Abstract
Autophagy is the process by which damaged regions of the cytoplasm and intracellular pathogens are degraded. This mechanism often serves an adaptive role in cells, enhancing their survival. It plays a direct or indirect role in the development of various pathological conditions within the body. This phenomenon is common in various malignant diseases, where autophagy is associated with the resistance of transformed cells to chemotherapy. Conversely, abnormal activation of autophagy can trigger cell death, a process often seen in neurodegenerative conditions. Given that dysregulation of autophagy is associated with the progression of numerous pathological conditions, this is of significant interest to the developers of drugs that can effectively modulate autophagy for both basic research and clinical applications. Here, we provide a brief description of the mechanism of macroautophagy, the most prevalent form of autophagy identified in humans. We also discuss the clinical potential of drugs that can modulate autophagy, highlighting their use in combating diseases associated with direct or indirect dysregulation of this essential process.
1. Introduction
Mechanism of Autophagy
Currently, several forms of autophagy have been identified, including macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. Although these processes are morphologically distinct, they all ultimately lead to the delivery of cellular cargo to the lysosome for degradation and recycling. The most prevalent form is macroautophagy, a vesicular process crucial for the degradation of dysfunctional organelles and misfolded or aggregated proteins. This pathway plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. During macroautophagy, the cell generates a double-membrane structure known as the phagophore, which subsequently matures into an autophagosome. The formation of an autophagosome around a lysate substrate is a central event in the autophagy process. This process involves the formation of a membrane around the substrate, which is a multistep process involving many signaling pathways and protein complexes. The first stage of autophagy is its initiation. During this stage, autophagy initiation complexes are assembled. These complexes are involved in the formation of the precursor to the autophagosomal membrane, the phagophore. The autophagic activity begins with the assembly of ULK (Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinases) complexes consisting of FIP200 (focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kD), Atg13 (autophagy-related protein 13), and ULK1/ULK2 proteins (Figure 1). Normally, mTORC1 complex—mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) complex 1, which acts as the main negative regulator of their assembly, inhibits Atg13 by binding to its protein. In a pathological state of cells associated with a lack of ATP, mTOR activity decreases, leading to the loss of its inhibitory effects on the ULK complex. The assembled ULK then initiates the formation of another autophagic complex called PI3KC3 (another term for the VPS34 complex). This complex consists of Beclin1, Atg14/UVRAG (autophagy-related protein 13/UV radiation resistance-associated gene protein), VPS15 (vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 15), and VPS34 proteins [1,2,3]. The next stage of autophagy is isolation. During this process, the autophagic initiator complexes formed during the initiation of autophagosome formation bind to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). This causes the protrusion of the ER membrane region and saturation of this region with phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P) molecules, which are realized with the participation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase C3 (PI3KC3) proteins [4].
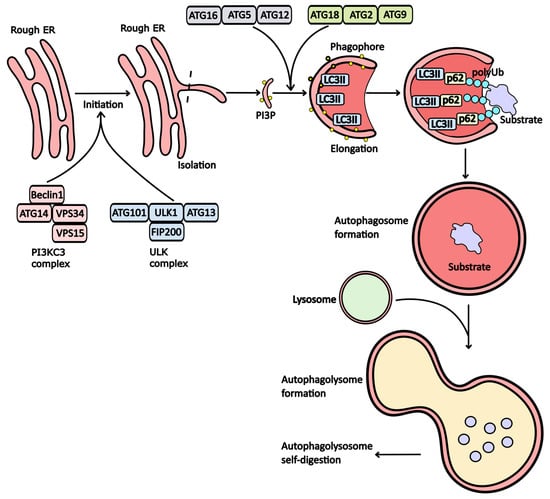
Figure 1.
The stages of autophagy. The initiation of autophagy begins with the assembly of the PI3KC3 and ULK1 complexes. Under normal conditions, proteins within these complexes remain inactive due to mTORC1 activity. However, when ATP and nutrient levels decline, this leads to the assembly of PI3KC3 and ULK1. These assembled complexes promote the protrusion of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane, enriching it with phosphoinositol triphosphate (PI3P). For further maturation of the phagophore, the conjugating complex (Atg16/Atg5/Atg12) modifies the LC3 receptor, facilitating its integration into the membrane and bending it to form the phagophore. The Atg18/Atg2/Atg9 complex further enriches the phagophore membrane with PI3P. LC3II plays a crucial role in attaching substrates to the phagophore membrane via p62 adapter proteins. Shortly after substrate incorporation, a vesicle known as an autophagosome forms, which subsequently fuses with a lysosome to create an autophagolysosome, where substrate degradation occurs.
The protruding portion of the membrane fully detached from the ER and transformed into a phagophore. This process involves the LC3 protein (microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3), which conjugates with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and binds to the inner surface of the membrane, forming an autophagosome. At this stage, the modified form of LC3 is referred to as LC3II. The primary complex responsible for LC3 conjugation and the curvature of phagophore membranes consists of Atg16, Atg5, and Atg12 [5].
Additionally, the formation of an autophagosome requires the enrichment of membranes with phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P) molecules. This enrichment is facilitated by the Atg18, Atg2, and Atg9 protein complex, which transports PI3P from the ER membrane [6]. Once these modifications are complete, substrates can associate with the phagophore membrane. However, substrates cannot attach directly to the phagophore; they require adapter proteins such as p62 and/or NBR1 (Neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1 protein). These proteins mediate the binding of substrates to the LC3II receptors (Figure 1).
Subsequently, the phagophore evolves into a double-membrane vesicle known as an autophagosome. For effective substrate degradation during autophagy, proteolytic enzymes must be present within this vesicle. To achieve this, the autophagic vesicle must fuse with a lysosome, resulting in the formation of an autolysosome. Within this structure, lysosomal enzymes break down the initial substrate.
