Comparison of the Results of Modeling Pulmonary Fibrosis in Sprague Dawley Rats by Intratracheal Administration of Bleomycin in the Form of Sulfate and Chloride at a Dose of 3 mg/kg
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Body Weight Gain
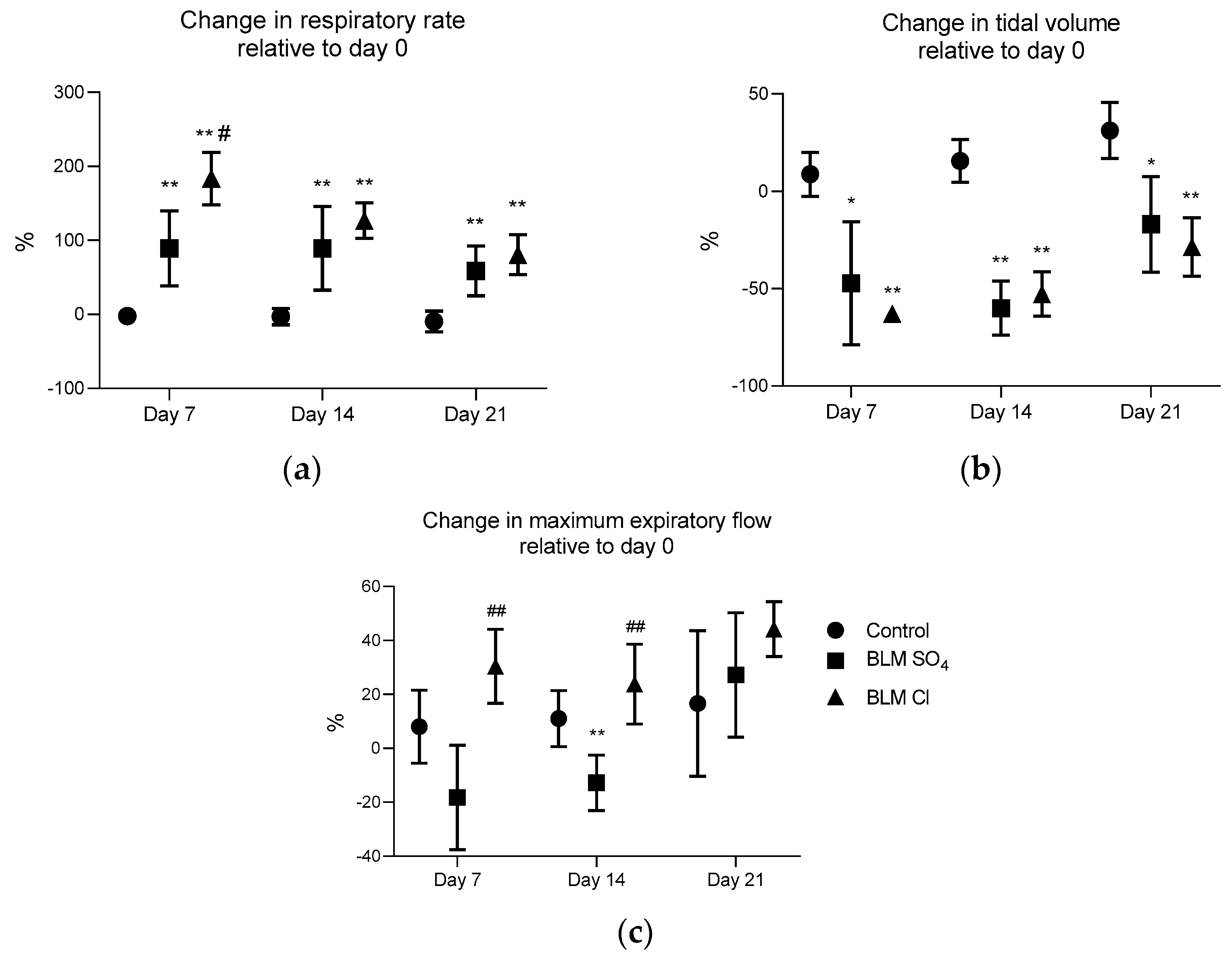
2.2. External Respiration Parameters (Spirometry)
2.3. Relative Lung Weight
2.4. BALF Cytology
2.5. Hydroxyproline ELISA
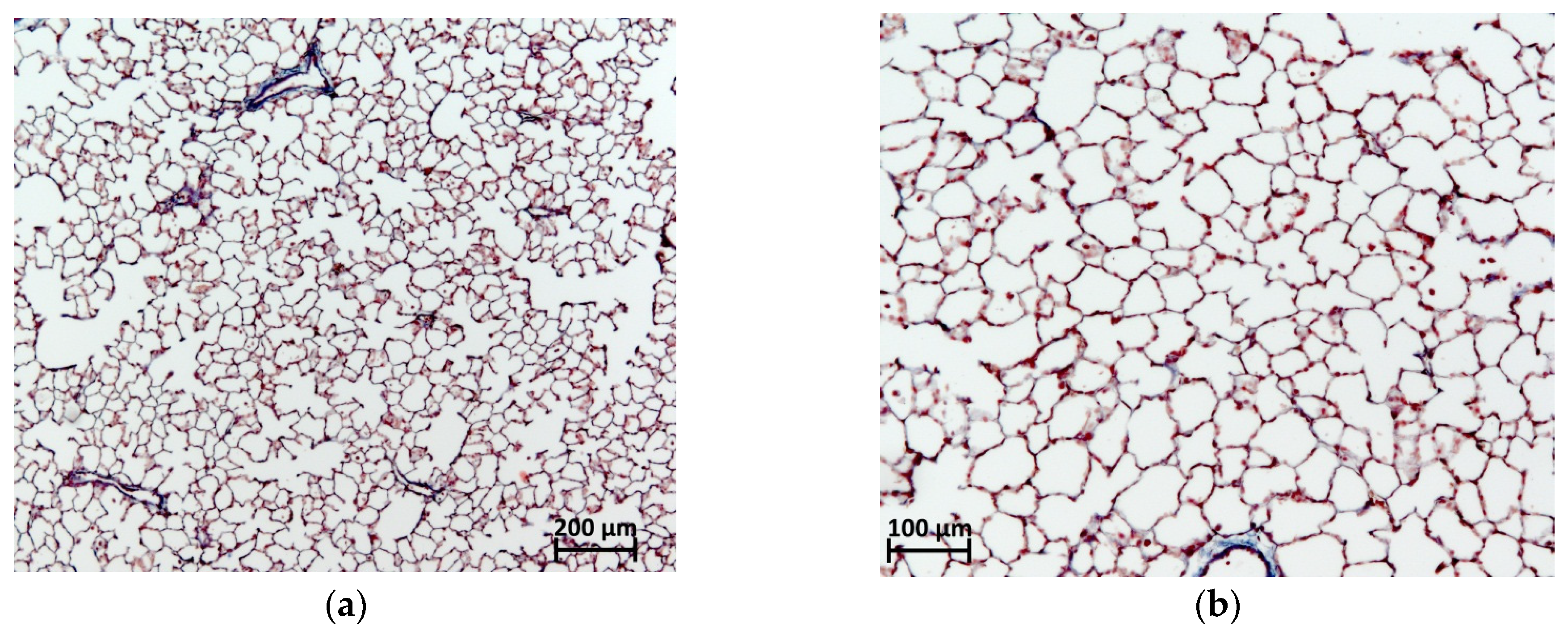
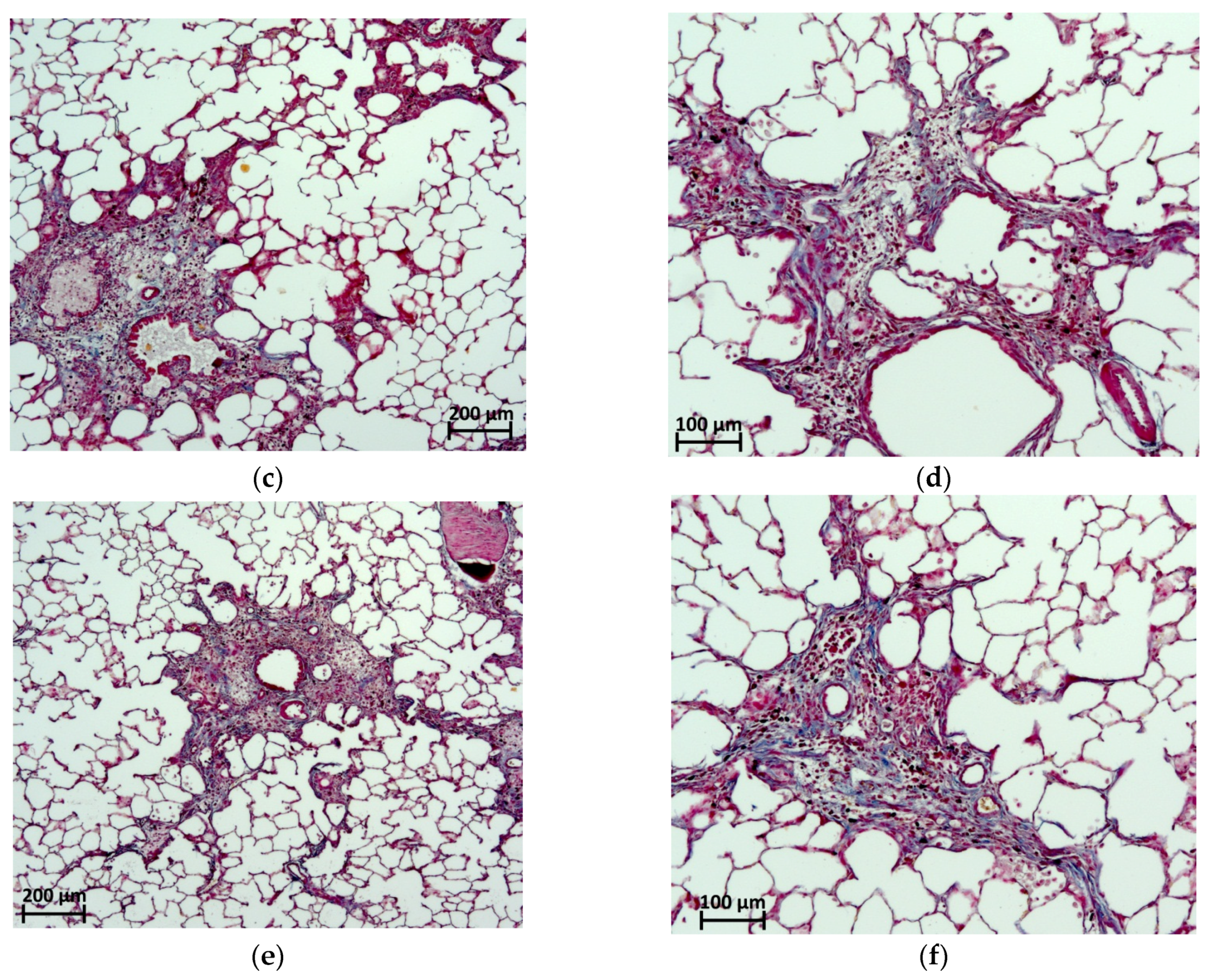
2.6. Histological Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Design Description
4.3. Modeling of PF
4.4. Body Weight Gain
4.5. External Respiration Parameters (Spirometry)
4.6. Euthanasia and Necropsy
4.7. Relative Lung Weight
4.8. BAL Performing
4.9. BALF Cytology
4.10. Taking Samples of Lung Tissue for Subsequent Analysis of Hydroxyproline Content
4.11. Sample Preparation for Analysis of Hydroxyproline in the Lung
4.12. Hydroxyproline Enzyme Immunoassay (ELISA)
4.13. Histological Evaluation
4.14. Statistical Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multi-disciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Thomson, C.C.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; Kreuter, M.; Lynch, D.A.; Maher, T.M.; Martinez, F.J.; et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fbrosis (an update) and progressive pulmonary fbrosis in adults: An ofcial ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic pulmonary fbrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.P.; Gerriets, V. Bleomycin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555895/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Li, L.; Cai, L.; Zheng, L.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, W. Gefitinib Inhibits Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via Alleviating the Oxidative Damage in Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 8249693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Ghaiad, H.R.; Gad, E.S.; Ahmed, K.A.; Abdelmonem, M. Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome by ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2023, 24, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Yang, F.; Xie, C.; Du, W.; Mohammadtursun, N.; Wang, B.; Le, J.; Dong, J. Pulmonary fibrosis model of mice induced by different administration methods of bleomycin. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Tang, Z.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.; Dong, J. Icariin attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting Hippo/YAP pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.-Y.; Qiang, W.-J.; Bao, J.-L.; Yang, R.-C.; Hou, J.; Tao, K.; Meng, Z.-Q.; Zhang, J.-H.; Zhang, A.-J.; Sun, X.-B. Jinbei Oral Liquid ameliorates bleomycin-induced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in rats via reversion of Th1/Th2 shift. Chin. Herb. Med. 2020, 12, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yu, W.; Guo, F. Pirfenidone suppresses bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and periostin expression in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Wei, L.; Wei, L.; et al. Dexamethasone combined with berberine is an effective therapy for bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Wang, F.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, P. Dexamethasone reduces serum level of IL-17 in Bleomycin-A5-induced rats model of pulmonary fibrosis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleomycin A5 Hydrochloride. Available online: https://www.biomol.com/products/chemicals/antibiotics/bleomycin-a5-hydrochloride-lkt-b4517.1?fs=1427117527 (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Bleomycin Prices, Coupons, Copay Cards & Patient Assistance. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/price-guide/bleomycin (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Kayhan, S.; Guzel, A.; Duran, L.; Tutuncu, S.; Guzel, A.; Gunaydın, M.; Salis, O.; Okuyucu, A.; Selcuk, M.Y. Effects of leflunomide on inflamation and fibrosis in bleomycine induced pulmonary fibrosis in wistar albino rats. