Novel and Promising Strategies for Therapy of Post-Transplant Chronic GVHD
Abstract
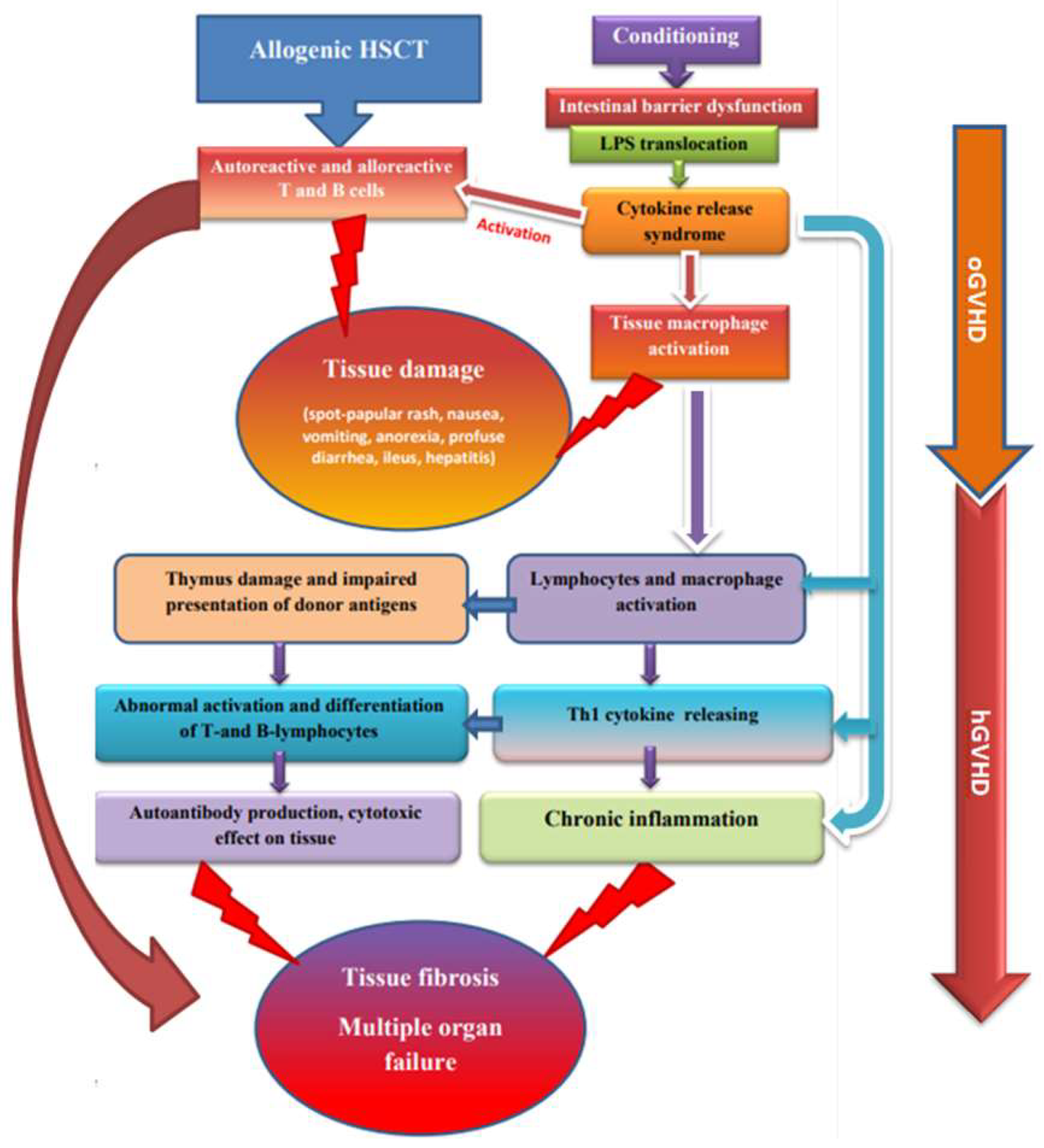
:1. Introduction
2. Approaches to cGVHD Diagnosis and Treatment
3. Cell Technologies and Extracorporeal Methods
3.1. Extracorporeal Photopheresis
3.2. Interleukine-2 and T Regulatory Cells
3.3. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
4. Novel Agents in cGVHD Treatment
4.1. Selective Inhibitor of Janus Kinases
4.2. Selective Inhibitor of Tyrosine Kinase
4.3. Ceramide
4.4. Selective Inhibitor of Rho-Associated Kinase
5. Experimental Therapy
6. Promising New Agents for Treatment of Hematopoietic Dysfunction and Hemostatic Disorders in cGVHD
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blazar, B.R.; Murphy, W.J.; Abedi, M. Advances in graft-versus-host disease biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, E.; Diaz-Ricart, M. Early Complications of Endothelial. In The EBMT Handbook; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, K.P.; Hill, G.R.; Blazar, B.R. Chronic graft-versus-host disease: Biological insights from preclinical and clinical studies. Blood 2017, 129, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naymagon, S. Acute graft-versus-host disease of the gut: Considerations for the gastroenterologist. Nature reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 711–726. [Google Scholar]
- Filipovich, A.H.; Weisdorf, D.; Pavletic, S. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005, 11, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagasia, M.H.; Greinix, H.T.; Arora, M.; Williams, K.M.; Wolff, D.; Cowen, E.W.; Palmer, J.; Weisdorf, D.; Treister, N.S.; Cheng, G.S.; et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: I. The 2014 Diagnosis and Staging Working Group report. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015, 21, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitko, C.L.; Pidala, J.; Schoemans, H.M.; Lawitschka, A.; Flowers, M.E.; Cowen, E.W.; Tkaczyk, E.; Farhadfar, N.; Jain, S.; Steven, P.; et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: IIa. The 2020 Clinical Implementation and Early Diagnosis Working Group Report. Transpl. Cell 2021, 27, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solh, M.; Zhang, X.; Connor, K. Donor type and disease risk predict the success of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: A single-center analysis of 613 adult hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients using a modified composite endpoint. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017, 23, 2192–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, M.; Holler, E.; Weber, D.; Holler, B.; Herr, W.; Wolff, D. Risk factors and outcome of chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation-results from a single-center observational study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016, 22, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, F.; Galimard, J.E.; Labopin, M. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with anti-thymocyte globulin versus allogeneic bone marrow transplantation without anti-thymocyte globulin. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Simón, J.A.; Encinas, C.; Silva, F. Prognostic factors of chronic graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: The national institutes health scale plus the type of onset can predict survival rates and the duration of immunosuppressive therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2008, 14, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metafuni, E.; Cavattoni, I.M.; Lamparelli, T.; Raiola, A.M.; Ghiso, A.; Galaverna, F.; Gualandi, F.; Di Grazia, C.; Dominietto, A.; Varaldo, R.; et al. The day 100 score predicts moderate to severe cGVHD, transplant mortality, and survival after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2309–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.I.; Rinsho, K. Graft-versus-host disease: Current understanding of immune pathogenesis and clinical treatment. Rinsho Ketsueki 2021, 62, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Presland, R.B. Biology of chronic graft-vs-host disease: Immune mechanisms and progress in biomarker discovery. World. J. Transpl. 2016, 6, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraverty, R.; Sykes, M. The role of antigen-presenting cells in triggering graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia. Blood 2007, 110, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skvortsova, Y.V.; Novichkova, G.A.; Maschan, A.A. New advances in pathogenesis, diagnostic and treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatric Hematol./Oncol. Immunopathol. 2018, 17, 121–135. (In Russia) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.J. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: VI. The 2014 Clinical Trial Design Working Group Report. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015, 21, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Stringer, J.; Hutt, D. Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GvHD). In The European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Textbook for Nurses: Under the Auspices of EBMT; Kenyon, M., Babic, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 22, pp. 221–251. [Google Scholar]
- Sarantopoulos, S.; Cardones, A.R.; Sullivan, K.M. How I treat refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2019, 133, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, J.A.; Trompeter, R.S. What is the calcineurin inhibitor of choice for pediatric renal transplantation? Pediatric Transpl. 2004, 8, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, S.S.; Rein, J.L. The Many Faces of Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity-What the FK? Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020, 27, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceberio, I.; Devlin, S.M.; Sauter, C.; Barker, J.N.; Castro-Malaspina, H.; Giralt, S.; Ponce, D.M.; Lechner, L.; Maloy, M.A.; Goldberg, J.D.; et al. Sirolimus, tacrolimus and low-dose methotrexate based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis after non-ablative or reduced intensity conditioning in related and unrelated donor allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Lai, X.