Autophagy is a crucial mechanism for cell survival, playing a significant role in the management of pathological changes linked to various diseases. This has spurred the development and testing of drugs that can modulate autophagy, either as inhibitors or inducers. However, it is important to note that many currently synthesized drugs lack specificity for particular targets. Consequently, their effects on autophagy can be complex and context-dependent, influenced by factors such as the experimental model, cell line, and methods employed to assess drug activity. This variability has implications for clinical practice and the outcomes of clinical trials involving these compounds. This review focuses on drugs that are currently used or hold promise for clinical application, particularly in relation to specific diseases. We will explore both inhibitory and activating effects on autophagy, highlighting their potential therapeutic relevance.
2. Drugs That Modulate Autophagy Activity
Currently, a huge number of drugs have been developed to modulate autophagy, influencing this crucial cellular process either directly or indirectly. These compounds can be broadly categorized into those that inhibit autophagy and those that activate it. Below, we outline some of the primary groups of drugs frequently employed in preclinical and clinical studies.
2.1. Inhibitors of Autophagy
Autophagy inhibitors can be categorized based on their mechanisms of action into several groups: phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors, Vps34 kinase inhibitors, vATPase (proton pump) inhibitors, ULK1 protein inhibitors, and agents that disrupt lysosomal function.
2.1.1. PI3K Inhibitors
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway plays a crucial role in regulating cell survival. Consequently, drugs targeting the proteins involved in this pathway significantly influence autophagy activity. PI3K is classified into three main classes, each with distinct cellular functions:
- -
- Class 1 PI3K (PI3KC1): Involved in the AKT signaling cascade and insulin receptor signaling.
- -
- Class 2 PI3K (PI3KC2): Plays a role in cell adhesion.
- -
- Class 3 PI3K (PI3KC3): Central to the formation of autophagosomes.
Most known PI3K inhibitors affect various classes of PI3K, leading to diverse impacts on autophagy regulation. Notably, many of these inhibitors also target proteins unrelated to PI3K signaling, which can indirectly influence autophagy. Inhibitors that selectively target PI3KC3 tend to have the most significant effect on autophagy inhibition.
Wortmannin is a well-known inhibitor that is used extensively in preclinical studies. Derived from the fungus Penicillium funiculosum, it features a steroid structure and inhibits all three classes of PI3K. By disrupting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, Wortmannin induces cell death. Specifically, its inhibition of PI3KC3 hampers the enrichment of the phagophore membrane with PI3P molecules, thereby reducing the efficiency of phagophore formation [7].
3-Methyladenine (3-MA) is another widely utilized autophagy inhibitor that targets both PI3KC1 and PI3KC3. While its inhibition of PI3KC1 is irreversible, its effect on PI3KC3 is temporary, allowing for reversible autophagy inhibition [8]. 3-MA has been used in studies investigating the molecular underpinnings of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and various cancers. A clinical trial has also assessed its efficacy in treating mantle cell lymphoma [9].
LY294002 is a specific inhibitor of PI3KC1 that effectively inhibits the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and enhances the expression of LC3, a marker associated with autophagy.
Its role in regulating autophagy is quite contradictory; it can act as either an autophagy inhibitor or an autophagy inducer, depending on the cell lines used and the methods employed in the study [10,11,12]. It was shown that both inhibitors, Wortmannin and LY294002, inhibit autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes, reducing the efficiency of autophagosome formation [10]. On the contrary, treatment of gastric cancer cells (SGC7901) with LY294002 has been shown to induce autophagy and apoptosis linked to the activation of p53, caspase-3, and PUMA (p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis). Activation of p53 [11]. A modified version, SF1126, has been explored in clinical trials for neuroblastoma treatment. SF1126 is a conjugate of LY294002 and the RGDS tetrapeptide (H-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-OH), which facilitates effective interaction with neuroblastoma cells enriched with integrins. This tetrapeptide is known for its high affinity for integrins due to its structural similarity to fibronectin. Unfortunately, the Phase 1 clinical trial for SF1126 was halted due to an insufficient number of participants.
Other notable PI3K inhibitors include ZSTK474 (a PI3KC1 inhibitor), GSK-2126458 (which targets both PI3KC1 and PI3KC3), and PT210 (also a dual inhibitor of PI3KC1 and PI3KC3). Based on the established targets and general mechanisms of action of PI3K inhibitors known to influence autophagy, it can be inferred that these inhibitors may also impact autophagy. However, it is important to note that the nature of this effect is likely to be dual-faceted.
2.1.2. Inhibitors of the PI3KC3 Complex (Vps34)
Inhibition of the Vps34 complex disrupts autophagy at its early stages. Several direct inhibitors of Vps34 have been identified, including VPS34-IN-1, Compound-31, SAR405, and PIK-III (Figure 2). Notably, Spautin-1 warrants special attention due to its unique mechanism of action. It directly inhibits ubiquitin-specific proteases USP10 (ubiquitin-specific peptidase 10) and USP13 (ubiquitin-specific peptidase 13), which are responsible for degrading polyubiquitin at the Lys-11 position of the Beclin-1 protein. This degradation inactivates Beclin-1, a crucial component for the formation of the PI3KC3 complex and the assembly of autophagic vesicles [13,14]. Consequently, Spautin-1 may significantly impact protein degradation mechanisms. In studies involving neuroblastoma cells, treatment with Spautin-1 has been shown to decrease p53 levels due to enhanced proteolysis and impaired deubiquitination [14].
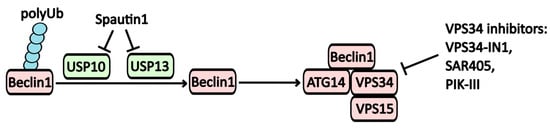
Figure 2.
The regulatory mechanisms affecting the Vps34 complex. One method for modulating Beclin-1 activity involves its polyubiquitilation. Beclin-1, when polyubiquitinated at Lys11, inhibits the assembly of the PI3KC3 complex. Spautin-1 inhibits the USP10 and USP13 ubiquitin-specific peptidase activity, thereby disrupting the assembly of the PI3KC3 complex, which includes Beclin-1, ATG14, VPS34, and VPS15.
Furthermore, Spautin-1 inhibits the EGFR signaling pathway, which contributes to a reduced survival rate of cancer cells [13], positioning this molecule as a promising candidate for potential cancer therapies. However, it is important to note that no clinical trials involving Spautin-1 have been conducted to date.