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghloul, M.S.; Abdel-Salam, R.A.; Said, E.; Suddek, G.M.; Salem, H.A.-R. Attenuation of Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats by flavocoxid treatment. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Vardanjani, H.R.; Hemmati, A.A.; Tabandeh, M.R.; Rezaie, A.; Pashmforosh, M.; Angali, K.A. Zingerone attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2019, 14, e80098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zheng, J.; Chen, B.; Zhuo, J.; Su, Z.; Lai, X.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.; et al. Efect of supercritical carbon dioxide fuid extract from Chrysanthemum indicum Linné on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Ruan, B.; Long, G.; Lin, W. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate lung inflammation and fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis rat model via caveolin-1/NF-κB Signaling Axis. Physiol. Res. 2022, 71, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, R.; Cavalu, S.; Saber, S.; Elmowafy, R.; Morsy, N.E.; Ibrahim, S.; Abdeldaiem, M.S.I.; Samy, M.; Abd-Eldayem, M.A.; Shata, A.; et al. Mirtazapine, an atypical antidepressant, mitigates lung fibrosis by suppressing NLPR3 inflammasome and fibrosis-related mediators in endotracheal bleomycin rat model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatti, M.; Pitozzi, V.; Caruso, P.; Pontis, S.; Pittelli, M.G.; Frati, C.; Mangiaracina, C.; Lagrasta, C.A.M.; Quaini, F.; Cantarella, S.; et al. Time-course transcriptome analysis of a double challenge bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis rat model uncovers ECM homoeostasis-related translationally relevant genes. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilakapati, S.R.; Serasanambati, M.; Manikonda, P.K.; Chilakapati, D.R.; Watson, R.R. Passion fruit peel extract attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.F.; Wilson, C.L.; Chow, Y.-H.; Liles, W.C.; Gharib, S.A.; Altemeier, W.A.; Schnapp, L.M. Effect of lung pericyte-like cell ablation on the bleomycin model of injury and repair. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2022, 322, L607–L616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.-Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.-X.; Chen, L.-M.; Sun, F.; Jia, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. IL-24 deficiency protects mice against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by repressing IL-4-induced M2 program in macrophages. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principi, L.; Ferrini, E.; Ciccimarra, R.; Pagani, L.; Chinello, C.; Previtali, P.; Smith, A.; Villetti, G.; Zoboli, M.; Ravanetti, F.; et al. Proteomic Fingerprint of Lung Fibrosis Progression and Response to Therapy in Bleomycin-Induced Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prêle, C.M.; Miles, T.; Pearce, D.R.; O’Donoghue, R.J.; Grainge, C.; Barrett, L.; Birnie, K.; Lucas, A.D.; Baltic, S.; Ernst, M.; et al. Plasma cell but not CD20-mediated B-cell depletion protects from bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2101469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Ryu, H.W.; Kim, J.-H.; Hahn, H.-J.; Jang, H.-J.; Ko, S.-K.; Oh, S.-R.; Lee, H.-J. Daphnetin Alleviates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through Inhibition of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and IL-17A. Cells 2023, 12, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, F.; Feng, A.; Li, X.; Yu, W. CXXC5 Attenuates Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Bleomycin-Induced Mouse Model and MLFs by Suppression of the CD40/CD40L Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7840652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhou, T.-T.; Huang, W.-J.; Huang, X.-T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.-H.; Sang, X.-X.; Luo, Y.-Y.; Tian, Y.-M.; Wu, B.; et al. Asarinin attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by activating PPARγ. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahori, D.; Inui, N.; Inoue, Y.; Yasui, H.; Hozumi, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Karayama, M.; Furuhashi, K.; Enomoto, N.; Fujisawa, T.; et al. Effect of Hypoxia on Pulmonary Endothelial Cells from Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Kang, Y.; Xue, S.; Zou, J.; Xu, J.; Tang, D.; Qin, H. In vivo therapeutic success of MicroRNA-155 antagomir in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36 (Suppl. S1), S160–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, J.; Yuan, R.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhai, X.; Wang, J.; Magalon, J.; Sabatier, F.; et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy for reverse bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, N.; Willis, G.R.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Reis, M.; Nassiri, S.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Kourembanas, S. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.M.; Mo, Y.; Bang, J.-Y.; Ko, Y.G.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Koh, J.; Yim, J.-J.; Kang, H.-R. Classical monocyte-derived macrophages as therapeutic targets of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: Comparison of intratracheal and intravenous administration in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, A.R.; Hong, J.; Song, K.S.; Jang, A.S.; Kim, D.J.; Chin, S.S.; Park, S.W. Spermidine attenuates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by inducing autophagy and inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-induced cell death in mice. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 2034–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Pan, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Du, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. Amifostine attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, O.; Koivunen, J.; Mäki, J.M.; Pihlajaniemi, T.; Heikkinen, A. Identification of suitable reference genes for normalization of reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) in the fibrotic phase of the bleomycin mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Kasuya, Y.; Hatano, R.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohnuma, K.; Morimoto, C.; Dudek, S.M.; Tatsumi, K.; et al. Functional roles of CD26/DPP4 in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, W.; Xu, S.; Gao, W.; Yu, Z. Effect of dermatan sulphate on a C57-mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 2655–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zeng, Z. Alpinetin ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by repressing fibroblast differentiation and proliferation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, N.; Hayashi, H.; Shimamura, M.; Baba, S.; Yoshida, S.; Morishita, R.; Rakugi, H.; Nakagami, H. Prevention of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by a RANKL peptide in mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecozzi, L.; Mambrini, M.; Ruscitti, F.; Ferrini, E.; Ciccimarra, R.; Ravanetti, F.; Sverzellati, N.; Silva, M.; Ruffini, L.; Belenkov, S.; et al. In-vivo lung fibrosis staging in a bleomycin-mouse model: A new micro-CT guided densitometric approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Yu, W.-K.; Su, V.Y.-F.; Hsu, H.-S.; Yang, K.-Y. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activates Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Focal Adhesion Kinase Pathway in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Yang, L.; Cheng, J.; Qu, H.; Gu, Y.; Ding, C.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, L. Gracillin relieves pulmonary fibrosis by suppressing the STAT3 axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 316, 116704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, A.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, J. Identification of the active compounds and functional mechanisms of Jinshui Huanxian formula in pulmonary fibrosis by integrating serum pharmacochemistry with network pharmacology. