View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
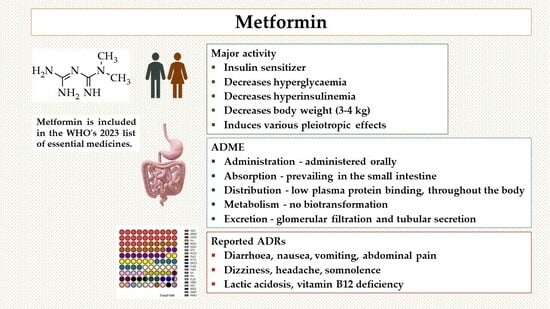
2.1. Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacological Targets
2.2. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME)
2.3. Metformin and Vascular Diseases
2.4. Metformin and Brain
2.5. Metformin and Cancer
2.6. Metformin and COVID-19
2.7. Metformin and Weight Control
2.8. Metformin and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
2.9. Metformin and Thyroid Disorders
2.10. Adverse Drug Reactions: The Benefit/Risk Ratio
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bailey, C.J.; Day, C. Metformin: Its Botanical Background. Pract. Diabetes Int. 2004, 21, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J. Metformin: Historical Overview. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werne, E.A.; Bell, J. The Preparation of Methylguanidine, and of Ββ-Dimethylguanidine by the Interaction of Dicyanodiamide, and Methylammonium and Dimethylammonium Chlorides Respectively. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1922, 121, 1790–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curd, F.H.S.; Davey, D.G.; Rose, F.L. Studies on Synthetic Antimalarial Drugs; Some Biguanide Derivatives as New Types of Antimalarial Substances with Both Therapeutic and Causal Prophylactic Activity. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1945, 39, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, E.Y. Flumamine, a New Synthetic Analgesic and Anti-Flu Drug. J. Philipp. Med. Assoc. 1950, 26, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J. Biguanides and NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1992, 15, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.N.; Hirsch, I.B. Diabetes and the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Essential Medicines, Health Product Policy and Standards, Medicines Selection, IP and Affordability. In WHO—Model List of Essential Medicines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; p. 47. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2021.02 (accessed on 18 February 2024).
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of Intensive Blood-Glucose Control with Metformin on Complications in Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998, 352, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Simpson, S.H.; Toth, E.L.; Majumdar, S.R. Reduced Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality Associated with Metformin Use in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A.W. 10-Year Follow-up of Intensive Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.R.; Molyneaux, L.M.; Constantino, M.I.; Twigg, S.M.; Yue, D.K. Long-Term Efficacy of Metformin Therapy in Nonobese Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2361–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, J.A.; Farmer, A.J.; Ali, R.; Roberts, N.W.; Stevens, R.J. Quantifying the Effect of Metformin Treatment and Dose on Glycemic Control. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, T.; De Block, C.; Schwartzbard, A.Z.; Newman, J.D. Diabetic Agents, From Metformin to SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP1 Receptor Agonists. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1956–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.; Retzik-Stahr, C.; Singh, V.; Plomondon, R.; Anderson, V.; Rasouli, N. Should Metformin Remain the First-Line Therapy for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes? Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 204201882098022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S140–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, K.Y.; Moon, M.K.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Yun, J.-S.; Baek, J.H.; Noh, J.; Lee, B.-W.; Oh, T.J.; et al. 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, N.; Federici, M.; Schütt, K.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Ajjan, R.A.; Antunes, M.J.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Crawford, C.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Eliasson, B.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 4043–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S158–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Das, S.R.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S179–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, S.; Ehrmann, D.A. Metformin Therapy for the Reproductive and Metabolic Consequences of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, B.; Lerman, A.; Lalia, A.Z.; Lerman, L.O.; Chang, A.Y. Effect of Metformin on Microvascular Endothelial Function in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. VigiBase: WHO’s Global Database Signalling Harm and Pointing to Safer Use; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- EudraVigilance. European Database of Suspected Adverse Drug Reaction Reports; EudraVigilance: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The Mechanisms of Action of Metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundal, R.S.; Inzucchi, S.E. Metformin: New Understandings, New Uses. Drugs 2003, 63, 1879–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMoia, T.E.; Shulman, G.I. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin Action. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiernsperger, N.F.; Bailey, C.J. The Antihyperglycaemic Effect of Metformin: Therapeutic and Cellular Mechanisms. Drugs 1999, 58, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z. Effect of Metformin on All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Coronary Artery Diseases: A Systematic Review and an Updated Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, G.; Fang, D.; Gao, X.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Zeng, M.; Luo, M. The Role of MicroRNA Networks in Tissue-Specific Direct and Indirect Effects of Metformin and Its Application. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Shan, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, Q.; Weng, J.; Jia, W.; et al. Gender-Differential Effects on Blood Glucose Levels between Acarbose and Metformin in Chinese Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Sub-Analysis of the MARCH Trial. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N. Effects of Metformin on Blood Glucose Levels and Bodyweight Mediated through Intestinal Effects. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 1420–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, V.; Benedetti, F.; Buriani, A.; Fortinguerra, S.; Caudullo, G.; Davinelli, S.; Zella, D.; Scapagnini, G. Immunomodulatory and Antiaging Mechanisms of Resveratrol, Rapamycin, and Metformin: Focus on mTOR and AMPK Signaling Networks. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Metformin: Update on Mechanisms of Action and Repurposing Potential. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Tian, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Tong, N.; Liao, J.; Ren, Y. Effects of Acarbose and Metformin on the Inflammatory State in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A One-Year Randomized Clinical Study. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Patnana, P.K.; Nimmagadda, S.C. Low-Dose Metformin and PEN2-Dependent Lysosomal AMPK Activation: Benefits Outnumber Side Effects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Tian, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Qu, Q.; Yu, Y.; et al. Low-Dose Metformin Targets the Lysosomal AMPK Pathway through PEN2. Nature 2022, 603, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Ares, I.; Lopez-Torres, B.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Wang, X.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.