellonella. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.T.; Onishi, M.; Mizusawa, M.; Kitagawa, R.; Kishino, T.; Matsubara, F.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kuroda, T.; Ogawa, W. The role of RND-type efflux pumps in multidrug-resistant mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Chenouf, N.S.; Carvalho, J.A.; Castro, A.P.; Silva, V.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Enes Dapkevicius, M.d.L.N.; Igrejas, G.; Torres, C. Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae harboring extended spectrum β-lactamase encoding genes isolated from human septicemias. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giske, C.G.; Monnet, D.L.; Cars, O.; Carmeli, Y. Clinical and economic impact of common multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cousins, S.; Witkowski, E. African cycad ecology, ethnobotany and conservation: A synthesis. Bot. Rev. 2017, 83, 152–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, W.; Abo El-Seoud, K.; Kabbash, A.; El-Aasr, M. Investigation of the Biological Activity Some Gymnosperm Plants Belong to Cycadales Order. J. Adv. Med. Pharm. Res. 2020, 1, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, W.A.; Abo El-Seoud, K.A.; Kabbash, A.; Kassab, A.A.; El-Aasr, M. Hepatoprotective, cytotoxic, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Dioon spinulosum leaves Dyer Ex Eichler and its isolated secondary metabolites. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, W.A.; Ibrahim, A.E.-R.S.; El-Seoud, K.A.; Attia, G.I.; Ragab, A.E. A new cytotoxic and antioxidant Amentoflavone Monoglucoside from Cycas revoluta Thunb growing in Egypt. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 8, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Moawad, A.; Hetta, M.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Jacob, M.R.; Hifnawy, M.; Ferreira, D. Phytochemical investigation of Cycas circinalis and Cycas revoluta leaflets: Moderately active antibacterial biflavonoids. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dora, G.; Edwards, J. Taxonomic status of Lanaria lanata and isolation of a novel biflavone. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, K.R.; Sheppard, C.; Geiger, H. 13C NMR studies of some naturally occurring amentoflavone and hinokiflavone biflavonoids. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 3335–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, H.; Seeger, T.; Hahn, H.; Zinsmeister, H.D.; Markham, K.R.; Wong, H. 1HNMR Assignments in Biflavonoid Spectra by Proton-Detected CH Correlation. Z. Nat. C 1993, 48, 821–826. [Google Scholar]
- Meurer-Grimes, B.; Yu, J. Chamaecyparin-a rare biflavone from Selaginella species. Z. Nat. C 1999, 54, 1143–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Banna, T.; Abd El-Aziz, A.; Sonbol, F.; El-Ekhnawy, E. Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates to benzalkonium chloride retards its growth and enhances biofilm production. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3437–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L. Chitosan kills bacteria through cell membrane damage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, M.; Lee, D.G. Silver nanoparticles against Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium: Role of inner membrane dysfunction. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Sarkar, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Saha, P.; Haldar, S.; Karmakar, S.; Sen, T. Alteration of Zeta potential and membrane permeability in bacteria: A study with cationic agents. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sonbol, F.I.; El-Banna, T.; Abd El-Aziz, A.A.; El-Ekhnawy, E. Impact of triclosan adaptation on membrane properties, efflux and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli clinical isolates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, E.; Trump, B. Histologic fixatives suitable for diagnostic light and electron microscopy. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1976, 100, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelaziz, A.; Sonbol, F.; Elbanna, T.; El-Ekhnawy, E. Exposure to sublethal concentrations of benzalkonium chloride induces antimicrobial resistance and cellular changes in Klebsiellae pneumoniae clinical isolates. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, U.