Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin in Rats following Treatment with Astragali Radix
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation
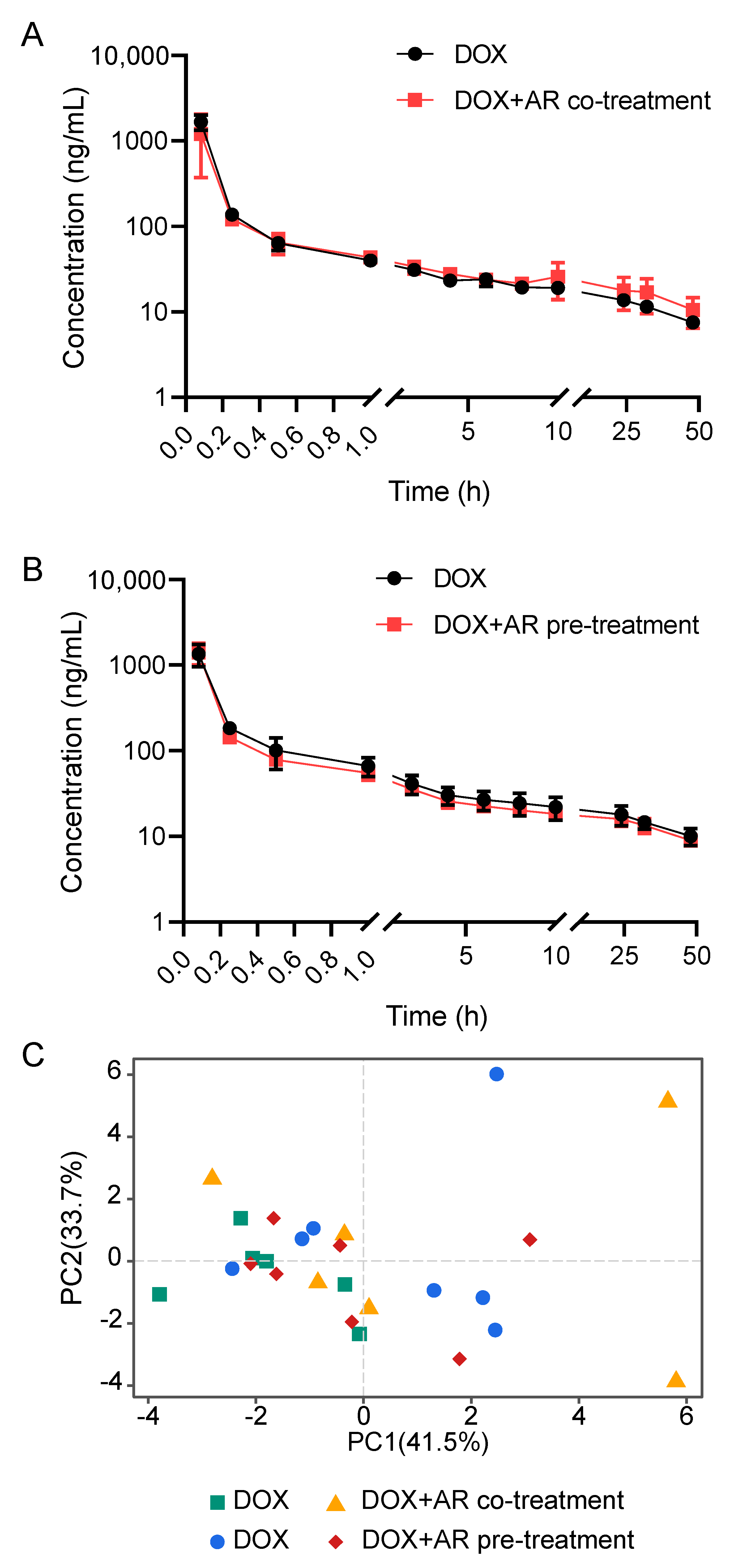
2.2. Effects of Astragali Radix on Doxorubicin Disposition
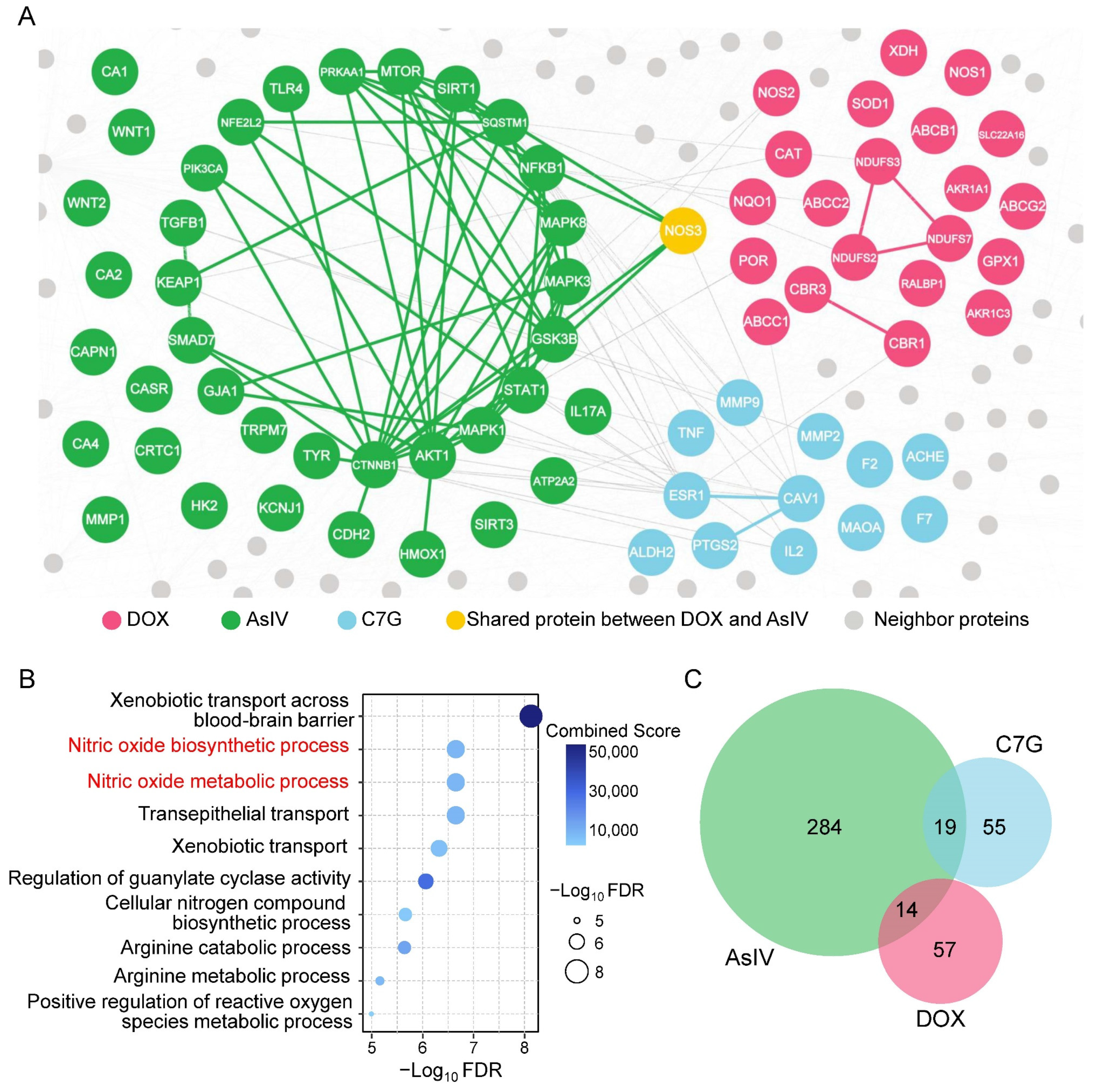
2.3. Network-Based Measures of Doxorubicin–Astragali Radix Relationship
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Astragali Radix Water Extract
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Method Validation
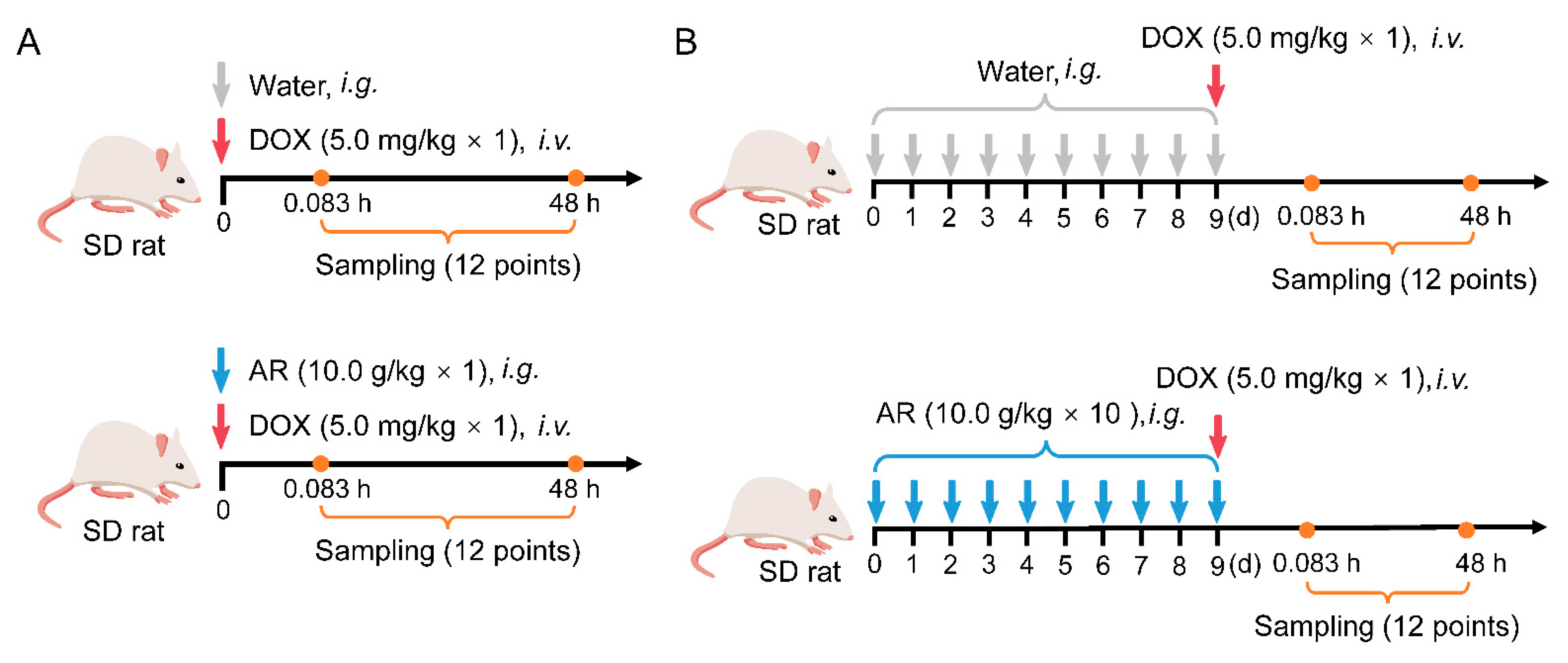
4.6. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution Studies
4.7. Network Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Zanden, S.Y.; Qiao, X.; Neefjes, J. New Insights into the Activities and Toxicities of the Old Anticancer Drug Doxorubicin. Febs J. 2021, 288, 6095–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; van der Zanden, S.Y.; Wander, D.P.A.; Borràs, D.M.; Song, J.-Y.; Li, X.; van Duikeren, S.; van Gils, N.; Rutten, A.; van Herwaarden, T.; et al. Uncoupling DNA Damage from Chromatin Damage to Detoxify Doxorubicin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 15182–15192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amgalan, D.; Garner, T.P.; Pekson, R.; Jia, X.F.; Yanamandala, M.; Paulino, V.; Liang, F.G.; Corbalan, J.J.; Lee, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. A Small-Molecule Allosteric Inhibitor of BAX Protects against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Song, M.; Hoang, D.H.; Tran, Q.H.; Choe, W.; Kang, I.; Kim, S.S.; Ha, J. Melatonin Prevents Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity through Suppression of AMPKα2-Dependent Mitochondrial Damage. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, A.; Huang, R.S. Computationally Predicting Clinical Drug Combination Efficacy with Cancer Cell Line Screens and Independent Drug Action. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-P.; He, S.-S.; Zhang, W.-N.; Zhang, C.-L.; Liu, Y.-T.; Li, K.; Qin, X.-M. Exploration the Active Compounds of Astragali Radix in Treatment of Adriamycin Nephropathy by Network Pharmacology Combined with Transcriptomic Approach. J. Ethnopharmacol 2020, 258, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-N.; Li, A.