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Q.; Ma, X.; Lin, Z.; Wu, D.; Xu, Y. Efficiency and Toxicity of Ruxolitinib as a Salvage Treatment for Steroid-Refractory Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 30, 673636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseev, I.S.; Morozova, E.V.; Bykova, T.A.; Paina, O.V.; Smirnova, A.G.; Dotsenko, A.A. Long-Term Outcomes of Ruxolitinib Therapy in Steroid-Refractory Graft-Versus-Host Disease in Children and Adults. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves Ruxolitinib for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease. 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-ruxolitinib-chronic-graft-versus-host-disease (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Drexler, B.; Buser, A.; Infanti, L.; Stehle, G.; Halter, J.; Holbro, A. Extracorporeal Photopheresis in Graft-versus-Host Disease. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2020, 47, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michallet, M.; Sobh, M.; Garban, F. Extracorporeal photopheresis for GVHD prophylaxis after reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A prospective multicenter phase 2 study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, M.; Wichert, S.; Berlin, G.; Toss, F. Extracorporeal photopheresis for graft-vs-host disease: A literature review and treatment guidelines proposed by the Nordic ECP Quality Group. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 104, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, M.E.D.; Apperley, J.F.; van Besien, K. A multicenter prospective phase 2 randomized study of extracorporeal photopheresis for treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2008, 112, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinix, H.T.; van Besien, K.; Elmaagacli, A.H. UVADEX Chronic GVHD Study Group. Progressive improvement in cutaneous and extracutaneous chronic graft-versus-host disease after a 24-week course of extracorporeal photopheresis--results of a crossover randomized study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2011, 17, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagasia, M.; Scheid, C.; Socié, G.; Ayuk, F.A.; Tischer, J.; Donato, M.; Bátai, Á.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.C.; Chin, T.; et al. Randomized controlled study of ECP with methoxsalen as first-line treatment of patients with moderate to severe cGVHD. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Death and Pulmonary Embolism Related to Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) Treatment—Letter to Health Care Providers. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/letters-health-care-providers/death-and-pulmonary-embolism-related-extracorporeal-photopheresis-ecp-treatment-letter-health-care (accessed on 5 February 2018).