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N. A comprehensive review on medicinal plants as antimicrobial therapeutics: Potential avenues of biocompatible drug discovery. Metabolites 2019, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chitemerere, T.A.; Mukanganyama, S. Evaluation of cell membrane integrity as a potential antimicrobial target for plant products. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Górniak, I.; Bartoszewski, R.; Króliczewski, J. Comprehensive review of antimicrobial activities of plant flavonoids. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latha, L.Y.; Darah, I.; Kassim, M.J.N.M.; Sasidharan, S. Antibacterial activity and morphological changes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells after exposure to Vernonia cinerea extract. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2010, 34, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, R. Efflux pump inhibitors for bacterial pathogens: From bench to bedside. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdankhah, S.P.; Scheie, A.A.; Høiby, E.A.; Lunestad, B.-T.; Heir, E.; Fotland, T.Ø.; Naterstad, K.; Kruse, H. Triclosan and antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: An overview. Microb. Drug Resist. 2006, 12, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFaddin, J. Biochemical Tests for Identification of Medical Bacteria; Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.C.; De, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Das, M. Antibacterial activity and Phytochemical analysis of Cardanthera difformis Druce leaf extracts from West Bengal, India. Int. J. Phytomed. 2013, 5, 446. [Google Scholar]
- Wayne, A. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; 20th Informational Supplement; CLSI Document; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Howard County, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Attallah, N.G.; Negm, W.A.; Elekhnawy, E.; Altwaijry, N.; Elmongy, E.I.; El-Masry, T.A.; Alturki, E.A.; Yousef, D.A.; Y Shoukheba, M. Antibacterial Activity of Boswellia sacra Flueck. Oleoresin Extract against Porphyromonas gingivalis Periodontal Pathogen. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Pensec, J.; Soumet, C. Resistance in Escherichia coli: Variable contribution of efflux pumps with respect to different fluoroquinolones. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
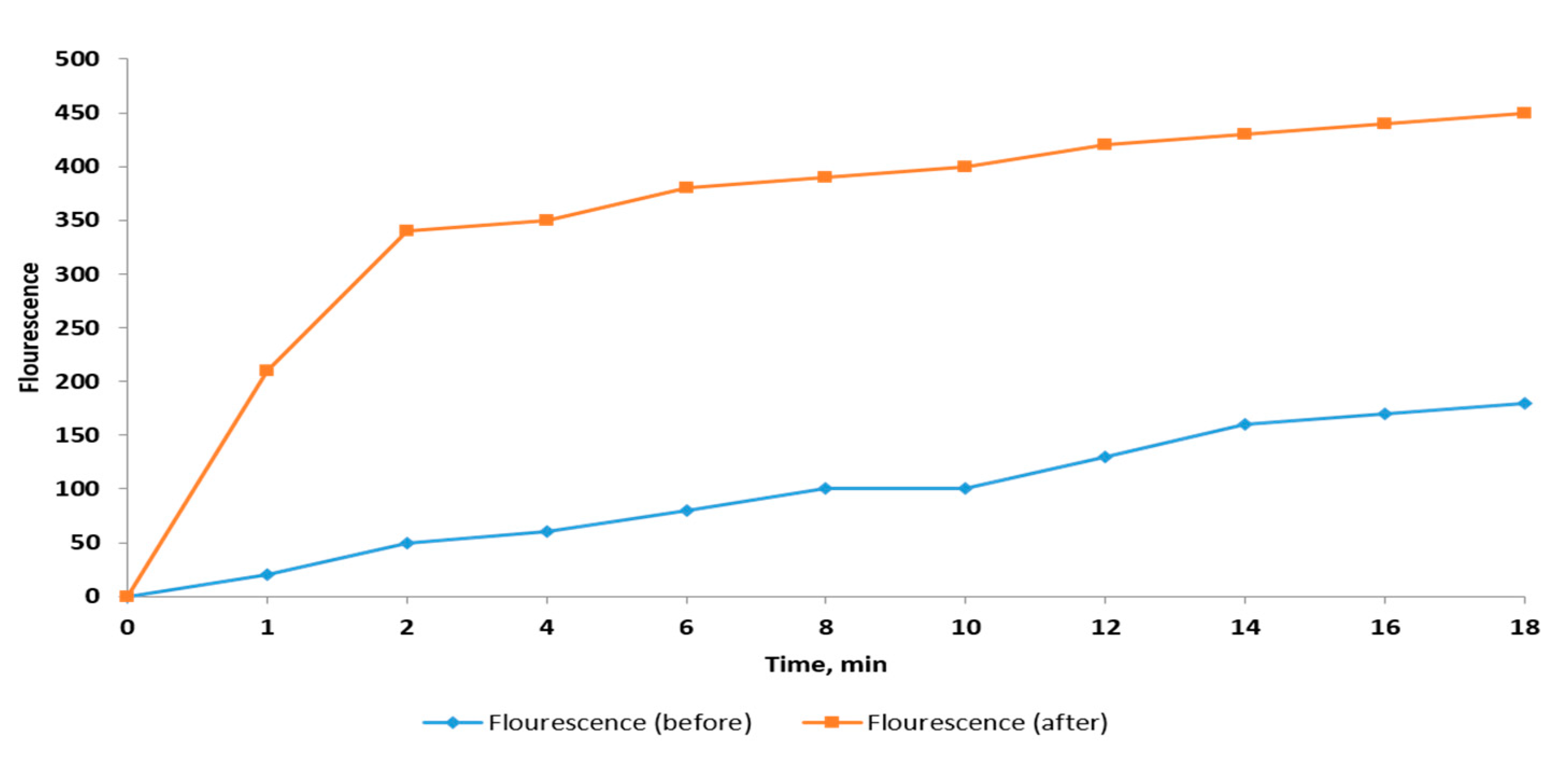

| EtBr Concentration (mg/L) * | Number of Bacterial Isolates (before Treatment) | Number of Bacterial Isolates (after Treatment) |
|---|---|---|
| ≤0.5 | 10 | 23 |
| 1 | 11 | 4 |
| 1.5 | 9 | 6 |
| 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Isolate Code | Relative Gene Expression * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| norE | acrB | mdfA | yihV | |
| K1 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2 |
| K2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.3 |
| K3 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.2 |
| K4 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.2 |
| K5 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| K6 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.8 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| K7 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
| K8 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 0.3 |
| K9 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negm, W.A.; El-Aasr, M.; Kamer, A.A.; Elekhnawy, E. Investigation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Effect of Cycas thouarsii R.Br. Extract against Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080756
Negm WA, El-Aasr M, Kamer AA, Elekhnawy E. Investigation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Effect of Cycas thouarsii R.Br. Extract against Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(8):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080756
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegm, Walaa A., Mona El-Aasr, Amal Abo Kamer, and Engy Elekhnawy. 2021. "Investigation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Effect of Cycas thouarsii R.Br. Extract against Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 8: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080756
APA StyleNegm, W. A., El-Aasr, M., Kamer, A. A., & Elekhnawy, E. (2021). Investigation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Effect of Cycas thouarsii R.Br. Extract against Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals, 14(8), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080756