-P.; Qi, Y.-S.; Qin, X.-M.; Li, Z.-Y. Metabolomics Coupled with System Pharmacology Reveal the Protective Effect of Total Flavonoids of Astragali Radix against Adriamycin-Induced Rat Nephropathy Model. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2018, 158, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Du, G.; Qin, X. Evaluations of the Effect of HuangQi against Heart Failure Based on Comprehensive Echocardiography Index and Metabonomics. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; Deng, X.; Yu, J.; Deng, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Network-Driven Targeted Analysis Reveals That Astragali Radix Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Maintaining Fatty Acid Homeostasis. J. Ethnopharmacol 2022, 287, 114967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-P.; Yang, L.; Cui, T.; Zhang, L.-C.; Liu, Y.-T.; Yan, Y.; Li, K.; Qin, X.-M. Uncovering the Mechanism of Astragali Radix against Nephrotic Syndrome by Intergrating Lipidomics and Network Pharmacology. Phytomedicine 2020, 77, 153274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Qiu, S.; Fan, X.; Jiao, G.; Zhou, X.; Sun, M.; Weng, N.; Gao, S.; Tao, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Evaluation of the Effect of Shengxian Decoction on Doxorubicin-Induced Chronic Heart Failure Model Rats and a Multicomponent Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study after Oral Administration in Normal and Model Rats. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 144, 112354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Zhou, S.; Chiang, M.; Zang, X.; Kim, T.H.; Kagan, L. Interspecies Prediction of Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin by Physiologically-based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2020, 41, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbelboer, I.R.; Lilienberg, E.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernaös, H. A Model-Based Approach to Assessing the Importance of Intracellular Binding Sites in Doxorubicin Disposition. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, Y.L.; Vaidya, T.R.; Ait-Oudhia, S. Anticancer and Cardio-Protective Effects of Liposomal Doxorubicin in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Targets 2018, 10, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.d.O.; Miranda, S.E.M.; Leite, E.A.; Sabino, A.d.P.; Borges, K.B.G.; Cardoso, V.N.; Cassali, G.D.; Guimarães, A.G.; Oliveira, M.C.; de Barros, A.L.B. Toxicological Study of a New Doxorubicin-Loaded PH-Sensitive Liposome: A Preclinical Approach. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 352, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ke, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Bi, K. Induction of P-Glycoprotein Expression by Dandelion in Tumor and Heart Tissues: Impact on the Anti-Tumor Activity and Cardiotoxicity of Doxorubicin. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network Medicine: A Network-Based Approach to Human Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guney, E.; Menche, J.; Vidal, M.; Barábasi, A.-L. Network-Based in Silico Drug Efficacy Screening. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wan, L.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Guo, C.; Li, X. Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetics and Cardiotoxicity of Doxorubicin in Rat Receiving Nilotinib. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2013, 272, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-P.; Wan, L.-L.; Yang, Q.-J.; Huo, Y.; Han, Y.-L.; Guo, C. Scutellarin Protects against Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity and Regulates Its Accumulation in the Heart. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.-H.; Shin, S.; Yoo, S.-D.; Shin, B.-S. Effects of phytochemical P-glycoprotein modulators on the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of doxorubicin in mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Commission of Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Pharmacopoeia, Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Chen, D.; Zhao, J.; Cong, W. Chinese Herbal Medicines Facilitate the Control of Chemotherapy-Induced Side Effects in Colorectal Cancer: Progress and Perspective. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Cao, C.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Herb-Drug Interactions between Aidi Injection and Doxorubicin in Rats with Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BMC Pharm. Toxicol. 