Hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Kompolti cv.) and Hop (Humulus lupulus L., Chinook cv.) Essential Oil and Hydrolate: HS-GC-MS Chemical Investigation and Apoptotic Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EOs Density and Refractive Index Determination
2.2. Chemical Analyses of Chinook Hop and Kompolti Hemp Hys and EOs
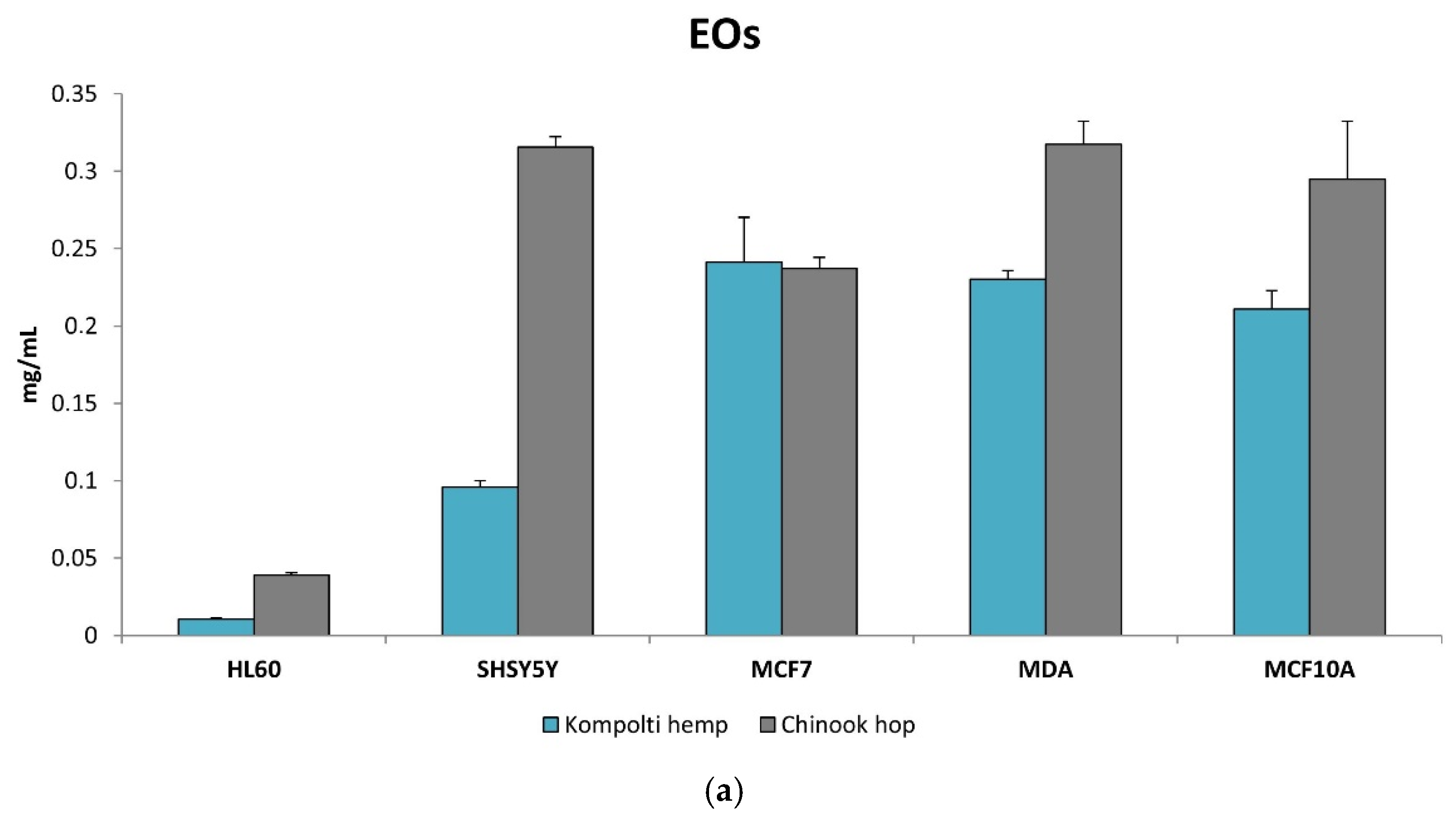
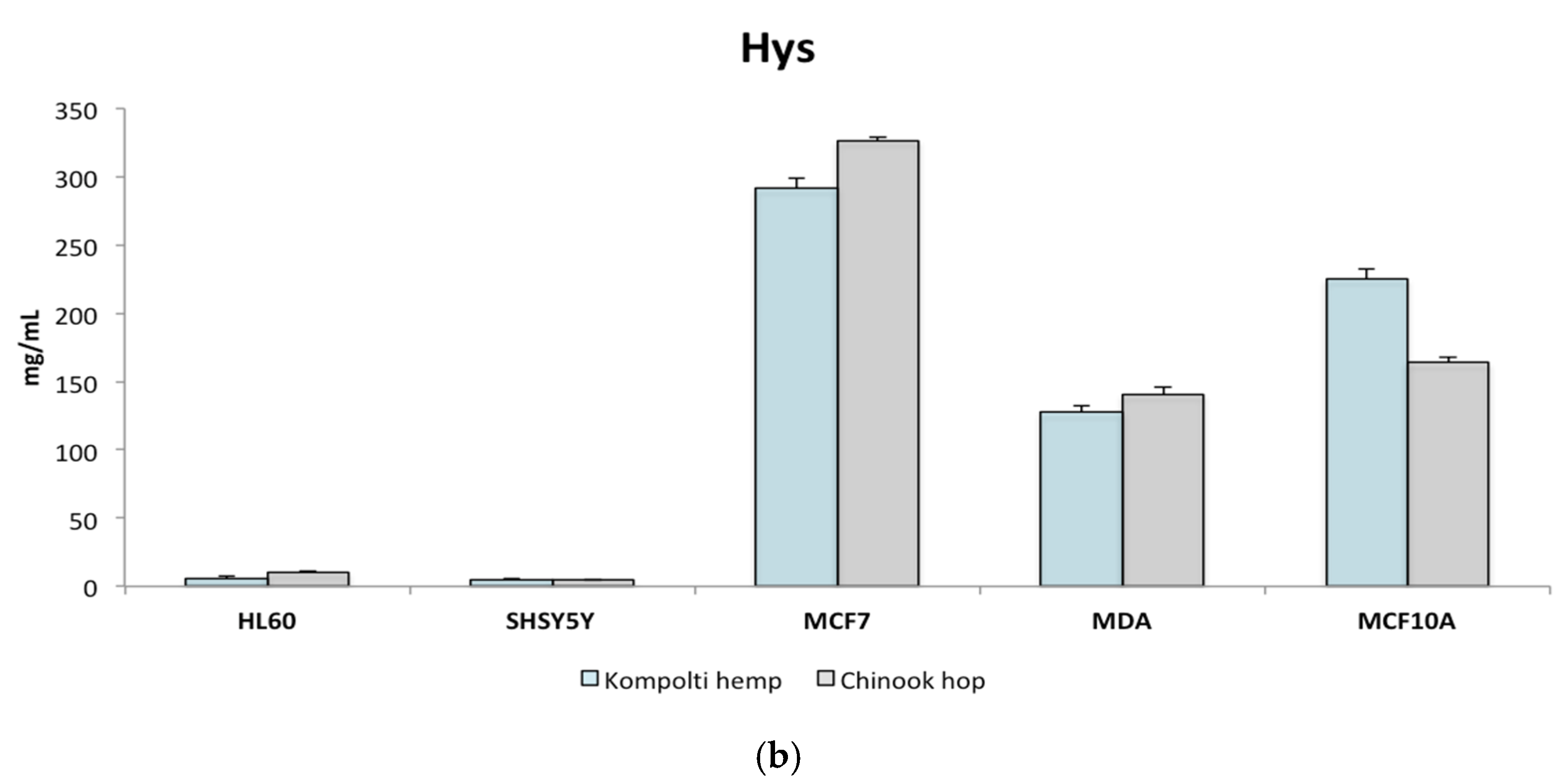
2.3. Cytotoxicity Determination of EOs and Hys Using MTT Assay
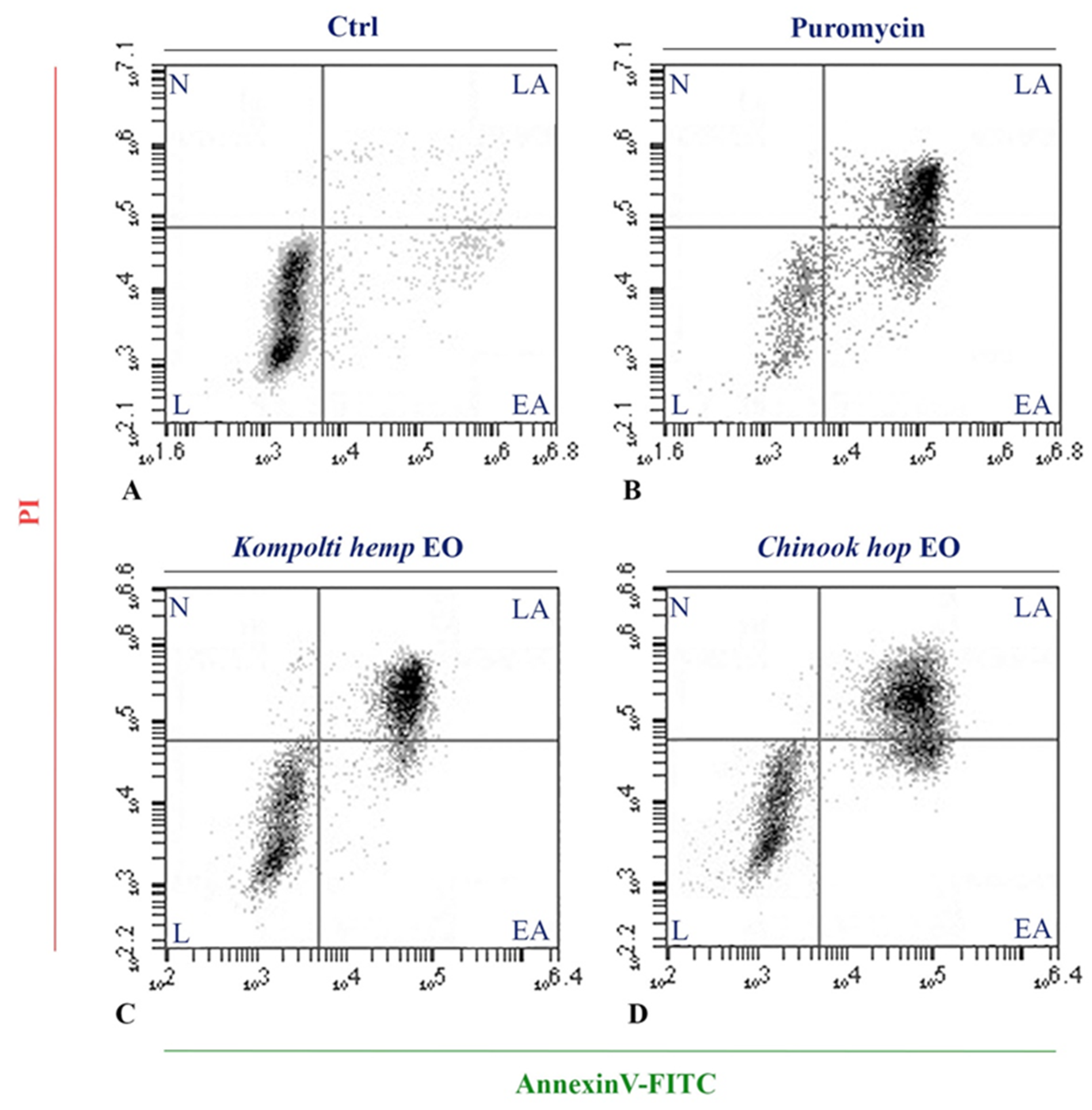
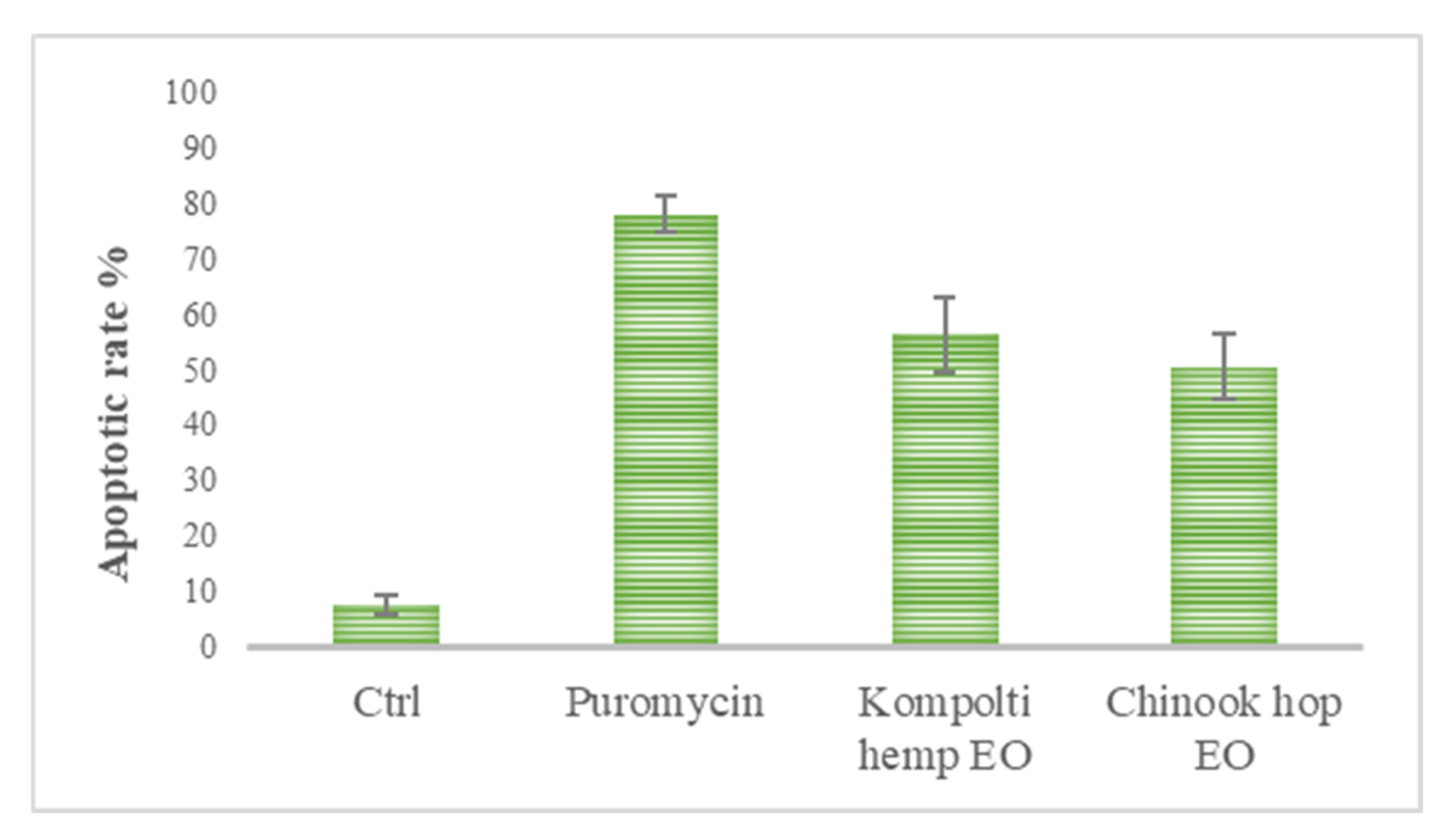
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
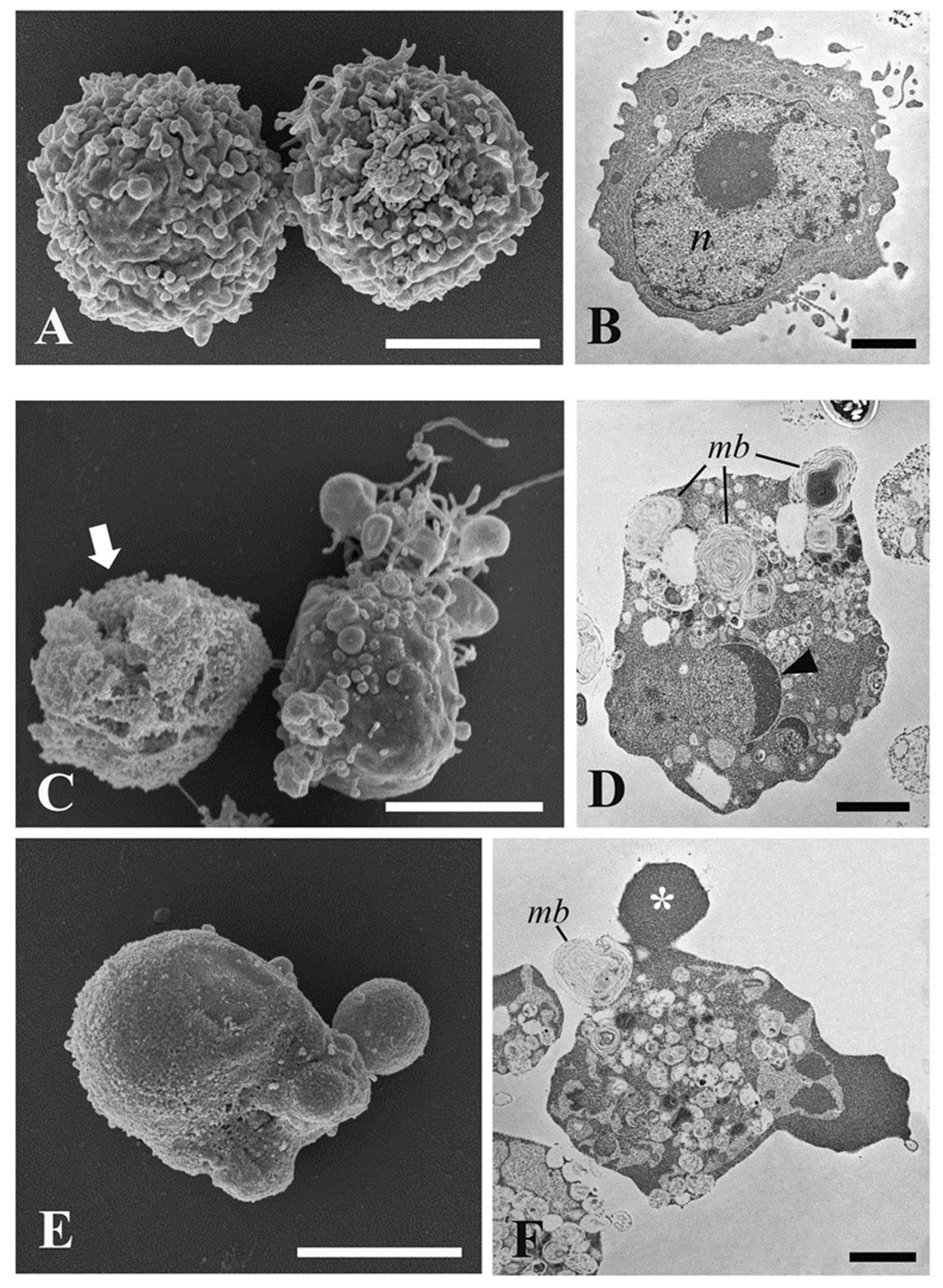
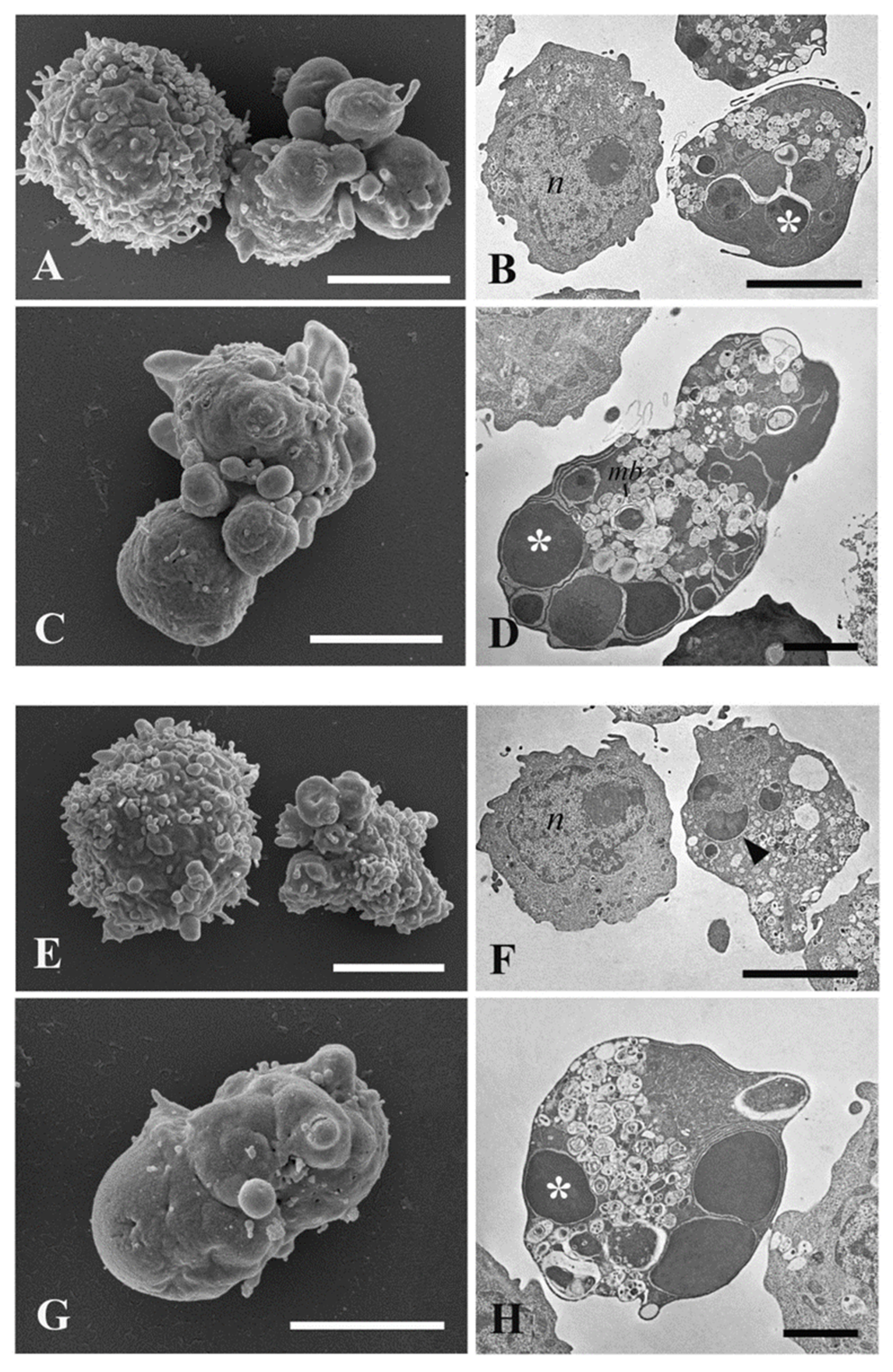
2.5. Ultrastructural Investigations by Transmission and Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Hydrodistillation (HD)
4.4. Moisture Content Evaluation of Frozen Hemp
4.5. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
4.6. Headspace–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (HS-GC-MS)
4.7. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis
4.8. Cell culture and Maintenance
4.8.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.8.2. Selective Index
4.9. Flow Cytometry
4.10. Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sytsma, K.J.; Morawetz, J.; Pires, J.C.; Nepokroeff, M.; Conti, E.; Zjhra, M.; Hall, J.C.; Chase, M.W. Urticalean rosids: Circumscription, Rosid ancestry, and phylogenetics based on rbcL, trnL-trnF, and ndhF sequences. Amer. J. Bot. 2002, 89, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.Q.; van Velzen, R.; Bakker, F.T.; Sattarian, A.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. Molecular phylogenetics and character evolution of Cannabaceae. Taxon 2013, 62, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, S.; Kayser, O. The cannabis plant: Botanical aspects. In Handbook of Cannabis and Related Pathologies; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Small, E. Classification of Cannabis sativa L. in relation to agricultural, biotechnological, medical and recreational utilization. In Cannabis sativa L.-Botany and Biotechnology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Moliterni, V.M.C.; Cattivelli, L.; Ranalli, P.; Mandolino, G. The sexual differentiation of Cannabis sativa L.: A morphological and molecular study. Euphytica 2004, 140, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Lata, H.; Chandra, S.; Khan, I.A.; ElSohly, M.A. Morpho-anatomy of marijuana (Cannabis sativa L.). In Cannabis sativa L. Botany and Biotechnology; Chandra, S., Lata, H., Elsohly, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Strzelczyk, M.; Lochynska, M.; Chudy, M. Systematics and botanical characteristics of industrial hemp Cannabis sativa L. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Tambaro, S.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Memo, M.; Mastinu, A. Cannabis sativa: A comprehensive ethnopharmacological review of a medicinal plant with a long history. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, W. Cannabinoid pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1986, 38, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona, F.; Takahashi, R. Psychopharmacology of the endocannabinoids: Far beyond anandamide. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R. The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soorni, A.; Fatahi, R.; Haak, D.C.; Salami, S.A.; Bombarely, A. Assessment of Genetic Diversity and Population Structure in Iranian Cannabis Germplasm. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafaei Dehnavi, M.; Ebadi, A.; Peirovi, A.; Taylor, G.; Salami, S.A. THC and CBD Fingerprinting of an Elite Cannabis Collection from Iran: Quantifying Diversity to Underpin Future Cannabis Breeding. Plants 2022, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, T.; Baghaei, K.; Moghadam, V.E.; Farrokhi, N.; Salami, S.A. Extracellular vesicles of cannabis with high CBD content induce anticancer signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, S.A.; Martinelli, F.; Giovino, A.; Bachari, A.; Arad, N.; Mantri, N. It is our turn to get cannabis high: Put cannabinoids in food and health baskets. Molecules 2020, 25, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meijer, E.; Bagatta, M.; Carboni, A.; Crucitti, P.; Moliterni, V.; Ranalli, P.; Mandolino, G. The inheritance of chemical phenotype in Cannabis sativa L. Genetics 2003, 63, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPartland, J.M. Cannabis systematics at the levels of family, genus, and species. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018, 3, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocquet, L.; Sahpaz, S.; Hilbert, J.L.; Rambaud, C.; Rivière, C. Humulus lupulus L., a very popular beer ingredient and medicinal plant: Overview of its phytochemistry, its bioactivity, and its biotechnology. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 1047–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E. Hop (Humulus lupulus)—A bitter crop with sweet prospects. Biodiversity 2016, 17, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoli, P.; Zavatti, M. Pharmacognostic and pharmacological profile of Humulus lupulus L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpelainen, H.; Pietiläinen, M. Hop (Humulus lupulus L.): Traditional and Present Use, and Future Potential. Econ. Bot. 2021, 75, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R. The chemistry of hop constituents. Chem. Rev. 1967, 67, 19–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzele, M. Centenary Review—100 Years of hop chemistry and its relevance to brewing. J. Inst. Brew. 1986, 92, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamand, S.R.; Aldenhoff, J.M. Bitter tasting compounds of beer. Chemistry and taste properties of some hop resin compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1973, 21, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.-F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novak, J.; Zitterl-Eglseer, K.; Deans, S.G.; Franz, C.M. Essential oils of different cultivars of Cannabis sativa L. and their antimicrobial activity. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2001, 16, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, S.; Maggio, F.; Pellegrini, M.; Ricci, A.; Serio, A.; Paparella, A.; Lo Sterzo, C. Effect of the Distillation Time on the Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Potential and Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils from Different Cannabis sativa L. Cultivars. Molecules 2021, 26, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzara, E.; Carletti, R.; Petrelli, R.; Mustafa, A.M.; Caprioli, G.; Fiorini, D.; Scortichini, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Sut, S.; Nuñez, S.; et al. Green extraction of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) using microwave method for recovery of three valuable fractions (essential oil, phenolic compounds and cannabinoids): A central composite design optimization study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieracci, Y.; Ascrizzi, R.; Terreni, V.; Pistelli, L.; Flamini, G.; Bassolino, L.; Fulvio, F.; Montanari, M.; Paris, R. Essential Oil of Cannabis sativa L: Comparison of Yield and Chemical Composition of 11 Hemp Genotypes. Molecules 2021, 26, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, L.; Zatta, A.; Stefanini, I.; Grandi, S.; Sgorbati, B.; Biavati, B.; Monti, A. Characterization and antimicrobial activity of essential oils of industrial hemp varieties (Cannabis sativa L.). Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuerich, M.; Ferfuia, C.; Zuliani, F.; Piani, B.; Sepulcri, A.; Baldini, M. Yield and Quality of Essential Oils in Hemp Varieties in Different Environments. Agronomy 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheljazkov, V.D.; Maggi, F. Valorization of CBD-hemp through distillation to provide essential oil and improved cannabinoids profile. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicaloni, V.; Salvini, L.; Vitalini, S.; Garzoli, S. Chemical Profiling and Characterization of Different Cultivars of Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by SPME-GC-MS and UPLC-MS. Separations 2022, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzara, E.; Torresi, J.; Fico, G.; Papini, A.; Kulbaka, N.; Dell’Acqua, S.; Sut, S.; Garzoli, S.; Mustafa, A.M.; Cappellacci, L.; et al. A Comprehensive Phytochemical Analysis of Terpenes, Polyphenols and Cannabinoids, and Micromorphological Characterization of 9 Commercial Varieties of Cannabis sativa L. Plants 2022, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, M. Hop aromatic compounds. In European Brewery Convention Monograph 22—Symposium on Hops, Zoeterwoude, The Netherlands, May/June 1994; Fachverlag Hans Carl: Nürnberg, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Eyres, G.; Dufour, J.-P. Hop essential oil: Analysis, chemical composition and odor characteristics. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, C.; Cook, D.; Huismann, M.; Wilson, C.; Ford, R. The multisensory perception of hop essential oil: A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2020, 126, 320–342. [Google Scholar]
- Mockute, D.; Bernotiene, G.; Nivinskiene, O.; Butkiene, R. Variability of volatiles of wild Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) growing in Eastern Lithuania. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2008, 20, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernotiene, G.; Nivinskiene, O.; Butkiene, R.; Mockute, D. Chemical composition of essential oils of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) growing wild in Aukštaitija. Chemija 2004, 15, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Malizia, R.A.; Molli, J.S.; Cardell, D.A.; Grau, R.J.A. Essential oil of hop cones (Humulus lupulus L.). J. Essent. Oil Res. 1999, 11, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eri, S.; Khoo, B.K.; Lech, J.; Hartman, T.G. Thermal desorption-gas-chromatography and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry profiling of hop (Humulus lupulus L.). J. Agr. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalaska, G.; Bouchentouf, S.; Kowalski, R.; Wyrostek, J.; Pankiewicz, U.; Mazurek, A.; Sujka, M.; Włodarczyk-Stasiak, M. The hop cones (Humulus lupulus L.): Chemical composition, antioxidant properties and molecular docking simulations. J. Herb. Med. 2022, 33, 100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Rodríguez-Solana, R.; Cortés-Diéguez, S.M.; Domínguez, J.M. Use of hydrodistillation and headspace solid-phase microextraction to characterize the volatile composition of different hop cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiotis, S.T.; Langezaal, C.R.; Scheffer, J.J.C.; Verpoorte, R. Comparative study of the essential oils from hops of various Humulus lupulus L. cultivars. Flavour. Fragr. J. 1989, 4, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirovetz, L.; Bail, S.; Buchbauer, G.; Denkova, Z.; Slavchev, A.; Stoyanova, A.; Schmidt, E.; Geissler, M. Antimicrobial testings, gas chromatographic analysis and olfactory evaluation of an essential oil of hop cones (Humulus lupulus L.) from Bavaria and some of its main compounds. Sci. Pharm. 2006, 74, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iannone, M.; Ovidi, E.; Vitalini, S.; Laghezza Masci, V.; Marianelli, A.; Iriti, M.; Tiezzi, A.; Garzoli, S. From Hops to Craft Beers: Production Process, VOCs Profile Characterization, Total Polyphenol and Flavonoid Content Determination and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. Processes 2022, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, J.L.; Forster, A.; De Keukeleire, D.; Moir, M.; Sharpe, F.R.; Verhagen, L.C.; Westwood, K.T. EBC Manual of Good Practice: Hops and Hop Products; Getränke-Fachverlag Hans Carl: Nürnberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hysert, D.; Probasco, G.; Forster, A.; Schmidt, R. Presented at the 64th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Brewing Chemists, Boston, MA, USA, 20–24 June 1998.
- Briggs, D.E.; Boulton, C.A.; Brookes, P.A.; Stevens, R. Brewing Science and Practice; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stankevičius, L.M.; Wenda-Piesik, A.; Obelevičius, K.; Ragažinskienė, O.; Stanius, Ž.; Maruška, A.; Buszewski, B. Comparative gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric evaluation of hop (Humulus lupulus L.) essential oils and extracts obtained using different sample preparation methods. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorini, D.; Molle, A.; Nabissi, M.; Santini, G.; Benelli, G.; Maggi, F. Valorizing industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products: Cannabidiol enrichment in the inflorescence essential oil optimizing sample pre-treatment prior to distillation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 128, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, A. Presented at the 48th International Hop Growers Congress, Canterbury, UK, 6–10 August 2001.