2.1.3. ULK1 Inhibitors
The ULK1 complex plays a crucial role as the primary initiator of autophagy. Disruption of its assembly impairs the initiation of this essential cellular process.
MRT68921 is a notable inhibitor of ULK1, and its application in acute myeloid leukemia cells has been linked to a decreased survival rate. While MRT68921 inhibits ULK1, it may also lead to the accumulation of LC3II and a reduction in phosphorylated levels of Atg13 and ULK (Ser555), which could theoretically induce autophagy. However, these effects are overshadowed by the predominant suppression of ULK activity, and the primary outcome of MRT68921 is the inhibition of autophagic processes. Additionally, MRT68921 suppresses the phosphorylation of eIF2 and PERK, resulting in reduced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and subsequent inhibition of autophagosome formation [15]. Notably, MRT68921 has been shown to arrest the cell cycle in the G2 phase when applied to chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. The combination of MRT68921 with the Bcl-2 inhibitor Venetoclax has demonstrated a synergistic effect in suppressing cell proliferation [16]. Other ULK1 inhibitors include Compound 6 and SBI-0206965.
2.1.4. V-ATPase (Proton Pump) and Lysosomal Inhibitors
Inhibition of proton pump activity on the lysosomal membrane disrupts lysosomal function due to decreased activity of lysosomal proteolytic enzymes, which require an acidic pH for optimal function. Concanamycin and Bafilomycin A1 are well-known inhibitors that interfere with proton pump operation (Figure 3).
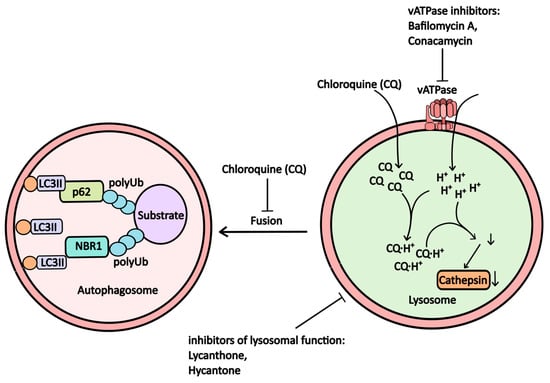
Figure 3.
The scheme illustrates how proton pump inhibitors, which alter lysosomal pH and microsomal function, affect autophagy (further explanations are provided in the accompanying text).
Bafilomycin A1, an antibiotic derived from *Streptomyces griseus*, inhibits V-ATPase in lysosomes, leading to increased lysosomal pH and suppressed autophagy (Рисунoк 3). It also stabilizes the Beclin-1/Bcl-2 heterodimer, resulting in reduced active Beclin-1 levels and further inhibition of autophagic processes [17,18]. While bafilomycin A1 is frequently used in in vitro studies to model lysosomal dysfunction, its clinical application has been limited due to toxicity concerns.
For effective autophagy, fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes is essential, forming autophagolysosomes where substrate degradation occurs. In cases of lysosomal dysfunction, autophagosomes may fail to form or may do so incompletely, impairing the activity of proteolytic enzymes such as cathepsins.
Chloroquine and its derivative, hydroxychloroquine, are among the most commonly used inhibitors of autophagy in clinical trials. Both alkaloids are derivatives of 4-aminoquinolines, with chloroquine having a long-established role in malaria treatment. The drug has garnered renewed interest for potential repurposing due to its nitrogen-rich heterocyclic aromatic structure, which undergoes protonation within lysosomes. This process raises lysosomal pH, disrupting the function of hydrolytic enzymes (Figure 3) [18] and diminishing substrate degradation efficiency within autophagosomes, as well as impairing the fusion between lysosomes and autophagosomes [19].
Currently, chloroquine is utilized as an immunosuppressive agent for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Its antiviral efficacy has been demonstrated in several studies [20]. Furthermore, the efficiency of chloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 was demonstrated, but the results from phase 4 clinical trials (NCT04331600) have raised concerns about its effectiveness for COVID-19 treatment. Ongoing research continues to explore the potential of chloroquine in cancer therapy (Table 1). Other compounds exhibiting similar cellular effects include Lys05 and ARN 5187.

Table 1.
Clinical trials of chloroquine.
Another drug that directly impacts lysosomal function is lucanthone. This compound increases lysosomal membrane permeability, leading to the release of cathepsin D and subsequent lysosomal dysfunction. This dysfunction results in reduced efficiency of autophagosome formation and the induction of apoptosis [21]. Notably, while lucanthone treatment promotes the binding of the LC3 protein to autophagosomes [21], this effect is minimal compared to the overarching lysosomal impairment.
In addition to its effects on autophagy, lucanthone inhibits DNA repair mechanisms and disrupts DNA replication, ultimately causing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through the inhibition of apurinic endopeptidase 1 (APE1) [22].
The efficacy of lucanthone, in combination with the antitumor alkylating agent temozolomide (TMZ), was evaluated in a clinical trial (NCT01587144) for the treatment of glioblastoma. Another study (NCT0201454) assessed its potential to enhance the effectiveness of radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer metastases in the brain.
Currently, lucanthone is used as an antihelmintic, with its effects linked to the inactivation of serotonin 5-HT receptors, resulting in tetany (uncontrolled muscle contractions) in nematodes such as S. haematobium and S. mansoni, ultimately leading to their death. Its analog, Hycanthone, exhibits a similar mechanism of action on eukaryotic cells.
Cathepsins are crucial for lysosomal proteolytic activity; thus, inhibitors of cathepsins also function as autophagy inhibitors [23]. Notable cysteine protease inhibitors include E64d (Aloxistatin), E64c, Leupeptin, k777, and Odanacatib. These compounds possess a broad range of effects and can inhibit various proteases, including those not directly associated with lysosomal activity.
