Polymeric Nanocapsules Loaded with Lidocaine: A Promising Formulation for Topical Dental Anesthesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
2.1.1. Particle Size, Encapsulation Efficiency, and Stability
2.1.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
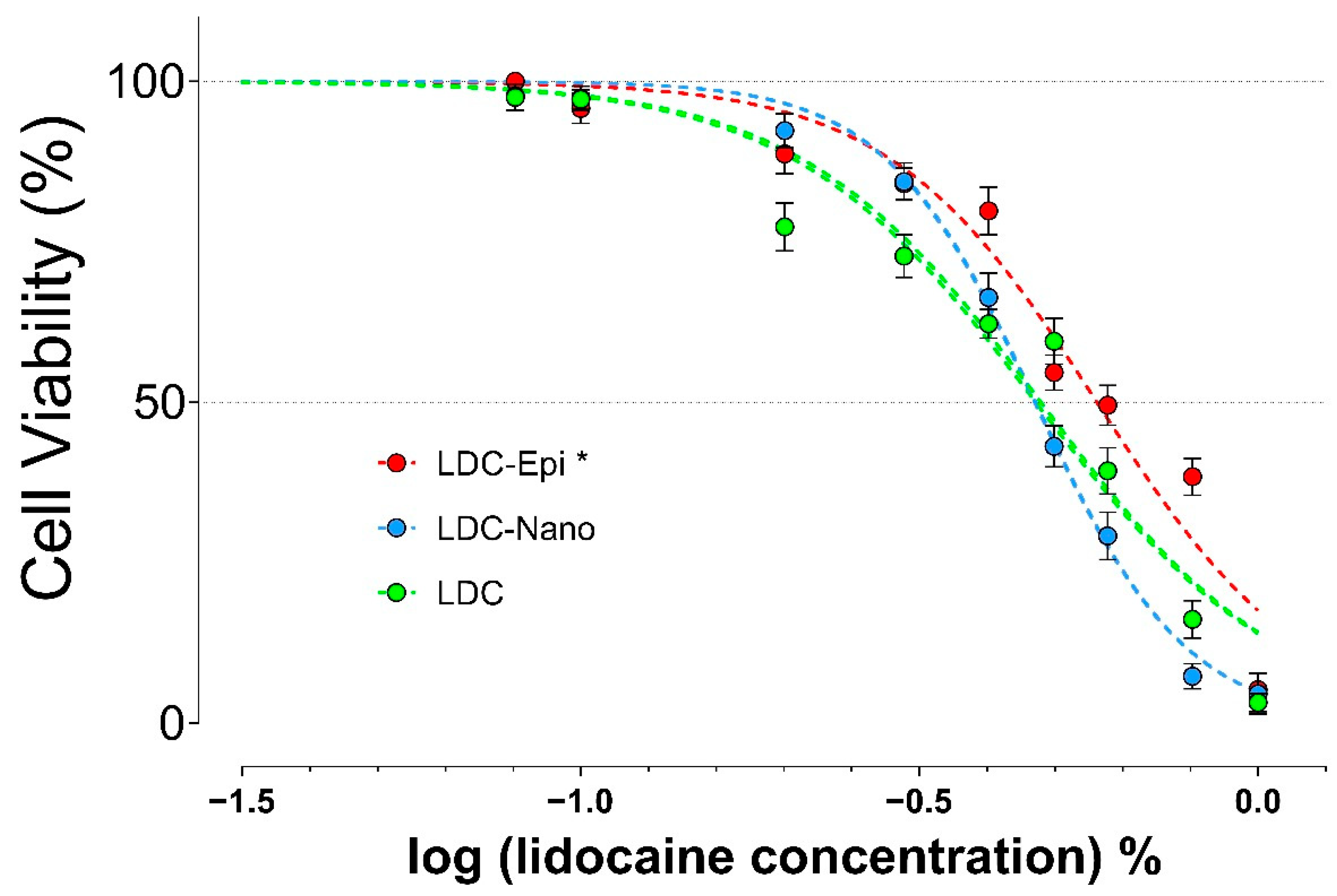
2.2. MTT Assay
2.3. Permeation Assay
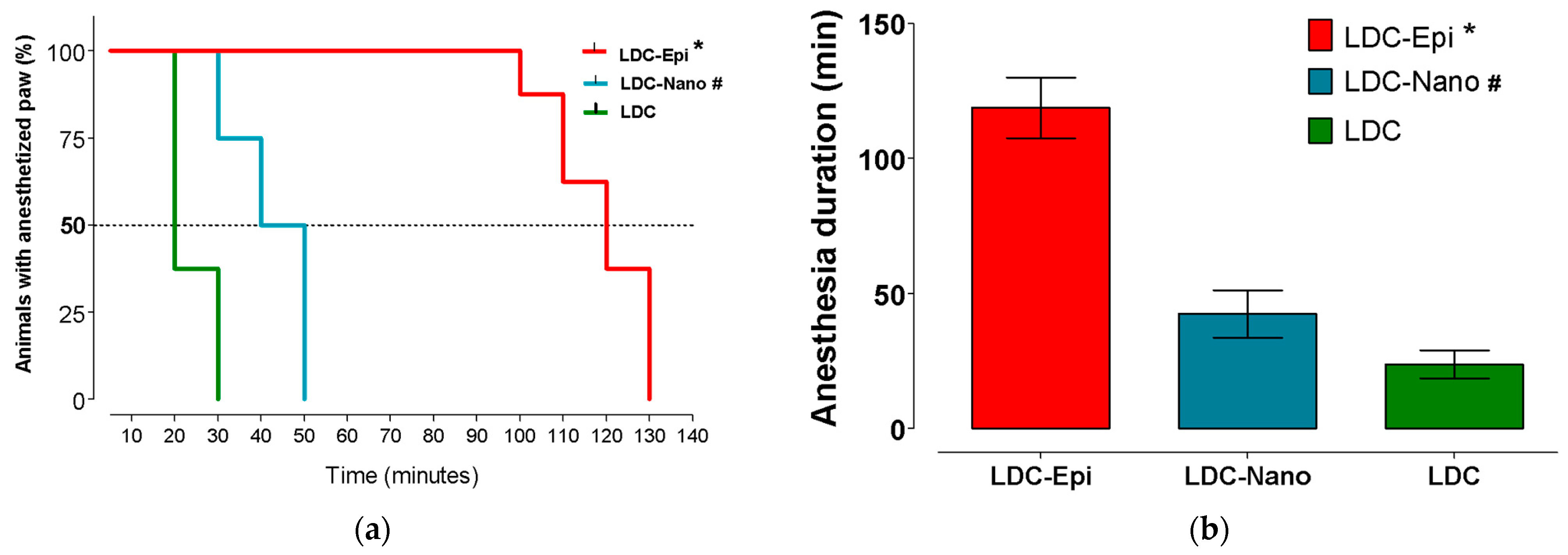
2.4. Anesthetic Efficacy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Rats
4.2. Formulation of Lidocaine Encapsulated
4.3. Lidocaine Analysis
4.4. Nanoparticle Characterization
4.4.1. Particle Size, Encapsulation Efficiency, and Stability
4.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.5. MTT Assay
4.5.1. Cell Culture
4.5.2. Cell Viability
4.6. Permeation Assays
4.6.1. Tissue Preparation and Selection
4.6.2. In Vitro Permeation Assay
4.7. Anesthetic Effectiveness
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mundiya, J.; Woodbine, E. Updates on topical and local anesthesia agents. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. 2022, 34, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamed, S. Handbook of Local Anesthesia, 6th ed.; Elsivier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013; p. 432. [Google Scholar]
- Franz-Montan, M.; Ribeiro, L.N.M.; Volpato, M.C.; Cereda, C.M.S.; Groppo, F.C.; Tofoli, G.R.; de Araújo, D.R.; Santi, P.; Padula, C.; de Paula, E. Recent advances and perspectives in topical oral anesthesia. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.; Liu, G.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, P. Safety and efficacy concerns of modern strategies of local anesthetics delivery. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Pan, Z.; Lai, B.; Zan, C.; Liu, H. Recent Research Advances in Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Local Anesthetics. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 2639–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, R.; de Melo, N.F.; de Araújo, D.R.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Polymeric alginate nanoparticles containing the local anesthetic bupivacaine. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, N.F.; De Araújo, D.R.; Grillo, R.; Moraes, C.M.; De Matos, A.P.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Benzocaine-loaded polymeric nanocapsules: Study of the anesthetic activities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Campos, E.V.; Silva de Melo, N.F.; Guilherme, V.A.