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, T.; Sun, P.; Yang, B.; Ying, Y. Qingfei Tongluo Mixture Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis through mTOR-Dependent Autophagy in Rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2024, 2024, 5573353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.-A.; Wang, S.-Y.; Yeh, C.-C.; Fu, T.-W.; Ko, T.-L.; Chiu, M.-M.; Chen, T.-H.; Tsai, P.-J.; Fu, Y.-S. Reversal of bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by a xenograft of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6646–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.H.; Schnitzer, J.E. Insights into Disease Progression of Translational Preclinical Rat Model of Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis through Endpoint Analysis. Cells 2024, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Kang, Q.; Zhai, H. Schisandra Inhibit Bleomycin-Induced Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats via Suppressing M2 Macrophage Polarization. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5137349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Fang, C. Shengxian decoction improves lung function in rats with bleomycin-induced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through the inhibition of PANoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 329, 118153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Song, L.; Hou, H.; Chen, T.; Ma, L.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Z. Salvianolic acid B inhalation solution enhances antifibrotic and anticoagulant effects in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Jiang, D.; Geng, J.; Dong, R.; Dai, H. Hydrogen inhalation attenuated bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1 and relevant oxidative stress and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 1942–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Liang, D.; Meng, Z.; Gan, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, X.; et al. Cepharanthine Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting the NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway, Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition and Inflammation. Molecules 2023, 28, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.-G.; Chen, T.-F.; Gao, Y.-H.; Song, L.; Yang, Y.-F.; Gao, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, G.-P. Panax notoginseng saponin alleviates pulmonary fibrosis in rats by modulating the renin-angiotensin system. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hela, A.A.; Hegazy, M.M.; Abbass, H.S.; Ahmed, A.H.; Abu Bakr, M.S.; Elkousy, R.H.; Ibrahim, A.E.; El Deeb, S.; Sayed, O.M.; Gad, E.S. Dinebra retroflexa Herbal Phytotherapy: A Simulation Study Based on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Retraction Potential in Swiss Albino Rats. Medicina 2022, 58, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surber, M.W.; Beck, S.; Pham, S.; Marsden, A.T.; Gandi, S.K.; Baily, J.; McElroy, M.C. Inhaled nintedanib is well-tolerated and delivers key pharmacokinetic parameters required to treat bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 63, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Ribeiro, D.; Lecocq, M.; de Beukelaer, M.; Verleden, S.; Bouzin, C.; Ambroise, J.; Dorfmuller, P.; Yakoub, Y.; Huaux, F.; Quarck, R.; et al. Disruption of GCN2 Pathway Aggravates Vascular and Parenchymal Remodeling during Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 68, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.-J.; Zhao, L.; Song, Z.-Z.; Shen, W.-P.; Ju, P.; Li, Y.-M. Expression and significance of miR-223 in rats with pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3951–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, K.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Bai, Y. Effective-compounds of Jinshui Huanxian formula ameliorates fibroblast activation in pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of mTOR signaling. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schols, A.M. Pulmonary cachexia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2002, 85, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D. Prevalence, incidence and clinical impact of cachexia: Facts and numbers—Update. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotler, D.P. Cachexia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 17, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsuzawa, T.; Shioya, S.; Kurita, D.; Haida, M.; Ohta, Y.; Yamabayashi, H. Muscle energy metabolism and nutritional status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A 31P magnetic resonance study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzberg, E.; Schols, A.; Bothmer-Quaedvlieg, F.; Wouters, E. Prevalence of an elevated resting energy expenditure in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in relation to body composition and lung function. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Martinez, F.J. The role of pulmonary function testing in pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2000, 6, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, I.; Lynch, J., III; Martinez, F. Role of physiologic assessment in advanced lung disease. In Management of Non-Neoplastic Advanced Lung Disease; Maurer, J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, M.J.; Pearson, M.G.; O’Grady, E.A.; Pellegrini, V.; Calverley, P.M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis with preserved lung volumes. Thorax 1997, 52, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Ohkubo, H.; Nakano, A.; Takeda, N.; Fukumitsu, K.; Fukuda, S.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Uemura, T.; Tajiri, T.; Maeno, K.; et al. Decreased peak expiratory flow rate associated with mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A preliminary report. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2022, 19, 14799731221114153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, F.; Tasaka, S.; Inoue, K.-I.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakano, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Yamada, W.; Shiraishi, Y.; Hasegawa, N.; Fujishima, S.; et al. Role of interleukin-6 in bleomycin-induced lung inflammatory changes in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, R.J.J.; Knight, D.A.; Richards, C.D.; Prêle, C.M.; Lau, H.L.; Jarnicki, A.G.; Jones, J.; Bozinovski, S.; Vlahos, R.; Thiem, S.; et al. Genetic partitioning of interleukin-6 signalling in mice dissociates Stat3 from Smad3-mediated lung fibrosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.S.; Madala, S.K.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Gochuico, B.R.; Rosas, I.O.; Cheever, A.W.; Wynn, T.A. Bleomycin and IL-1betamediated pulmonary fibrosis is IL-17A dependent. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, N.; Harokopos, V.; Zalevsky, J.; Valavanis, C.; Kotanidou, A.; Szymkowski, D.E.; Kollias, G.; Aidinis, V. Soluble TNF mediates the transition from pulmonary inflammation to fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Margetts, P.J.; Anthony, D.C.; Pitossi, F.; Gauldie, J. Transient expression of IL-1beta induces acute lung injury and chronic repair leading to pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klech, H. Clinical guidelines and indications for bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): Report of the European society of pneumology task group on BAL. Eur. Resp. J. 1990, 3, 937–974. [Google Scholar]
- Heukels, P.; Moor, C.C.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Kool, M. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir. Med. 2019, 147, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.D. M1 and M2 macrophages: Oracles of health and disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Chawla, A.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature 2013, 496, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative Activation of Macrophages: Mechanism and Functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, N.; Wolfson, B.; Zhou, Q. Mechanisms of the alternative activation of macrophages and non-coding RNAs in the devel-opment of radiation-induced lung fibrosis. World J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 7, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futosi, K.; Fodor, S.; Mocsai, A. Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways. Int. Immunopharm. 2013, 17, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschwandtner, M.; Strutzmann, E.; Teixeira, M.M.; Anders, H.J.; Diedrichs-Möhring, M.; Gerlza, T.; Wildner, G.; Russo, R.C.; Adage, T.; Kungl, A.J. Glycosaminoglycans are important mediators of neutrophilic inflammation in vivo. Cytokine 2017, 91, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashitani, J.I.; Mukae, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Ihi, T.; Kadota, J.I.; Kohno, S.; Matsukura, S. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor levels in bron-choalveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 1999, 54, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Car, B.D.; Meloni, F.; Luisetti, M.; Semenzato, G.; Gialdroni-Grassi, G.; Walz, A. Elevated IL-8 and MCP-1 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, J.; Henket, M.; Corhay, J.L.; Moermans, C.; Louis, R. Sputum biomarkers in IPF: Evidence for raised gene expression and protein level of IGFBP-2, IL-8 and MMP-7. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Gong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Short courses of low dose dexamethasone delay bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 536, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, R.-H.; Gitter, W.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Mathiak, M.; Both, M.; Bolte, H.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bewig, B. Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. BioTechniques 2008, 44, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palikova, Y.A.; Palikov, V.A.; Novikova, N.I.; Slashcheva, G.A.; Rasskazova, E.A.; Tukhovskaya, E.A.; Danilkovich, A.V.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Belogurov, A.A., Jr.; Kudriaeva, A.A.; et al. Derinat® has an immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effect on the model of acute lung injury in male SD rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1111340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Rudenko, P.A.; Kazakov, V.A.; Borozdina, N.A.; Kravchenko, I.N.; Pakhomova, I.A.; Kazakova, E.N.; Slashcheva, G.A.; Semushina, S.G.; et al. Modeling of Chronic Lung Inflammation in Rats by Repeated In-tratracheal Administration of LPS. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 173, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.F.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Pelosi, P. Role of the extracellular matrix in the genesis of ventilator-induced lung injury. Med. Klin. Intensiv. Notfallmedizin 2017, 113, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.L.; Negrini, D.; Rocco, P.R.M. Mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury in healthy lungs. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 29, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group Number | Group Description | BLM Dose | Drug | Number of Animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SHAM | 0 | Vehicle | 5 |
| 2 | BLM | 3 mg/kg | Vehicle | 5 |
| 3 | BLM | 3 mg/kg | Test article | 5 |
| 4 | BLM | 3 mg/kg | Comparison article | 5 |
| #№ | BLM Salt (Hydrochloride or Sulfate) | BLM Form (Reagent or Pharmaceutical) | Manufacturer | Type of Animal (Mice or Rat), Dose | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMACEUTICAL Co., Ltd. Bleomycin chloride | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [10] |
| 2 | Sulfate | Reagent | 630-107-M010, Enzo Life Sciences, USA | Rats, 2.5 mg/kg | [16] |
| 3 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [17] |
| 4 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [18] |
| 5 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Zhejiang Hai Zheng Pharmaceuticals | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [19] |
| 6 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). | Rats, 3 mg/kg | [9] |
| 7 | Sulfate | Reagent | Merck, Darmstadt, Germany | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [20] |