2.2. Inducers of Autophagy
Drugs that activate autophagy can be categorized based on their mechanisms of action: mTOR inhibitors, ER stress inducers, IMRase (inositol monophosphatase) inhibitors, MTMR14 (myotubularin-related protein 14)/jumpy inhibitors, mTOR-independent autophagy inducers, calpain inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, Bcl-2 inhibitors, AMPK (5′ AMP-activated protein kinase) activators, and TFEB (Transcription factor EB) activators.
2.2.1. mTOR Inhibitors
The mTOR protein is a key component of the mTORC1 complex, which negatively regulates the activity of TFEB and ULK complexes, thereby inhibiting autophagy. Drugs that suppress mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin), such as Rapamycin and Everolimus (RAD001) and Temsirolimus (AP23576), stimulate autophagy by inhibiting this pathway.
Rapamycin, an antibiotic derived from *Streptomyces hygroscopicus*, has immunosuppressive properties and is often used to prevent organ rejection in transplantation. By inhibiting mTOR within the mTORC complex, rapamycin activates Atg13 and initiates autophagy (see Figure 1) [24,25].
Beyond its role in autophagy, mTOR also regulates translation. It is part of a complex known as the mTOR/Raptor/GβL complex, which inhibits the activity of 4E-BP1—a negative regulator of eIF4—and activates S6K, a protein involved in ribosome assembly. Consequently, rapamycin can also inhibit translation by blocking this complex’s activity.
Rapamycin has been extensively studied in over 700 clinical trials to explore its potential for treating various conditions. The research includes investigations into its combination with trastuzumab for HER2+ breast cancer (Phase 2, NCT01827943) and its efficacy in enhancing radiotherapy outcomes for rectal cancer (Phase 2, NCT00409994).
Temsirolimus, a prodrug of rapamycin, has also been evaluated in phase 2 trials for bladder (NCT01827943) and prostate (NCT00919035) cancers.
Everolimus, like Temsirolimus, is a modified rapamycin derivative used to mitigate rejection reactions in kidney and liver transplants while also exhibiting anti-cancer properties. The potential of everolimus in treating malignant diseases has been explored in several clinical trials, including its efficacy in combination with prednisone for kidney cancer (NCT02479490).
2.2.2. ER-Stress Inductors
The induction of ER stress leads to increased expression of genes encoding autophagy proteins, particularly through the PERK/eIF2/ATF4 (Protein Kinase RNA-Like ER Kinase Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2/Activating transcription factor 4) pathway. Key inducers of ER stress include Tunicamycin, Thapsigargin, and Brefeldin A. Disruption of the ubiquitin-proteasome system is a major factor associated with the development of ER stress. Proteasome inhibitors such as Bortezomib and NPI-0052 act as indirect activators of autophagy by inhibiting proteasomal activity.
Brefeldin A, an antibiotic derived from the fungus Eupenicillium brefeldianum, disrupts vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. It inhibits GBF1 (Golgi-specific brefeldin A-resistance guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1), which normally exchanges GDP for GTP, thereby regulating Arf1 (ADP-ribosylation factor 1) activity involved in COPI (Coat protein I) vesicle formation on the Golgi membrane. This disruption leads to impaired homeostatic regulation of ER protein transport [26], resulting in ER stress.
Notably, brefeldin A has been shown to activate gene expression and proteins involved in autophagy. Treatment of liver cancer cells with brefeldin A significantly increases the accumulation of LC3II, ATG5, and Beclin1 proteins in the cytoplasm, effectively activating autophagy [27].
Bortezomib, marketed under the trade name Velcade, targets the 20S core of the 26S proteasome, disrupting its function and inducing ER stress and autophagy [28,29]. In clinical practice, bortezomib is utilized as an anti-cancer agent for multiple myeloma treatment, with numerous clinical trials investigating its use alone or in combination with other therapies [30,31].
NPI-0052 (Marizomib, Salinosporamide A) is another drug that inhibits the 26S proteasome. The molecular structure of this drug includes a β-lactone ring, which provides binding to threonine in the structure of β5i, β2i, and β1i subunits of the 20S proteasome complex. This interaction disrupts protein degradation and induces autophagy via ER stress [31]. Currently, NPI-0052 is undergoing clinical trials for multiple myeloma treatment.
2.2.3. Inhibitors of Inositol Monophosphatase (IMPase)
Inositol diphosphatase plays a crucial role in hydrolyzing phosphodiester bonds in inositol diphosphate, converting it into inositol monophosphate. This phosphodiesterase activity is essential for maintaining cellular inositol levels; disruptions can lead to reduced triphosphorylated inositol and subsequent autophagy induction. Lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate and lithium chloride, along with their specific inhibitor L-690/330, are commonly used as IMRase inhibitors. Additionally, drugs that interact directly with inositol, like carbamazepine and valproic acid, can interfere with IP3 accumulation [32].
L-690/330 acts as a competitive inhibitor of IMRase (inositol monophosphatase) [33]. Treatment with this drug has been shown to induce autophagy in cells. Disruption of inositol triphosphate (IP3) turnover reduces the activity of the IP3R Ca2+ channel, leading to decreased cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels [34]. Calcium plays a dual role in regulating autophagy—both activating and inhibiting it—but L-690/330 specifically enhances autophagic activity.
2.2.4. MTMR14 (Jumpy) Inhibitors
MTMR14, a myotubularin-binding protein, serves as an inhibitor of autophagy due to its phosphoinositide phosphatase activity. It hydrolyzes PI3P on the autophagic membrane to PI2P, thereby suppressing autophagic assembly. Consequently, the inhibition of MTMR14 activates autophagy [35]. Compounds such as AUTEN99 and AUTEN67 have been identified as potential inhibitors of MTMR14 (Figure 4).
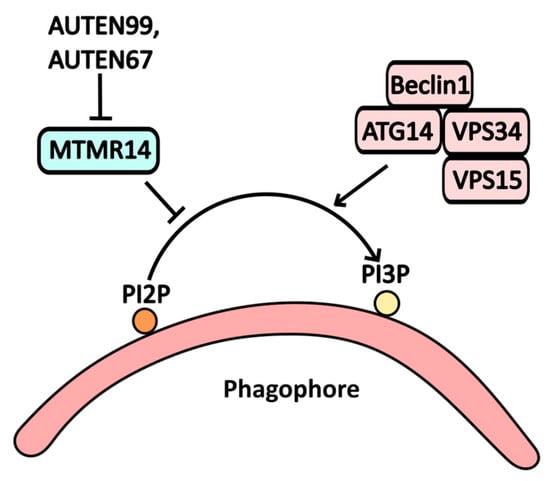
Figure 4.