- Gerber, D.; Segal, J.; Levy, M. The incidence of and risk factors for venous thromboembolism (VTE) and bleeding among 1514 patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Implications for VTE prevention. Blood 2008, 112, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, F.; Mousson, C. Ultraviolet light-induced regulatory (suppressor) T cells: An approach for promoting induction of operational allograft tolerance? Transplantation 2004, 77, S29–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, S.; Neuber, B.; Schubert, M.L.; Sauer, T.; Hückelhoven-Krauss, A.; Luft, T.; et al. Response to extracorporeal photopheresis therapy of patients with steroid-refractory/-resistant GvHD is associated with up-regulation of Th22 cells and Tfh cells. Cytotherapy 2022, 24, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, K.; Rommel, K.; Mani, J. Modulation of lymphocyte subpopulations by extracorporeal photopheresis in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease or graft rejection. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Di Biaso, I.; Leoni, V. Extracorporeal photochemotherapy is accompanied by increasing levels of circulating CD4+CD25+GITR+Foxp3+CD62L+ functional regulatory T-cells in patients with graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 2007, 84, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, A.; Schwarz, A.; Bullinger, A.; Morita, A.; Peritt, D.; Schwarz, T. Experimental extracorporeal photopheresis inhibits the sensitization and effector phases of contact hypersensitivity via two mechanisms: Generation of IL-10 and induction of regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5956–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinen, T.; Kannan, A.K.; Levine, A.G. An essential role for the IL-2 receptor in Treg cell function. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizaire, R.; Kim, H.T.; Poryanda, S.J.; Mirkovic, N.V.; Hipolito, E.; Savage, W.J.; Reynolds, C.G.; Fields, M.J.; Whangbo, J.; Kubo, T.; et al. Efficacy and immunologic effects of extracorporeal photopheresis plus interleukin-2 in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whangbo, J.S.; Kim, H.T.; Nikiforow, S.; Koreth, J.; Alho, A.C.; Falahee, B.; Kim, S.; Dusenbury, K.; Fields, M.J.; Reynolds, C.G.; et al. Functional analysis of clinical response to low-dose IL-2 in patients with refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Koreth, J.; Whangbo, J.; Nikiforow, S.; Reynolds, C.G.; Stowe, P.; Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.S.; Antin, J.H.; Soiffer, R.J.; et al. Organ-specific response after low-dose interleukin-2 therapy for steroid refractory chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Blood Adv. 2022, 26, 4392–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.A.; Lees, C.J.; Blazar, B.R. The infusion of ex vivo activated and expanded CD4+CD25+ immune regulatory cells inhibits graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood 2002, 99, 3493–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunstein, C.G.; Miller, J.S.; Cao, Q.; McKenna, D.H.; Hippen, K.L.; Curtsinger, J.; Defor, T.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Rubinstein, P. Infusion of ex vivo expanded T regulatory cells in adults transplanted with umbilical cord blood: Safety profile and detection kinetics. Blood 2011, 117, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber, A.; Teles, A.; Zenclussen, A.C. Regulatory T cells and their role in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whangbo, J.; Nikiforow, S.; Kim, H.T.; Wahl, J.; Reynolds, C.G.; Chamling, R.S.; Kim, S.; Burden, A.T.; Alho, A.; Lacerda, J.F.; et al. A phase 1 study of donor regulatory T-cell infusion plus low-dose interleukin-2 for steroid-refractory chronic graft-vs-host disease. Blood Adv. 2022, 27, bloodadvances.2021006625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landwehr-Kenzel, S.; Müller-Jensen, L.; Kuehl, J.S.; Abou-El-Enein, M.; Hoffmann, H.; Muench, S.; Kaiser, D.; Roemhild, A.; von Bernuth, H.; Voeller, M.; et al. Adoptive transfer of ex vivo expanded regulatory T cells improves immune cell engraftment and therapy-refractory chronic GvHD. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, N.A.; Lamarche, C.; Hoeppli, R.E.; Bergqvist, P.; Fung, V.; McIver, E.; Huang, Q.; Gillies, J.; Speck, M.; Orban, P.C.; et al. Systematic testing and specificity mapping of alloantigen-specific chimeric antigen receptors in regulatory T cells. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e123672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.I.; Coker, K.E.; Winn, D.W.; Deng, M.Z.; Shukla, D.; Bhoj, V.; Milone, M.C.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Naji, A.; et al. Trafficking and persistence of alloantigen-specific chimeric antigen receptor regulatory T cells in Cynomolgus macaque. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ghazanfari, R.; Zacharaki, D. Isolation and characterization of primary bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1370, 109–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Rasmusson, I.; Sundberg, B.; Götherström, C.; Hassan, M.; Uzunel, M. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet 2004, 393, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselevskii, M.V.; Vlasenko, R.Y.; Stepanyan, N.G.; Shubina, I.Z.; Sitdikova, S.M.; Kirgizov, K.I.; Varfolomeeva, S.R. Secretome of Mesenchymal Bone Marrow Stem Cells: Is It Immunosuppressive or Proinflammatory? Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, K.; Miyamura, K.; Ohashi, K.; Murata, M.; Eto, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Taniguchi, S. Unrelated allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase I/II study. Int. J. Hematol. 2013, 98, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muroi, K.; Miyamura, K.; Okada, M.; Yamashita, T.; Murata, M.; Ishikawa, T. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (JR-031) for steroid-refractory grade III or IV acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase II/III study. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 103, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Public Assessment Report for Remestemcel-L, Ex Vivo Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells; TGA: Woden, Australia, 2015; Volume 74.