| 8 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Cell Pharm GmbH (Bad Vilbel, Germany) | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [21] |
| 9 | Sulfate | Reagent | Sigma, USA | Rats, 2 mg/kg | [22] |
| 10 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Bleocip 15IU, Cipla Pharmaceutical Company, Mumbai, India | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [7] |
| 11 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Zhejiang Hai Zheng Pharmaceuticals | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [6] |
| 12 | Sulfate | Reagent | Sigma chemical company, USA | Mice | [23] |
| 13 | Sulfate | Pharmaceutical drug | SICOR Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Irvine, CA or TEVA | Mice, 0.8 mg/kg | [24] |
| 14 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan, H20090885 | Mice, 2 mg/kg | [25] |
| 15 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Hanhui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China | Mice, 3 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg | [8] |
| 16 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Baxter Healthcare GmbH, 1020 Wien | Mice, 0.3 mg/kg | [26] |
| 17 | Sulfate | Pharmaceutical drug | Hospira, Melbourne, VIC, Australia | Mice, 1 mg/kg | [27] |
| 18 | Sulfate | Reagent | B1141000, Sigma-Aldrich Inc. | Mice, 4 mg/kg | [28] |
| 19 | Sulfate | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich Inc. | Mice 2 mg/kg | [29] |
| 20 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan, H20090885 | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [30] |
| 21 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan, H20090885 | Mice, 2 mg/kg | [31] |
| 22 | Sulfate | Pharmaceutical drug | Hisun-Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, Shanghai, China | Mice, 5мг | [32] |
| 23 | Sulfate | Not indicated | Not indicated | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [33] |
| 24 | Sulfate | Not indicated | Not indicated | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [34] |
| 25 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan, H20090885 | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [35] |
| 26 | Sulfate | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich Inc. | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [36] |
| 27 | Hydrochloride | Reagent | MedChemExpress, HY-17565A | Mice, 5 mg/kg | [37] |
| 28 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Baxter Healthcare GmbH, 1020 Wien | Mice, 1.25 mg/kg | [38] |
| 29 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan, H20090885 | Mice, 4 mg/kg | [39] |
| 30 | Sulfate | Reagent | Selleck, Shanghai, China | Mice, 5 mg/kg | [40] |
| 31 | Sulfate | Reagent | MedChemExpress, New Jersey, USA | Mice, 1.5 mg/kg | [41] |
| 32 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan | Mice, 1.7 mg/kg | [42] |
| 33 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Baxter Healthcare GmbH, 1020 Wien | Mice, 1 mg/kg | [43] |
| 34 | Sulfate | Reagent | Merck, Darmstadt, Germany | Mice, 1.5 mg/kg | [44] |
| 35 | Sulfate | Reagent | GlpBio Technology Inc. (Montclair, CA, USA) | Mice, 3 mg/kg | [45] |
| 36 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Hanhui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [46] |
| 37 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Hanhui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China) | Rats, 10 mg/kg | [47] |
| 38 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku, Japan | Rats, 8 mg/kg | [48] |
| 39 | Sulfate | Pharmaceutical drug | Zydus Hospira Oncology Private Ltd., Gujarat, India | Rats, 1.5 mg/kg, 2 mg/kg, 2.5 mg/kg | [49] |
| 40 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., Japan; Batch No. 440392; Import Drug Registration Certification No. H20090885 | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [50] |
| 41 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Hanhui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., batch number 20067411 | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [51] |
| 42 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Taizhou, Zhejiang, China). | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [52] |