-A. Mitochondria as an Important Target of Metformin: The Mechanism of Action, Toxic and Side Effects, and New Therapeutic Applications. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agius, L.; Ford, B.E.; Chachra, S.S. The Metformin Mechanism on Gluconeogenesis and AMPK Activation: The Metabolite Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Myers, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Fenyk-Melody, J.; Wu, M.; Ventre, J.; Doebber, T.; Fujii, N.; et al. Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Mechanism of Metformin Action. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmirczak, F.; Hartweck, L.M.; Vogel, N.T.; Mendelson, J.B.; Park, A.K.; Raveendran, R.M.; O-Uchi, J.; Jhun, B.S.; Prisco, S.Z.; Prins, K.W. Intermittent Fasting Activates AMP-Kinase to Restructure Right Ventricular Lipid Metabolism and Microtubules. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2023, 8, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, H.J.; Yao, P.; Huynh, F.K.; Escoubas, C.C.; Goncalves, R.L.; Burkewitz, K.; Laboy, R.; Hirschey, M.D.; Mair, W.B. Dietary Restriction and AMPK Increase Lifespan via Mitochondrial Network and Peroxisome Remodeling. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 884–896.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Partridge, L. Promoting Health and Longevity through Diet: From Model Organisms to Humans. Cell 2015, 161, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebokova, E.; Klimes, I.; Moss, R.; Mitkova, A.; Wiersma, M.; Bohov, P. Decreased Glucose Transporter Protein (GLUT4) in Skeletal Muscle of Hypertriglyceridaemic Insulin-Resistant Rat. Physiol. Res. 1995, 44, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Houseknecht, K.L.; Stenbit, A.E.; Katz, E.B.; Charron, M.J. Reduced Glucose Uptake Precedes Insulin Signaling Defects in Adipocytes from Heterozygous GLUT4 Knockout Mice. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, E.D.; Peroni, O.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.-B.; Boss, O.; Hadro, E.; Minnemann, T.; Shulman, G.I.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose-Selective Targeting of the GLUT4 Gene Impairs Insulin Action in Muscle and Liver. Nature 2001, 409, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leguisamo, N.M.; Lehnen, A.M.; Machado, U.F.; Okamoto, M.M.; Markoski, M.M.; Pinto, G.H.; Schaan, B.D. GLUT4 Content Decreases along with Insulin Resistance and High Levels of Inflammatory Markers in Rats with Metabolic Syndrome. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, B.J.; Griesel, B.A.; King, C.D.; Josey, M.A.; Olson, A.L. Moderate GLUT4 Overexpression Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Fasting Triglyceridemia in High-Fat Diet–Fed Transgenic Mice. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Maianu, L.; Huecksteadt, T.P.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Molina, J.M.; Ciaraldi, T.P. Pretranslational Suppression of a Glucose Transporter Protein Causes Insulin Resistance in Adipocytes from Patients with Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doehner, W.; Gathercole, D.; Cicoira, M.; Krack, A.; Coats, A.J.S.; Camici, P.G.; Anker, S.D. Reduced Glucose Transporter GLUT4 in Skeletal Muscle Predicts Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetic Chronic Heart Failure Patients Independently of Body Composition. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 138, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, R.; Kravos, N.A.; Jensterle, M.; Janež, A.; Dolžan, V. Metformin and Insulin Resistance: A Review of the Underlying Mechanisms behind Changes in GLUT4-Mediated Glucose Transport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadt, A.; Al-Hasani, H. Glucose Transporters in Adipose Tissue, Liver, and Skeletal Muscle in Metabolic Health and Disease. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2020, 472, 1273–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahne, E.; Sun, E.W.L.; Young, R.L.; Hansen, M.; Sonne, D.P.; Hansen, J.S.; Rohde, U.; Liou, A.P.; Jackson, M.L.; De Fontgalland, D.; et al. Metformin-Induced Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion Contributes to the Actions of Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e93936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannucci, E.; Ognibene, A.; Cremasco, F.; Bardini, G.; Mencucci, A.; Pierazzuoli, E.; Ciani, S.; Messeri, G.; Rotella, C.M. Effect of Metformin on Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) and Leptin Levels in Obese Nondiabetic Subjects. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melson, E.; Ashraf, U.; Papamargaritis, D.; Davies, M.J. What Is the Pipeline for Future Medications for Obesity? Int. J. Obes. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.D.; Irwin, N.; Duffy, N.A.; Gault, V.A.; O’Harte, F.P.M.; Flatt, P.R. Inhibition of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Activity by Metformin Enhances the Antidiabetic Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 547, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Hang, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, F.; Ding, Y.; Li, M.; Nie, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhuo, Y.; et al. Microbial-Host-Isozyme Analyses Reveal Microbial DPP4 as a Potential Antidiabetic Target. Science 2023, 381, eadd5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryrup, T.; Thomsen, C.W.; Kern, T.; Allin, K.H.; Brandslund, I.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Vestergaard, H.; Hansen, T.; Hansen, T.H.; Pedersen, O.; et al. Metformin-Induced Changes of the Gut Microbiota in Healthy Young Men: Results of a Non-Blinded, One-Armed Intervention Study. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, A.H.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Yu, K.-S.; Jang, I.-J.; Chung, J.-Y.; Cho, J.-Y. Changes in the Gut Microbiome Influence the Hypoglycemic Effect of Metformin through the Altered Metabolism of Branched-Chain and Nonessential Amino Acids. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 178, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Esteve, E.; Tremaroli, V.; Khan, M.T.; Caesar, R.; Mannerås-Holm, L.; Ståhlman, M.; Olsson, L.M.; Serino, M.; Planas-Fèlix, M.; et al. Metformin Alters the Gut Microbiome of Individuals with Treatment-Naive Type 2 Diabetes, Contributing to the Therapeutic Effects of the Drug. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, A.; Miller, S.; Nicholls, A.W.; Baker, D.; Van Horn, S.; Thomas, E.; Rajpal, D.; Spivak, A.; Brown, J.R.; Nunez, D.J. Novel Gut-Based Pharmacology of Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Nielsen, T.; Falony, G.; Le Chatelier, E.; Sunagawa, S.; Prifti, E.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Krogh Pedersen, H.; et al. Disentangling Type 2 Diabetes and Metformin Treatment Signatures in the Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craciun, C.-I.; Neag, M.-A.; Catinean, A.; Mitre, A.-O.; Rusu, A.; Bala, C.; Roman, G.; Buzoianu, A.-D.; Muntean, D.-M.; Craciun, A.-E. The Relationships between Gut Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus, and Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Dingli, D. Metformin Inhibits IL-6 Signaling by Decreasing IL-6R Expression on Multiple Myeloma Cells. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.; El-Mahdy, H.A.; Eldeib, M.G.; Doghish, A.S. miRNAs as Cornerstones in Diabetic Microvascular Complications. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 138, 106978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Xing, W.; Xie, L. Regulatory Roles of MicroRNAs in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, H.-Y.; Lee, T.-P.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, L.