- Vitalini, S.; Iriti, M.; Ovidi, E.; Laghezza Masci, V.; Tiezzi, A.; Garzoli, S. Detection of Volatiles by HS-SPME-GC/MS and Biological Effect Evaluation of Buddha’s Hand Fruit. Molecules 2022, 27, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, E.N.Ş.; Bozkurt, M.; Tulukcu, E.; Uysal, T. Comparative Cytotoxic Effects of the Hydrosols of Some Ethnobotanic Plants. CUPMAP 2020, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zengin, G.; Menghini, L.; Di Sotto, A.; Mancinelli, R.; Sisto, F.; Carradori, S.; Grande, R. Chromatographic analyses, in vitro biological activities, and cytotoxicity of Cannabis sativa L. essential oil: A multidisciplinary study. Molecules 2018, 23, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moccia, S.; Siano, F.; Russo, G.L.; Volpe, M.G.; La Cara, F.; Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Picariello, G. Antiproliferative and antioxidant effect of polar hemp extracts (Cannabis sativa L., Fedora cv.) in human colorectal cell lines. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A. Cytotoxicity, anti-acute leukemia, and an-tioxidant properties of gold nanoparticles green-synthesized using Cannabis sativa L. leaf aqueous extract. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janatová, A.; Doskočil, I.; Božik, M.; Fraňková, A.; Tlustoš, P.; Klouček, P. The chemical composition of ethanolic extracts from six genotypes of medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) and their selective cytotoxic activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 353, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Esteban, J.I.; Pinela, J.; Ćirić, A.; Calhelha, R.C.; Soković, M.; Ferreira, I.; Barros, L.; Torija-Isasa, E.; de Cortes Sánchez-Mata, M. Chemical composition and biological activities of whole and dehulled hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P.; Cappelli, A.; Marinelli, O.; Valzano, M.; Pavoni, L.; Bonacucina, G.; Nabissi, M. Mosquitocidal and anti-inflammatory properties of the essential oils obtained from monoecious, male, and female inflorescences of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and their encapsulation in nanoemulsions. Molecules 2020, 25, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sotto, A.; Gullì, M.; Acquaviva, A.; Cchini, M.; Di Simone, S.C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Recinella, L.; Leoe, S.; Brunetti, L.; Orlando, G.; et al. Phytochemical and pharmacological profiles of the essential oil from the inflorescences of the Cannabis sativa L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taatjes, D.J.; Sobel, B.E.; Budd, R.C. Morphological and cytochemical determination of cell death by apoptosis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araújo-Filho, H.G.; Dos Santos, J.F.; Carvalho, M.T.B.; Picot, L.; Fruitier-Arnaudin, I.; Groult, H.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Quintans, J.S.S. Anticancer activity of limonene: A systematic review of target signaling pathways. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4957–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, F.; Pallio, G.; Corsaro, R.; Minutoli, L.; Altavilla, D.; Vermiglio, G.; Allegra, A.; Eid, A.H.; Bitto, A.; Squadrito, F.; et al. Beta-Caryophyllene Exhibits Anti-Proliferative Effects through Apoptosis Induction and Cell Cycle Modulation in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahham, S.S.; Tabana, Y.; Asif, M.; Ahmed, M.; Babu, D.; Hassan, L.E.; Ahamed, M.B.K.; Sandai, D.; Barakat, K.; Siraki, A.; et al. β-Caryophyllene Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lacerda Leite, G.M.; de Oliveira Barbosa, M.; Lopes, M.J.P.; de Araújo Delmondes, G.; Bezerra, D.S.; Araújo, I.M.; Kerntof, M.R. Pharmacological and toxicological activities of α-humulene and its isomers: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzoli, S.; Masci, V.; Caradonna, V.; Tiezzi, A.; Giacomello, P.; Ovidi, E. Liquid and vapor phase of four conifer-derived essential oils: Comparison of chemical compositions and antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovidi, E.; Laghezza Masci, V.; Zambelli, M.; Tiezzi, A.; Vitalini, S.; Garzoli, S. Laurus nobilis, Salvia sclarea and Salvia officinalis Essential Oils and Hydrolates: Evaluation of Liquid and Vapor Phase Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. Plants 2021, 10, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzoli, S.; Masci, V.L.; Ovidi, E.; Turchetti, G.; Zago, D.; Tiezzi, A. Chemical investigation of a biologically active Schinus molle L. leaf extract. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 8391263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Indrayanto, G.; Putra, G.S.; Suhud, F. Validation of in-vitro bioassay methods: Application in herbal drug research. Profiles Drug Subst. Excip. Relat. Methodol. 2021, 46, 273–307. [Google Scholar]