The scheme illustrates the action of AUTEN99 and AUTEN67 on autophagy, where the MTMR1/Jumpy protein acts as a functional antagonist to the PI3K complex. This interaction leads to the degradation of phosphoinositol phosphate PI3P at the phagosome membrane, disrupting autophagy. By inhibiting MTMR activity, AUTEN99 and AUTEN67 facilitate the accumulation of PI3P at the phagosome membrane.
As a relatively new synthetic molecule, AUTEN99 blocks the phosphatase activity of MTMR14, preventing the conversion of PI3P to PI2P [35]. While it is not yet employed in clinical practice, experimental studies have shown that AUTEN99 reduces α-synuclein protein aggregates in the nervous tissue of Drosophila models of Parkinson’s disease [36].
2.2.5. mTOR-Independent Inducers
This category includes drugs that induce autophagy without directly interacting with components of the mTORc1 complex. Instead, they activate signaling pathways that influence mTORc1 activity. Notable compounds in this group include Corynoxine and W09.
Corynoxine, an indole alkaloid derived from the *Uncaria* plant in the Rubiaceae family, has been shown to activate autophagy. This effect is linked to the induction of the PI3KC3 complex and a reduction in the phosphorylation levels of mTOR, AKT, and p70S6K [37]. Although not currently utilized in conventional medicine, Corynoxine has been employed in traditional Chinese medicine for its hypotensive properties and has demonstrated potential in reducing α-synuclein and β-amyloid levels in neurons [38], making it a promising candidate for treating neurodegenerative diseases.
W09 functions as an activator of autophagy and apoptosis dependent on Atg7. Treatment with W09 enhances the transcription of the p62 gene and stimulates autophagy via the EGFR/RAS/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK1-3 pathway. This mechanism was confirmed in studies using the MAPK 1-3 inhibitor U0126, which inhibited MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) activity and subsequently reduced both autophagic and caspase-dependent apoptotic responses induced by W09. Additionally, W09 can activate PARP, a protein involved in DNA repair and autophagy via the AMP/LKB (liver kinase B)/AMPK signaling pathway [39]. Despite promising experimental data, clinical studies involving this molecule have yet to be conducted.
2.2.6. Calpain Inhibitors
Calpains, a family of calcium-dependent cytoplasmic proteases, play a significant role in regulating various signaling cascades associated with cell survival. One mechanism by which calpains inhibit autophagy is through the degradation of PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog) phosphatase, leading to PI3P accumulation and inhibition of the TSC1/TSC2 (tuberous sclerosis 1/2) complex. This sequence results in increased GTP-bound Rheb levels, which activate the mTORC1 complex and subsequently inhibit autophagic activity [40] (Figure 5).
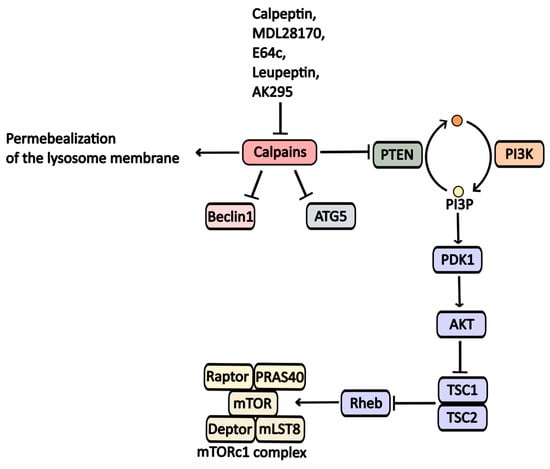
Figure 5.
Calpaine inhibitors and their impact on autophagy regulation. Calpaines suppress Beclin1, ATG5, and PTEN, ultimately inhibiting autophagic processes.
Furthermore, calpains contribute to the degradation of key proteins involved in phagophore formation, such as Atg5 and Beclin1 [41].
Calpains also affect lysosomal function; they can permeabilize lysosomal membranes, causing dysfunction. Inhibiting calpain activity has been shown to enhance autophagy.
Protease inhibitors like Calpeptine, MDL-28170, E64c, AK295, and Leupeptine target calpain enzymes and exhibit a broad range of activity against them [42].
MDL-28170 is a calpain inhibitor. It was found that this molecule can penetrate the hemato-encephalic barrier and inhibit the work of calpains. It was found that the course of therapy of this drug in laboratory mice with a model of brain injury (FPE—fluid percussion injury) leads to a pronounced neuroprotective effect and has a stimulating effect on damage healing [43].
AK-295. Like MDL28170, it causes neuroprotective effects and is a calpain inhibitor. In mice with damaged spinal cord, AK295 reduces calpain-induced apoptosis and improves the functioning of neurons [44].
Leupeptin. It is an inhibitor of calpain 5 and cathepsins B6, H, and L7 [45]. Calpeptin is an inhibitor of calpain and caspase-3. Using a model of cerebral ischemia in mice, it was found that Calpeptin reduces the induction of apoptosis of nerve cells in the CA1 region of the hippocampus [46].
2.2.7. Bcl-2 Inhibitors
One mechanism by which Bcl-2 influences autophagy involves the formation of heterodimeric complexes with key autophagy proteins, such as Bcl-2/Beclin-1 and Bcl-2/BNIP3 (BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3). Notable inhibitors of Bcl-2 include the broad-spectrum inhibitor Obatoclax and the selective Bcl-2 inhibitor Venetoclax (Figure 6). Venetoclax is primarily used in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and its mechanism of action on autophagic activity is linked to its ability to activate Beclin-1 by releasing it from its complex with Bcl-2 [16].