-S.; Li, W.-C. Circulating microRNA as a Diagnostic Marker in Populations with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Complications. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pordzik, J.; Jakubik, D.; Jarosz-Popek, J.; Wicik, Z.; Eyileten, C.; De Rosa, S.; Indolfi, C.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Czajka, P.; Postula, M. Significance of Circulating microRNAs in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Platelet Reactivity: Bioinformatic Analysis and Review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirsoy, İ.H.; Ertural, D.Y.; Balci, Ş.; Çınkır, Ü.; Sezer, K.; Tamer, L.; Aras, N. Profiles of Circulating miRNAs Following Metformin Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Med. Biochem. 2018, 37, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noren Hooten, N.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Dluzen, D.F.; Zhang, Y.; Bernier, M.; Zonderman, A.B.; Becker, K.G.; Gorospe, M.; Cabo, R.; Evans, M.K. Metformin-mediated Increase in DICER1 Regulates microRNA Expression and Cellular Senescence. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgeman, S.C.; Ellison, G.C.; Melton, P.E.; Newsholme, P.; Mamotte, C.D.S. Epigenetic Effects of Metformin: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wan, J.; Shan, Y.; Song, X.; Jin, J.; Su, Q.; Chen, S.; Lu, X.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; et al. MicroRNA-185-5p Inhibits Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Reduces Fasting Blood Glucose Levels by Suppressing G6Pase. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7829–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, P.J. The Effects of High- and Medium-Dose Metformin Therapy on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type II Diabetes. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, A.J.; Duncan, T.G.; Goodman, A.M.; Mills, D.J.; Rohlf, J.L. Efficacy of Metformin in Type II Diabetes: Results of a Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Response Trial. Am. J. Med. 1997, 103, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, Y.; Kazumori, K.; Takeshima, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Tanaka, Y. Effects of Increasing Metformin Dose vs Adding/Switching to Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, I.; Rizzo, M.; Zabuliene, L. Metformin: Sex/Gender Differences in Its Uses and Effects—Narrative Review. Medicina 2022, 58, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M.; Buse, J.B.; Davidson, M.B.; Ferrannini, E.; Holman, R.R.; Sherwin, R.; Zinman, B. Medical Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Consensus Algorithm for the Initiation and Adjustment of Therapy. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarry-Adkins, J.L.; Grant, I.D.; Ozanne, S.E.; Reynolds, R.M.; Aiken, C.E. Efficacy and Side Effect Profile of Different Formulations of Metformin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Fonseca, V. Overview of Metformin: Special Focus on Metformin Extended Release. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonde, L.; Dailey, G.E.; Jabbour, S.A.; Reasner, C.A.; Mills, D.J. Gastrointestinal Tolerability of Extended-Release Metformin Tablets Compared to Immediate-Release Metformin Tablets: Results of a Retrospective Cohort Study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, P.; Li, S. Long-Acting Metformin Vs. Metformin Immediate Release in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 669814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, G.G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R.O.; Doogue, M.P.; Duong, J.K.; Furlong, T.J.; Greenfield, J.R.; Greenup, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Giacomini, K.M. Transporters Involved in Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Treatment Response. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1996, 30, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, G.; Casey, C.; Phillips, P.; Connor, H.; Ward, J.; Woods, H. Metformin Kinetics in Healthy Subjects and in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 12, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From Mechanisms of Action to Therapies. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.M.H.; Brasch-Andersen, C.; Green, H.; Nielsen, F.; Damkier, P.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Brosen, K. The Pharmacogenetics of Metformin and Its Impact on Plasma Metformin Steady-State Levels and Glycosylated Hemoglobin A1c. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2011, 21, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz-Rodríguez, M.; Ochoa, D.; Zubiaur, P.; Navares-Gómez, M.; Román, M.; Camargo-Mamani, P.; Luquero-Bueno, S.; Villapalos-García, G.; Alcaraz, R.; Mejía-Abril, G.; et al. Identification of Transporter Polymorphisms Influencing Metformin Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymczak-Pajor, I.; Wenclewska, S.; Śliwińska, A. Metabolic Action of Metformin. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, A.; Gong, C.; Xu, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, X.; Hong, W.; Yan, J. Association between Organic Cation Transporter Genetic Polymorphisms and Metformin Response and Intolerance in T2DM Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1183879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, R.; Maccourtney, D.; Vashi, M.; Mohamed, A. A Case of Metformin-Associated Lactic Acidosis. Cureus 2023, 15, e38222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Guan, Z.; Li, R.; Zhao, W.; Hao, G.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liao, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetics and Dosing Optimization of Metformin in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Medicine 2020, 99, e23212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalau, J.-D.; Lacroix, C. Measurement of Metformin Concentration in Erythrocytes:Clinical Implications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2003, 5, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.; Chung, H.; Yoon, J.; Moon, S.; Yoon, S.H.; Yu, K.; Kim, K.; Chung, J. Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Metformin in Healthy Elderly Subjects. J. Clin. Pharma 2016, 56, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.-L.; Liu, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.-H. Effects of Food on Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Metformin Hydrochloride Tablets: A Meta-Analysis of Pharmacokinetic, Bioavailability, or Bioequivalence Studies. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalau, J.-D.; Lemaire-Hurtel, A.-S.; Lacroix, C. Establishment of a Database of Metformin Plasma Concentrations and Erythrocyte Levels in Normal and Emergency Situations. Clin. Drug Investig. 2011, 31, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Shah, R.B.; Singhal, S.; Dutta, S.B.; Bansal, S.; Sinha, S.; Haque, M. Metformin: A Review of Potential Mechanism and Therapeutic Utility Beyond Diabetes. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2023, 17, 1907–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambol, N.C.; Brookes, L.G.; Chiang, J.; Goodman, A.M.; Lin, E.T.; Liu, C.Y.; Benet, L.Z. Food Intake and Dosage Level, but Not Tablet vs Solution Dosage Form, Affect the Absorption of Metformin HC1 in Man. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 42, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Bianchi, C.; Burlina, S.; Formoso, G.; Manicardi, E.; Sculli, M.A.; Resi, V. Position Paper of the Italian Association of Medical Diabetologists (AMD), Italian Society of Diabetology (SID), and the Italian Study Group of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Metformin Use in Pregnancy. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 1421–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orloff, J.; Min, J.Y.; Mushlin, A.; Flory, J. Safety and Effectiveness of Metformin in Patients with Reduced Renal Function: A Systematic Review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Gao, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, K.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Diabetic Vascular Diseases: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadivelu, R.; Vijayvergiya, R. Panvascular Risk Factor—Diabetes. Cor Vasa 2018, 60, e18–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, W.T. Diabetes-Related Microvascular and Macrovascular Diseases in the Physical Therapy Setting. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Garcia, E.; McLachlan, S.; Price, A.H.; MacGillivray, T.J.; Strachan, M.W.J.; Wilson, J.F.; Price, J.F. Retinal Arteriolar Tortuosity and Fractal Dimension Are Associated with Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Chawla, R.; Jaggi, S. Microvasular and Macrovascular Complications in Diabetes Mellitus: Distinct or Continuum? Indian J. Endocr. Metab. 2016, 20, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Canto, E.; Ceriello, A.; Rydén, L.; Ferrini, M.; Hansen, T.B.; Schnell, O.; Standl, E.; Beulens, J.W. Diabetes as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor: An Overview of Global Trends of Macro and Micro Vascular Complications. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzewoski, J.; Hanefeld, M. The Current and Potential Therapeutic Use of Metformin—The Good Old Drug. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, S.; Sugawara, K.; Yokoi, N.; Takahashi, H. β-Cell Signalling and Insulin Secretagogues: A Path for Improved Diabetes Therapy. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suades, R.; Cosentino, F.; Badimon, L. Glucose-Lowering Treatment in Cardiovascular and Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 39, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Feng, B.; Ge, J.; Guo, L.; Huo, Y.; Ji, L.; Jia, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. Chinese Expert Consensus on the Risk Assessment and Management of Panvascular Disease Inpatients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (2022 Edition). Cardiol. Plus 2022, 7, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Aprea, C.; Albanese, G.; Di Martino, A.; Ricozzi, C.; et al. Can Metformin Exert as an Active Drug on Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Subjects? Biomedicines 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ling, P.; Feng, X.; Luo, S.; Zheng, X.; Little, P.J.; Xu, S.; Weng, J. Metformin in Cardiovascular Diabetology: A Focused Review of Its Impact on Endothelial Function. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9376–9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venu, V.K.P.; Saifeddine, M.; Mihara, K.; Faiza, M.; Gorobets, E.; Flewelling, A.J.; Derksen, D.J.; Hirota, S.A.; Marei, I.; Al-Majid, D.; et al. Metformin Prevents Hyperglycemia-Associated, Oxidative Stress-Induced Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction: Essential Role for the Orphan Nuclear Receptor Human Nuclear Receptor 4A1 (Nur77). Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 100, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggle, C.R.; Marei, I.; Ye, K.; Ding, H.; Anderson, T.J.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Hill, M.A. Repurposing Metformin for Vascular Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 3955–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramoto, J.S.; Katz, R.; Weisman, S.; Conte, M. Gender-Specific Risk Factors for Peripheral Artery Disease in a Voluntary Screening Population. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, W.B.; McGee, D.L. Update on Some Epidemiologic Features of Intermittent Claudication: The Framingham Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1985, 33, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, K.; Rochon, P. Gender Differences in Peripheral Vascular Disease. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 35, 009–016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresierra-Ayala, M.Á.; García Rojas, A. Association between Peripheral Arterial Disease and Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Med. Univ. 2017, 19, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvoipati, T. Peripheral Artery Disease in Patients with Diabetes: Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Outcomes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Armstrong, E.J.; Sherif, W.; Alvandi, B.; Westin, G.G.; Singh, G.D.; Amsterdam, E.A.; Laird, J.R. Association of Elevated Fasting Glucose with Lower Patency and Increased Major Adverse Limb Events among Patients with Diabetes Undergoing Infrapopliteal Balloon Angioplasty. Vasc. Med. 2014, 19, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowkes, F.G.R.; Rudan, D.; Rudan, I.; Aboyans, V.; Denenberg, J.O.; McDermott, M.M.; Norman, P.E.; Sampson, U.K.; Williams, L.J.; Mensah, G.A.; et al. Comparison of Global Estimates of Prevalence and Risk Factors for Peripheral Artery Disease in 2000 and 2010: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballotari, P.; Ranieri, S.C.; Luberto, F.; Caroli, S.; Greci, M.; Giorgi Rossi, P.; Manicardi, V. Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Mortality in Diabetics and Nondiabetic Subjects: A Population-Based Study (Italy). Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 914057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, E.W.; Gu, Q.; Cheng, Y.J.; Venkat Narayan, K.M.; Cowie, C.C. Mortality Trends in Men and Women with Diabetes, 1971 to 2000. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 147, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.Z.; Rivero, M.; Nader, N.D.; Cherr, G.S.; Harris, L.M.; Dryjski, M.L.; Dosluoglu, H.H. Metformin Is Associated with Improved Survival and Decreased Cardiac Events with No Impact on Patency and Limb Salvage after Revascularization for Peripheral Arterial Disease. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 55, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Goudot, G.; Arnoux, A.; Tran, Y.; Maissoro, H.; Poenou, G.; Detriche, G.; Khider, L.; Mohamedi, N.; Mirault, T.; et al. Occurrence of Major Local Lower Limb Events in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Lower Extremity Arterial Disease: Impact of Metformin. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 90, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, K.M.; Althouse, A.D.; Forman, D.E.; Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Vodovotz, Y.; Zamora, R.; Raffai, R.L.; Hall, D.E.; Tzeng, E. MetfOrmin BenefIts Lower Extremities with Intermittent Claudication (MOBILE IC): Randomized Clinical Trial Protocol. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2023, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, A.M.; Mechanic-Hamilton, D.; Xie, S.X.; Combs, M.F.; Cappola, A.R.; Xie, L.; Detre, J.A.; Wolk, D.A.; Arnold, S.E. Effects of the Insulin Sensitizer Metformin in Alzheimer Disease: Pilot Data from a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2017, 31, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, Y.N.; Angelopoulou, E.; Piperi, C.; Shaikh, M.F.; Othman, I. Emerging Neuroprotective Effect of Metformin in Parkinson’s Disease: A Molecular Crosstalk. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Yue, H.; Ma, S.; Guan, F. Aging and Age-related Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Biogerontology 2021, 22, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.A.B.; Livingston, J.; Garcia-Flores, E.; Kehtari, T.; Morshead, C.M. Metformin Improves Functional Outcomes, Activates Neural Precursor Cells, and Modulates Microglia in a Sex-Dependent Manner After Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2023, 12, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatt, M.; Hsu, K.; He, L.; Wondisford, F.; Miller, F.D.; Kaplan, D.R.; Wang, J. Metformin Acts on Two Different Molecular Pathways to Enhance Adult Neural Precursor Proliferation/Self-Renewal and Differentiation. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gallagher, D.; DeVito, L.M.; Cancino, G.I.; Tsui, D.; He, L.; Keller, G.M.; Frankland, P.W.; Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. Metformin Activates an Atypical PKC-CBP Pathway to Promote Neurogenesis and Enhance Spatial Memory Formation. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadwal, P.; Mahmud, N.; Sinai, L.; Azimi, A.; Fatt, M.; Wondisford, F.E.; Miller, F.D.; Morshead, C.M. Activating Endogenous Neural Precursor Cells Using Metformin Leads to Neural Repair and Functional Recovery in a Model of Childhood Brain Injury. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Jiang, F.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gao, R.; Chen, G. Neuroprotective Effects of Metformin on Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats Associated with NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 140, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiBona, V.L.; Shah, M.K.; Krause, K.J.; Zhu, W.; Voglewede, M.M.; Smith, D.M.; Crockett, D.P.; Zhang, H. Metformin Reduces Neuroinflammation and Improves Cognitive Functions after Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 172, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Masuda, T.; Misumi, Y.; Ando, Y.; Ueda, M. Metformin Attenuates Vascular Pathology by Increasing Expression of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme in a Mixed Model of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 762, 136136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.; Chávez-Castillo, M.; Bautista, J.; Ortega, Á.; Nava, M.; Salazar, J.; Díaz-Camargo, E.; Medina, O.; Rojas-Quintero, J.; Bermúdez, V. Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Pathophysiologic and Pharmacotherapeutics Links. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 745–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Leng, S.; Song, D. Link between Type 2 Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Epidemiology to Mechanism and Treatment. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 2015, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito-Cuesta, I.; Ordóñez-Gutiérrez, L.; Wandosell, F. AMPK Activation Does Not Enhance Autophagy in Neurons in Contrast to MTORC1 Inhibition: Different Impact on β-Amyloid Clearance. Autophagy 2021, 17, 656–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.M.; Shin, H.-J.; Byun, J.; Kook, S.Y.; Moon, M.; Chang, Y.J.; Mook-Jung, I. Metformin Facilitates Amyloid-β Generation by β- and γ-Secretases via Autophagy Activation. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Kwak, Y.-D.; Ma, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Zhao, Y.; Smith, L.; Gasparini, L.; et al. Antidiabetic Drug Metformin (Glucophage R) Increases Biogenesis of Alzheimer’s Amyloid Peptides via up-Regulating BACE1 Transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3907–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Juan, M.; Ordóñez-Gutiérrez, L.; Wandosell, F. Clearance of Β-amyloid Mediated by Autophagy Is Enhanced by MTORC1 Inhibition but Not AMPK Activation in APP/PSEN1 Astrocytes. Glia 2024, 72, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.P.; Feng, L.; Yap, K.B.; Lee, T.S.; Tan, C.H.; Winblad, B. Long-Term Metformin Usage and Cognitive Function among Older Adults with Diabetes. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 41, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, R.; Ruddy, R.M.; Cox, E.; Oyefiade, A.; Derkach, D.; Laughlin, S.; Ades-aron, B.; Shirzadi, Z.; Fieremans, E.; MacIntosh, B.J.; et al. Assessment of Cognitive and Neural Recovery in Survivors of Pediatric Brain Tumors in a Pilot Clinical Trial Using Metformin. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, F.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y. Association between Metformin and Neurodegenerative Diseases of Observational Studies: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilidis, K.K.; Kasimis, J.C.; Lopez, D.S.; Ntzani, E.E.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer: Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies. BMJ 2015, 350, g7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Sasazuki, T.; Noda, M. Significantly Increased Risk of Cancer in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Hou, T.; Gu, K.; Yan, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Sheng, C.-S.; et al. Association Between Age at Diabetes Diagnosis and Subsequent Incidence of Cancer: A Longitudinal Population-Based Cohort. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.M.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and Reduced Risk of Cancer in Diabetic Patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, G.; Donnelly, L.A.; Donnan, P.T.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D.; Evans, J.M.M. New Users of Metformin Are at Low Risk of Incident Cancer. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lega, I.C.; Shah, P.S.; Margel, D.; Beyene, J.; Rochon, P.A.; Lipscombe, L.L. The Effect of Metformin on Mortality Following Cancer among Patients with Diabetes. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, Y.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, C.M.; Ko, M.J.; Seo, Y.S.; Moon, S.M.; Choi, J.A. Association between Metformin Use and Survival in Nonmetastatic Rectal Cancer Treated with a Curative Resection: A Nationwide Population Study. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransgaard, T.; Thygesen, L.C.; Gögenur, I. Metformin Increases Overall Survival in Patients with Diabetes Undergoing Surgery for Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.I.; Jeon, S.M.; Hong, S.P.; Cheon, J.H.; Kim, W.H. The Effects of Metformin on the Survival of Colorectal Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Menamin, Ú.C.; Murray, L.J.; Hughes, C.M.; Cardwell, C.R. Metformin Use and Survival after Colorectal Cancer: A Population-based Cohort Study. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransgaard, T.; Thygesen, L.C.; Gögenur, I. Association between Metformin Use after Surgery for Colorectal Cancer and Oncological Outcomes: A Nationwide Register-based Study. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Du, S.; Du, J. Effect of Metformin on the Mortality of Colorectal Cancer Patients with T2DM: Meta-Analysis of Sex Differences. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2020, 35, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Tsai, H.-N.; Chang, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-C. Type 2 Diabetes Increases and Metformin Reduces Total, Colorectal, Liver and Pancreatic Cancer Incidences in Taiwanese: A Representative Population Prospective Cohort Study of 800,000 Individuals. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Tan, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. Association of Metformin Use with Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, L. Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 20075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, T.; Peters, S.A.E.; Woodward, M. Sex Differences in the Association between Diabetes and Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 121 Cohorts Including 20 Million Individuals and One Million Events. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2140–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, C. Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on the Severity and Fatality of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gęca, T.; Wojtowicz, K.; Guzik, P.; Góra, T. Increased Risk of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus—Current Challenges in Pathophysiology, Treatment and Prevention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froldi, G.; Dorigo, P. Endothelial Dysfunction in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Gender and Age Influences. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Highton, P.; Rees, K.; Onakpoya, I.; Suklan, J.; Curtis, F.; O’Mahoney, L.; Morris, E.; Kudlek, L.; Morgan, J.; et al. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Associated Disruptions in Health-Care Provision on Clinical Outcomes in People with Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Griga, V.; Mohammed, I.; Loshak, K.; Poliak, I.; Kamyshnyiy, A. Effects of Metformin, Insulin on Hematological Parameters of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Arch. 2022, 76, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, S.M.; Fenno, S.L.; Barzilai, N.; Kuchel, G.; Bartley, J.M.; Justice, J.N.; Buse, J.B.; Bramante, C.T. Metformin for Treatment of Acute COVID-19: Systematic Review of Clinical Trial Data Against SARS-CoV-2. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, A.B.; Grimes, T.; Li, P.; Might, M.; Ovalle, F.; Shalev, A. Metformin Use Is Associated with Reduced Mortality in a Diverse Population With COVID-19 and Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 600439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukito, A.A.; Pranata, R.; Henrina, J.; Lim, M.A.; Lawrensia, S.; Suastika, K. The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunti, K.; Knighton, P.; Zaccardi, F.; Bakhai, C.; Barron, E.; Holman, N.; Kar, P.; Meace, C.; Sattar, N.; Sharp, S.; et al. Prescription of Glucose-Lowering Therapies and Risk of COVID-19 Mortality in People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Observational Study in England. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramante, C.T.; Ingraham, N.E.; Murray, T.A.; Marmor, S.; Hovertsen, S.; Gronski, J.; McNeil, C.; Feng, R.; Guzman, G.; Abdelwahab, N.; et al. Metformin and Risk of Mortality in Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e34–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; Tan, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Tian, M.; Lu, Z.; et al. Association of Metformin with Mortality or ARDS in Patients with COVID-19 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 173, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Rubino, F.; Khunti, K.; Mingrone, G.; Hopkins, D.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Boehm, B.; Amiel, S.; Holt, R.I.; Skyler, J.S.; et al. Practical Recommendations for the Management of Diabetes in Patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.-M.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Lei, F.; Qin, J.-J.; Chen, Z.; Deng, K.-Q.; Lin, L.; Chen, M.-M.; et al. Metformin Is Associated with Higher Incidence of Acidosis, but Not Mortality, in Individuals with COVID-19 and Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 537–547.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielka, W.; Przezak, A.; Pawlik, A. Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Bae, J.H.; Kwon, H.-S.; Nauck, M.A. COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adapa, S.; Aeddula, N.R.; Konala, V.M.; Chenna, A.; Naramala, S.; Madhira, B.R.; Gayam, V.; Balla, M.; Muppidi, V.; Bose, S. COVID-19 and Renal Failure: Challenges in the Delivery of Renal Replacement Therapy. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 12, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; Sehgal, K.; Nair, N.; Mahajan, S.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Bikdeli, B.; Ahluwalia, N.; Ausiello, J.C.; Wan, E.Y.; et al. Extrapulmonary Manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piché, M.-E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa-Kotara, K.; Dakowska, D. Impact of Obesity on Risk of Cancer. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2021, 29, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bona, M.D.; Torres, C.H.D.M.; Lima, S.C.V.C.; Morais, A.H.D.A.; Lima, A.Â.M.; Maciel, B.L.L. Intestinal Barrier Permeability in Obese Individuals with or without Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, X.; Novák, P.; Gui, Q.; Yin, K. Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Efficiency: A Novel Metabolic Diseases Therapy. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1120168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Khalil, M.; Angelis, M.D.; Calabrese, F.M.; D’Amato, M.; Wang, D.Q.-H.; Di Ciaula, A. Intestinal Barrier and Permeability in Health, Obesity and NAFLD. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, A.; Martínez, I.; Ojeda-Rodríguez, A.; Azcona-Sanjulian, M.C. Higher Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein and Chemerin Concentrations Were Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Features in Pediatric Subjects with Abdominal Obesity during a Lifestyle Intervention. Nutrients 2021, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilves, C.; Yeh, H.-C.; Maruthur, N.; Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J.; Mueller, N.T. A Behavioral Weight-Loss Intervention, but Not Metformin, Decreases a Marker of Gut Barrier Permeability: Results from the SPIRIT Randomized Trial. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentolouris, A.; Vlachakis, P.; Tzeravini, E.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, N. SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Antidiabetic and Cardioprotective Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, D.M.; Ahmed, N.; Tariq, H.; Walgamage, M.; Walgamage, T.; Mohammed, A.; Chou, J.T.-T.; Kałużna-Oleksy, M.; Lesiak, M.; Straburzyńska-Migaj, E. SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure—A Concise Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieg, T.; Vallon, V. Development of SGLT1 and SGLT2 Inhibitors. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez Rieg, J.A.; Xue, J.; Rieg, T. Tubular Effects of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Intended and Unintended Consequences. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Aragón-Herrera, A.; Otero-Santiago, M.; Anido-Varela, L.; Moraña-Fernández, S.; Tarazón, E.; Roselló-Lletí, E.; Portolés, M.; Gualillo, O.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; et al. Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in the Regulation of Inflammatory Processes in Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshizaka, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishibashi, R.; Maezawa, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Uchida, D.; Nakamura, S.; Yamaga, M.; Yokoh, H.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. Comparing the Effects of Ipragliflozin versus Metformin on Visceral Fat Reduction and Metabolic Dysfunction in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Sitagliptin: A Prospective, Multicentre, Open-label, Blinded-endpoint, Randomized Controlled Study (PRIME-V Study). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshizaka, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishibashi, R.; Takahashi, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Yokoh, H.; Baba, Y.; Ide, S.; Ide, K.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Comparison of Visceral Fat Reduction by Ipragliflozin and Metformin in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Sub-Analysis of a Randomized-Controlled Study. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukagoshi-Yamaguchi, A.; Koshizaka, M.; Ishibashi, R.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Shoji, M.; Ide, S.; Ide, K.; Baba, Y.; Terayama, R.; et al. Metabolomic Analysis of Serum Samples from a Clinical Study on Ipragliflozin and Metformin Treatment in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Exploring Human Metabolites Associated with Visceral Fat Reduction. Pharmacotherapy 2023, 43, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.M.; Stogios, N.; Ahsan, Z.A.; Lockwood, J.T.; Duncan, M.J.; Takeuchi, H.; Cohn, T.; Taylor, V.H.; Remington, G.; Faulkner, G.E.J.; et al. Pharmacological Interventions for Prevention of Weight Gain in People with Schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, CD013337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, R.; Narwal, V.; Dang, A.; Pundir, C. The Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Brief Systematic Review. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Metformin: Current Knowledge. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozdag, G.; Mumusoglu, S.; Zengin, D.; Karabulut, E.; Yildiz, B.O. The Prevalence and Phenotypic Features of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 2841–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, W.; Wattick, R.; Kinkade, O.; Olfert, M. Geographical Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome as Determined by Region and Race/Ethnicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teede, H.J.; Misso, M.L.; Costello, M.F.; Dokras, A.; Laven, J.; Moran, L.; Piltonen, T.; Norman, R.J.; Andersen, M.; Azziz, R.; et al. Recommendations from the International Evidence-Based Guideline for the Assessment and Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2018, 110, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.M.; Franks, S. Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021, 95, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.M.; Hanson, P.; Weickert, M.O.; Franks, S. Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Implications for Pathogenesis and Novel Management Strategies. Clin. Med. Insights Reprod. Health 2019, 13, 117955811987404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.; Feng, H.; Duan, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lan, Y.; Yue, R. Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 980405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xing, C.; Cheng, X.; He, B. Canagliflozin Combined with Metformin versus Metformin Monotherapy for Endocrine and Metabolic Profiles in Overweight and Obese Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Single-Center, Open-Labeled Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1003238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; He, B. Effect of Metformin versus Metformin plus Liraglutide on Gonadal and Metabolic Profiles in Overweight Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 945609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greff, D.; Juhász, A.E.; Váncsa, S.; Váradi, A.; Sipos, Z.; Szinte, J.; Park, S.; Hegyi, P.; Nyirády, P.; Ács, N.; et al. Inositol Is an Effective and Safe Treatment in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2023, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Xing, C.; He, B. Short Period-Administration of Myo-Inositol and Metformin on Hormonal and Glycolipid Profiles in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 1792–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melin, J.; Forslund, M.; Alesi, S.; Piltonen, T.; Romualdi, D.; Spritzer, P.M.; Tay, C.T.; Pena, A.; Witchel, S.F.; Mousa, A.; et al. Metformin and Combined Oral Contraceptive Pills in the Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e817–e836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joham, A.E.; Norman, R.J.; Stener-Victorin, E.; Legro, R.S.; Franks, S.; Moran, L.J.; Boyle, J.; Teede, H.J. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtmauer, L.A. Should Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Be Treated with Metformin?: Benefits of Insulin Sensitizing Drugs in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome—Beyond Ovulation Induction. Hum. Reprod. 2002, 17, 3016–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legro, R.S.; Arslanian, S.A.; Ehrmann, D.A.; Hoeger, K.M.; Murad, M.H.; Pasquali, R.; Welt, C.K. Diagnosis and Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4565–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udesen, P.B.; Glintborg, D.; Sørensen, A.E.; Svendsen, R.; Nielsen, N.L.S.; Wissing, M.L.M.; Andersen, M.S.; Englund, A.L.M.; Dalgaard, L.T. Metformin Decreases miR-122, miR-223 and miR-29a in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraison, E.; Kostova, E.; Moran, L.J.; Bilal, S.; Ee, C.C.; Venetis, C.; Costello, M.F. Metformin versus the Combined Oral Contraceptive Pill for Hirsutism, Acne, and Menstrual Pattern in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD005552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretta, R.; Sansone, M.; Romanelli, F.; Appetecchia, M. Gender in Endocrinological Diseases: Biological and Clinical Differences. Ital. J. Gend. Specif. Med. 2017, 3, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, P.B. Age and Sex Associations of 40 Autoimmune Diseases. Am. J. Med. 1994, 96, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effraimidis, G.; Wiersinga, W.M. Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Autoimmune Thyroid Disease: Old and New Players. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, R241–R252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Oh, E.S.; Yasar, S.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Mammen, J.S. Endogenous and Exogenous Thyrotoxicosis and Risk of Incident Cognitive Disorders in Older Adults. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B.; Kahaly, G.J.; Robertson, R.P. Thyroid Dysfunction and Diabetes Mellitus: Two Closely Associated Disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 789–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.S.; Wilson, J.R.; Bernet, V.J. Links between Thyroid Disorders and Glucose Homeostasis. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloot, Y.J.E.; Janssen, M.J.R.; Van Herwaarden, A.E.; Peeters, R.P.; Netea-Maier, R.T.; Smit, J.W.A. The Influence of Energy Depletion by Metformin or Hypocaloric Diet on Thyroid Iodine Uptake in Healthy Volunteers: A Randomized Trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, T.; Alevizaki, M. Metformin and Thyroid: An Update. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2013, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondi, M.; Cappelli, C.; Magri, F.; Botta, R.; Dionisio, R.; Iacobello, C.; De Cata, P.; Nappi, R.E.; Castellano, M.; Chiovato, L. Thyroidal Effect of Metformin Treatment in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Metformin Therapy and TSH. Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 75, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, C.; Kut, A.; Atesagaoglu, B.; Nar, A.; Bascil Tutuncu, N.; Gursoy, A. Metformin Decreases Thyroid Volume and Nodule Size in Subjects with Insulin Resistance: A Preliminary Study. Med. Princ. Pract. 