Intranasal Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Marine Sources to Manage Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
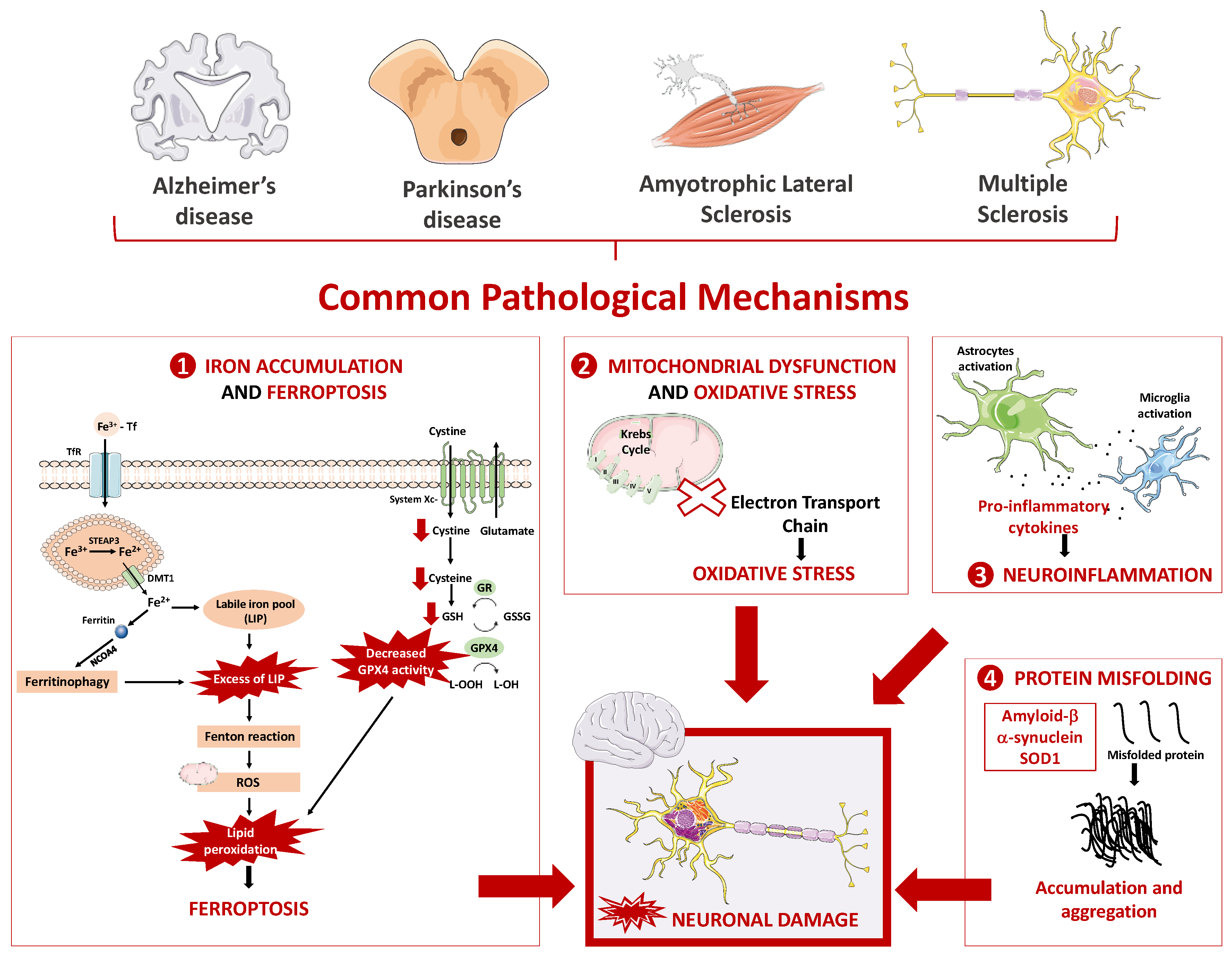
2. Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.1. Main Pathophysiological Mechanism Underlying Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.1.1. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
2.1.2. Neuroinflammation
2.1.3. Protein Misfolding
2.1.4. Iron Overload and Ferroptosis
3. Marine Derived Biomolecules with Antioxidant Properties
3.1. Carotenoids
3.2. Bioactive Peptides
3.3. Polysaccharides
4. Intranasal Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Marine Bioactive Compounds for the Management of Neurodegenerative Diseases
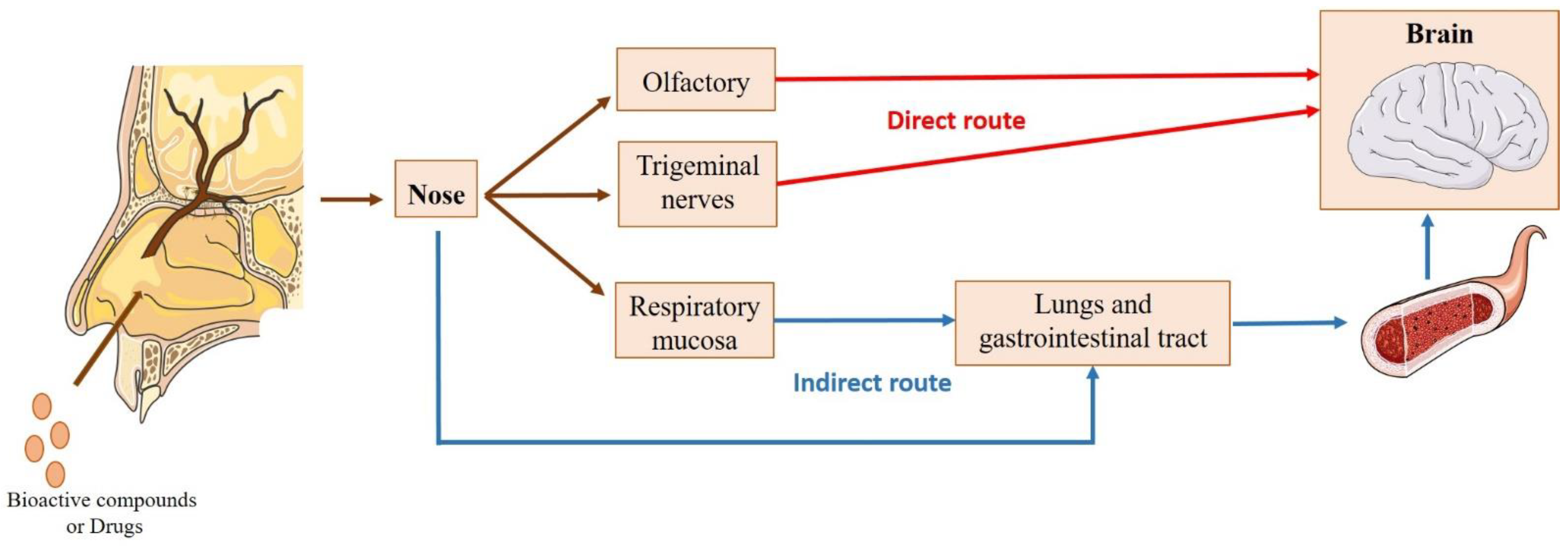
4.1. Intranasal Administration
4.1.1. Nose-to-Brain Transport
4.1.2. Factors Affecting Intranasal Absorption
4.2. Using Lipid Nanoparticles for Nose-to-Brain Transport of Marine Bioactive Compounds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maschmeyer, T.; Luque, R.; Selva, M. Upgrading of marine (fish and crustaceans) biowaste for high added-value molecules and bio(nano)-materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4527–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Othman, S.; Joudu, I.; Bhat, R. Bioactives From Agri-Food Wastes: Present Insights and Future Challenges. Molecules 2020, 25, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shavandi, A.; Hou, Y.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.; Bekhit, A.E.A. Marine Waste Utilization as a Source of Functional and Health Compounds. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 87, 187–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.; Khan, F.F.; Khan, M.I.; Iqbal, J. Marine bioactive peptides: Types, structures, and physiological functions. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 33, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.Q.T.; Jafari, S.M.; Assadpour, E.Q.S.; Aadil, R.M.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rashed, M.M.A.; Sajid, B.; Mushtaq, W.A. Carotenoid-loaded nanocarriers: A comprehensive review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, Y.; Bardakci, H.; Yücel, Ç.; Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Küpeli Akkol, E.; Hakan Barak, T.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Oxidative Stress and Marine Carotenoids: Application by Using Nanoformulations. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagappan, H.; Pee, P.P.; Kee, S.H.Y.; Ow, J.T.; Yan, S.W.; Chew, L.Y.; Kong, K.W. Malaysian brown seaweeds Sargassum siliquosum and Sargassum polycystum: Low density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), α-amylase, and α-glucosidase inhibition activities. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99 Pt 2, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State of the World Fisheries and Aquaculture, Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-5-130562-1.
- Yan, N.; Chen, X. Sustainability: Don’t waste seafood waste. Nature 2015, 524, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabir, T.; Uddin, S.; Jeandet, P.; Emran, T.; Mitra, S.; Albadrani, G.; Sayed, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.; Simal-Gandara, J. Anti-Alzheimer’s Molecules Derived from Marine Life: Understanding Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, R.N.L.; Chaulagain, B.; Trivedi, R.; Gothwal, A.; Layek, B.; Singh, J. A Review of the Common Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Therapeutic Approaches and the Potential Role of Nanotherapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, A.C.; Monteiro, A.R.; Silva, R.; Moreira, J.N.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.P.; Moreira, J.N.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Intranasal delivery of nanostructured lipid carriers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions: A current overview of in vivo studies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.; Forbes, B.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Improving Drug Delivery for Alzheimer’s Disease through Nose-to-Brain Delivery Using Nanoemulsions, Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) and in situ Hydrogels. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 4373–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Moreira, J.N.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Nose-to-brain delivery of lipid-based nanosystems for epileptic seizures and anxiety crisis. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2019, 295, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.P.; Barreiro, S.; Moreira, J.N.; Silva, R.; Almeida, H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. In Vitro Studies on Nasal Formulations of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) and Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN). Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G. Molecular pathology of neurodegenerative diseases: Principles and practice. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.G. Concepts and classification of neurodegenerative diseases. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 145, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Erkkinen, M.G.; Kim, M.-O.; Geschwind, M.D. Clinical Neurology and Epidemiology of the Major Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a033118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 327–406. [CrossRef]