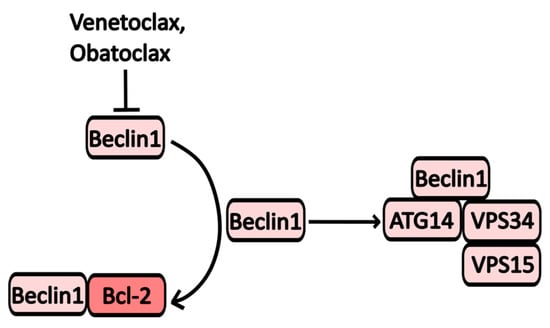
Figure 6.
The scheme of Obatoclax and Venetoclax action on autophagy. Inhibition of Bcl-2 leads to an accumulation of Beclin-1, which forms complexes that promote the formation of autophagosomes.
Obatoclax (GX15-070) targets various members of the Bcl-2 family, including Bcl-XL, Mcl-1, and Bcl-2 [47]. By inhibiting these proteins, Obatoclax triggers mitochondrial apoptosis and the formation of oligomeric channels in the mitochondrial outer membrane, exerting effects on autophagy similar to those of Venetoclax. Additionally, treatment with Obatoclax activates Atg7 and Atg5, enhancing LC3 processing and initiating PI3KC3 assembly (see Figure 1) [47,48,49,50].
However, some studies indicate that Obatoclax may also suppress autophagy due to decreased lysosomal activity resulting from cathepsin inhibition [51]. It has been shown to induce cell death in Hodgkin’s lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and small-cell lung cancer cells. Currently, several clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of Obatoclax in combination with other anti-cancer agents. For instance, combinations with rituximab, a monoclonal CD20 inhibitor for follicular lymphoma (NCT00427856), and bortezomib for multiple myeloma (NCT0719901) are being investigated. As a standalone treatment, Obatoclax has shown promise for acute myeloid leukemia (NCT68491), with over 30 trials conducted to date.
2.2.8. AMPK Activators
AMPK serves as a crucial nutrient sensor, activating in response to significant AMP (adenosine monophosphate) accumulation, which occurs during starvation or catabolic states. AMP activators include RSVA 314/405 and Metformin (Figure 7) [52].
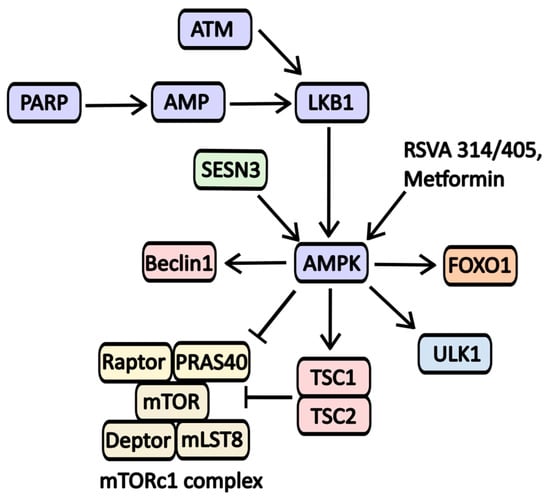
Figure 7.
The scheme of AMPK activators action on signaling pathways involved in autophagy regulation. One of the key triggers for AMPK activation is the accumulation of AMP, often resulting from nutrient deprivation or cellular stress from various sources, including DNA damage. The DNA repair protein PARP has been shown to activate AMPK; however, this process requires NAD·H and ATP. A decreased level of ATP levels leads to activation of LKB1, resulting in AMPK phosphorylation and activation. LKB1 also relies on ATM-kinase, another protein involved in DNA repair. Furthermore, AMPK activity is influenced by metabolic regulators such as Sestrin-3 (SESN3). AMPK promotes autophagy by inhibiting mTORC1 activity while activating essential proteins like Beclin-1, ULK1, and the mTORC inhibitor complex TSC-1/2.
Metformin is widely recognized for its ability to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), primarily through the inhibition of the first complex in the electron transport chain. This activation occurs in response to metabolic stress and is linked to the regulation of numerous signaling molecules involved in autophagy (see Figure 7). While Metformin is primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus, it is also being explored as a potential treatment for various other conditions. Notably, its effectiveness has been evaluated in combination with chloroquine for cancers with IDH1/2 (Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2) mutations. Additionally, Metformin’s impact has been studied in the context of lung adenocarcinoma (Phase 2 trials), vitiligo (NCT05607316), polycystic ovary syndrome (Stein-Leventhal syndrome, NCT03086005), childhood obesity (NCT02274948), and glaucoma (NCT05426044).
2.2.9. TFEB Activators
TFEB is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes containing the so-called CLEAR (Coordinated Lysosomal Expression and Regulation) element in their sequence. Many of these genes encode proteins involved in the initiation and formation of autophagosomes and in the biogenesis of lysosomes and endosomes, in particular, p62, UVRAG, LC3, ATG5, and Beclin-1. In the case of cellular stress, there is a decrease in the amount of the phosphorylated form of TFEB as a result of a decrease in the activity of mTORC1. This leads to its release from the 14-3-3σ/TFEB complex and promotes its transport to the nucleus, where its transcriptional activity is carried out. MSL-7 can be considered a drug that causes dephosphorylation of TFEB and its activation. The mechanism of action of this drug is associated with the activation of calcineurin, a cellular phosphatase involved in the phosphorylation of TFEB [53]. It has been shown in laboratory animal models (mice) that MSL-7 reduces the accumulation of hIAPP amyloid (human islet amyloid polypeptide) in the islets of pancreatic Langerhans and prevents the development of a local inflammatory process, as well as associated damage to pancreatic tissues [54]. MSL-7 has been found to reduce glucose tolerance in pancreatic β-cells and promote the survival of insulin-producing cells [54]. In this regard, this drug may be promising for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, but clinical trials have not yet been conducted.
3. Conclusions
Macroautophagy is a crucial mechanism for normal cell functioning. It plays a vital role in cell survival, as it directly or indirectly affects the regulation of autophagic processes. Disruption of these mechanisms has been linked to the development and progression of various diseases, making them promising targets for treatment. Many inhibitors and activators of autophagy have been tested in clinical trials, either in combination with other medications or as monotherapy agents (Table 2). Despite promising initial results, there are still many aspects of their mechanisms that remain unknown, making them of significant interest to scientists.