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; de Araújo, D.R.; Fraceto, L.F. Preparation and characterization of poly(ε-caprolactone) nanospheres containing the local anesthetic lidocaine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, B.V.; Baratelli, D.; Di Carla, S.; Serpe, L.; da Silva, C.B.; Guilherme, V.A.; Ribeiro, L.N.M.; Cereda, C.M.S.; de Paula, E.; Volpato, M.C.; et al. Hybrid Hydrogel Composed of Polymeric Nanocapsules Co-Loading Lidocaine and Prilocaine for Topical Intraoral Anesthesia. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista da Silva, C.; Volpato, M.C.; Muniz, B.V.; Dos Santos, C.P.; Serpe, L.; Ferreira, L.E.N.; de Melo, N.F.S.; Fraceto, L.F.; Groppo, F.C.; Franz-Montan, M. Promising potential of articaine-loaded poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanocapules for intraoral topical anesthesia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanraj, V.J.; Chen, Y.J. Nanoparticles—A Review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2006, 5, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, P.; Nagarsenker, M. Formulation and evaluation of lidocaine lipid nanosystems for dermal delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.P.d. Characterization, Biocompatibility, Permeation Profile and Anesthetic Efficacy of a Formulation of Lidocaine-Loaded Poly(Epsiloncaprolactone) Nanocapsules. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, SP, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, P.C.L.; de Moura, L.D.; de Lima, F.F.; da Silva, G.H.R.; Souza, R.I.C.; de Paula, E. Lipid nanocapsules loaded with prilocaine and lidocaine and incorporated in gel for topical application. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffazick, S.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Freitas, L.d.L.; Pohlmann, A.R. Caracterização e estabilidade físico-química de sistemas poliméricos nanoparticulados para administração de fármacos. Química Nova 2003, 26, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Campos, E.; de Melo, N.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.; Fraceto, L. Screening of conditions for the preparation of poly(ε-caprolactone) nanocapsules containing the local anesthetic articaine. J. Colloid Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, N.F.; Grillo, R.; Guilherme, V.A.; de Araujo, D.R.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanocapsules containing benzocaine: Influence of the composition of the oily nucleus on physico-chemical properties and anesthetic activity. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, C.M.; de Matos, A.P.; de Paula, E.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Benzocaine loaded biodegradable poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanocapsules: Factorial design and characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2009, 165, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, N.F.; Grillo, R.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F.; Dias Filho, N.L.; Paula, E.D.; Araújo, D.R. Desenvolvimento e caracterização de nanocápsulas de poli(L-lactideo) contendo benzocaína. Química Nova 2010, 33, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwala, V.K.; Shekhar, N.; Aggarwal, S.; Mandal, U. Biodegradation of poly (ε-caprolactone)(PCL) film by Alcaligenes faecalis. J. Polym. Environ. 2008, 16, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrro, R.M.D.; Miyashita, D.; Albuquerque, V.B.d.; Cruz, A.A.V.; Cunha Júnior, A.d.S. Sistemas biodegradáveis contendo acetato de prednisolona para administração orbitária. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2009, 72, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Perez-Castro, R.; Patel, S.; Garavito-Aguilar, Z.V.; Rosenberg, A.; Recio-Pinto, E.; Zhang, J.; Blanck, T.J.; Xu, F. Cytotoxicity of local anesthetics in human neuronal cells. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 108, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malet, A.; Faure, M.-O.; Deletage, N.; Pereira, B.; Haas, J.; Lambert, G. The comparative cytotoxic effects of different local anesthetics on a human neuroblastoma cell line. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, A.-C.; Atlan, M.; Bencharif, K.; Gunasekaran, M.K.; Delarue, P.; Hulard, O.; Lefebvre-d’Hellencourt, C.; Roche, R.; Hoareau, L.; Festy, F. New insights into lidocaine and adrenaline effects on human adipose stem cells. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2013, 37, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, T.F.; Vansintjan, P.S.; Roels, N.; Herregods, S.S.; Verbruggen, G.; Herregods, L.L.; Almqvist, K.F. The effect of Lidocaine on the viability of cultivated mature human cartilage cells: An in vitro study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, H.J.; Busfield, B.T.; Kim, H.J.; Scuderi, G.J.; Dragoo, J.L. The effect of local anaesthetics on synoviocytes: A possible indirect mechanism of chondrolysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2013, 21, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, A.B.; McCarthy, M.B.; Dang, A.B.; Chowaniec, D.M.; Mazzocca, A.D. Effects of adding epinephrine to arthroscopic irrigation fluid on cultured chondrocyte survival in vitro. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2011, 27, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.N.M.; Franz-Montan, M.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Rodrigues da Silva, G.H.; de Castro, S.R.; Guilherme, V.A.; de Araújo, D.R.; de Paula, E. Nanohybrid hydrogels designed for transbuccal anesthesia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 15, 6453–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, C.A.; Squier, C.A.; Cruchley, A.; Williams, D.M.; Speight, P. The permeability of human oral mucosa and skin to water. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squier, C.A.; Hall, B.K. In-vitro permeability of porcine oral mucosa after epithelial separation, stripping and hydration. Arch. Oral Biol. 1985, 30, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.O.; McConville, J.T. Novel strategies for the buccal delivery of macromolecules. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Del Consuelo, I.; Pizzolato, G.P.; Falson, F.; Guy, R.H.; Jacques, Y. Evaluation of pig esophageal mucosa as a permeability barrier model for buccal tissue. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Del Consuelo, I.; Jacques, Y.; Pizzolato, G.P.; Guy, R.H.; Falson, F. Comparison of the lipid composition of porcine buccal and esophageal permeability barriers. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiras, A.; Pais, A.A.; Veiga, F.J. A comprehensive development strategy in buccal drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.; Neumann, D.; Lamprecht, A. Lipid nanocapsules for dermal application: A comparative study of lipid-based versus polymer-based nanocarriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz-Montan, M.; Baroni, D.; Brunetto, G.; Sobral, V.R.; da Silva, C.M.; Venâncio, P.; Zago, P.W.; Cereda, C.M.; Volpato, M.C.; de Araújo, D.R.; et al. Liposomal lidocaine gel for topical use at the oral mucosa: Characterization, in vitro assays and in vivo anesthetic efficacy in humans. J. Liposome Res. 2015, 25, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz-Montan, M.; Cereda, C.M.; Gaspari, A.; da Silva, C.M.; de Araújo, D.R.; Padula, C.; Santi, P.; Narvaes, E.; Novaes, P.D.; Groppo, F.C.; et al. Liposomal-benzocaine gel formulation: Correlation between in vitro assays and in vivo topical anesthesia in volunteers. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 23, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Brennan, T.J. The pathophysiology of acute pain: Animal models. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 24, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, T.J.; Zahn, P.K.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M. Mechanisms of incisional pain. Anesthesiol. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 23, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modaresi, J.; Dianat, O.; Soluti, A. Effect of pulp inflammation on nerve impulse quality with or without anesthesia. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshbaten, A.; Ferrell, W. Responses of blood vessels in the rabbit knee to acute joint inflammation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1990, 49, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Carpenter, R.L.; Chiu, A.A.; McGill, T.J.; Mantell, S.A. Epinephrine prolongs duration of subcutaneous infiltration of local anesthesia in a dose-related manner:: Correlation with magnitude of vasoconstriction. Reg. Anesth. Pain. Med. 1995, 20, 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- Borman, P.; Elder, D. Q2 (R1) validation of analytical procedures: Text and methodology. In ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation Guide; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 127–166. [Google Scholar]
- Silva de Melo, N.F.; Campos, E.V.; Gonçalves, C.M.; de Paula, E.; Pasquoto, T.; de Lima, R.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Development of hydrophilic nanocarriers for the charged form of the local anesthetic articaine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos Silva, M.; Cocenza, D.S.; Grillo, R.; de Melo, N.F.S.; Tonello, P.S.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Cassimiro, D.L.; Rosa, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Paraquat-loaded alginate/chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and soil sorption studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubayachi, C.; Couto, R.O.; de Gaitani, C.M.; Pedrazzi, V.; Freitas, O.; Lopez, R.F. Needle-free buccal anesthesia using iontophoresis and amino amide salts combined in a mucoadhesive formulation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, T.J.; Vandermeulen, E.P.; Gebhart, G.F. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain 1996, 64, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, G.J.; Lax, J.; Susser, L.; Zakowski, M.; Weissman, T.E.; Turndorf, H. Wound infiltration with liposomal bupivacaine prolongs analgesia in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1997, 41, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
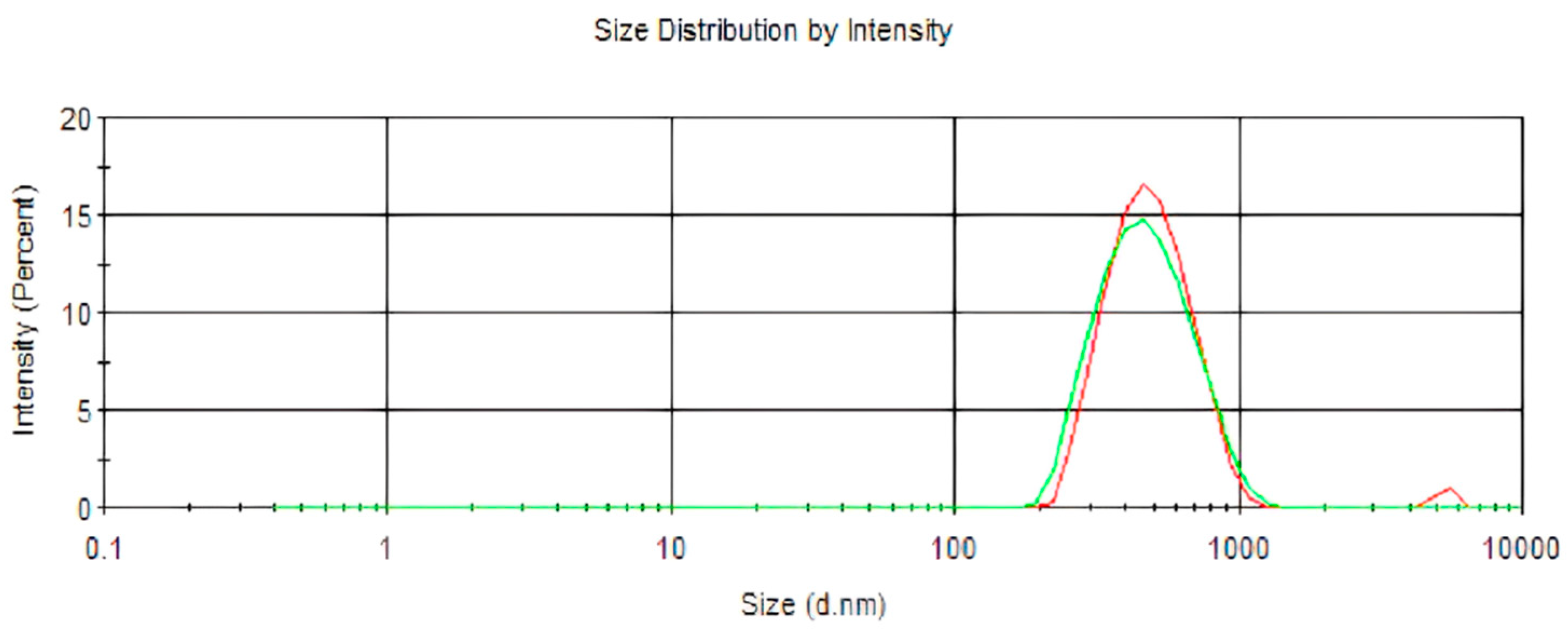
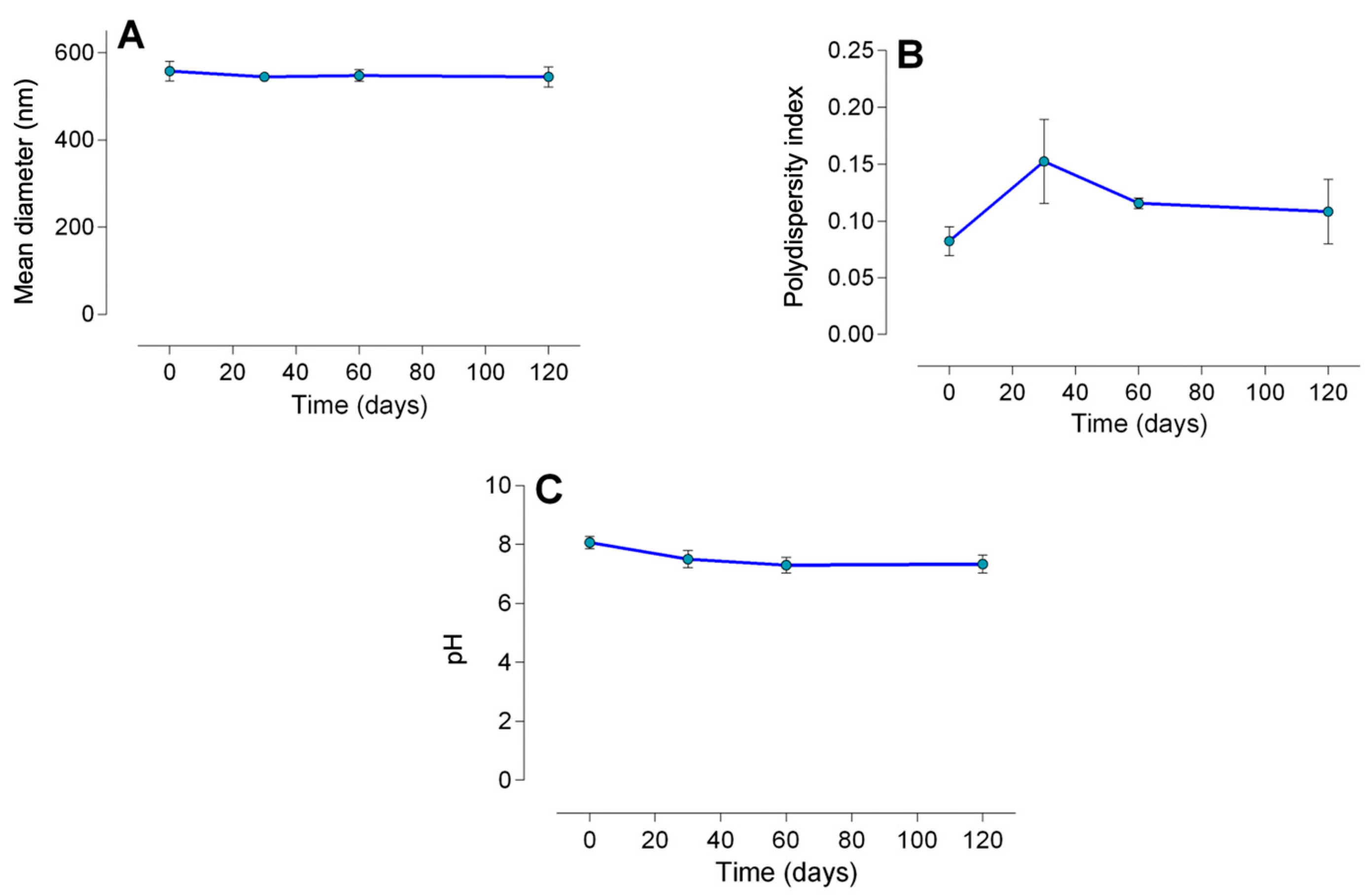


| pH | Polydispersity Index (PDI) | Mean Diameter (nm) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDC-Nano | 8.1 ± 0.21 *** | 0.08 ± 0.01 ** | 557.8 ± 22.7 * | 51.8 ± 1.87 |
| Nano | 6.3 ± 0.21 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 530.5 ± 9 | - |
| Formulation | Jss (μg·cm−2·h−1) | ER * | Q5h (μg·cm−2) | ER # | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDC | 41.53 ± 9.04 | 1.0 | 224.80 ± 40.46 | 1.0 | 0.98 ± 0.003 |
| LDC-Nano | 309.71 ± 55.41 *** | 7.46 | 1485.76 ± 394.11 ** | 6.61 | 0.993 ± 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, C.B.; dos Santos, C.P.; Serpe, L.; Sanchez, J.B.; Ferreira, L.E.N.; de Melo, N.F.S.; Groppo, F.C.; Fraceto, L.F.; Volpato, M.C.; Franz-Montan, M. Polymeric Nanocapsules Loaded with Lidocaine: A Promising Formulation for Topical Dental Anesthesia. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040485
da Silva CB, dos Santos CP, Serpe L, Sanchez JB, Ferreira LEN, de Melo NFS, Groppo FC, Fraceto LF, Volpato MC, Franz-Montan M. Polymeric Nanocapsules Loaded with Lidocaine: A Promising Formulation for Topical Dental Anesthesia. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040485
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Camila Batista, Cleiton Pita dos Santos, Luciano Serpe, Jonny Burga Sanchez, Luiz Eduardo Nunes Ferreira, Nathalie Ferreira Silva de Melo, Francisco Carlos Groppo, Leonardo Fernandes Fraceto, Maria Cristina Volpato, and Michelle Franz-Montan. 2024. "Polymeric Nanocapsules Loaded with Lidocaine: A Promising Formulation for Topical Dental Anesthesia" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040485
APA Styleda Silva, C. B., dos Santos, C. P., Serpe, L., Sanchez, J. B., Ferreira, L. E. N., de Melo, N. F. S., Groppo, F. C., Fraceto, L. F., Volpato, M. C., & Franz-Montan, M. (2024). Polymeric Nanocapsules Loaded with Lidocaine: A Promising Formulation for Topical Dental Anesthesia. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040485