2021, 22, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cui, W.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.-H.; Xu, X. Curcumin Reverses Doxorubicin Resistance in Colon Cancer Cells at the Metabolic Level. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2021, 201, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Cai, H.; Yang, J.; Qiu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, M. Pharmacokinetics and Cardiotoxicity of Doxorubicin and Its Secondary Alcohol Metabolite in Rats. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 116, 108964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.; He, F.; Huang, Y.-F.; Ma, H.-L.; Wang, Y.-P.; Cheng, C.-S.; Cheng, J.-L.; Lao, C.-C.; Chen, D.-A.; Zhang, Z.-F.; et al. Discovery of Chemical Markers for Identifying Species, Growth Mode and Production Area of Astragali Radix by Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Phytomedicine 2020, 67, 153155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebel, C.; Lanvers-Kaminsky, C.; Würthwein, G.; Hempel, G.; Boos, J. Bioanalysis of Doxorubicin Aglycone Metabolites in Human Plasma Samples–Implications for Doxorubicin Drug Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menche, J.; Sharma, A.; Kitsak, M.; Ghiassian, S.D.; Vidal, M.; Loscalzo, J.; Barabási, A.-L. Uncovering Disease-Disease Relationships through the Incomplete Interactome. Science 2015, 347, 1257601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysi, D.M.; Valle, Í.d.; Zitnik, M.; Ameli, A.; Gan, X.; Varol, O.; Ghiassian, S.D.; Patten, J.J.; Davey, R.A.; Loscalzo, J.; et al. Network Medicine Framework for Identifying Drug-Repurposing Opportunities for COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025581118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biological Matrix | Linear Range | Calibration Curve | r2 | LLOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | 5–5000 ng/mL | Y = 0.0116263X + 0.0132798 | 0.9993 | 5 ng/mL |
| Liver | 20–2400 ng/g | Y = 0.00274442X + 0.00861329 | 0.9988 | 20 ng/g |
| Heart | 20–2400 ng/g | Y = 0.00283048X + 0.0101572 | 0.9975 | 20 ng/g |