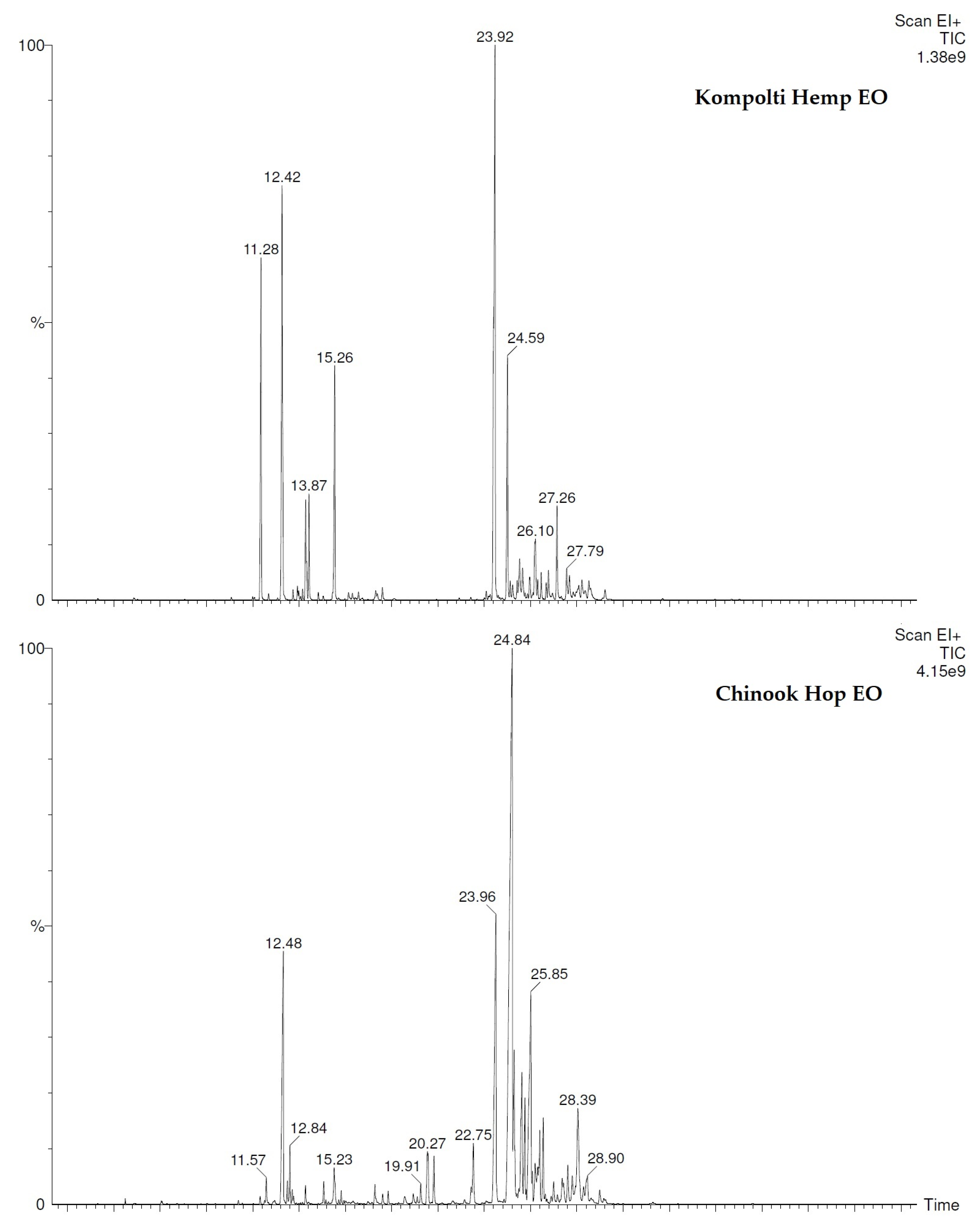
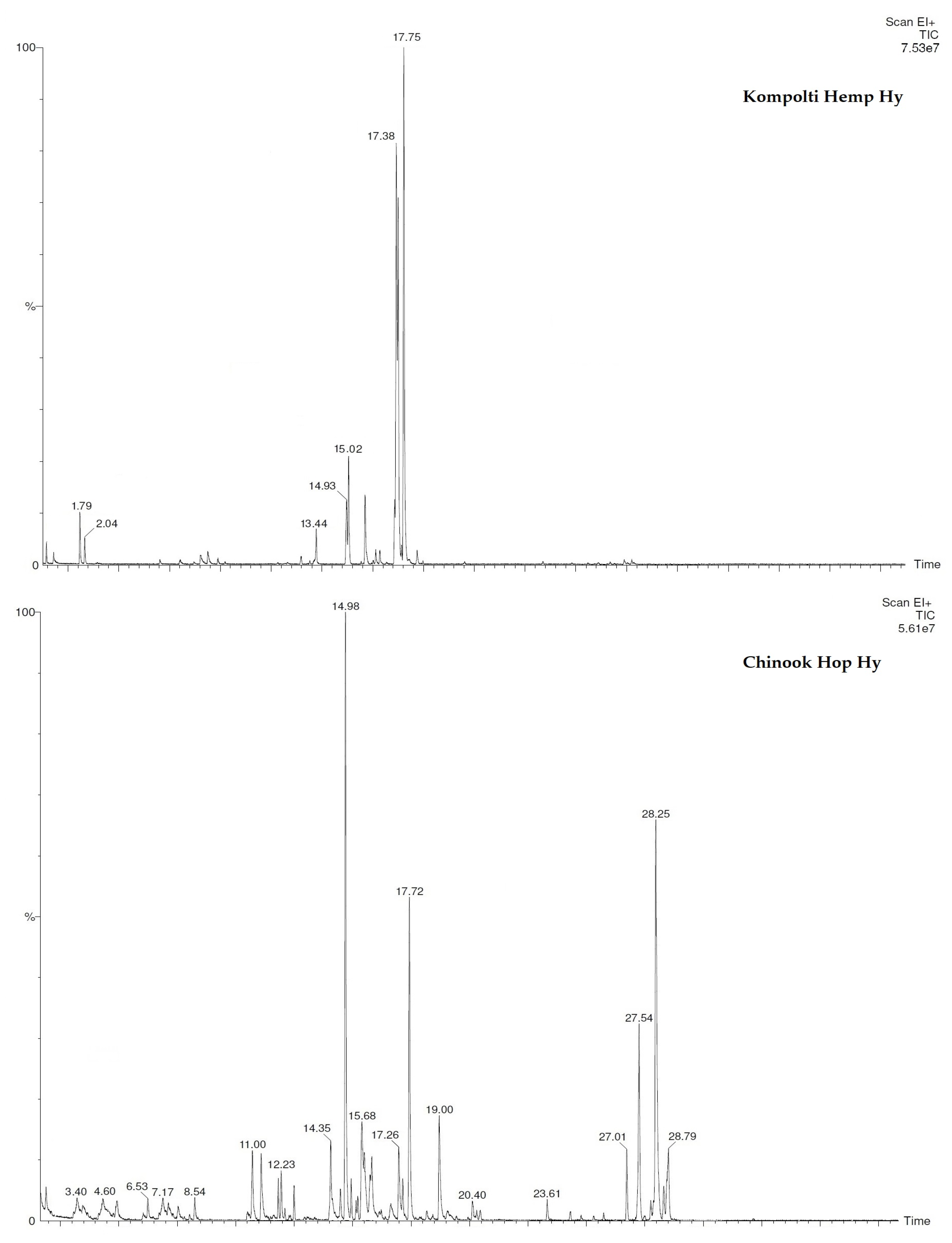
| N. | COMPONENT 1 | LRI 2 | LRI 3 | Hop EO 4 | Hemp EO 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | α-thujene | 821 | 823 | - | tr |
| 2 | α-pinene | 941 | 943 | tr | 8.6 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | camphene | 948 | 946 | - | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| 4 | β-thujene | 960 | 968 | - | tr |
| 5 | β-myrcene | 990 | 987 | 9.4 ± 0.04 | 12.4 ± 0.02 |
| 6 | propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-methylbutyl ester | 991 | 989 | 1.1 ± 0.02 | - |
| 7 | propanoic acid, 2-methyl-3-methylbutyl ester | 993 | 996 | 0.4 ± 0.02 | - |
| 8 | α-phellandrene | 1006 | 1005 | - | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 9 | 3-carene | 1010 | 1008 | - | 0.3 ± 0.02 |
| 10 | heptanoic acid, methyl ester | 1011 | 1008 | 0.2 ± 0.02 | - |
| 11 | α-terpinene | 1014 | 1010 | - | 0.2 ± 0.03 |
| 12 | p-cymene | 1018 | 1016 | - | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| 13 | limonene | 1021 | 1023 | 0.4 ± 0.02 | 27.9 ± 0.02 |
| 14 | cis-β-ocimene | 1036 | 1037 | - | 2.1 ± 0.02 |
| 15 | γ-terpinene | 1056 | 1054 | - | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 16 | cis-sabinene hydrate | 1063 | 1059 | - | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| 17 | terpinolene | 1072 | 1080 | - | 6.2 ± 0.02 |
| 18 | linalool | 1094 | 1095 | 1.3 ± 0.02 | - |
| 19 | fenchol | 1096 | 1098 | - | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 20 | octanoic acid, methyl ester | 1118 | 1122 | 0.2 ± 0.02 | - |
| 21 | isoborneol | 1130 | 1134 | - | tr |
| 22 | terpinen-4-ol | 1155 | 1160 | - | 0.1 ± 0.01 |
| 23 | octanoic acid | 1169 | 1170 | tr | - |
| 24 | methyl 6-methyloctanoate | 1180 | * | 0.6 ± 0.02 | - |
| 26 | α-terpineol | 1185 | 1183 | 0.2 ± 0.02 | 0.3 ± 0.02 |
| 27 | nonanoic acid, methyl ester | 1226 | 1224 | 0.3 ± 0.03 | - |
| 28 | 2-undecanone | 1280 | 1276 | 0.3 ± 0.02 | - |
| 29 | 4-decenoic acid, methyl ester | 1292 | * | 2.2 ± 0.06 | - |
| 30 | (Z)-methyl geranate | 1318 | 1323 | 1.2 ± 0.02 | - |
| 31 | ylangene | 1266 | 1376 | 0.5 ± 0.03 | - |
| 32 | α-copaene | 1385 | 1392 | 1.8 ± 0.02 | - |
| 33 | isocaryophyllene | 1398 | * | - | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 34 | α-gurjunene | 1418 | 1420 | - | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 35 | β-caryophyllene | 1438 | 1440 | 12.2 ± 0.01 | 22.2 ± 0.06 |
| 36 | α-himachalene | 1451 | 1447 | - | 0.7 ± 0.03 |
| 37 | humulene | 1466 | 1473 | 38.0 ± 0.04 | 6.5 ± 0.02 |
| 38 | β-eudesmene | 1481 | 1483 | 4.3 ± 0.03 | 1.1 ± 0.23 |
| 39 | α-farnesene | 1483 | 1486 | - | 0.3 ± 0.02 |
| 40 | γ-muurolene | 1488 | 1486 | 3.6 ± 0.02 | - |
| 41 | γ-gurjunene | 1490 | 1477 | - | 0.7 ± 0.02 |
| 42 | β-maaliene | 1492 | * | - | 2.3 ± 0.03 |
| 43 | α-selinene | 1495 | 1489 | 2.1 ± 0.02 | - |
| 44 | δ-cadinene | 1510 | 1511 | 9.4 ± 0.04 | - |
| 45 | selina-3,7(11)-diene | 1536 | 1540 | 1.9 ± 0.02 | 0.6 ± 0.03 |
| 46 | caryophyllenyl alcohol | 1545 | * | 0.5 ± 0.03 | - |
| 47 | caryophyllene oxide | 1586 | 1583 | 0.7 ± 0.02 | 2.7 ± 0.03 |
| 48 | humulene epoxide II | 1601 | 1606 | 1.0 ± 0.06 | 0.7 ± 0.02 |
| 49 | α-eudesmol | 1611 | 1615 | 1.4 ± 0.02 | - |
| 50 | cedr-8-en-15-ol | 1642 | * | - | 0.6 ± 0.03 |
| 51 | ledene oxide II | 1450 | * | - | 0.7 ± 0.02 |
| 52 | α-bisabolol | 1671 | 1665 | - | 0.6 ± 0.02 |
| 53 | τ-cadinol | 1638 | 1630 | 4.5 ± 0.02 | - |
| 54 | eudesm-7(11)-en-4-ol | 1682 | 1678 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 0.4 ± 0.04 |
| SUM | 99.8 | 99.7 | |||
| Monoterpenoids | 14.8 | 59.0 | |||
| Sesquiterpenoids | 79.7 | 40.5 | |||
| Others | 5.3 | - |
| N. | COMPONENT 1 | LRI 2 | LRI 3 | Hop Hy 4 | Hemp Hy 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | butanal, 3-methyl- | 648 | 650 | - | 2.2 ± 0.02 |