- Dotoli, G.M.; De Santis, G.C.; Orellana, M.D.; de Lima, P.K.; Caruso, S.R.; Fernandes, T.R.; Rensi Colturato, V.A.; Kondo, A.T.; Hamerschlak, N.; Simões, B.P.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell infusion to treat steroid-refractory acute GvHD III/IV after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017, 52, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebriaei, P.; Hayes, J.; Daly, A.; Uberti, J.; Marks, D.I.; Soiffer, R. A phase 3 randomized study of remestemcel-L versus placebo added to second-line therapy in patients with steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2020, 26, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Lin, R.; Fan, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, X.; Xuan, L.; Wang, S.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells plus basiliximab, calcineurin inhibitor as treatment of steroid-resistant acute graft-versus-host disease: A multicenter, randomized, phase 3, open-label trial. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselevskiy, M.; Vlasenko, R.; Reshetnikova, V.; Chikileva, I.; Shubina, I.; Osmanov, E.; Valiev, T.; Sidorova, N.; Batmanova, N.; Stepanyan, N.; et al. Potential Use of Mesenchymal Multipotent Cells for Hemopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Pro and Contra. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 43, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingo, D.M.; Redaelli, D.; Rossella, V. Bone marrow-derived CD34−fraction: A rich source of mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical application. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraci, M.; Ricci, E.; Bagnasco, F.; Pierri, F.; Giardino, S.; Girosi, D.; Olcese, R.; Castagnola, E.; Michele Magnano, G.; Lanino, E. Imatinib melylate as second-line treatment of bronchiolitis obliterans after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.A.; Choi, J.; Staser, K.; DiPersio, J.F. The Role of Janus Kinase Signaling in Graft-Versus-Host Disease and Graft Versus Leukemia. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018, 24, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiser, R.; Socié, G. The development of ruxolitinib for glucocorticoid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3789–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Present and Future. Cancer J. 2019, 25, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.; Cutler, C.S.; Arora, M.; Waller, E.K.; Jagasia, M.; Pusic, I.; Flowers, M.E.; Logan, A.C.; Nakamura, R.; Blazar, B.R.; et al. Ibrutinib for chronic graft-versus-host disease after failure of prior therapy. Blood 2017, 130, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutré, S.E.; Furman, R.R.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.; Sharman, J.; Jones, J.; Wierda, W.; Zhao, W.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Extended Treatment with Single-Agent Ibrutinib at the 420 mg Dose Leads to Durable Responses in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Jurdi, N.; Rayes, A.; MacMillan, M.L.; Holtan, S.G.; DeFor, T.E.; Witte, J.; Arora, M.; Young, J.A.; Weisdorf, D.J. Steroid-dependent acute GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: Risk factors and clinical outcomes. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffmann, S.; Hartmann, D.; Fuchs, S.; Birod, K.; Ferreiròs, N.; Schreiber, Y.; Zivkovic, A.; Geisslinger, G.; Grösch, S.; Stark, H. Inhibitors of specific ceramide synthases. Biochimie 2012, 94, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, M.H.; Tian, L.; Schutt, S.; Khan, I.; Choi, H.J.; Wu, Y.; Bastian, D.; Ticer, T.; Kassir, M.F.; Atilgan, F.C.; et al. Ceramide synthase 6 impacts T-cell allogeneic response and graft-versus-host disease through regulating N-RAS/ERK pathway. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Weiss, J.M.; Nyuydzefe, M.S.; Chen, W.; Scher, J.U.; Mo, R.; Depoil, D.; Rao, N.; Liu, B.; Wei, J.; et al. Selective oral ROCK2 inhibitor down-regulates IL-21 and IL-17 secretion in human T cells via STAT3-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16814–16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynarovich, A.; Lepik, K.; Mikhailova, N.; Borzenkova, E.; Volkov, N.; Moiseev, I.; Zalyalov, Y.; Kondakova, E.; Kozlov, A.; Stelmakh, L.; et al. Favorable outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with fludarabine-bendamustine conditioning and posttransplantation cyclophosphamide in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanis, E.; Stea, B.; Kovacs, K.; Truscott, L.; Husnain, M.; Khurana, S.; Roe, D.J.; Simpson, R.J. Feasibility and efficacy of partially replacing post-transplantation cyclophosphamide with bendamustine in pediatric and young adult patients undergoing haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Transpl. Cell Ther. 2022, 20, S2666–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, R.; Paz, K.; Du, J.