2016, 25, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, R.J.O.; Zakikhani, M.; Fantus, I.G.; Pollak, M.; Sonenberg, N. Metformin Inhibits Mammalian Target of Rapamycin–Dependent Translation Initiation in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10804–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheder, S.; Sisley, K.; Hadad, S.; Balasubramanian, S.P. Effects of Prolonged Exposure to Low Dose Metformin in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, D.; Hu, C.; Xu, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; Tang, W. Role of Metformin in the Treatment of Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2019, 29, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Di, H.; Liu, C.; Fan, Y. Efficacy of Metformin for Benign Thyroid Nodules in Subjects with Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, F.; Scheen, A. Understanding and Overcoming Metformin Gastrointestinal Intolerance. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Han, K.; Oh, H.; Tan, K.E.; Sothiratnam, R.; Tjokroprawiro, A.; Klein, M. Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Metformin Extended-release Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: An Observational Trial in Asia. J. Diabetes 2012, 4, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreight, L.J.; Bailey, C.J.; Pearson, E.R. Metformin and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubeddu, L.X.; Bönisch, H.; Göthert, M.; Molderings, G.; Racké, K.; Ramadori, G.; Miller, K.J.; Schwörer, H. Effects of Metformin on Intestinal 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Release and on 5-HT3 Receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 361, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujic, T.; Zhou, K.; Tavendale, R.; Palmer, C.N.A.; Pearson, E.R. Effect of Serotonin Transporter 5-HTTLPR Polymorphism on Gastrointestinal Intolerance to Metformin: A GoDARTS Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, S.W.; Lin, L.; Merski, M.; Keiser, M.J.; Gupta, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chien, H.-C.; Shoichet, B.K.; Giacomini, K.M. Prediction and Validation of Enzyme and Transporter Off-Targets for Metformin. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2015, 42, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, S.T.; Denig, P.; Ekhart, C.; Mol, P.G.M.; van Puijenbroek, E.P. Sex Differences in Adverse Drug Reactions of Metformin: A Longitudinal Survey Study. Drug Saf. 2020, 43, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, L.; Härmark, L.; van Puijenbroek, E. Time Course, Outcome and Management of Adverse Drug Reactions Associated with Metformin from Patient’s Perspective: A Prospective, Observational Cohort Study in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Long-Term Safety, Tolerability, and Weight Loss Associated with Metformin in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Lipska, K.J.; Mayo, H.; Bailey, C.J.; McGuire, D.K. Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-K.; Liu, J.-S.; Kuo, K.-L.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Tarng, D.-C. Metformin Use and Mortality in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: National, Retrospective, Observational, Cohort Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stage, T.B.; Brøsen, K.; Christensen, M.M.H. A Comprehensive Review of Drug–Drug Interactions with Metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkir Maideen, N.M.; Jumale, A.; Balasubramaniam, R. Drug Interactions of Metformin Involving Drug Transporter Proteins. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, J.; Hashim, N.M.; Han, H.C. A Comprehensive Review on Potential Drug–Drug Interactions of Proton Pump Inhibitors with Antidiabetic Drugs Metformin and DPP-4 Inhibitors. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyiğit, F.; Paşalı Kilit, T.; Onbaşı, K. Polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions among patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Hippocrates Med. J. 2023, 3, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.I.; Rizvi, A.A.; Verma, S.; Abbas, M.; Siddiqi, Z.; Mishra, D.; Verma, S.; Raza, S.T.; Mahdi, F. Interactions between Diabetic and Hypertensive Drugs: A Pharmacogenetics Approach. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2023, 298, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.V.; Pan, Q.; Aroda, V.R.; Crandall, J.P.; Kriska, A.; Piromalli, C.; Wallia, A.; Temprosa, M.; Florez, H.; for the Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Long-Term Effects of Lifestyle and Metformin Interventions in DPP on Bone Density. Osteoporos Int. 2021, 32, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, M.; Leoni, M.; Caprio, M.; Fabbri, A. Long-Term Metformin Therapy and Vitamin B12 Deficiency: An Association to Bear in Mind. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cai, X.; Wu, H.; Ji, L. Associations between Metformin Use and Vitamin B 12 Levels, Anemia, and Neuropathy in Patients with Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. J. Diabetes 2019, 11, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wile, D.J.; Toth, C. Association of Metformin, Elevated Homocysteine, and Methylmalonic Acid Levels and Clinically Worsened Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklewicz, A.; Smith, A.D.; Smith, A.; Holzer, A.; Klein, A.; McCaddon, A.; Molloy, A.M.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; Nexo, E.; McNulty, H.; et al. The Importance of Vitamin B12 for Individuals Choosing Plant-Based Diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Qin, X.; Wu, T.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y. Metformin Treatment and Risk of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Beijing, China. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1082720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christine, C.W.; Auinger, P.; Saleh, N.; Tian, M.; Bottiglieri, T.; Arning, E.; Tran, N.K.; Ueland, P.M.; Green, R.; The Parkinson Study Group—DATATOP Investigators. Relationship of Cerebrospinal Fluid Vitamin B12 Status Markers with Parkinson’s Disease Progression. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Metformin. In VigiBase—WHO’s Global Database VigiBase; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Oktora, M.P.; de Vos, S.; de Vries, S.T.; Hak, E.; Denig, P. Sex Disparities in Treatment Patterns after Metformin Initiation among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug 2023, 32, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi Yan Chan, J.; Moullet, M.; Williamson, B.; Arends, R.H.; Pilla Reddy, V. Harnessing Clinical Trial and Real-World Data Towards an Understanding of Sex Effects on Drug Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Efficacy. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 874606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, I.; Prendergast, B.J. Sex Differences in Pharmacokinetics Predict Adverse Drug Reactions in Women. Biol. Sex Differ. 2020, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Female versus Male | References | |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes mellitus | Higher all-cause mortality | [122,123] |
| Higher risk PAD | [115,116,117] | |
| Higher RR for oral, stomach, and kidney cancers, and leukemia | [160] | |
| Met: antihyperglycemic effect | No difference | [31] |
| Met: pharmacokinetics | No difference, considering weight difference and monitoring eGFR. | [76] |
| Met: ADRs | Higher | [23,24] |
| Met: CRC-specific mortality * | Lower | [156] |
| Met: CRC incidence rate * | Lower | [157] |
| Met: COVID-19 * | Lower severity and mortality | [170,171] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Froldi, G. View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040478
Froldi G. View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040478
Chicago/Turabian StyleFroldi, Guglielmina. 2024. "View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040478
APA StyleFroldi, G. (2024). View on Metformin: Antidiabetic and Pleiotropic Effects, Pharmacokinetics, Side Effects, and Sex-Related Differences. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040478