- Möller, H.J.; Graeber, M.B. The case described by Alois Alzheimer in 1911. Historical and conceptual perspectives based on the clinical record and neurohistological sections. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1998, 248, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lane, D.J.R.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I. Iron and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update on Emerging Mechanisms. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, S379–S395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyketsos, C.G.; Carrillo, M.C.; Ryan, J.M.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Trzepacz, P.; Amatniek, J.; Cedarbaum, J.; Brashear, R.; Miller, D.S. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2011, 7, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jagadeesan, A.J.; Murugesan, R.; Vimala Devi, S.; Meera, M.; Madhumala, G.; Vishwanathan Padmaja, M.; Ramesh, A.; Banerjee, A.; Sushmitha, S.; Khokhlov, A.; et al. Current trends in etiology, prognosis and therapeutic aspects of Parkinson’s disease: A review. Acta Biomed. 2017, 88, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.; Jenner, P. Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitz, J.M. Parkinson’s disease: A review. Front. Biosci. 2014, 6, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, E.; Moreau, T.; Fromont, A.; Edan, G. Epidemiology of multiple sclerosis. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.S.Y.; Djelloul, M.; Steiner, E.; Bernard, S.; Salehpour, M.; Possnert, G.; Brundin, L.; Frisén, J. Dynamics of oligodendrocyte generation in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2019, 566, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwibel, H.L. Contribution of impaired mobility and general symptoms to the burden of multiple sclerosis. Adv. Ther. 2009, 26, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreau, C.; Danel, V.; Devedjian, J.C.; Grolez, G.; Timmerman, K.; Laloux, C.; Petrault, M.; Gouel, F.; Jonneaux, A.; Dutheil, M.; et al. Could Conservative Iron Chelation Lead to Neuroprotection in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masrori, P.; Van Damme, P. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A clinical review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbott, E.O.; Malek, A.M.; Lacomis, D. The epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 138, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saberi, S.; Stauffer, J.E.; Schulte, D.J.; Ravits, J. Neuropathology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Its Variants. Neurol. Clin. 2015, 33, 855–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, A.V.; Balachandran, B. Role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutr. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, M.; Moreno-Lastres, D.; Marín-Buera, L.; Arenas, J.; Martín, M.A.; Ugalde, C. Mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction: Implications in neurodegeneration. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreyev, A.Y.; Kushnareva, Y.E.; Starkov, A.A. Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry 2005, 70, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas, E.; Davies, K.J. Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, J.M. Superoxide-dependent formation of hydroxyl radicals from ferric-complexes and hydrogen peroxide: An evaluation of fourteen iron chelators. Free Radic. Res. Commun. 1990, 9, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, L.-D. Mitochondrial biogenesis: An update. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 4892–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breuer, M.; Koopman, W.; Koene, S.; Nooteboom, M.; Rodenburg, R.; Willems, P.H.; Smeitink, J. The role of mitochondrial OXPHOS dysfunction in the development of neurologic diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 51, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, T.E.; Pfeiffer, D.R. Mechanisms by which mitochondria transport calcium. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 258 Pt 1, C755–C786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardi, P.; Di Lisa, F.; Fogolari, F.; Lippe, G. From ATP to PTP and Back: A Dual Function for the Mitochondrial ATP Synthase. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, N.; Xu, Z.; Qu, C.; Zhang, J. Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-κB signal pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 98, 107844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hambright, W.S.; Na, R.; Ran, Q. Ablation of the Ferroptosis Inhibitor Glutathione Peroxidase 4 in Neurons Results in Rapid Motor Neuron Degeneration and Paralysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28097–28106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweig, J.A.; Brandes, M.S.; Brumbach, B.H.; Caruso, M.; Wright, K.M.; Quinn, J.F.; Soumyanath, A.; Gray, N.E. Prolonged Treatment with Centella asiatica Improves Memory, Reduces Amyloid-β Pathology, and Activates NRF2-Regulated Antioxidant Response Pathway in 5xFAD Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 81, 1453–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, L.; Fischer, M.T.; Frischer, J.M.; Bauer, J.; Höftberger, R.; Botond, G.; Esterbauer, H.; Binder, C.J.; Witztum, J.L.; Lassmann, H. Oxidative damage in multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 2011, 134 Pt 7, 1914–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puspita, L.; Chung, S.Y.; Shim, J. Oxidative stress and cellular pathologies in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pegoretti, V.; Swanson, K.A.; Bethea, J.R.; Probert, L.; Eisel, U.L.M.; Fischer, R. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Multiple Sclerosis: Consequences for Therapy Development. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 7191080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, S.C.; Shaw, P.J. Oxidative stress in ALS: Key role in motor neuron injury and therapeutic target. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohl, K.; Tenbrock, K.; Kipp, M. Oxidative stress in multiple sclerosis: Central and peripheral mode of action. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 277, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Montezinho, L.; Mendes, C.; Firuzi, O.; Saso, L.; Oliveira, P.J.; Silva, F.S.G. Oxidative Stress in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Pathophysiology and Opportunities for Pharmacological Intervention. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5021694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Franco Silva, D.; Segura, L.; Baldeiras, I.; Marques, R.; Rosenstock, T.; Oliveira, P.J.; Silva, F.S. Oxidative stress profiles of lymphoblasts from Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis patients with or without known SOD1 mutations. bioRxiv. 2022. Available online: http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2022/03/04/2022.03.03.482309.abstract (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Dias, V.; Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2013, 3, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.E.; Rhie, S.J.; Yoon, S. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.-J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.-W. Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Rep. 2016, 4, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassidy, L.; Fernandez, F.; Johnson, J.B.; Naiker, M.; Owoola, A.G.; Broszczak, D.A. Oxidative stress in alzheimer’s disease: A review on emergent natural polyphenolic therapeutics. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102294. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0965229919315237 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.-Q.; Zhou, J.-W. Neuroinflammation in the central nervous system: Symphony of glial cells. Glia 2019, 67, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badanjak, K.; Fixemer, S.; Smajić, S.; Skupin, A.; Grünewald, A. The Contribution of Microglia to Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatnani, H.; Maniatis, T. Astrocytes in neurodegenerative disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acioglu, C.; Li, L.; Elkabes, S. Contribution of astrocytes to neuropathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. 2021, 1758, 147291. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006899321000160 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, E.; Andreasen, N.; Tarkowski, A.; Blennow, K. Intrathecal inflammation precedes development of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodacki, B.; Staszewski, J.; Toczyłowska, B.; Kozłowska, E.; Drela, N.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Stępien, A. Serum interleukin (IL-2, IL-10, IL-6, IL-4), TNFalpha, and INFgamma concentrations are elevated in patients with atypical and idiopathic parkinsonism. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 441, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, H.C.; Evert, B.O.; Kaut, O.; Riederer, P.F.; Waha, A.; Wüllner, U. Different methylation of the TNF-alpha promoter in cortex and substantia nigra: Implications for selective neuronal vulnerability. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 32, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.R.; Cagnin, A.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Miller, C.C.J.; Shaw, C.E.; Brooks, D.J.; Leigh, P.N.; Banati, R.B. Evidence of widespread cerebral microglial activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 15, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Engler, H.; Blomquist, G.; Scott, B.; Wall, A.; Aquilonius, S.-M.; Långström, B.; Askmark, H. Evidence for astrocytosis in ALS demonstrated by [11C](L)-deprenyl-D2 PET. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 255, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Jian, C.; Liao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zou, D.; Wu, Y. The role of microglia in multiple sclerosis. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.C.; Cawston, E.E.; Chen, G.; Brooks, C.; Douwes, J.; McLean, D.; Graham, E.S.; Dragunow, M.; Scotter, E.L. Serum biomarkers of neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier leakage in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotemeyer, A.; McFleder, R.L.; Wu, J.; Wischhusen, J.; Ip, C.W. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease—Putative Pathomechanisms and Targets for Disease-Modification. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Karpf, L.; Bohl, D. Neuroinflammation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia and the Interest of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Study Immune Cells Interactions With Neurons. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelobaba, I.; Savic, D.; Lavrnja, I. Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroinflammation: The Overview of Current and Prospective Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 693–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F. Role of Neuroinflammation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Cellular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araújo, B.; Caridade-Silva, R.; Soares-Guedes, C.; Martins-Macedo, J.; Gomes, E.D.; Monteiro, S.; Teixeira, F.G. Neuroinflammation and Parkinson’s Disease-From Neurodegeneration to Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soria Lopez, J.A.; González, H.M.; Léger, G.C. Alzheimer’s disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 167, 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M.E.; Hensley, K.; Butterfield, D.A.; Leedle, R.A.; Carney, J.M. Direct evidence of oxidative injury produced by the Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptide (1-40) in cultured hippocampal neurons. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 131, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Akram, M.; Daniyal, M.; Zainab, R. Awareness and current knowledge of Parkinson’s disease: A neurodegenerative disorder. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 55–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanis, L. α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludtmann, M.H.R.; Angelova, P.R.; Horrocks, M.H.; Choi, M.L.; Rodrigues, M.; Baev, A.Y.; Berezhnov, A.V.; Yao, Z.; Little, D.; Banushi, B.; et al. α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parakh, S.; Atkin, J.D. Protein folding alterations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Res. 2016, 1648 Pt B, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lillo, C.; Jonsson, P.; Velde, C.V.; Ward, C.M.; Miller, T.M.; Subramaniam, J.R.; Rothstein, J.D.; Marklund, S.; Andersen, P.M.; et al. Toxicity of familial ALS-linked SOD1 mutants from selective recruitment to spinal mitochondria. Neuron 2004, 43, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paré, B.; Lehmann, M.; Beaudin, M.; Nordström, U.; Saikali, S.; Julien, J.-P.; Gilthorpe, J.D.; Marklund, S.L.; Cashman, N.R.; Andersen, P.M.; et al. Misfolded SOD1 pathology in sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, E.; Chandrasekhar, G.; Anbarasu, K.; Vickram, A.S.; Karunakaran, R.; Rajasekaran, R.; Srikumar, P.S. Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 736978. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2021.736978 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.-D.; Wang, Y.-D. β-Amyloid: The Key Peptide in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 221. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2015.00221 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gitler, A.D.; Bevis, B.J.; Shorter, J.; Strathearn, K.E.; Hamamichi, S.; Su, L.J.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Rochet, J.-C.; McCaffery, J.M.; et al. The Parkinson’s disease protein a-synuclein disrupts cellular Rab homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 145–150. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.0710685105 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chisholm, C.G.; Yerbury, J.J.; McAlary, L. Protein Aggregation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. In Spectrums of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 105–121. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781119745532.ch6 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H., 3rd. Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uranga, R.M.; Salvador, G.A. Unraveling the Burden of Iron in Neurodegeneration: Intersections with Amyloid Beta Peptide Pathology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2850341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, P.T.; Heiskala, M.; Peterson, P.A.; Yang, Y. The roles of iron in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2001, 22, 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayisaba, A.; Kaindlstorfer, C.; Wenning, G.K. Iron in Neurodegeneration—Cause or Consequence? Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ke, Y.; Qian, Z.M. Brain iron metabolism: Neurobiology and neurochemistry. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 83, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muckenthaler, M.U.; Galy, B.; Hentze, M.W. Systemic iron homeostasis and the iron-responsive element/iron-regulatory protein (IRE/IRP) regulatory network. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2008, 28, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.-D.; Pang, P.; Zhou, X.-T.; Hu, F.; Xiong, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, D.; Hu, Y.-Z.; et al. Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1548–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofic, E.; Riederer, P.; Heinsen, H.; Beckmann, H.; Reynolds, G.P.; Hebenstreit, G.; Youdim, M.B.H. Increased iron (III) and total iron content in post mortem substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J. Neural. Transm. 1988, 74, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Rathore, K.I.; Schulz, K.; Ponka, P.; Arosio, P.; David, S. Dysregulation of iron homeostasis in the CNS contributes to disease progression in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhelum, P.; Santos-Nogueira, E.; Teo, W.; Haumont, A.; Lenoël, I.; Stys, P.K.; David, S. Ferroptosis Mediates Cuprizone-Induced Loss of Oligodendrocytes and Demyelination. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 9327–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Dai, R.; Ismail, N.; Su, W.; Li, B. Ferroptosis and Its Potential Role in Human Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 239. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fphar.2020.00239/full (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Jeandriens, J.; Parkes, H.G.; So, P.-W. Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, L.; Wang, T.; Hua, W.; Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Gu, W.; Li, T.; Li, N.; et al. Activation of p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Protects 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Ferroptosis in Dopaminergic Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 4628–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.P.; Henry, Y.K.; Henkel, J.S.; Smith, R.G.; Appel, S.H. Increased lipid peroxidation in sera of ALS patients: A potential biomarker of disease burden. Neurology 2004, 62, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-L.; Fan, Y.-G.; Yang, Z.-S.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Guo, C. Iron and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Wang, N.; Qi, F.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Che, F.; Li, W. Serum ferritin is a candidate biomarker of disease aggravation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biomed Rep. 2018, 9, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Azad, M.G.; Dharmasivam, M.; Richardson, V.; Quinn, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Pountney, D.L.; Tonissen, K.F.; Mellick, G.D.; Yanatori, I.; et al. Parkinson’s disease: Alterations in iron and redox biology as a key to unlock therapeutic strategies. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101896. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213231721000446 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, K.; Khan, H.; Kanojia, N.; Singh, T.G.