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Taylor, P.A.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Vulic, A.; Luznik, L.; MacDonald, K.K.; Hill, G.R.; et al. Targeted Rho-associated kinase 2 inhibition suppresses murine and human chronic GVHD through a Stat3-dependent mechanism. Blood 2016, 127, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, C.; Lee, S.J.; Arai, S.; Rotta, M.; Zoghi, B.; Lazaryan, A.; Ramakrishnan, A.; DeFilipp, Z.; Salhotra, A.; Chai-Ho, W.; et al. Belumosudil for chronic graft-versus-host disease after 2 or more prior lines of therapy: The ROCKstar study. Blood 2021, 138, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, D.J.; Chen, Y.B.; DeFilipp, Z. Recent FDA Approvals in the Treatment of Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Oncologist 2022, 27, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalniz, F.F.; Murad, M.H.; Lee, S.J.; Pavletic, S.Z.; Khera, N.; Shah, N.D.; Hashmi, S.K. Steroid Refractory Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease: Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018, 24, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saidu, N.E.B.; Bonini, C.; Dickinson, A.; Grce, M.; Inngjerdingen, M.; Koehl, U.; Toubert, A.; Zeiser, R.; Galimberti, S. New Approaches for the Treatment of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 578314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, J.; Wei, W. Advance in Targeted Immunotherapy for Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegawa, S.; Matsuoka, K.I. Harnessing Treg Homeostasis to Optimize Posttransplant Immunity: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 713358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.J. Study design and endpoints in graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2008, 21, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsohn, D.A.; Chen, A.R.; Zahurak, M.; Piantadosi, S.; Anders, V.; Bolaños-Meade, J.; Higman, M.; Margolis, J.; Kaup, M.; Vogelsang, G.B. Phase II study of pentostatin in patients with corticosteroid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naserian, S.; Leclerc, M.; Shamdani, S.; Uzan, G. Current Preventions and Treatments of aGVHD: From Pharmacological Prophylaxis to Innovative Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 607030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulanic, D.; Lozier, J.N.; Pavletic, S.Z. Thrombocytopenia and hemostatic disorders in chronic graft versus host disease. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2009, 44, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, S.; Seol, M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, W.K. Failure of trilineage blood cell reconstitution after initial neutrophil engraftment in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation–frequency and outcomes. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2004, 33, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelink, I.H.; Belitser, S.V.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; Danhof, M.; de Pagter, A.J.; Egberts, T.C.G.; Boelens, J.J. Immune reconstitution kinetics as an early predictor for mortality using various hematopoietic stem cell sources in children. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013, 19, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malard, F.; Huang, X.J.; Sim, J.P.Y. Treatment and unmet needs in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kekre, N.; Kim, H.; Ho, V. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is associated with graft-versus-host disease and increased non-relapse mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangaraju, R.; Chen, Y.; Hageman, L.; Wu, J.; Francisco, L.; Kung, M.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Forman, S.J.; Arora, M.; Armenian, S.H.; et al. Late-occurring venous thromboembolism in allogeneic blood or marrow transplant survivors: A BMTSS-HiGHS2 risk model. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4102–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrador, J.; Lopez-Anglada, L.; Perez-Lopez, E. Analysis of incidence, risk factors and clinical outcome of thromboembolic and bleeding events in 431 allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. Haematologica 2013, 98, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolliger, D.; Santer, D.; Tanaka, K.A. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia in Patients with Mechanical Circulatory Support. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 1880–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A. Clinical Practice. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uaprasert, N.; Tangcheewinsirikul, N.; Rojnuckarin, P.; Patell, R.; Zwicker, J.I.; Chiasakul, T. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4521–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Tsvetkova, E.N.; Krylov, V.B.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Krukovskaya, N.V.; Li, C.; et al. Fucoidans as a platform for new anticoagulant drugs discovery. Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilan, M.I.; Vinogradova, E.V.; Tsvetkova, E.A.; Grachev, A.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A sulfated glucuronofucan containing both fucofuranose and fucopyranose residues from the brown alga Chordaria flagelliformis. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Andryukov, B.G.; Makarenkova, I.D.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Besednova, N.N.; Fedyanina, L.N.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Shchelkanov, M.Y. The Potency of Seaweed Sulfated Polysaccharides for the Correction of Hemostasis Disorders in COVID-19. Molecules 2021, 26, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Ushakova, N.A.; Zyuzina, K.A.; Bilan, M.I.; Elizarova, A.L.; Somonova, O.V.; Madzhuga, A.V.; Krylov, V.B.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; Usov, A.I.; et al. Influence of Fucoidans on Hemostatic System. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2444–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Helley, D.; Ayman, H.Z. Effect of low molecular weight fucoidan and low molecular weight heparin in a rabbit model of arterial thrombosis. J. Vasc. Res. 2008, 45, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müskens, K.F.; Lindemans, C.A.; Belderbos, M.E. Hematopoietic Dysfunction during Graft-Versus-Host Disease: A Self-Destructive Process? Cells 2021, 10, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Bilan, M.I.; Donenko, F.V.; Morozevich, G.E.; Yashunskiy, D.V.; Usov, A.I.; Siminyan, N.G.; Kirgisov, K.I.; Varfolomeeva, S.R.; et al. Chondroitin sulfate and fucosylated chondroitin sulfate as stimulators of hematopoiesis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenette, P.S.; Weiss, L. Sulfated glycans induce rapid hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization: Evidence for selectin-dependent and independent mechanisms. Blood 2000, 96, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, N.Y.; Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Donenko, F.V.; Ushakova, N.A.; Usov, A.I.; Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Nifantiev, N.E. Influence of modified fucoidan and related sulfated oligosaccharides on hematopoiesis in cyclophosphamide-induced mice. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Peired, A.J.; Weiss, L.A.; Katayama, Y.; Frenette, P.S. The integrin alphaMbeta2 anchors hematopoietic progenitors in the bone marrow during enforced mobilization. Blood 2004, 104, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. New insight on the structural diversity of holothurian fucosylated chondroitin sulfates. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Borodina, E.Y.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A highly regular fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Massinium magnum: Structure and effects on coagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Silchenko, A.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfates from the Sea Cucumbers Paracaudina chilensis and Holothuria hilla: Structures and Anticoagulant Activity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Shashkov, A.S.; Ponce, N.M.A.; Stortz, C.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Hemioedema spectabilis: Structure and influence on cell adhesion and tubulogenesis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Tsvetkova, E.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structural characterization of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus and Actinopyga mauritiana. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Tsvetkova, E.A.; Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Depolymerization of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Cucumaria japonica: Structure and biological activity of the product. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 281, 119072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. The structure of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, V.B.; Kaskova, Z.M.; Vinnitskiy, D.Z.; Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Grachev, A.A.; Chizhov, A.O.; Nifantiev, N.E. Acid-promoted synthesis of per-O-sulfated fucooligosaccharides related to fucoidan fragments. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnitskiy, D.Z.; Krylov, V.B.; Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E. The synthesis of heterosaccharides related to the fucoidan from Chordaria flagelliformis bearing α-L-fucofuranosyl unit. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Fomitskaya, P.A.; Gerbst, A.G.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E. Synthesis of the oligosaccharides related to branching sites of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from sea cucumbers. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglowski, S.M.; Devine, S.M. Graft-versus-host disease: Why have we not made more progress? Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2014, 21, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Simón, J.A.; Sánchez-Abarca, I.; Díez-Campelo, M.; Caballero, D.; San Miguel, J. Chronic graft-versus-host disease: Patho-genesis and clinical management. Drugs 2006, 66, 1041–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawara, I.; Maeda, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lowler, K.P.; Liu, C.; Toubai, T.; McKenzie, A.N.; Reddy, P. Combined Th2 cytokine deficiency in donor T cells aggravates experimental acute graft-vs-host disease. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozmus, J.; Schultz, K.R. Biomarkers in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2011, 4, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatza, E.; Choi, S.W. Approaches for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease following hematopoietic cell transplantation. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 4, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.; Fatobene, G.; Rocha, V.; Kröger, N.; Flowers, M.E. Steroid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease: Treatment options and patient management. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021, 56, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, M.E.D.; Martin, P.J. How we treat chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2015, 125, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, K.R.; Luznik, L.; Sarantopoulos, S.; Hakim, F.T.; Jagasia, M.; Fowler, D.H.; van den Brink, M.R.M.; Hansen, J.A.; Parkman, R.; Miklos, D.B.; et al. The Biology of Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Task Force Report from the National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017, 23, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, C.; Muthukumar, T.; Suthanthiran, M. Immunosuppressive drug therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a015487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, M.; Murray, J.; Quinn, B. Late Effects and Long-Term Follow-Up. 2017 Nov 22. In The European Blood and Marrow Transplantation; Kenyon, M., Babic, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Machneva, E.B.; Panarina, V.Y.; Aliev, T.Z.; Shevtsov, D.V.; Suleymanova, A.M.; Konstantinova, V.V.; Burya, A.E.; Stepanyan, N.G.; Skvortsova, Y.V.; Sidorova, N.V.; et al. Chronic “graft versus host” disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Basic characteristics, pathogenetic mechanisms, treatment strategies and problems of clinical practice. Russ. J. Pediatric Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 7, 94–111. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostareva, I.; Kirgizov, K.; Machneva, E.; Ustyuzhanina, N.; Nifantiev, N.; Skvortsova, Y.; Shubina, I.; Reshetnikova, V.; Valiev, T.; Varfolomeeva, S.; et al. Novel and Promising Strategies for Therapy of Post-Transplant Chronic GVHD. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091100
Kostareva I, Kirgizov K, Machneva E, Ustyuzhanina N, Nifantiev N, Skvortsova Y, Shubina I, Reshetnikova V, Valiev T, Varfolomeeva S, et al. Novel and Promising Strategies for Therapy of Post-Transplant Chronic GVHD. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091100
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostareva, Irina, Kirill Kirgizov, Elena Machneva, Nadezhda Ustyuzhanina, Nikolay Nifantiev, Yulia Skvortsova, Irina Shubina, Vera Reshetnikova, Timur Valiev, Svetlana Varfolomeeva, and et al. 2022. "Novel and Promising Strategies for Therapy of Post-Transplant Chronic GVHD" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091100
APA StyleKostareva, I., Kirgizov, K., Machneva, E., Ustyuzhanina, N., Nifantiev, N., Skvortsova, Y., Shubina, I., Reshetnikova, V., Valiev, T., Varfolomeeva, S., & Kiselevskiy, M. (2022). Novel and Promising Strategies for Therapy of Post-Transplant Chronic GVHD. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091100