| Kidney | 50–6000 ng/g | Y = 0.00107142X + 0.00120827 | 0.9978 | 50 ng/g |
| Spleen | 20–2400 ng/g | Y = 0.00244706X − 0.00562543 | 0.9950 | 20 ng/g |
| Lung | 20–2400 ng/g | Y = 0.00276342X + 0.00405469 | 0.9979 | 20 ng/g |
| Skeletal muscle | 20–2400 ng/g | Y = 0.00282242X + 0.0109277 | 0.9977 | 20 ng/g |
| Biological Matrix | Concentration | Intra-Day (n = 5) | Inter-Day (n = 15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | Precision (RSD%) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (RSD%) | ||
| Plasma | 5 ng/mL | 96.08 | 6.44 | 97.12 | 5.46 |
| 10 ng/mL | 94.82 | 6.12 | 95.70 | 6.53 | |
| 500 ng/mL | 100.59 | 4.30 | 101.79 | 5.48 | |
| 4000 ng/mL | 98.15 | 3.54 | 100.75 | 6.13 | |
| Liver | 20 ng/g | 95.66 | 6.22 | 97.25 | 5.85 |
| 40 ng/g | 90.33 | 4.56 | 93.10 | 5.45 | |
| 400 ng/g | 92.23 | 6.50 | 95.75 | 5.67 | |
| 2000 ng/g | 93.88 | 4.05 | 98.00 | 5.89 | |
| Heart | 20 ng/g | 99.82 | 6.85 | 95.99 | 8.79 |
| 40 ng/g | 103.21 | 4.28 | 100.30 | 5.15 | |
| 400 ng/g | 96.43 | 3.47 | 100.41 | 5.54 | |
| 2000 ng/g | 104.26 | 5.39 | 100.07 | 6.06 | |
| Spleen | 20 ng/g | 96.44 | 6.36 | 97.96 | 6.39 |
| 40 ng/g | 91.86 | 5.61 | 95.55 | 6.06 | |
| 400 ng/g | 89.15 | 2.11 | 95.04 | 7.75 | |
| 2000 ng/g | 92.44 | 4.49 | 96.44 | 5.98 | |
| Kidney | 50 ng/g | 99.50 | 5.46 | 98.78 | 5.90 |
| 100 ng/g | 98.54 | 6.05 | 95.03 | 7.72 | |
| 1000 ng/g | 102.07 | 5.90 | 94.98 | 7.68 | |
| 5000 ng/g | 100.59 | 4.86 | 96.87 | 6.11 | |
| Lung | 20 ng/g | 90.87 | 10.16 | 95.79 | 9.23 |
| 40 ng/g | 91.56 | 2.22 | 99.08 | 7.90 | |
| 400 ng/g | 99.31 | 6.76 | 97.93 | 5.50 | |
| 2000 ng/g | 103.38 | 4.95 | 101.80 | 4.40 | |
| Skeletal muscle | 20 ng/g | 96.81 | 9.01 | 97.02 | 8.55 |
| 40 ng/g | 91.89 | 1.17 | 92.36 | 3.78 | |
| 400 ng/g | 95.22 | 3.69 | 99.25 | 5.23 | |
| 2000 ng/g | 98.20 | 4.39 | 100.40 | 4.93 | |
| Parameters # | Unit | AR Co-Treatment (n = 6 per Group) | AR Pre-Treatment (n = 7 per Group) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOX | DOX + AR (10g/kg × 1) | p-Value $ | DOX | DOX + AR (10g/kg × 10) | p-Value $ | ||
| AUC(0-t) | μg/L*h | 1212.08 ± 107.82 | 1265.88 ± 226.98 | 0.642 | 1303.35 ± 271.74 | 1208.74 ± 145.35 | 0.467 |
| AUC(0-∞) | μg/L*h | 1561.04 ± 147.02 | 1773.14 ± 288.55 | 0.174 | 1763.3 ± 339.93 | 1626.07 ± 231.54 | 0.430 |