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, G. Therapeutic Insights on Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 930, 175133. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014299922003946 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Jakaria, M.; Belaidi, A.A.; Bush, A.I.; Ayton, S. Ferroptosis as a mechanism of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2021, 159, 804–825. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jnc.15519 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Majerníková, N.; den Dunnen, W.F.A.; Dolga, A.M. The Potential of Ferroptosis-Targeting Therapies for Alzheimer’s Disease: From Mechanism to Transcriptomic Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 745046. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2021.745046 (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- White, A.R. Ferroptosis drives immune-mediated neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tomas, D.; Perera, N.D.; Cuic, B.; Luikinga, S.; Viden, A.; Barton, S.K.; McLean, C.A.; Samson, A.L.; Southon, A.; et al. Ferroptosis mediates selective motor neuron death in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Adachi-Tominari, K.; Sano, O.; Kamei, T.; Nogami, M.; Ogi, K.; Okano, H.; Yano, M. Involvement of ferroptosis in human motor neuron cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 566, 24–29. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006291X2100886X (accessed on 1 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Sun, L. The Potential Role of Ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 80, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney-Sánchez, L.; Bouchaoui, H.; Ayton, S.; Devos, D.; Duce, J.A.; Devedjian, J.-C. Ferroptosis and its potential role in the physiopathology of Parkinson’s Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 196, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, M.; Kozani, P.S.; Kozani, P.S.; Pierre, G.; Michaud, P.; Delattre, C. Marine Bacteria versus Microalgae: Who Is the Best for Biotechnological Production of Bioactive Compounds with Antioxidant Properties and Other Biological Applications? Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Q.; Wei, B.; Wang, S.; Ke, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. The Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides Derived from Marine Organisms: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Sansone, C.; Lauritano, C.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A. Marine microorganisms as a promising and sustainable source of bioactive molecules. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanesi, M.; Caioni, G.; Castelli, V.; Benedetti, E.; d’Angelo, M.; Cimini, A. Benefits under the Sea: The Role of Marine Compounds in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, C.; Orefice, I.; Pellone, P.; Cirino, P.; Miele, R.; Ianora, A.; Brunet, C.; Sansone, C. On the Neuroprotective Role of Astaxanthin: New Perspectives? Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sztretye, M.; Dienes, B.; Gönczi, M.; Czirják, T.; Csernoch, L.; Dux, L.; Szentesi, P.; Keller-Pintér, A. Astaxanthin: A Potential Mitochondrial-Targeted Antioxidant Treatment in Diseases and with Aging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3849692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, M.P.; Poppe, S.C.; Bondan, E.F. Neuroprotective properties of the marine carotenoid astaxanthin and omega-3 fatty acids, and perspectives for the natural combination of both in krill oil. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1293–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Lu, W.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y.; Ding, R.; Wang, L. Extraction and purification of astaxanthin from shrimp shells and the effects of different treatments on its content. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meresse, S.; Fodil, M.; Fleury, F.; Chenais, B. Fucoxanthin, a Marine-Derived Carotenoid from Brown Seaweeds and Microalgae: A Promising Bioactive Compound for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullan, K.; Williams, M.A.; Cardwell, C.R.; McGuinness, B.; Passmore, P.; Silvestri, G.; Woodside, J.V.; McKay, G.J. Serum concentrations of vitamin E and carotenoids are altered in Alzheimer’s disease: A case-control study. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 3, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, K.C.; Gao, X.; Kim, I.Y.; Rimm, E.B.; Wang, M.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A. Intake of antioxidant vitamins and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.S.; Shin, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.B. Recent Advances in Studies on the Therapeutic Potential of Dietary Carotenoids in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4120458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoka, T. Carotenoids in marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Jimenez, G.M.; Burgos-Hernandez, A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with anticancer potential: Sources from marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 963–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila Rodríguez, M.I.; Rodríguez Barroso, L.G.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.; Gopal, J.; Chun, S.; Devadoss, A.J.P.; Hasan, N.; Sivanesan, I. Crustacean Waste-Derived Chitosan: Antioxidant Properties and Future Perspective. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Liu, P.; Cheng, Q.; Tahi, T.; Gu, W.; Li, B. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1962–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y. An Overview of the Protective Effects of Chitosan and Acetylated Chitosan Oligosaccharides against Neuronal Disorders. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahidi, F.; Abuzaytoun, R. Chitin, chitosan, and co-products: Chemistry, production, applications, and health effects. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2005, 49, 93–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, V.; Salatti-Dorado, J.; Barzegari, A.; Nicolas-Boluda, A.; Houaoui, A.; Caballo, C.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Sicilia, D.; Venegas, J.B.; Pauthe, E.; et al. Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Preservation of Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zahi, M.R.; Yuan, Q.; Tian, F.; Liang, H. Preparation and stability of astaxanthin solid lipid nanoparticles based on stearic acid. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonocito, D.; Raciti, G.; Campisi, A.; Sposito, G.; Panico, A.; Siciliano, E.; Sarpietro, M.; Damiani, E.; Puglia, C. Astaxanthin-Loaded Stealth Lipid Nanoparticles (AST-SSLN) as Potential Carriers for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Formulation Development and Optimization. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, K. Novel Antioxidative Activity of Astaxanthin and Its Synergistic effect with vitamin E. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S109–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra Bhatt, P.; Srivastava, P.; Pandey, P.; Khan, W.; Panda, B.P. Nose to brain delivery of astaxanthin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Fabrication, radio labeling, optimization and biological studies. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10001–10010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, H. Inhibitory Effect of Astaxanthin on Oxidative Stress-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction-A Mini-Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Han, J. Development and Evaluation of Astaxanthin as Nanostructure Lipid Carriers in Topical Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.; Basirnejad, M.; Shahbazi, S.; Bolhassani, A. Carotenoids: Biochemistry, pharmacology and treatment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1290–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Selva, M.; Issaabadi, Z.; Luque, R. Waste-to-wealth: Biowaste valorization into valuable bio(nano)materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4791–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, S.; Aneva, I.Y.; Farzaei, M.H.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E. The Neuroprotective Effects of Astaxanthin: Therapeutic Targets and Clinical Perspective. Molecules 2019, 24, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, Q.; Hai, K.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ye, Z.; Liu, X. Investigation of the protective effect of heparin pre-treatment on cerebral ischaemia in gerbils. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berthon, J.Y.; Nachat-Kappes, R.; Bey, M.; Cadoret, J.P.; Renimel, I.; Filaire, E. Marine algae as attractive source to skin care. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Qu, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhen, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, Y.; Wang, W. The protective effect of astaxanthin on learning and memory deficits and oxidative stress in a mouse model of repeated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 131, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Saleem, S.; Perveen, T.; Tabassum, S.; Batool, Z.; Sadir, S.; Liaquat, L.; Madiha, S. Age-related learning and memory deficits in rats: Role of altered brain neurotransmitters, acetylcholinesterase activity and changes in antioxidant defense system. Age 2014, 36, 9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shibata, T.; Hisaka, S.; Osawa, T. Astaxanthin inhibits reactive oxygen species-mediated cellular toxicity in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells via mitochondria-targeted protective mechanism. Brain Res. 2009, 1254, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiko, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Satoh, A.; Tsuduki, T.; Furukawa, K.; Arai, H.; Miyazawa, T. Amyloid β levels in human red blood cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, B.F.; Veloso, C.A.; Nogueira-Machado, J.A.; de Moraes, E.N.; dos Santos, R.R.; Cintra, M.T.G.; Chaves, M.M. Ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol, and beta-carotene reduce oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines in mononuclear cells of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Nutr. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Honarvar, N.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Abdolahi, M.; Shayeganrad, A.; Taheri Sangsari, G.; Hassanzadeh Rad, B.; Muench, G. Molecular Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms of Retinoids and Carotenoids in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of Current Evidence. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 61, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, T.; Salim, C.; Rajini, P.S.; Suresh, P.V. Antioxidant and neuroprotective potential of chitooligomers in Caenorhabditis elegans exposed to Monocrotophos. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Ahmad, Z.; Shakya, P.; Kumar, A.; Arif, M. Nano formulation: A novel approach for nose to brain drug delivery. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Bourganis, V.; Kammona, O.; Alexopoulos, A.; Kiparissides, C. Recent advances in carrier mediated nose-to-brain delivery of pharmaceutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 337–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Liu, M.; Khan, M.W.; Zhai, G. Progress in brain targeting drug delivery system by nasal route. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 364–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadab; Bhattmisra, S.K.; Zeeshan, F.; Shahzad, N.; Mujtaba, A.; Meka, V.S.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Kesharwani, P.