| 2 | butanal, 2-methyl- | 665 | 662 | - | 1.2 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | 1-butanol, 2-methyl- | 747 | 744 | 1.0 ± 0.02 | - |
| 4 | 2-butanal, 3-methyl- | 752 | 748.4 | 0.8 ± 0.02 | - |
| 5 | hexanal | 802 | 800 | 1.1 ± 0.03 | 0.3 ± 0.02 |
| 6 | butanoic acid, 3-methyl | 842 | 839 | 1.6 ± 0.02 | - |
| 7 | 1-hexanol | 871 | 868 | - | 1.0 ± 0.04 |
| 8 | 2-octen-4-one | 875 | * | 3.3 ± 0.03 | - |
| 9 | 3-heptanone | 890 | 885 | 0.9 ± 0.02 | - |
| 10 | 1-hepten-6-one | 991 | 987 | 3.2 ± 0.03 | - |
| 11 | p-cymene | 1018 | 1016 | - | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 12 | 1,8-cineole | 1026 | 1025 | - | 2.0 ± 0.03 |
| 13 | cis-linalooloxide | 1064 | 1066 | 4.0 ± 0.01 | - |
| 14 | trans-linalooloxide | 1078 | 1082 | 1.1 ± 0.03 | - |
| 15 | p-cymenene | 1088 | 1091 | - | 4.3 ± 0.02 |
| 16 | linalool | 1091 | 1095 | 21.2 ± 0.04 | 6.2 ± 0.02 |
| 17 | myrcenol | 1095 | 1097 | 0.5 ± 0.02 | - |
| 18 | fenchol | 1096 | 1098 | - | 4.4 ± 0.02 |
| 19 | 1,3,8-p-menthatriene | 1107 | * | - | 0.7 ± 0.02 |
| 20 | isoborneol | 1130 | 1134 | 2.7 ± 0.02 | 2.5 ± 0.02 |
| 21 | cis-p-mentha-2,8-dien-1-ol | 1141 | 1138 | - | 25.7 ± 0.02 |
| 22 | terpinen-4-ol | 1155 | 1160 | 1.1 ± 0.02 | 18.1 ± 0.02 |
| 23 | α-terpineol | 1185 | 1183 | 12.7 ± 0.03 | 31.2 ± 0.04 |
| 24 | cis-geraniol | 1241 | 1236 | 5.1 ± 0.02 | - |
| 25 | caryophyllenyl alcohol | 1545 | * | 2.4 ± 0.03 | - |
| 26 | caryophyllene oxide | 1586 | 1583 | 9.0 ± 0.02 | - |
| 27 | τ-cadinol | 1638 | 1460 | 22.9 ± 0.02 | - |
| 28 | germacrene D | 1451 | 1477 | 1.2 ± 0.04 | - |
| 29 | α-eudesmol | 1611 | 1615 | 4.2 ± 0.02 | - |
| SUM | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| Monoterpenoids | 48.4 | 95.3 | |||
| Sesquiterpenoids | 39.7 | - | |||
| Others | 11.9 | 4.7 |
| EO | HL60 | SH-SY5Y | MCF-7 | MDA | MCF-10A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kompolti hemp | EC50 mg/mL (×10−3) | 10.49 ± 1.37 | 95.87 ± 7.10 | 241.10 ± 5.23 | 230.17 ± 9.80 | 210.97 ± 2.31 |
| SI | 20.11 | 2.20 | 0.88 | 0.92 | - | |
| Chinook hop | EC50 mg/mL (×10−3) | 38.92 ± 3.10 | 315.60 ± 1.92 | 237.20 ± 2.51 | 317.51 ± 2.76 | 294.71 ± 4.96 |
| SI | 7.57 | 0.93 | 1.24 | 0.93 | - |
| Hy | HL60 | SH-SY5Y | MCF-7 | MDA | MCF-10A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kompolti hemp | EC50 mg/mL | 6.05 ± 1.54 | 4.90 ± 0.82 | 291.96 ± 6.82 | 127.53 ± 4.77 | 225.47 ± 6.92 |
| SI | 37.25 | 45.99 | 0.77 | 1.77 | - | |
| Chinook hop | EC50 mg/mL | 10.46 ± 0.52 | 4.49 ± 0.58 | 326.76 ± 2.68 | 140.81 ± 4.72 | 163.92 ± 3.73 |
| SI | 15.67 | 36.53 | 0.50 | 1.16 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ovidi, E.; Laghezza Masci, V.; Taddei, A.R.; Torresi, J.; Tomassi, W.; Iannone, M.; Tiezzi, A.; Maggi, F.; Garzoli, S. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Kompolti cv.) and Hop (Humulus lupulus L., Chinook cv.) Essential Oil and Hydrolate: HS-GC-MS Chemical Investigation and Apoptotic Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080976
Ovidi E, Laghezza Masci V, Taddei AR, Torresi J, Tomassi W, Iannone M, Tiezzi A, Maggi F, Garzoli S. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Kompolti cv.) and Hop (Humulus lupulus L., Chinook cv.) Essential Oil and Hydrolate: HS-GC-MS Chemical Investigation and Apoptotic Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(8):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080976
Chicago/Turabian StyleOvidi, Elisa, Valentina Laghezza Masci, Anna Rita Taddei, Jacopo Torresi, William Tomassi, Matteo Iannone, Antonio Tiezzi, Filippo Maggi, and Stefania Garzoli. 2022. "Hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Kompolti cv.) and Hop (Humulus lupulus L., Chinook cv.) Essential Oil and Hydrolate: HS-GC-MS Chemical Investigation and Apoptotic Activity Evaluation" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 8: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080976
APA StyleOvidi, E., Laghezza Masci, V., Taddei, A. R., Torresi, J., Tomassi, W., Iannone, M., Tiezzi, A., Maggi, F., & Garzoli, S. (2022). Hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Kompolti cv.) and Hop (Humulus lupulus L., Chinook cv.) Essential Oil and Hydrolate: HS-GC-MS Chemical Investigation and Apoptotic Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals, 15(8), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080976