| AUMC(0-t) | h*h*μg/L | 13,438.17 ± 881.77 | 18,109.93 ± 6093.09 | 0.148 | 17,173.75 ± 3436.44 | 15,248.33 ± 1891.35 | 0.252 |
| AUMC(0-∞) | h*h*μg/L | 46,004.25 ± 8764.93 | 67427.17 ± 25,880.54 | 0.129 | 60,856.88 ± 14,612.33 | 55,604.05 ± 15,045.69 | 0.551 |
| MRT(0-t) | h | 11.13 ± 0.74 | 14.38 ± 3.67 | 0.105 | 13.24 ± 1.11 | 12.69 ± 1.51 | 0.486 |
| MRT(0-∞) | h | 29.34 ± 4.25 | 37.7 ± 11.6 | 0.161 | 34.59 ± 6.48 | 33.81 ± 5.55 | 0.826 |
| VRT(0-t) | h^2 | 197.67 ± 4.35 | 209.5 ± 15.52 | 0.154 | 212.17 ± 6.72 | 211.82 ± 7.21 | 0.933 |
| VRT(0-∞) | h^2 | 1766.66 ± 538.86 | 2213.68 ± 1222.38 | 0.472 | 2022.61 ± 650.14 | 2067.43 ± 786.43 | 0.916 |
| λz | 1/h | 0.023 ± 0.004 | 0.022 ± 0.004 | 0.621 | 0.022 ± 0.003 | 0.023 ± 0.005 | 0.830 |
| C_last | μg/L | 7.86 ± 0.8 | 10.85 ± 3.98 | 0.156 | 10.04 ± 2.17 | 8.99 ± 1.02 | 0.307 |
| t1/2 | h | 30.52 ± 4.47 | 32.59 ± 7.48 | 0.607 | 31.79 ± 5.12 | 32.05 ± 6.95 | 0.944 |
| V | L/kg | 141.38 ± 18.15 | 135.98 ± 35.78 | 0.770 | 133.85 ± 28.5 | 142.17 ± 25.7 | 0.605 |
| CL | L/h/kg | 3.23 ± 0.33 | 2.89 ± 0.43 | 0.189 | 2.92 ± 0.43 | 3.13 ± 0.38 | 0.390 |
| Cmax | μg/L | 1667.94 ± 304.04 | 1211.41 ± 764.75 | 0.243 | 1351.21 ± 364.86 | 1411.01 ± 368.38 | 0.782 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Yang, F.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin in Rats following Treatment with Astragali Radix. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091104
Huang Y, Yang F, Guo L, Xu Y, Yu X, Zhang Z, Zhang Y. Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin in Rats following Treatment with Astragali Radix. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091104
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yin, Fang Yang, Linling Guo, Yan Xu, Xiaxia Yu, Zunjian Zhang, and Yuxin Zhang. 2022. "Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin in Rats following Treatment with Astragali Radix" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091104
APA StyleHuang, Y., Yang, F., Guo, L., Xu, Y., Yu, X., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Doxorubicin in Rats following Treatment with Astragali Radix. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091104