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Nano-carrier enabled drug delivery systems for nose to brain targeting for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, F.; Dias-Teixeira, M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Grosso, C. Critical Review of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as Carriers of Neuroprotective Drugs and Extracts. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Lalotra, A.S.; Agrawal, S.; Mishrai, G. Nose-to-Brain drug delivery via nanocarriers for the management of neurodegenerative disorders: Recent advances and future. Biol. Sci. 2021, 1, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinis, M.A.; Rodriguez-Gascon, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Preat, V. Nanostructured lipid carriers: Promising drug delivery systems for future clinics. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkar, T.B.; Tekade, A.R.; Khandelwal, K.R. Surface engineered nanostructured lipid carriers for efficient nose to brain delivery of ondansetron HCl using Delonix regia gum as a natural mucoadhesive polymer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.P.; Butani, S.B. Resveratrol anchored nanostructured lipid carrier loaded in situ gel via nasal route: Formulation, optimization and in vivo characterization. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosa, A.; Reddi, S.; Saha, R.N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobo, J.M.S.; Silva, A.C. Lipid Nanoparticles for Nasal/Intranasal Drug Delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2017, 34, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdo, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, A.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of intranasal delivery route of drug administration for brain targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, M.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Antimisiaris, S.G.; Chougule, M.B.; Shoyele, S.A.; Alexander, A. Nose-to-brain drug delivery: An update on clinical challenges and progress towards approval of anti-Alzheimer drugs. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Intranasal Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Nose-to-Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.; Almeida, H.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobo, J.M.S.; Silva, A.C. Intranasal lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 6553–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illum, L. Nasal drug delivery—Possibilities, problems and solutions. J. Control. Release 2003, 87, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, H.; Li, F.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Wu, W. An update on the role of nanovehicles in nose-to-brain drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, H.R.; Illum, L.; Brandt, G.; Johnson, P.H.; Quay, S.C. Intranasal delivery: Physicochemical and therapeutic aspects. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassin-Delyle, S.; Buenestado, A.; Naline, E.; Faisy, C.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Couderc, L.-J.; Le Guen, M.; Fischler, M.; Devillier, P. Intranasal drug delivery: An efficient and non-invasive route for systemic administration: Focus on opioids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Cossu, M.; Brundu, A.; Cerri, G.; Marchetti, N.; Ferraro, L.; Regan, R.F.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E.; et al. Solid microparticles based on chitosan or methyl-β-cyclodextrin: A first formulative approach to increase the nose-to-brain transport of deferoxamine mesylate. J. Control. Release 2015, 201, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pires, P.C.; Santos, A.O. Nanosystems in nose-to-brain drug delivery: A review of non-clinical brain targeting studies. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Pandey, A.N.; Jain, S.K. Nasal-nanotechnology: Revolution for efficient therapeutics delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavian, F.; Shams, N. Oral and Intra-nasal Administration of Nanoparticles in the Cerebral Ischemia Treatment in Animal Experiments: Considering its Advantages and Disadvantages. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, G.; Tsang, W.C.; Schatzlein, A.G.; Uchegbu, I.F. Nose-to-Brain Delivery. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kälviäinen, R. Intranasal therapies for acute seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 49, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostamabadi, H.; Falsafi, S.R.; Jafari, S.M. Nanoencapsulation of carotenoids within lipid-based nanocarriers. J. Control. Release 2019, 298, 38–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.; Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Samani, S. Solid Lipid nanoparticles and nanostructure lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Scioli Montoto, S.; Muraca, G.; Ruiz, M.E. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Pharmacological and Biopharmaceutical Aspects. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, A.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Formulations based on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for cutaneous use: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, M.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C. 20 Years of Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): Present State of Development & Industrial Applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, R.H.; Petersen, R.D.; Hommoss, A.; Pardeike, J. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic dermal products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi, L.; Battaglia, L.; Peira, E.; Chirio, D.; Muntoni, E.; Solazzi, I.; Gallarate, M.; Dosio, F. Solid lipid nanoparticles as vehicles of drugs to the brain: Current state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, I.P.; Bhandari, R.; Bhandari, S.; Kakkar, V. Potential of solid lipid nanoparticles in brain targeting. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapeinos, C.; Battaglini, M.; Ciofani, G. Advances in the design of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for targeting brain diseases. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 306–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Bendayan, R. Nanotechnological advances for the delivery of CNS therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobo, J.M.; Lopes, C.M. Lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labouta, H.I.; Sarsons, C.; Kennard, J.; Gomez-Garcia, M.J.; Villar, K.; Lee, H.; Cramb, D.T.; Rinker, K.D. Understanding and improving assays for cytotoxicity of nanoparticles: What really matters? RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23027–23039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.H.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Mattei, B.; Zanetti-Ramos, B.G.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. In vitro biocompatibility of solid lipid nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapani, A.; Guerra, L.; Corbo, F.; Castellani, S.; Sanna, E.; Capobianco, L.; Monteduro, A.; Manno, D.; Mandracchia, D.; Di Gioia, S.; et al. Cyto/Biocompatibility of Dopamine Combined with the Antioxidant Grape Seed-Derived Polyphenol Compounds in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Molecules 2021, 26, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, S.; Sharma, T.; Jain, A.; Kaur, H.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Systematically designed chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles of ferulic acid for effective management of Alzheimer’s disease: A preclinical evidence. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Bo, F.; Yang, S.; Feng, A. Primary Studies on Construction and Evaluation of Ion-Sensitive in situ Gel Loaded with Paeonol-Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Intranasal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3137–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Junior, E.R.; Truzzi, E.; Ferraro, L.; Fogagnolo, M.; Pavan, B.; Beggiato, S.; Rustichelli, C.; Maretti, E.; Lima, E.M.; Leo, E.; et al. Nasal administration of nanoencapsulated geraniol/ursodeoxycholic acid conjugate: Towards a new approach for the management of Parkinson’s disease. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh Malvajerd, S.; Azadi, A.; Izadi, Z.; Kurd, M.; Dara, T.; Dibaei, M.; Zadeh, M.S.; Javar, H.A.; Hamidi, M. Brain Delivery of Curcumin Using Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Preparation, Optimization, and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourehab, M.A.S.; Khames, A.; Genedy, S.; Mostafa, S.; Khaleel, M.A.; Omar, M.M.; El Sisi, A.M. Sesame Oil-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers of Nicergoline, Intranasal Delivery System for Brain Targeting of Synergistic Cerebrovascular Protection. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo El-Enin, H.A.; Elkomy, M.H.; Naguib, I.A.; Ahmed, M.F.; Alsaidan, O.A.; Alsalahat, I.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Eid, H.M. Lipid Nanocarriers Overlaid with Chitosan for Brain Delivery of Berberine via the Nasal Route. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomolecule | Natural Source | Therapeutic Properties and Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Astaxanthin | Shrimp/crab shells Haematococcus pluvialis | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. | [117,121,122,123,124,125] |
| Fucoxanthin | Brown algae Laminaria japonica | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. | [7,121,126] |
| β-carotene | Turban shell Microalga Dunaliella salina | Antioxidant properties. Prevention of liver fibrosis, acute and chronic coronary syndrome, and neurodegenerative diseases. Protection against UV radiation. | [117,127,128,129,130] |
| Collagen | Cod skin | Antioxidant properties. Anti-aging. | [2,131,132] |
| Gelatin | Tuna (Thunnus spp.) Flying squid (Ommastrephes batramii) | Antioxidant and anti-proliferative properties. Prevention of cancer. | [131] |
| Chitin | Crustaceans Cuttlefish Squid pen | Antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial, and anticoagulant properties. Immune system boosting. Wound healing. | [133,134,135,136] |
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
|
|
| Type of Lipid Nanoparticle | Natural Bioactive Compound | Relevant Outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLN | Astaxanthin |
| [141] |
| SLN | Dopamine combined with antioxidant grape seed-derived polyphenol compounds (GSE) |
| [196] |
| SLN coated with chitosan | Ferulic acid |
| [197] |
| SLN in situ gel | Paeonol |
| [198] |
| SLN | Geraniol combined with ursodeoxycholic acid (GER/UDCA) |
| [199] |
| SLN and NLC | Curcumin |
| [200] |
| NLC | Nicergoline |
| [201] |
| NLC coated with chitosan | Berberine |
| [202] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres, J.; Costa, I.; Peixoto, A.F.; Silva, R.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Intranasal Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Marine Sources to Manage Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020311
Torres J, Costa I, Peixoto AF, Silva R, Sousa Lobo JM, Silva AC. Intranasal Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Marine Sources to Manage Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020311
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres, Joana, Inês Costa, Andreia F. Peixoto, Renata Silva, José Manuel Sousa Lobo, and Ana Catarina Silva. 2023. "Intranasal Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Marine Sources to Manage Neurodegenerative Diseases" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020311
APA StyleTorres, J., Costa, I., Peixoto, A. F., Silva, R., Sousa Lobo, J. M., & Silva, A. C. (2023). Intranasal Lipid Nanoparticles Containing Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Marine Sources to Manage Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020311