| 43 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd., Japan | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [53] |
| 44 | Sulfate | Reagent | MCE, Dallas, TX, USA | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [54] |
| 45 | Sulfate | Not indicated | Not indicated | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [55] |
| 46 | Sulfate | Pharmaceutical drug | Cipla Pharmaceuticals, Mumbai, India) | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [56] |
| 47 | Sulfate | Reagent | Apollo Scientific Stockport, Cheshire, UK | Rats, 1 mg/kg | [57] |
| 48 | Sulfate | Pharmaceutical drug | Sanofi | Rats, 7.5 mg/kg | [58] |
| 49 | Hydrochloride | Pharmaceutical drug | Hisun Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Zhejiang, China, State Drug Approval Document Number: H20055883 | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [59] |
| 50 | Sulfate | Reagent | Selleck, S1214 | Rats, 5 mg/kg | [60] |
| Parameter | Control N = 5 | BLM Sulfate N = 5 | BLM Chloride N = 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total cell concentration ×105/mL | 2.57 ± 1.17 | 14.5 ± 5.29 ** | 4.65 ± 2.28 ## |
| Alveolar macrophages, % | 98.1 ± 1.1 | 90.6 ± 2.6 ** | 92.6 ± 1.4 ** |
| Alveolar macrophages, ×105/mL | 2.53 ± 1.17 | 13.25 ± 5.15 ** | 4.31 ± 2.11 ## |
| Band neutrophils, % | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.01 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Band neutrophils, ×105/mL | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.018 ± 0.028 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Segmented neutrophils, % | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 4.1 ± 1.8 ** | 2.7 ± 0.9 **## |
| Segmented neutrophils, ×105/mL | 0.005 ± 0.006 | 0.532 ± 0.151 ** | 0.117 ± 0.056 ** |
| Eosinophils, % | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.2 |
| Eosinophils, ×105/mL | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.05 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Lymphocytes,% | 1.7 ± 1.2 | 4.9 ± 1.6 * | 4.6 ± 1.2 * |
| Lymphocytes, ×105/mL | 0.037 ± 0.025 | 0.663 ± 0.175 ** | 0.220 ± 0.138 *## |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tukhovskaya, E.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Severyukhina, M.S.; Ismailova, A.M.; Palikov, V.A.; Slashcheva, G.A.; Borozdina, N.A.; Mikhaylov, E.S.; Kravchenko, I.N.; Kazakov, V.A.; et al. Comparison of the Results of Modeling Pulmonary Fibrosis in Sprague Dawley Rats by Intratracheal Administration of Bleomycin in the Form of Sulfate and Chloride at a Dose of 3 mg/kg. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101360
Tukhovskaya EA, Palikova YA, Severyukhina MS, Ismailova AM, Palikov VA, Slashcheva GA, Borozdina NA, Mikhaylov ES, Kravchenko IN, Kazakov VA, et al. Comparison of the Results of Modeling Pulmonary Fibrosis in Sprague Dawley Rats by Intratracheal Administration of Bleomycin in the Form of Sulfate and Chloride at a Dose of 3 mg/kg. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101360
Chicago/Turabian StyleTukhovskaya, Elena A., Yulia A. Palikova, Mariya S. Severyukhina, Alina M. Ismailova, Victor A. Palikov, Gulsara A. Slashcheva, Natalya A. Borozdina, Evgeniy S. Mikhaylov, Irina N. Kravchenko, Vitaly A. Kazakov, and et al. 2024. "Comparison of the Results of Modeling Pulmonary Fibrosis in Sprague Dawley Rats by Intratracheal Administration of Bleomycin in the Form of Sulfate and Chloride at a Dose of 3 mg/kg" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101360
APA StyleTukhovskaya, E. A., Palikova, Y. A., Severyukhina, M. S., Ismailova, A. M., Palikov, V. A., Slashcheva, G. A., Borozdina, N. A., Mikhaylov, E. S., Kravchenko, I. N., Kazakov, V. A., Kazakova, E. N., Kalabina, E. A., Rasskazova, E. A., Shinelev, M. V., Rzhevsky, D. I., Rykov, V. A., Dyachenko, I. A., & Murashev, A. N. (2024). Comparison of the Results of Modeling Pulmonary Fibrosis in Sprague Dawley Rats by Intratracheal Administration of Bleomycin in the Form of Sulfate and Chloride at a Dose of 3 mg/kg. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101360