Table 2.
Summarizing the table of drugs discussed in the review.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, U.K. and P.S.; writing—review and editing, P.S., S.S., V.P. and E.S.; visualization, U.K. and P.S.; supervision, P.S. and V.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Selection and analysis of literature data were supported by the Russian Science Foundation grant No. 23-64-10018. Writing—the original draft preparation was supported by the Russian Science Foundation by grant No. 22-14-00353. Writing—review and visualization was supported by grant No. 075-15-2019-1660 from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this review are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tooze, S.A. Autophagy Pathway: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. Autophagy 2017, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H.; Xia, H.G.; Yuan, J. Pharmacologic agents targeting autophagy. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, M.; Ezazi Erdi, S.; Jorba, G.; Maestro, I.; Farrés, J.; Kirkin, V.; Martinez, A.; Pless, O. Targeting autophagy in disease: Established and new strategies. Autophagy 2022, 18, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.; Joachim, J.; Tooze, S.A. Autophagosome Formation—The Role of ULK1 and Beclin1–PI3KC3 Complexes in Setting the Stage. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lystad, A.H.; Carlsson, S.R.; Simonsen, A. Toward the Function of Mammalian ATG12–ATG5-ATG16L1 Complex in Autophagy and Related Processes. Autophagy 2019, 15, 1485–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Hegedűs, K.; Pircs, K.; Varga, Á.; Juhász, G. Different Effects of Atg2 and Atg18 Mutations on Atg8a and Atg9 Trafficking During Starvation in Drosophila. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluer, T.; Sonmez, P.K.; Akogullari, D.; Onal, M.; Tanriover, G.; Inan, S. Do Wortmannin and Thalidomide Induce Apoptosis by Autophagy Inhibition in 4T1 Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo? Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 6236–6247. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Tan, H.-L.; Shui, G.; Bauvy, C.; Huang, Q.; Wenk, M.R.; Ong, C.N.; Codogno, P.; Shen, H.-M. Dual Role of 3-Methyladenine in Modulation of Autophagy via Different Temporal Patterns of Inhibition on Class I and III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10850–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Zhang, H. 3-Methyladenine but Not Antioxidants to Overcome BACH2-Mediated Bortezomib Resistance in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blommaart, E.F.C.; Krause, U.; Schellens, J.P.M.; Vreeling-Sindelárová, H.; Meijer, A.J. The Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitors Wortmannin and LY294002 Inhibit Autophagy in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Zhu, B.; Liu, H.; Yao, H.; Zhang, L. Class I Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitor LY294002 Activates Autophagy and Induces Apoptosis Through p53 Pathway in Gastric Cancer Cell Line SGC7901. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Sun, W.; Ren, P. Autophagy Inhibitor (LY294002) and 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Combination-Based Nanoliposome for Enhanced Efficacy Against Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, H. Inhibition of EGFR Signaling with Spautin-1 Represents a Novel Therapeutics for Prostate Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xia, H.; Kim, M.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Vakifahmetoglu Norberg, H.; Zhang, T.; Furuya, T.; et al. Beclin1 Controls the Levels of p53 by Regulating the Deubiquitination Activity of USP10 and USP13. Cell 2011, 147, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Jeung, H.-K.; Seol, S.-Y.; Chung, H.; Kim, Y.R.; Cheong, J.-W.; Min, Y.H. Inhibition of Unc-51-Like Kinase 1 (ULK1) with Novel Small Molecular Inhibitor MRT68921 Preferentially Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in FLT3-ITD-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsec, D.; Jakoš Djordjevič, A.T.; Kandušer, M.; Podgornik, H.; Škerget, M.; Mlinarič-Raščan, I. Targeting Autophagy Triggers Apoptosis and Complements the Action of Venetoclax in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, N.; Song, L.; Zhang, S.; Lin, W.; Cao, Y.; Xu, F.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; et al. Bafilomycin A1 Targets Both Autophagy and Apoptosis Pathways in Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, A.O.; Proud, C.G. Chloroquine and Bafilomycin A Mimic Lysosomal Storage Disorders and Impair mTORC1 Signalling. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauthe, M.; Orhon, I.; Rocchi, C.; Zhou, X.; Luhr, M.; Hijlkema, K.J.; Coppes, R.P.; Engedal, N.; Mari, M.; Reggiori, F. Chloroquine Inhibits Autophagic Flux by Decreasing Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salata, C.; Calistri, A.; Parolin, C.; Baritussio, A.; Palù, G. Antiviral Activity of Cationic Amphiphilic Drugs. Expert Rev. Anti-Infective Ther. 2017, 15, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carew, J.S.; Espitia, C.M.; Esquivel, J.A.; Mahalingam, D.; Kelly, K.R.; Reddy, G.; Giles, F.J.; Nawrocki, S.T. Lucanthone is a novel inhibitor of autophagy that induces cathepsin D-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 6602–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, M.D.; Agarwal, R.; Pena, L.A.; Cunha, L.; Mezei, M.; Shen, M.; Wilson, D.M.; Liu, Y.; Sanchez, Z.; Chaudhary, P.; et al. Lucanthone and Its Derivative Hycanthone Inhibit Apurinic Endonuclease-1 (APE1) by Direct Protein Binding. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Lee, J.; Seo, H.-Y.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, E.K. Cathepsin Inhibition-Induced Lysosomal Dysfunction Enhances Pancreatic Beta-Cell Apoptosis in High Glucose. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugume, Y.; Kazibwe, Z.; Bassham, D.C. Target of Mycin in Control of Autophagy: Puppet Master and Signal Integrator. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolewski, P. Recent Developments in Targeting the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Kinase Pathway. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2006, 17, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.-K.; Pfeifer, A.C.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Jackson, C.L. Dynamics of GBF1, a Brefeldin A-Sensitive Arf1 Exchange Factor at the Golgi. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Yu, H.; Bai, J. Study of Brefeldin A on Induction of Autophagy in HepG2 Cells. Environ. Chem. 2022, 41, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Dunner, K.; McConkey, D. Proteasome Inhibitors Activate Autophagy as a Cytoprotective Response in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B. Progress on the Application of Bortezomib and Bortezomib-Based Nanoformulations. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, P.; Robak, T. Bortezomib for the Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies: 15 Years Later. Drugs R D 2019, 19, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, J.C., Jr.; Liu, R.; Xia, L.; Chao, T.H.; Pien, C.; Niu, W.; Palombella, V.J.; Neuteboom, S.T.; Palladino, M.A. NPI-0052 Enhances Tumoricidal Response to Conventional Cancer Therapy in a Colon Cancer Model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6758–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Inositol and IP3 Levels Regulate Autophagy—Biology and Therapeutic Speculations. Autophagy 2006, 2, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.-W.; Choi, H.; Cotman, S.L.; Jung, Y.-K. Lithium Rescues the Impaired Autophagy Process in CbCln3Δex7/8/Δex7/8 Cerebellar Cells and Reduces Neuronal Vulnerability to Cell Death via IMPase Inhibition. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicencio, J.; Ortiz, C.; Criollo, A.; Jones, A.W.E.; Kepp, O.; Galluzzi, L.; Joza, N.; Vitale, I.; Morselli, E.; Tailler, M.; et al. The Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor Regulates Autophagy through Its Interaction with Beclin 1. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, T.; Billes, V.; Komlós, M.; Hotzi, B.; Manzéger, A.; Tarnóci, A.; Papp, D.; Szikszai, F.; Szinyákovics, J.; Rácz, Á.; et al. The Small Molecule AUTEN-99 (Autophagy Enhancer-99) Prevents the Progression of Neurodegenerative Symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, T.; Szinyákovics, J.; Billes, V.; Murányi, G.; Varga, V.B.; Bjelik, A.; Légrádi, Á.; Szabó, M.; Sándor, S.; Kubinyi, E.; et al. A Conserved MTMR Lipid Phosphatase Increasingly Suppresses Autophagy in Brain Neurons during Aging. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, L.F.; Su, C.F.; Liu, J.; Tong, B.C.-K.; Iyaswamy, A.; Krishnamoorthi, S.; Sreenivasmurthy, S.G.; Guan, X.-J.; Kan, Y.-X.; et al. Corynoxine B Derivative CB6 Prevents Parkinsonian Toxicity in Mice by Inducing PIK3C3 Complex-Dependent Autophagy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2511–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-L.; Song, J.-X.; Lu, J.-H.; Yuan, Z.-W.; Liu, L.-F.; Durairajan, S.S.K.; Li, M. Corynoxine, a Natural Autophagy Enhancer, Promotes the Clearance of Alpha-Synuclein via Akt/mTOR Pathway. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, Z.; Ling, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Xia, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. w09, a Novel Autophagy Enhancer, Induces Autophagy-Dependent Cell Apoptosis via Activation of the EGFR-Mediated RAS-RAF1-MAP2K-MAPK1/3 Pathway. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1093–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briz, V.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Li, Y.; Lee, E.; Bi, X.; Baudry, M. Calpain-2-Mediated PTEN Degradation Contributes to BDNF-Induced Stimulation of Dendritic Protein Synthesis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4317–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, D.-H.; Xie, S.-T.; Song, X.-Y.; Wang, G.-F.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhou, B.-C.; et al. Calpain, Atg5 and Bak Play Important Roles in the Crosstalk between Apoptosis and Autophagy Induced by Influx of Extracellular Calcium. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Garg, N.; Singh, T.G.; Kaur, A.; Thapa, K. Calpain Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutic Modulators in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 1125–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, J.; Liu, E.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Baker, A.J. Calpain Inhibitor MDL-28170 Reduces the Functional and Structural Deterioration of Corpus Callosum Following Fluid Percussion Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 960–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, A.; Karaoğlan, A.; Kaya, M.; Sağmanligil, A.; Akdemir, O.; Şahan, E.; Çelik, Ö. Calpain Inhibitor AK 295 Inhibits Calpain-Induced Apoptosis and Improves Neurologic Function After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Neurocirugía 2009, 20, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, T.; Campbell, R.L.; Cuerrier, D.; Davies, P.L. Crystal Structures of Calpain–E64 and –Leupeptin Inhibitor Complexes Reveal Mobile Loops Gating the Active Site. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Kuang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Cheng, Q. The Protective Effects and Potential Mechanism of Calpain Inhibitor Calpeptin Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joudeh, J.; Claxton, D. Obatoclax Mesylate: Pharmacology and Potential for Therapy of Hematological Neoplasms. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.-Z.; Ma, B.; Liang, Y.-J.; Liu, H.-C.; Zhang, T.-H.; Zheng, G.S.; Su, Y.-X.; Liao, G.-Q. Obatoclax Induces Beclin 1- and ATG5-Dependent Apoptosis and Autophagy in Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Cells. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, F.; Cristofanon, S.; Fulda, S. Obatoclax (GX15-070) Triggers Necroptosis by Promoting the Assembly of the Necrosome on Autophagosomal Membranes. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, B.C.; Jassowicz, A.; Scherr, A.L.; Lorenz, S.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Kautz, N.; Elssner, C.; Weiss, J.; Jaeger, D.; Schneider, M.; et al. Pan-Bcl-2 Inhibitor Obatoclax is a Potent Late Stage Autophagy Inhibitor in Colorectal Cancer Cells Independent of Canonical Autophagy Signaling. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S. Autophagy in Cancer Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Wu, Z.; Shang, J.; Xie, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C. The Effects of Metformin on Autophagy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Lim, Y.M.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, Y.E.; Park, K.; Kim, J.; Hwang, H.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Pagire, H.; Kwon, H.J.; et al. A Novel Autophagy Enhancer as a Therapeutic Agent Against Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, K.; Kim, M.J.; Lim, H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.J.; Hur, K.Y.; et al. An Autophagy Enhancer Ameliorates Diabetes of Human IAPP-Transgenic Mice Through Clearance of Amyloidogenic Oligomer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).